Abstract
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an effective and safe medical treatment that improves the lives of patients with a wide range of neurological and psychiatric diseases, and has been consolidated as a first-line tool in the last two decades. Closed-loop deep brain stimulation (CLDBS) pushes this tool further by automatically adjusting the stimulation parameters to the brain response in real time. The main contribution of this paper is a low-size/power-controlled, compact and complete CLDBS system with two simultaneous acquisition channels, two simultaneous neurostimulation channels and wireless communication. Each channel has a low-noise amplifier (LNA) buffer in differential configuration to eliminate the DC signal component of the input. Energy management is efficiently done by the control and communication unit. The battery supports almost 9 h with both the acquisition and stimulation circuits active. If only the stimulation circuit is used as an Open Loop DBS, the battery can hold sufficient voltage for 24 h of operation. The whole system is low-cost and portable and therefore it could be used as a wearable device.
1. Introduction
Most human motor impairment and dysfunctions originate in the nervous system and the signal transmission between neurons is electrochemical. In this context, electrophysiology studies how these interactions work and an important procedure that is used in this branch of neuroscience is deep brain stimulation (DBS). DBS is a treatment that uses an electrode attached to an implantable pulse generator (IPG) or a neurostimulator that generates electrical impulses inside the brain and, therefore, the central nervous system partially or totally recovers motor functions in patients with neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s and essential tremors [1]. Figure 1 depicts the concept and positioning of a DBS system.
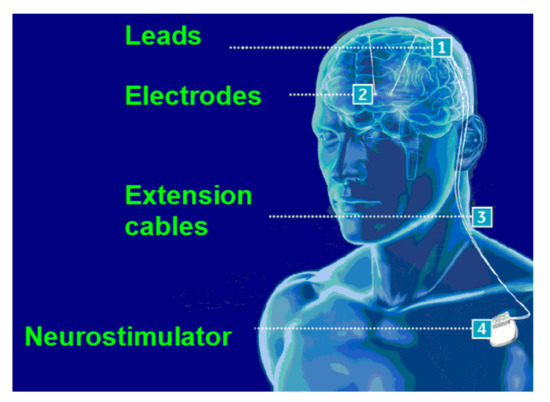
Figure 1.
DBS system positioning (adapted from [1]).
The application of DBS in motor rehabilitation is an alternative to treatments that use remedy and surgery to remove some of the symptoms of motor impairments. The first surgery procedures used to reduce tremors caused damage to the brain and subsequent procedures involved the use of Levodopa which is a remedy that relieves involuntary movements [2]. However, Levodopa had collateral effects such as psychosis and hallucinations. As a solution that does not harm the brain and does not create psychological dysfunctions, DBS was successfully used to treat Parkinson’s disease [3,4], essential tremors [5,6], dystonia [7,8] and chronic pain [9,10]. Furthermore, DBS is also used to treat behavioral dysfunctions such as obsessive–compulsive disorder [11], morbid obesity [12] and depression [13,14,15].
The DBS system control of the amplitude and frequency is performed either by a user that manually changes the values or by itself through acquiring biomarkers and adjusting the parameters according to the response of the patient. For example, a biomarker may be an electrical signal generated by cells of a human organism and is an indicator of the response of the human body to electrical stimuli. The first described system is called an open-loop DBS whereas the second one is called a closed DBS. Open-loop DBS has around 75% efficacy in motor treatment; however, the use of open-loop DBS in psychiatric diseases does not return good results, which indicates that a sophisticated closed-loop DBS may be more suitable for these applications [16].
Figure 2 illustrates the types of control on DBS systems with a comparison between open-loop DBS and closed-loop DBS [16]. Figure 2 also illustrates the concept behind the connections required for stimulation and for the acquisition of biopotentials. Figure 2a is the simple open-loop DBS with fixed parameters and a continuous pulse sequence and Figure 2b is a similar system with bursts of pulses separated by a constant time interval. In both cases, the parameters can only be modified by a healthcare worker and frequency and amplitude are constant. Figure 2c shows an on/off responsive control, which is a closed-loop DBS where the system responds to the activation of brain cells by changing the pulse width. When the biopotential exceeds a threshold value, the DBS system stops the stimulation, and as the biopotential achieves a value below the threshold, the DBS reactivates the stimulation. Bouthour et al. [17] propose an on/off responsive DBS system by monitoring the frequency components registered by local field potentials produced in the subthalamic nucleus of the brain. A setpoint value is defined, and, if an amplitude signal of the biomarker is greater than the setpoint, the neurostimulation signal is interrupted. Otherwise, if the biomarker signal is lower than the setpoint, the neurostimulation signal is reactivated. Figure 2d depicts a closed-loop DBS named adaptive control, like in Figure 2c, but with a variation in the pulse width and the amplitude of the stimulation signal. Finally, Figure 2e illustrates the dynamic stimulation signal control, which is the most complete closed-loop DBS system, since it uses multiple channels to generate pulses in addition to the other features of the system of Figure 2d. Figure 2f shows the connections required for stimulation and acquisition.
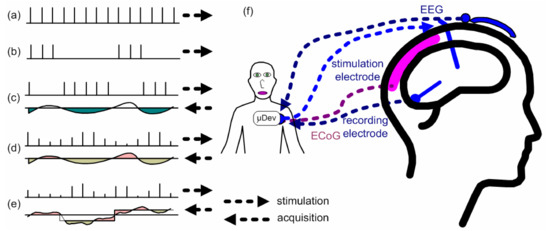
Figure 2.
Types of control on DBS systems with a comparison between (a,b) open-loop DBS and (c–e) closed-loop DBS, and (f) illustration of the connections required for stimulation and for the acquisition of biopotentials. Adapted from Hoang et al., [16].
