Abstract
The predominant means of communication is speech; however, there are persons whose speaking or hearing abilities are impaired. Communication presents a significant barrier for persons with such disabilities. The use of deep learning methods can help to reduce communication barriers. This paper proposes a deep learning-based model that detects and recognizes the words from a person’s gestures. Deep learning models, namely, LSTM and GRU (feedback-based learning models), are used to recognize signs from isolated Indian Sign Language (ISL) video frames. The four different sequential combinations of LSTM and GRU (as there are two layers of LSTM and two layers of GRU) were used with our own dataset, IISL2020. The proposed model, consisting of a single layer of LSTM followed by GRU, achieves around 97% accuracy over 11 different signs. This method may help persons who are unaware of sign language to communicate with persons whose speech or hearing is impaired.
1. Introduction
There are various ways of communication or expression, but the predominant mode of human communication is speech; when it is hindered, people must use a tactile-kinesthetic mode of communication instead. In India, the overall percentage of persons with this disability in the population was 2.2 percent from July 2018 to December 2018, according to the National Statistical Office survey report (76th round of the National Sample Survey (NSS) []). Sign language is one of the greatest adaptations for persons with speech and hearing impairments. It is also known as a visual language. Generally, it has five basic parameters: hand shape, orientation, movement, location, and components such as mouth shape and eyebrow movements. Research has been conducted on voice generation using smart gloves [], which could give a voice to sign language movements. However, those who do not know sign language usually undervalue or reject persons with such an impairment because of the lack of proper communication between them. Hence, this paper proposes a system aimed at removing the communication gap and giving every individual a fair and equal chance. It involves taking a video of the person making hand gestures, processing it, and passing it to the proposed model, which predicts words one by one. The system then generates a meaningful sentence out of those words that can then be converted into the language selected by the communicator.
Sign language can be divided into two main categories: static and dynamic. Static signs are steady hand and face gestures, while dynamic signs are further divided into isolated signs and continuous signs. Isolated signs are hand gestures and facial expressions for a single word, i.e., ‘home’, ‘love’, and many more, while continuous signs are a sequence of isolated signs involving both hand gestures and facial expressions, i.e., ‘welcome to my new home’.
There are more than 120 distinct sign languages, such as American sign language, Indian Sign Language, Italian sign language, etc. In the proposed system, the authors used Indian sign language to provide an example []. The dataset for this system was customized; there are 11 static signs and 630 samples in total. The signs that were included are commonly used words, such as hello, goodbye, good morning, etc. The system was designed so that it uses the natural gesture input to create a sign language and then passes this to the system for further pre-processing and processing tasks to predict the exact word that the gesture expressed.
The aim of the present study was to develop a system that recognizes sign language, and that can be used offline. A vision-based approach was developed to obtain the data from the signer. One of the main features of this study is the ability of the system to identify and recognize the words included in IISL2020 (our customized dataset). The IISL2020 dataset consists of 11 words; for each word, there are about 1100 video samples of 16 research participants, including males and females. The IISL2020 dataset was created considering natural conditions—without extra brightness, orientation, background adjustments, gloves, etc. Unlike most sign language datasets, the authors did not use any external help, such as sensors or smart gloves to detect hand movements.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 provides an overview of the current literature on state-of-the-art isolated and continuous SLR (sign language recognition). Section 3 describes the methodology for implementing an isolated SLR system for real-time sign language detection and recognition, which involves pre-processing, feature extraction, training, and testing steps. This research paper proposes a feedback-based learning methodology using these options, based on a combination of LSTM and GRU: (1) a combination of two layers of LSTM and GRU and (2) a combination of a single layer of LSTM with GRU, and vice versa. In Section 4 and Section 5, the custom dataset (IISL2020) is discussed, and the results of the conducted experiments are analyzed. Finally, in Section 6, concluding remarks are made, and future lines of research are proposed.
2. Related Work
Indian Sign Language is a visual–spatial language that was developed in India. Indian Sign Language is a natural language with its own phonology, morphology, and grammar. It uses arm motions, hands, facial expressions, and the body/head, which generate semantic information conveying words and emotions [].
Nandy et al. [] proposed an approach for detecting and recognizing Indian Sign Language gestures from gray-scaled images. In their approach [], a video source that contains signing gestures is converted into gray-scaled frames, from which features are extracted by applying a directional histogram. Lastly, clustering is used to classify the signs, according to their features, into one of the pre-defined classes. The authors achieved a 100% sign recognition rate in their study and concluded that the 36-bin histogram method was more accurate than the 18-bin histogram method.
