Abstract
At the end of 2019, a new virus (SARS-CoV-2) called COVID-19 was reported in Wuhan, China, and spread rapidly worldwide. After two years later, several variants of this virus were created, infecting 608 million people and causing 6.51 million deaths. Due to the insufficient sensitivity of RT-PCR test kits, one of the main tools for detecting the virus, chest X-ray images are a popular tool for diagnosing the virus in patients with respiratory symptoms. Models based on deep learning are showing promising results in combating this pandemic. A novel convolutional neural network, FirecovNet, is suggested in this study that detects COVID-19 infection automatically based on raw chest X-ray images. With an architecture inspired by the integration of DarkNet and SqueezeNet networks, the proposed model has fewer parameters than state-of-the-art models and is trained using COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, normal, lung opacity, and viral pneumonia images, which were collected from two public datasets and also are symmetric in the distribution in class. FirecovNet performance has been verified using the stratified 5-fold cross-validation method. A total of five classification tasks are performed, including four 4-class classifications, and one 5-class classification, and the accuracy of all tasks was at least 95.9%. For all classification tasks, the proposed network has demonstrated promising results in precision, sensitivity, and F1-score. Moreover, a comparison was made between the proposed network and eight deep transfer learning networks and in terms of accuracy, precision, sensitivity, F1-score, speed, and size of the saved model; FirecovNet was very promising. Therefore, FirecovNet can be useful as a tool for more accurate diagnosis of the COVID-19 virus, along with diagnostic tests, in situations where the number of specialist radiologists may be limited.
1. Introduction
Since December 2019, a deadly virus of the coronavirus family called COVID-19 has appeared in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the disease a pandemic. It should be noted that, since the beginning of the pandemic, several COVID-19 variants have been identified, for instance, Alpha (B.1.1.7), Delta (B.1.617.2), and Omicron (B.1.1.529) that was first reported to WHO from South Africa on 24 November 2021. This variant spreads more rapidly than other variants and is considered a variant of concern [1]. The common symptoms of COVID-19 variants are fever, shortness of breath, fatigue, cough, and loss of sense of taste and smell [2], and it is mainly spread through droplets when sneezing, coughing, or even talking. Since the onset of this disease until 7 September 2022, more than 608 million cases have been confirmed, and 6.51 million deaths have been reported worldwide. Out of 608 million people, Europe has the highest number of infected people of all the continents, with 223 million people infected. The United States is also considered a country with a high infection rate, with 94 million infected people. On the other hand, accurate infection statistics from African countries are not available [3]. So far, different vaccines have been discovered and produced worldwide, each with different efficiencies. Nevertheless, due to the unfair distribution of vaccines, people in backward and poor countries still do not have adequate vaccines. Only 21% of people in low-income countries have been administered at least one dose of vaccines [3]. On the other hand, according to studies, COVID-19 vaccines have a little lower efficacy against the variants. Therefore, social distancing and the accurate and faster diagnosis of this disease are the essential measures that must be taken in all countries to deal with this situation.
According to the recommendation of WHO, the primary diagnosis and screening method for COVID-19 is reverse transcription polymerase reaction (RT-PCR) [4]. However, the sensitivity of this method is very variable because it has false-negative or false-positive results. Therefore, the possibility of COVID-19 infection is not ruled out by a negative test result and should not be used as the sole treatment criterion or patient management decisions [5].
Recently, rapid diagnostic tests called RPT have been used to detect COVID-19 viral proteins, and the result is prepared in 10 to 30 min. This method has a sensitivity of 34% to 80% [6]. The results depend on the concentration of antigen in the sample, the time of onset, and some other factors. Moreover, serology testing methods detect antibodies that the body has produced in response to the fight against the virus. However, these antibodies only form in the body two weeks after infection, so they are not proper for early diagnosis [7]. It would seem that the use of RT-PCR combined with clinical features such as chest imaging can facilitate this disease’s management. Therefore, chest imaging (X-ray or CT scan) is a standard method for quick and easy diagnosis. Imaging characteristics of COVID-19 are quite different from other types of viral pneumonia [8].
CT scan is highly sensitive to detect COVID-19 [9]. In contrast, X-ray images show COVID-19-related visual cues [10]. There are several benefits to using X-ray imaging to detect COVID-19, especially in areas with limited resources and severely affected areas. In many clinical settings and imaging institutions, X-ray imaging is easily available and is supposed standard equipment in most healthcare facilities. In developing countries, CT scanners are used less because of higher maintenance costs. Moreover, the portability of X-ray systems allows imaging to take place in an isolated room. As a result, the risk of transmitting the COVID-19 virus through fixed systems like CT scanners and in rooms with fixed imaging systems is reduced [11]. Moreover, the dose of CT imaging radiation is high, and in contrast to X-ray, the dose is 30 to 70 times lower [12]. However, one of the biggest challenges we face is that interpreting radiology images requires radiologists. Because with the spread of the disease, delicate abnormalities such as ground-glass opacities (GGO) are created in the lungs, which a specialist radiologist can only interpret. Moreover, when many people die because of the virus every day worldwide, time is valuable. Therefore, considering the large number of people with COVID-19 symptoms and the limited number of qualified radiologists, an automatic approach to identifying the abnormalities can help the diagnosis process and increase the early diagnosis rate with high accuracy.