The majority of works found in the literature and in the market comprise simple neurostimulators for conventional DBS without acquisition. In fact, only a small portion of works allow DBS with adaptive stimulation. The lack of works regarding closed-loop DBS systems (CLDBS) was one of the main motivations behind the proposed system. The main contribution of this paper is a low-size/power-controlled, compact and complete CLDBS system with two simultaneous acquisition channels, two simultaneous neurostimulation channels and wireless communication. This CLDBS system was designed for its low size and easy positioning and at the same time for energy management targeting high efficiency.
2. Proposed Design
2.1. Low-Noise Amplifier (LNA)
The DBS system presented in this paper is a closed-loop system with both acquisition and stimulation circuits. Figure 3a shows the block diagram of the proposed DBS system. To provide a constant electrical current and to control the waveform parameters, a Howland current pump (HCP) was used alongside a microcontroller. The HCP receives a control signal from a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) [18,19]. The DAC that generates the waveform is internal to the ESP32 microcontroller, which will receive the information from the signals acquired through an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which is also internal to the ESP32. The choice of the ESP32 development platform is also justified based on its wireless communication interfaces, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Moreover, the ESP32 has two cores, which allows the DBS system to control the stimulation and acquisition tasks individually. An internal program receives the input signal data and controls the values of the stimulation waveform parameters. Figure 3b shows the block diagram of the stimulation system, composed of the wireless module (ESP32 board), the DAC converters, the buffers, the constant current HCP circuits and the stimulation electrodes.
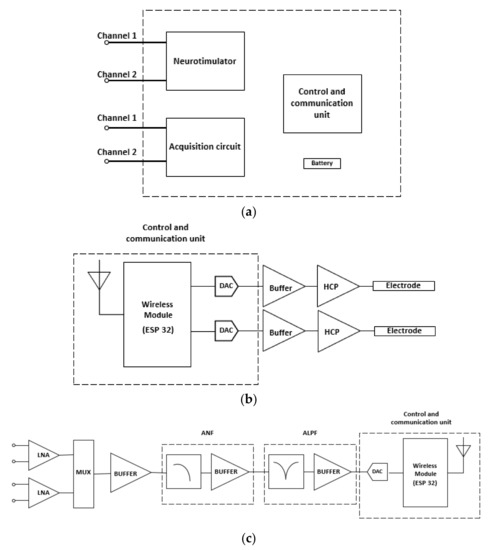
Figure 3.
(a) Block Diagram for the stimulator circuit of the DBS system. (b) Neurostimulator block diagram. (c) Acquisition system block diagram.
The acquisition circuit receives the signals delivered by electrodes inserted in brain regions of interest monitoring during stimulation of the brain, sites that can provide biomarker signals for a better analysis of the performance of the DBS and be the feedback loop in a closed-loop stimulation system. The first stage of the circuit has two channels with low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) in the differential configuration and is insensitive to DC levels present in the input signal. Both LNAs have the function of improving the signal from the electrodes and blocking the DC levels that are often present on the acquired signal. The second stage has two acquisition channels that conduct the output signals to a multiplex (MUX) and a buffer to promote a good impedance match between the stages. The next stage is an analog notch filter (ANF) to remove the noise component from the supply. The subsequent stage of the circuit consists of an active low-pass filter (ALPF) that will promote the attenuation of high-frequency noise and provide more gain to the signal. Finally, the signal is conducted to an ADC from the microcontroller ESP32. Figure 3c shows the diagram of blocks of the biopotential acquisition circuit.
The operational amplifier chosen for the design of the signal conditioning is the AD8609 manufactured by Analog Devices, a low-power precision amplifier with low-noise rail-to-rail input technology, a typical common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) of 100 dB at the output and noise density of 22 nVHz-1/2. The gain of the first stage was designed to be around 33 dB and the gain of the ALPF at approximately 21 dB, so the total loop gain is 54 dB. The frequency of ANF was designed for 60 Hz, while the cutoff frequency of the ALPF was designed to be at approximately 10.6 kHz.
2.2. Neurostimulator
The control unit generates the stimulation signal by an analog output created by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) of the control unit, which is the input of each channel of the neurostimulator. Even though the pulse amplitude is defined by the control unit the amplitude value could be affected by the impedance of the brain tissue which could vary according to the region where the electrode is implanted. To bypass this problem, the stimulation circuit generates an electrical current with a value proportional to the voltage input and constant regarding the brain impedance. This system is the HCP represented in Figure 4. The quantity Iout is the output current and ZL is the impedance of the brain tissue represented as the load impedance.
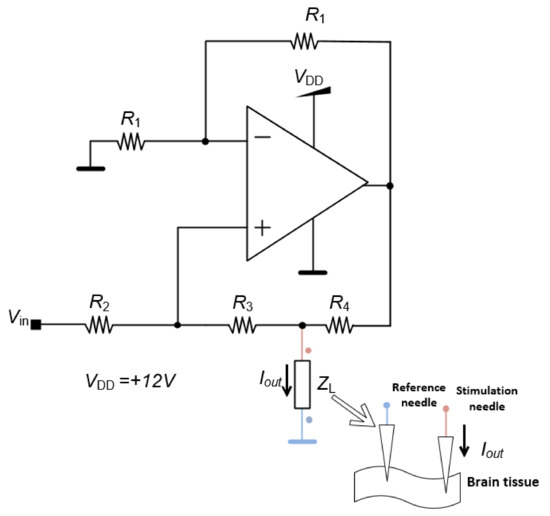
Figure 4.
Howland current pump (HCP) circuit diagram.
The quantity Vin is the input voltage given by the control unit and R1, R2, R3 and R4 are fixed parameters, which means that the microcontroller can directly alter the current even if the impedance of the body tissue changes during the application of the DBS.
The output electrical current Iout produced by the HCP circuit is given by the following equation:
The values used for the built circuit are R1 = R2 = 12.1 kΩ, R3 = 10 kΩ and R4 = 2.2 kΩ, and the output current Iout is 1.4 mA for the maximum output voltage of the DAC.
