Benefits from Using Very Thin Channel Layer for TFTs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. As-Deposited Micro-Poly Crystalline Silicon Based TFTs as an Example of the Effect of Channel Layer Thickness Variation
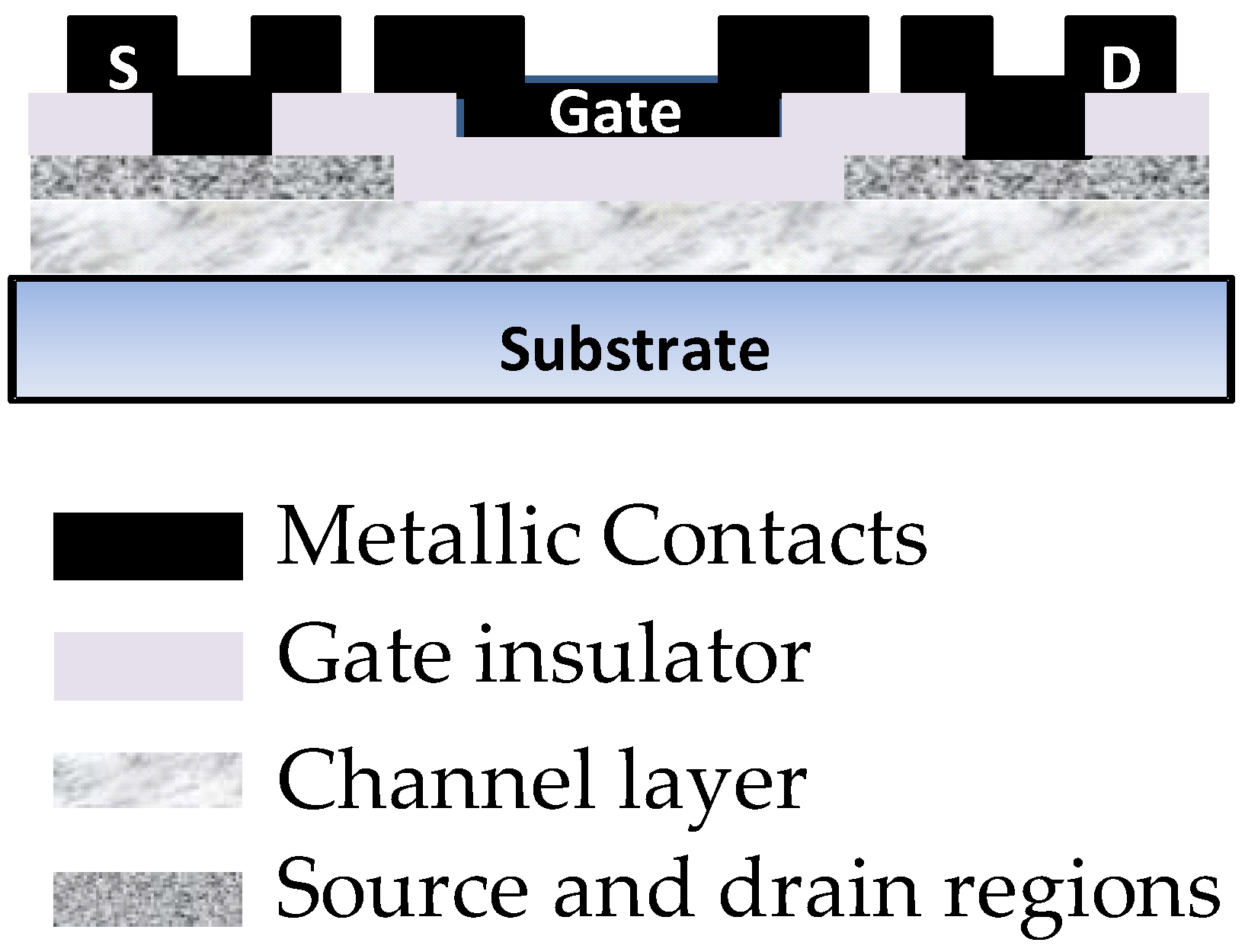
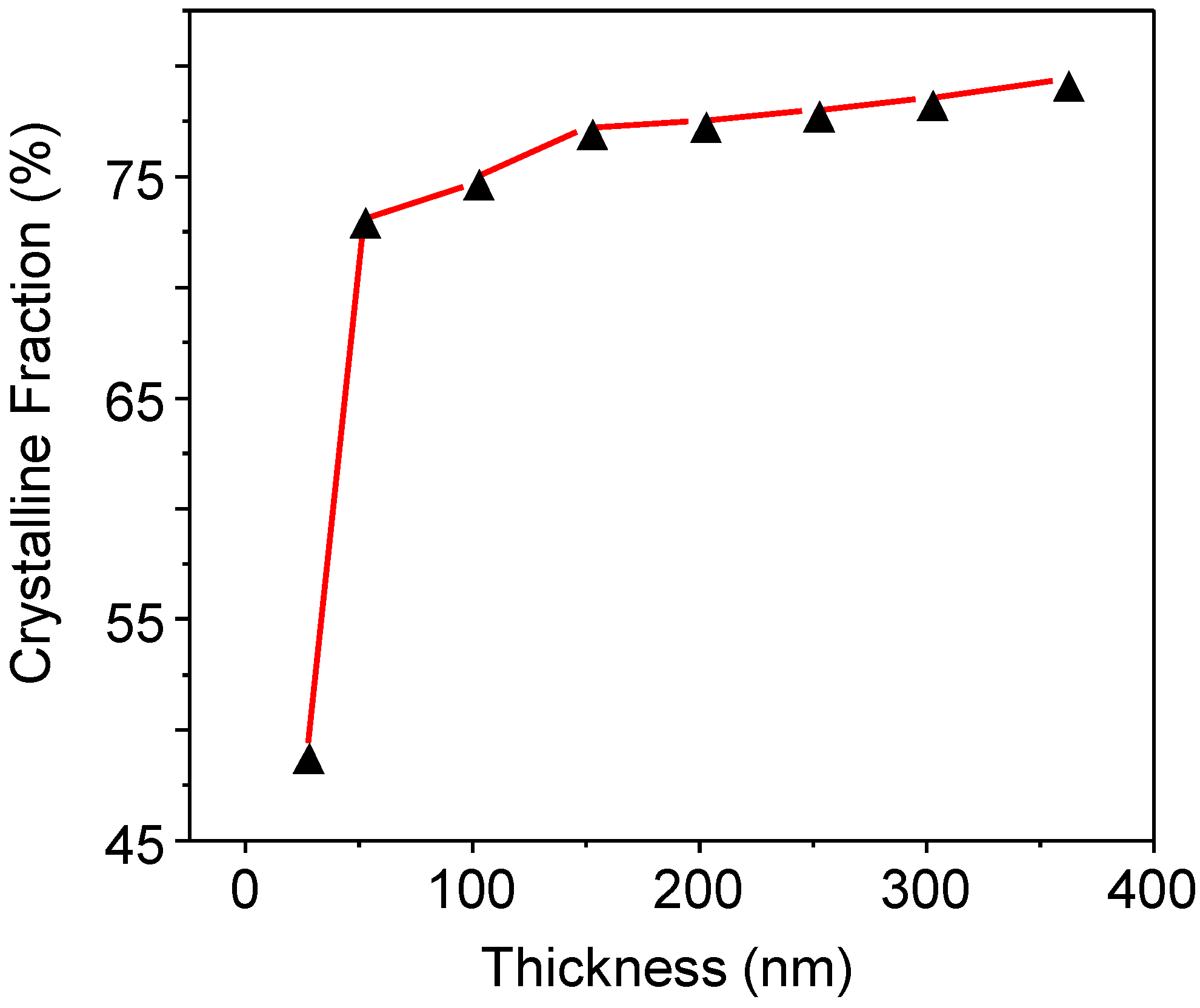
2.1. Process
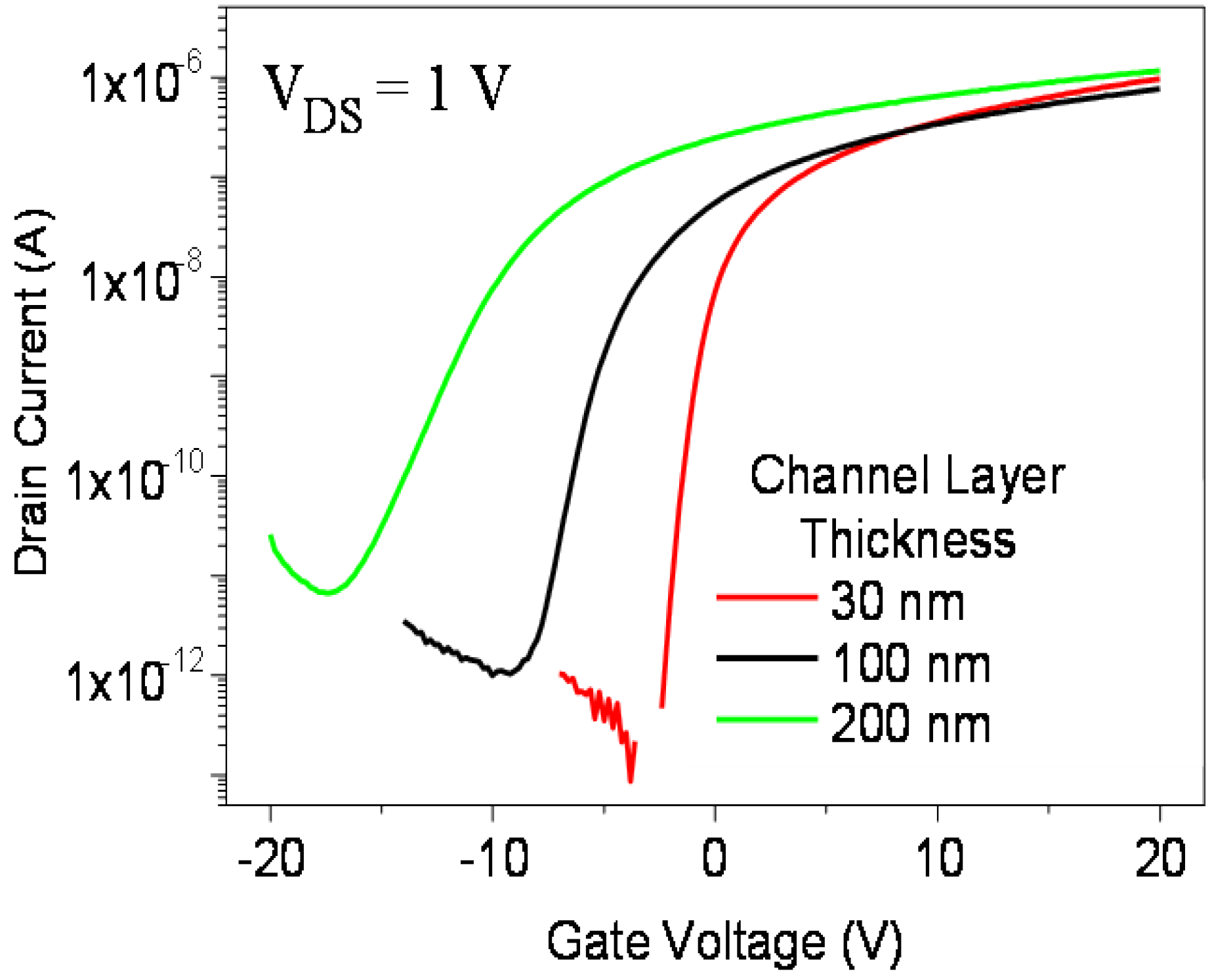
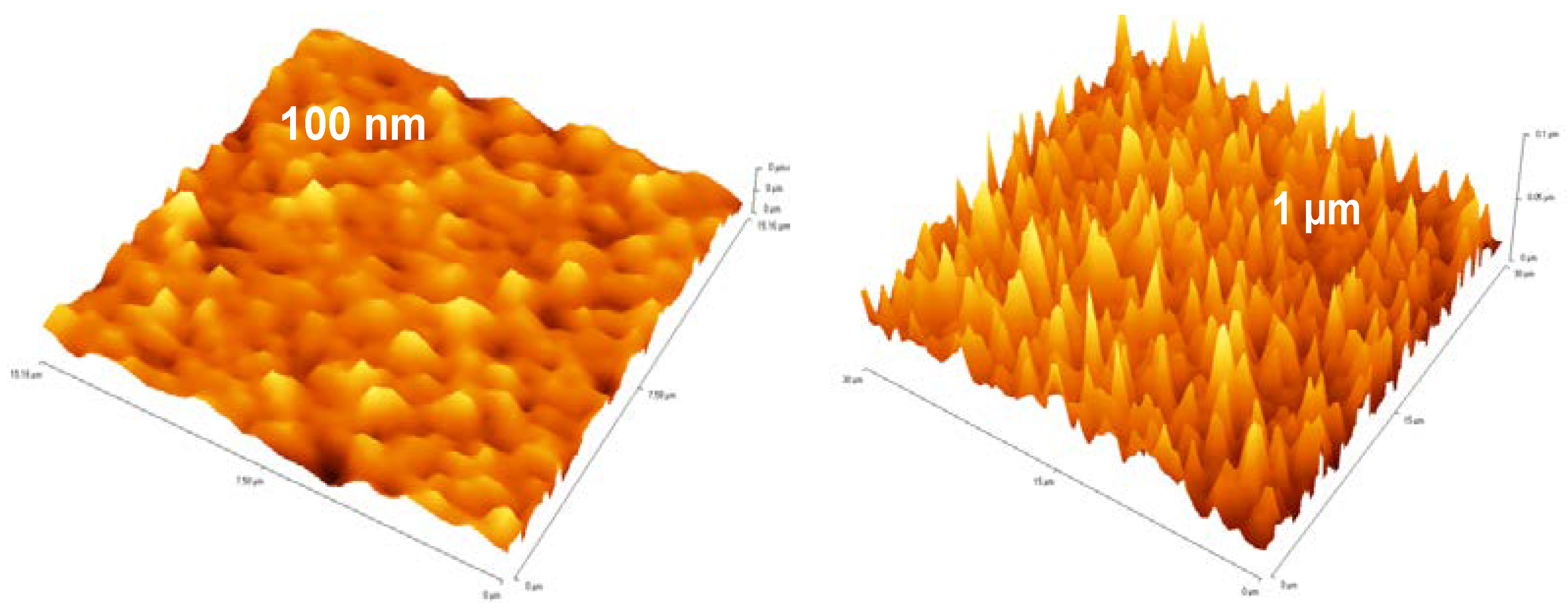
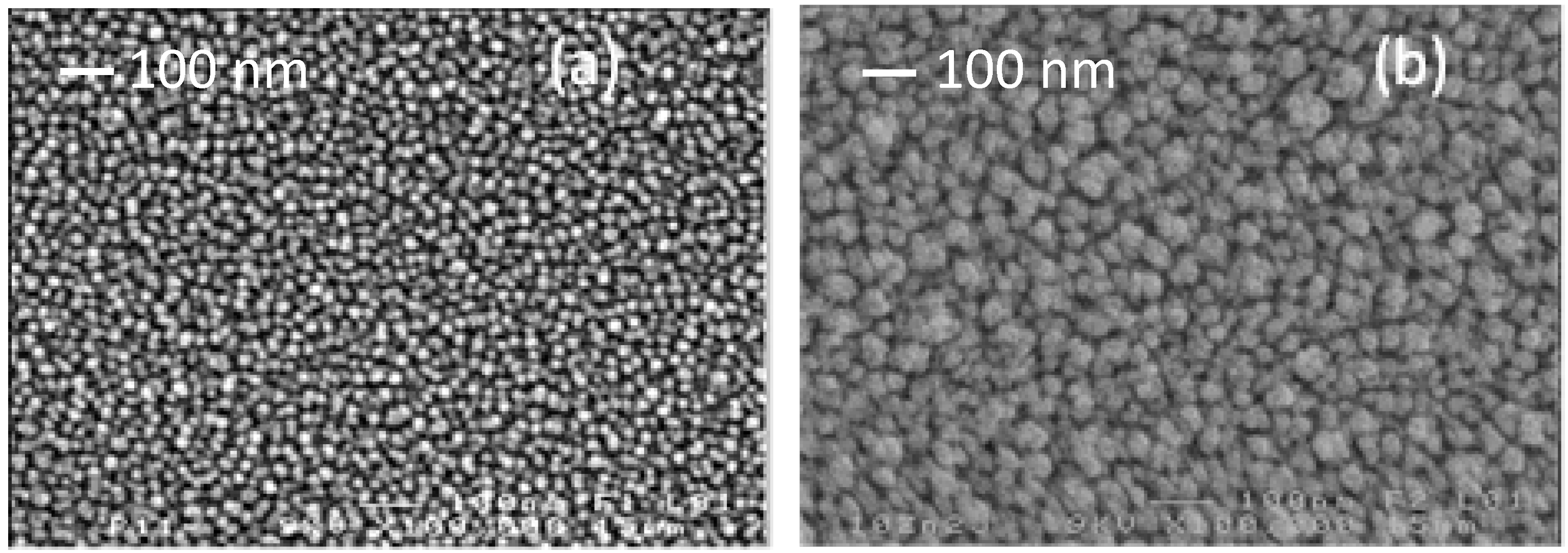
2.2. Electrical Characterisation of TFTs Having a Channel Layer with a Different Thickness
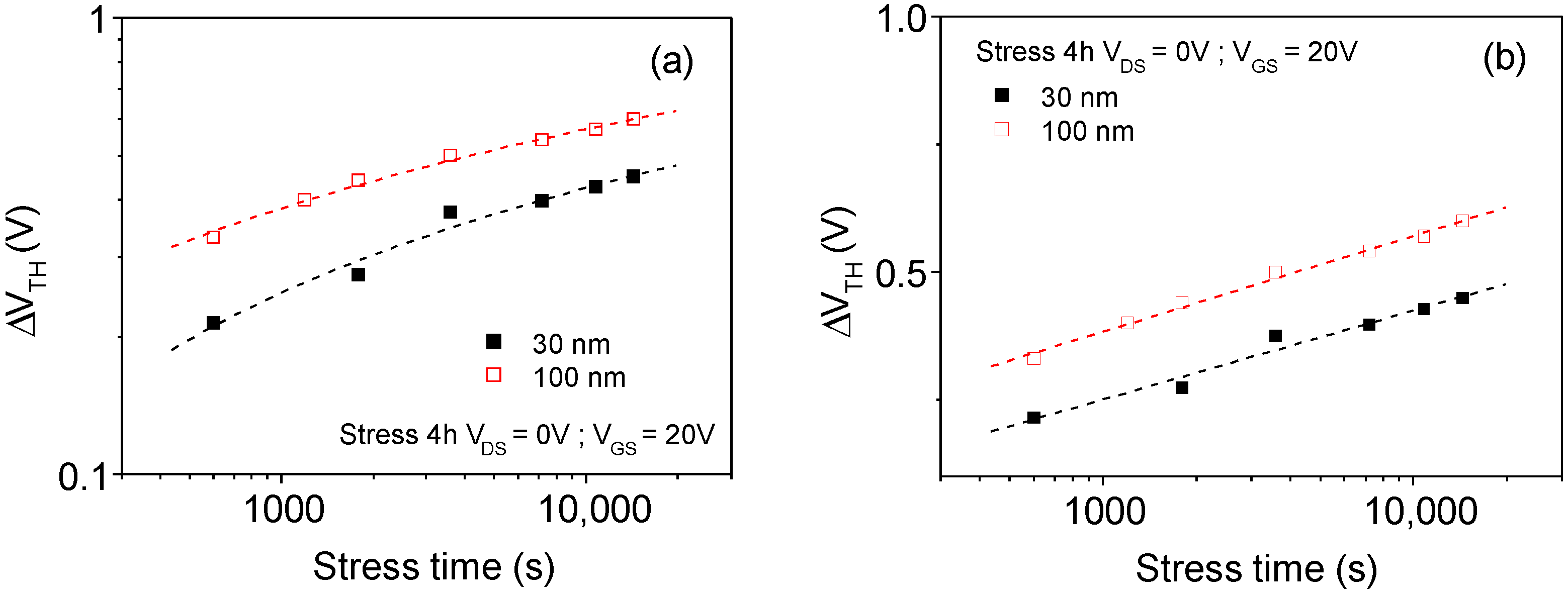
3. Electrical Stability of Thin Channel Layer-Based TFTs
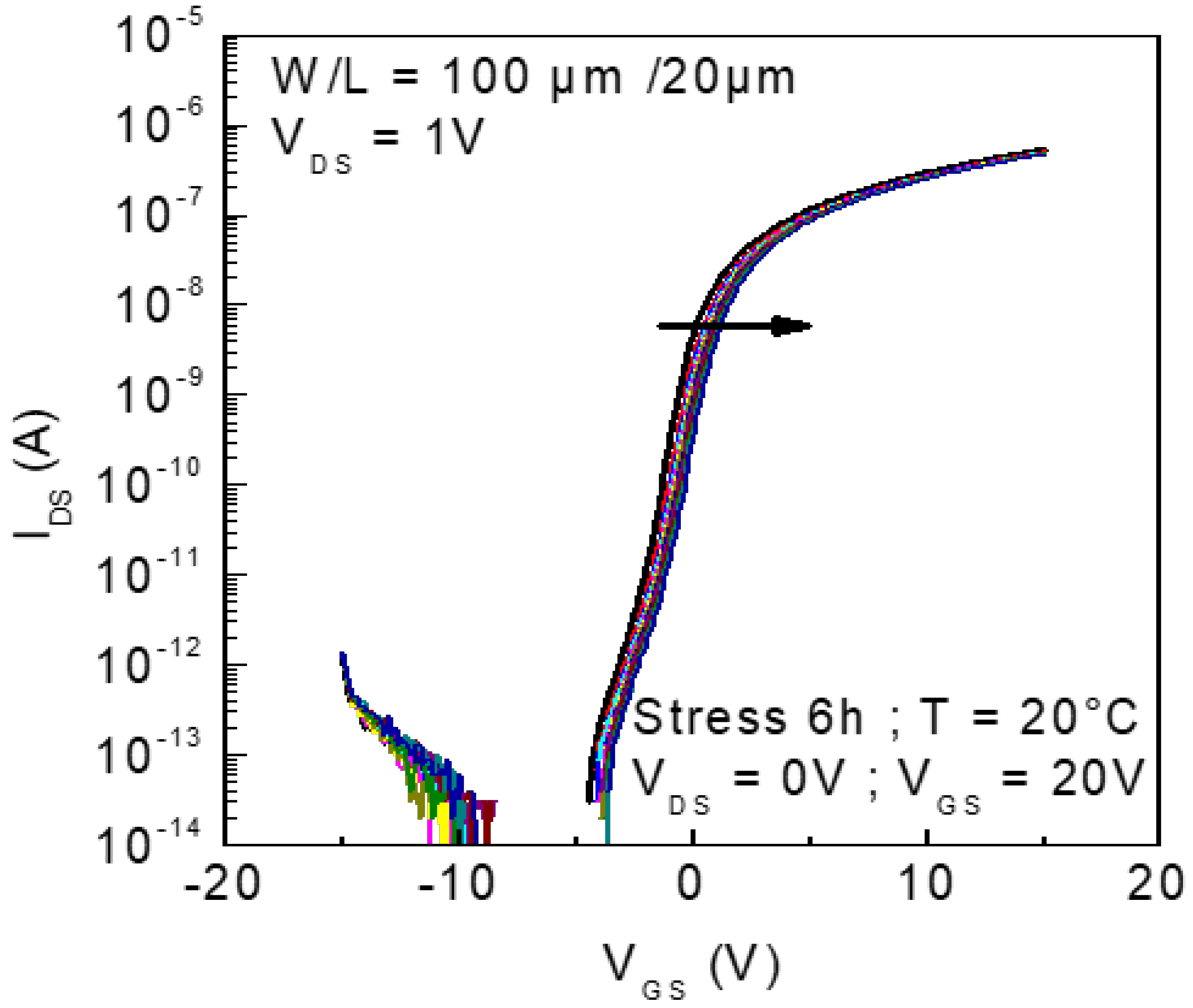
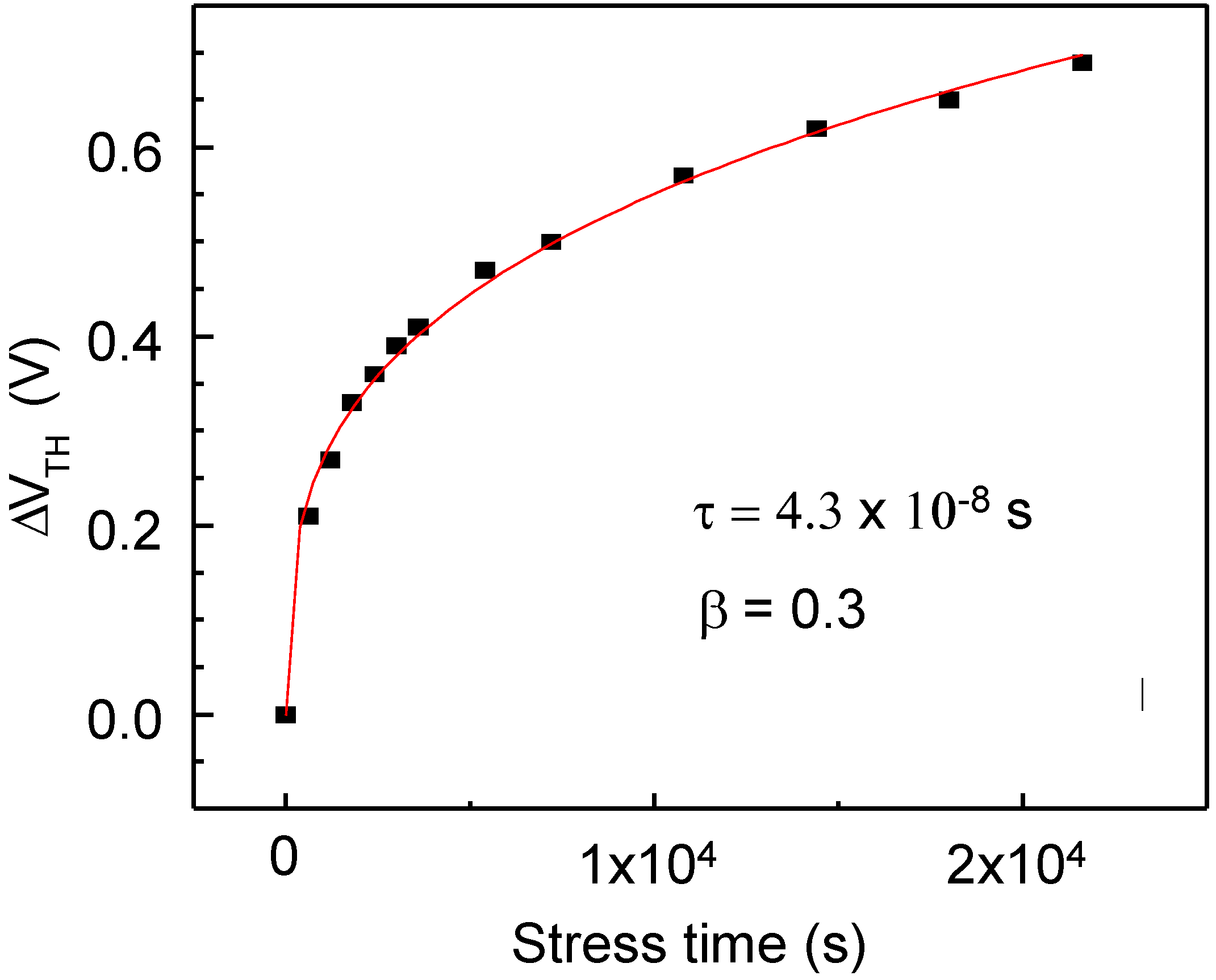
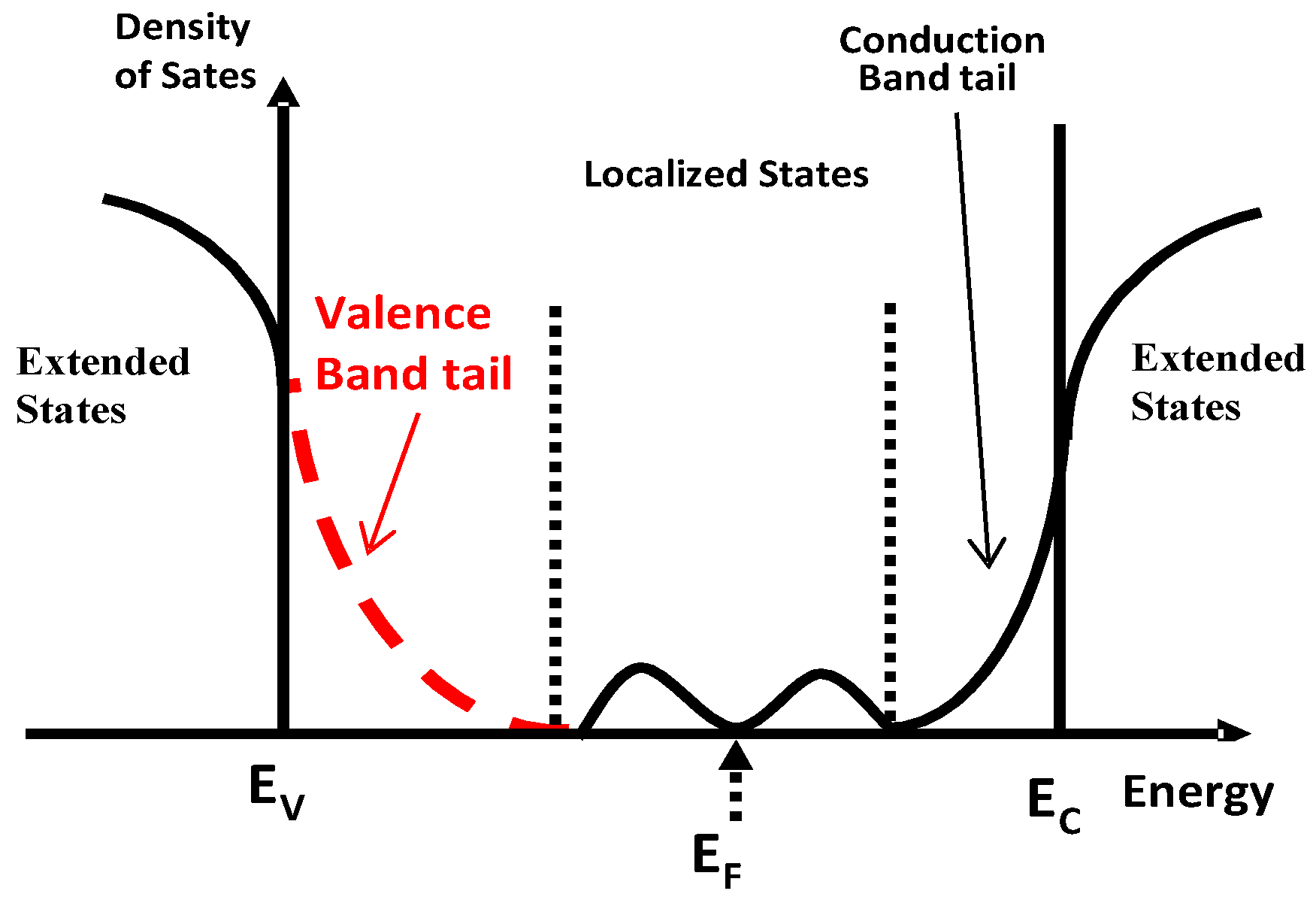
3.1. Electrical Stability of TFTs with a 100 nm Thick Channel Layer
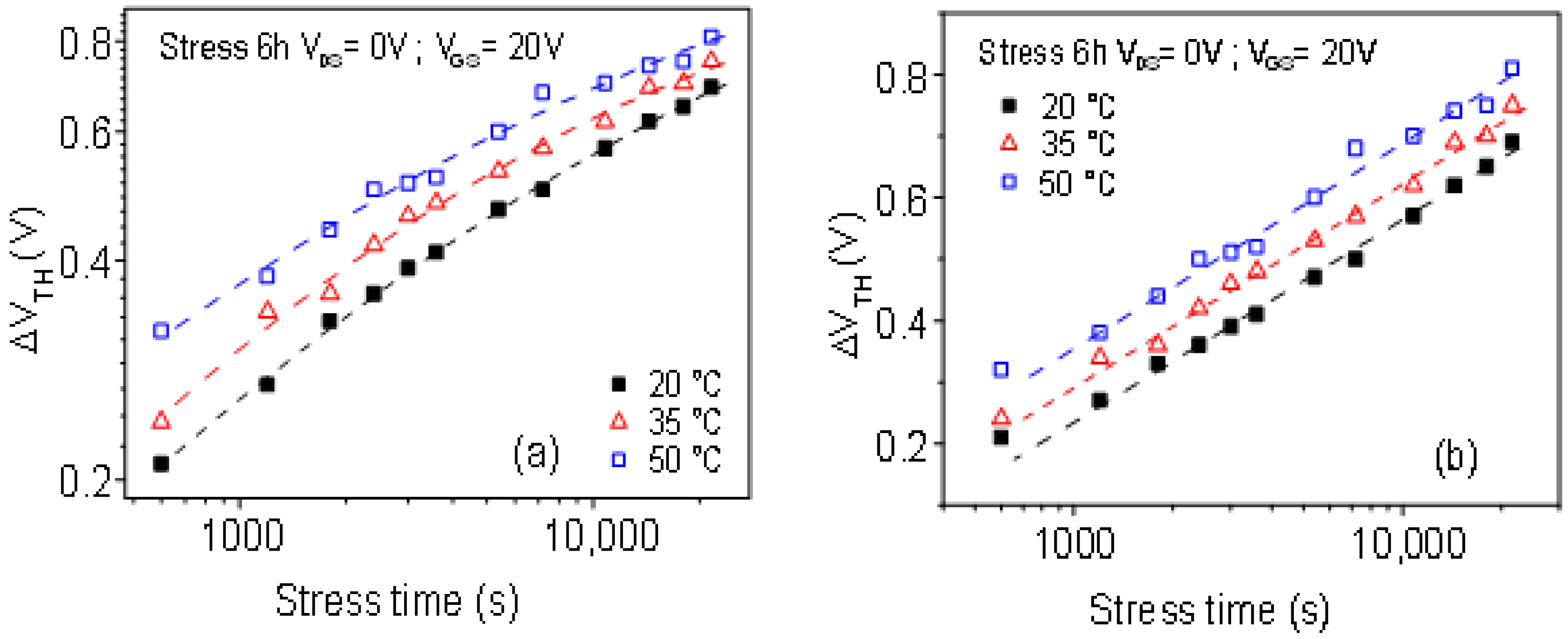