Mekala et al. [] proposed neural network architecture for recognizing and tracking sign language and generating real-time text from the video stream. The system architecture consists of different phases, such as framing, pre-processing images, extracting the features based on hand movement and hand position, etc. These hand attributes are represented using a point of interest (POI) of the hand []. By using this method, 55 different features were extracted, which were used as an input for the neural network architecture proposed by the authors, consisting of CNN layers that predicted the signs. In their study, they trained and tested the model on the English alphabet, from A to Z, and claimed to achieve a 100% recognition rate and 48% of noise immunity.
Chen [] proposed a model with a self-made dataset of 1200 samples of ten static signs/letters. In order to recognize the gestures, pre-processing was performed initially through edge segmentation to detect the edges of the hand, and for skin color segmentation, the approach was to convert RGB images to YUQ or YIQ color spaces []. Then, the fingers were detected from the already identified hand using the convex hull method. Finally, neural networks were used as the classification method. The final accuracy obtained by this model was 98.2%.
Sharma et al. [] developed a system on the basis of the Indian Sign Language for communicating with persons who had impaired speech or hearing. First, the data were pre-processed after capturing the image by converting it from RGB to grayscale, using a Matlab environment []. Then, a Sobel detector was used to detect the edges of the image using a 3 × 3 filter. Finally, a hierarchical centroid method was applied to the reduced image with 600 elements; 124 features were obtained using this method. The used classification techniques were KNN and neural networks. The accuracy obtained by this methodology was 97.10%.
Agarwal et al. [] aimed to bridge the gap between people with speech impairment and people with normal speech abilities by using a sensor glove for signing, processing those signs, and presenting the output in a meaningful sentence. The subjects performed the gestures using the sensor gloves []. The gestures were matched with the database, and then the recognized gesture was passed on to be parsed to generate a sentence. In version 1 of the application, the accuracy was 33.33%. In version 2, a keyword was added for the required tense; hence, 100% accuracy was achieved to tackle simple and continuous tenses.
Wazalwar and Shrawankar [] proposed a method for the interpretation of sign language from input video through framing and segmentation []. Their approach used the CamShift algorithm for tracking and the P2DHMM algorithm for hand tracking. In order to identify the signs, a Haar Cascade classifier was used. Once the sign was recognized, the WordNet POS tagger assigned a tag to each word, and the LALR parser framed the sentence and provided the output in the form of a text, creating a meaningful sentence in English.
Shivashankara and Srinath [] developed a system based on American Sign Language (ASL) for recognizing signs/gestures. The authors proposed a model in which they used YCbCr, which optimized the performance of skin color clustering []. This model was used for image pre-processing. In order to recognize the gesture, the centroid of the hand was identified in the pre-processed image; then, the peak offset was found to identify the gesture. The overall accuracy of this model was 93.05%.
Camgoz et al. [] proposed a system that showed how sign language and its translation into spoken language is not one-to-one mapping but instead sequence-to-sequence mapping. The authors introduced a new vision method in which they mirrored the tokenization and embedding steps of the standard neural machine translation. The neural machine translation step, which translates sign videos to spoken language, integrates the CNN architecture [] with an attention-based encoder and decoder that models the conditional probability of generating a spoken language from a given signing video. The authors started from word embedding and translated a sparse vector into a denser form where words with similar meanings were closer. The encoder-decoder phase was used to maximize the conditional probability. Encoding generated a fixed-size vector of the sign videos’ features. The inputs were the previously hidden state and word embedding in the decoding phase. This helped to predict the next word. In addition to this, to avoid the problems of long-term dependencies and vanishing gradients, the authors added an attention mechanism in the decoding phase. They created a continuous sign language translation dataset called PHOENIX14T.
Mariappan and Gomathi [] proposed a novel approach for recognizing real-time signing for Indian Sign Language (ISL) []. For this, they proposed an approach consisting of a region of interest (ROI)-based method for identifying and tracking signs using the skin segmentation feature of OpenCV. For sign prediction, they employed a fuzzy C-means (FCM) clustering technique. They collected a dataset of 80 words and 50 sentences from 10 different people for training and testing purposes. To reduce noise from the digital source, they also applied filtering on the colored images and morphological operations on the binary image generated after applying skin segmentation to enhance the features. As a result, they achieved an accuracy of 75% in recognizing 40 words from ISL using the FCM technique.
