A More Effective Zero-DCE Variant: Zero-DCE Tiny
Abstract
:1. Introduction
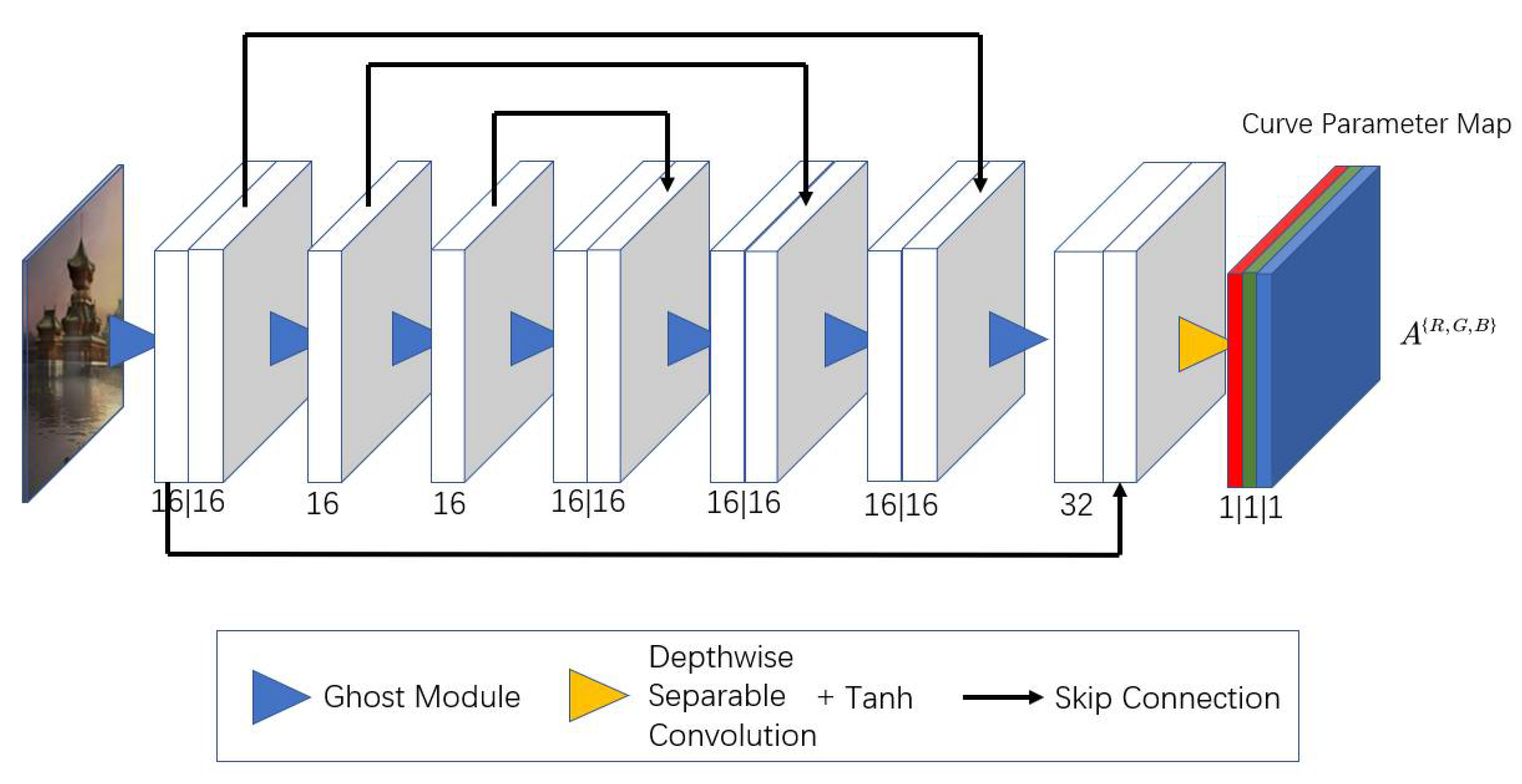
- The CSPNet structure is introduced into the original U-net structure, which can reduce the amount of computation and achieve a richer gradient combination. At the same time, except for the last layer, the Ghost module is used to replace the depth separable convolution, which further reduces the size of the image enhancement model.
