Quantitative Analysis of Steel Alloy Elements Based on LIBS and Deep Learning of Multi-Perspective Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
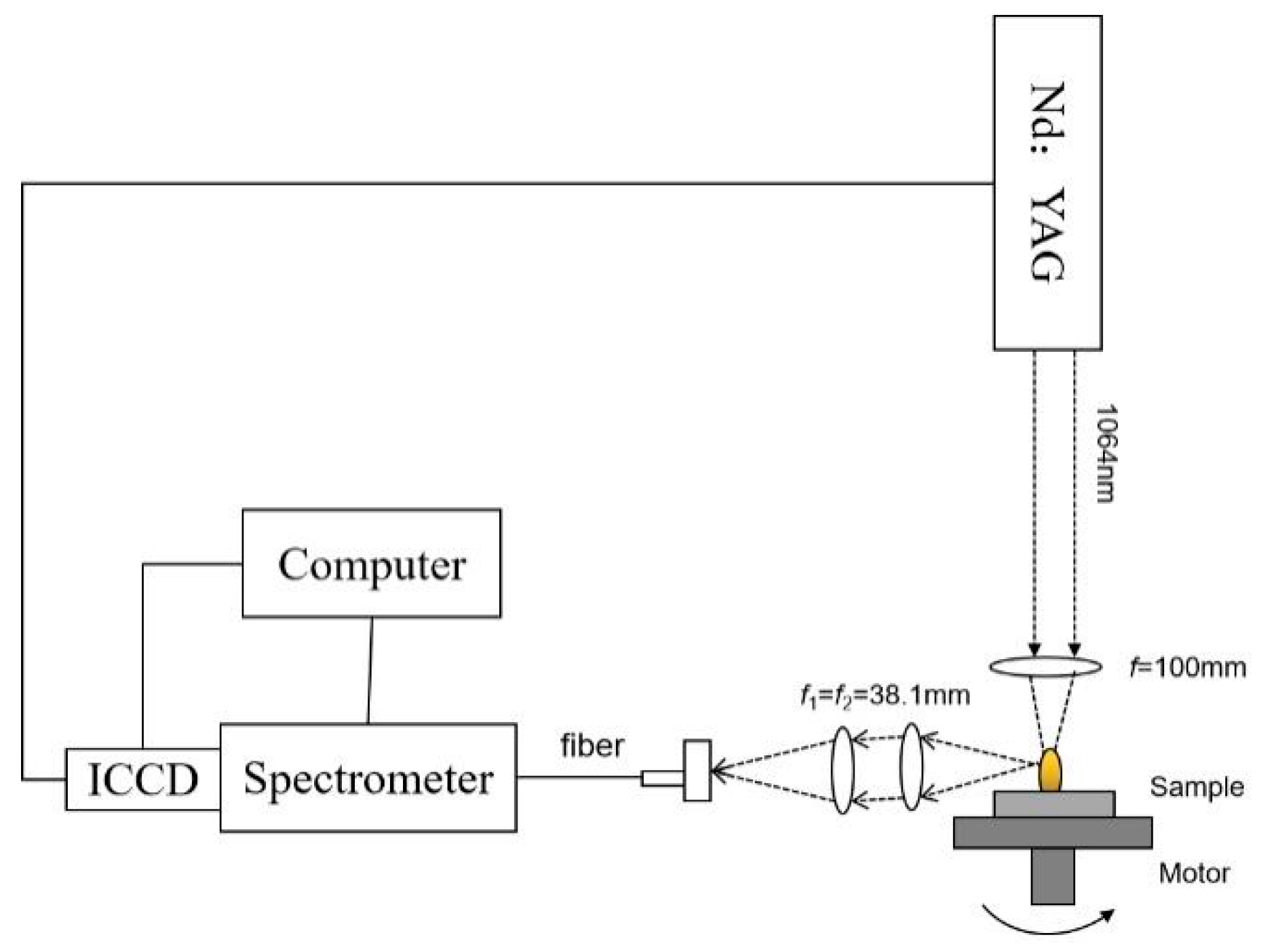
2.1. LIBS Instrumentation
2.2. Steel Alloy Samples
2.3. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
3. Results and Discussion
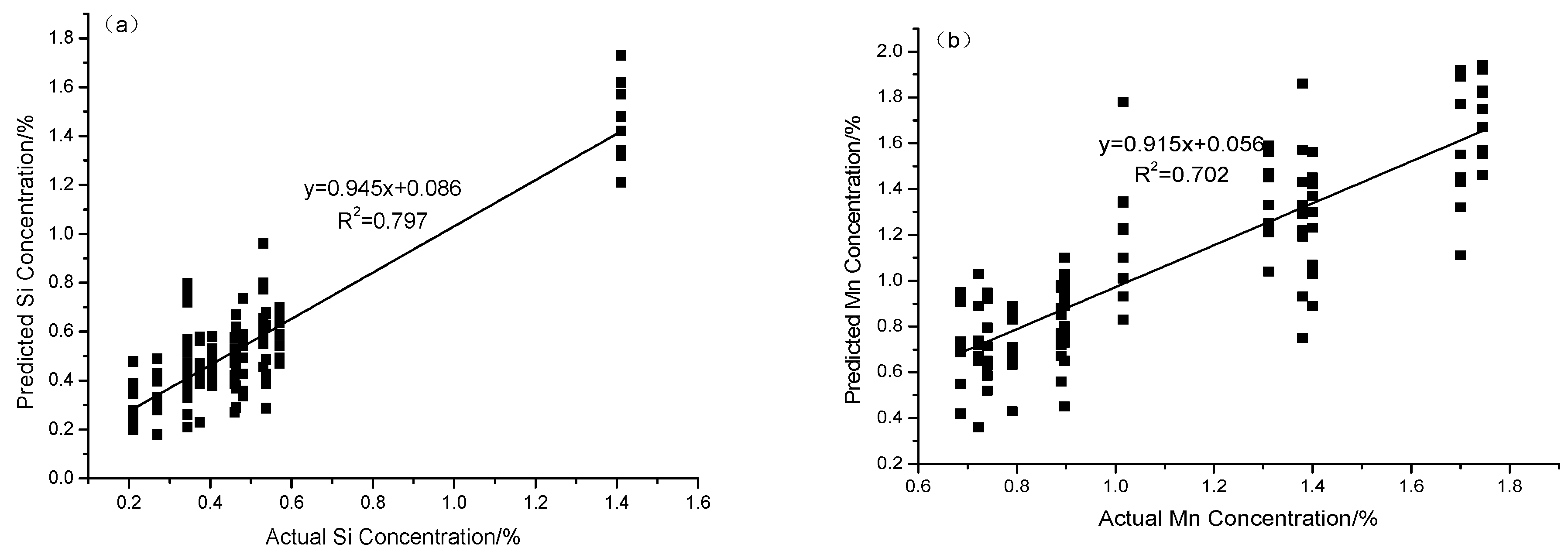
3.1. Traditional Calibration Method
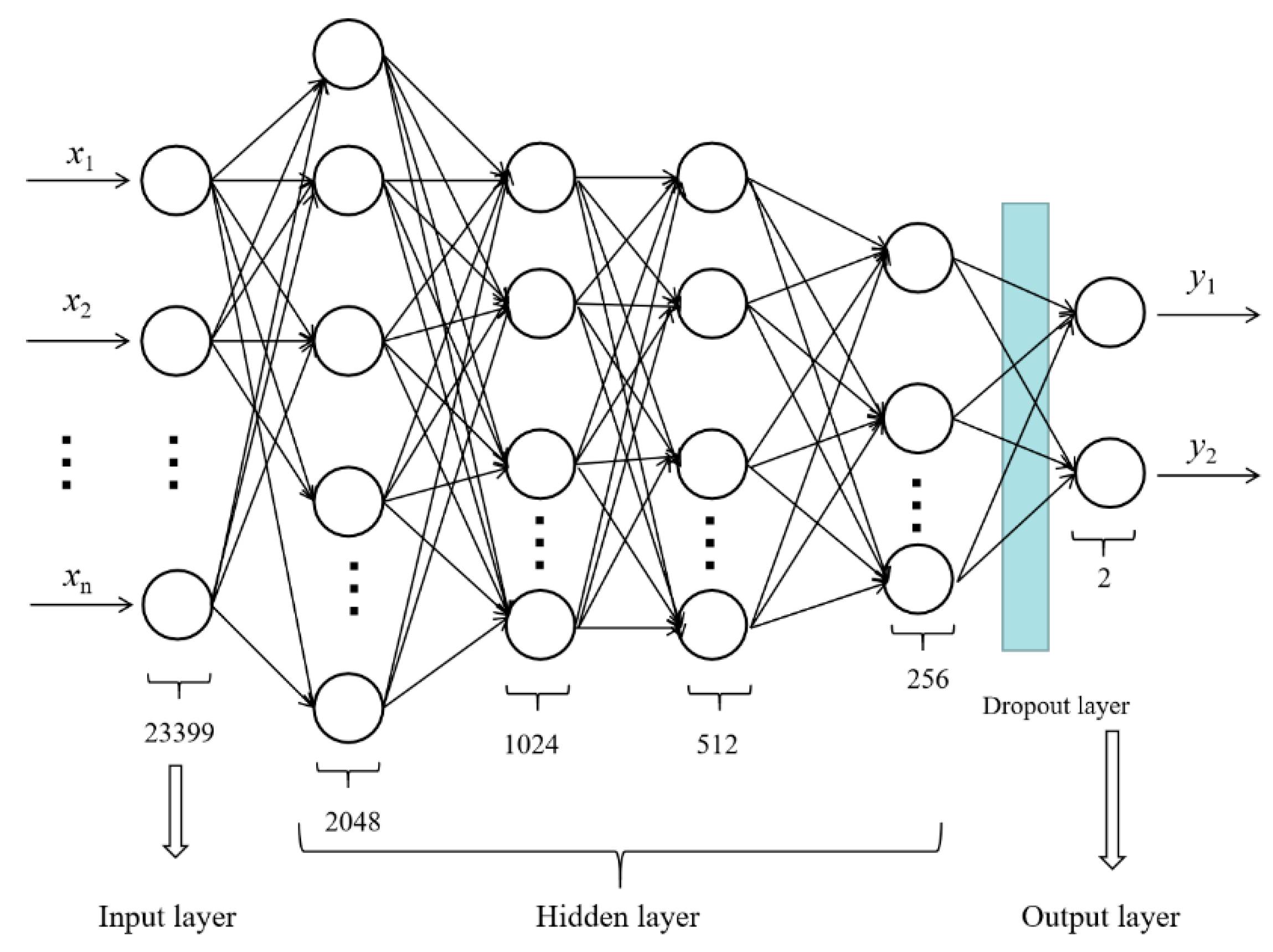
3.2. Deep Neural Networks (DNN)
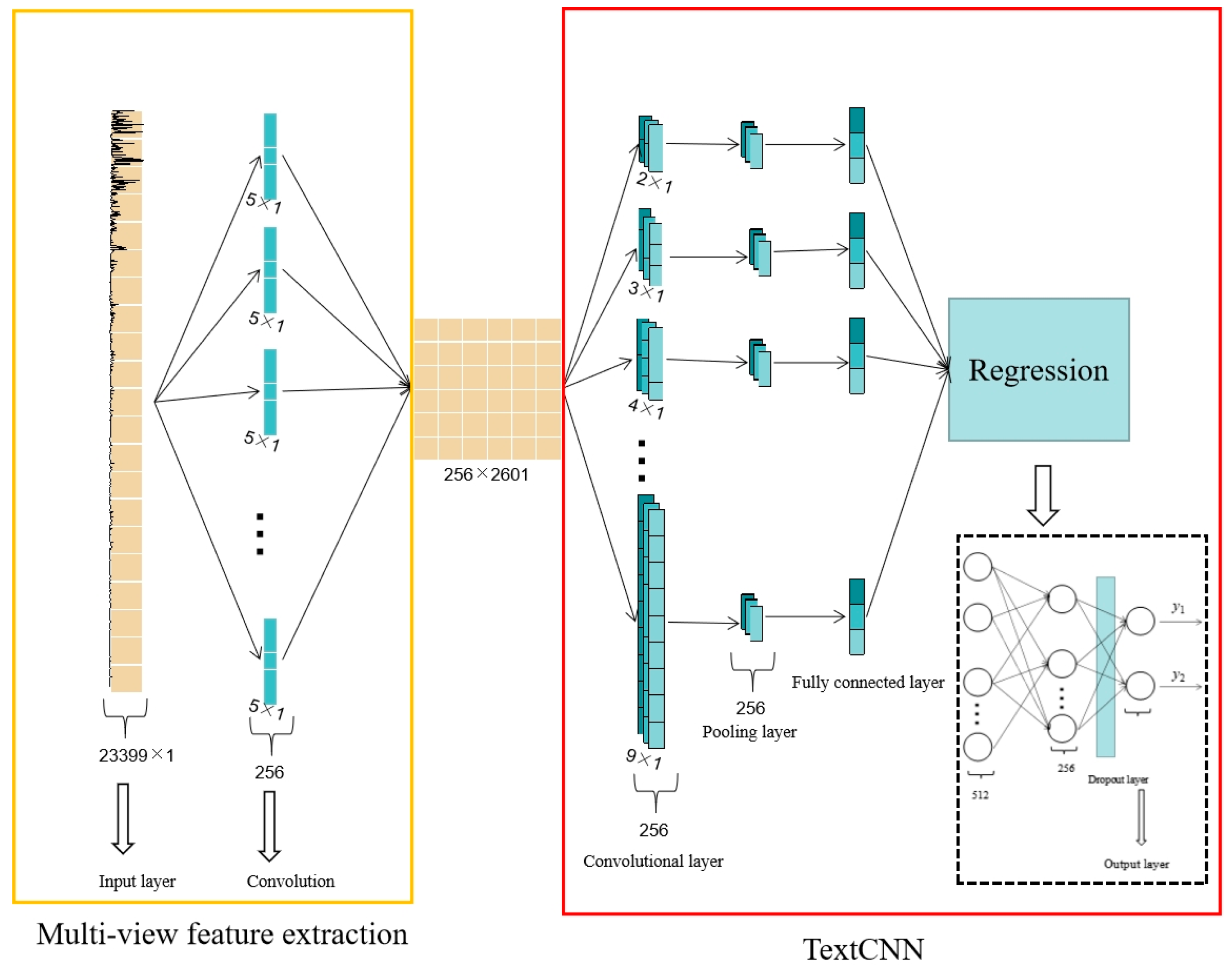
3.3. TextCNN
3.4. Backward-Differential TextCNN
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, S.; Rani, A.M.A.; Altaf, K.; Hussain, P.; Prakash, C.; Hastuty, S.; Na Rao, T.V.V.L.; Aliyu, A.A.; Subramaniam, K. Investigation of Alloy Composition and Sintering Parameters on the Corrosion Resistance and Microhardness of 316L Stainless Steel Alloy. Adances Manuf. II 2019, 4, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Xu, P.; Yao, L.; Li, X.; Pang, C.; Yang, L.; Liang, Y. Nb reinforced Fe-Mn-Si shape memory alloy composite coating fabricated by laser cladding on 304 stainless steel surface. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 5027–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenedy, G.R.; Lin, Y.