Mittal et al. [] proposed a system that used an LSTM model with leap motion for continuous sign language recognition []. They employed a four-gated LSTM cell with a 2D CNN architecture for sign sentence recognition and assigned a particular label to every word. When the three basic gates were used as an input gate, a forget gate that took the output at the t-1 time generated output at the output gate and returned the label showing the word that was specifically associated with that label. They added a special symbol, $, which indicated the transition between the two consecutive signs in the video. The RESET flag was used when they encountered the transition between two signs, which was indicated by the $ sign []. They trained this modified LSTM model over a dataset and achieved a maximum accuracy of 72.3% using a 3-layer LSTM model for sign sentence recognition. For sign word recognition, the achieved accuracy was 89.50%.
De Coster et al. [] used a transformer network to recognize sign language from videos, including non-manual parts such as the mouth and eyebrow orientation []. They proposed a pose transformer network, video transformer network, and multimodal transformer network to recognize signs over different neural networks.
Jiang et al. [] introduced a multi-model-based sign language recognition system in which the authors used the skeleton base graph technique to identify isolated signs. SL-GCN and SSTCN models were used to generate skeleton key points and feature extraction, and the authors proposed a SAM-SLR framework to recognize isolated signs []. The proposed framework was evaluated on the AULTS dataset.
Liao et al. [] proposed BLSTM-3DRN to recognize dynamic sign language. The authors used a bi-directional LSTM model that is serialized in three phases: hand localization, the extraction of spatiotemporal features, and finally, the identification of gestures over DEVISIGN_D (Chinese hand sign language) [].
Adaloglou et al. [] introduced I3D, a ResNet with B-LSTM, for the continuous sign language recognition of syntax formation. The authors applied the proposed framework over different data of RGB + D, especially in the case of Greek sign language, with three annotation levels []. Table 1 shows the performance comparison of different models of deep learning, especially the combination of CNN-LSTM over different data sets.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of various deep learning models/methods.
Mathieu De Coster et al. [] also used Pose Transformer by combining pose LSTM and Transformer Network. This work recognizes the signs from video frames. The proposed method was tested (using the proposed methodology as keypoint estimation using OpenPose) on the Flemish Sign Language corpus. It obtained an accuracy of 74.7% for 100 classes.
The proposed research work introduced a methodology (combining various deep learning algorithms, especially LSTM and GRU) for Indian Sign Language recognition, which does not require any specific environment or camera set-up for inference. The real-time Indian scenario was taken into consideration in the data set and experiments. The isolated signs were considered in the experiments, and the four different combinations of LSTM and GRU were used in the simulation.
3. Methodology
In proposals to solve the problem of gradient vanishing, an RNN structure (using forgetting units such as long short-term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent units (GRU)) is usually proposed to enable the storage units. Such a mechanism is used to determine when to forget certain information and determine the optimal time delay. The methodology proposed in this research employs a combination of GRU and LSTM; given the known features of these methods, a combination may be expected to detect and identify sign language gestures from a video source and to generate the associated English word. In this method, the video source is provided as an input, consisting of ISL sign-language gesture sequences. The primary purpose of this system is to identify the words from signing gestures used in real life. Therefore, the foremost task is to divide the video file containing the sequence of ISL gestures for various words into separate sub-section videos containing different words. This is performed by identifying the start and end of each different gesture. After dividing up the videos, the next step is to divide the resulting subsection videos into frames. The frames are generated by applying sampling techniques to the video sequence. In order to extract the features from the frames, InceptionResNetV2 was used in the proposed architecture [,,]. InceptionResNetV2 performs better when compared to its earlier variant. The video frames are resized and passed to the inceptionResNetV2 model, using mobile net pre-trained weights to extract the features from the gestures. The output of the inceptionResNetV2 model is an array consisting of the feature vector. These features are passed to a recurrent neural network to predict the correct word.
