Reconfigurable Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting Application: Current Trends, Challenges, and Solutions from Design Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Reviewing the considerations of RF energy harvesting, analyzing its potential utilization of ambient RF signals, and addressing the growing presence of IoT, WSNs, and RFIDs.
- Proposing and investigating a metasurface reflector-based CP reconfigurable antenna, aiming to advance the practical implementation of efficient RF energy harvesting systems.
- Evaluating the RF energy harvesting capability through integration with the GVD rectifier circuit. Theoretical analogies are derived for parameters such as RF-to-DC power conversion efficiency (∘, %) and DC harvested voltage (Vout, V) to assess system performance.
- Presenting a theoretical framework for demonstrating circular polarization (CP) and emphasizing the importance of finding a DC biasing mechanism for polarization reconfigurability, particularly the dynamic switching from LP to CP.
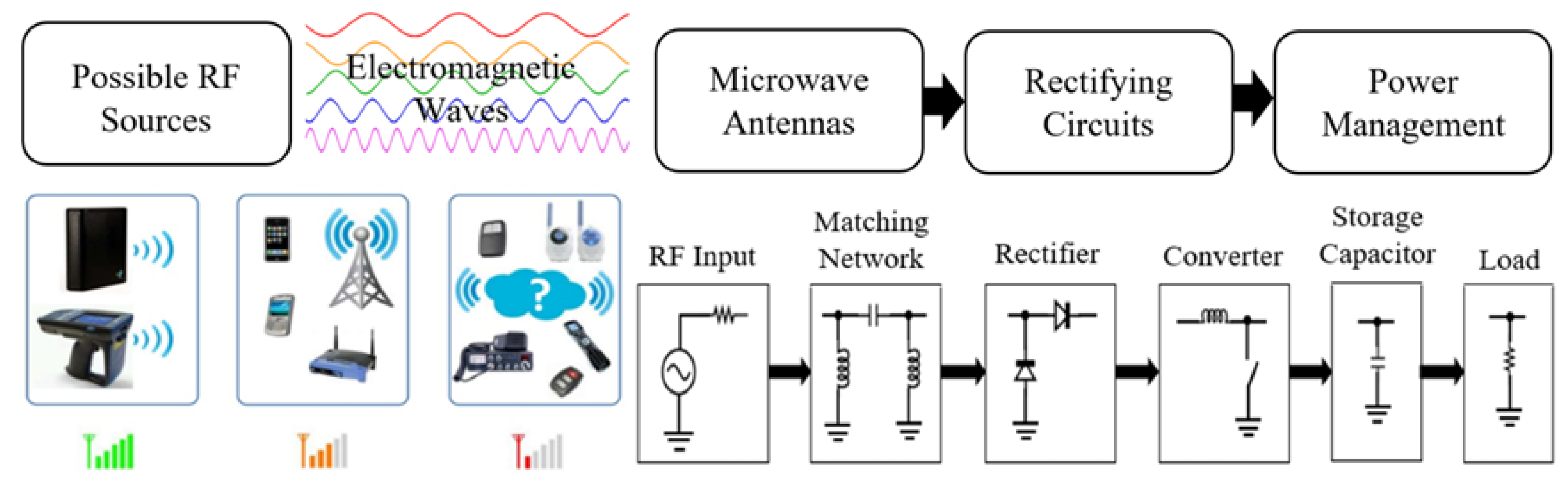
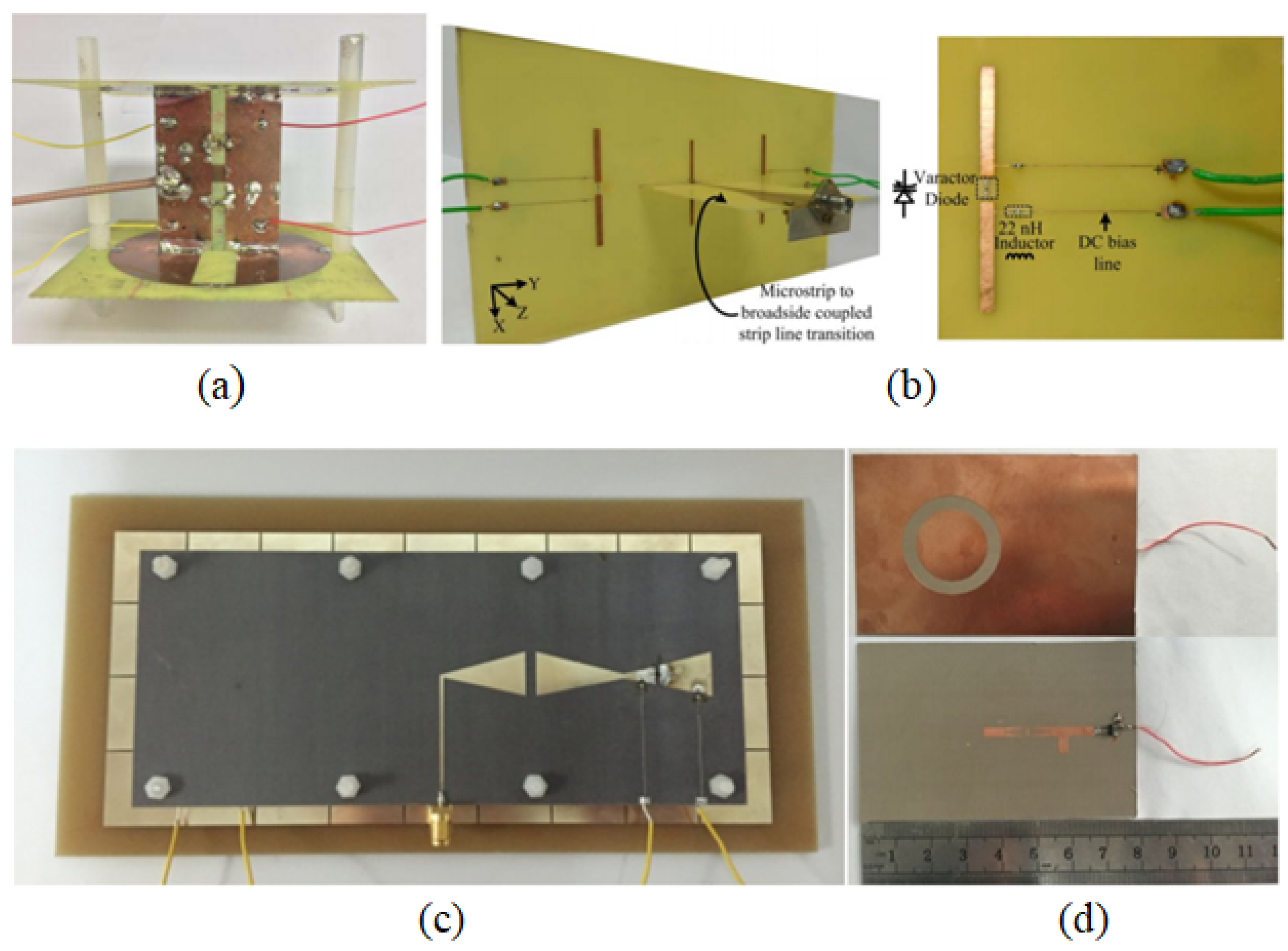
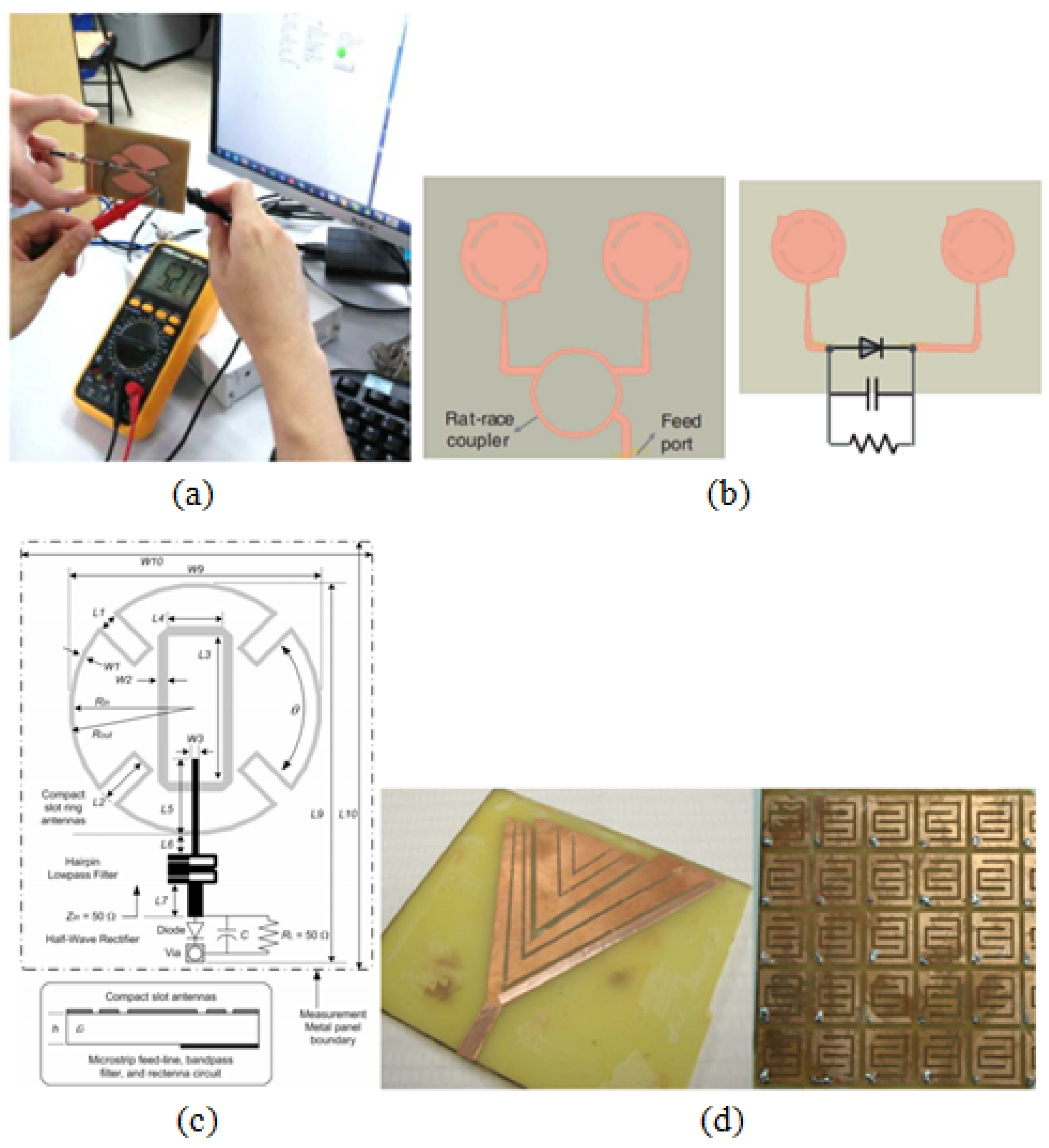
2. Reconfigurable Antennas and Their Usage in RF Energy Harvesting Application
3. Case Study: Solution from Design Perspective
4. Insights
- Phenomenon-A: Transition from LP-to-CP characteristics.
- Phenomenon-B: Intuition behind the implementation of metasurface reflector.
- Phenomenon-C: Understanding the DC biasing mechanism toward reconfigurability.
- Phenomenon-D: Exploration for RF energy harvesting as a prospective application.