-J.; Cheng, W.-C. Evidence of Martensitic Transformation in Fe-Mn-Al Steel Similar to Maraging Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Yu, H.; Li, F.; Gao, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z. Hot Deformation Behaviors and Process Parameters Optimization of Low-Density High-Strength Fe–Mn–Al–C Alloy Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2022, 28, 2498–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Gu, W.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. A calibration-free model for laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using non-gated detectors. Front. Phys. 2022, 17, 62503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Sakka, T. A Review of Underwater Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy of Submerged Solids. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and Its Application. Chin. J. Lasers 2022, 49, 146–177. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.-B.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L.-X.; Yao, S.-C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Ding, H.-B.; Lu, Y.; Hou, Z.-Y. Development in the application of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy in recent years: A review. Front. Phys. 2021, 16, 22500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.H.; Ullah, M.H.; Rahman, B.; Talukder, A.I.; Wahadoszamen, M.; Abedin, K.M.; Haider, A.F.M.Y. Evaluation of the prediction precision capability of partial least squares regression approach for analysis of high alloy steel by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: At. Spectrosc. 2015, 108, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fiodor, S.; Francesco, C.G.F.; Francesconi, M.; Marsili; Cristoforetti, P.; Legnaioli, G.; Palleschi, S.; Tognoni, V. Fast analysis of complex metallic alloys by double-pulse time-integrated laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2009, 64, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Tang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Yao, J.; Guo, L. Identification of Graves’ ophthalmology by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with machine learning method. Front. Optoelectron. 2021, 14, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, H.; Akram, M.U.; Shaukat, A.; Khan, S.A.; Alghamdi, N.S.; Khawaja, S.G.; Nazir, N. Correction to: Extraction of Retinal Layers Through Convolution Neural Network (CNN) in an OCT Image for Glaucoma Diagnosis. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Hao, X.; Hao, W.; Pan, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Jin, H. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectral Separation Method for Bauxite Based on Convolutional Neural Network. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2022, 89, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengfei, Z.; Ting, Z.; Daohua, X.; Li, Z. Quantitative analysis research of ChemCam-LIBS spectral data of Curiosity rover. Infrared Laser Eng. 2022, 51, 323–332. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Guindo, M.L.; Xu, X.; Sun, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Deep learning associated with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for the prediction of lead in soil. Appl. Spectrosc. 2019, 73, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Du, C.; Ma, F.; Shen, Y.; Wu, K.; Liang, D.; Zhou, J. Detection of soil organic matter from laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) and mid-infrared spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR) coupled with multivariate techniques. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Dong, J.; Yu, P.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, S.; Zhu, Z. Quantitative analysis of lithium in brine by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based on convolutional neural network. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1178, 338799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





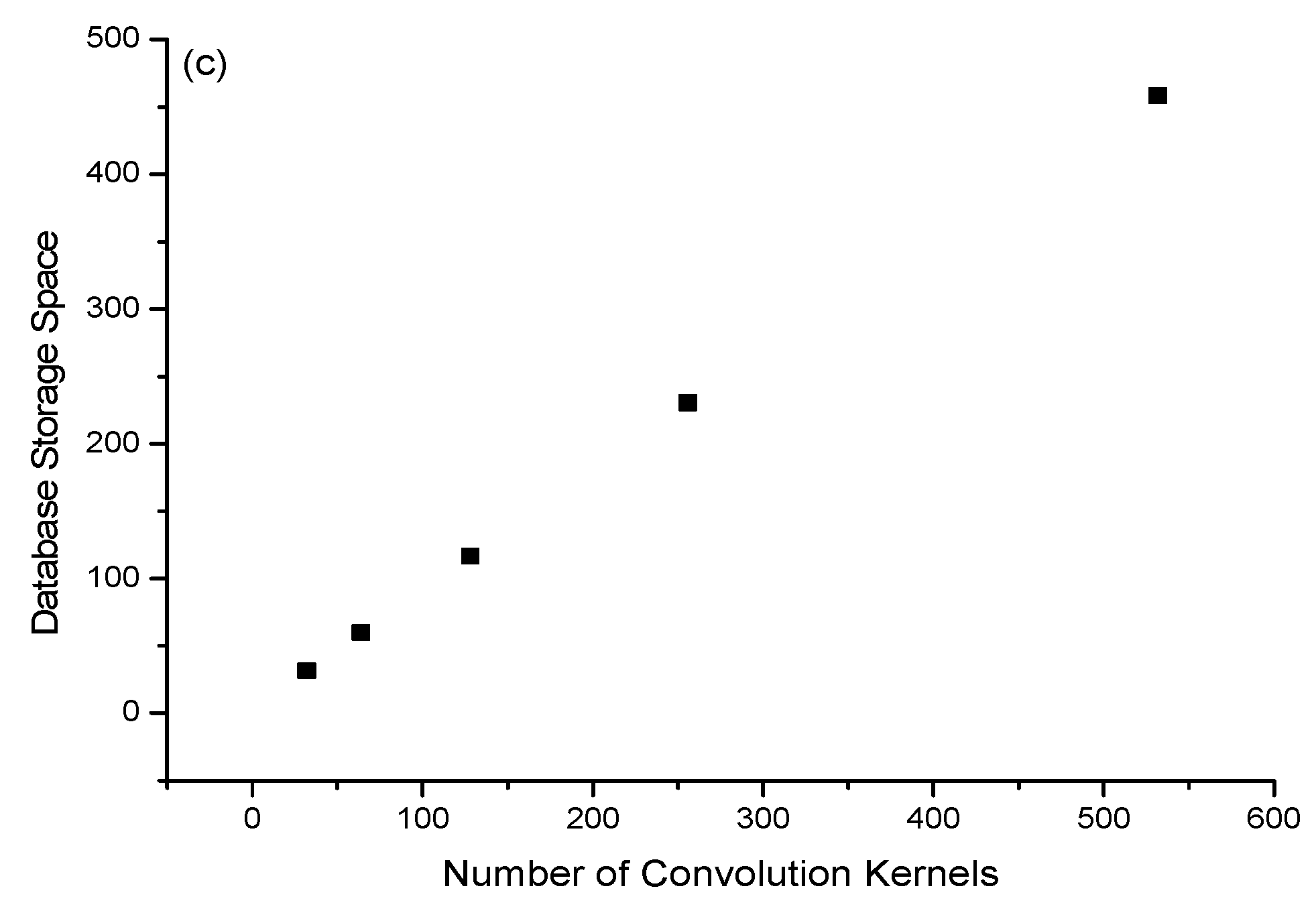



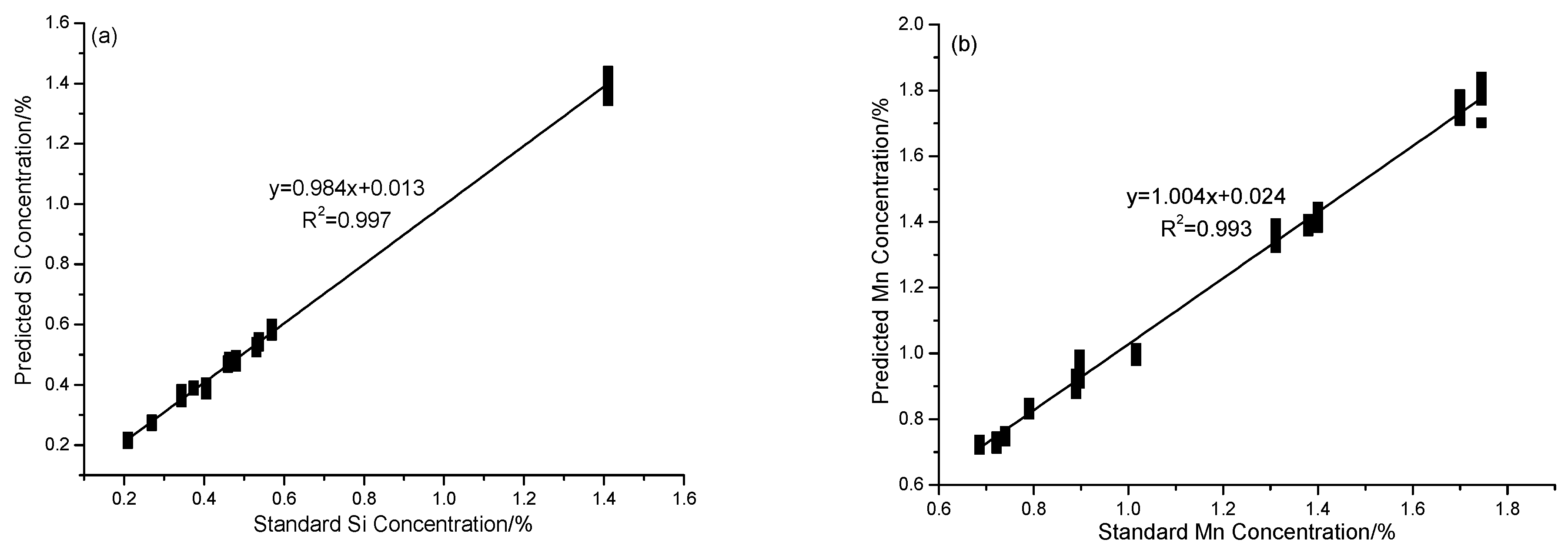

| Sample | Si | Mn | C | Cr | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 0.460 | 0.740 | 0.092 | 12.350 | 12.550 | — |
| 2# | 0.374 | 0.686 | 0.0103 | 14.724 | 6.124 | 0.0138 |
| 3# | 0.463 | 0.722 | 0.0345 | 11.888 | 12.850 | 0.0304 |
| 4# | 0.270 | 1.400 | 0.0190 | 18.460 | 10.200 | 0.2650 |
| 5# | 0.570 | 0.791 | 0.0860 | 25.390 | 20.05 | — |
| 6# | 0.405 | 1.380 | 0.0660 | 17.310 | 9.24 | 0.0920 |
| 7# | 0.480 | 1.311 | 0.0141 | 17.840 | 10.20 | — |
| 8# | 1.410 | 1.700 | 0.1430 | 17.960 | 8.90 | — |
| 9# | 0.210 | 0.890 | 0.0500 | 14.140 | 5.66 | 1.590 |
| 10# | 0.537 | 1.745 | 0.0201 | 16.811 | 10.720 | 2.1110 |
| 11# | 0.531 | 1.016 | 0.0489 | 14.630 | 24.680 | — |
| 12# | 0.344 | 0.897 | 0.0223 | 18.370 | 12.330 | — |
| 13# | 0.344 | 0.897 | 0.0223 | 18.370 | 12.330 | — |