2.3. Acquisition Circuit
The first stage has an LNA with an elevated gain to amplify low-amplitude signals from biomarkers and improve those signals for the following stages. The LNA also has a high entrance impedance. The LNA circuit has a differential configuration to remove DC components from the input signal. Figure 5 shows the circuit diagram of the LNA with C1 and C2 capacitances to remove the DC component alongside two resistances R1 to polarize the circuit. The electrical supply of the LNA is provided by a single VDD, while the common-mode voltage Vcm is equal to half of the voltage supply, i.e., Vcm = VDD/2 = (3.3 V)/2 = 1.65 V.
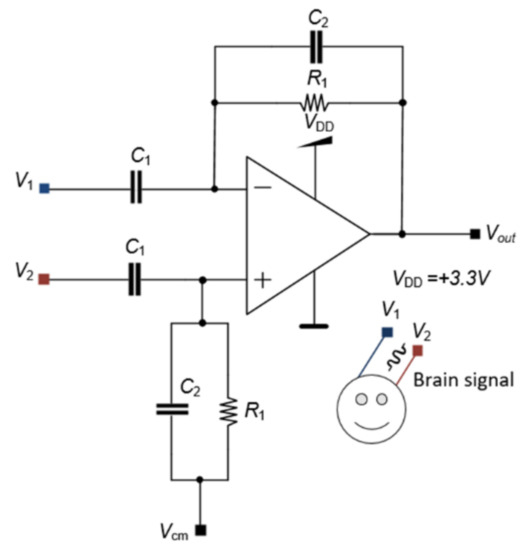
Figure 5.
LNA circuit diagram.
The schematic circuit of Figure 6 has both the inverter and non-inverter configurations that generate V1 and V2, respectively. Both the input and feedback impedances Z1 and Z2 are given by:
and
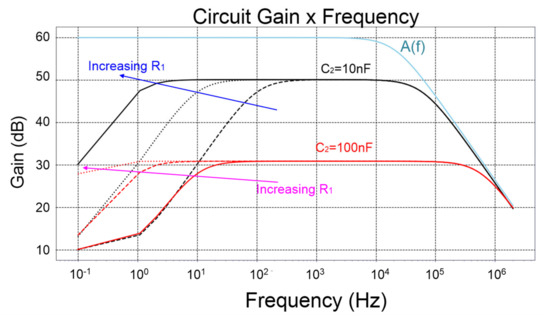
Figure 6.
Closed−loop gains for a few combinations of C2 = {10, 100} nF, and R1 = {1, 10, 100} MΩ, and their comparison with the open-loop gain A(f) of a generic OpAmp with only one pole.
The ratio of the impedances Z1 and Z2 with (Z1 + Z2) is given by:
and
The complete LNA forms a difference amplifier; thus, the voltage Vout at the output of LNA is given by:
The feedback factor β and its inverse are defined, respectively, as:
and
Therefore, the gain of the LNA (i.e., the feedback gain) Af(s) is given by:
At the medium frequencies, C1 + C2 ≈ C1, and [sR2(C1 + C2) + 1] ≈ sR2C1, making the midband voltage gain equal to:
Normally, in the majority of commercial operational amplifiers, A(s) can be expressed with a single pole, or at least with a dominant pole next to the origin. However, the additional poles must be taken into account if they exist. This particular case is a good and general example to deduce the feedback gain and to understand the respective frequency behavior. In the particular case of only one pole:
At the medium frequencies, A(s) » 1, and the midband voltage gain results on:
At the medium frequencies, it is already known that [sR2(C1 + C2) + 1] ≈ sR2C1, which is combined with [sR2C2 + 1] ≈ sR2C2 at these frequencies, so the midband voltage gain is then equal to:
Figure 6 illustrates plots of generic transfer functions of the closed-loop gains, where it is possible to observe the existence of one zero and two poles, as well as their relative positions. These positions are similar to the zeros and poles of the LNA of this paper, because Equation (11), i.e., the full equation of the gain of the LNA for all frequencies, also contains a zero fz = 0 Hz in the origin. This zero is canceled by the first pole fL = 1/(2πR2C2), flattening the feedback gain. The feedback gain starts to decrease from the midband gain of A1[dB] at the frequency of:
Figure 7 shows the active notch filter (ANF) used to remove the 60 Hz frequency from the energy supply. The R value used was 10 MΩ and the C value was 270 pF.
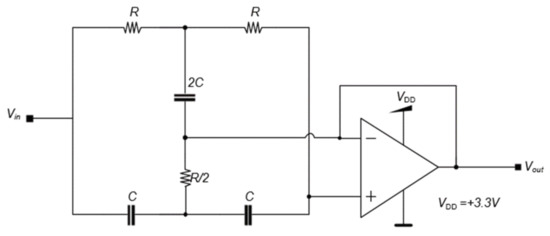
Figure 7.
Active notch filter (ANF) circuit diagram.
A low-pass filter with gain (ALPF) was built as shown in Figure 8 with R1 = 100 kΩ, R2 = 1 MΩ, R3 = 15 kΩ and C = 1 nF. The gain and cutoff frequency are then given by:
and
Figure 8.
Active low-pass filter circuit diagram.
This means that the cutoff frequency was settled to 10.6 kHz and the gain settled to 11× or ≈20.8 dB.
2.4. Control and Communication Unit
The resolution of the ADC of the ESP32 microcontroller is defined as the minimum voltage that the ESP32 could read. The signal that the ADC receives is amplified by the LNA and the ANF, which improves the resolution of the ADC, as the real value of the biological signal is lower than the read value. The resolution and the total gain of the circuit Gtotal are given by:
and
The LNA gain GLNA is 45 v/v, the GALPF is 11 v/v and Nbits is 12 for the ESP32. The maximum voltage input VADC that the ESP32 can read is 3.3 V. Substituting these values in Equations (15) and (16) the resolution of the DBS acquisition is 1.628 µV/bit. The resolution is in the same order as the amplitude of biopotentials.