Approaches based on artificial intelligence are a possible tool to overcome these challenges. Deep learning is one of the most widely used branches of artificial intelligence in various research scenarios. In deep learning methods, unlike classical machine learning approaches where the extraction of features was performed manually, a deep end-to-end network is used to automate the feature extraction [13]. The use of deep learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), has outperformed classical computer vision and medical image processing. They have recently become one of the most potent strategies for detecting and classifying COVID-19 using radiographic images and have demonstrated high accuracy. Most of the current research uses standard CNN architectures and transfer learning techniques, but developing customized architectures unique to data and tasks can be useful in detecting and classifying actual cases.
This study presents a deep learning method to diagnose COVID-19 infection from chest radiographic images. The proposed CNN model, called FireCovNet, classifies raw X-ray images of normal, COVID-19, viral pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, and lung opacity through two different schemas (4-class and 5-class classification) using five various tasks. The proposed model has an end-to-end learning scheme to learn features without extracting hand-crafted features. Since deep learning methods have recently focused on reducing network parameters despite maintaining and even increasing network accuracy, the proposed network in this study has been tried to be aligned with the intended purpose. The FireCovNet design is inspired by the SqueezeNet, which uses Fire modules that, despite extracting important features, have fewer parameters (0.6 million). It also causes reducing feature dimensions, increases stability, speeds up the training process, and increases convergence and detection accuracy. The type of arrangement and proper placement of the Fire modules next to the convolution blocks and the use of pooling layers has tried to achieve a suitable architecture with fast and very accurate output in detecting COVID-19 disease. A dataset collected from two different datasets was used to train the suggested model. FireCovNet has been evaluated by stratified five-fold cross-validation. A model that can accurately and quickly diagnose COVID-19 infection can help physicians and nurses manage and follow-up with COVID-19 patients. In addition, to compare the performance of the proposed network in terms of accuracy, speed, and model size, eight transfer learning networks, including EfficientNetB0 [14], InceptionV3 [15], MobileNet [16], ResNet50 [17], VGG16 [18], VGG19 [18], Xception [19], SqueezeNet [20], have been used.
This study consists of the following contributions:
- Designing a CNN model called FirecovNet to detect COVID-19 in 4-class and 5-class classification.
- Developing an end-to-end network requires neither feature extraction nor feature selection.
- Integration of DarkNet and SqueezeNet networks features for reducing feature dimensions, increasing stability, and increasing detection speed and accuracy.
- Evaluating the proposed network and comparing it with eight transfer learning networks in terms of speed, accuracy, and model size.
- Using 4000 images that were not used in the training process to test and evaluate FirecovNet.
The rest of the study is explained as follows: A summary of some recent studies can be found in Section 2. Section 3 is the material and methods that include a description of the collected data set, details of the FirecovNet model, and network training. The results of this research and discussion are given in Section 4 and finally, in Section 5, the conclusion and future work is set out.
2. Related Works
Researchers are seeking to discover some particular features of chest X-ray images of COVID-19 patients. Some of the recent research can be summarized as follows.
One of the most leading methods for COVID-19 diagnosis was proposed by Wang et al. [11]. They used a deep residual architecture called COVID-Net to classify chest X-rays into four classes (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. viral pneumonia vs. bacterial pneumonia). COVID-Net obtained 83.5% accuracy for 4-class and 93.3% accuracy for 3-class classification. Zebin and Rezvy [21] used pre-trained VGG16, ResNet50, and EfficientNetB0 convolutional networks, and in the 3-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. pneumonia), 90%, 94.3%, and 96.8% accuracy are obtained, respectively. Ucar and Korkmaz [22] proposed a method in which SqueezeNet was tuned with the Bayesian optimization. As a result of the research, the 3-class (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. pneumonia) classification accuracy was 98.3%. Marques et al. [23] proposed a CNN model based on the EfficientNet architecture and tested it using stratified ten-fold cross-validation. The accuracy of 2-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal) is 99.62% and for multi-classification (COVID-19 vs. Normal vs. Pneumonia) is 96.70%. Chowdhury et al. [24] developed a model called PDCOVIDNet that can extract the features of COVID-19 by dilated convolution in the parallel stack of convolution blocks. The classification accuracy of the 3-class (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. viral pneumonia) is 96.58%. A new serial network containing five convolution layers was proposed by Nour et al. [25]. This CNN model was used as a deep feature extractor, and the extracted features were fed into the machine learning algorithms: decision tree, k-nearest neighbor, and support vector machine (SVM). Hyperparameters were also optimized utilizing the Bayesian optimization algorithm. The best results were achieved by SVM with 98.97% accuracy for 3-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. Viral pneumonia). Mahmud et al. [26] proposed a new CNN-based architecture called CovXNet that used depth-wise convolution with modifying dilation rates that can extract diversified features efficiently. First, they used normal and pneumonia radiography images to train the model and then trained the network using the generated weights to diagnose COVID-19 in several classification tasks. The accuracy obtained was 97.4% for the 2-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal), 