MSTPose: Learning-Enriched Visual Information with Multi-Scale Transformers for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose MSTPose in this study, which fully leverages the characteristics of CNN and Transformer to enable the network to learn rich visual representations, thereby significantly improving the network’s modeling ability in complex scenes.
- The coordinate attention mechanism is introduced at the output location of the backbone network to obtain position-sensitive feature maps, which helps the Transformer extract spatial features from images.
- Considering the semantic differences between different branches, we propose the MST module. By using a parallel structure, different-scale branches are separately fed into the Transformer for training. This allows the network to capture more complex semantic information and improve its detection ability for different instances.
- Conventional heatmap methods are discarded to overcome the drawback of repetitive dimensionality changes that disrupt the spatial structure of feature maps when combined with Transformer. Furthermore, we successfully integrate the VeR method with Transformer for the first time, resulting in improved predictive accuracy.
- In this study, we test MSTPose on the primary public benchmark datasets, COCO and MPII, and achieve better performance compared to CNN-based and CNN + Transformer networks.
2. Related Work
2.1. CNN-Based Human Pose Estimation
2.2. Transformer-Based Human Pose Estimation
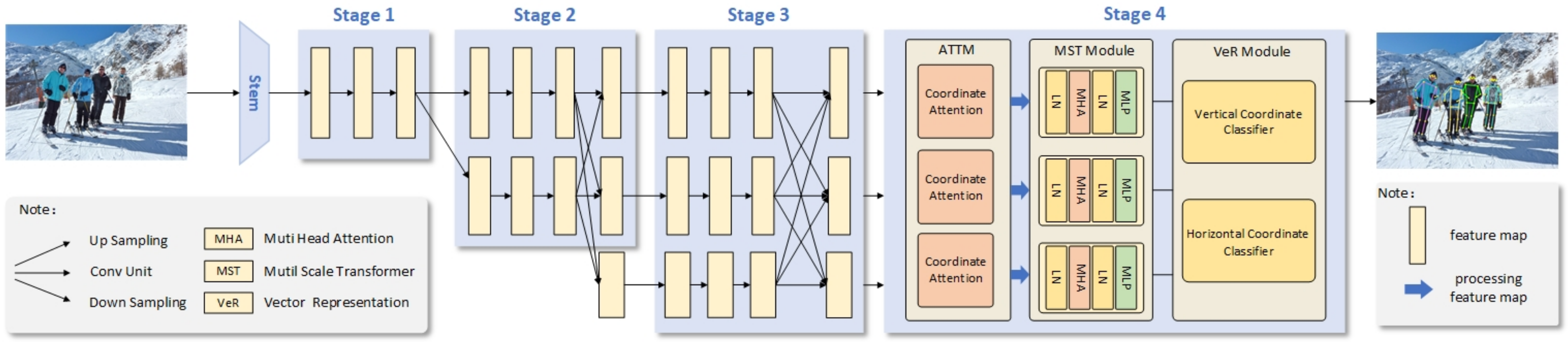
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Backbone Network
3.2. ATTM
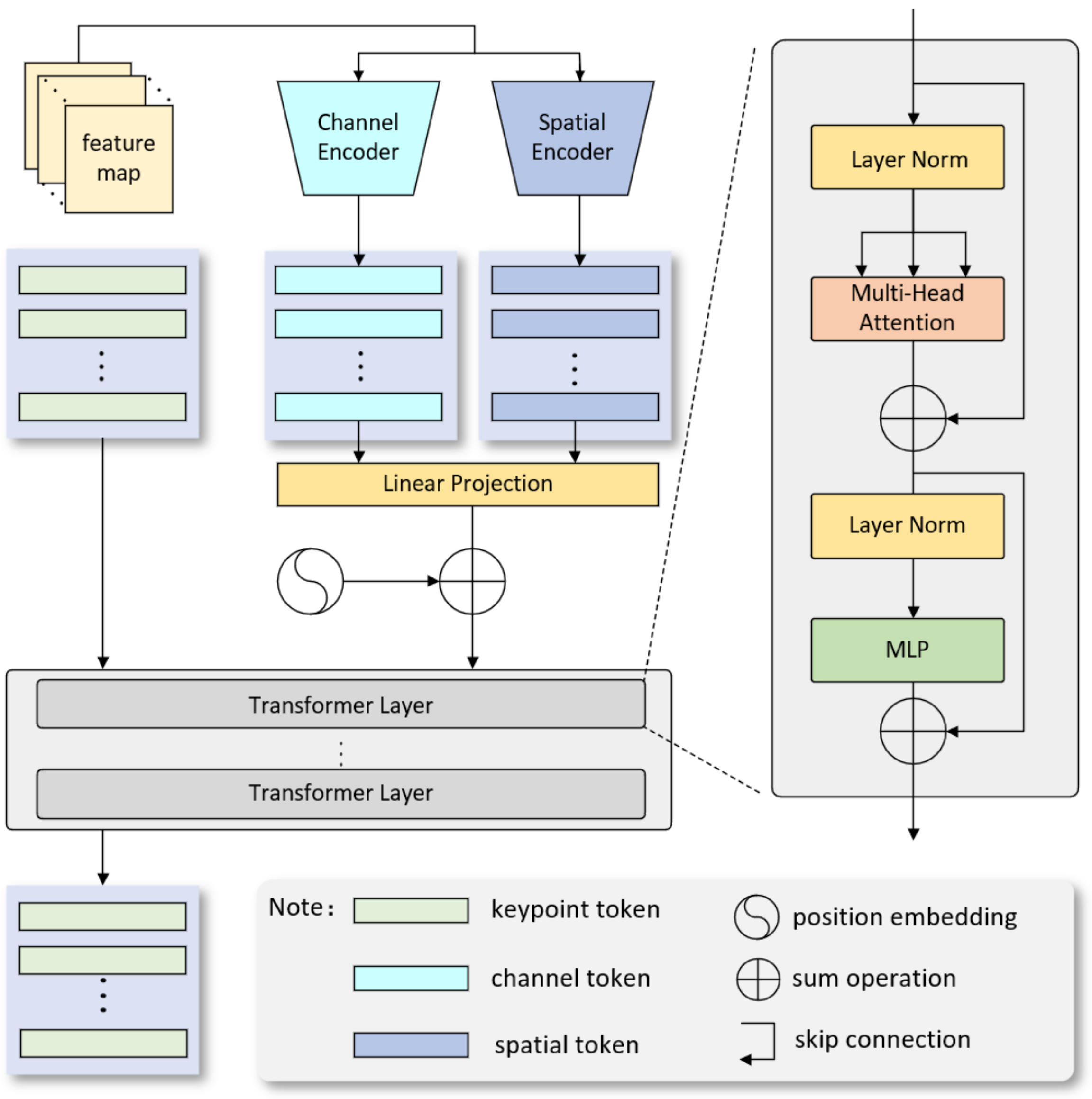
3.3. MST Module
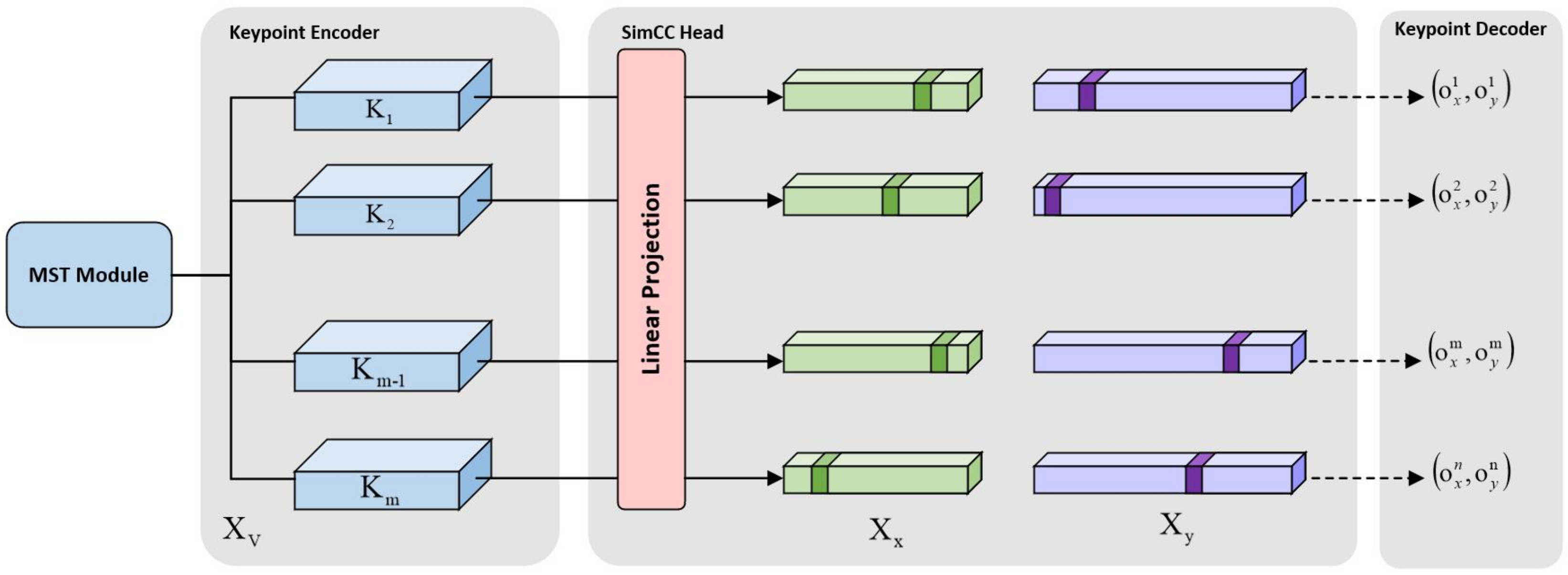
3.4. VeR Module
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Details
4.1.1. Datasets and Evaluation Indicators
4.1.2. Implementation Details
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Quantitative Experimental Results
4.2.2. Qualitative Experimental Results
4.3. Ablation Experiments
4.3.1. Ablation Experiment of ATTM
4.3.2. Ablation Experiment of MST Module
4.3.3. Ablation Experiment of VeR Module
4.3.4. Ablation Experiment of MSTPose
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Guo, C.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, N.; Zhang, Z. Recent Progress in Sensing and Computing Techniques for Human Activity Recognition and Motion Analysis. Electronics 2020, 9, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, T.; Generosi, A.; Ceccacci, S.; Khamaisi, R.K.; Peruzzini, M.; Mengoni, M. Preliminary Validation of a Low-Cost Motion Analysis System Based on RGB Cameras to Support the Evaluation of Postural Risk Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskeliūnas, R.; Damaševičius, R.; Blažauskas, T.; Canbulut, C.; Adomavičienė, A.; Griškevičius, J. BiomacVR: A Virtual Reality-Based System for Precise Human Posture and Motion Analysis in Rehabilitation Exercises Using Depth Sensors. Electronics 2023, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. ARHPE: Asymmetric relation-aware representation learning for head pose estimation in industrial human–computer interaction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7107–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Subramanian, S. Precise head pose estimation on HPD5A database for attention recognition based on convolutional neural network in human-computer interaction. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 116, 103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, R.; Ji, Q. Human computer interaction with head pose, eye gaze and body gestures. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, FG, Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; p. 789. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Part VIII 14. pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Ge, Y.; Shen, C.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Tfpose: Direct human pose estimation with transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.15320. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Xia, S.T. SimCC: A Simple Coordinate Classification Perspective for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision-ECCV 2022: 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Part VI. pp. 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C. Deeppose: Human pose estimation via deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, V.; Munoz, D.; Hebert, M.; Andrew Bagnell, J.; Sheikh, Y. Pose machines: Articulated pose estimation via inference machines. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Part II 13. pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.E.; Ramakrishna, V.; Kanade, T.; Sheikh, Y. Convolutional pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, L.C.; Gidaris, S.; Tompson, J.; Murphy, K. Personlab: Person pose estimation and instance segmentation with a bottom-up, part-based, geometric embedding model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, T.; Charles, J.; Zisserman, A. Flowing convnets for human pose estimation in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1913–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Li, S.; Ouyang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Learning feature pyramids for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1281–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.; Yang, W.; Ouyang, W.; Ma, C.; Yuille, A.L.; Wang, X. Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1831–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, T.S.; Zhang, L. Higherhrnet: Scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5386–5395. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. 2018. Available online: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/openai-assets/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. Bart: Denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13461. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Roller, S.; Goyal, N.; Artetxe, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Dewan, C.; Diab, M.; Li, X.; Lin, X.V.; et al. Opt: Open pre-trained transformer language models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.01068. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part I 16. pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Song, H.; Zhao, S.; Shen, J.; Zhao, S.; Hoi, S.C.; Ling, H. Learning unsupervised video object segmentation through visual attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3064–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Tao, R.; Shen, J. Matnet: Motion-attentive transition network for zero-shot video object segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8326–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Quan, Z.; Nie, M.; Yang, W. Transpose: Keypoint localization via transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11802–11812. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Tu, Z. Pose recognition with cascade transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1944–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, B.; Shi, Q.; Yang, F. MSRT: Multi-scale representation transformer for regression-based human pose estimation. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2023, 26, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Feng, J.; Jiang, M. CSIT: Channel Spatial Integrated Transformer for human pose estimation. IET Image Process. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Doll’ar, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Pishchulin, L.; Gehler, P.; Schiele, B. 2d human pose estimation: New benchmark and state of the art analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 3686–3693. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Xia, S.T.; Zhou, E. Tokenpose: Learning keypoint tokens for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11313–11322. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, D. Vitpose: Simple vision transformer baselines for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 38571–38584. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Shen, C. Directpose: Direct end-to-end multi-person pose estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07451. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, S. Point-set anchors for object detection, instance segmentation and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part X 16. pp. 527–544. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Xiao, B.; Wei, F.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y. Integral human pose regression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]


