All-Weather Pedestrian Detection Based on Double-Stream Multispectral Network
Abstract
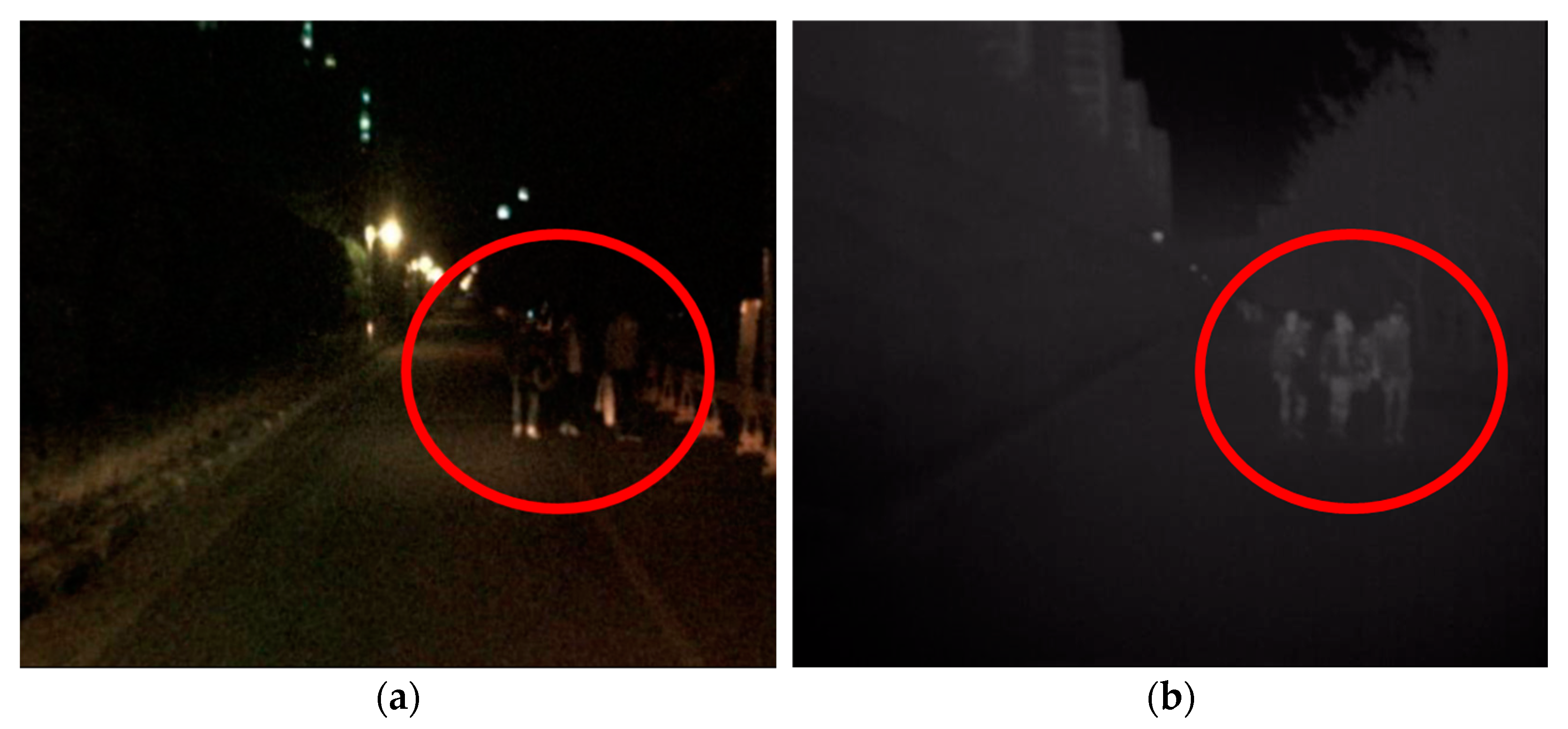
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Proposed Double-Stream Multispectral Network (DSMN)
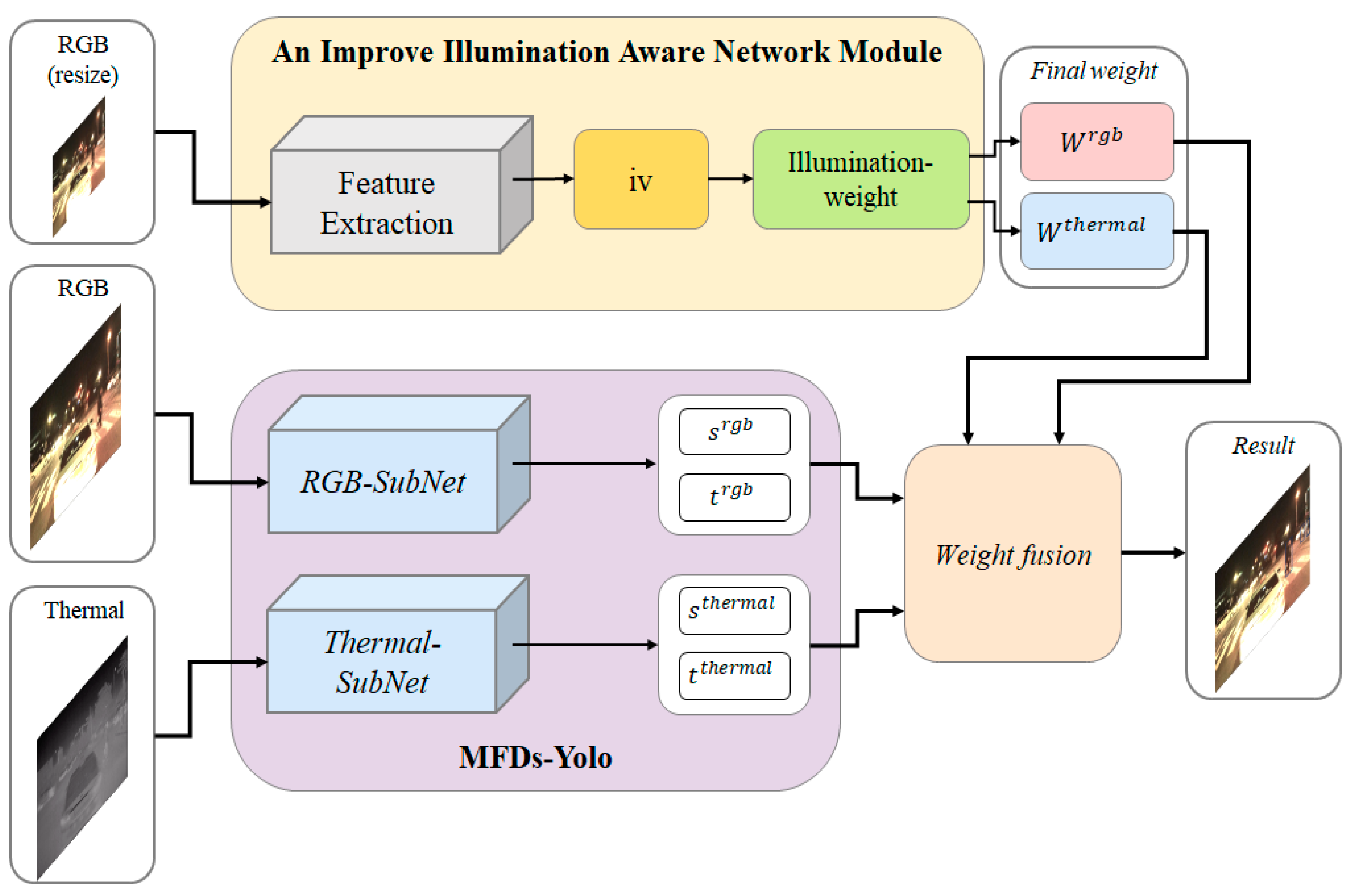
2.2. A Multispectral Fusion and Double-Stream Detector with Yolo-Based Detectors (MFDs-Yolo)
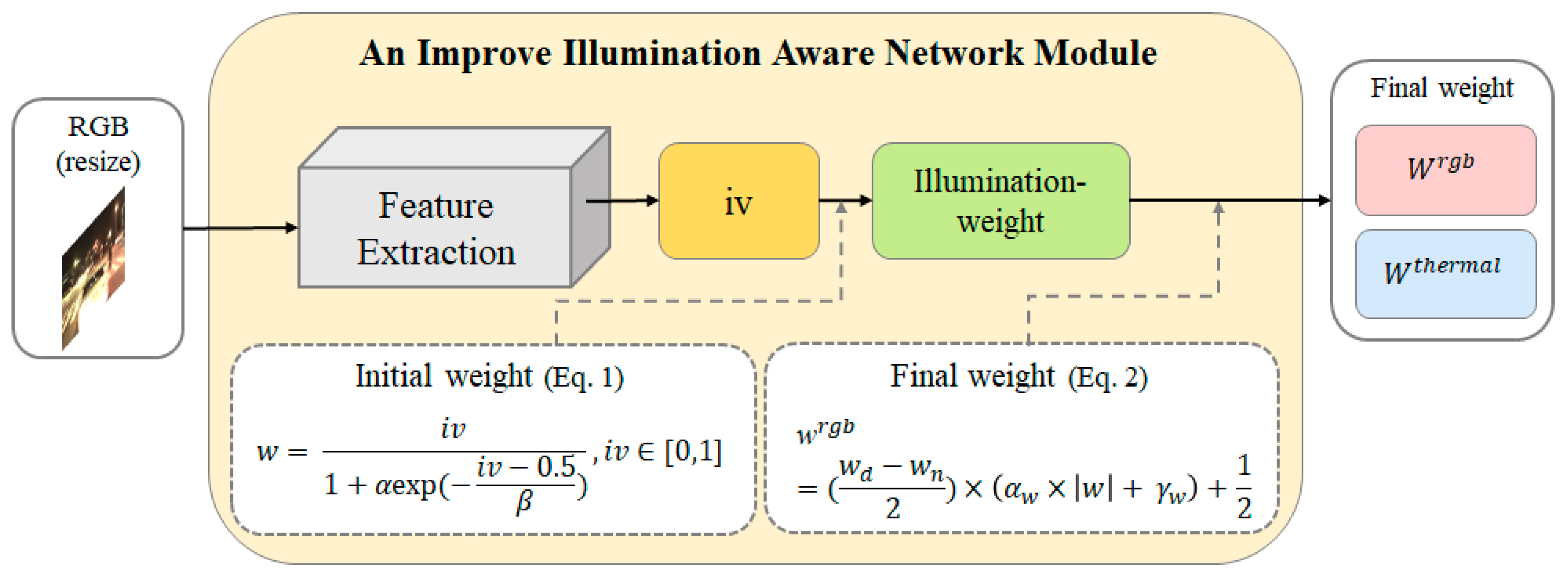
2.3. An Improved Illumination Modality Module (i-IAN)
3. Discussion
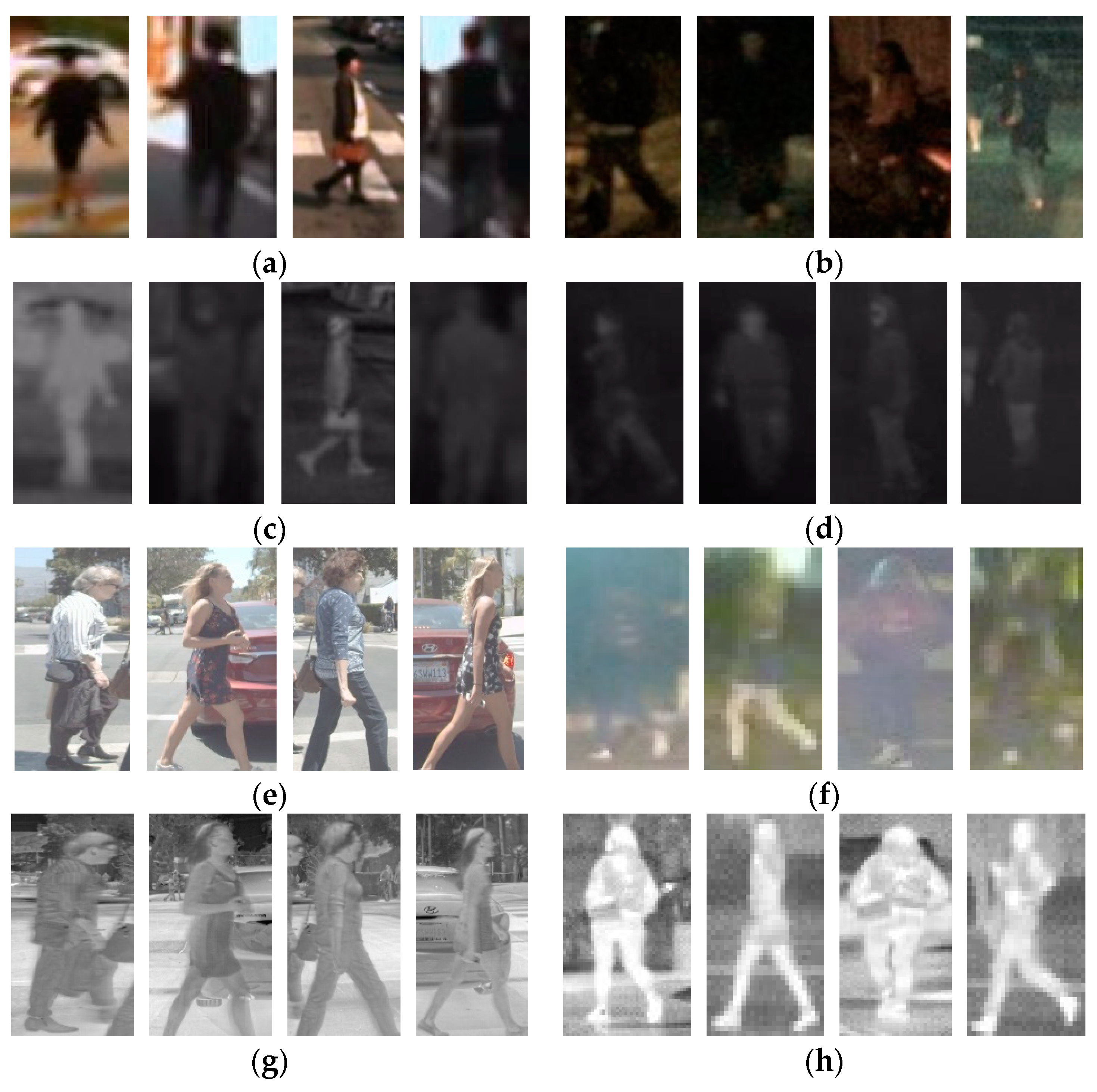
3.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
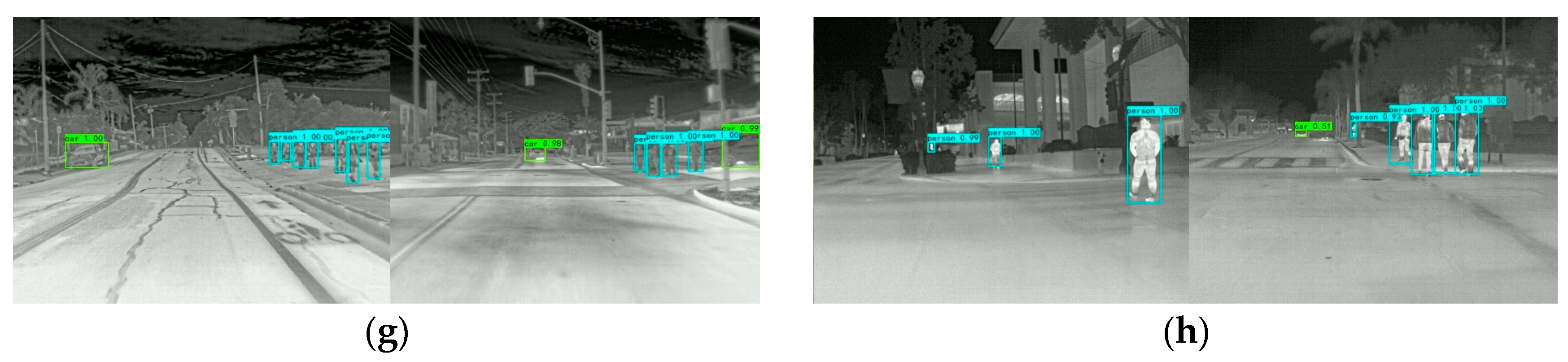
3.2. Implement Details and Quantitative Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeong, D.J.; Velasco-Hernandez, G.; Barry, J.; Walsh, J. Sensor and sensor fusion technology in autonomous vehicles: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAA, Inc. Automatic Emergency Braking with Pedestrian. 2019. Available online: https://www.aaa.com/AAA/common/aar/files/Research-Report-Pedestrian-Detection.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Shopovska, I.; Jovanov, L.; Philips, W. Deep visible and thermal image fusion for enhanced pedestrian visibility. Sensors 2019, 19, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, K.; Tang, Z.; Xiong, Z. Enhanced object detection with deep convolutional neural networks for advanced driving assistance. