Autonomous Technology for 2.1 Channel Audio Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
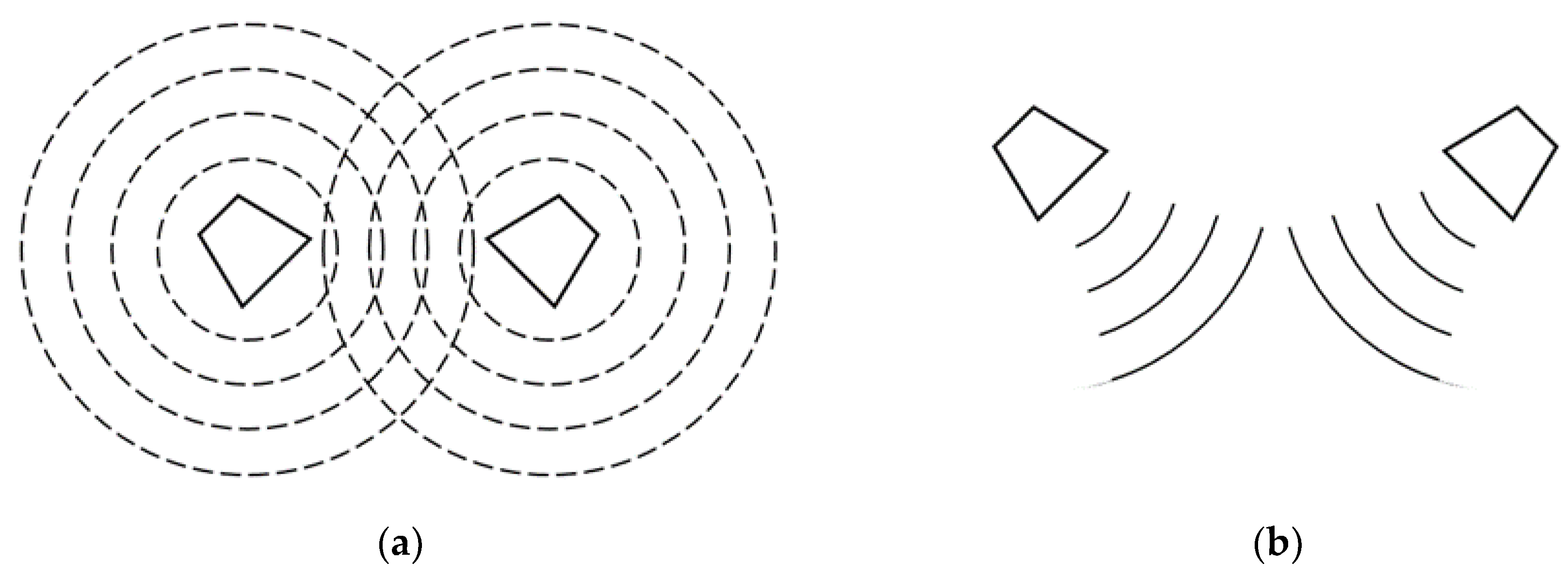
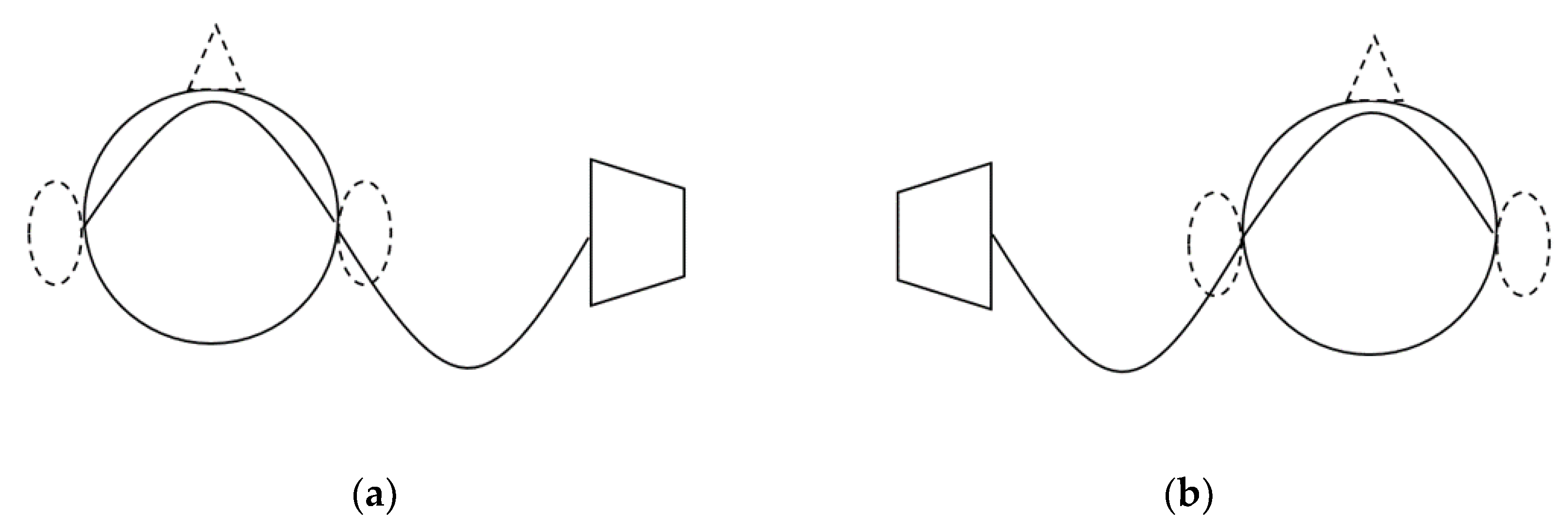
2. Sound Wave Theory
3. Robotic System for Stereophonics
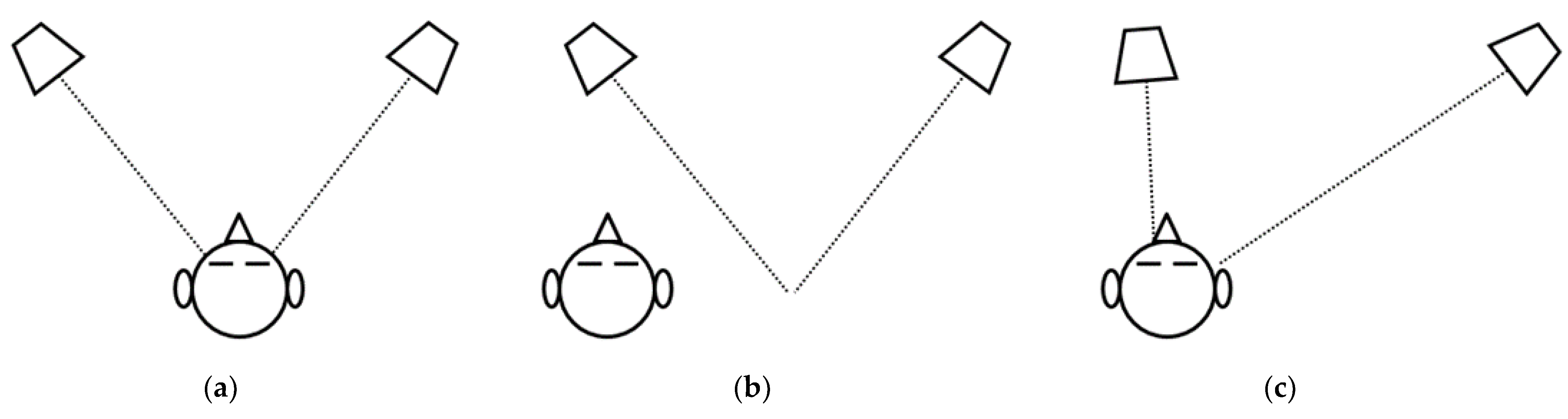
3.1. Computer Vision
3.2. Robotic System
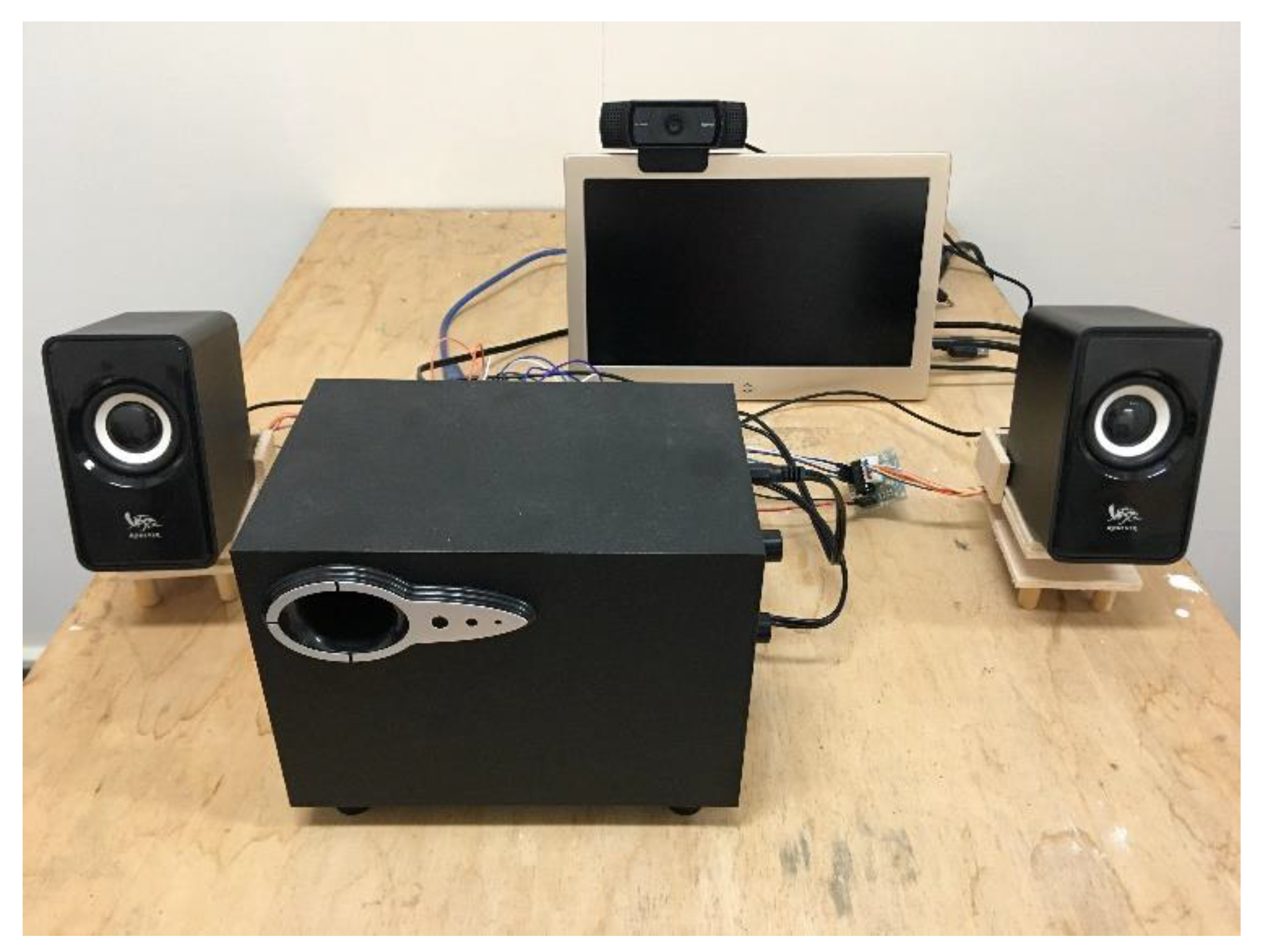
3.3. System Integration
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
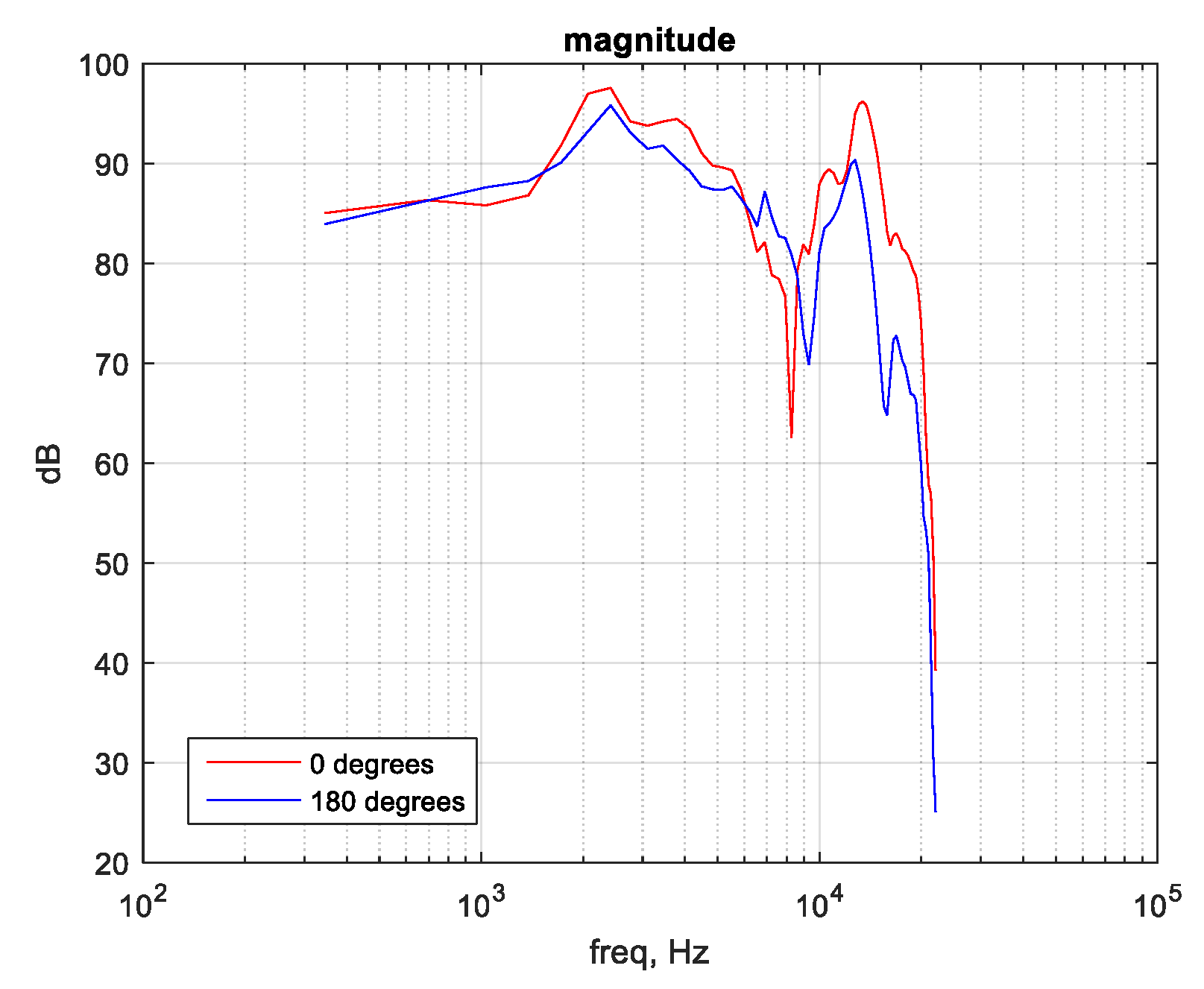
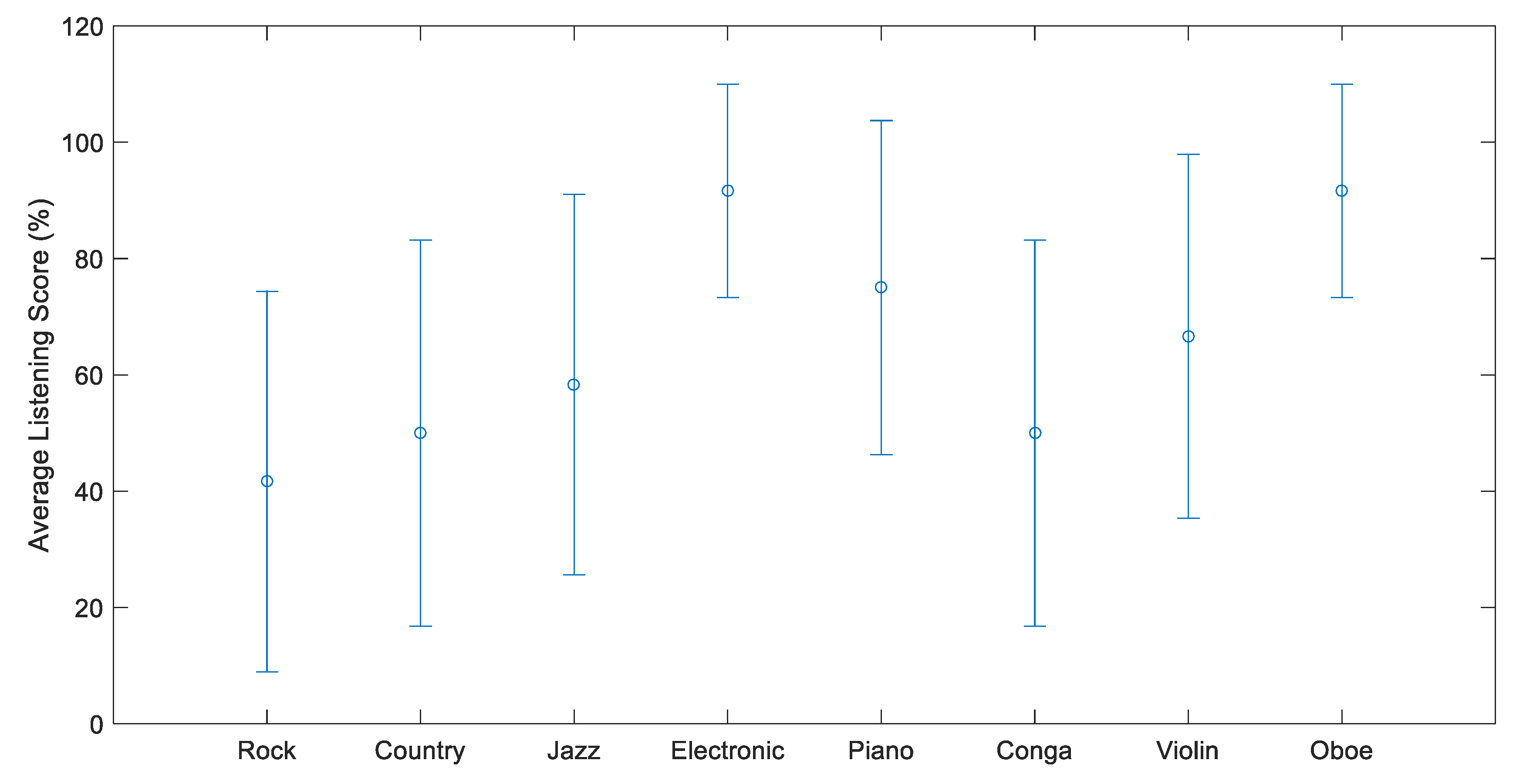
4.1. Objective Listening Test
4.2. Subjective Listening Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, D.L.; Delfabbro, P.H.; Billieux, J.; Potenza, M.N. Problematic online gaming and the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Behav. Addict. 2020, 9, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seetharaman, P. Business models shifts: Impact of Covid-19. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 54, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razmjooy, N.; Ramezani, M.; Namadchian, A. A new LQR optimal control for a single-link flexible joint robot manipulator based on grey wolf optimizer. Majlesi J. Electr. Eng. 2016, 10, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kona, S.; Butler, N.; Vijayasekar, R.; Adzimah, W.; Kim, J.