Deep Comparisons of Neural Networks from the EEGNet Family
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Databases
2.1.1. Physionet
2.1.2. Giga
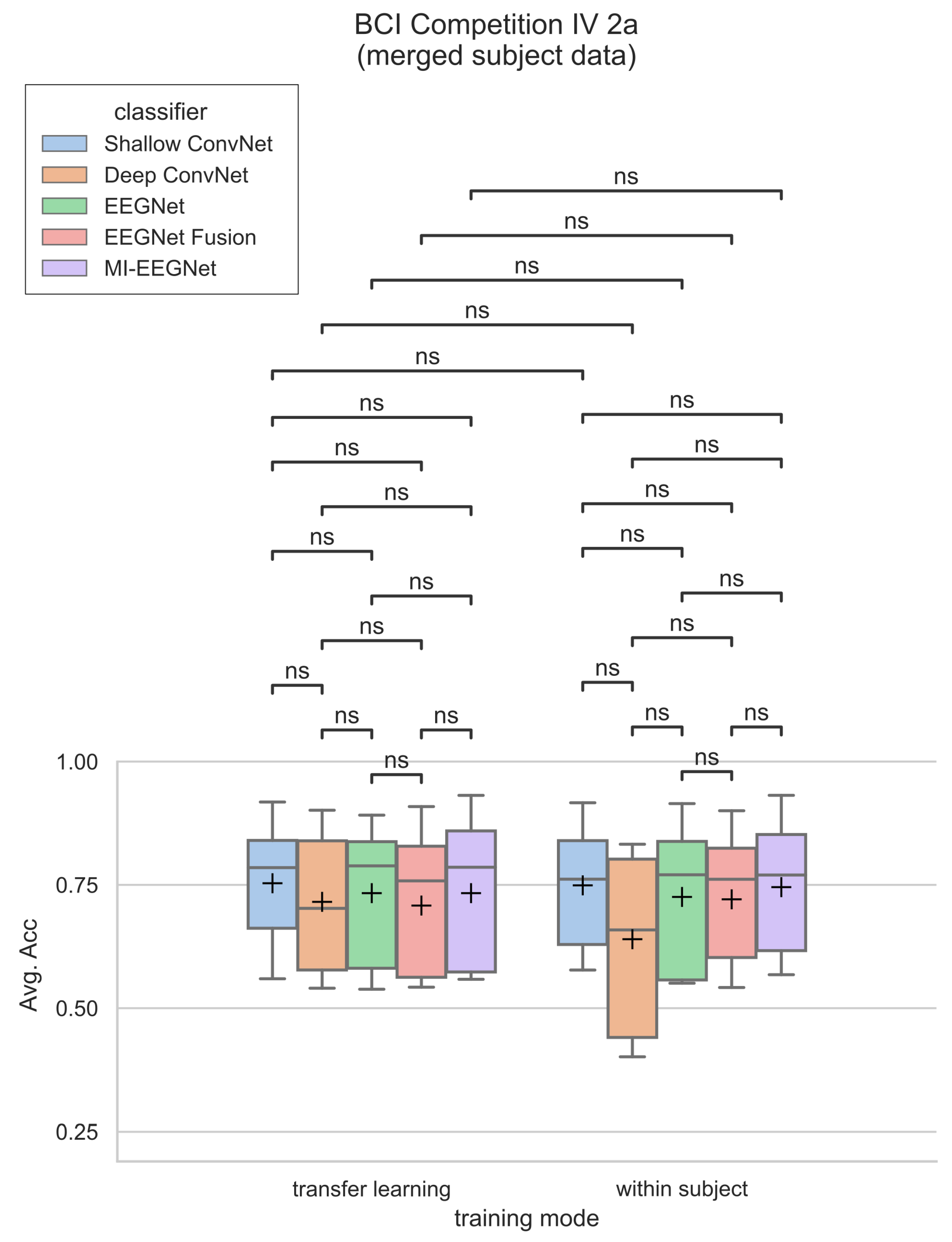
2.1.3. BCI Competition IV 2a
2.1.4. TTK
2.2. Signal Processing
2.3. Neural Networks
2.3.1. Callbacks
2.3.2. ConvNets
2.3.3. EEGNets
2.4. Transfer Learning
2.5. EEGNet Family Comparison
2.6. Significance Investigation of Databases
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCI | Brain–Computer Interface |
| MI | Motor Imagery |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| CSP | Common Spatial Patterns |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| FBCSP | Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern |
| TTK | Research Centre for Natural Sciences (HUN) |
| GoPar | General Offline Paradigm |
References
- Schirrmeister, R.T.; Springenberg, J.T.; Fiederer, L.D.J.; Glasstetter, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Tangermann, M.; Hutter, F.; Burgard, W.; Ball, T. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5391–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Muller, K.R.; Curio, G.; Vaughan, T.; Schalk, G.; Wolpaw, J.; Schlogl, A.; Neuper, C.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Hinterberger, T.; et al. The BCI competition 2003: Progress and perspectives in detection and discrimination of EEG single trials. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Muller, K.R.; Krusienski, D.; Schalk, G.; Wolpaw, J.; Schlogl, A.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Millan, J.; Schroder, M.; Birbaumer, N. The BCI competition III: Validating alternative approaches to actual BCI problems. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2006, 14, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajda, P.; Gerson, A.; Muller, K.R.; Blankertz, B.; Parra, L. A data analysis competition to evaluate machine learning algorithms for use in brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangermann, M.; Müller, K.R.; Aertsen, A.; Birbaumer, N.; Braun, C.; Brunner, C.; Leeb, R.; Mehring, C.; Miller, K.; Mueller-Putz, G.; et al. Review of the BCI Competition IV. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet. Circulation 2000, 101, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schalk, G.; McFarland, D.J.; Hinterberger, T.; Birbaumer, N.; Wolpaw, J.R. BCI2000: A general-purpose brain-computer interface (BCI) system. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med Eng. 2004, 51, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, Y.E.; Williamson, J.; Fazli, S.; Lee, S.W. EEG dataset and OpenBMI toolbox for three BCI paradigms: An investigation into BCI illiteracy. GigaScience 2019, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köllőd, C.; Adolf, A.; Márton, G.; Wahdow, M.; Fadel, W.; Ulbert, I. TTK Dataset—4 Class Motor-Imagery EEG. 2022. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/21.15109/CONCORDA/UOQQVK (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Riener, R.; Seward, L.J. Cybathlon 2016. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; pp. 2792–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, D.; Sigrist, R.; Gerig, N.J.; Wyss, D.; Bauer, R.; Götz, U.; Riener, R. Benchmarking Brain-Computer Interfaces Outside the Laboratory: The Cybathlon 2016. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdikis, S.; Tonin, L.; Saeedi, S.; Schneider, C.; Millán, J.d.R. The Cybathlon BCI race: Successful longitudinal mutual learning with two tetraplegic users. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2003787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statthaler, K.; Schwarz, A.; Steyrl, D.; Kobler, R.; Höller, M.K.; Brandstetter, J.; Hehenberger, L.; Bigga, M.; Müller-Putz, G. Cybathlon experiences of the Graz BCI racing team Mirage91 in the brain-computer interface discipline. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benaroch, C.; Sadatnejad, K.; Roc, A.; Appriou, A.; Monseigne, T.; Pramij, S.; Mladenovic, J.; Pillette, L.; Jeunet, C.; Lotte, F. Long-Term BCI Training of a Tetraplegic User: Adaptive Riemannian Classifiers and User Training. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 635653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehenberger, L.; Kobler, R.J.; Lopes-Dias, C.; Srisrisawang, N.; Tumfart, P.; Uroko, J.B.; Torke, P.R.