Proposed LSTM-GRU-Based Model
For the given application, Figure 1 displays the proposed model in graphics. The authors used different GRU and LSTM to compare and find the best architecture and the appropriate hyper-parameters. These models were trained using a custom dataset for ISL that was created by the authors. For each video sequence, the following steps were performed, as per Figure 1:
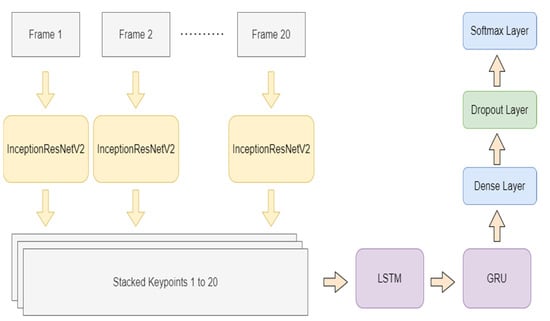
Figure 1.
Multi-layer system architecture using InceptionResNetV2, LSTM, and GRU for sign recognition in video frames.
- The feature vectors are extracted using InceptionResNetV2 and passed to the model. Here, the video frames are classified into objects with InceptionResNet-2; then, the task is to create key points stacked for video frames;
- The first layer of the neural network is composed of a combination of LSTM and GRU. This composition can be used to capture the semantic dependencies in a more effective way;
- The dropout is used to reduce overfitting and improve the model’s generalization ability;
- The final output is obtained through the ‘softmax’ function.
The GRU and LSTM methods are used because of their ability to remember previous inputs with the help of gates. The corresponding word is learned on the basis of the previous activation and current input feature, and the weights are adjusted accordingly. The training dataset is further split into 80:20 ratios, sorting the data into training and validation datasets. The validation dataset can be useful to test the learning achieved by the model after each epoch. By proceeding in this way, the training process may be monitored and validated, and it is possible to check whether the training was completed correctly. K-fold cross-validation is used with ten folds to confirm that the model is performing accurately on the dataset. Each model was trained with the help of 10 different combinations of the training set and cross-validation set.
Hochreiter and Schmidhuber proposed long short-term memory [] (a development of RNN) to overcome the previously described shortcomings of RNNs by adding more interactions per module (or cell). LSTM is a type of RNN that can learn new things with long-term dependencies and can memorize information for extended periods. The LSTM model (as depicted in Figure 2) is organized in a chain structure. Nonetheless, the structure of a repeated module may be different for different applications. Rather than using a single neural network, a one-of-a-kind communication system with four interconnected layers is proposed by Le Xuan []. The LSTM’s structure is as follows: ht−1 is the previous output block; Ct−1 is a memory block of the previous block; xt is an input vector; ct is a memory block from the current block; ht is the output block of the current block.
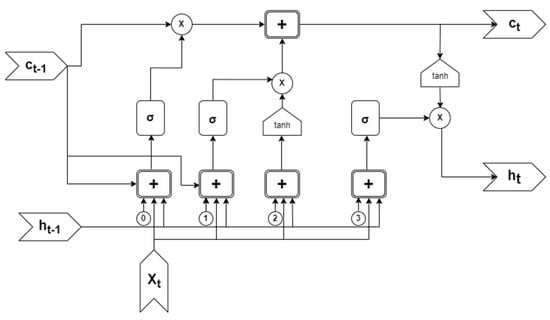
Figure 2.
The basic diagram of the long short−term memory (LSTM) neural network (Yan []).
Similar to LSTM, GRUs are used for enhancement in the hidden cells. GRUs were developed to overcome the vanishing gradient problem by retaining prior memory to aid future decision-making. The GRU was created in response to a query (whether all of the components found in the LSTM are required for managing amnesia and the unit time scale) [,,,].
The GRU has gating units that modulate the flow of information inside the unit without having separate memory cells. Activation in GRU can be represented as considering as the previous activation [,]:
where an update gate decides how much the unit updates its activation The update gate can be computed using Equation (2): be the input received, W and U are weight vectors,
The parameters are shown in Figure 3, covering the detailed structure of LSTM-GRU along with other layers, such as dense layers and dropout layers. After extracting the requisite features, the values are passed to the input layer with a shape of (40, 2048). The next steps are followed, as per Figure 3:
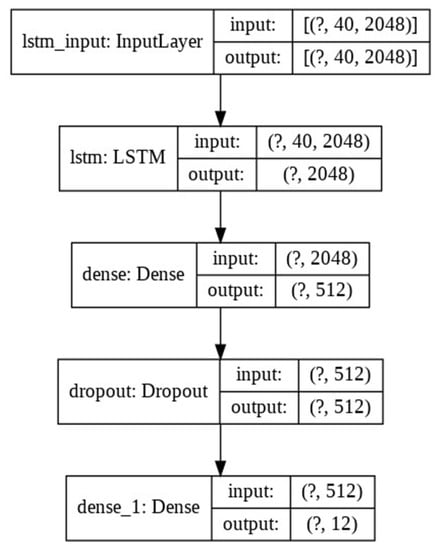
Figure 3.