3.2. Electrical Stability of TFTs with a Different Thick Channel Layer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasaki, N.; Togei, R. Effect of silicon film thickness on threshold voltage of SOS-MOSFETs. Solid State Electron. 1979, 22, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinge, J. Subthreshold slope of thin-film SOI MOSFETs. IEEE-EDL 1986, 7, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiaoi, T.C.; Wang, A.W.; Saraswat, K.; Woo, J.C.S. An alternative gate electrode material of fully depleted SOI CMOS for low power applications. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International SOI Conference, Fish Camp, CA, USA, 6–9 October 1997; pp. 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Balestra, F.; Benachir, M.; Brini, J.; Ghibaudau, G. Analystical Models of Subthreshold Swing and Threshold voltage for thin- and Ultra-Thin-Film SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1990, 37, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Noguchi, T.; Oshima, T. Polysilicon Super-Thin-Fim Transistor (SFT). Jpn. J. Apply. Phys. 1984, 23, L819–L820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Hayashi, H.; Ohshima, T. Low Temperature Polysilicon Super-Thin-Film Transistor (LSTS). Jpn. J. Apply. Phys. 1986, 25, L121–L123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Chiang, C.-S.; Nahm, J.-Y.; Li, T.; Kanicki, J.; Ugai, Y. Influence of the Amorphous Silicon Thickness on Top-gate Thin-Film Transistor Electrical Performances. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquinha, P.; Pimentel, A.; Marques, A.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E. Influence of the semiconductor thickness on the electrical properties of transparent TFTs based on indium zinc oxide. J. Non-Crystalline Sol. 2006, 352, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Goh, G.; Demir, H.; Yu, H. Influence of the Channel Layer Thickness on the Electrical Performance of Inkjet-Printed In-Ga-Zn Oxide Thin Film Transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2011, 58, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Furuta, M.; Tomai, S.; Yano, K. Understanding the role of Temperature and Drain Current Stress in InSnZnO TFTs with Various Active Layer Thickness. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Cha, H.-S.; Jeong, H.-S.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kwon, H.-I. Effects of Active Layer Thickness on the Electrical Characteristics and Stability of High-Mobility Amorphous Indium-Gallium-Tin Oxide Thin-Film Transistors. Electronics 2021, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoussi, K.; Simon, C.; Coulon, N.; Mohammed-Brahim, T.; Moreac, A. Undoped and arsenic-doped low temperature (~165 °C) microcrystalline silicon for electronic devices. J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 2006, 352, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belarbi, K.; Kandoussi, K.; Coulon, N.; Simon, C.; Cherfi, R.; Fedala, A.; Mohammed-Brahim, T. Stability of microcrystalline silicon TFTs. ECS Trans. 2009, 23, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Samb, M.; Dong, H.; Jacques, E.; Sissoko, G.; Seidou-Maiga, A.; Mohammed-Brahim, T. Thinning the active layer of TFTs. ECS Trans. 2014, 64, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoussi, K.; Simon, C.; Coulon, N.; Belarbi, K.; Mohammed-Brahim, T. Nanocrystalline silicon TFT process using silane diluted in argon-hydrogen mixtures. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samb, M.L. Modelisation de Transistors en Couches Minces (TFT) Fabriques en Technologies Silicium Microcristallin Tres Basse Temperature. PhD Thesis, University of Rennes 1, Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- SILVACO International. ATHENA User’s Manual, Device Simulation Software; SILVACO International: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- SILVACO International. ATLAS User’s Manual, Device Simulation Software; SILVACO