-H. Design of an intelligent robotic audio system for smart home environment. In Proceedings of the Conference on Recent Advances in Robotics, Miami, FL, USA, 8–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.-N. Headphone-based immersive audio for virtual reality headsets. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2017, 63, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.-N.; Chen, L.J. HRTF adjustments with audio quality assessments. Arch. Acoust. 2013, 38, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qi, X. Pre-trained-based individualization model for real-time spatial audio rendering system. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 128722–128733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.-N. Driver filter design for software-implemented loudspeaker crossovers. Arch. Acoust. 2014, 39, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Razmjooy, N.; Ramezani, M. Analytical solution for optimal control by the second kind Chebyshev polynomials expansion. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A: Sci. 2016, 41, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjooy, N.; Ramezani, M. Uncertain method for optimal control problems with uncertainties using Chebyshev inclusion functions. Asian J. Control. 2018, 21, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.N.; Collins, T.; Jančovič, P. Hybrid method for designing digital Butterworth filters. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2012, 38, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjooy, N.; Ramezani, M.; Nazari, E. Using LQG/LTR optimal control method for car suspension system. SCRO Res. Annu. Rep. 2015, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Razmjooy, N.; Ramezani, M. Interval structure of Runge-Kutta methods for solving optimal control problems with uncertainties. Comput. Methods Differ. Equ. 2019, 7, 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Kabzinski, T.; Jax, P. A causality-constrained frequency-domain least-squares filter design method for crosstalk cancellation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 2942–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, E.C.; Fazi, F.M. Weighted orthogonal vector rejection method for loudspeaker-based binaural audio