2.5. Energy Control
The power supply of the system consists of a 3.7 V lithium polymer battery that supplies +5 V step-up from an MT3608 integrated circuit that generates 5 V. A battery with a capacity of 1800 mAh was used; however, other batteries with smaller capacity could be used at the cost of a small useful life. The resulting voltage supplies both a +3.3 V step-down and a +12 V step-up. The +12 V output supplies the circuit and an inverter from an ICL7660A integrated circuit, which results in a symmetrical supply of +12 V and −12 V. The power conversion efficiency for a maximum supply current of 20 mA provided by the ICL7660A is higher than 95%. It is recommended to not exceed this value with the penalty to decrease the efficiency.
The block diagram in Figure 9a illustrates the battery and circuits used to supply the DBS system. Figure 9b illustrates the individual voltages used to supply the neurostimulator, the control and communication unit and the acquisition circuit.
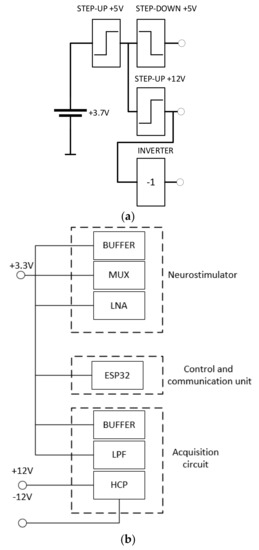
Figure 9.
(a) Block diagram of the battery and circuit used to supply the DBS system, and (b) the individual voltages used to supply the neurostimulator, the control and communication unit and the acquisition circuit.
Figure 9 shows the configuration used to supply the system. The 3.3 V output is used in the ESP32 microcontroller and the symmetrical output is used to polarize the amplifiers.
To optimize the use of the battery, and, therefore, to increase the lifetime of the system, the ESP32 can activate the stimulation and the acquisition portion separately.
2.6. Prototype
For the design and building of the printed circuit board, Altium software (Student License) was used, due to its versatility in designing flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs). The PCB has the acquisition and stimulation, power management and wireless communication circuits. To miniaturize the system, the design configuration was flex–rigid, which has flexible parts and reduces the area of the PCB.
The PCB (without folds) had dimensions of 91 cm × 96 cm, totaling an area of 8736 cm2. After performing the folds, it had dimensions of 56 cm × 35 cm and a height of 1.2 cm, totaling an area of 1960 cm2. Thus, the space occupied by the printed circuit board had an area reduction of approximately 77.56%.
After carrying out the printed circuit board project, and with all the dimensions, the mechanical envelope was defined to house the electronic part. For the design of the box, the Autodesk Inventor 2022 (Student License) software was used. The box, after being finished, had dimensions of 58 cm × 37 cm × 29 cm. After the design, 3D printing was used to manufacture the box. Figure 10 shows views of the PCB project, while Figure 11 shows views of the manufactured and the PCB inserted in the box after manufacture.
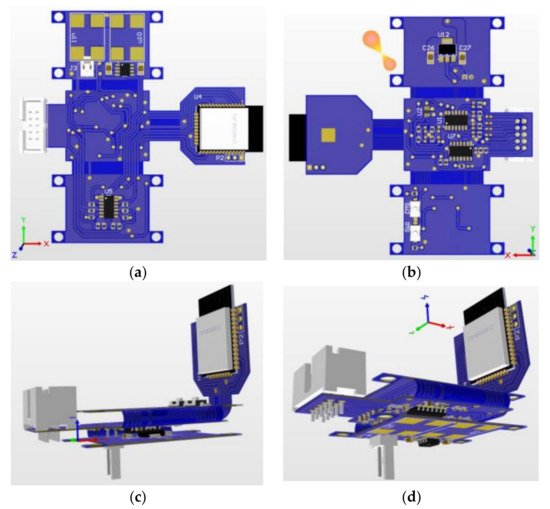
Figure 10.
(a) Top and (b) bottom views of the flex–rigid PCB project. (c,d) Two other perspectives.
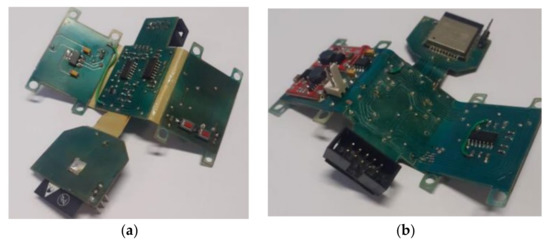
Figure 11.
(a) Top and (b) bottom views of the manufactured PCB. (c,d) Two other perspectives.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Neurostimulator
The neurostimulator was tested in a saline solution (also known as normal saline solution of NSS, or NS or N/S) that simulated brain tissue [20]. The concentration of a saline solution is 9 g of salt per liter of water (wd = 0.9%) and it is widely prescribed by medical doctors for intravenous infusion, despite the true concentration of salt in human blood being only 0.6%. There are no documented studies about the wide adoption of the saline solution by the medical industry. A possible explanation is the ease, convenience, and low cost of mixing common salt with water. The objective of this experiment was to measure the electrical current indirectly by measuring the voltage applied over a variable impedance. A resistor was inserted in series with the electrodes to emulate a variation in the impedance of the electrode and neural tissue interface. Two tests were carried out with two values for this resistance, namely 1 kΩ and 10 kΩ, to promote a 10-fold variation in the magnitude of the impedance. Figure 12a,b show, respectively, the block diagram and the photography of the experiment setup used to test the stimulation circuit.
