Anomalous Behavior Detection Based on the Isolation Forest Model with Multiple Perspective Business Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement
3. Related Works
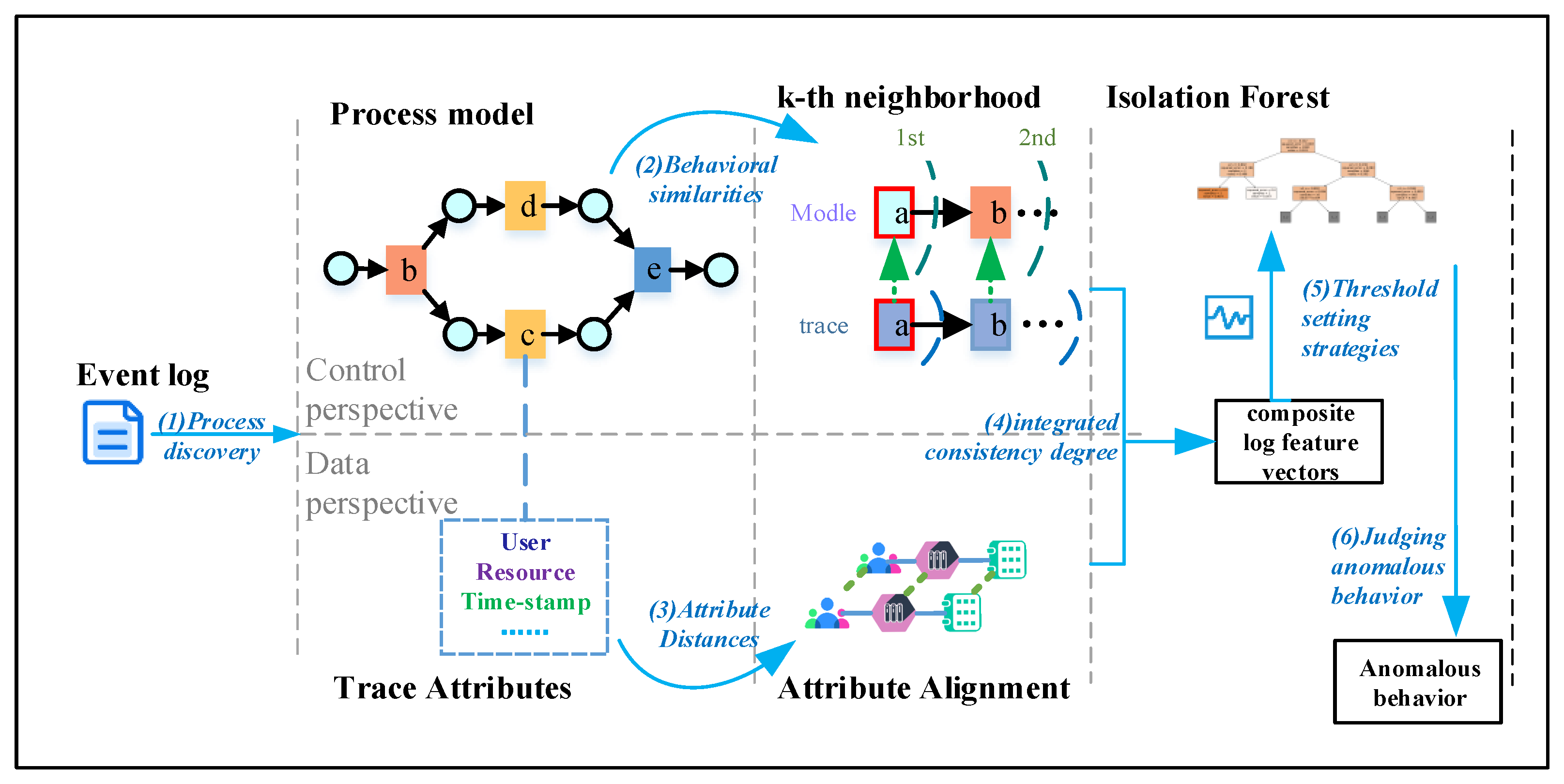
4. Preliminary
4.1. Behavioral Relationships in Event Logs
4.2. Anomaly Detection Based on the Isolation Forest Model
5. Multi-View Process Similarity Metric
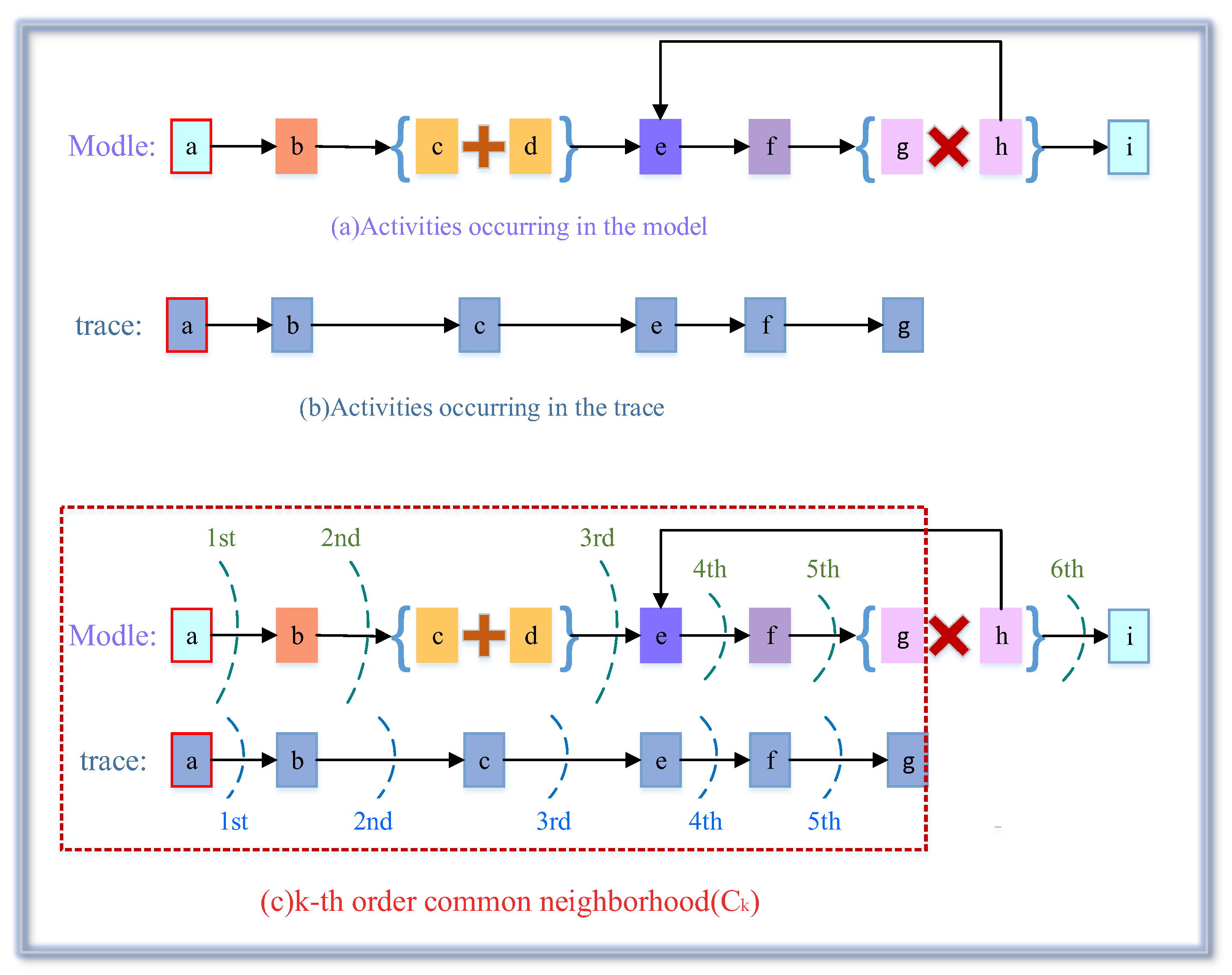
5.1. Behavioral Similarity Analysis Based on K-order Neighborhoods
| Algorithm 1: Calculation of Behavioral Conformance Degree |
 |
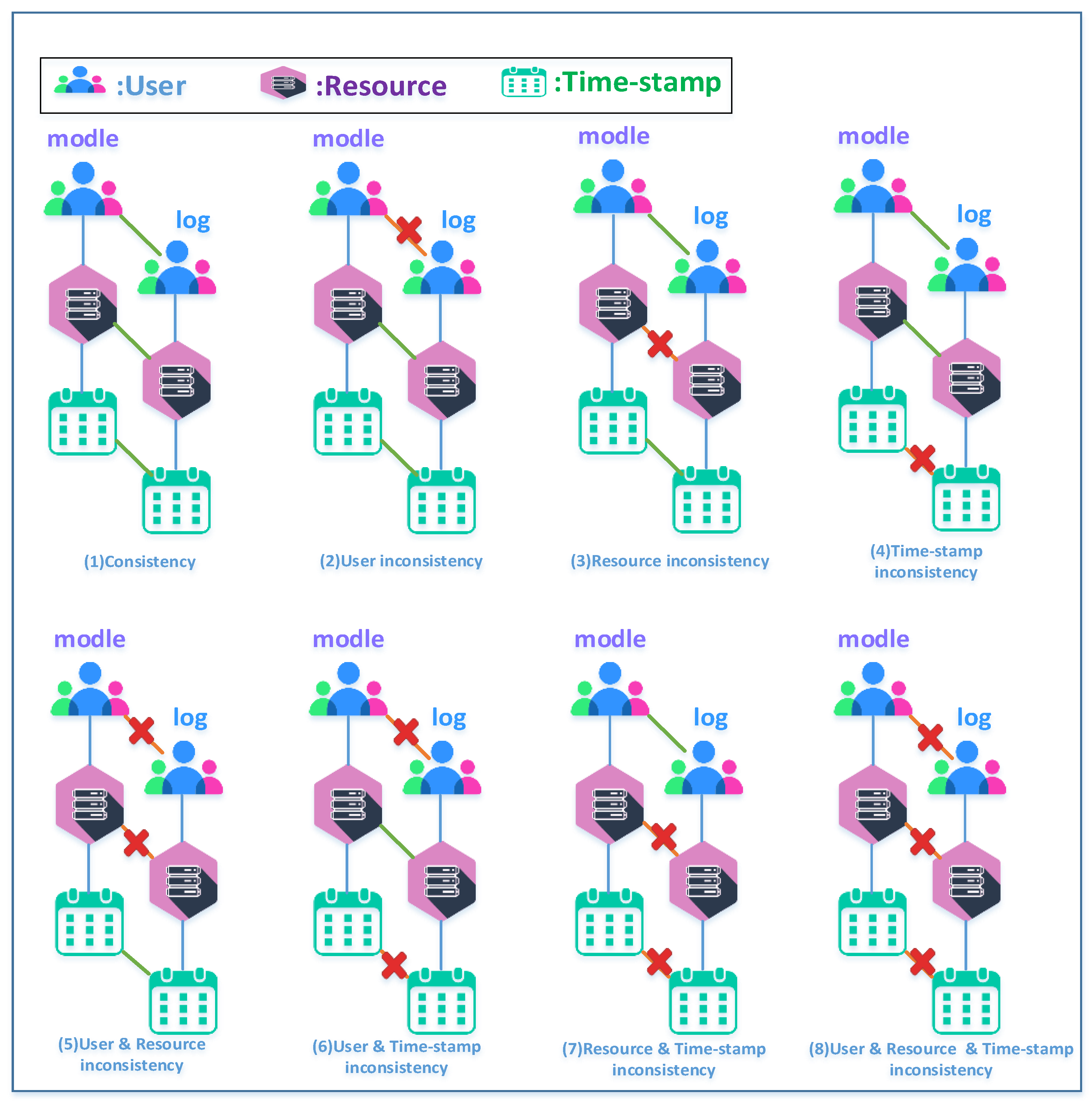
5.2. Alignment-Based Attribute Distance Metric
| Algorithm 2: Calculation of Attribute Conformance Degree |
 |
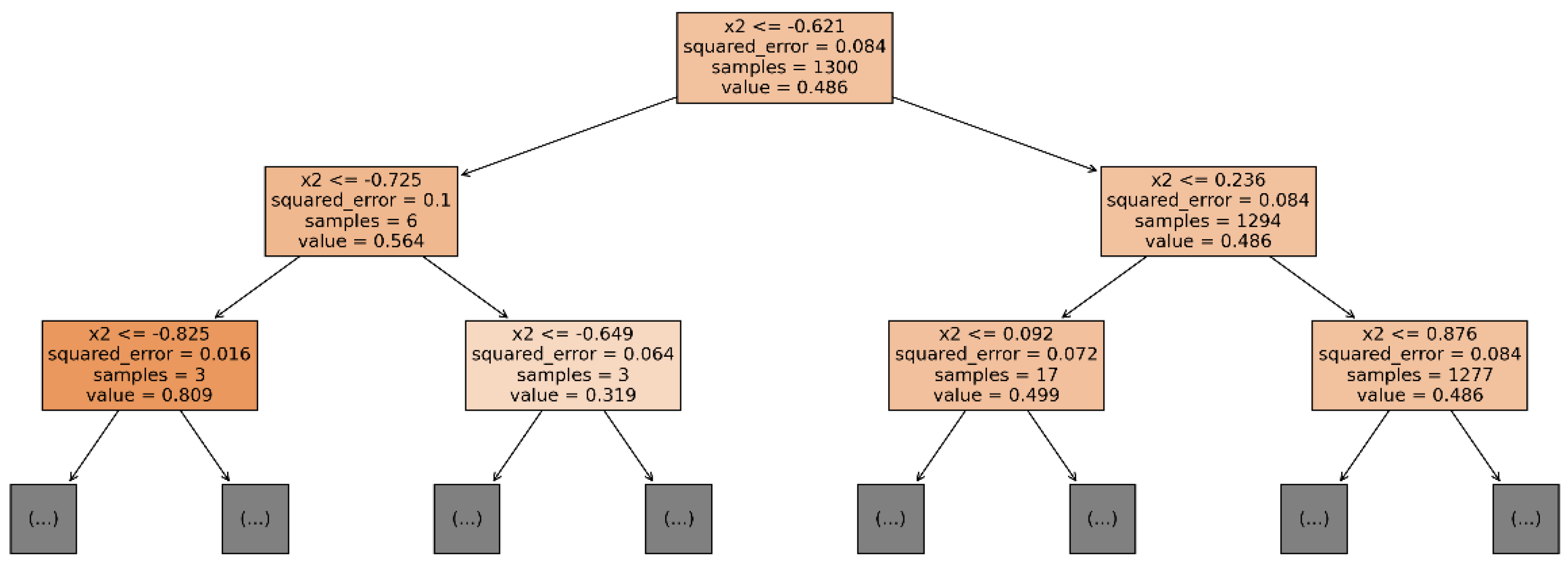
6. Anomalous Behavior Detection Using Isolation Forests
| Algorithm 3: Detect anomalous behavior |
 |
7. Evaluation
7.1. Experimental Setup
- Skip: some required event (no more than 3) is skipped during execution;
- Insertion: some random activity is added during execution (no more than 3);
- Rework: during execution, some events are repeated (no more than 3);
- Advance: during execution, some events occur earlier (no more than 2);
- Delay: during execution, some events are delayed (no more than 2);
- Attributes: during execution, the attributes of some events were incorrectly set (more than 3).
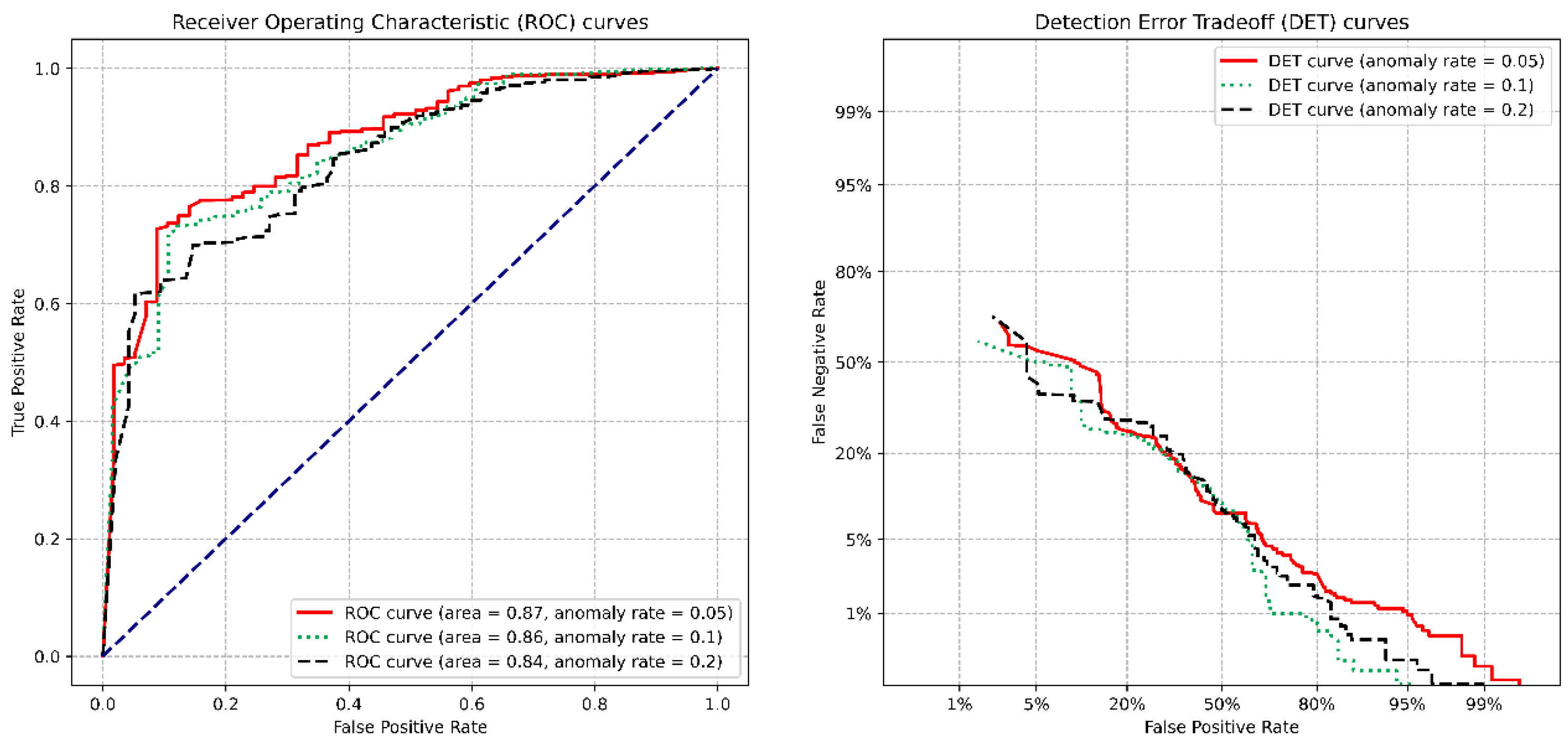
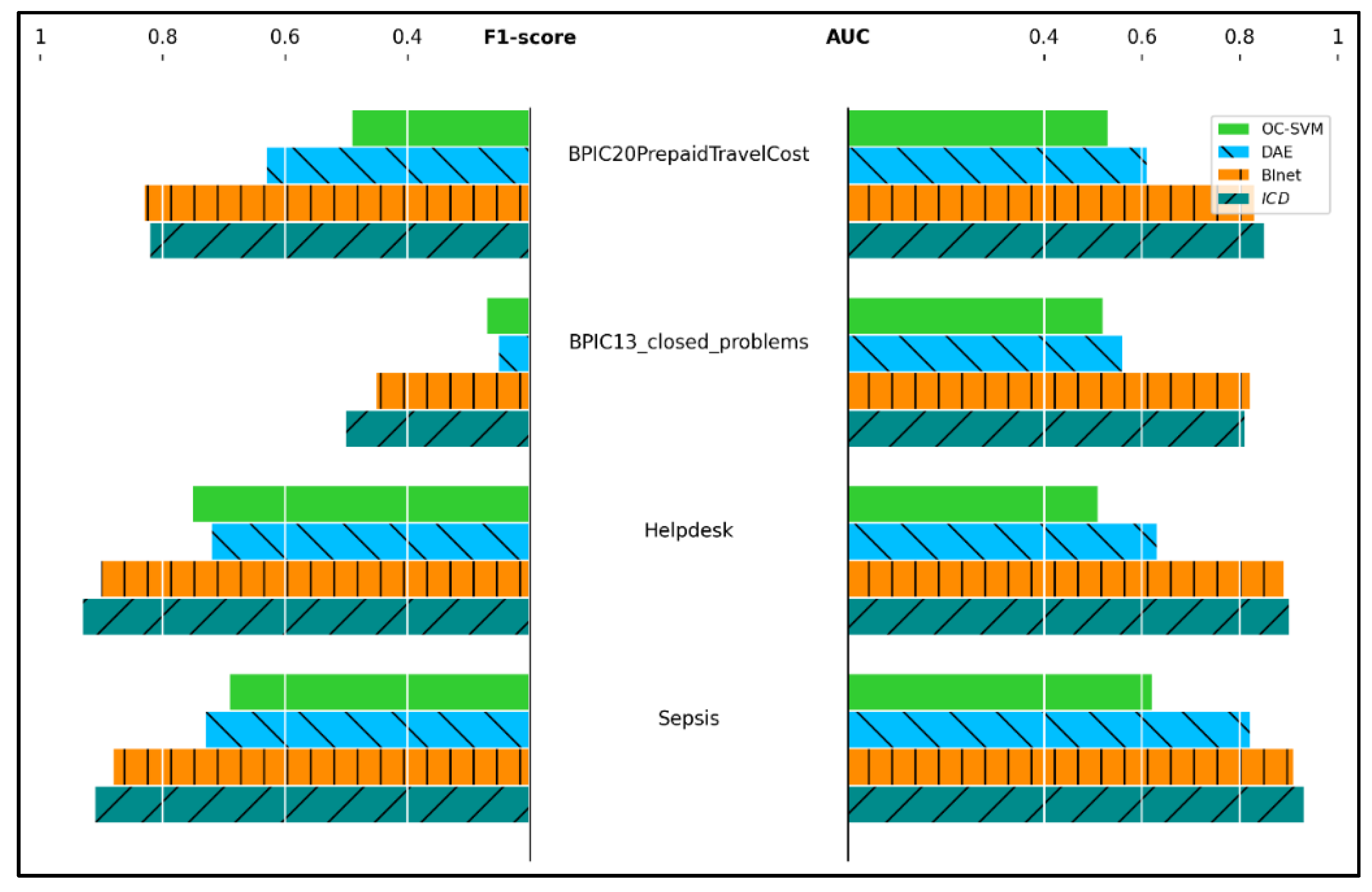