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, R.; Ainouz, S.; Canu, S.; Meriaudeau, F. A new multimodal RGB and polarimetric image dataset for road scenes analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruthiventi, S.S.S.; Sahay, P.; Biswal, R. Low-light pedestrian detection from RGB images using multi-modal knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the 2017 24th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 4207–4211. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; So Kweon, I. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.; Fischer, V.; Herman, M.; Sven, B. Multispectral pedestrian detection using deep fusion convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 22–24 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Multispectral pedestrian detection via simultaneous detection and segmentation. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Tan, X. Robust Pedestrian Detection Based on Multi-Spectral Image Fusion and Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefevre, S.; Avignon, B. Multispectral fusion for object detection with cyclic fuse-and-refine blocks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Qiao, H.; Huang, K.; Hussain, A. Cross-modality interactive attention network for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fromont, E.; Lefevre, S.; Avignon, B. Guided attentive feature fusion for multispectral pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, A.; Teutsch, M.; Sarfraz, M.S.; Stiefelhagen, R. Anchor-free small-scale multispectral pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Virtual, 7–10 September 2020; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nataprawira, J.; Gu, Y.; Goncharenko, I.; Kamijo, S. Pedestrian detection using multispectral images and a deep neural network. Sensors 2021, 21, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Illumination-aware faster R-CNN for robust multispectral pedestrian detection. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y. Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. Improving multispectral pedestrian detection by addressing modality imbalance problems. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Pu, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y. Illumination and temperature-aware multispectral networks for edge-computing-enabled pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Metaxas, D. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2016, New York, NY, USA, 20 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y. YoloV4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- FLIR Starter Thermal Dataset. Available online: https://www.flir.com/oem/adas/adas-dataset-form/ (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, Z. Weakly aligned cross-modal learning for multispectral pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, D.; Adam, M.; Jarvers, C.; Layher, G.; Neumann, H.; Teutsch, M. Fully convolutional region proposal networks for multispectral person detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. The cross-modality disparity problem in multispectral pedestrian detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.02645. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, D.; Desai, S.M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Fiterau, M.; Rahman, T. Pedestrian detection in thermal images using saliency maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 988–997. [Google Scholar]
- Kristo, M.; Ivasic-Kos, M.; Pobar, M. Thermal object detection in difficult weather conditions using YOLO. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 125459–125476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, F.; Azam, S.; Jeon, M. SSTN: Self-supervised domain adaptation thermal object detection for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, K.; Das, A.; Das, S.; Bhattacharya, U.; Yogamani, S. Spatio-contextual deep network-based multimodal pedestrian detection for autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15940–15950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaguptapu, C.; Akolekar, N.; Sharma, M.M.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Borrow from anywhere: Pseudo multi-modal object detection in thermal imagery. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kieu, M.; Bagdanov, A.D.; Bertini, M. Bottom-up and layerwise domain adaptation for pedestrian detection in thermal images. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2021, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, H. LGADet: Light-weight anchor-free multispectral pedestrian detection with mixed local and global attention. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Methods | MR (IoU@0.5) (%) | MR (IoU@0.75) (%) | Platform | Speed (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Day | Night | All | Day | Night | |||
| ACF [7] | 47.32 | 42.57 | 56.17 | 88.79 | 87.70 | 91.22 | MATLAB | 7.73 |
| Proposed YOLOv3 [10] | 43.25 | 46.99 | 35.84 | — | — | — | 1080 Ti | — |
| Halfway fusion [20] | 25.75 | 24.88 | 26.59 | 81.29 | 78.43 | 86.80 | TITAN X | 0.43 |
| Fusion RPN+BF [25] | 18.29 | 19.57 | 16.27 | 72.97 | 68.14 | 81.35 | MATLAB | 0.80 |
| IAF R-CNN [16] | 15.73 | 14.55 | 18.26 | 75.50 | 72.34 | 81.12 | TITAN X | 0.21 |
| IATDNN + IASS [17] | 14.95 | 14.67 | 15.72 | 76.69 | 76.46 | 77.05 | TITAN X | 0.25 |
| RFA [26] | 14.61 | 16.78 | 10.21 | — | — | — | TITAN X | 0.08 |
| CIAN [12] | 14.12 | 14.77 | 11.13 | — | — | — | 1080 Ti | 0.08 |
| MSDS-RCNN [9] | 11.34 | 10.53 | 12.94 | 70.57 | 67.36 | 79.25 | TITAN X | 0.22 |
| AR-CNN [23] | 9.34 | 9.94 | 8.38 | 64.22 | 57.87 | 76.82 | 1080 Ti | 0.12 |
| MBNet [18] | 8.13 | 8.28 | 7.86 | 60.12 | 54.90 | 68.34 | 1080 Ti | 0.07 |
| This work | 14.33 | 13.34 | 22.36 | 50.76 | 47.85 | 53.76 | 3090 Ti | 0.76 |
| Methods | mAP (%) |
|---|---|
| PiCA-Net [27] | 65.80 |
| R3Net [27] | 70.85 |
| tY [28] | 63.00 |
| SSTN101 [29] | 73.22 |
| MuFEm + ScoFA [30] | 78.03 |
| This work | 80.30 |
| Category | mAP (%) | AP (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score | MR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 80.30 | 93.21 | 92.89 | 86.82 | 0.90 | 4.62 |
| People | 64.29 | 89.47 | 44.74 | 0.60 | 28.94 | |
| Cyclist | 83.41 | 88.99 | 74.05 | 0.81 | 11.45 |