87.3% for 2-class classification (COVID-19 vs. viral pneumonia), 94.7% for 2-class classification (COVID-19 vs. bacterial pneumonia), 89.6% for 3-class classification (COVID-19 vs. viral pneumonia vs. bacterial pneumonia), and 90.3% for the 4-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. viral pneumonia vs. Bacterial pneumonia). Aslan et al. [27] introduced an ANN-based automatic lung segmentation technique and also a new hybrid structure containing bidirectional long short-term memories (BiLSTM) layer to detect COVID-19, both of which used AlexNet. The achieved accuracy for the 3-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. viral pneumonia) was 98.70%. Gupta et al. [28] proposed a deep convolution network called InstaCovNet-19. In the proposed method, the images were first pre-processed using the stacking method to enhance quality. Then five pre-trained and fine-tuned networks (ResNet101, Xception, InceptionV3, MobileNet, and NASNet) were used, while only their last convolution layer was trained. The outputs of these networks were combined using the integrated stacking method to create a larger and more robust stacked model. They achieved 99.53% accuracy in the 2-class classification (COVID-19 vs. non-COVID-19) and 99.08% accuracy in the 3-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. pneumonia). A deep model based on the DarkNet19 was provided by Ozturk et al. [29]. Their model includes 17 convolution layers, and an accuracy of 98.08% for 2-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal) and 87.02% for 3-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. pneumonia) was achieved. Khan et al. [30] developed a network called CoroNet based on Xception architecture. The developed model was pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset and then re-trained on a prepared dataset that includes COVID-19 and other chest pneumonia X-ray images. The accuracy was 89.6% and 95% respectively in the 4-class (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. viral pneumonia vs. bacterial pneumonia) and 3-class (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. pneumonia) classifications. CoroDet, a 22-layer CNN model, was presented in [31] and achieved an accuracy of 99.1% for 2-class classification, 94.2% for 3-class classification, and 91.2% for 4-class classification. In [32], white balance followed by contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) is used as an image preprocessing step for enhancing the visibility of chest X-ray images, and a depth-wise separable convolutional neural network (DSCNN) trained is used for image classification with lesser parameters and significantly lighter in size. The proposed method which named COVIDLite, achieved 99.58% for binary classification (COVID-19 vs. normal), whereas 96.43% for multi-class classification (COVID-19 vs. normal vs. viral pneumonia). A combined CNN-BiLSTM network design in [33] introduced a deep feature augmentation framework, which helped mitigate the lack of annotated data in COVID-19 detection to provide more compact and more powerful low-dimensional augmented reality features than raw CNN for detecting COVID-19. In [34], seven convolutional neural networks are used, including ResNet50V2, DenseNet121, Xception, InceptionV3, EfficientNet-B0, MobileNetV2, and EfficientNetV2; also proposed is LightEfficientNetV2, which is intended for a limited number of chest X-rays and CT scans. On the chest X-ray image dataset, InceptionV3 had the highest accuracy, 96.50%, before fine-tuning, followed by EfficientNetV2, with 97.73% after fine-tuning. On chest X-ray images, the LightEfficientNetV2 model proposed in this study had an accuracy of 98.33%. The chest X-ray images are used in seven scenarios according to normal, viral, bacterial, and COVID-19 classes for 2–4 classification in [35]. A fusion of deep transfer learning and LSTM networks is used in the proposed architecture, along with generative adversarial networks (GANs). In all scenarios except one, they achieved more than 90 percent accuracy, and they also succeeded in separating COVID-19 from normal with 99% accuracy. By analyzing chest X-rays and CT scans, authors of [36] proposed a deep convolutional neural network, “COV-RadNet,” to detect COVID-19, viral pneumonia, lung opacity, and normal, healthy people. In the four-class classification, they achieved 97% accuracy. In [37], eight pre-trained convolutional neural networks (CNN) were used to classify images from the chest X-ray dataset as COVID-19, pneumonia, pneumothorax, tuberculosis, or normal. The highest accuracy was achieved by Densenet-201, with 97.2%.
Most studies have focused only on classifying the two healthy and COVID-19 classes. The number of 2-class classification studies to detect COVID-19 is greater than the number of multi-class classification studies performed. Furthermore, the detection of different lung diseases is challenging due to the similarity of the chest X-Ray images to each other. As a result, it is necessary to consider more comprehensive tasks to detect COVID-19 from other infectious lung diseases. Moreover, most studies have used transfer learning networks, which often require high computational time for training and testing, and most have a large-sized saved model and are not suitable for deploying on FPGAs.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. X-ray Image Dataset
In CNN-based methods, having a proper database with enough data to train the network is important. The dataset used in this research is, therefore, a collection of two different datasets of chest X-ray images that are publicly available. The first dataset [38] collected from several different public datasets, contains 3616 COVID-19 images, 6012 lung opacity images, 10,200 normal images, and 1345 viral pneumonia images. For the purpose of achieving symmetry in class distribution, without the use of any data augmentation techniques, 1345 images were selected from each class. In addition, 1345 bacterial pneumonia images from [39] were added to the final dataset. It should be noted that the remaining images were used for the final testing of the network. Some examples of the collected chest X-ray images are also shown in Figure 1. There is no discernible difference between COVID-19 and other images; thus, this disease is not detectable visually.
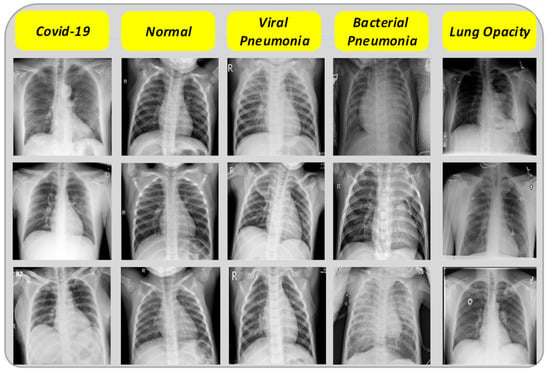
Figure 1.