7.2. Experimental Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nolle, T.; Luettgen, S.; Seeliger, A.; Mühlhäuser, M. BINet: Multi-perspective business process anomaly classification. Inf. Syst. 2022, 103, 101458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burattin, A.; Josep, C. A Framework for online conformance checking. In Business Process Management Workshops. In Business Process Management Workshops; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 308, pp. 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, M.M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Ng, R.T.; Sander, J. LOF: Identifying density-based local outliers. In Proceedings of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data—SIGMOD ‘00, Dallas, TX, USA, 15–18 May 2000; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christy, A.; Gandhi, G.M.; Vaithyasubramanian, S. Cluster Based Outlier Detection Algorithm for Healthcare Data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 50, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillutla, M.R.; Raval, N.; Bansal, P.; Srinathan, K.; Jawahar, C.V. LSH based outlier detection and its application in distributed setting. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management—CIKM ’11, Glasgow, UK, 24–28 October 2011; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 2289–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannhardt, F.; de Leoni, M.; Reijers, H.A.; van der Aalst, W.M.P. Balanced multi-perspective checking of process conformance. Computing 2016, 98, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.F.; van Zelst, S.J.; van der Aalst, W.M.P. Repairing Outlier Behaviour in Event Logs using Contextual Behaviour. Enterp. Model. Inf. Syst. Archit. (EMISAJ) 2019, 14, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolle, T.; Luettgen, S.; Seeliger, A.; Mühlhäuser, M. Analyzing business process anomalies using autoencoders. Mach. Learn. 2018, 107, 1875–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, F.; Wainer, J. Algorithms for anomaly detection of traces in logs of process aware information systems. Inf. Syst. 2013, 38, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genga, L.; Alizadeh, M.; Potena, D.; Diamantini, C.; Zannone, N. Discovering anomalous frequent patterns from partially ordered event logs. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2018, 51, 257–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zelst, S.J.; Bolt, A.; Hassani, M.; van Dongen, B.F.; van der Aalst, W.M.P. Online conformance checking: Relating event streams to process models using prefix-alignments. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2019, 8, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghionna, L.; Greco, G.; Guzzo, A.; Pontieri, L. Outlier detection techniques for process mining applications. In Foundations of Intelligent Systems; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, R.V.; Tavares, G.; Ceravolo, P.; Barbon, S. On the use of online clustering for anomaly detection in trace streams. In Proceedings of the XVII Brazilian Symposium on Information Systems, Uberlândia, Brazil, 7–10 June 2021; ACM: Uberlândia, Brazil, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Yilmaz, Y. Online Anomaly Detection in Multivariate Settings. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 29th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–16 October 2019; IEEE: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxhammar, R.; Falkman, G. Online Learning and Sequential Anomaly Detection in Trajectories. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhmer, K.; Rinderle-Ma, S. Multi Instance Anomaly Detection in Business Process Executions. In Business Process Management; Carmona, J., Engels, G., Kumar, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leoni, M.; Felli, P.; Montali, M. "Integrating BPMN and DMN: Modeling and Analysis. J. Data Semant. 2021, 10, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.M.; da Costa, V.G.T.; Martins, V.E.; Ceravolo, P.; Barbon, S. Anomaly Detection in Business Process based on Data Stream Mining. In Proceedings of the XIV Brazilian Symposium on Information Systems—SBSI’18, Caxias do Sul, Brazil, 4–8 June 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: Caxias do Sul, Brazil, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, M.; Golpayegani, S.A.H. Anomaly detection in business processes logs using social network analysis. J. Comput. Virol. Hack. Tech. 2022, 18, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Aalst, W.M.P. Process Mining: Data Science in Action, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, N.N.; Yongsiriwit, K.; Gaaloul, W.; Mendling, J. Mining Event Logs to Assist the Development of Executable Process Variants. In Advanced Information Systems Engineering; Springer: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2014; Volume 8484, pp. 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyvyanyy, A.; Smirnov, S.; Weske, M. Business process model abstraction. In Handbook on Business Process Management 1; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 01 January 2014; pp. 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, X. An Optimized Method of Business Process Mining Based on the Behavior Profile of Petri Nets. Inf. Technol. J. 2013, 13, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.-H. “Isolation Forest. In Proceedings of the 2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining; IEEE: Pisa, Italy, 19 December, 2008; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Ting, K.M.; Zhou, Z.