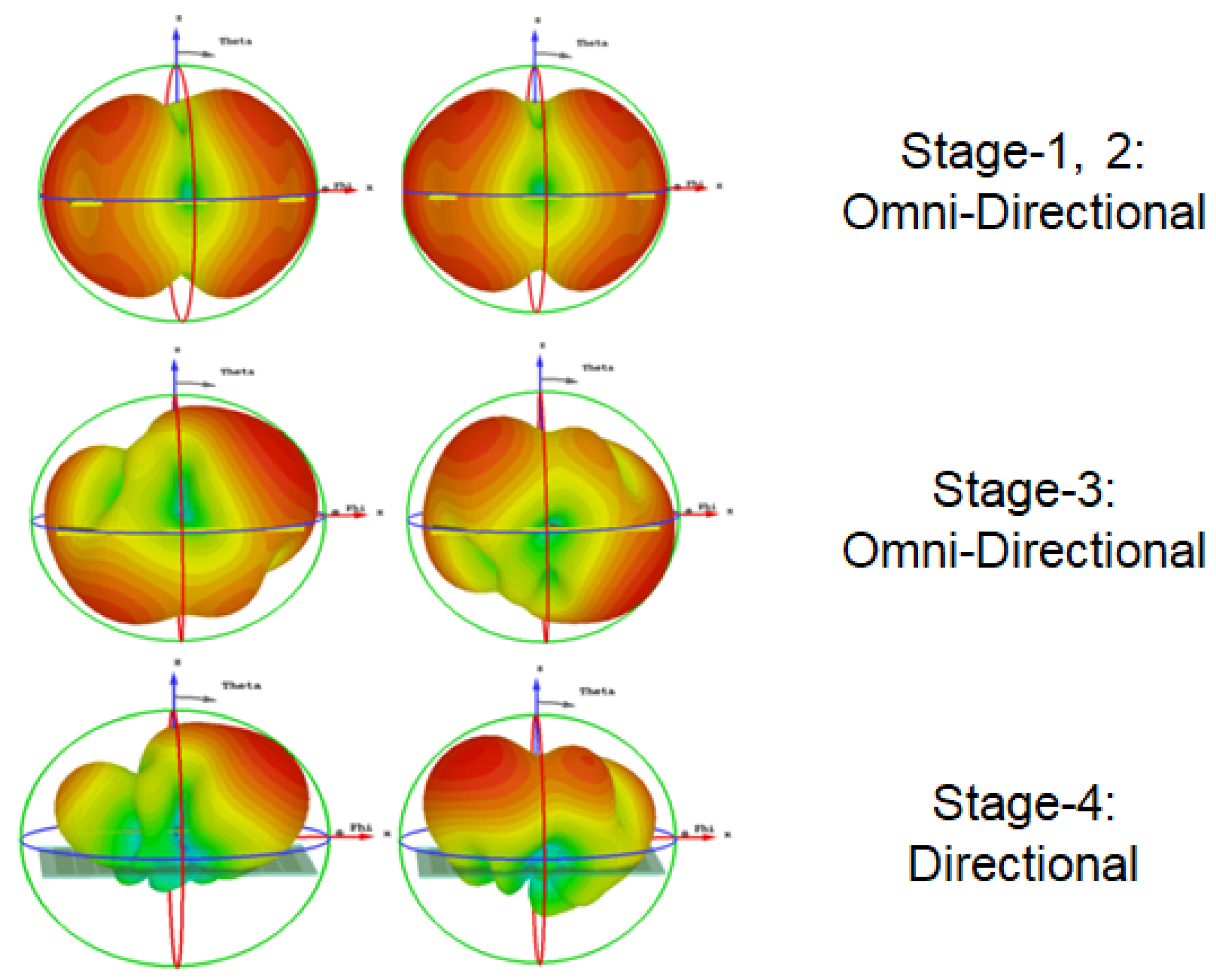
4.1. Transition from LP-to-CP
4.2. Intuition behind Implementation of Metasurface Reflector
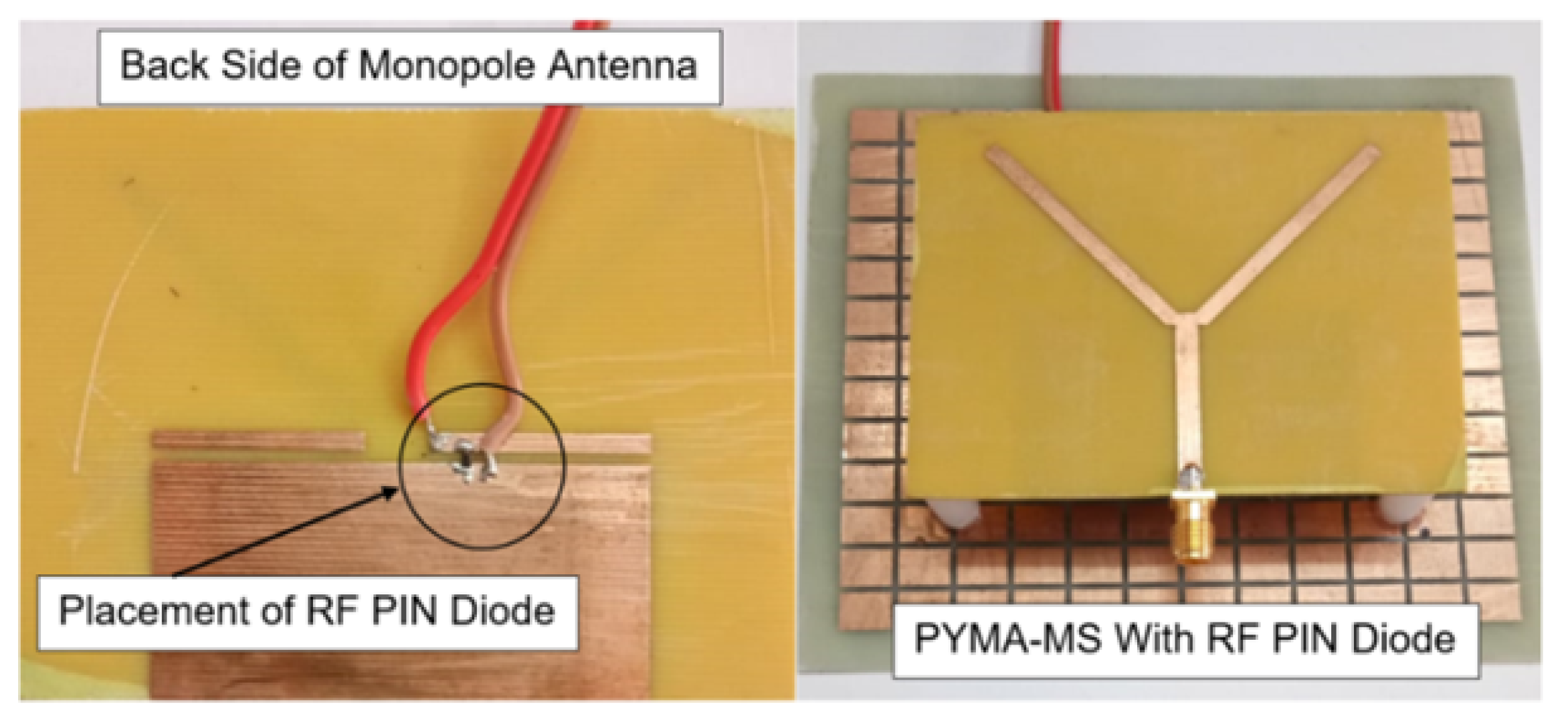
4.3. Understanding DC Biasing Mechanism
4.4. RF Energy Harvesting: Prospective Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valenta, C.R.; Durgin, G.D. Harvesting wireless power: Survey of energy-harvester conversion efficiency in far-field wireless power systems. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2014, 15, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, P.; Niyato, D.; Kim, D.I.; Han, Z. Wireless networks with RF energy harvesting: A contemporary survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 184, 266–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soyata, T.; Copeland, L.; Heinzelman, W. RF energy harvesting for embedded systems: A survey of trade-offs and methodology. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2016, 16, 22–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.G.; Cha, H.K.; Park, W.T. RF power harvesting: A review on designing methodologies and applications. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2017, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alimenti, F.; Palazzi, V.; Mariotti, C.; Mezzanotte, P.; Correia, R.; Carvalho, N.B.; Roselli, L. Smart hardware for smart objects: Microwave electronic circuits to make objects smart. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2018, 19, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakaran, S.K.; Krishna, D.D.; Nasimuddin. RF energy harvesting systems: An overview and design issues. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behera, B.R.; Meher, P.R.; Mishra, S.K. Microwave antennas-An intrinsic part of RF energy harvesting systems: A contingent study about design methodologies and state-of-the-art technologies in current scenario. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2020, 30, e22148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surender, D.; Khan, T.; Talukdar, F.A.; De, A.; Antar, Y.M.; Freundorfer, A.P. Key components of rectenna system: A comprehensive survey. IETE J. Res. 2020, 22, 3379–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surender, D.; Khan, T.; Talukdar, F.A.; Antar, Y.M. Rectenna design and development strategies for wireless applications: A review. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2021, 64, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherazi, H.H.R.; Zorbas, D.; O’Flynn, B. A comprehensive survey on RF energy harvesting: Applications and performance determinants. Sensors 2022, 22, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K. A single-layered metasurface inspired broadband polarization reconfigurable printed monopole antenna for hybrid wireless applications. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2022, 156, 154405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K. Investigation of a high-gain and broadband circularly polarized monopole antenna for RF energy harvesting application. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2022; first view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Behera, B.R.; Esselle, K.P.; Alsharif, M.H.; Jahid, A.; Mohsan, S.A.H. Investigation of a dual-layer metasurface-inspired fractal antenna with dual-polarized/-modes for 4G/5G applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.R.; Meher, P.R.; Mishra, S.K. Metasurface superstrate inspired printed monopole antenna for RF energy harvesting application. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2021, 110, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.R.; Srikanth, P.; Meher, P.R.; Mishra, S.K. A compact broadband circularly polarized printed monopole antenna using twin parasitic conducting strips and rectangular metasurface for RF energy harvesting application. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 120, 153233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.K.; Mishra, S.K. Compact dual-band dual-polarized monopole antennas using via-free metasurfaces for off-body communications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 21, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, N.K.; Mishra, S.K. Polarization converting metasurface inspired dual band dual circularly polarized monopole antennas for OFF body communications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 22, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, L.; Xue, W.; Vladimir, K.; Qi, J. An optimal electric dipole antenna model and its field propagation. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2016, 2016, 8601497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almoneef, T.S.; Sun, H.; Ramahi, O.M. A 3-D folded dipole antenna array for far-field electromagnetic energy transfer. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.S.; Akhtar, M.J. A dual band meandered printed dipole antenna for RF energy harvesting applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 26–29 July 2016; pp. 93–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, H.; Gohar, M.; Ali, M.; Rahman, A.U.; Ahmad, W.; Ghani, A.; Choi, J.-G.; Koh, S.-J. Zero energy IoT devices in smart cities using RF energy harvesting. Electronics 2023, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrawatia, M.; Baghini, M.S.; Kumar, G. Broadband bent triangular omnidirectional antenna for RF energy harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M.; Agarwal, A. A compact coplanar waveguide wideband monopole antenna for RF energy harvesting applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2018, 63, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurvey, M.; Kunte, A. Harvesting RF energy using slotted tri-stepped rectangular monopole antenna. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 126, 3465–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashad, L.; Mohanta, H.C.; Mohamed, H.G. A compact circular rectenna for RF-energy harvesting at ISM band. Micromachines 2023, 14, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, A.; Arai, H. Small loop rectenna for RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference Proceedings, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 5–8 November 2013; pp. 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Stoopman, M.; Keyrouz, S.; Visser, H.J.; Philips, K.; Serdijn, W.A. Co-design of CMOS rectifier & small loop antenna for highly sensitive RF energy harvesters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 622–634. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, M.; Sultan, K.; Kanaya, H. Compact dual-band tapered open-ended slot-loop antenna for energy harvesting systems. Electronics 2020, 9, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Andrenko, A.S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Tan, H.Z. A compact fractal loop rectenna for RF energy harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 2424–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Yamauchi, Y. Printed slot and wire antennas: A review. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, A.; Jun, S.; Sanz-Izquierdo, B.; Aldawas, H.; Ahmed, Q.; Sobhy, M. Evaluation of low-cost inkjet printed slot antenna for energy harvesting applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference, Loughborough, UK, 14–15 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-S.; Cheng, C.-M.; Liao, B.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L.; Wang, H.-Y. Triple-band slot antenna array for energy harvesting for wireless sensor networks. Sensors Mater. 2018, 30, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhammad, S.; Smida, A.; Waly, M.I.; Mallat, N.K.; Iqbal, A.; Khan, S.R.; Alibakhshikenari, M. Design of wideband circular-slot antenna for harvesting RF energy. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 2022, 5964753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursianis, A.D.; Papadopoulou, M.S.; Koulouridis, S.; Rocca, P.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Goudos, S.K. Triple-band single-layer rectenna for outdoor RF energy harvesting applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrawatia, M.S.; Baghini, M.S.; Kumar, G. Differential microstrip antenna for RF energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabban, A. Wearable circular polarized antennas for health care, 5G, energy harvesting, and IoT systems. Electronics 2022, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavaddat, A.; Armaki, S.H.M.; Erfanian, A.R. Millimeter-wave energy harvesting using 4×4 microstrip patch antenna array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.J. The Vivaldi aerial. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference, Brighton, UK, 17–20 September 1979; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, J.; Mrnka, M.; Gamec, J.; Gamcova, M.; Raida, Z. Vivaldi antenna for RF energy harvesting. Radioengineering 2016, 25, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jing, J.; Fan, Y.; Yang, L.; Pang, J.; Wang, M. Efficient RF energy harvest with novel broadband Vivaldi rectenna. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Choi, J.; Itoh, T. Vivaldi antenna with pattern diversity for 0.7 to 2.7 GHz cellular band applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Gupta, R.D.; Parihar, M.S.; Kondekar, P.N. A wideband and high gain dielectric resonator antenna for the RF energy harvesting application. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 78, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, P.R.; Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K. A compact circularly polarized cubic DRA with unit-step feed for Bluetooth/ISM/Wi-Fi/Wi-MAX applications. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 128, 153521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, P.R.; Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K.; Althuwayb, A.A. Design and analysis of a compact circularly polarized DRA for off-body communications. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 138, 153880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surender, D.; Halimi, M.A.; Khan, T.; Talukdar, F.A.; Antar, Y.M. Circularly polarized DR-rectenna for 5G and Wi-Fi bands RF energy harvesting in smart city applications. IETE Tech. Rev. 2021, 39, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.D. The helical antenna. Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, R.A.; Hassan, S.I.S.; Malek, F.; Junita, M.N.; Jamlos, M.F. An investigation of ambient radio frequency as a candidate for energy harvesting source. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Bandung, Indonesia, 25–28 September 2012; pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Jing, J.; Fan, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, M. Design of a novel compact and efficient rectenna for Wi-Fi energy harvesting. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2018, 83, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alex-Amor, A.; Palomares-Caballero, Á.; Fernández-González, J.M.; Padilla, P.; Marcos, D.; Sierra-Castañer, M.; Esteban, J. RF energy harvesting system based on an archimedean spiral antenna for low-power sensor applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, G.; Wang, P. Research progress in Yagi antenna. Procedia Eng. 2012, 29, 2116–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Guo, Y.X.; He, M.; Zhong, Z. A dual-band rectenna using broadband Yagi antenna array for ambient RF power harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, Z.; Korhummel, S.; Dunbar, S.; Scheeler, R.; Dolgov, A.; Zane, R.; Falkenstein, E.; Hagerty, J. Scalable RF energy harvesting. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhosht, R.; Hammad, H. A dualband rectenna design for RF energy scavenging using a modified yagi-uda antenna. In Proceedings of the International Microwave and Antenna Symposium (IMAS), Cairo, Egypt, 7–9 February 2023; pp. 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Hamadameen, J.A. Analysis, design and simulation of the log periodic antenna for mobile communication bands. WSEAS Trans. Commun. 2008, 7, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, H.; Arrawatia, M.; Kumar, G. Broadband planar log-periodic dipole array antenna based RF-energy harvesting system. IETE J. Res. 2019, 65, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, H.S.; Awais, M.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, W.T. A high gain six band frequency independent dual CP planar log periodic antenna for ambient RF energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall, Singapore, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 3024–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Tiang, J.-J.; Roslee, M.B.; Ahmed, M.T.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Mahmud, M.A.P. Design of a highly efficient wideband multi-frequency ambient RF energy harvester. Sensors 2022, 22, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkmen, F.; Almoneef, T.S.; Ramahi, O.M. Scalable electromagnetic energy harvesting using frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, V.; Hester, J.; Bito, J.; Alimenti, F.; Kalialakis, C.; Collado, A.; Mezzanotte, P.; Georgiadis, A.; Roselli, L.; Tentzeris, M.M. A novel ultra-lightweight multiband rectenna on paper for RF energy harvesting in the next generation LTE Bands. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasis, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chattha, H.T.; Jamil, M.; Qiang, H.; Khawaja, B.A. A compact rectenna system with high conversion efficiency for wireless energy harvesting. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35857–35866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, S.E.; Proynov, P.; Hilton, G.S.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Beeby, S.P.; Craddock, I.J.; Stark, B.H. A flexible 2.45-GHz power harvesting wristband with net system output from -24.3 dBm of RF power. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowler, C.; Zhou, J. A metamaterials inspired approach to RF energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Choi, S.-I.; Kim, H.-I.; Hwang, S.; Jeon, S.; Yoon, Y.-K. Metamaterial-integrated high-gain rectenna for RF sensing and energy harvesting applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Mei, Z.; Zhong, H.; You, R.; Lu, W.; You, Z.; Zhao, J. WiFi energy-harvesting antenna inspired by the resonant magnetic dipole metamaterial. Sensors 2022, 22, 6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawe, M.E.I.; Ramahi, O.M. Efficient metasurface rectenna for electromagnetic wireless power transfer and energy harvesting. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2018, 161, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasimuddin, N.; Cheng, Z.N.; Qing, X. Bandwidth enhancement of a single-feed circularly polarized antenna using metasurface. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2016, 58, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Nasimuddin, N.; Alphones, A. Wideband circularly polarized AMC reflector backed aperture antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 61, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, S.B.; Nasimuddin, N.; Alphones, A. Stubs-integrated-microstrip antenna design for wide coverage of circularly polarised radiation. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2017, 11, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Le, M.T. Multiband ambient RF energy harvester with high gain wideband circularly polarized antenna toward self-powered wireless sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgun, U.; Chen, C.C.; Volakis, J.L. Investigation of rectenna array configurations for enhanced RF power harvesting. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwareth, H.; Ibrahim, I.M.; Zakaria, Z.; Al-Gburi, A.J.A.; Ahmed, S.; Nasser, Z.A. A wideband high-gain microstrip array antenna integrated with frequency-selective surface for sub-6 GHz 5G applications. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jandhyala, V. Design of retrodirective antenna arrays for short-range wireless power transmission. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Geyi, W.; Sun, H. Optimum design of wireless power transmission system using microstrip patch antenna arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1824–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rajendran, J.; Mariappan, S.; Rawat, A.S.; Sal Hamid, S.; Kumar, N.; Othman, M.; Nathan, A. CMOS radio frequency energy harvester (RFEH) with fully on-chip tunable voltage-booster for wideband sensitivity enhancement. Micromachines 2023, 14, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkirisami Churchill, K.K.; Ramiah, H.; Chong, G.; Chen, Y.; Mak, P.-I.; Martins, R.P. A fully-integrated ambient RF energy harvesting system with 423-μW output power. Sensors 2022, 22, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkalfate, C.; Ouslimani, A.; Kasbari, A.-E.; Feham, M. A new RF energy harvesting system based on two architectures to enhance the DC output voltage for WSN feeding. Sensors 2022, 22, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, M.A.; Shome, P.P.; Khan, T.; Rengarajan, S.R. Efficient single and broadband microwave rectifiers for RFEH/WPT enabled low power 5G sub-6 GHz devices. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2023, 165, 154645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Luk, K. Frequency-reconfigurable low-profile circular monopolar patch antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 3443–3449. [Google Scholar]
- Magray, M.I.; Muzaffar, K.; Wani, Z.; Singh, R.K.; Karthikeya, G.S.; Koul, S.K. Compact frequency reconfigurable triple band notched monopole antenna for ultrawideband applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e29142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuvel, S.K.; Choukiker, Y.K. Frequency tunable circularly polarized antenna with branch line coupler feed network for wireless applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, I.H.; Hamid, M.R.; Kamardin, K.; Rahim, M.K.A. A multi to wideband frequency reconfigurable antenna. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2018, 28, e21216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shao, B.-C.; Yang, F.; Elsherbeni, A.Z.; Gong, B. A polarization reconfigurable patch antenna with loop slots on the ground plane. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sim, C.; Lin, H. Annular ring slot antenna design with reconfigurable polarization. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2016, 26, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheroghli, H.; Zaker, R. Double triangular monopole-like antenna with reconfigurable single/dual-wideband circular polarization. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2018, 28, e21267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.H.; Park, H.C. Wideband polarization reconfigurable circularly polarized antenna with omnidirectional radiation pattern. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hong, J.-S.; Song, G.; Wang, B.-Z. Design and analysis of a compact wideband pattern-reconfigurable antenna with alternate reflector and radiator. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2012, 6, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Row, J.; Wu, Y. Pattern reconfigurable slotted-patch array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 1580–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurav, K.; Sarkar, D.; Srivastava, K.V. Multi-band pattern reconfigurable Yagi-Uda antenna. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2017, 27, e21116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Li, X.J.; Awan, W.A.; Naqvi, A.H.; Hussain, N.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Limiti, E. A flexible and pattern reconfigurable antenna with small dimensions and simple layout for wireless communication systems operating over 1.65–2.51 GHz. Electronics 2021, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainarry, S.N.M.; Nguyen-Trong, N.; Fumeaux, C. A high-gain dual-band directional/omnidirectional reconfigurable antenna for WLAN systems. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Smida, A.; Mallat, N.K.; Ghayoula, R.; Elfergani, I.; Rodriguez, J.; Kim, S. Frequency and pattern reconfigurable antenna for emerging wireless communication systems. Electronics 2019, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koutinos, A.; Xanthopoulou, G.; Kyriacou, G.; Chryssomallis, M. A reconfigurable polarization-frequency supershape patch antenna with enhanced bandwidth. Electronics 2020, 9, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rathi, A.; Al-Khafaji, H.M.R.; Siddiqui, M.G.; Yadav, A.K.S. Hybrid mode reconfigurable antenna with V-shaped extrudes for cognitive radio applications. Electronics 2023, 12, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Khan, M.U.; Sharawi, M.S. An integrated dual MIMO antenna system With dual-function GND-plane frequency-agile antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, J.; Hou, Z.; Zeng, Y. A compact antenna with frequency and pattern reconfigurable characteristics. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2015, 57, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quin, P.-Y.; Guo, Y.J.; Weily, A.R.; Liang, C.-H. A pattern reconfigurable U-Slot antenna and its applications in MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Cheng, G.; Han, G.; Zhang, W. Reconfigurable ultra-wideband monopole antenna with single-, dual-, and triple-band notched functions. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, Y.; Costantine, J.; Hemmady, S.; Balakrishnan, G.; Avery, K.; Christodoulou, C.G. Demonstration of a cognitive radio front end using an optically pumped reconfigurable antenna system (OPRAS). IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, Y.; Albrecht, A.R.; Hemmady, S.; Balakrishnan, G.; Christodoulou, C.G. Optically pumped frequency reconfigurable antenna design. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2010, 9, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathi, V.; Ehtheshami, N.; Nourinia, J. Optically tuned frequency reconfigurable microstrip antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 1018–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, R. Optically controlled reconfigurable antenna for cognitive radio applications. Electron. Lett. 2011, 47, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran Saleem, M.; Alkanhal, M.A.; Sheta, A.F. Switched beam dielectric resonator antenna array with six reconfigurable radiation patterns. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2016, 26, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, D.; Jofre, L.; Cetiner, B. Circular beam-steering reconfigurable antenna with liquid metal parasitics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, A.; Denidni, T.A.; Sebak, A.-R.; Trueman, C.W.; Rosca, L.D.; Hoa, S.V. Mechanically reconfigurable antennas using anisotropic carbon-fibre composite ground. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyakath, R.A.; Takshi, A.; Mumcu, G. Multilayer stretchable conductors on polymer substrates for conformal and reconfigurable antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 13, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.K.; Ksiksi, M.A.; Ajlani, H.; Gharsallah, A. Terahertz graphene-based reconfigurable patch antenna. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2017, 71, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlali, A.; Houaneb, Z.; Zair, H. Dual-band reconfigurable graphene-based patch antenna in terahertz band: Design, analysis and modeling using WCIP method. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2018, 87, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Langley, R.J. Liquid crystal tunable microstrip patch antenna. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.B.; Zeng, L.; Huang, T.; Zhang, H. A tunable wide-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna regulated by the gravity field. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yang, X.-S.; Li, J.-L.; Wang, B.Z. Polarization reconfigurable broadband rectenna with tunable matching network for microwave power transmission. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yang, X.-S.; Li, J.-L.; Wang, B.Z. A compact frequency reconfigurable rectenna for 5.2- and 5.8-GHz wireless power transmission. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6006–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Huang, K.M.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wu, L. Frequency-reconfigurable rectenna with an adaptive matching stub for microwave power transmission. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuma, E.L.; Iano, Y.; Costa, M.S.; Manera, L.T.; Roger, L.L.B. A compact-integrated reconfigurable rectenna array for RF power harvesting with a practical physical structure. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2018, 70, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, V.; Karl Max, L.R. Micro-controlled tree shaped reconfigurable patch antenna with RF-energy harvesting. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 94, 2769–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yang, X.; Wang, B. A two-channel frequency reconfigurable rectenna for microwave power transmission and data communication. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6976–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yang, X.-S.; Wang, B.-Z. Reconfigurable rectenna array design with mutual coupling analysis. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 61, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haung, F.; Yo, T.-C.; Lee, C.-M.; Luo, C.-H. Design of circular polarization antenna with harmonic suppression for rectenna application. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2012, 11, 592–595. [Google Scholar]
