Critical Review of Basic Methods on DoA Estimation of EM Waves Impinging a Spherical Antenna Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Five DoA estimation techniques are presented and investigated in this study. MUSIC, plane-wave decomposition (PWD), weighted subspace fitting (WSF), and both deterministic (D) and stochastic (S) ML techniques were applied in the analysis of EM waves using SAA processing for the first time in this study. WSF is the large sample approximation of SML.
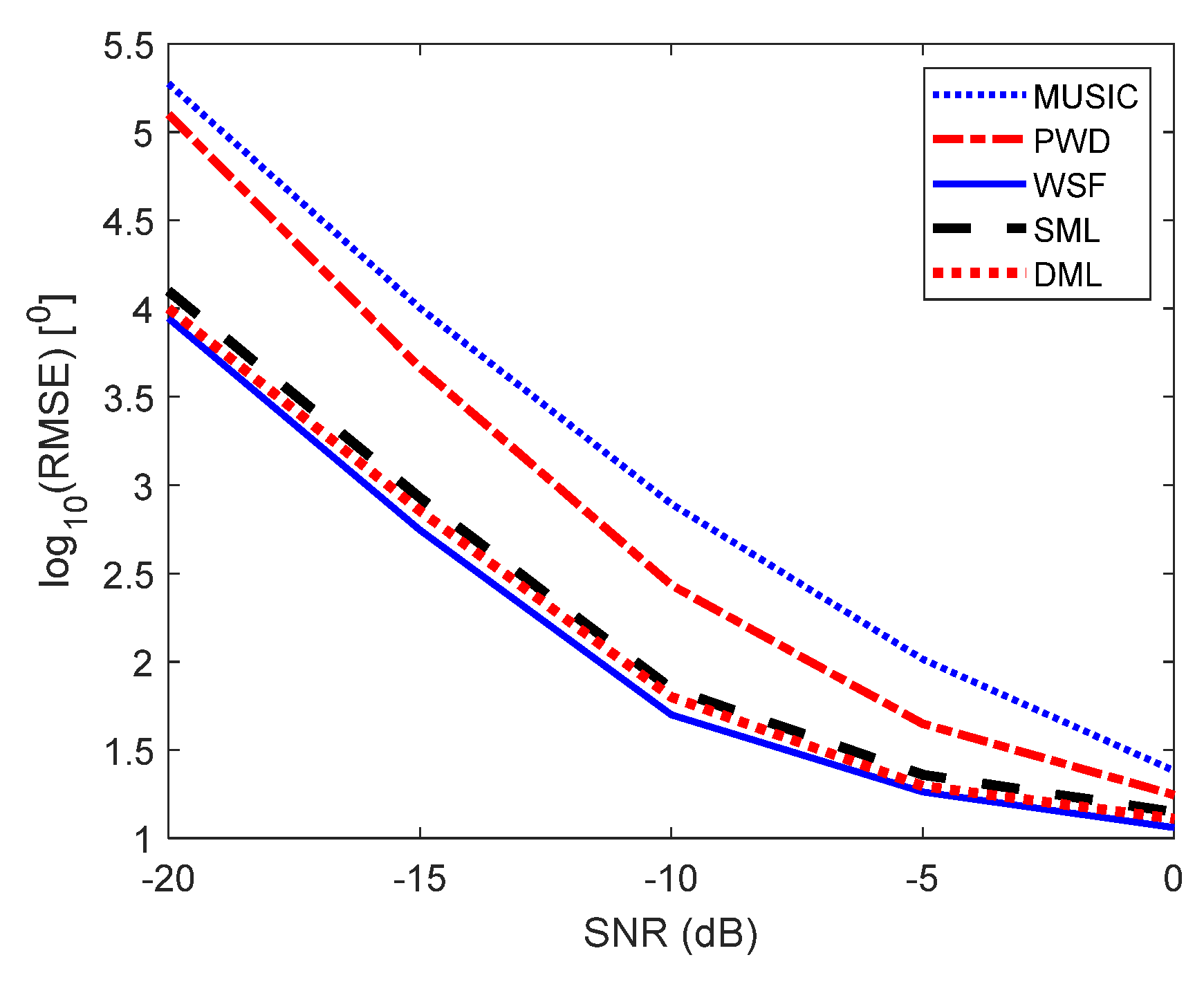
- We adopted ML techniques in the spatial signal analysis with SAA and confirmed their suitability in DoA estimation using an SAA. It is numerically demonstrated how ML techniques outweighed MUSIC and beamforming methods and how WSF produces the best DoA estimation among the ML techniques.