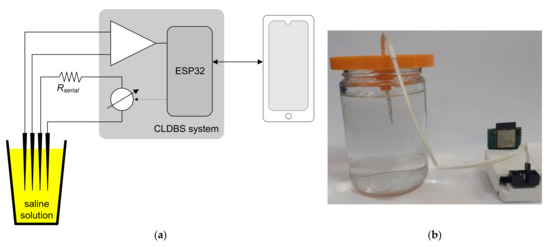
Figure 12.
(a) Block diagram and (b) photo of the experimental setup to test the DBS system in a saline solution.
Figure 13a,b show the experimental results of the tests done on a saline solution for serial resistors Rserial of 1 kΩ and 10 kΩ, respectively. The fitted lines on the two plots agree very well with the measurements with correlation coefficients of 99.98%.
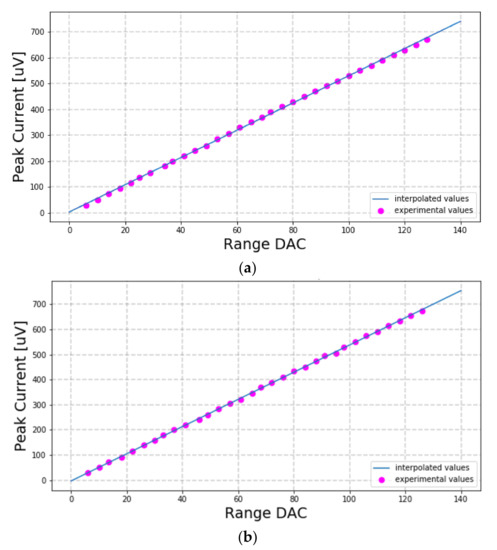
Figure 13.
Tests on a saline solution with series resistor Rserial of value (a) 1 kΩ and (b) 10 kΩ.
3.2. Acquisition System
The acquisition system for biopotentials was tested to obtain the frequency response of the gain of the circuit. These tests were made using a small amplitude signal generator with a sine waveform and starting frequency of 1 Hz. The frequency gradually increased until a decrease of 3 dB of the gain, which occurs in the cutoff frequency. The gain plot is depicted in Figure 14. The blue dots represent the experimental values of gain measured by the oscilloscope. The average gain for most frequencies is approximately 53 dB and the cutoff frequency is roughly 7.5 kHz. The attenuation after the cutoff frequency is around 60 dB per decade.
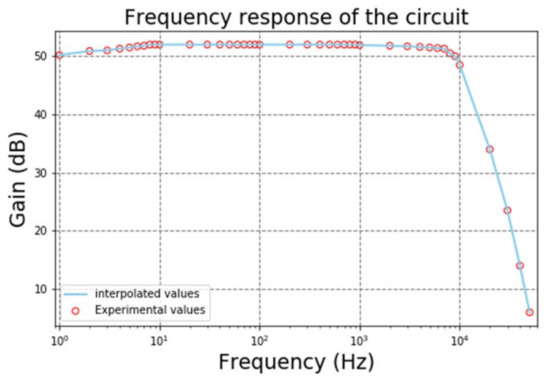
Figure 14.
Experimental values of the gain of the biopotential LNA.
Another important parameter is the acquisition rate, which was obtained experimentally by applying a sinusoidal 1 kHz signal to the ADC of the ESP32. By the time of one whole period of 1 ms, 115 samples were obtained, which implies a sample rate of 115,000 samples per second.
3.3. Software Implementation
Figure 15 shows the software routine used to control the test. Initially, the timer receives the period value and successive iterations are performed until the timer reaches zero. The number of iterations before the overflow happens is the acquisition rate by milliseconds which is the period of the signal.
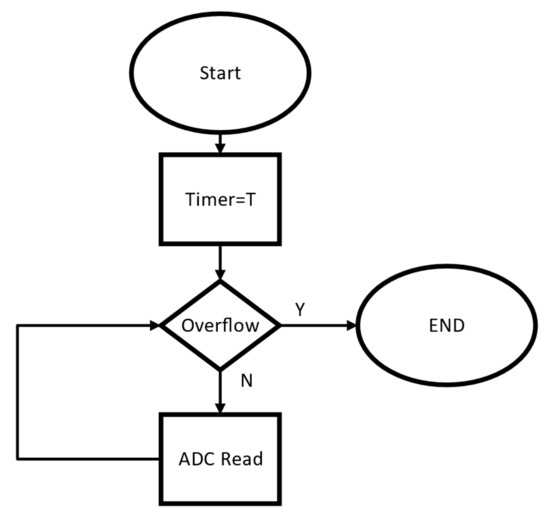
Figure 15.
Software routine used to test the acquisition rate of the internal ADC of the ESP32.
The software that controls the DBS system was developed in C#. It receives data provided by the user, such as waveform, frequency, pulse width and amplitude, and transfers this information to the ESP32. The ESP32 has two cores that control separately the acquisition and stimulation circuits. The ADC reads 100 samples and then the software activates the DAC, which generates the stimulation signal.
The pulse waveform is divided into four parts. The first step is the positive pulse, the second step is the time between pulses, the third step is the negative pulse and the final step is the time interval between pulses. Figure 16 shows a diagram of a generic waveform generated by the system.
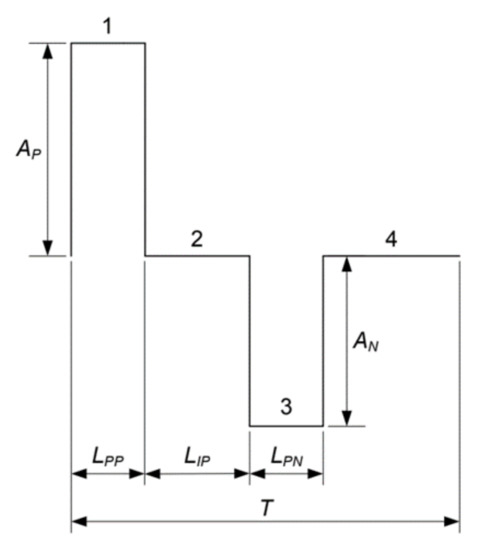
Figure 16.