Sample X-ray images.
3.2. FirecovNet
CNN networks are very similar to simple neural networks; except that they have convolutional layers to process the input data and also pooling layers to reduce unnecessary features and make processing easier. The deep architecture of these networks helps to learn complex features, while the shallow neural networks are not capable of learning these features. The main idea behind CNNs is to combine local features extracted from the upper layers with more complicated features extracted from the lower layers [40].
The proposed network, called FirecovNet, whose idea is inspired by the features of the Squeezenet and DarkNet-19 networks, is a lightweight deep learning network with fewer parameters and faster training than other well-known networks. The advantage of a lightweight network is that deploying these CNNs on FPGAs and other limited memory hardware is more feasible, because there is typically no off-chip memory for FPGAs, and they typically have less than 10 MB of on-chip memory [41]. On the other hand, FirecovNet is large enough to detect cases by extracting COVID-19-related features. The network architecture is illustrated in Figure 2. As shown, FirecovNet consists of three parts. In the first part, like the DarkNet-19 network, the input images are first fed to a 3 × 3 convolution layer, and then a 2 × 2 Max pooling is applied. Then these two operations are repeated.
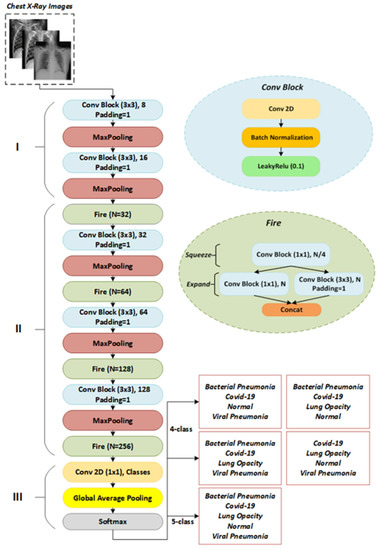
Figure 2.
The architecture of FirecovNet.
In the Squeezenet, however, the first layer is a 7 × 7 convolution, followed by a 3 × 3 max pooling, which leads to more parameters. Moreover, like DarkNet-19, a conv block has a convolutional layer, followed by a batch normalization [42] operator and a Leaky ReLU [43] activation function. For standardizing inputs, the batch normalization operator is used. It also has other advantages, such as stabilizing the training process, speeding up convergence, and regularizing the model. Leaky ReLU is a type of ReLU operator that is used to prevent the dying ReLU [44] problem. Because unlike other activation functions with zero derivatives for all negative inputs, it has a small slope for negative values to overcome this problem. The function of Leaky ReLU is defined as follows:
The Maxpool method reduces each feature map’s length and width by computing the maximum of a region defined by its filter. The size of all Max Pooling filters in FirecovNet is 2 × 2 with stride 2. The second part of the FirecovNet has four Fire modules, which were first introduced in the SqueezeNet [41], which has resulted in the same accuracy as the AlexNet network but with fewer parameters. The structure of SqueezeNet with eight Fire modules is such that it causes to decrease the memory consumption and the processing time for classification compared with other multi-layered deep learning models. The Fire module consumes much less space than normal convolution filters to store weight parameters but still achieves satisfactory results. The Fire module is the main module of proposed network and has squeeze (which has only 1 × 1 convolution) and expand (mix of 1 × 1 and 3 × 3 convolutions) structures. The purpose of using this module is to replace 1 × 1 filters with 3 × 3 filters and reduce the number of input channels to 3 × 3 filters and thus reduce the network parameters. Moreover, using this squeezing and expanding scheme, the latent features are better extracted. The following conditions must be satisfied by the Fire module:
where is the number of 1 × 1 filters in the squeeze layer and is the number of 1 × 1 filters in the expand layer, and is the number of 3 × 3 filters in the expand layer. The conv block is also used in the squeeze and expand sections, and like SqueezeNet, the number of fire modules filters has gradually increased. In order to have the same height and width in the extracted features of the 1 × 1 and 3 × 3 filters, zero-padding was applied to the 3 × 3 filter input in the expansion section. In fact, one-pixel zero-padding is applied to all 3 × 3 filters in the proposed model. The SqueezeNet network can also balance its performance and model size by adjusting the squeeze ratio (SR), which is the ratio of the number of squeeze layer filters to the expand layer. Therefore, it is possible to make the best use of the Fire module by setting this hyper parameter according to the device’s computing power. In the FirecovNet, SR = 0.25 was considered. There are also three conv blocks in the second part of the FirecovNet, each followed by a Max Pooling layer. Using these Max Pooling layers, the feature map size is reduced by a factor of 8, and it is another effective way to diminish the computational load of the network. Finally, like SqueezeNet and DarkNet-19, the third part of the proposed network consists of a 1 × 1 convolution layer with a number of filters equal to the number of classification classes, followed by a global average pooling layer, which was first developed by Lin et al. [45]. The main advantages of using the global average pooling layer instead of the fully connected layer are that no optimization of parameters is required and the number of parameters and computational complexity is also significantly reduced [46]. FirecovNet ends with a Softmax classifier that provides multi-class probability distributions. The network details are shown in Table 1. Table 2 also presents the total number of trainable and non-trainable parameters (weights).

Table 1.
Detailed layer configuration of FirecovNet. (N = Number of classes).

Table 2.
Number of FirecovNet parameters in 4 and 5-class classification.