- The results obtained from ML techniques are compared to beamforming and MUSIC methods throughout the simulation and analysis section. The ML-based DoA estimation is more appropriate, less biased, and more robust against noise than beamforming and MUSIC techniques. In addition, the WSF technique exhibits lower computational complexity than DML and SML.
- We explain how DoA estimation performance with a rigid sphere is expressed as a function of frequency. In addition, the radius of the sphere affects the estimation accuracy at a particular frequency. For instance, for a given SAA with a radius of 8.4 cm, the most accurate performance was achieved at 16 GHz. If similar performance were required, for example, at about 8 GHz, then a larger radius of SAA would be required.
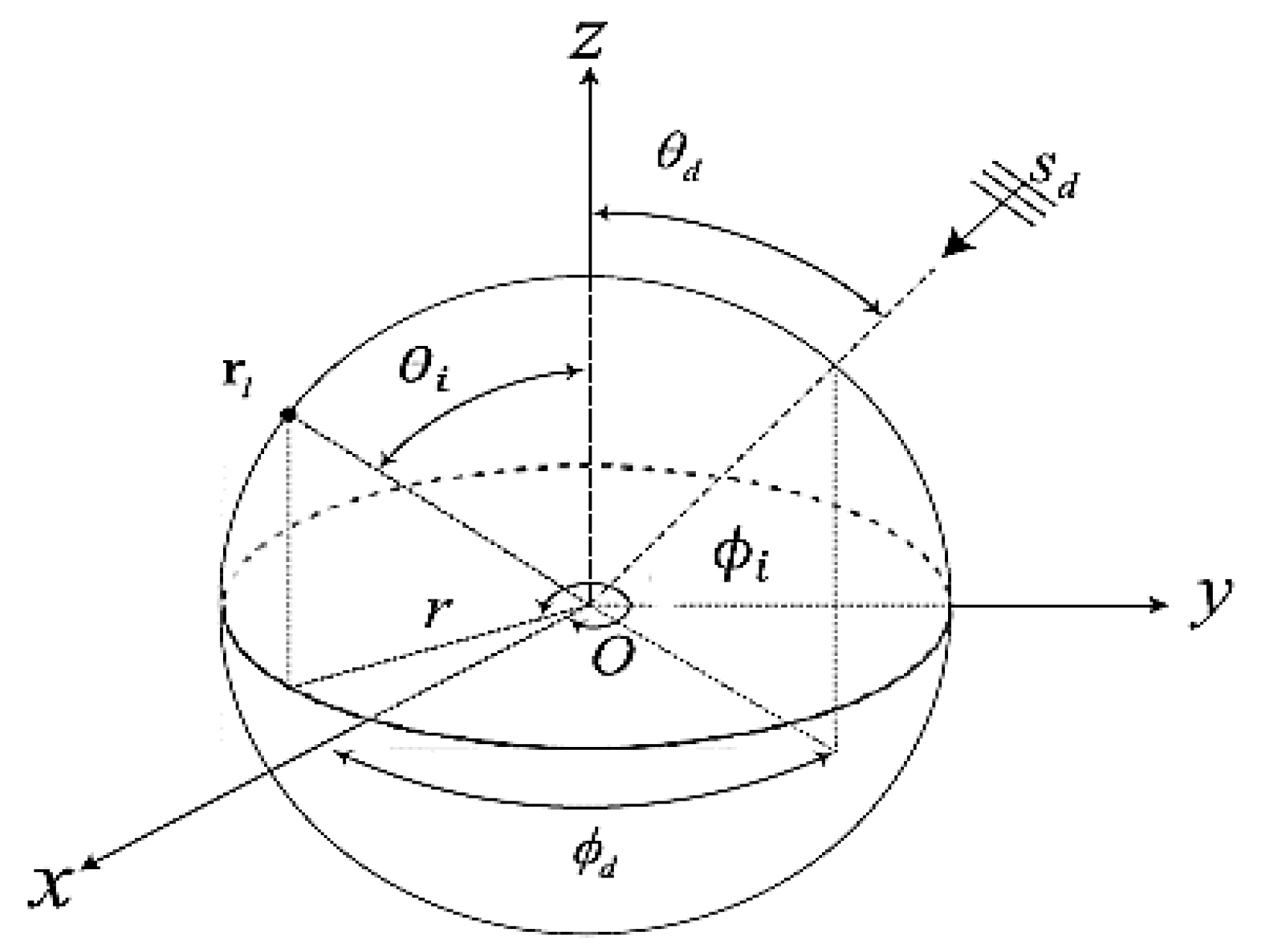
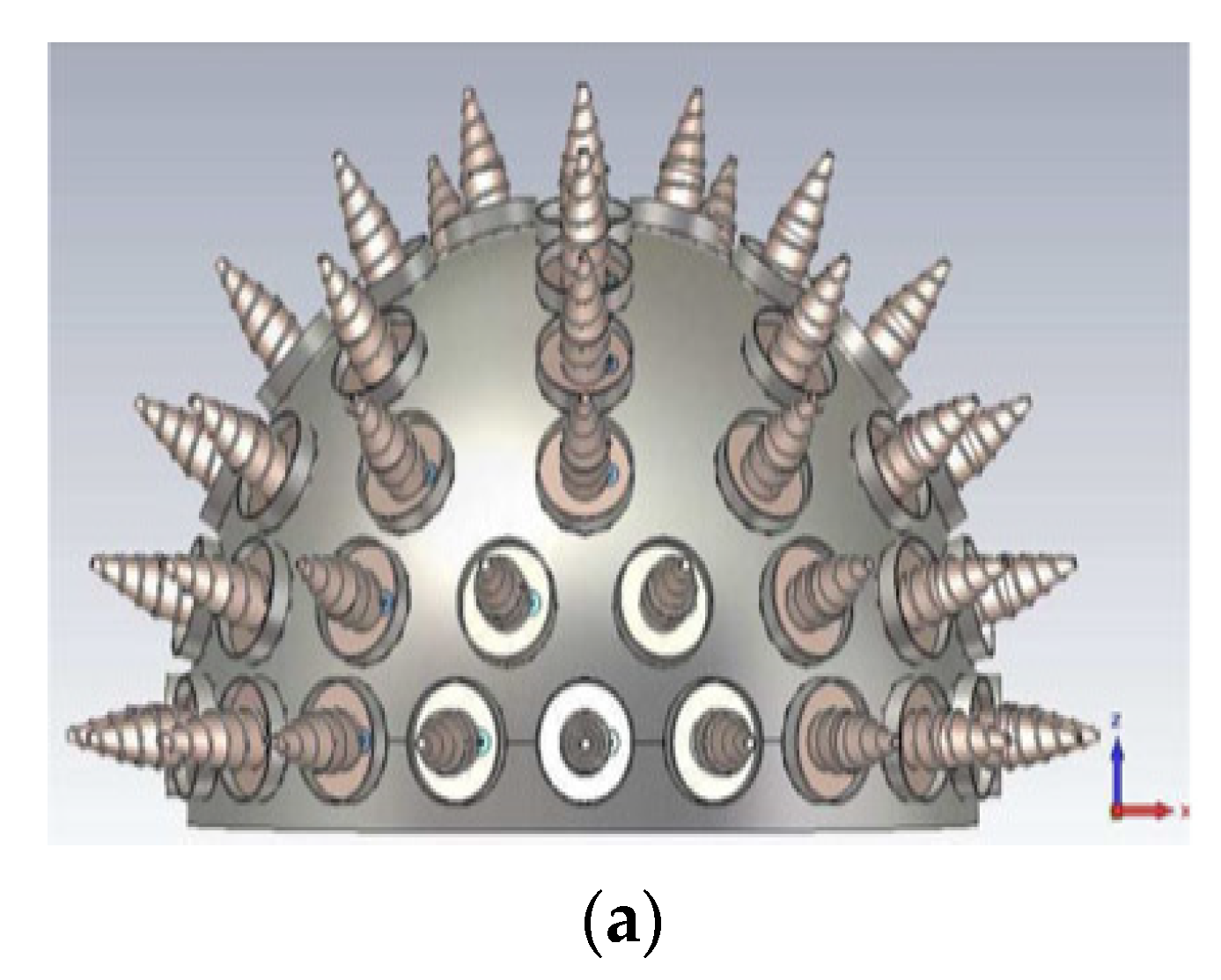
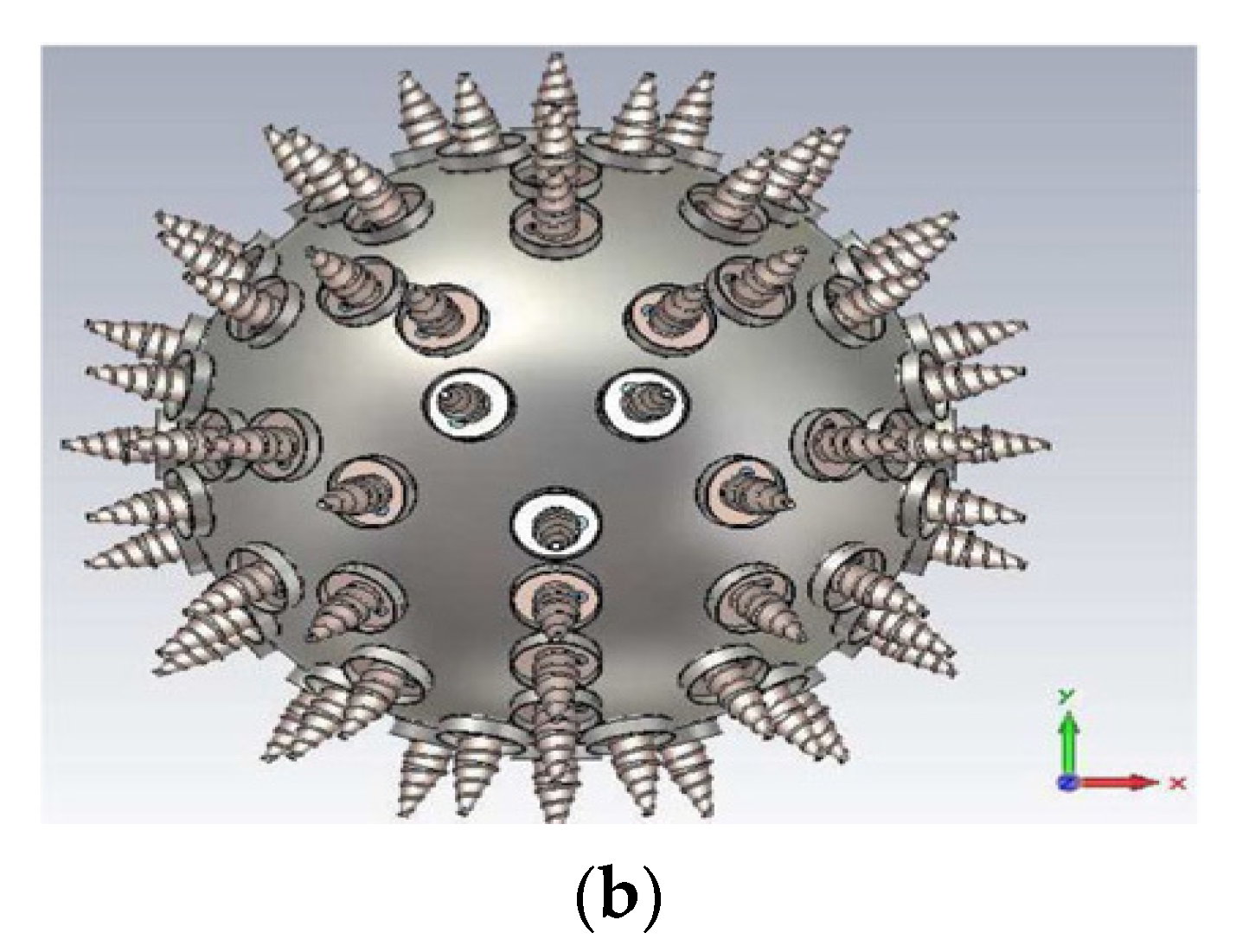
2. General Configuration of SAA
3. Mathematical Formulations
3.1. EM Waves in Free Space
3.2. Analysis of the Space Domain
3.3. Spherical Harmonic Decomposition
3.4. Spherical Antenna Array (SAA) with Spherical Harmonic Decomposition (SHD)
4. DoA Estimation
4.1. Smoothing in Time Domain
4.2. Steering Vector
4.3. Beamforming
4.4. MUSIC
4.5. ML Techniques
4.5.1. Stochastic ML Technique
4.5.2. Deterministic ML Technique
4.6. Weighted Subspace Fitting Technique
4.7. Estimation Accuracy: Cramér–Rao Lower Bound
4.8. Signal Detection
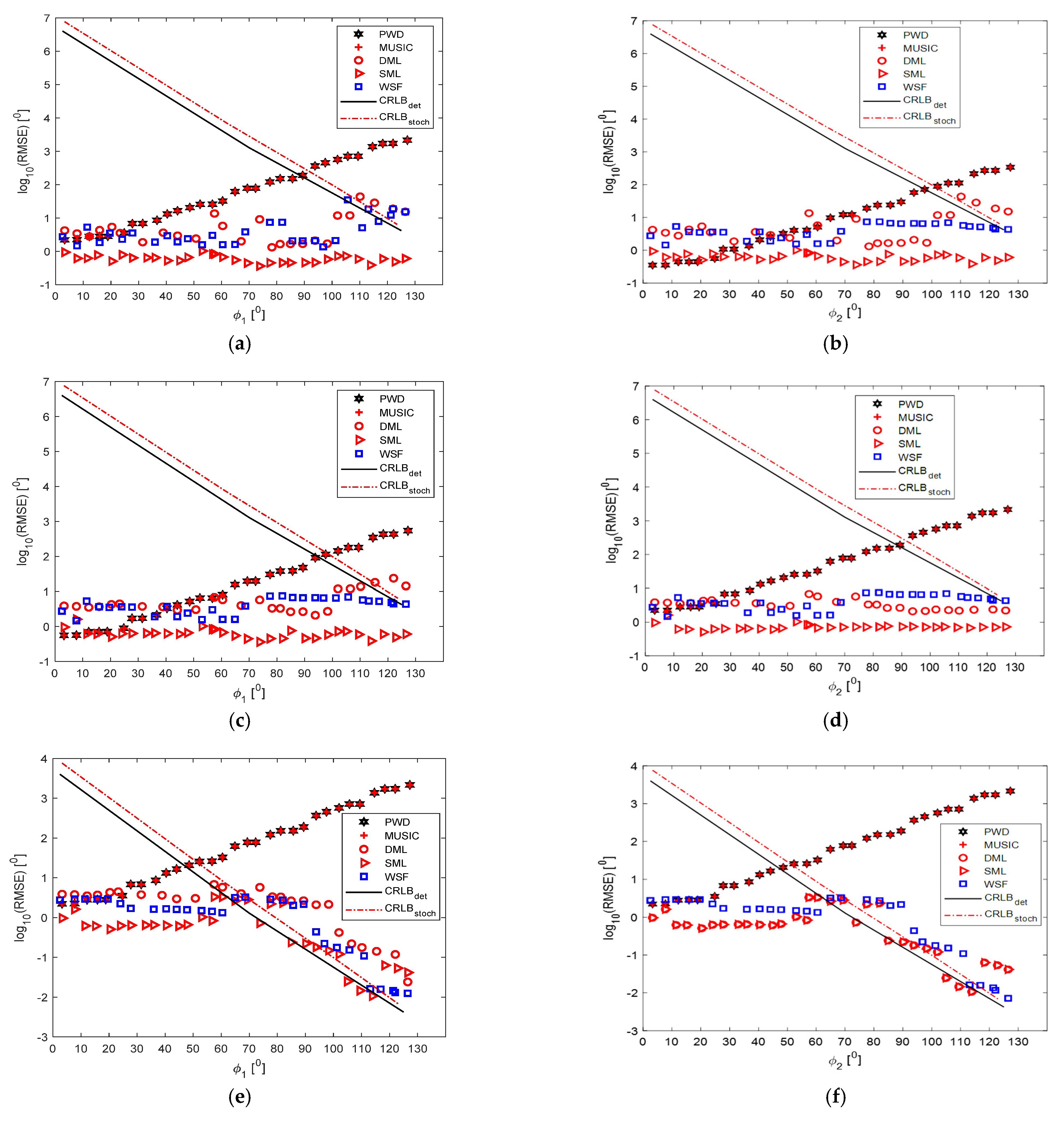
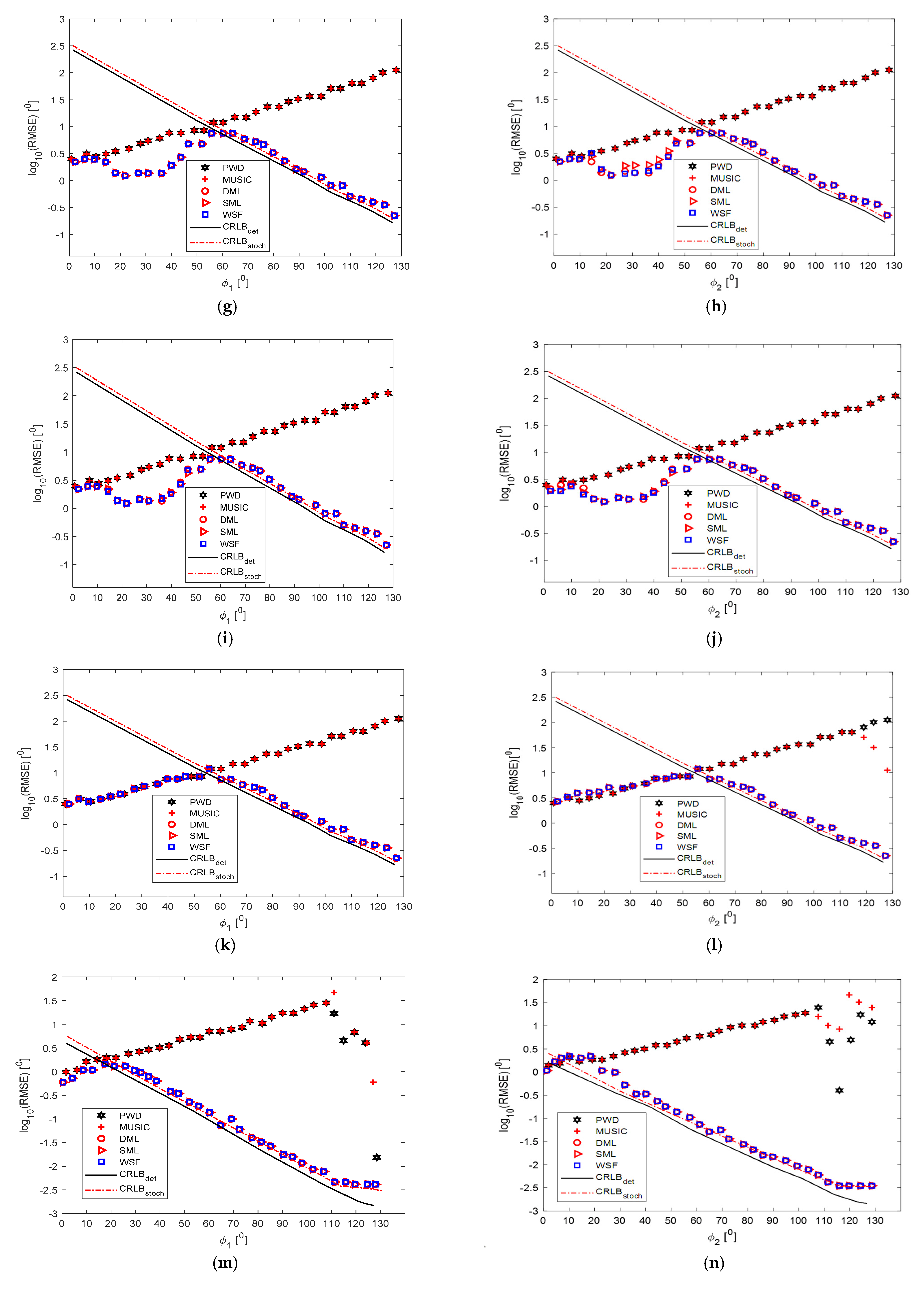
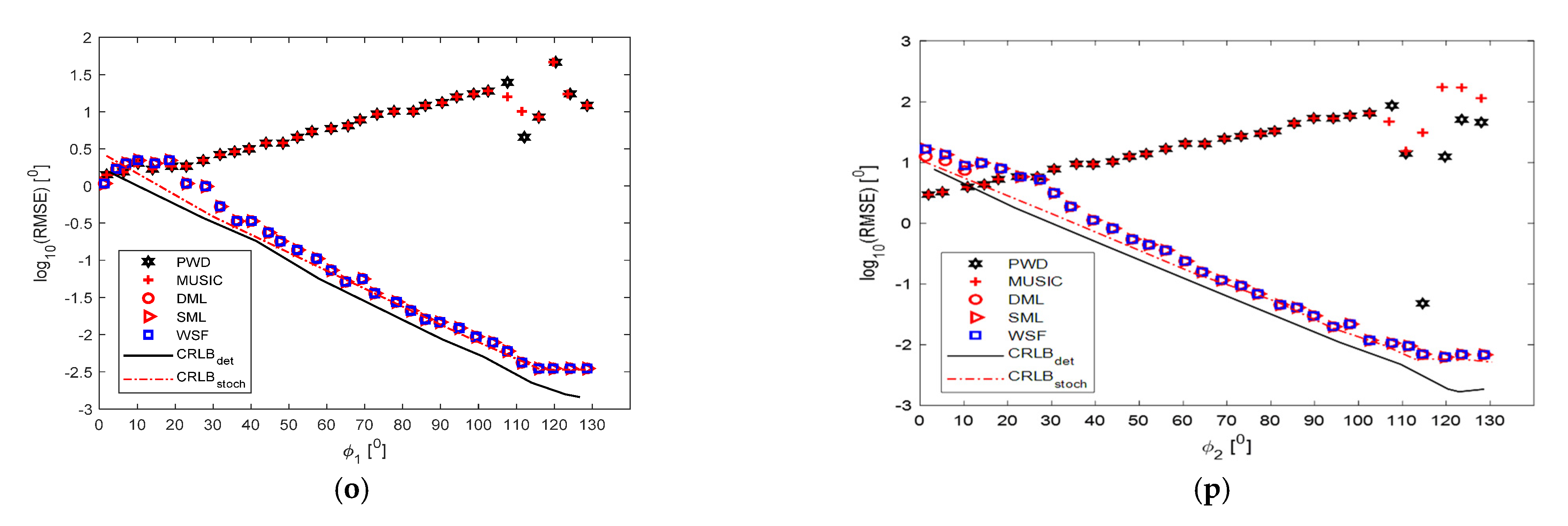
5. Numerical Experiments, Results, and Discussion
5.1. Using Nonlinear Optimization Techniques for Global Minimum/Maximum Search