Pulse width and amplitude diagram.
The complete routine from the pulse generation and the timer count is shown in Figure 17. The variables A and L are two arrays that store the values of the pulse amplitude and of the pulse width over time, respectively. The variables A[i] and A[i] are the values stored in the ith position of the arrays A and L, respectively. The amplitude value shown in Figure 17 is expressed in bits and varies from 0 to 255. The 127 value is attributed to A[2] and to A[4] as the middle of the maximum and minimum values that could be achieved by the stimulator, whereas the Ap and An values, which are assigned to A[1] and A[3], are the maximum and minimum values used for the pulse. Figure 17 also shows the timer count routine with values like those illustrated in the flowchart of Figure 15.
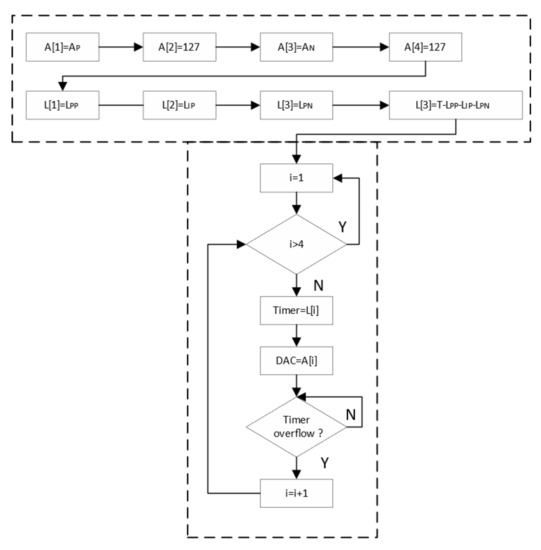
Figure 17.
Complete diagram for pulse generation.
The pulses generated by the routine presented in Figure 17 were collected in an oscilloscope and depicted in Figure 18. The currents were injected into a resistor of 15 kΩ to produce voltage signals in their terminals to ease observation of the current shapes on an oscilloscope. This observation was even more facilitated because the resistor was connected between the output of the stimulator and the ground, e.g., to 0 V.
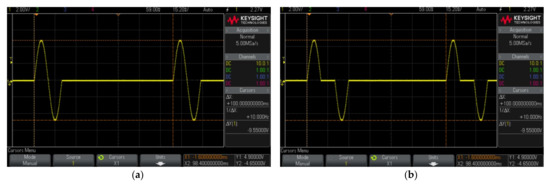
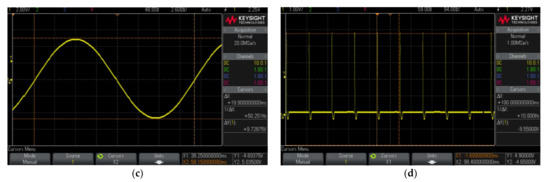
Figure 18.
Pulses generated with several shapes by the program and collected on the oscilloscope to illustrate the ability of the proposed stimulator. These signals are currents with (a) sinusoidal shape with amplitudes of ±322 μA with interpulse interval of 0 s, positive and negative pulse widths of 10 ms (50 Hz), and frequency of 10 Hz; (b) sinusoidal shape with amplitudes of ±322 μA with interpulse interval of 10 ms, positive and negative pulse widths of 10 ms (50 Hz), and frequency of 10 Hz, (c) sinusoidal shape with amplitudes of ±322 μA with interpulse interval of 0 s, positive and negative pulse widths of 10 ms (50 Hz), and frequency of 50 Hz; and (d) pulsed shape with positive amplitude of −322 μA, with negative amplitude of −32 μA, positive pulse width of 10 ms, negative pulse width of 20 ms, and frequency of 10 Hz.
3.4. Closed-Loop Ex-Vivo Tests
Figure 12a also shows that one of the LNAs was connected to the saline solution to do loop-back tests for the CLDBS system. These tests also emulate ex-vivo conditions to derive clinical protocols for future in-vivo experimentation with rodents. Figure 19 illustrates the shapes of the current signals that were injected into the saline solution, while Figure 20 illustrates the corresponding signals that were acquired by a selected acquisition channel.
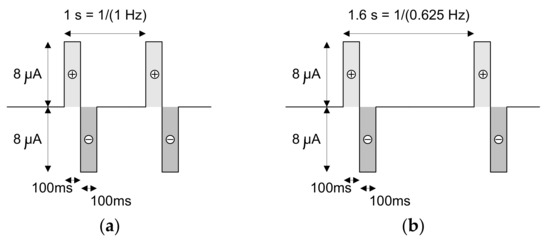
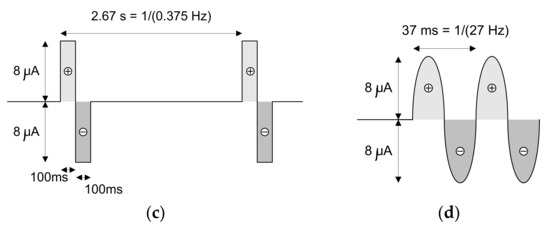
Figure 19.
Shapes of the current signals that were injected in the saline solution during the loop-back tests. These current signals present positive and negative amplitudes of 8 μA and frequencies of (a) 1 Hz, (b) 0.625 Hz, (c) 0.375 Hz and (d) 27 Hz.
Figure 20.
Signals acquired during the loop-back tests in response to the current signals that were injected into the saline solution. The acquired signals also present frequencies of (a) 1 Hz, (b) 0.625 Hz, (c) 0.375 Hz and (d) 27 Hz. These acquired signals correspond to the injected signals illustrated in Figure 19a–d, respectively.