reproduction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertins, A.; Maass, M.; Katzberg, F. Room impulse response reshaping and crosstalk cancellation using convex optimization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. On our perception of sound direction. Philosoph. Mag. 1907, 13, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.I.; Wakefield, G.H. Introduction to head-related transfer functions (HRTFs): Representations of HRTFs in time, frequency, and space. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2001, 49, 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Popper, A.N.; Fay, R.R. Sound Source Localization; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Chapter 2.2; pp. 131–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, B.; Martin, K. HRTF Measurements of a KEMAR Dummy-Head Microphone; MIT Media Lab: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Algazi, V.R.; Duda, R.O.; Thompson, D.P.; Avendano, C. The CIPIC HRTF database. In Proceedings of the IEEE WASPAA01, New Paltz, NY, USA, 21–24 October 2001; pp. 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- IRCAM LISTEN HRTF Database. Available online: http://recherche.ircam.fr/equipes/salles/listen/ (accessed on 2 January 2022).
- ITU-R Rec. BS.1116. Methods for the Subjective Assessment of Small Impairments in Audio Systems including Multichannel Sound Systems; International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Thiede, T.; Treurniet, W.C.; Bitto, R.; Schmidmer, C.; Sporer, T.; Beerends, J.G.; Colomes, C. PEAQ-The ITU standard for objective measurement of perceived audio quality. J. Audio Eng. Society. 2000, 48, 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.P.; Duda, R.O. A structural model for binaural sound synthesis. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1998, 6, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zolzer, U. DAFX Digital Audio Effects; John Wiley and Sons Publishing: West Sussex, UK, 2003; Chapter 6.3.4; 155p. [Google Scholar]










| Motor Type | Servo Motor SG90 | Stepper Motor 28BYJ-48 |
|---|---|---|
| Action | Quick | Slow |
| Noise | High | Low |
| Driver Board | None | ULN2003 Driver |
| Music Genres | Leaning a Little to the Left | Leaning to the Left |
|---|---|---|
| Rock | −1.618 | −3.555 |
| Country | −2.599 | −3.708 |
| Jazz | −2.590 | −3.69 |
| Electronic | −2.334 | −3.459 |
| Music Genres | Nonideal Situation | Nonideal Situation with Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Rock | 7 | 5 |
| Country | 6 | 6 |
| Jazz | 5 | 7 |
| Electronic | 1 | 11 |
| Overall | 19 | 29 |
| Music Instruments | Nonideal Situation | Nonideal Situation with Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Piano | 3 | 9 |
| Conga Drums | 6 | 6 |
| Violin | 4 | 8 |
| Oboe | 1 | 11 |
| Overall | 14 | 34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, S.-N.; Huang, C.-W. Autonomous Technology for 2.1 Channel Audio Systems. Electronics 2022, 11, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11030339
Yao S-N, Huang C-W. Autonomous Technology for 2.1 Channel Audio Systems. Electronics. 2022; 11(3):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11030339
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Shu-Nung, and Chang-Wei Huang. 2022. "Autonomous Technology for 2.1 Channel Audio Systems" Electronics 11, no. 3: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11030339
APA StyleYao, S.-N., & Huang, C.-W. (2022). Autonomous Technology for 2.1 Channel Audio Systems. Electronics, 11(3), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11030339







