A 0.00426 mm2 77.6-dB Dynamic Range VCO-Based CTDSM for Multi-Channel Neural Recording
Abstract
1. Introduction
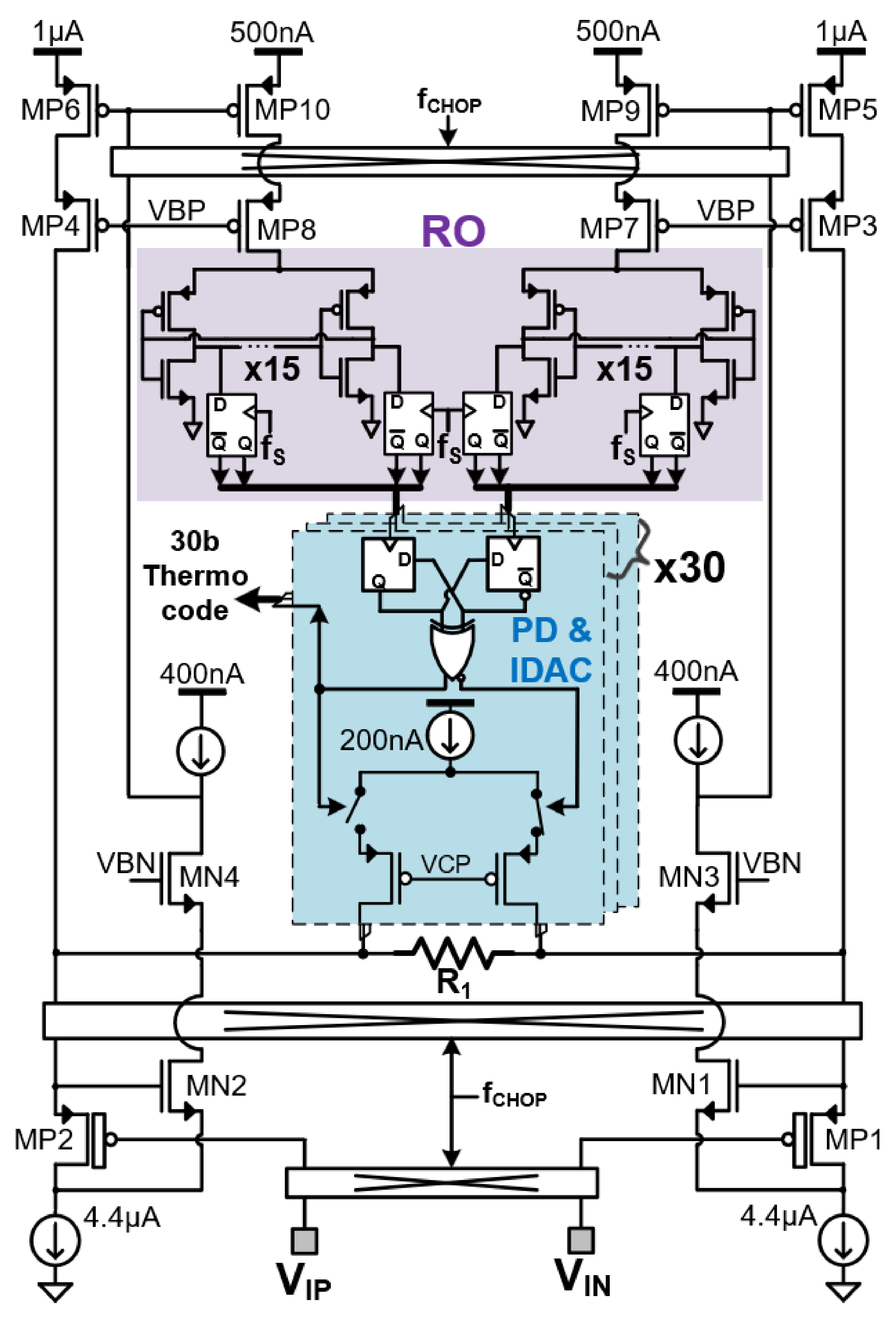
2. Modulator Architecture
3. Schematic Design
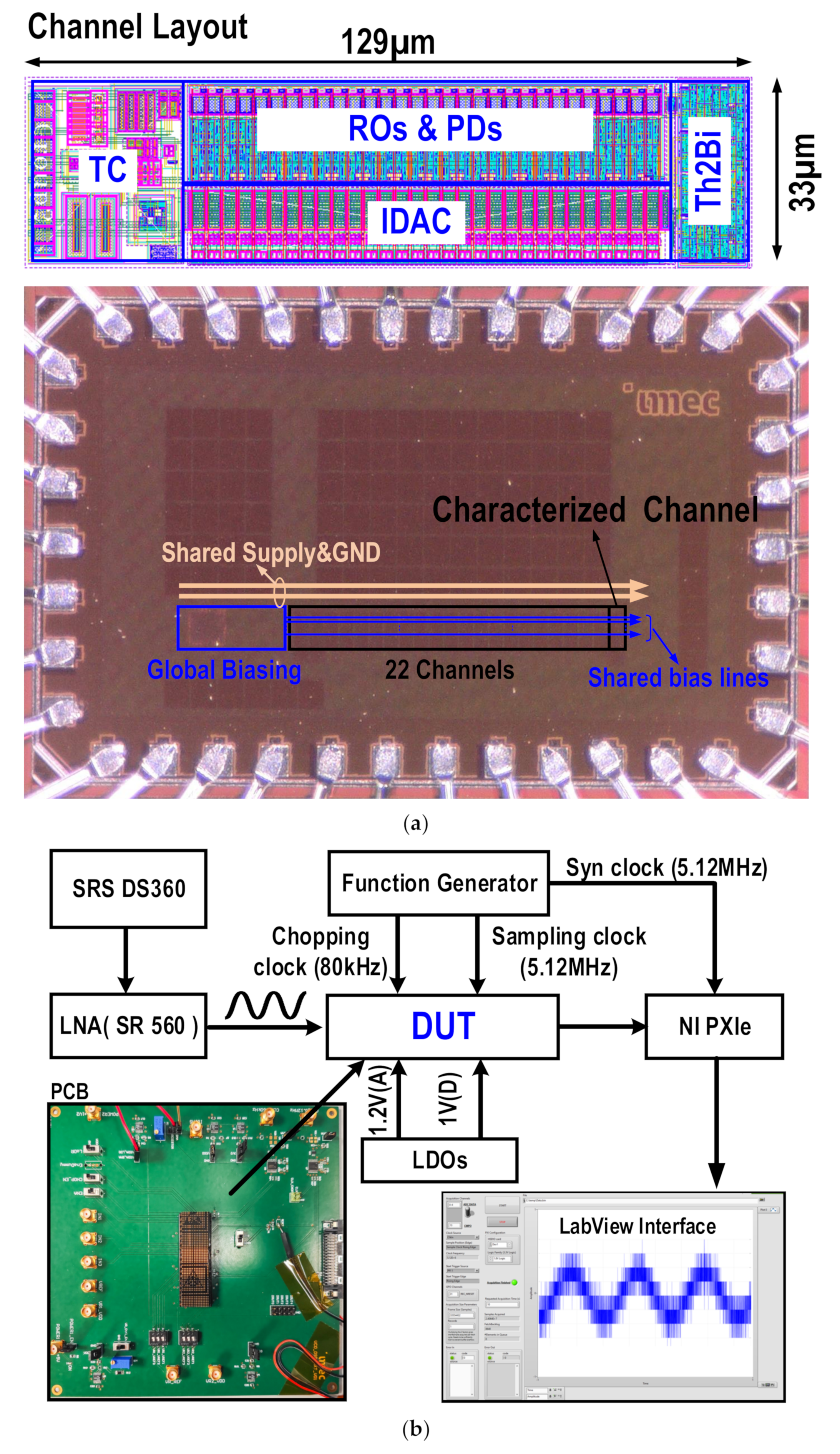
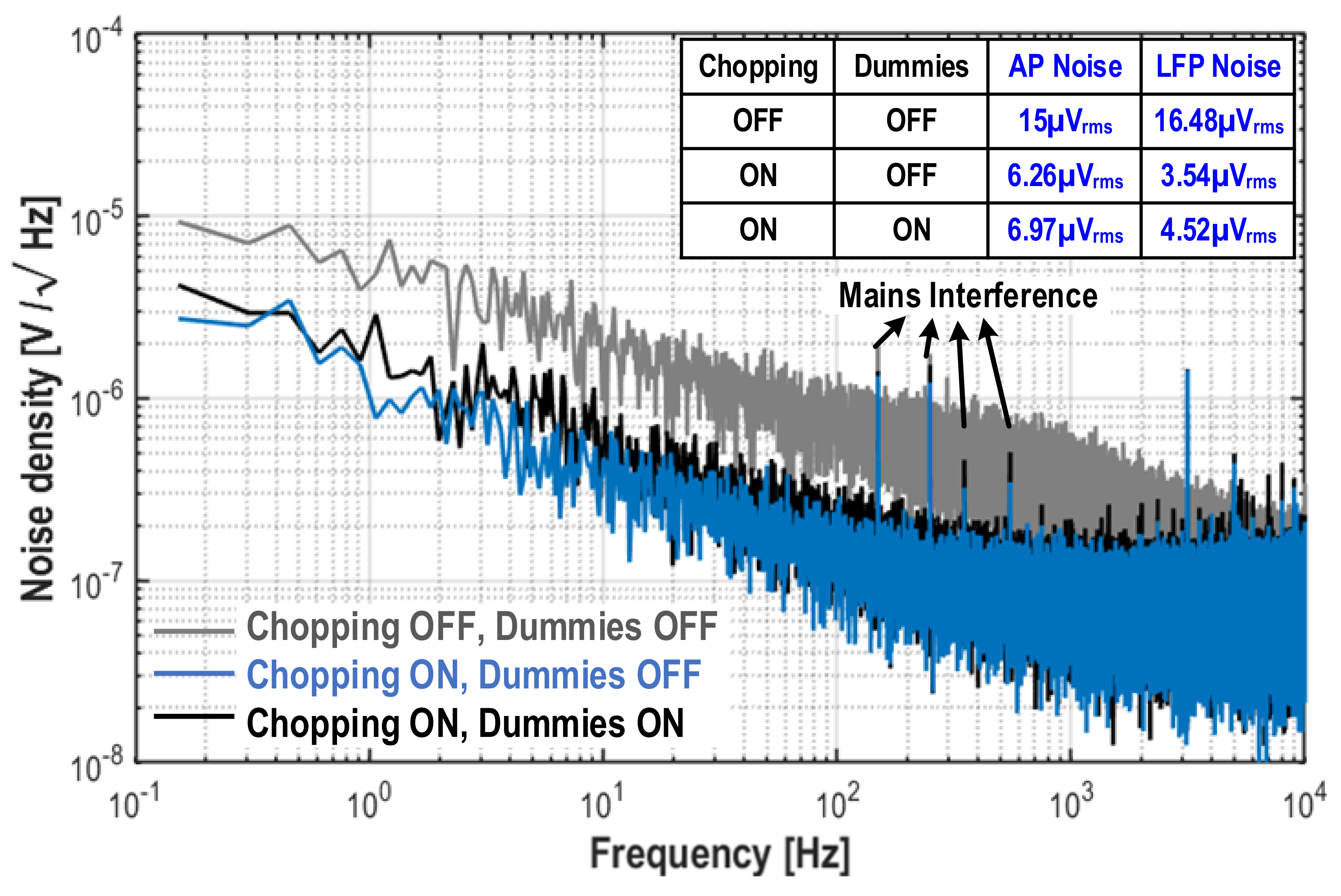
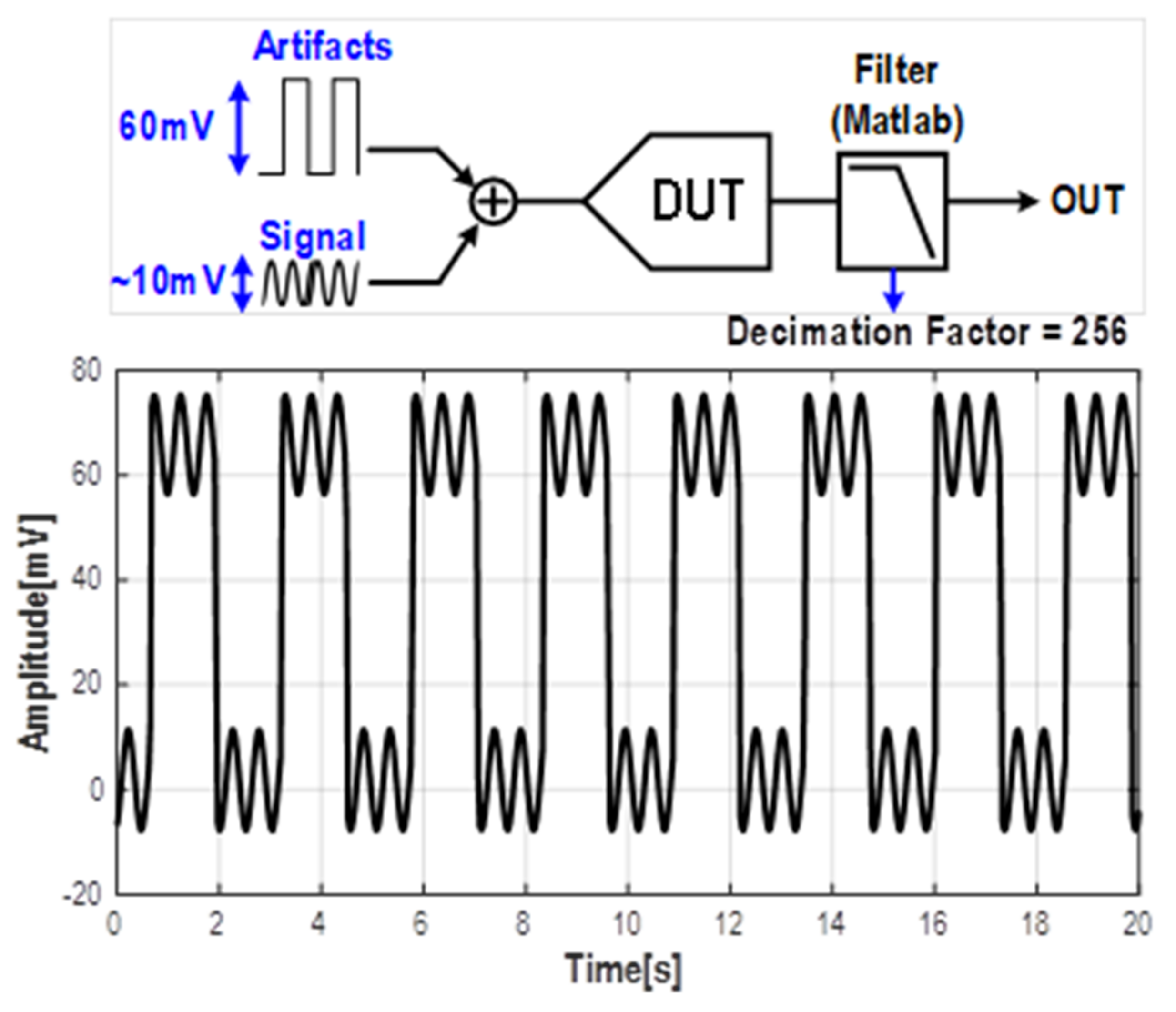
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jun, J.J.; Steinmetz, N.A.; Siegle, J.H.; Denman, D.J.; Bauza, M.; Barbarits, B.; Lee, A.K.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Andrei, A.; Aydin, C.; et al. Fully integrated silicon probes for high-density recording of neural activity. Nature 2017, 551, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, N.A.; Aydin, C.; Lebedeva, A.; Okun, M.; Pachitariu, M.; Bauza, M.; Beau, M.; Bhagat, J.; Böhm, C.; Broux, M.; et al. Neuropixels 2.0: A miniaturized high-density probe for stable, long-term brain recordings. Science 2021, 372, 6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, C.; Pachitariu, M.; Steinmetz, N.; Reddy, C.B.; Carandini, M.; Harris, K.D. Spontaneous behaviors drive multidimensional brainwide activity. Science 2019, 364, 6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, N.A.; Zatka-Haas, P.; Carandini, M.; Harris, K.D. Distributed coding of choice, action and engagement across the mouse brain. Nature 2019, 576, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, R.J.; Hermansen, E.; Pachitariu, M.; Burak, Y.; Baas, N.A.; Dunn, B.A.; Moser, M.-B.; Moser, E.I. Toroidal topology of population activity in grid cells. Nature 2022, 602, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urai, A.E.; Doiron, B.; Leifer, A.M.; Churchland, A.K. Large-scale neural recordings call for new insights to link brain and behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Cho, J.; Na, K.; Yoon, E. Modular 128-Channel Δ − ΔΣ analog front-end architecture using spectrum equalization scheme for 1024-Channel 3-D neural recording microsystems. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2018, 53, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.M.; Putzeys, J.; Raducanu, B.C.; Ballini, M.; Wang, S.; Andrei, A.; Rochus, V.; Vandebriel, R.; Severi, S.; Van Hoof, C.; et al. A Neural Probe With Up to 966 Electrodes and Up to 384 Configurable Channels in 0.13 µm SOI CMOS. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2017, 11, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Garakoui, S.K.; Chun, H.; Salinas, D.G.; Sijbers, W.; Putzeys, J.; Martens, E.; Craninckx, J.; Van Helleputte, N.; Lopez, C.M. A Compact Quad-Shank CMOS Neural Probe With 5,120 Addressable Recording Sites and 384 Fully Differential Parallel Channels. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 60, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.-Y.; Pinto, S.; Chung, S.; Merolla, P.; Koh, T.-W.; Seo, D. A 1024-channel simultaneous recording neural SoC with stimulation and real-time spike detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 13–19 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ballini, M.; Sawigun, C.; Hsu, W.-Y.; Weijers, J.-W.; Putzeys, J.; Lopez, C.M. A 128-Channel AC-Coupled 1st-order Δ-Δ∑ IC for Neural Signal Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits (VLSI Technology and Circuits), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 June 2022; pp. 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luan, S.; Williams, I.; Rapeaux, A.; Constandinou, T.G. A 64-Channel Versatile Neural Recording SoC With Activity-Dependent Data Throughput. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2017, 11, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, M.; Muller, J.; Livi, P.; Chen, Y.; Frey, U.; Stettler, A.; Shadmani, A.; Viswam, V.; Lloyd Jones, I.; Jackel, D.; et al. A 1024-Channel CMOS Microelectrode Array with 26,400 Electrodes for Recording and Stimulation of Electrogenic Cells In Vitro. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2014, 49, 2705–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragas, J.; Viswam, V.; Shadmani, A.; Chen, Y.; Bounik, R.; Stettler, A.; Radivojevic, M.; Geissler, S.; Obien, M.E.J.; Muller, J.; et al. In Vitro Multi-Functional Microelectrode Array Featuring 59 760 Electrodes, 2048 Electrophysiology Channels, Stimulation, Impedance Measurement, and Neurotransmitter Detection Channels. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2017, 52, 1576–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dorigo, D.; Moranz, C.; Graf, H.; Marx, M.; Wendler, D.; Shui, B.; Herbawi, A.S.; Kuhl, M.; Ruther, P.; Paul, O.; et al. Fully Immersible Subcortical Neural Probes with Modular Architecture and a Delta-Sigma ADC Integrated Under Each Electrode for Parallel Readout of 144 Recording Sites. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2018, 53, 3111–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jeon, T.; Jang, M.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Huh, Y.; Chae, Y. A 6.5-μW 10-kHz BW 80.4-dB SNDR Gₘ-C-Based CT ΔΣ Modulator with a Feedback-Assisted Gₘ Linearization for Artifact-Tolerant Neural Recording. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2020, 60, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, D.; De Dorigo, D.; Amayreh, M.; Bleitner, A.; Marx, M.; Manoli, Y. A 0.0046-mm2 Two-Step Incremental Delta—Sigma Analog-to-Digital Converter Neuronal Recording Front End With 120-mVpp Offset Compensation. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ballini, M.; Yang, X.; Sawigun, C.; Weijers, J.-W.; Biswas, D.; Van Helleputte, N.; Lopez, C.M. A Compact Chopper Stabilized Δ-ΔΣ Neural Readout IC with Input Impedance Boosting. IEEE Open J. Solid State Circuits Soc. 2021, 1, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ballini, M.; Wang, S.; Miccoli, B.; Van Hoof, C.; Gielen, G.; Craninckx, J.; Van Helleputte, N.; Lopez, C.M. A Compact, Low-Power Analog Front-end With Event-Driven Input Biasing for High-Density Neural Recording in 22-nm FDSOI. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs. 2022, 69, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, S.; Schreier, R.; Temes, G.C. Understanding Delta-Sigma Data Converter; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Hokhikyan, V.; Chandrakumar, H.; Karkare, V.; Markovic, D. A ±50mV linear-input-range VCO-based neural-recording front-end with digital nonlinearity correction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 31 January–4 February 2016; pp. 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Bang, J.-S.; Jung, Y.; Choi, I.; Je, M. A High DR, DC-Coupled, Time-Based Neural-Recording IC with Degeneration R-DAC for Bidirectional Neural Interface. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2019, 54, 2658–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, T.; Yan, P.; Qi, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. A Hybrid 1st/2nd-Order VCO-Based CTDSM with Rail-to-Rail Artifact Tolerance for Bidirectional Neural Interface. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II. Exp. Briefs. 