- The channel consistency loss is introduced into the non-reference loss: using KL divergence to enhance the consistency between the original image and the enhanced image on the difference between channels.
2. Related Works
2.1. Zero Sample Learning for Image Enhancement
2.2. Model Lightweight Method
3. Materials and Methods
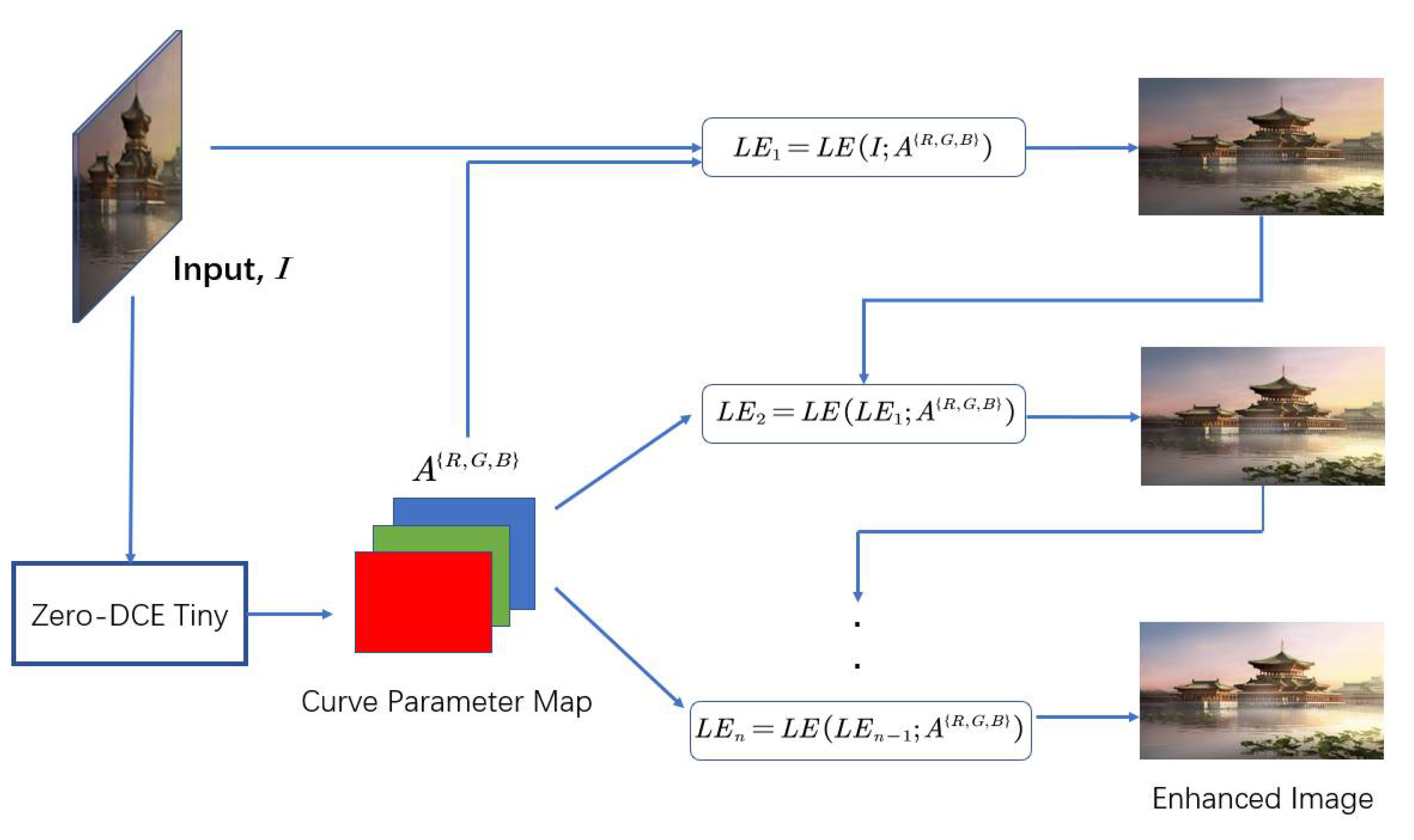
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. DCE-Net Tiny
3.3. Non-Reference Loss Functions
4. Results
4.1. Ablation Study
4.1.1. Ablation Study of Each Loss
4.1.2. Ablation Study of Backbone Network
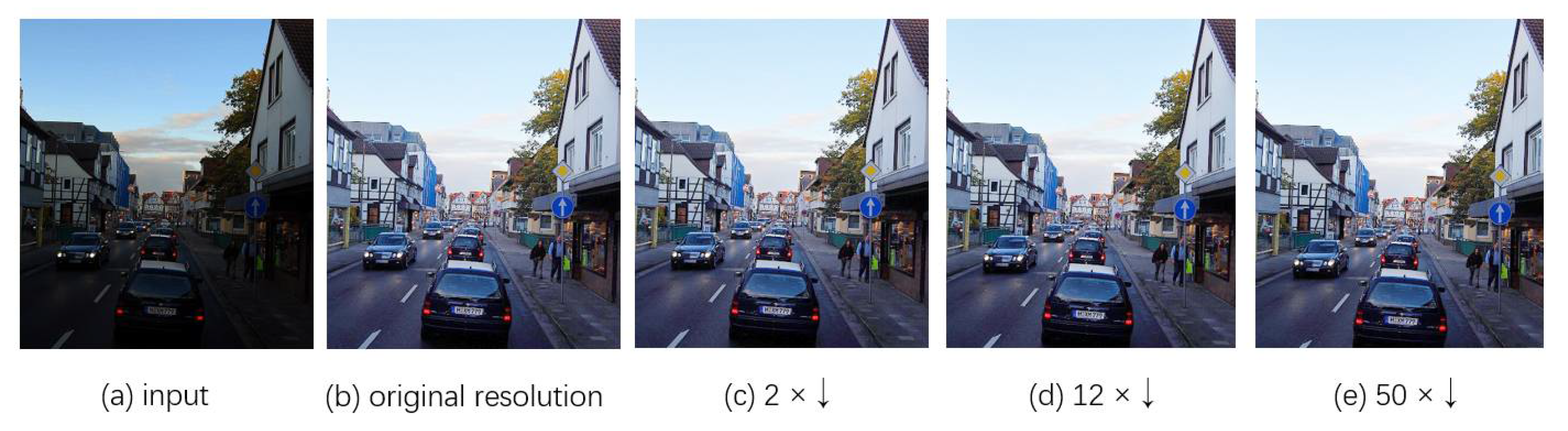
4.1.3. Ablation Study of Input Size
4.2. Benchmark Evaluations
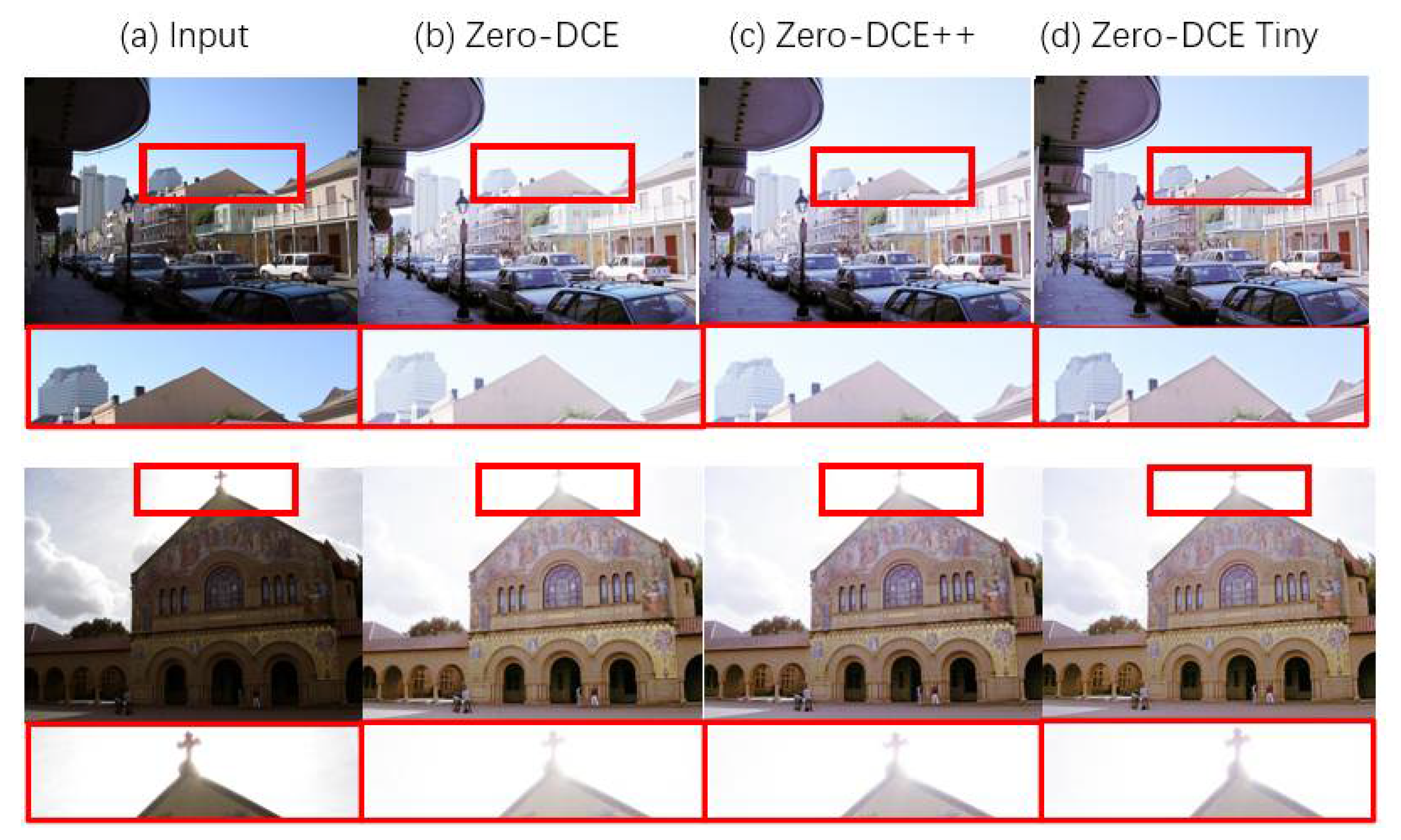
4.2.1. Visual and Perceptual Comparisons
4.2.2. Quantitative Comparisons
4.2.3. Object Detection in the Dark
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iqbal, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Bin, L.; Khan, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Deep learning recognition of diseased and normal cell representation. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020, 32, e4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainetter, S.; Fraundorfer, F. End-to-end Trainable Deep Neural Network for Robotic Grasp Detection and Semantic Segmentation from RGB. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Kabir, H.; Dewan, M.A.A.; Chae, O. A Dynamic Histogram Equalization for Image Contrast Enhancement. Int. Conf. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.; Li, B. Naturalness Preserved Enhancement Algorithm for Non-Uniform Illumination Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-Reference Deep Curve Estimation for Low-Light Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning to Enhance Low-Light Image via Zero-Reference Deep Curve Estimation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.00860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lore, K.G.; Akintayo, A.; Sarkar, S. LLNet: A Deep Autoencoder Approach to Natural Low-light Image Enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 61, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Lu, F.; Wu, J.; Lim, C. MBLLEN: Low-Light Image/Video Enhancement Using CNNs. Br. Mach. Vis. Conf. 2018, 220, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep Retinex Decomposition for Low-Light Enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Kindling the Darkness: A Practical Low-light Image Enhancer. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, Q.; Xu, X.; Cao, X.; Du, J.; Yang, M. Low-Light Image Enhancement via a Deep Hybrid Network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4364–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kim, W.J. DSLR: Deep Stacked Laplacian Restorer for Low-Light Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J. Beyond Brightening Low-light Images. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1013–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, S. Zero-Shot Restoration of Back-lit Images Using Deep Internal Learning. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y. Zero-Shot Restoration of Underexposed Images via Robust Retinex Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, 6–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Xiong, B.; Wang, L.; Ou, Q.; Yu, L.; Kuang, F. RetinexDIP: A Unified Deep Framework for Low-light Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Deep Image Prior. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 128, 1867–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Luo, Z. Retinex-inspired Unrolling with Cooperative Prior Architecture Search for Low-light Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liao, H.M.; Yeh, I.-H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, P.; Hsieh, J. CSPNet: A New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Learning a Deep Single Image Contrast Enhancer from Multi-Exposure Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2049–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Lee, C.; Kim, C.-S. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 965–968. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Guo, J.; Porikli, F.; Pang, Y. LightenNet: A convolutional neural network for weakly illuminated image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 104, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, A.Z. EnlightenGAN: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.06972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, Y.P.; Chan, C.S. Getting to Know Low-light Images with The Exclusively Dark Dataset. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 178, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Method | Total Params | Total Memory | Total Flops | Total MAdd | Total MemR + W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-DCE | 79,416 | 62.00 MB | 10.38 GFlops | 5.21 GMAdd | 143.05 MB |
| Zero-DCE++ | 10,561 | 129.50 MB | 1.32 GFlops | 694.22 MMAdd | 283.04 MB |
| Only CSPNet structure | 5153 | 93.50 MB | 632.68 MFlops | 339.8 MMAdd | 199.02 MB |
| only Ghost module | 5331 | 112.75 MB | 689.96 MFlops | 361.96 MMAdd | 273.52 MB |
| Zero-DCE Tiny | 2731 | 104.75 MB | 353.37 MFlops | 190.51 MMAdd | 215.51 MB |