The LSTM model architecture.
- The LSTM layer of 1536 units, 0.3 dropouts, and a kernel regularizer of ′l2′ receive data from the input layer;
- Then, the data are passed from the GRU layer using the same parameters;
- Results are passed to a fully connected dense layer;
- The output is fed to the dropout layer, with an effective value of 0.3.
The model has a training batch size of 16 and has an activation function ‘softmax’ with ten folds. Each fold has ten epochs for every single layer of LSTM or GRU. The final output class is predicted after the data are passed from the dense layer, with an activation function as ‘softmax’. The architecture with a two-layer neural network (with a hidden layer of 100 LSTM/GRU units) has a classifying layer with 12 neurons. The inputs were 2048 dimensional sequences of 40 time steps. The proposed method aims to provide optimized performance regarding Indian Sign Language and recognizes isolated Indian signs, using the sequential model in a combination of LSTM and GRU. Parameter values are common over the different combinations of LSTM and GRU (LSTM-LSTM, GRU-GRU, LSTM-GRU, GRU-LSTM), which helps the system recognize response times for the different signs (testing phase) on the same platform. Moreover, all the input frames (from the IISL2020 dataset) include real-time scenarios (combining daylight and night (artificial light) samples), which help the data to be used in real-time sign language recognition.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Dataset
We created our dataset (IISL2020) for training and testing. The dataset was collected from 16 subjects aged between 20 and 25 and included both female and male participants. We obtained the relevant data for specific dynamic-based isolated gestures. All the video samples have an average of 28 FPS and a resolution of 1920 × 1080, with an average length of 2 s. The dataset consisted of 11 words; for each word, about 1100 video samples were created with the 16 subjects. This dataset was created under natural conditions—without any extra brightness, orientation, Kinect sensor, background adjustments, gloves, etc. The dataset can be found here: https://github.com/DeepKothadiya/Custom_ISLDataset/tree/main (the authors’ permission is required to access the dataset) (accessed on 25 March 2022). Unlike most sign language datasets, these can be used as the unique dimensions under consideration. Furthermore, the authors did not use any external help from sensors or smart gloves to detect hand movements, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Samples from the custom Indian Sign Language (ISL) dataset (IISL2020).
4.2. Results
During this study, the authors considered six different combinations of GRU and LSTM: single-layer LSTM, double-layer LSTM (LSTM-LSTM), single-layer GRU, double-layer GRU (GRU-GRU), GRU followed by LSTM (GRU-LSTM), and LSTM followed by GRU (LSTM-GRU). Following the calculations, Table 2 shows the averages obtained from the K-fold cross-validations for each model. This table shows the accuracy of all 11 classes per model: the LSTM-GRU model’s accuracy is the highest. The model was developed using the Keras/TensorFlow libraries. The training was performed on a SuperServer 7049GP-TRT workstation using a second-generation Intel Xeon scalable processor with 28 cores, with a 16GB GDDR6 GPU. Initially, the video was divided into frames for feature extraction using InceptionResNetV2, resulting in a NumPy array value sequenced to the training model. Then, the identification of sign language detection was performed. The results can be further improved by increasing the size of the dataset and incorporating more samples per word, providing more effective samples for the model to train on.

Table 2.
Experimental results, with the various parameters.
Moreover, other limitations affected the accuracy of the results, such as the resolution and orientation of the camera used. In order to create the dataset, videos were recorded using mobile phones, which have lower resolution than a high-definition digital camera. Moreover, not using any external aid in terms of gloves or sensors also affects the performance. However, not using a fixed resolution, orientation, or external aid helps us to imitate the real-world scenario in a more realistic manner. As Table 2 shows, the performed methodologies have an impactful recognition rate over different sign language datasets and IISL2020 (our dataset). The recognition rate may vary depending on the dataset environment (either using a real-time (normal) environment or when recorded in control environments, using a green background, or using sensors and gloves). Our dataset (IISL2020) and learning models give good results for real-time sign detection and recognition in the Indian Sign Language scenario.