3.3. Network Implementation and Training Process
In this research, five classification tasks were considered to identify COVID-19 cases using chest radiography images. Table 3 summarizes the classification tasks considered for this study. The sizes of the X-ray images in the collected dataset were not uniform. Therefore, the color-space of the images was changed to RGB, and their size was converted into the same size as 224 × 224 × 3. All tasks were implemented in Keras 2.3.1 on top of Tensorflow 1.14.0 using a system with Intel® Core™ i7-7700 K CPU @ 4.20 GHz, 16 GB RAM, with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Super-8GB GPU. The categorical cross-entropy and binary cross-entropy loss functions were used for multi-class and binary classification, respectively. The developed model was trained end-to-end using the ADAM optimizer [47]. The initial learning rate was 0.001, but the ReduceLROnPlateau technique lowered the learning rate when a metric stopped improving. This callback monitors improvement and reduces the learning rate if no progress is seen for a “patience” number of epochs.

Table 3.
Considered classification tasks in this research.
Moreover, the batch size was set to 8 images with 50 backpropagation epochs. All evaluations were done using the stratified five-fold cross-validation (CV) technique using 80% for the training set and 20% for the test set (unseen folds). During training in each fold, 10% of the training data were used as a validation set to prevent overfitting.
3.4. Metrics
The confusion matrix was used to obtain a more comprehensive picture of model performance and show the relationship between model output and actual values. This matrix is used in artificial intelligence to visualize important prediction analysis, such as accuracy, precision sensitivity, and F1-score. The following equations present how these metrics can be calculated:
where TP, TN, FN, and FP are true positive, true negative, false negative, and false positive, respectively.
The AUC-ROC curve is used to evaluate classification models’ ability to distinguish between classes and graphically observe their performance. The receiver performance characteristic curve (ROC) is a probability graph, and the degree of separability in the classification is indicated by the AUC (area under the curve).
4. Results and Discussion
The results of the COVID-19 automatic detection from chest X-ray images based on FirecovNet in all classification tasks are presented and discussed in this section. Because of using the stratified 5-fold cross-validation method, evaluation metrics of all folds were averaged for all tasks. The loss and accuracy curves of 5th fold for all classification tasks are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. As can be seen, the loss and accuracy curves for all tasks converge with the number of epochs and reach their steady-state value. The overlapped confusion matrix of all tasks is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Moreover, the quantitative results of the 4, and 5-class classifications for all folds are given in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. As can be seen, all of the classification tasks have promising results. In 4-class classification, the best performance was achieved in the BCLV task. The reported average accuracy is 98.64%. Moreover, average precision, sensitivity, and F1-score are 98.64%, 98.63%, and 98.64%. Furthermore, in 4-class classification, CLNV was underperformed. The average accuracy value of all folds is 95.92%. The overall average is 95.9% for precision, 95.94% for sensitivity, and 95.9% for F1-score. Ultimately, the average values reported in the 5-class classification task are 96.96%, 96.97%, 96.97%, and 96.96% for precision, accuracy, sensitivity, and F1-score, respectively. The AUC-ROC curves for 5th fold of all classification tasks are shown in Figure 7 to demonstrate the high performance of FirecovNet. In Table 6, the running times of both test and training phases for all classification tasks are provided.
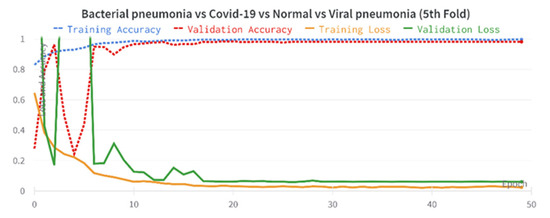
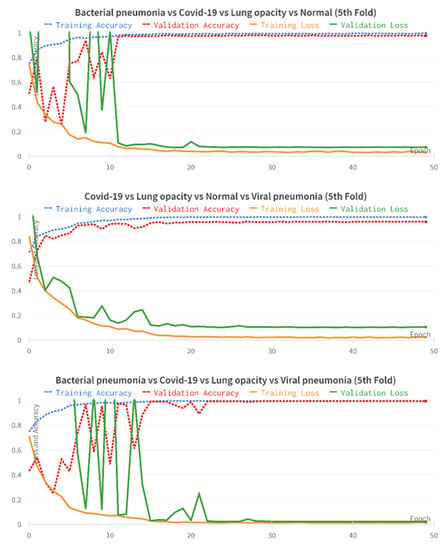
Figure 3.
Accuracy and loss plots over 50 training epochs for 4-class experiments (5th fold).
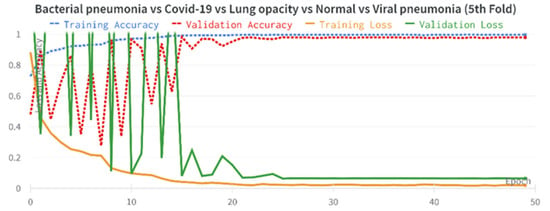
Figure 4.
Accuracy and loss plots over 50 training epochs for 5-class experiments (5th fold).