2022, 69, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Tang, X.; Shen, L.; Lu, N.; Pan, D.Z.; Sun, N. A 0.025-mm2 0.8-V 78.5-dB SNDR VCO-Based Sensor Readout Circuit in a Hybrid PLL-ΔΣ M Structure. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2020, 55, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Mercier, P.P. A 178.9-dB FoM 128-dB SFDR VCO-Based AFE for ExG Readouts with a Calibration-Free Differential Pulse Code Modulation Technique. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs. 2022, 69, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochet, C.; Hall, D.A. A 4.4µW 2.5 kHz-BW 92.1dB-SNDR 3rd-Order VCO-Based ADC with Pseudo Virtual Ground Feedforward Linearization. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2021, 56, 3236–3246. [Google Scholar]




| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| TC transconductance (gm) | 30.5 µS |
| IDAC LSB current (ILSB) | 200 nA |
| RO gain () | 610 GHz/A |
| Quantization levels () | 30 |
| Quantizer gain () | 30/2 π = 4.77 |
| Feed-in coefficient () | 22.9 |
| Feedback coefficient () | 0.15 |
| Sampling rate () | 5.12 MHz (256 × OSR) |
| Parameters | This Work | [18] | [17] | [16] | [24] †† | [25] †† | [26] †† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 55 nm | 55 nm | 180 nm | 110 nm | 40 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm |
| Supply voltage (V) | 1.2 (Analog)/1.0 (Digital) | 1.2 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.8 (Analog)/0.6 (Digital) | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Channel topology | 1st-order VCO-based CTDSM | 2nd-order ∆-∆Σ CTDSM | Two-step CT Incremental ∆Σ | 2nd-order CTDSM (VCO as 2nd integrator) | 2nd-order VCO-PLL hybrid | 1st-order VCO-based | 3rd-order VCO-based CTDSM |
| Input Impedance (Ω) | 640 M@10 Hz | 663 M@10 Hz | ∞@DC * | ∞@DC *; 13.3 M@10 kHz | 222 k ~ 14.2 M * | 8 M | Unknown * |