| Method | Backbone | GFLOPs | #Params | Input Size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SimCC [13] | ResNet50 | 3.8 | 25.7M | 256 × 192 | 70.8 | - | - | - | - |
| Simple Baseline [15] | ResNet50 | 8.9 | 34.0M | 256 × 192 | 70.4 | 88.6 | 78.3 | 67.1 | 77.2 |
| Simple Baseline [15] | ResNet101 | 12.4 | 53.0M | 256 × 192 | 71.4 | 89.3 | 79.3 | 68.1 | 78.1 |
| Simple Baseline [15] | ResNet152 | 15.7 | 68.6M | 256 × 192 | 72.0 | 89.3 | 79.8 | 68.7 | 78.9 |
| TFPose [11] | ResNet50 | 20.4 | - | 384 × 288 | 72.4 | - | - | - | - |
| PRTR [37] | ResNet101 | 33.4 | 60.4M | 512 × 348 | 72.0 | 89.3 | 79.4 | 67.3 | 79.7 |
| PRTR [37] | HRNetW32 | 21.6 | 57.2M | 384 × 288 | 73.1 | 89.3 | 79.4 | 67.3 | 79.8 |
| PRTR [37] | HRNetW32 | 37.8 | 57.2M | 512 × 348 | 73.3 | 89.2 | 79.9 | 69.0 | 80.9 |
| MSRT [38] | ResNet101 | - | - | 512 × 348 | 72.2 | 89.1 | 79.2 | 68.1 | 79.4 |
| TransPose [36] | HRNetW32-s | - | 8.0M | 256 × 192 | 74.2 | - | - | - | - |
| TokenPose [43] | HRNetW32-s | 5.7 | 13.5M | 256 × 192 | 74.7 | 89.8 | 81.4 | 71.3 | 81.4 |
| ViTPose [44] | ViT-L | - | 307M | 256 × 192 | 78.3 | - | - | - | - |
| MSTPose | HRNetW48-s | 14.6 | 31.2M | 256 × 192 | 77.2 | 92.9 | 84.1 | 73.9 | 81.7 |
| Method | Backbone | GFLOPs | #Params | Input Size | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepPose [14] | ResNet101 | 7.7 | - | 256 × 192 | 57.4 | 86.5 | 64.2 | 55.0 | 62.8 | - |
| DeepPose [14] | ResNet152 | 11.3 | - | 256 × 192 | 59.3 | 87.6 | 66.7 | 56.8 | 64.9 | - |
| CenterNet [42] | Hourglass | - | - | - | 63.0 | 86.8 | 69.6 | 58.9 | 70.4 | - |
| DirectPose [45] | ResNet50 | - | - | - | 62.2 | 86.4 | 68.2 | 56.7 | 69.8 | - |
| PointSetNet [46] | HRNetW48 | - | - | - | 68.7 | 89.9 | 76.3 | 64.8 | 75.3 | - |
| Integral Pose [47] | ResNet101 | 11.0 | - | 256 × 256 | 67.8 | 88.2 | 74.8 | 63.9 | 74.0 | - |
| TFPose [11] | ResNet50+T | 20.4 | - | 384 × 288 | 72.2 | 90.9 | 80.1 | 69.1 | 78.8 | 74.1 |
| PRTR [37] | HRNetW48+T | - | - | - | 64.9 | 87.0 | 71.7 | 60.2 | 72.5 | 78.8 |
| PRTR [37] | HRNetW32+T | 21.6 | 57.2M | 384 × 288 | 71.7 | 90.6 | 79.6 | 67.6 | 78.4 | 79.4 |
| PRTR [37] | HRNetW32+T | 37.8 | 57.2M | 512 × 384 | 72.1 | 90.4 | 79.6 | 68.1 | 79.0 | |
| SimCC [13] | ResNet50 | 20.2 | 25.7M | 384 × 288 | 72.7 | 91.2 | 80.1 | 69.2 | 79.0 | 78.0 |
| TransPose [36] | HRNetW32+T | - | 8.0M | 256 × 192 | 73.4 | 91.6 | 81.1 | 70.1 | 79.3 | - |
| TokenPose [43] | HRNetW32+T | 5.7 | 13.5M | 256 × 192 | 74.0 | 91.9 | 81.5 | 70.6 | 79.8 | 79.1 |