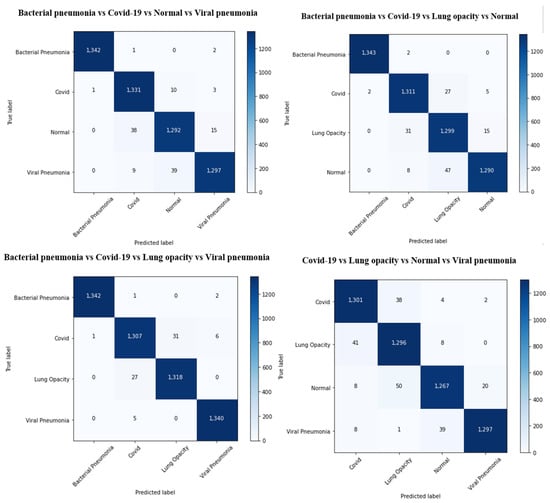
Figure 5.
Overlapped confusion matrix of 4-class classifications.
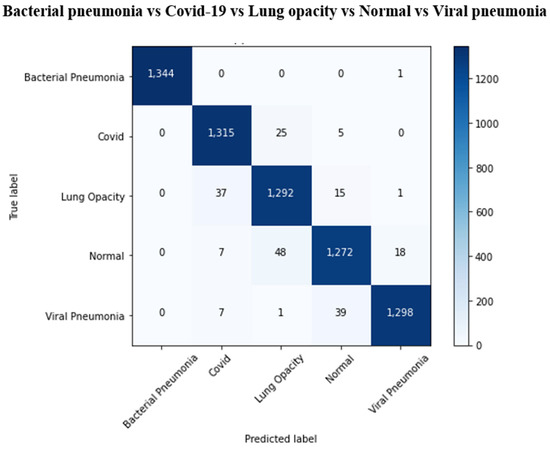
Figure 6.
Overlapped confusion matrix of 5-class classifications.

Table 4.
Performance of FirecovNet on each fold in the 4-class classification tasks.

Table 5.
Performance of FirecovNet on each fold in the 5-class classification tasks.
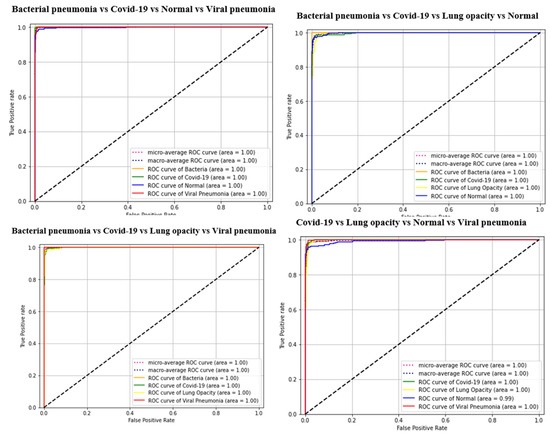
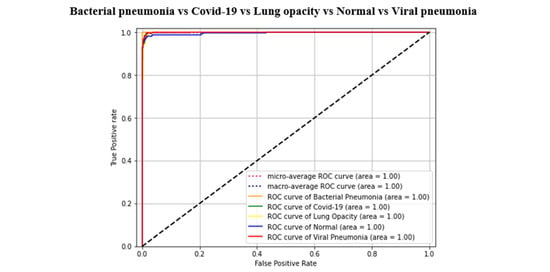
Figure 7.
AUC-ROC curves of all classification tasks (5th fold).

Table 6.
Running time for all classification tasks by FirecovNet in 50 epochs.
According to Table 6, the testing and training phases require more time for BCLNV task than for other tasks.
To further investigate the performance of the FirecovNet network, the 5-class classification task was simulated using eight transfer learning networks. EfficientNetB0, InceptionV3, MobileNet, ResNet50, VGG16, VGG19, Xception, SqueezeNet are eight comparison networks that have been widely used in recent studies to detect COVID-19. Figure 8 shows the loss and accuracy curves of the mentioned networks and the proposed network (5th fold). As can be seen, FirecovNet performed better than SqueezeNet, and after 30 epochs reached its steady-state, which is almost equal to other networks. Additionally, Figure 9 presents the running time of BCLNV task based on FirecovNet compared to the eight networks mentioned above in 50 iterations. It can be seen that the proposed model has a shorter running time for both phases. This is due to the fact that in transfer learning-based networks, the computation time is often high. As well, the bar graph of all networks for comparison, which includes accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F1-score, is shown in Figure 10. Xception and inceptionv3 networks performed best. The VGG19 network, on the other hand, had the worst performance. As shown, the FirecovNet network performed almost similar to other networks and even better than some. Table 7 also compares the proposed network with other networks in terms of the number of parameters and the size of the saved model. As mentioned, although the FirecovNet network does not have the best performance in terms of accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F1-score, it has the least training and testing time, with having the smallest number of parameters, and the size of the saved model is smaller. Therefore, the proposed network is still promising in terms of speed and being small-sized and is very suitable and promising for deploying on FPGA.
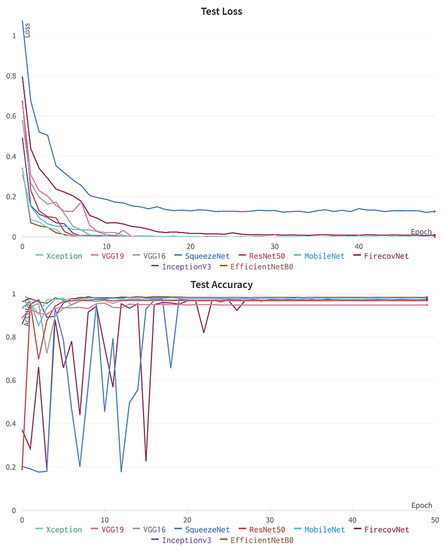
Figure 8.