- Quddious, A.; Abbasi, M.A.B.; Saghir, A.; Arain, S.; Antoniades, M.A.; Polycarpou, A.; Vryonides, P.; Nikolaou, S. Dynamically reconfigurable SIR filter using rectenna and active booster. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quddious, A.; Abbasi, M.A.B.; Tahir, F.A.; Antoniades, M.A.; Vryonides, P.; Nikolaou, S. UWB antenna with dynamically reconfigurable notch band using rectenna and active booster. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019, 13, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, J.; Lin, D.-B.; Weng, K.-L.; Li, H.-J. All polarization receiving rectenna with harmonic rejection property for wireless power transmission. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 5242–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Geyi, W. A new rectenna with all-polarization-receiving capability for wireless power transmission. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Ziolkowski, R.W.; Huang, J. Electrically small, low-profile, highly efficient, huygens dipole rectennas for wirelessly powering internet-of-things devices. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 3670–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.J.; Chang, K. 5.8-GHz circularly polarized dual-diode rectenna and rectenna array for microwave power transmission. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2006, 54, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Bertacchini, A.; Larcher, L.; Maini, M.; Vincetti, L.; Scorcioni, S. Reconfigurable RF energy harvester with customized differential PCB antenna. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2015, 5, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Yang, X. Pattern reconfigurable rectenna with omni-directional/directional radiation modes for MPT with multiple transmitting antennas. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2019, 29, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Lin, X.; Tang, C.; Mei, P.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y. 2.45-GHz wideband harmonic rejection rectenna for wireless power transfer. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2019, 9, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, W.; Cao, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Liu, H. A circular polarized rectenna with out-of-band suppression for microwave power transmission. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2016, 2016, 8628496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, D.; Chaudhary, K. Design of differential source fed circularly polarized rectenna with embedded slots for harmonics suppression. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2018, 84, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Farooqui, M.F.; Chang, K. A compact dual-frequency rectifying antenna with high-order harmonic-rejection. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheakh, D.N.; Elsadek, H.A.; Abdallah, E.A. Reconfigurable microstrip monopole patch antenna with electromagnetic band-gap structure design for ultrawideband wireless communication systems. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2011, 53, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, S.-J.; Hwang, I.-J.; Lee, W.-S.; Yu, J.-W. Hybrid power combining rectenna array for wide incident angle coverage in RF energy transfer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 3409–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, R.; Baginski, M.; Dean, R. A 2.45-GHz frequency-selective rectenna for wireless energy harvesting. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 58, 2508–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harouni, Z.; Osman, L.; Gharsallah, A. Efficient 2.45 GHz rectenna design with high harmonic rejection for wireless power transmission. Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2010, 7, 424–427. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, I.A.; Hayat, S.; Basir, A.; Zada, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Ullah, S. Design and analysis of a hexa-band frequency reconfigurable antenna for wireless communication. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 98, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Yang, G.; Dougal, R. A new circularly polarized rectenna for wireless power transmission and data communication. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2005, 4, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, H.; Choukiker, Y.K. Design of frequency reconfigurable antenna with ambient RF-energy harvester system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Information Communication and Embedded Systems, Chennai, India, 25–26 February 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Anuradha, A.P.; Lahudkar, S.L. Compact asymmetric fractal frequency and pattern reconfigurable monopole antenna. AEUE-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2019, 111, 152915. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, J.; Row, J. Design of frequency sensor based on reconfigurable rectenna. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2014, 56, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harouni, Z.; Cirio, L.; Osman, L.; Gharsallah, A.; Picon, O. A dual circularly polarized 2.45-GHz rectenna for wireless power transmission. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cai, Y.-M.; Yin, Y.; Hu, W. A wideband E-plane pattern reconfigurable antenna with enhanced gain. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2019, 29, e21530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledimo, B.K.; Moaro, P.; Ramogomana, R.; Mosalaosi, M.; Basutli, B. Design procedure of a frequency reconfigurable metasurface antenna at mmwave band. Telecom 2022, 3, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Sun, D. A single-layer multimode metasurface antenna with a CPW-fed aperture for UWB communication applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Tran, H.H.; Althuwayb, A.A. Wideband circularly polarized antenna based on a non-uniform metasurface. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Ma, X.; Huang, X. Low-cost broadband circularly polarized array antenna with artificial magnetic conductor for indoor applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, P.R.; Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K.; Althuwayb, A.A. A chronological review of circularly polarized dielectric resonator antenna: Design and developments. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2021, 31, e22589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, P.R.; Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K. Broadband circularly polarized edge feed rectangular dielectric resonator antenna using effective glueless technique. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Behera, B.R. Dynamically switched dual-band dual-polarized dual-sense low-profile compact slot circularly polarized antenna assisted with high gain reflector for sub-6GHz and X-band applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 2021, 110, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.R.; Mohanty, A.; Nasimuddin, N. Dual-polarized metasurface-based monopole antenna design using characteristics mode theory for UHF RFID applications. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2022, 32, e23325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Pu, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y. RF energy harvesting wireless communications: RF environment, device hardware and practical issues. Sensors 2019, 19, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mouapi, A. Radiofrequency energy harvesting systems for internet of things applications: A comprehensive overview of design issues. Sensors 2022, 22, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H.; Kim, S.; Kuruoğlu, N. Energy harvesting techniques for wireless sensor networks/radio-frequency identification: A review. Symmetry 2019, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, I.; Dildar, H.; Khan, W.U.R.; Shah, S.A.A.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, S.; Umar, S.M.; Albreem, M.A.; Alsharif, M.H.; Vasudevan, K. Design and experimental analysis of multiband compound reconfigurable 5G antenna for sub-6 GHz wireless applications. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 5588105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Dildar, H.; Khan, W.U.R.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, S.; Albreem, M.A.; Alsharif, M.H.; Uthansakul, P. Frequency reconfigurable antenna for multi standard wireless and mobile communication systems. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 2563–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H.; Hossain, M.; Jahid, A.; Khan, M.A.; Choi, B.J.; Mostafa, S.M. Milestones of wireless communication networks and technology prospect of next generation (6g). Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 4803–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.H.; Jahid, A.; Kelechi, A.H.; Kannadasan, R. Green IoT: A review and future research directions. Symmetry 2023, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sources | Frequency of Operation | Emission Power Levels | Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| FM Tower | 88–108 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | WPTs |
| TV Tower | 180–220 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | WPTs |
| AM Tower | 530–1620 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | WPTs |
| CDMA Band | 824–890 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| GSM 900 Band (UL) | 890–915 MHz | ±(5 dBm to 39 dBm) | Energy Scavenging |
| GSM 900 Band (DL) | 935–960 MHz | ±(5 dBm to 39 dBm) | Energy Scavenging |
| GPS | 1575 ± 10 MHz | —— | —— |
| GSM 1800 Band (UL) | 1710–1780 MHz | ±(2 dBm to 36 dBm) | Energy Scavenging |
| GSM 1800 Band (DL) | 1810–1900 MHz | ±(2 dBm to 36 dBm) | Energy Scavenging |
| 3G (Band-I) | 1920–1980 MHz | ±(2 dBm to 33 dBm) | Energy Scavenging |
| 3G (Band-II) | 2110–2170 MHz | ±(2 dBm to 33 dBm) | Energy Scavenging |
| 4G (LTE/LTE-A) | 2300–2400 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| Wi-Fi Band | 2400 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| Bluetooth Band | 2450 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| ISM Band | 2400–2484 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| ISM Band | 2400 MHz | −36 dBm to +36 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| WiMAX | 3300–3700 MHz | −30 dBm to +30 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| ISM Band | 3600 MHz | −30 dBm to +30 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| ISM Band | 5000 MHz | −41 dBm to +41 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| ISM Band | 5200 MHz | −41 dBm to +41 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| IEEE 802.11 | 5500 MHz | −41 dBm to +41 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| IEEE 802.11 | 5800 MHz | −41 dBm to +41 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| WLAN (LOWER) | 5150–5725 MHz | −41 dBm to +41 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| WLAN (UPPER) | 5725–5875 MHz | −41 dBm to +41 dBm | Energy Scavenging |
| References | Operating Band | Antenna Gain | o | Vout |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [110] | WLAN | 5.7 dBi | 43% | 1.5 V |
| [111] | WLAN | 6.7 dBi | 71% | —— |
| [112] | WLAN | 4.5 dBi | 55.1% | —— |
| [113] | ISM | 4 dBi | 65.3% | 3.2 V |
| [114] | WLAN | —— | —— | 4.9 V |
| [115] | WLAN | 5.68 dBi | 50.2% | 1.2 V |
| [116] | ISM | —— | 69.1% | —— |
| [117] | ISM | —— | 37.8% | 2.76 V |
| [118] | ISM | —— | 47% | 0.43 V |
| [119] | 5.6 GHz | 7.6 dBi | 43% | 2.1 V |
| [120] | ISM | 8 dBi | 82.3% | —— |
| [121] | ISM | 7.5 dBi | 61% | —— |
| [122] | 915 MHz | 3.8 dBi | 88.5% | 4.6 V |
| [123] | 5.8 GHz | 6.38 dBi | 76% | —— |
| [124] | 915 MHz | 1.6 dBi | 18% | 2 V |
| [125] | ISM | 2.84 dBi | 35.5–52.2% | —— |
| [126] | ISM | 5 dBi | 70.2% | 4 V |
| [127] | ISM | —— | 75.5% | 5.21 V |
| [128] | ISM | —— | 41.63% | —— |
| [129] | ISM | 2.19 dBi | 65% | 2.6 V |
| [130] | UWB | 15 dBi | —— | —— |
| [131] | ISM | 5.9 dBi | 55.3% | 3.3 V |
| [132] | ISM | —— | 79% | 4.13 V |
| [133] | ISM | 6.4 dBi | 74% | 2.9 V |
| [134] | UWB | 2.1–4.3 dBi | —— | —— |
| [135] | WLAN | 8.6 dBi | 57.3% | 1.74 V |
| [136] | ISM | 1.94 dBi | —— | —— |
| [137] | 1.8/5.2 GHz | 4.5 dBi | —— | —— |
| [138] | 2.8 GHz | 2–8 dBi | 10–80% | 7 V |
| [139] | ISM | 6.8 dBi | 63% | 2.82 V |
| Parameters | Stage-1 | Stage-2 | Stage-3 | Stage-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry Traits | Initial | OFF-State | ON-State | Final |
| Polarization | LP | LP | CP | CP |
| IBW | 830 MHz | 620 MHz | 2.11 GHz | 2.38 GHz |
| ARBW | —— | —— | 460 MHz | 1.23 GHz |
| HPBW | —— | —— | 60° | >110° |
| Antenna Gain | 2.3 dBi | 2.4 dBi | 3.6 dBic | >8.35 dBic |
| o | —— | —— | —— | >55% @12 dBm |
| Vout | —— | —— | —— | >4.8 V @12 dBm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behera, B.R.; Mishra, S.K.; Alsharif, M.H.; Jahid, A. Reconfigurable Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting Application: Current Trends, Challenges, and Solutions from Design Perspective. Electronics 2023, 12, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122723
Behera BR, Mishra SK, Alsharif MH, Jahid A. Reconfigurable Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting Application: Current Trends, Challenges, and Solutions from Design Perspective. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122723
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehera, Bikash Ranjan, Sanjeev Kumar Mishra, Mohammed H. Alsharif, and Abu Jahid. 2023. "Reconfigurable Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting Application: Current Trends, Challenges, and Solutions from Design Perspective" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122723
APA StyleBehera, B. R., Mishra, S. K., Alsharif, M. H., & Jahid, A. (2023). Reconfigurable Antennas for RF Energy Harvesting Application: Current Trends, Challenges, and Solutions from Design Perspective. Electronics, 12(12), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122723