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Long-Term Mutual Training for the CYBATHLON BCI Race with a Tetraplegic Pilot: A Case Study on Inter-Session Transfer and Intra-Session Adaptation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 635777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korik, A.; McCreadie, K.; McShane, N.; Du Bois, N.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Stow, J.; McElligott, J.; Carroll, A.; Coyle, D. Competing at the Cybathlon championship for people with disabilities: Long-term motor imagery brain–computer interface training of a cybathlete who has tetraplegia. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, N.; Chouhan, T.; Mihelj, E.; Kratka, P.; Debraine, F.; Wenderoth, N.; Guan, C.; Lehner, R. Design Considerations for Long Term Non-invasive Brain Computer Interface Training with Tetraplegic CYBATHLON Pilot. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 648275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, S.; Beraldo, G.; Bettella, F.; Formaggio, E.; Rubega, M.; Del Felice, A.; Masiero, S.; Carli, R.; Petrone, N.; Menegatti, E.; et al. Neural correlates of user learning during long-term BCI training for the Cybathlon competition. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turi, F.; Clerc, M.; Papadopoulo, T. Long Multi-Stage Training for a Motor-Impaired User in a BCI Competition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 647908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Dornhege, G.; Krauledat, M.; Müller, K.R.; Curio, G. The non-invasive Berlin Brain–Computer Interface: Fast acquisition of effective performance in untrained subjects. NeuroImage 2007, 37, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barachant, A.; Bonnet, S.; Congedo, M.; Jutten, C. Riemannian Geometry Applied to BCI Classification. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Proceedings of the Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation, St. Malo, France, 27–30 September 2010; Vigneron, V., Zarzoso, V., Moreau, E., Gribonval, R., Vincent, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotte, F.; Guan, C. Regularizing Common Spatial Patterns to Improve BCI Designs: Unified Theory and New Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ang, K.K.; Chin, Z.Y.; Wang, C.; Guan, C.; Zhang, H. Filter Bank Common Spatial Pattern Algorithm on BCI Competition IV Datasets 2a and 2b. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakhavi, S.; Guan, C.; Yan, S. Parallel convolutional-linear neural network for motor imagery classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Nice, France, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 2736–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, I.; Lapuschkin, S.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.R. Interpretable deep neural networks for single-trial EEG classification. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 274, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabar, Y.R.; Halici, U. A novel deep learning approach for classification of EEG motor imagery signals. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xue, Y.; Hu, L.; Liuli, H. S-EEGNet: Electroencephalogram Signal Classification Based on a Separable Convolution Neural Network with Bilinear Interpolation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 131636–131646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roots, K.; Muhammad, Y.; Muhammad, N. Fusion Convolutional Neural Network for Cross-Subject EEG Motor Imagery Classification. Computers 2020, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musallam, Y.K.; AlFassam, N.I.; Muhammad, G.; Amin, S.U.; Alsulaiman, M.; Abdul, W.; Altaheri, H.; Bencherif, M.A.; Algabri, M. Electroencephalography-based motor imagery classification using temporal convolutional network fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 69, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bria, A.; Marrocco, C.; Tortorella, F. Sinc-based convolutional neural networks for EEG-BCI-based motor imagery classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, B.; Yu, N.; Liu, K.; Sun, K. Advanced TSGL-EEGNet for Motor Imagery EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 25118–25130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyad, M.; Khalil, M.; Adib, A. MI-EEGNET: A novel convolutional neural network for motor imagery classification. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 353, 109037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, B. A channel-mixing convolutional neural network for motor imagery EEG decoding and feature visualization. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 103021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyad, M.; Khalil, M.; Adib, A. A novel multi-scale convolutional neural network for motor imagery classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaheri, H.; Muhammad, G.; Alsulaiman, M. Physics-inform attention temporal convolutional network for EEG-based motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, M.; Zhang, R.; Xiu, C. Motor imagery EEG classification algorithm based on CNN-LSTM feature fusion network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 72, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yin, F. A parallel multi-scale time-frequency block convolutional neural network based on channel attention module for motor imagery classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 79, 104066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, R.; Hui, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Na, R.; Sun, Y.; Ding, W.; Zheng, D.; Chen, X. TCACNet: Temporal and channel attention convolutional network for motor imagery classification of EEG-based BCI. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Liu, K.; Deng, X.; Tang, X.; Yu, H. FB-EEGNet: A fusion neural network across multi-stimulus for SSVEP target detection. J. Neurosci. Methods 2022, 379, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Convolutional neural network and riemannian geometry hybrid approach for motor imagery classification. Neurocomputing 2022, 507, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokur, Z.; Olmez, T. Classification of motor imagery electroencephalogram signals by using a divergence based convolutional neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 113, 107881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, W.; Wahdow, M.; Kollod, C.; Marton, G.; Ulbert, I. Chessboard EEG Images Classification for BCI Systems Using Deep Neural Network. In Bio-inspired Information and Communication Technologies, Proceedings of the 12th EAI International Conference, BICT 2020, Shanghai, China, 7–8 July 2020; Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering; Chen, Y., Nakano, T., Lin, L., Mahfuz, M.U., Guo, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, W.; Kollod, C.; Wahdow, M.; Ibrahim, Y.; Ulbert, I. Multi-Class Classification of Motor Imagery EEG Signals Using Image-Based Deep Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Republic of Korea, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Luo, J.; Li, L.; Li, X. A classification method for EEG motor imagery signals based on parallel convolutional neural network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, L.; Xie, L. Joint spatial and temporal features extraction for multi-classification of motor imagery EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Song, Y.; Xie, L. Excellent fine-tuning: From specific-subject classification to cross-task classification for motor imagery. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.M. Adaptive transfer learning-based multiscale feature fused deep convolutional neural network for EEG MI multiclassification in brain–computer interface. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Wang, D. A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 2016, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khademi, Z.; Ebrahimi, F.; Kordy, H.M. A transfer learning-based CNN and LSTM hybrid deep learning model to classify motor imagery EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, F.; Porcaro, C.; Baldassarre, G. A 1D CNN for high accuracy classification and transfer learning in motor imagery EEG-based brain-computer interface. J. Neural Eng. 2022, 18, 066053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zong, Q.; Dou, L.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z. Hybrid deep neural network using transfer learning for EEG motor imagery decoding. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, H.; Whelan, R.; Reilly, R.B. FASTER: Fully Automated Statistical Thresholding for EEG artifact Rejection. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 192, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noboa, E.; Rácz, M.; Szűcs, L.; Galambos, P.; Márton, G.; Eigner, G. Development of an EMG based SVM supported control solution for the PlatypOUs education mobile robot using MindRove headset. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.; Lobaugh, N.J.; Joordens, S.; McIntosh, A.R. EEG variability: Task-driven or subject-driven signal of interest? NeuroImage 2022, 252, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. M3CV: A multi-subject, multi-session, and multi-task database for EEG-based biometrics challenge. NeuroImage 2022, 264, 119666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiblanco Jimenez, I.A.; Gomez Acevedo, J.S.; Olivetti, E.C.; Marcolin, F.; Ulrich, L.; Moos, S.; Vezzetti, E. User Engagement Comparison between Advergames and Traditional Advertising Using EEG: Does the User’s Engagement Influence Purchase Intention? Electronics 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Yang, H.; Hou, Z.G.; Ni, Z.L.; Chen, S.; Fang, Z. Bilinear neural network with 3-D attention for brain decoding of motor imagery movements from the human EEG. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2021, 15, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köllőd, C.; Adolf, A.; Márton, G.; Wahdow, M.; Fadel, W.; Ulbert, I. Closed loop BCI System for Cybathlon 2020. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.04172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechelt, L. Early Stopping — But When? In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, 2nd ed.; Montavon, G., Orr, G.B., Müller, K.R., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, P.; Laskar, S.H.; Hazarika, J.; Mahamune, R. CWT Based Transfer Learning for Motor Imagery Classification for Brain computer Interfaces. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 345, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Nerual Network | Reference |
|---|---|
| Shallow ConvNet | [1] |
| Deep ConvNet | |
| EEGNet | [25] |
| S-EEGNet | [29] |
| EEGNet Fusion | [30] |
| TCNet Fusion | [31] |
| Sinc-EEGNet | [32] |
| TSGL-EEGNet | [33] |
| MI-EEGNet | [34] |
| Channel-Mixing-ConvNet | [35] |
| AMSI-EEGNet | [36] |
| ATCNet | [37] |
| FFCL | [38] |
| MTFB-CNN | [39] |
| TCACNet | [40] |
| FB-EEGNet | [41] |
| CRGNet | [42] |
| Level | p-Value Range |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10 < p <= 5 × 10 |
| 2 | 10 < p <= 10 |
| 3 | 10 < p <= 10 |
| 4 | p <= 10 |
| Classifier | Avg. Acc. Improvement from Chance Level | Rank | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Within subject | Shallow ConvNet | 0.2071 | 2 |
| Deep ConvNet | 0.1249 | 5 | |
| EEGNet | 0.1997 | 3 | |
| EEGNet Fusion | 0.1871 | 4 | |
| MI-EEGNet | 0.2306 | 1 | |
| Transfer learning | Shallow ConvNet | 0.2721 | 1 |
| Deep ConvNet | 0.2598 | 2 | |
| EEGNet | 0.2521 | 4 | |
| EEGNet Fusion | 0.2312 | 5 | |
| MI-EEGNet | 0.2537 | 3 |
| Rank | Neural Networks | Physionet | Giga | TTK | BCI Comp IV 2a | Avg. Impr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Deep ConvNet | 0.1557 | 0.1418 | 0.0708 | 0.0614 | 0.1075 |
| 2 | Shallow ConvNet | 0.0928 | 0.0497 | 0.0509 | 0.0141 | 0.0519 |
| 3 | EEGNet | 0.0716 | 0.0487 | 0.0288 | −0.0065 | 0.0357 |
| 4 | EEGNet Fusion | 0.0381 | 0.0586 | 0.0379 | 0.0007 | 0.0338 |
| 5 | MI-EEGNet | −0.0058 | 0.0475 | 0.0564 | −0.0015 | 0.0241 |
| Significance Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Database | Sum | Count | Subjects |
| Physionet | 63 | 18 | 105 |
| Giga | 49 | 15 | 108 |
| TTK | 45 | 16 | 25 |
| BCI Comp IV 2a | 31 | 15 | 18 |
| BCI Comp IV 2a- merged subject data | 0 | 0 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Köllőd, C.M.; Adolf, A.; Iván, K.; Márton, G.; Ulbert, I. Deep Comparisons of Neural Networks from the EEGNet Family. Electronics 2023, 12, 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122743
Köllőd CM, Adolf A, Iván K, Márton G, Ulbert I. Deep Comparisons of Neural Networks from the EEGNet Family. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122743
Chicago/Turabian StyleKöllőd, Csaba Márton, András Adolf, Kristóf Iván, Gergely Márton, and István Ulbert. 2023. "Deep Comparisons of Neural Networks from the EEGNet Family" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122743
APA StyleKöllőd, C. M., Adolf, A., Iván, K., Márton, G., & Ulbert, I. (2023). Deep Comparisons of Neural Networks from the EEGNet Family. Electronics, 12(12), 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122743