The current signals that were injected in the saline solution present positive and negative amplitudes of 8 μA and frequencies of (a) 1 Hz, (b) 0.625 Hz, (c) 0.375 Hz and (d) 27 Hz, respectively. The first three signals have rectangular shapes, while the fourth is a sinusoid. It is important to not forget that the acquisition channels limit the bandwidth of the acquired and amplified signal to 7.5 kHz. This effect is observable when the signals with square shapes are injected into the saline solution rather than the sinusoidal shape.
3.5. Power Consumption Tests
The battery was tested by allowing the CLDBS to work until the battery output value reached below 2.3 V and, therefore, the control unit stopped working. Three scenarios were experimented with: only the stimulation channel on and acquisition off; both stimulation and acquisition on; and only the acquisition on and stimulation off. The results are presented in Figure 21, showing the behavior of the voltage at the terminals of the lithium polymer battery that supplied the CLDBS for the three power consumption profiles. The nominal voltage and capacity of the battery used in these tests are, respectively, 3.7 V and 1800 mAh. When both circuits were on, the battery could hold up to 10 h with the ESP32 working well. For more than 8 h, the voltage remained above 3.5 V. When only the stimulation was turned on, the battery could hold the voltage over 3.5 V for more than 20 h. Finally, when only the acquisition was on, the battery voltage also decreased, but at a later time, after around 13 h. It must be noted that a second experimental setup based on an Arduino board was used to read the voltage that supplied the ESP32, and, hence, the supply voltage of the proposed CLDBS system.
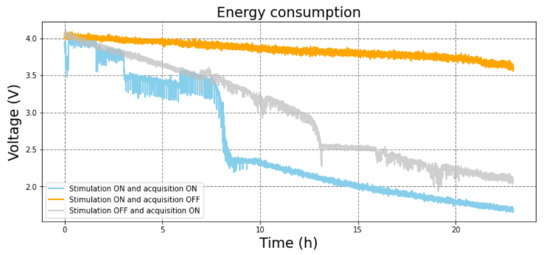
Figure 21.
Voltage at the terminals of the lithium polymer battery that supplied the CLDBS during the consumption tests.
3.6. Comparison with the State-of-the-Art
Table 1 shows the properties of the present work compared with other DBS systems. The main difference between this work and most of the other works is the integration of two acquisition channels that are used to adjust the parameters of the generated wave for stimulation. Another innovation is that the frequency of operation for this work is significantly higher than that of most other applications. The proposed CLDBS system is the one that presents the best current range, i.e., a quasi-symmetrical current range in both directions to maintain electrical safety. The neurostimulator circuit was designed to offer the capability of generating current with a biphasic waveform, which can invert the direction of charge injection in the neuronal tissue. The phenomenon to nullify charge accumulation is called charge balance [21]. Table 1 also contains two DBS systems with active and continuous neurostimulation circuits based on Howland current pumps. However, only the proposed CLDBS system contains two stimulation channels, acquisition and power control. Moreover, the majority of the listed works ensure the inversion of the current direction with H-topology bridges, with the disadvantage of requiring transistors for current inversion, increasing the number of necessary components and the programming complexity. However, the biggest disadvantage of the H-topology is that it requires access to two different contact points on the electrodes, which are normally unipolar. For these reasons, the option of the circuit responsible for injecting the current into the electrodes fell on the Howland current pump (HCP).

Table 1.
Comparison of the present work with other DBS systems.
4. Conclusions
This paper presented a portable and low-cost CLDBS system with two channels for stimulation and two channels for acquisition.
The control and communication unit can improve the durability of the battery by activating individually the acquisition and stimulation circuit. As seen in Figure 20, the battery voltage only decreases significantly after 8 h when both the acquisition and circuit are active. If only the acquisition circuit is active the system works for around 13 h. This result may lead to the conclusion that the communication of the ESP32 with the computer via Bluetooth is the most energy-consuming attribute of the circuit, even though, in a real application, it would require very few battery exchanges or recharges during the day. Additionally, if only the stimulation channels are used, the lifespan of the battery would be longer than a day. Therefore, the system could operate as a CLDBS for 8 h straight or as an OLDBS for more than a day.