| Methods | mAP (%) | AP (%) | MR (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | Bicycle | Car | Person | Bicycle | Car | ||
| Baseline | 53.97 | 54.69 | 39.66 | 67.57 | — | — | — |
| MMTOD-CG [31] | 61.40 | 63.31 | 50.26 | 70.63 | — | — | — |
| MMTOD-UNIT [31] | 61.54 | 64.47 | 49.43 | 70.72 | — | — | — |
| TD(T, T) [32] | 71.40 | 75.50 | 51.90 | 86.90 | — | — | — |
| BU(AT, T) [32] | 73.10 | 76.10 | 56.10 | 87.00 | — | — | — |
| BU(LT, T) [32] | 73.20 | 75.60 | 57.40 | 86.50 | — | — | — |
| LGADet [33] | — | 74.52 | — | — | 28.43 | — | — |
| This work | 70.66 | 70.13 | 65.01 | 77.03 | 21.53 | 22.43 | 17.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsia, C.-H.; Peng, H.-C.; Chan, H.-T. All-Weather Pedestrian Detection Based on Double-Stream Multispectral Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102312
Hsia C-H, Peng H-C, Chan H-T. All-Weather Pedestrian Detection Based on Double-Stream Multispectral Network. Electronics. 2023; 12(10):2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102312
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsia, Chih-Hsien, Hsiao-Chu Peng, and Hung-Tse Chan. 2023. "All-Weather Pedestrian Detection Based on Double-Stream Multispectral Network" Electronics 12, no. 10: 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102312
APA StyleHsia, C.-H., Peng, H.-C., & Chan, H.-T. (2023). All-Weather Pedestrian Detection Based on Double-Stream Multispectral Network. Electronics, 12(10), 2312. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12102312