| Si | Mn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Concentration/% | Predicted Concentration/% | Relative Error/% | Actual Concentration/% | Predicted Concentration/% | Relative Error/% |
| 0.460 | 0.436 | 5.217 | 0.740 | 0.814 | 10.000 |
| 0.374 | 0.385 | 2.941 | 0.686 | 0.934 | 36.152 |
| 0.463 | 0.448 | 3.24 | 0.722 | 0.802 | 11.080 |
| 0.270 | 0.321 | 18.899 | 1.400 | 1.374 | 1.857 |
| 0.570 | 0.626 | 9.825 | 0.791 | 0.994 | 25.664 |
| 0.405 | 0.396 | 2.222 | 1.380 | 1.277 | 7.464 |
| 0.480 | 0.370 | 22.917 | 1.311 | 1.329 | 1.373 |
| 1.410 | 0.900 | 36.17 | 1.700 | 1.432 | 15.765 |
| 0.210 | 0.230 | 9.524 | 0.890 | 1.023 | 14.944 |
| 0.537 | 0.592 | 10.242 | 1.745 | 1.596 | 8.539 |
| 0.531 | 0.520 | 2.072 | 1.016 | 1.01 | 0.591 |
| 0.344 | 0.368 | 6.977 | 0.897 | 0.9 | 0.334 |
| 0.344 | 0.341 | 0.872 | 0.897 | 0.901 | 0.450 |
| Si | Mn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Concentration/% | Predicted Concentration/% | Relative Error/% | Actual Concentration/% | Predicted Concentration/% | Relative Error/% |
| 0.460 | 0.433 | 5.87 | 0.740 | 0.758 | 2.432 |
| 0.374 | 0.406 | 8.556 | 0.686 | 0.844 | 23.032 |
| 0.463 | 0.45 | 2.808 | 0.722 | 0.731 | 1.247 |
| 0.270 | 0.306 | 13.333 | 1.400 | 1.338 | 4.429 |