-H. "Isolation-Based Anomaly Detection. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data 2012, 6, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemen, V.; Van Zelst, S.; Van der Aalst, W.; Van Dongen, B.; Van de Pol, J. Aligning observed and modelled behaviour by maximizing synchronous moves and using milestones. Information Systems 2022, 103, 101456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S. Python Machine Learning; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mannhardt, F.; Blinde, D. Analyzing the Trajectories of Patients with Sepsis using Process Mining. RADAR 2017, 1859, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wressnegger, C.; Schwenk, G.; Arp, D.; Rieck, K. A close look on n-grams in intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Berlin, Germany, 4 November 2013; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 4 November, 2013; pp. 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Event Id | Case Id | Activity | User | Resource | Timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 671 | 476 | a | client | certifications | Monday |
| 672 | 476 | b | staff | archive | Monday |
| 673 | 477 | h | manager | \ | Thursday |
| 674 | 476 | c | staff | loggers | Tuesday |
| 675 | 477 | e | staff | check | Wednesday |
| 676 | 478 | a | client | certifications | Monday |
| 677 | 476 | e | staff | check | Wednesday |
| 678 | 476 | f | staff | quoted price | Thursday |
| 679 | 478 | b | staff | archive | Tuesday |
| 680 | 476 | g | manager | staff | Friday |
| 681 | 477 | d | staff | evaluation | Tuesday |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Judgment | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal | Normal | ||
| Actual | Abnormal | TA | FN |
| Normal | FA | TN | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, N.; Fang, X.; Lu, K. Anomalous Behavior Detection Based on the Isolation Forest Model with Multiple Perspective Business Processes. Electronics 2022, 11, 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213640
Fang N, Fang X, Lu K. Anomalous Behavior Detection Based on the Isolation Forest Model with Multiple Perspective Business Processes. Electronics. 2022; 11(21):3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213640
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Na, Xianwen Fang, and Ke Lu. 2022. "Anomalous Behavior Detection Based on the Isolation Forest Model with Multiple Perspective Business Processes" Electronics 11, no. 21: 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213640
APA StyleFang, N., Fang, X., & Lu, K. (2022). Anomalous Behavior Detection Based on the Isolation Forest Model with Multiple Perspective Business Processes. Electronics, 11(21), 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213640