| MSTPose | HRNetW48+T | 14.6 | 31.2M | 256 × 192 | 74.7 | 91.9 | 81.7 | 71.4 | 80.1 | 79.8 |
| Method | Backbone | Hea | Sho | Elb | Wri | Hip | Kne | Ank | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Baseline [15] | ResNet50 | 96.4 | 95.3 | 89.0 | 83.2 | 88.4 | 84.0 | 79.6 | 88.5 |
| Simple Baseline [15] | ResNet101 | 96.9 | 95.9 | 89.5 | 84.4 | 88.4 | 84.5 | 80.7 | 89.1 |
| Simple Baseline [15] | ResNet152 | 97.0 | 95.9 | 90.0 | 85.0 | 89.2 | 85.3 | 81.3 | 89.6 |
| HRNet [8] | HRNetW32 | 96.9 | 96.0 | 90.6 | 85.8 | 88.7 | 86.6 | 82.6 | 90.1 |
| MSRT [38] | ResNet101 | 97.0 | 94.9 | 89.0 | 84.0 | 89.6 | 85.7 | 80.3 | 89.1 |
| PRTR-R101 [37] | ResNet101 | 96.3 | 95.0 | 88.3 | 82.4 | 88.1 | 83.6 | 77.4 | 87.9 |
| PRTR-R152 [37] | ResNet152 | 96.4 | 94.9 | 88.4 | 82.6 | 88.6 | 84.1 | 78.4 | 88.2 |
| MSTPose | HRNetW48 | 97.1 | 96.0 | 90.8 | 86.8 | 89.5 | 86.8 | 82.8 | 90.2 |
| Method | Branch1 | Branch2 | Branch3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 76.7 | |||
| CA | 🗸 | 77.0 | ||
| CA | 🗸 | 77.0 | ||
| CA | 🗸 | 76.9 | ||
| CA | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 77.2 |
| Method | Branch1 | Branch2 | Branch3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer | 76.3 | |||
| Transformer | 🗸 | 76.9 | ||
| Transformer | 🗸 | 76.7 | ||
| Transformer | 🗸 | 76.7 | ||
| Transformer | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 77.2 |
| Method | VeR | Heatmap | |
|---|---|---|---|
| method1 | 🗸 | 77.2 | |
| method2 | 🗸 | 75.1 |
| Method | ATTM | MST Module | VeR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| method1 | 🗸 | 75.9 | ||
| method2 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 76.3 | |
| method3 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 76.7 | |
| method4 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 77.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Wei, X.; Li, S.; Zhan, A. MSTPose: Learning-Enriched Visual Information with Multi-Scale Transformers for Human Pose Estimation. Electronics 2023, 12, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12153244
Wu C, Wei X, Li S, Zhan A. MSTPose: Learning-Enriched Visual Information with Multi-Scale Transformers for Human Pose Estimation. Electronics. 2023; 12(15):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12153244
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chengyu, Xin Wei, Shaohua Li, and Ao Zhan. 2023. "MSTPose: Learning-Enriched Visual Information with Multi-Scale Transformers for Human Pose Estimation" Electronics 12, no. 15: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12153244
APA StyleWu, C., Wei, X., Li, S., & Zhan, A. (2023). MSTPose: Learning-Enriched Visual Information with Multi-Scale Transformers for Human Pose Estimation. Electronics, 12(15), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12153244