International: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.; Kang, J.; Yun, I. Effects of channel thickness variation on bias stress instability of InGaZnO thin-film transistors. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.; Marshall, J.; Moyer, M. Role of hydrogen in the formation of metastable defects in hydrogenated amorphous silicon. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlin, R.; Mozurkewich, G.; Orbach, R. Time Decay of the Remanent Magnetization in Spin-Glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 52, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. The longtime properties of diffusion in a medium with static traps. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 6281–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaudre, R.; Meaudre, M.; Jensen, P.; Guiraud, G. Thermal-equilibrium processes and electronic transport in undoped hydrogenated amorphous silicon. Phil. Mag. Lett. 1988, 57, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppson, K.; Svenson, C. Negative Bias Stress of MOS Devices at High Electric Fields and Degradation of MNOS Devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.; Van Berkel, C.; Hughes, J. Time and temperature dependence of instability mechanisms in amorphous silicon thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1989, 54, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.; Ayres, J. Negative Gate Bias Instability in Polycrystalline Silicon TFTs. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1995, 42, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
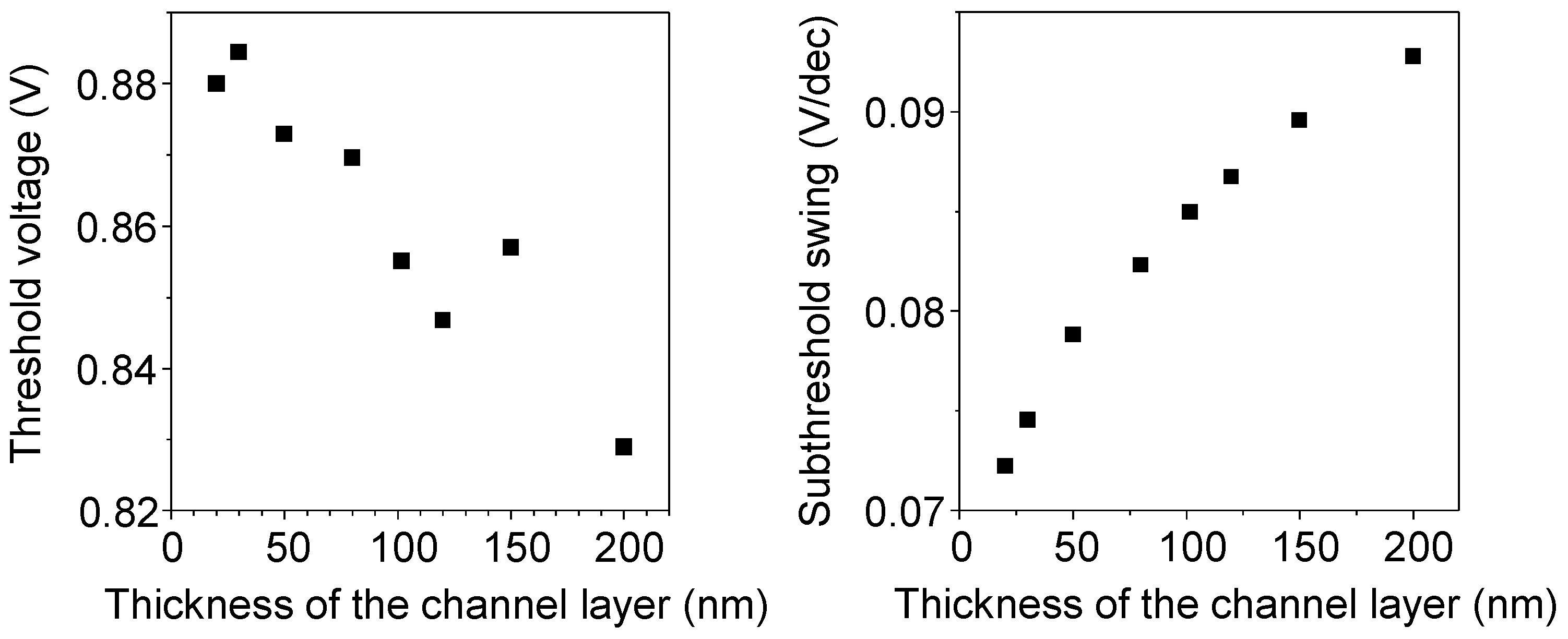
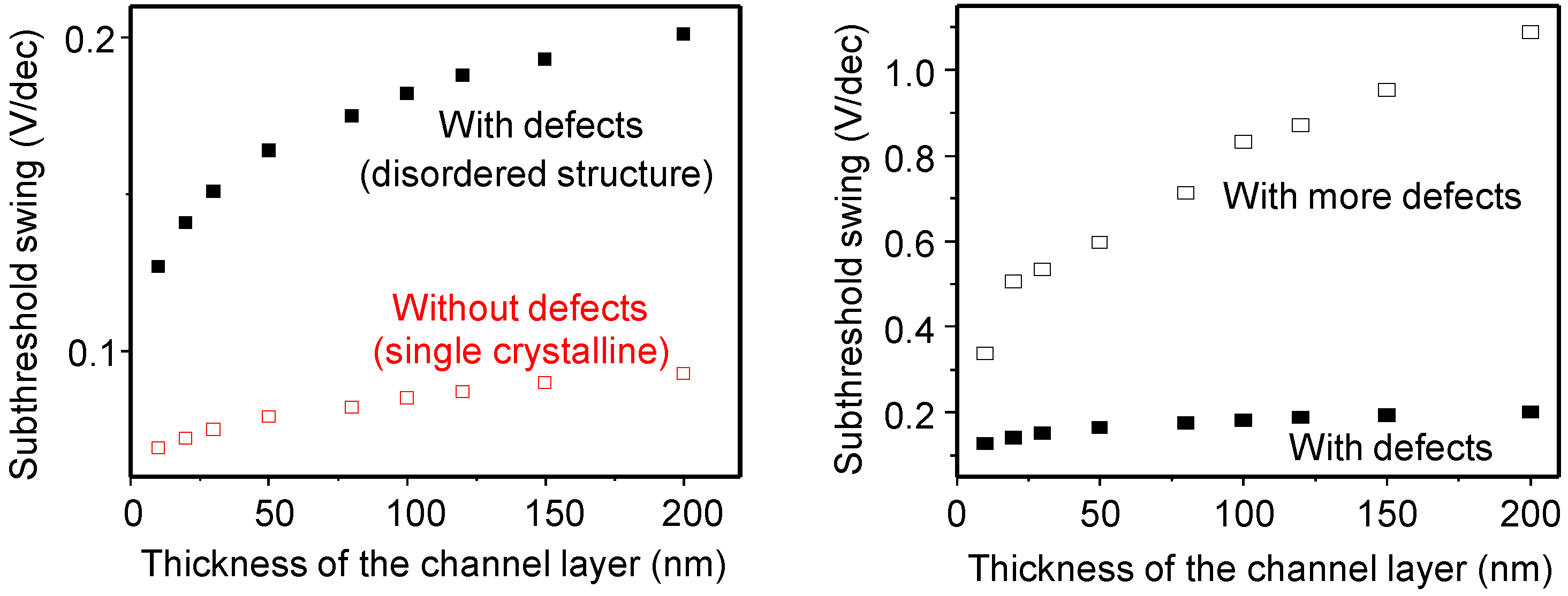
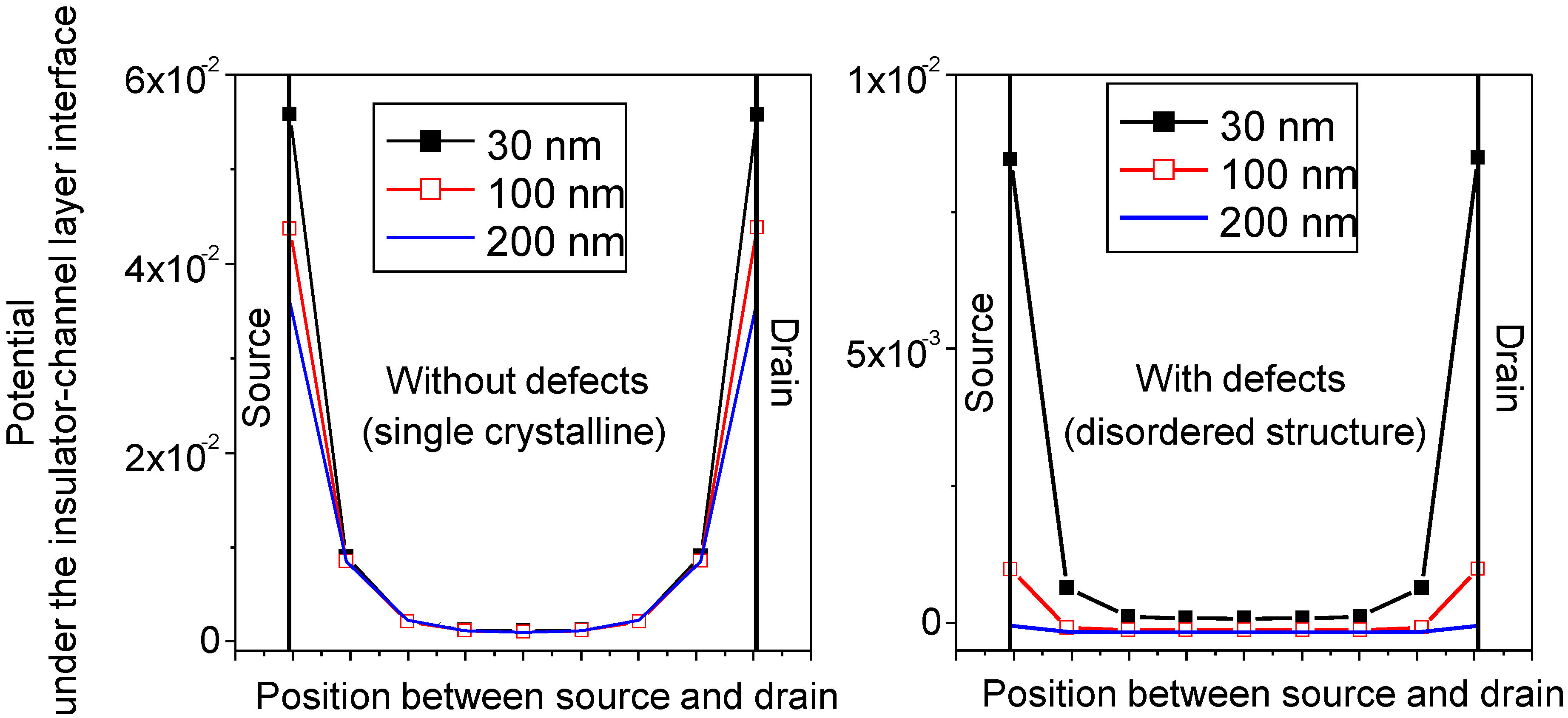
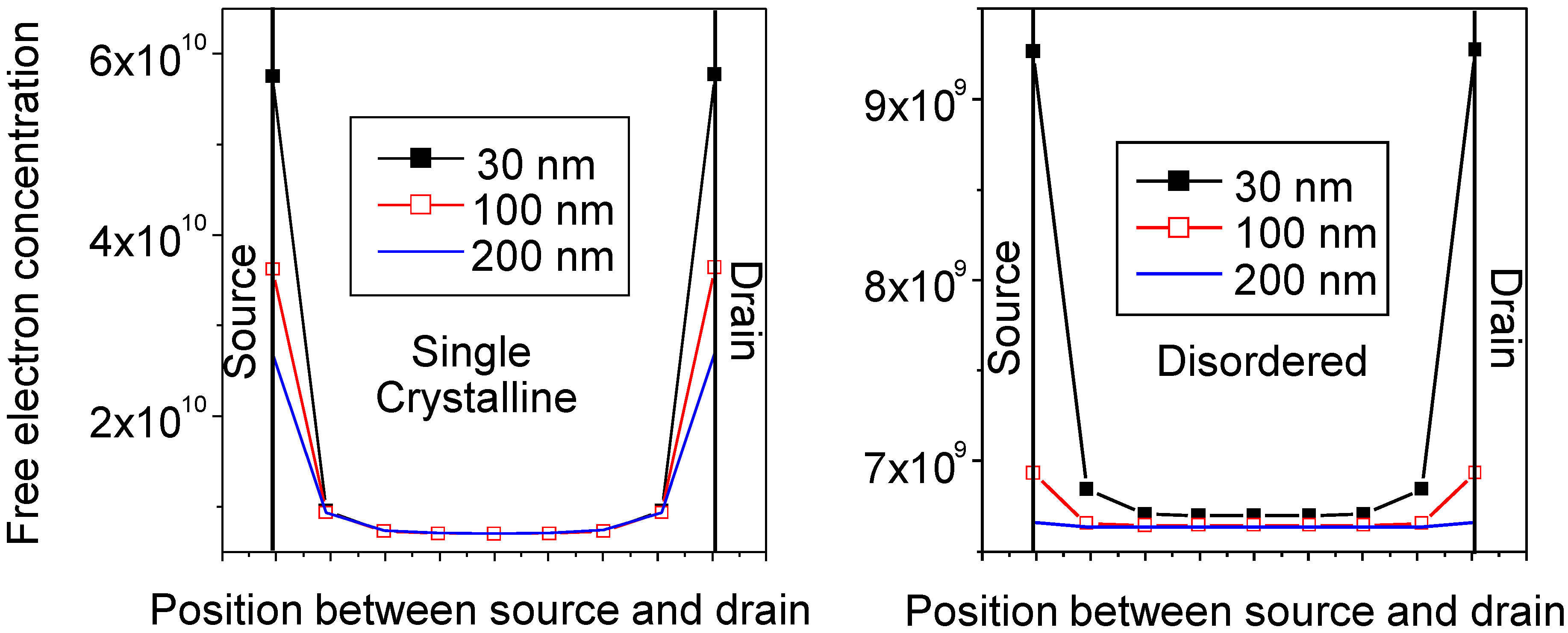
| T (nm) | µ (cm2/V.s) | SS (V/dec) | VTH (V) | ION/IOFF | g (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 6 | >107 | 20 |
| 100 | 0.52 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 106 | 60 |
| 200 | 0.63 | 1.92 | −1.2 | 105 | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samb, M.L.; Jacques, E.; Maiga, A.S.; Mohammed-Brahim, T. Benefits from Using Very Thin Channel Layer for TFTs. Electronics 2023, 12, 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122694
Samb ML, Jacques E, Maiga AS, Mohammed-Brahim T. Benefits from Using Very Thin Channel Layer for TFTs. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122694
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamb, Mamadou Lamine, Emmanuel Jacques, Amadou Seidou Maiga, and Tayeb Mohammed-Brahim. 2023. "Benefits from Using Very Thin Channel Layer for TFTs" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122694
APA StyleSamb, M. L., Jacques, E., Maiga, A. S., & Mohammed-Brahim, T. (2023). Benefits from Using Very Thin Channel Layer for TFTs. Electronics, 12(12), 2694. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122694