Accuracy and loss plots of proposed network comparing with other networks over 50 epochs for 5-class classification (5th fold).
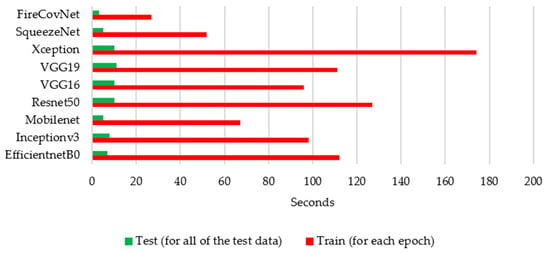
Figure 9.
Running time for FirecovNet comparison with eight networks for 5-class classification in 50 epochs.
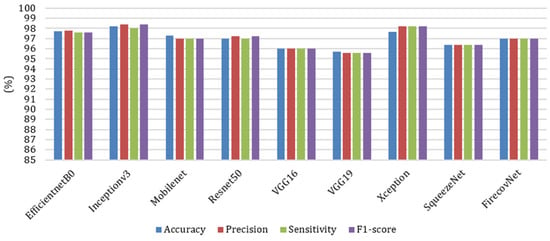
Figure 10.
Comparison of different networks in terms of accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F1-score in 5-class classification task.

Table 7.
Comparison of the number of parameters and size of the saved model for different networks in a 5-class classification task.
FirecovNet should be evaluated with data that are not used as training data to be used in practice. Therefore, the trained model in the BCLN task was tested on 4000 images (1000 bacterial pneumonia, 1000 COVID-19, 1000 lung opacity, and 1000 normal) which were split from the remaining images in the collected dataset. Figure 11 shows the confusion matrix and bar chart of accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F1-score. According to this figure, although the proposed model performed poorly in detecting normal images, it had an acceptable performance in the detection of other classes and, in total, achieved 94% accuracy. Therefore, FirecovNet can perform well in a dataset that was not used in its training phase.
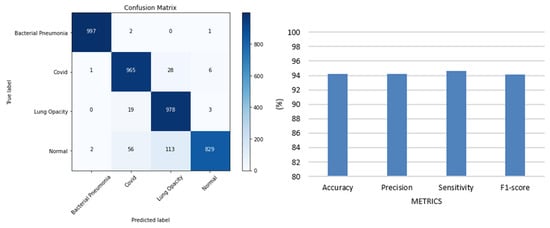
Figure 11.
Confusion matrix and bar chart diagram of accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and F1-score of FirecovNet for the dataset that was not used in its training phase.
Deep learning has recently focused on networks that, in addition to being highly accurate and competing with other state-of-the-art networks, have fewer parameters. Because having fewer parameters makes the training stage more efficient and faster, and due to the small size of these models, they are easy to move. It is also easier to implement them for embedded systems and also to store them on FPGAs. Table 8 shows the performance of the proposed FirecovNet compared to recent state-of-art research. In implementation of networks with a large number of parameters, FPGAs will require a significant amount of storage, external memory bandwidth, and computational resources on the order of billions of operations per second.

Table 8.
Comparison of the FirecovNet results with other state-of-art studies.
As can be observed, FirecovNet surpassed recent studies in terms of the number of classification tasks studied and the number of classified classes. Although the data distribution for training and evaluation sets is the same in all previous studies, in some of them k-fold cross-validation has not been used. Therefore, due to the differences in datasets, simulation environments, and techniques, it is important to be aware that it is not possible to perform a one-to-one comparison.
However, FirecovNet, despite the small number of parameters, achieved promising results in all classification tasks. Although transfer learning and pretrained networks have been used in most studies, however, in this research, a new CNN model is presented that is trained to diagnose COVID-19 infection from scratch and does not require manual feature extraction. This robust model is efficient and fast, and it has a lower computational cost because of fewer parameters.
Due to the FirecovNet architecture, the low number of parameters is because of using Fire modules, the down-sampling between layers, and the placement of the global average pooling layer’s placement instead of the fully connected layers. Moreover, no skip or residual connection has been used. This model has achieved promising outcomes and can detect a positive patient with COVID-19 in less than one second. In this study, to prevent data leakage errors, images in training, validation, and testing sets were not randomly selected. However, this has not been mentioned in many studies, and the results may not be accurate for this reason.
The limitation of the number of classes in the database is a challenge. There were a total of five categories in this study. Therefore, it needs to be evaluated using a more extensive data set and more classes of other lung infectious diseases such as SARS, MERS, etc.