Figure 5 shows the heat maps for the confusion matrix of different combinations of the proposed model, such as the two-layer GRU, two-layer LSTM, GRU followed by LSTM, and LSTM followed by GRU. The confusion matrix is used to evaluate the classification model (LSTM/GRU). The heat map represents the confusion matrix so that it can identify the classification rate for input data (isolated sign language), and it can represent false identification.
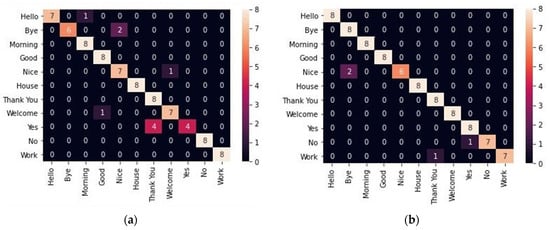
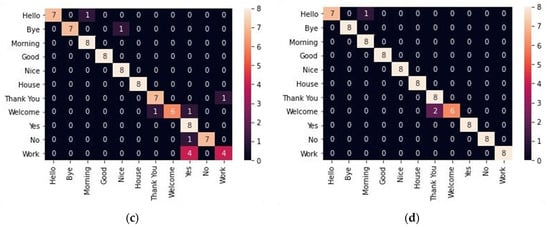
Figure 5.
Validation Confusion matrix for all four combinations with fold value 1, the rest of the parameters are the same as in the training: (a) GRU-GRU; (b) LSTM-LSTM; (c) GRU-LSTM; (d) LSTM-GRU.
The authors implemented the different models using various datasets, such as American Sign Language (ASL), Greek Sign Language (GSL), the Ankara University Turkish Sign Language dataset (AUTSL), and IISL2020 (generated by the authors). As a result, it can be seen from Figure 6 that the proposed research model has an accuracy rate of approximately 95% at correctly identifying the signs from various datasets. The parameters for training and testing are the same as the initial simulations (mentioned in Figure 3). (40,2048) is taken as input frame over the 100 hidden layers of each LSTM and GRU, dropout, fold, and learning rate.
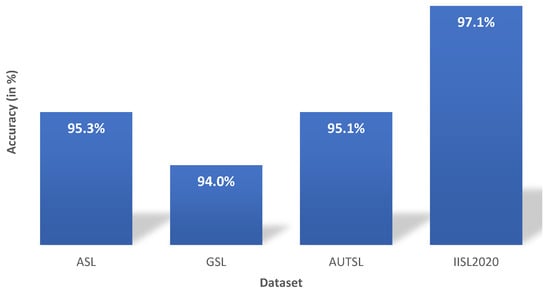
Figure 6.
Implementation of the proposed model using different benchmark datasets.
5. Discussion and Limitations
Any standard dynamic sign language dataset is challenging due to its high intricacy; it is particularly challenging when working on specific region-based languages such as Indian Sign Language. Table 1 gives details of recent work published on sign language recognition with deep learning models such as LSTM and CNN. The datasets used in the research work were designed in the ideal environment or were stranded. In this research, the proposed methodology used a dataset that was recorded in a control-free environment and executed with the proposed methodology, which is a combination of LSTM followed by GRU, and achieves an accuracy of 97% in sign identification from the ISL custom dataset (IISL2020). In a true, real-time detection environment, this is the best reported performance so far in the area of Indian Sign Language recognition.
The proposed model can be further enhanced by improving the classes of the dataset, the sets of words, video samples, etc. We believe that collecting data from professional signers make the proposed model more generalized. Improvement is also needed in terms of non-stable and angular input data frames. The proposed methodology can be simulated for continuous sign language recognition with minor experimental changes. Different levels of brightness can be a challenge for sign recognition. However, the researchers may use image augmentation at the data preparation stage to generalize the video frames for data from a low-brightness environment.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents Indian Sign Language recognition using LSTM and GRU on an IISL2020 dataset of different hand gestures. The proposed model outperforms all others currently available for ISL on commonly used words such as ‘hello’, ‘good morning’, ‘work’, etc. Furthermore, increasing the number of layers in the LSTM and GRU, and applying LSTM followed by GRU, helps the model achieve higher accuracy in recognition of ISL.
In future research, the model’s accuracy could be improved by developing different datasets under ideal conditions, changing the orientation of the camera, and even using wearable devices. Currently, the developed models work in terms of isolated signs; this approach could be utilized for interpreting continuous sign language that leads to syntax generation, especially in the context of ISL. The use of vision transformers can lead to more accurate results than those of feedback-based learning models.