5.2. Single Wideband Signal Scenario
5.3. Two Wideband Signals
5.4. Two Signals in One Frequency
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlin, M.; Rocca, P.; Oliveri, G.; Viani, F.; Massa, A. Directions-of-Arrival Estimation Through Bayesian Compressive Sensing Strategies. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralon, M.G.; Del Galdo, G.; Landmann, M.; Hein, M.A.; Thoma, R.S. Suitability of Compact Antenna Arrays for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 7244–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, C.; Kumar, S.; Srinivasan, V. Active spherical phased array design for satellite payload data transmission. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2015, 63, 4783–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshikenari, M.; Virdee, B.S.; Azpilicueta, L.; Naser-Moghadasi, M.; Akinsolu, M.O.; See, C.H.; Liu, B.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Falcone, F.; Huynen, I.; et al. A comprehensive survey of metamaterial transmission-line based antennas: Design, challenges, and applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 144778–144808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshikenari, M.; Babaeian, F.; Virdee, B.S.; Aïssa, S.; Azpilicueta, L.; See, C.H.; Althuwayb, A.A.; Huynen, I.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Falcone, F.; et al. A comprehensive survey on “various decoupling mechanisms with focus on metamaterial and metasurface principles applicable to SAR and MIMO antenna systems”. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 192965–193004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famoriji, O.J.; Shongwe, T. Source Localization of EM Waves in the Near-Field of Spherical Antenna Array in the Presence of Unknown Mutual Coupling. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famoriji, O.J.; Shongwe, T. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation of Electromagnetic Wave Impinging on Spherical Antenna Array in the Presence of Mutual Coupling Using a Multiple Signal Classification Method. Electronics 2021, 10, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirkolaei, M.M.; Ghalibafan, J. Scannable Leaky-Wave Antenna Based on Ferrite-Blade Waveguide Operated Below the Cutoff Frequency. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, I.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Babaeian, F.; Althuwayb, A.; Virdee, B.S.; Azpilicueta, L.; Khan, S.; Huynen, I.; Falcone, F.J.; Denidni, T.A.; et al. Circular polarized antennas for existing and emerging wireless communication technologies. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 55, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, C.; Kumar, B.P.; Kumar, V.S.; Srinivasan, V.V. Dual Circularly Polarized Spherical Phased-Array Antenna for Spacecraft Application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 61, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervo, S.; Politis, A. Direction of Arrival Estimation of Reflections from Room Impulse Responses Using a Spherical Microphone Array. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, M.; Randazzo, A. A smart antenna system for direction of arrival estimation based on a support vector regression. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swindlehurst, A.; Kailath, T. A performance analysis of subspace based methods in the presence of model errors. I. The MUSIC algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 1578–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Zoltowski, M.D.; Haardt, M.; Mathews, C.P. Closed-form 2-D angle estimation with rectangular arrays in element space or beam space via unitary ESPRIT. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Gershman, B. A generalized ESPRIT approach to direction-of-arrival estimato. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 12, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziskind, I.; Wax, M. Maximum likelihood localization of multiple sources by alternating projection. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1988, 36, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Gershman, A. Maximum-likelihood DOA estimation by data-supported grid search. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1999, 6, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fang, J.; Duan, H.; Li, H. Phased-Array-Based Sub-Nyquist Sampling for Joint Wideband Spectrum Sensing and Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 6110–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, N.N. Fundamentals of Electromagnetics for Electrical and Computer Engineering; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, M. Conventions for the analysis of spherical arrays. IRE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1963, 11, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottersten, B.; Kailath, T. Direction-of-arrival estimation for wide-band signals using the ESPRIT algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kaveh, M. Coherent signal-subspace processing for the detection and estimation of angles of arrival of multiple wide-band sources. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1985, 33, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z. Efficient Method of DOA Estimation for Uncorrelated and Coherent Signals. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaely, B. Spherical array configurations. In Fundamentals of Spherical Array Processing; Springer Topics in Signal Processing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 16, pp. 81–102. [Google Scholar]
- Huleihel, N.; Rafaely, B. Spherical array processing for acoustic analysis using room impulse responses and time-domain smoothing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 3995–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizovic, I.; Nilsen, C.-I.C.; Holm, S. Transformation Between Uniform Linear and Spherical Microphone Arrays with Symmetric Responses. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 20, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellermann, W.; Kowalczyk, K.; Mabande, E.; Sun, H. Comparison of Subspace-Based and Steered Beamformer-Based Reflection Localization Methods. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th European Signal Processing Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 29 August–2 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, R.; Bogaert, I.; Rogier, H. Phase-Mode Processing for Spherical Antenna Arrays With a Finite Number of Antenna Elements and Including Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 3783–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krim, H.; Viberg, M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottersten, B.; Viberg, M.; Stoica, P.; Nehorai, A. Exact and Large Sample Maximum Likelihood Techniques for Parameter Estimation and Detection in Array Processing. In Radar Array Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 99–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.L.; Smith, T.; Larson, R. Radiation characteristics of a spherical array of circularly polarized elements. IRE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1968, 16, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondyopadhyay, P.K. Geodesic sphere phased arrays for LEO satellite communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium. Transmitting Waves of Progress to the Next Millennium. 2000 Digest. Held in Conjunction with: USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 16–21 July 2000; pp. 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Famoriji, O.J.; Akingbade, K.; Ogunti, E.; Apena, W.; Fadamiro, A.; Lin, F. Analysis of phased array antenna system via spherical harmonics decomposition. IET Commun. 2019, 13, 3097–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockton, R.; Hockensmith, R. Application of spherical arrays—A simple approach. Proc. IEEE AP-S Int. Symp. 1977, 15, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Han, L.; Blum, R.S.; Xu, Z. Mutiple-snapshot newtonalized orthogonal matching pursuit for line spectrum estimation with multiple measurement vector. Signal Process. 2019, 65, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Hegde, R.M. Stochastic Cramér-Rao Bound Analysis for DOA Estimation in Spherical Harmonics Domain. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 22, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, M.; Randazzo, A. The SVM-Based Smart Antenna for Estimation of the Directions of Arrival of Electromagnetic Waves. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2006, 55, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zooghby, A.; Christodoulou, C.; Georgiopoulos, M. Performance of radial-basis function networks for direction of arrival estimation with antenna arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1997, 45, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famoriji, O.J.; Ogundepo, O.Y.; Qi, X. An Intelligent Deep Learning-Based Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Scheme Using Spherical Antenna Array with Unknown Mutual Coupling. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179259–179271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Famoriji, O.J.; Shongwe, T. Critical Review of Basic Methods on DoA Estimation of EM Waves Impinging a Spherical Antenna Array. Electronics 2022, 11, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020208
Famoriji OJ, Shongwe T. Critical Review of Basic Methods on DoA Estimation of EM Waves Impinging a Spherical Antenna Array. Electronics. 2022; 11(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020208
Chicago/Turabian StyleFamoriji, Oluwole John, and Thokozani Shongwe. 2022. "Critical Review of Basic Methods on DoA Estimation of EM Waves Impinging a Spherical Antenna Array" Electronics 11, no. 2: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020208
APA StyleFamoriji, O. J., & Shongwe, T. (2022). Critical Review of Basic Methods on DoA Estimation of EM Waves Impinging a Spherical Antenna Array. Electronics, 11(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11020208