| Max. input range (mVpp) | 149 | 148 | 15.2 | 300 | 100/400 | 460 | 1800 |
| THD @1 kHz input | 0.09~0.18%@ 10 mVpp AC ± 68 mV DC | 0.05~0.44%@ 20 mVpp AC ± 70 mV DC | 0.078% @10 mVpp | 0.0095% @285 mVpp | 0.01% @90 mVpp | <0.002% @460 mVpp (90 Hz) | <0.0025% @1.8 Vpp (322 Hz) |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| AP band noise (µVrms) | 6.26 † ~ 6.97 | 5.53 | 4.46 | 9.5 (1 Hz ~10 kHz) † | 3.6 (10 Hz ~ 10 kHz) † | 2.6 (10 ~500 Hz) † | 15.8 (1 Hz ~2.5 kHz) † |
| LFP band noise (µVrms) | 3.54 † ~ 4.52 | 2.88 | 2.51 | ||||
| Power/channel (µW) | 13.75 ** | 48.7 | 14.62 | 6.5 ** | 4.68 ** | 1.68 ** | 4.4 ** |
| Area/channel (mm2) | 0.00426 ** | 0.0077 | 0.00462 | 0.078 ** | 0.025 ** | 0.056 ** | 0.1 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Vilouras, A.; Lopez, C.M. A 0.00426 mm2 77.6-dB Dynamic Range VCO-Based CTDSM for Multi-Channel Neural Recording. Electronics 2022, 11, 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213477
Wang S, Yang X, Wang C, Vilouras A, Lopez CM. A 0.00426 mm2 77.6-dB Dynamic Range VCO-Based CTDSM for Multi-Channel Neural Recording. Electronics. 2022; 11(21):3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213477
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shiwei, Xiaolin Yang, Chaohan Wang, Anastasios Vilouras, and Carolina Mora Lopez. 2022. "A 0.00426 mm2 77.6-dB Dynamic Range VCO-Based CTDSM for Multi-Channel Neural Recording" Electronics 11, no. 21: 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213477
APA StyleWang, S., Yang, X., Wang, C., Vilouras, A., & Lopez, C. M. (2022). A 0.00426 mm2 77.6-dB Dynamic Range VCO-Based CTDSM for Multi-Channel Neural Recording. Electronics, 11(21), 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213477