In the future, the proposed CLDBS system can be further improved by including safety mechanisms. This goal can be achieved by adding new software features in the data link layer protocol to enhance the confidentiality, integrity, availability and authenticity of the wireless link.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.M.N., G.A.G., R.G. and J.P.C.; methodology, T.M.N., G.A.G., R.G., M.M.A.M. and J.P.C.; validation, T.M.N., M.M.A.M. and R.G.; writing—original draft preparation, T.M.N., G.A.G., M.M.A.M., R.G. and J.P.C.; writing—review and editing, J.A.A., V.M. and J.L.A.; supervision, E.T.F. and E.C.; project administration, J.P.C., J.A.A., V.M. and J.L.A.; funding acquisition, J.P.C., J.A.A., V.M. and J.L.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the FAPESP agency (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) through the project with the reference 2019/05248-7. Professor João Paulo Carmo was supported by a PQ scholarship with the reference CNPq 304312/2020-7.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mayfield Clinic. Deep Brain Stimulation for Movement Disorders. Mayfield Clinic. 2018. Available online: https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-dbs.htm (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Hickey, P.; Stacy, M. Deep brain stimulation: A paradigm shifting approach to treat Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittar, R.G.; Burn, S.C.; Bain, P.G.; Owen, S.L.; Joint, C.; Shlugman, D.; Aziz, T.Z. Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders and pain. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2005, 12, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, R.G.; Galhardoni, R.; Fonoff, E.T.; Lloret, S.P.; Ghilardi, M.G.S.; Barbosa, E.R.; Teixeira, M.J.; de Andrade, D.C. Sensory abnormalities and pain in Parkinson disease and its modulation by treatment of motor symptoms. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehncrona, S.; Johnels, B.; Widner, H.; Törnqvist, A.L.; Hariz, M.; Sydow, O. Long-term efficacy of thalamic deep brain stimulation for tremor: Double blind assessments. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, M.G.S.; Ibarra, M.; Alho, E.J.L.; Reis, P.R.; Contreras, W.O.L.; Hamani, C.; Fonoff, E.T. Double-target DBS for essential tremor: 8-contact lead for cZI and Vim aligned in the same trajectory. Neurology 2018, 90, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonoff, E.T.; Ghilardi, M.G.S.; Cury, R.G. Neurocirurgia funcional para o Clínico: Estimulação Cerebral Profunda em Doença de Parkinson, Distonia e Outros Distúrbios do movimento. In Capítulo de Livro, Condutas em Neurologia, 11th ed.; Nitrini, R., Ed.; Manole Editora: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2016; pp. 53–67. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Vidailhet, M.; Vercueil, L.; Houeto, J.L.; Krystkowiak, P.; Benabid, A.L.; Cornu, P.; Lagrange, C.; Tézenas du Montcel, S.; Dormont, D.; Grand, S.; et al. Bilateral deep-brain stimulation of the globus pallidus in primary generalized dystonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, S.L.; Green, A.L.; Stein, J.F.; Aziz, T.Z. Deep brain stimulation for the alleviation of poststroke neuropathic pain. Pain 2006, 120, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, S.; Kupers, R.C.; Bushnell, M.C.; Duncan, G.H. Analgesic and placebo effects of thalamic stimulation. Pain 2003, 105, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadot, R.; Najera, R.; Hiran, S.; Anand, A.; Storch, E.; Goodman, W.K.; Shofty, B.; Sheth, S.A. Efficacy of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Fonoff, E.T.; Alvarenga, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Miguel, E.C.; Teixeira, M.J.; Damiani, D.; Hamani, C. DBS for Obesity. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobisz, D.; Damborská, A. Deep brain stimulation targets for treating depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figee, M.; Riva-Posse, P.; Choi, K.S.; Bederson, L.; Mayberg, H.S.; Kopell, B.H. Deep Brain Stimulation for Depression. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, S.A.; Bijanki, K.R.; Metzger, B.; Allawala, A.; Pirtle, V.; Adkinson, J.A.; Myers, J.; Mathura, R.K.; Oswalt, D.; Tsolaki, E.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation for Depression Informed by Intracranial Recordings. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 92, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, K.B.; Cassar, I.R.; Grill, W.M.; Turner, D.A. Biomarkers and stimulation algorithms for adaptive brain stimulation. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouthour, W.; Mégevand, P.; Donoghue, J.; Lüscher, C.; Birbaumer, N.; Krack, P. Biomarkers for closed-loop deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease and beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AN-1515, A Comprehensive Study of the Howland Current Pump, 26 April 2013, Texas Instruments. Available online: https://www.ti.com/lit/an/snoa474a/snoa474a.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Nordi, T.M.; Barbosa, V.M.; Gounella, R.H.; Assan, G.; Luppe, M.; Junior, J.N.S.; Carmo, J.P.; Fonoff, E.T.; Colombari, E. Charge Pump Circuit in 65nm CMOS for Neural Stimulation on Deep Brain Stimulation. In Proceedings of the XXXVI Conference on Design of Circuits and Integrated Circuits (DCIS 2021), Vila do Conde, Portugal, 24–26 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Štanfel, D.; Kalogjera, L.; Ryazantsev, S.V.; Hlača, K.; Radtsig, E.Y.; Teimuraz, R.; Hrabač, P. The Role of Seawater and Saline Solutions in Treatment of Upper Respiratory Conditions. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölbl, F.; N’Kaoua, G.; Naudet, F.; Berthier, F.; Faggiani, E.; Renaud, S.; Benazzouz, A.; Lewis, N. An Embedded Deep Brain Stimulator for Biphasic Chronic Experiments in Freely Moving Rodents. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnell, R.C.; de Vasconcelos, A.P.; Cassel, J.C.; Hofmann, U.G. A miniaturized programmable deep-brain stimulator for group-housing and water maze use. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, S.G.; Lipski, W.J.; Grace, A.A.; Winter, C. An inexpensive charge-balanced rodent deep brain stimulation device a step-by-step guide to its procurement and construction. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 219, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzani, A.Z.; Abulseoud, O.A.; Tye, S.J.; Hosain, M.D.K.; Berk, M. A low power micro deep brain stimulation device for murine preclinical research. IEEE J. Translacional Eng. Health Med. 2013, 1, 1500109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, S.G.; Porr, B.; Riddell, J.; Winter, C.; Grace, A.A. SaBer DBS: A fully programmable, rechargeable, bilateral, charge;balanced preclinical microstimulator for long-term neural stimulation. J. Neurosci. Methods 2013, 213, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.D.; Bennet, K.E.; Tye, S.J.; Berk, M.; Kouzani, A.Z. Development of a miniature device for emerging deep brain stimulation paradigms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibara, H.; Naudeta, F.; Kölblc, F.; Ribota, B.; Faggiania, E.; Kaouac, G.N.; Renaudc, S.; Lewisc, N.; Benazzouza, A. In vivo validation of a new portable stimulator for chronic deep brain stimulation in freely moving rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 333, 108577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluri, F.; Mützel, T.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Krstić, M.; Endres, H.; Volkmann, J. Development of a head-mounted wireless microstimulator for deep brain stimulation in rats. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 291, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnell, R.C.; Dempster, J.; Pratt, J. Miniature wireless recording and stimulation system for rodent behavioural testing. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 066015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).