Author Contributions
D.K.: Data Curation, Investigation, Writing—original draft, C.B.: Methodology, Project administration, Writing—review and editing, K.S.: Data curation, Investigation, Software, K.P.: Data curation, Investigation, Software, A.-B.G.-G.: Methodology, Writing—review and editing, J.M.C.: Methodology, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the Institute for Business Competitiveness of Castilla y León and the European Regional Development Fund under grant CCTT3/20/SA/0002 (AIR-SCity project).
Data Availability Statement
The dataset can be found here: https://github.com/DeepKothadiya/Custom_ISLDataset/tree/main (the authors’ permission is required when accessing the dataset) accessed on 25 March 2022.
Acknowledgments
Our past UG students played essential role for dataset generation. We are thankful to our students Riya Patel, Yashvi Raythatha and Siddharth Patel for their contribution and active involvement in dataset generation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation. Available online: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1593253 (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Manware, A.; Raj, R.; Kumar, A.; Pawar, T. Smart Gloves as a Communication Tool for the Speech Impaired and Hearing Impaired. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2017, 4, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wadhawan, A.; Kumar, P. Sign language recognition systems: A decade systematic literature review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 785–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastratis, I.; Chatzikonstantinou, C.; Konstantinidis, D.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Daras, P. Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Sign Language. Sensors 2021, 21, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandy, A.; Prasad, J.; Mondal, S.; Chakraborty, P.; Nandi, G. Recognition of Isolated Indian Sign Language Gesture in Real Time. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2010, 70, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mekala, P.; Gao, Y.; Fan, J.; Davari, A. Real-time sign language recognition based on neural network architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE 43rd Southeastern Symposium on System Theory, Auburn, AL, USA, 14–16 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.K. Sign Language Recognition with Unsupervised Feature Learning; CS229 Project Final Report; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Pal, R.; Sahoo, A. Indian sign language recognition using neural networks and KNN classifiers. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2014, 9, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.R.; Agrawal, S.B.; Latif, A.M. Article: Sentence Formation in NLP Engine on the Basis of Indian Sign Language using Hand Gestures. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 116, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wazalwar, S.S.; Shrawankar, U. Interpretation of sign language into English using NLP techniques. J. Inf. Optim. Sci. 2017, 38, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivashankara, S.; Srinath, S. American Sign Language Recognition System: An Optimal Approach. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 2018, 10, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Camgoz, N.C.; Hadfield, S.; Koller, O.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Neural Sign Language Translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Muthu Mariappan, H.; Gomathi, V. Real-Time Recognition of Indian Sign Language. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Data Science, Haryana, India, 6–7 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Kumar, P.; Roy, P.P.; Balasubramanian, R.; Chaudhuri, B.B. A Modified LSTM Model for Continuous Sign Language Recognition Using Leap Motion. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 7056–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, M.; Herreweghe, M.V.; Dambre, J. Sign Language Recognition with Transformer Networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2020), Marseille, France, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 6018–6024. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, K.; Fu, Y. Skeleton aware multi-modal sign language recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 21–24 June 2021; pp. 3413–3423. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Xiong, P.; Min, W.; Min, W.; Lu, J. Dynamic Sign Language Recognition Based on Video Sequence with BLSTM-3D Residual Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38044–38054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaloglou, N.; Chatzis, T. A Comprehensive Study on Deep Learning-based Methods for Sign Language Recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, C.; Geetha, M. CNN and Stacked LSTM Model for Indian Sign Language Recognition. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1203, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07261. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Martinez, C.; Visuña, L.; Khandhar, H.; Bhatt, C.; Carretero, J. Detection and Analysis of COVID-19 in medical images using deep learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likhar, P.; Bhagat, N.K.; Rathna, G.N. Deep Learning Methods for Indian Sign Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 10th International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 9–11 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.-H.; Hung, V.; Ho, G.L.; Sungho, J. Application of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Neural Network for Flood Forecasting. Water 2019, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, S. Understanding LSTM and Its Diagrams. Available online: https://medium.com/mlreview/understanding-lstm-and-its-diagrams-37e2f46f1714 (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Chen, J. CS231A Course Project Final Report Sign Language Recognition with Unsupervised Feature Learning. 2012. Available online: http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs231a_autumn1213_internal/project/final/writeup/distributable/Chen_Paper.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).