| Metrics | Original Resolution | 2 × ↓ | 4 × ↓ | 6 × ↓ | 12 × ↓ | 20 × ↓ | 50 × ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | 16.14 | 16.22 | 16.38 | 16.45 | 16.42 | 15.95 | 15.02 |
| FLOPs | 5.82 | 1.46 | 0.355 | 0.158 | 0.039 | 0.014 | 0.002 |
| Metrics | PSNR | SSIM | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBLLEN | 15.02 | 0.52 | 119.14 |
| RetinexNet | 15.99 | 0.53 | 104.81 |
| LightenNet | 13.17 | 0.55 | 140.92 |
| EnlighenGAN | 16.21 | 0.59 | 102.78 |
| Zero-DCE | 16.57 | 0.59 | 98.78 |
| Zero-DCE++ | 16.42 | 0.58 | 102.87 |
| Zero-DCE Tiny | 16.50 | 0.61 | 102.52 |
| Metrics | Runtime (s) | Total Params | Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBLLEN | 13.9949 | 450,171 | TensorFlow (GPU) |
| RetinexNet | 0.1200 | 555,205 | TensorFlow (GPU) |
| LightenNet | 25.7716 | 29,532 | MATLAB (CPU) |
| EnlighenGAN | 0.0078 | 8,636,675 | PyTorch (GPU) |
| Zero-DCE | 0.0025 | 79,416 | PyTorch (GPU) |
| Zero-DCE++ | 0.0012 | 10,561 | PyTorch (GPU) |
| Zero-DCE Tiny | 0.0008 | 2731 | PyTorch (GPU) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y. A More Effective Zero-DCE Variant: Zero-DCE Tiny. Electronics 2022, 11, 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172750
Mu W, Liu H, Chen W, Wang Y. A More Effective Zero-DCE Variant: Zero-DCE Tiny. Electronics. 2022; 11(17):2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172750
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Weiwen, Huixiang Liu, Wenbai Chen, and Yiqun Wang. 2022. "A More Effective Zero-DCE Variant: Zero-DCE Tiny" Electronics 11, no. 17: 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172750
APA StyleMu, W., Liu, H., Chen, W., & Wang, Y. (2022). A More Effective Zero-DCE Variant: Zero-DCE Tiny. Electronics, 11(17), 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11172750