| 0.570 | 0.618 | 8.421 | 0.791 | 0.909 | 14.918 |
| 0.405 | 0.416 | 2.716 | 1.380 | 1.275 | 7.609 |
| 0.480 | 0.411 | 14.375 | 1.311 | 1.299 | 0.915 |
| 1.410 | 1.272 | 9.787 | 1.700 | 1.498 | 11.882 |
| 0.210 | 0.229 | 9.048 | 0.890 | 0.866 | 2.697 |
| 0.537 | 0.603 | 12.291 | 1.745 | 1.609 | 7.794 |
| 0.531 | 0.538 | 1.318 | 1.016 | 0.999 | 1.673 |
| 0.344 | 0.344 | 0.000 | 0.897 | 0.888 | 1.003 |
| 0.344 | 0.352 | 2.326 | 0.897 | 0.879 | 2.007 |
| Si | Mn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual Concentration/% | Predicted Concentration/% | Relative Error/% | Actual Concentration/% | Predicted Concentration/% | Relative Error/% |
| 0.460 | 0.430 | 6.522 | 0.740 | 0.753 | 1.757 |
| 0.374 | 0.362 | 3.209 | 0.686 | 0.715 | 4.227 |
| 0.463 | 0.441 | 4.752 | 0.722 | 0.762 | 5.540 |
| 0.270 | 0.291 | 7.778 | 1.400 | 1.398 | 0.143 |
| 0.570 | 0.576 | 1.053 | 0.791 | 0.841 | 6.321 |
| 0.405 | 0.397 | 1.975 | 1.380 | 1.348 | 2.319 |
| 0.480 | 0.449 | 6.458 | 1.311 | 1.350 | 2.975 |
| 1.410 | 1.350 | 4.255 | 1.700 | 1.540 | 9.412 |
| 0.210 | 0.227 | 8.095 | 0.890 | 0.890 | 0.000 |
| 0.537 | 0.567 | 5.587 | 1.745 | 1.692 | 3.037 |
| 0.531 | 0.537 | 1.13 | 1.016 | 1.032 | 1.575 |
| 0.344 | 0.312 | 9.302 | 0.897 | 0.851 | 5.128 |
| 0.344 | 0.321 | 6.686 | 0.897 | 0.816 | 9.030 |
| DNN | TextCNN | Backward-Differential TextCNN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Mn | Si | Mn | Si | Mn |
| 10.086 | 10.324 | 6.988 | 6.280 | 5.139 | 3.959 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Nian, F. Quantitative Analysis of Steel Alloy Elements Based on LIBS and Deep Learning of Multi-Perspective Features. Electronics 2023, 12, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122566
Gu Y, Chen Z, Chen H, Nian F. Quantitative Analysis of Steel Alloy Elements Based on LIBS and Deep Learning of Multi-Perspective Features. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122566
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Yanhong, Zhiwei Chen, Hao Chen, and Fudong Nian. 2023. "Quantitative Analysis of Steel Alloy Elements Based on LIBS and Deep Learning of Multi-Perspective Features" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122566
APA StyleGu, Y., Chen, Z., Chen, H., & Nian, F. (2023). Quantitative Analysis of Steel Alloy Elements Based on LIBS and Deep Learning of Multi-Perspective Features. Electronics, 12(12), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122566