5. Conclusions
The COVID-19 virus has now spread worldwide, infecting and killing many people. The low sensitivity of COVID-19 diagnosis tests, such as RT-PCR, may lead to inaccurate results. Therefore, a combination of these tests and chest imaging can facilitate the management of this disease. Over the past year, the use of CNN models and chest radiography images to rapidly diagnose COVID-19 has become popular. These models have an end-to-end learning structure without the need for hand-crafted feature extraction. This study introduced a deep-learning-based model for automatically detecting COVID-19 cases from chest radiography images for five categories: bacterial pneumonia, COVID-19, lung opacity, normal, and viral pneumonia. By implementing five scenarios, the proposed model was able to achieve an accuracy of at least 95% in 4 and 5-class classifications. The proposed network is also lightweight, and due to its low computational cost, it is a rapid model to help physicians correctly detect COVID-19 cases. An interesting approach that can be used in future research is evaluating other patient symptoms and risk factors along with chest x-rays. Because this deadly virus has plagued the world for more than two years, artificial intelligence-based systems, especially deep learning with the rapid, accurate, and automatic diagnosis of this disease, can play an important role in combating the virus.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, L.H., writing—review and editing, S.M., R.A., A.F. and E.G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Research Management Center (RMC), and by the Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sabah (UMS) under Grant SDK0213-2020.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://github.com/hassanlougithub/FirecovNet_data (accessed on 10 August 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classifications.html (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_3 (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Ritchie, H.; Mathieu, E.; Rodés-Guirao, L.; Appel, C.; Giattino, C.; Ortiz-Ospina, E.; Hasell, J.; Macdonald, B.; Beltekian, D.; Roser, M. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- WHO. WHO Lists Two COVID-19 Tests for Emergency Use; Word Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tahamtan, A.; Ardebili, A. Real-Time RT-PCR in COVID-19 Detection: Issues Affecting the Results. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Advice on the Use of Point-of-Care Immunodiagnostic Tests for COVID-19; WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, R.; Menaka, R.; Hariharan, M. Learning Distinctive Filters for COVID-19 Detection from Chest X-ray Using Shuffled Residual CNN. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2020, 99, 106744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, C.; Gill, J.; Chun, D.; Babu, B.A. Retracted article: Deep Learning System to Screen Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia. Appl. Intell. 2020. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L. Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanne, J.P.; Little, B.P.; Chung, J.H.; Elicker, B.M.; Ketai, L.H. Essentials for Radiologists on COVID-19: An Update-Radiology Scientific Expert Panel. Radiology 2020, 296, E113–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A Tailored Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of COVID-19 Cases from Chest X-ray Images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.C. Radiation Risk from Medical Imaging. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.-I. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv Prepr. 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv Prepr. 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-Level Accuracy with 50× Fewer Parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv Prepr. 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebin, T.; Rezvy, S. COVID-19 Detection and Disease Progression Visualization: Deep Learning on Chest X-rays for Classification and Coarse Localization. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, F.; Korkmaz, D. COVIDiagnosis-Net: Deep Bayes-SqueezeNet Based Diagnosis of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) from X-ray Images. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.; Agarwal, D.; de la Torre Díez, I. Automated Medical Diagnosis of COVID-19 through EfficientNet Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2020, 96, 106691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Kabir, M.A. PDCOVIDNet: A Parallel-Dilated Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Detecting COVID-19 from Chest X-ray Images. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2020, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, M.; Cömert, Z.; Polat, K. A Novel Medical Diagnosis Model for COVID-19 Infection Detection Based on Deep Features and Bayesian Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2020, 97, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Fattah, S.A. CovXNet: A Multi-Dilation Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic COVID-19 and Other Pneumonia Detection from Chest X-ray Images with Transferable Multi-Receptive Feature Optimization. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 122, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.F.; Unlersen, M.F.; Sabanci, K.; Durdu, A. CNN-Based Transfer Learning–BiLSTM Network: A Novel Approach for COVID-19 Infection Detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 98, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Anjum; Gupta, S.; Katarya, R. InstaCovNet-19: A Deep Learning Classification Model for the Detection of COVID-19 Patients Using Chest X-ray. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 99, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Rajendra Acharya, U. Automated Detection of COVID-19 Cases Using Deep Neural Networks with X-ray Images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A Deep Neural Network for Detection and Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray Images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, E.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Lee, I.; Tamanna, T.; Parvez, M.Z. CoroDet: A Deep Learning Based Classification for COVID-19 Detection Using Chest X-ray Images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 142, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddhartha, M.; Santra, A. COVIDLite: A Depth-Wise Separable Deep Neural Network with White Balance and CLAHE for Detection of COVID-19. arXiv Prepr. 2020, arXiv:2006.13873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, U.; Hoque, M.Z.; Oussalah, M.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Seppänen, T.; Sarder, P. SAM: Self-Augmentation Mechanism for COVID-19 Detection Using Chest X-ray Images. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.-L.; Liao, Y.-C. A Lightweight CNN-Based Network on COVID-19 Detection Using X-ray and CT Images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheykhivand, S.; Mousavi, Z.; Mojtahedi, S.; Yousefi Rezaii, T.; Farzamnia, A.; Meshgini, S.; Saad, I. Developing an Efficient Deep Neural Network for Automatic Detection of COVID-19 Using Chest X-ray Images. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 2885–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Habiba, S.U.; Khan, T.A.; Tasnim, F. COV-RadNet: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-rays and CT Scans. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. Update 2022, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaddi, S.H.; Sharma, L.D. Automated Multi-Class Classification of Lung Diseases from CXR-Images Using Pre-Trained Convolutional Neural Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 211, 118650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Radiography Database|Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Chest X-ray Images (Pneumonia). Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Wan, J.; Wang, D.; Hoi, S.C.H.; Wu, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Deep Learning for Content-Based Image Retrieval: A Comprehensive Study. In Proceedings of the MM 2014—Proceedings of the 2014 ACM Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Han, S.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. Arxiv E-Prints 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y. Rectifier Nonlinearities Improve Neural Network Acoustic Models. In Proceedings of the ICML 2013, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; Volume 30, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on Imagenet Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network In Network. arXiv Prepr. 2013, arXiv:1312.4400. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, R.C. Real-Time Facial Affective Computing on Mobile Devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv Prepr. 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).