A 1/f Noise Detection Method for IGBT Devices Based on PSO-VMD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Theory of 1/f Noise in IGBT
3. Principle of PSO-VMD Algorithm
3.1. Variational Mode Decomposition Algorithm (VMD)
- Initialize , , , and n. Set the initial value to 0;
- Define and execute the entire loop;
- Define the number of cycles as . Perform the first and second loops of the inner layer according to the step size of 1. Update , Formulas (8) and (9) until .
- Update according to in the outer loop.
3.2. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm (PSO)
3.3. PSO-VMD Algorithm
- First, the parameters of the particle swarm algorithm are set to complete an optimal parameter combination search;
- After optimization of the first particle swarm, a set of parameter combinations is obtained. The initial position of the next PSO algorithm particle is set by , and the quadratic particle swarm optimization is performed. Generally, the parameter combination is considered to be the global optimal solution;
- Consequently, is adopted to set the value of the VMD model penalty parameter and the number of the decomposition modulus. Thereafter, use is made of the VMD model of the optimized parameter to realize the 1/f signal detection;
- Lastly, the measured signal is processed by the VMD algorithm, and several modal components are obtained. The component IMFk with the largest output signal-to-noise ratio is selected; that is, IMFk is regarded as the 1/f signal. This completes the detection of the 1/f signal.
4. PSO-VMD Simulation Experiment
4.1. Experimental Condition
4.2. Experimental Process
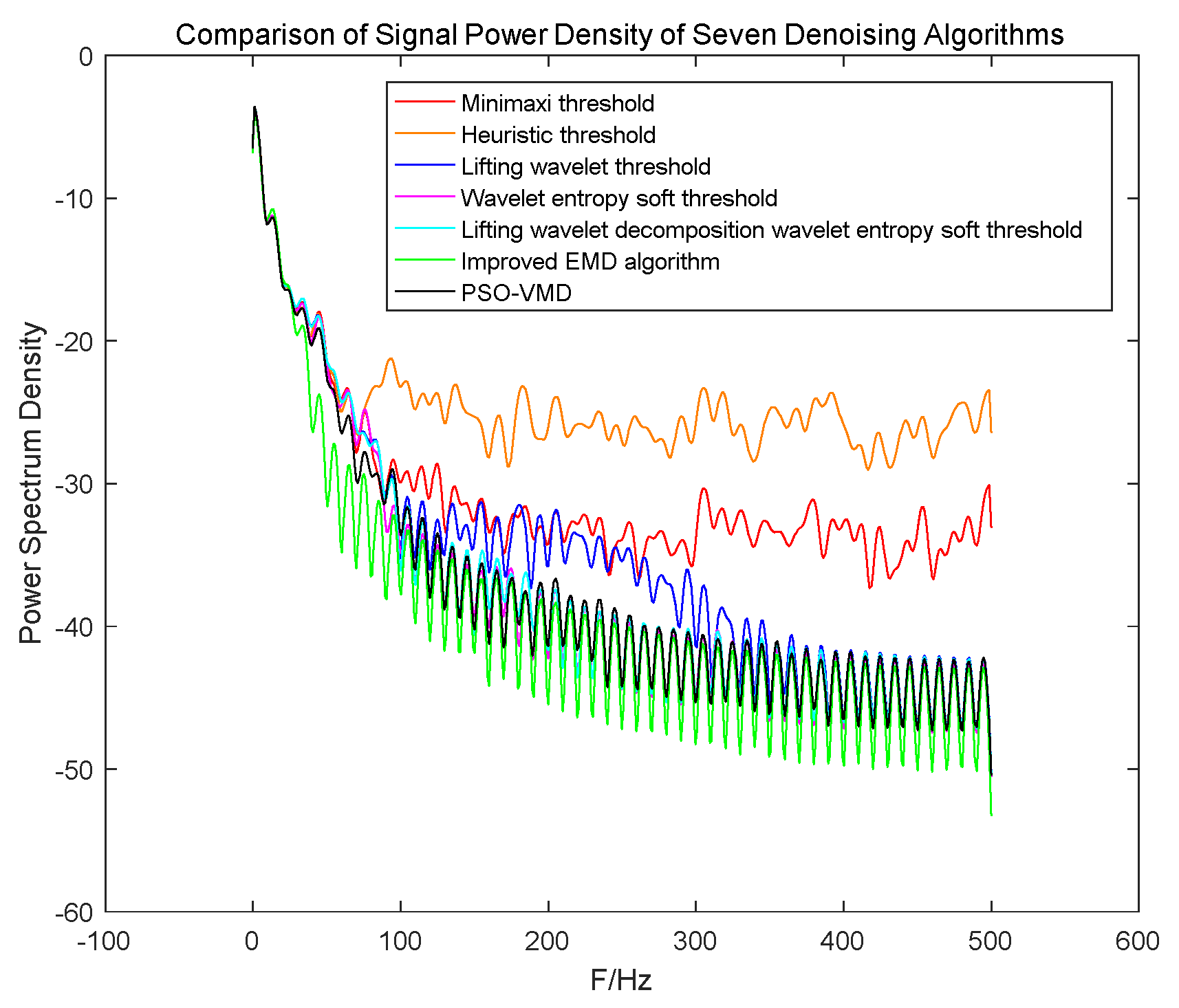
4.3. Simulation Algorithm Performance Analysis
5. Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Musallam, M.; Johnson, C.M.; Yin, C.; Lu, H.; Bailey, C. In-service life consumption estimation in power modules. In Proceedings of the 13th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Poznan, Poland, 1–3 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Xiang, D.; Bryant, A.; Mawby, P.; Ran, L.; Tavner, P. Condition monitoring for device reliability in power electronic converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 25, 2734–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Makinwa, K.A.; Huijsing, J.H. A chopper current-feedback instrumentation amplifier with a 1 mHz 1/f noise corner and an AC-coupled ripple reduction loop. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2009, 44, 3232–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, H. Low-frequency noise study in electron devices: Review and update. Microelectron. Reliab. 2003, 43, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongbiao, Z.; Haiyan, H.; Youbing, F. Study on weak signal detection method based on wavelet entropy. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 28, 2078. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.J.; Yan, Z.J.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, X.H.; Cheng, D. Signal de-noising based on empirical mode decomposition and wavelet soft threshold. J. Qingdao Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 464–467. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Xiang, Y.; Qian, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, S. Noise source identification of diesel engine based on variational mode decomposition and robust independent component analysis. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 116, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zi, Y.; Pan, J. Independence-oriented VMD to identify fault feature for wheel set bearing fault diagnosis of high speed locomotive. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, C.J.; Lenahan, P.M.; Lelis, A.J. An electrically detected magnetic resonance study of performance limiting defects in SiC metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 14506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, C.T.; Hielsher, F.H. Evidence of the Surface Origin of the 1/f Noise. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 17, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, F.M. Characterization of low 1/f noise in MOS transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1971, 18, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaubert, P.; Teramoto, A.; Sugawa, S. 1/f Noise Performances and Noise Sources of Accumulation Mode Si(100) n-MOSFETs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials, Sapporo, Japan, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 96–97. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, B.L.S.; Inaba, F.K.; Salles, E.O.T.; Ciarelli, P.M. Outlier Robust Extreme Machine Learning for multi-target regression. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 140, 112877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berghout, T.; Mouss, L.H.; Kadri, O.; Saïdi, L.; Benbouzid, M. Aircraft engines remaining useful life prediction with an improved online sequential extreme learning machine. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, J.; Han, J. Fault diagnosis method based on BP neural network. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2002, 06, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. The development of IGBT devices. Power Electron. Technol. 2012, 12, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, Y.; Sato, S. Theoretical Models for Low-Frequency Noise Behaviors of Buried-Channel MOSFETs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE SOI-3D-Subthreshold Microelectronics Technology Unified Conference (S3S), Burlingame, CA, USA, 16–19 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Hitchcock, C.W.; Stum, Z.; Dahal, R.P.; Bhat, I.B.; Chow, T.P. Operating Principles, Design Considerations, and Experimental Characteristics of High-Voltage 4H-SiC Bidirectional IGBTs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2016, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. A Low-Noise Chopper Amplifier Designed for Multi-Channel Neural Signal Acquisition. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2019, 54, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Chen, C.; Volker, P.; Naayagi, R.T.; Ji, B. Gate–Emitter Pre-threshold Voltage as a Health-Sensitive Parameter for IGBT Chip Failure Monitoring in High-Voltage Multichip IGBT Power Modules. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 9, 9158–9169. [Google Scholar]










| Test Number | Broadband Voltage (5 Hz–100 Hz) (V) | Narrowband Noise (V2/Hz) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Hz | 10 | 100 | 1000 | ||
| Normal device group | 1.16 × 10−7 | 5.76 × 10−16 | 1.28 × 10−16 | 7.29 × 10−17 | 8.91 × 10−17 |
| Aging test device group 1 | 2.56 × 10−6 | 4.95 × 10−13 | 8.62 × 10−14 | 2.23 × 10−14 | 6.65 × 10−15 |
| Aging test device group 2 | 5.32 × 10−6 | 6.28 × 10−13 | 9.79 × 10−14 | 2.25 × 10−14 | 6.33 × 10−15 |
| Genmax | Sizepop | c1 | c2 | Vmax | Vmin | Popmax | Popmin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 80 | 1.49445 | 1.49445 | 1 | −1 | 40 | 2 |
| VMD Algorithm for Optimizing Parameters to Detect 1/f Noise | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal to Noise Ratio | SNR | MSE | Penalty Parameterα | Decomposition Modulus K |
| 1.44 dB | 6.3891 | 0.6648 | 37 | 4 |
| −3.56 dB | 4.5942 | 0.8043 | 28 | 4 |
| −8 dB | 2.9838 | 1.0025 | 4 | 8 |
| Signal to Noise Ratio | Parameter | Improved EMD Algorithm | Heuristic Threshold | Minimaxi Threshold | Lifting Wavelet Threshold | Wavelet Entropy Soft Threshold | Lifting Wavelet Decomposition Wavelet Entropy Soft Threshold | PSO-VMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.44 dB | SNR | 3.8410 | 3.5747 | 5.6157 | 5.8679 | 5.8219 | 5.9898 | 6.3891 |
| MSE | 0.8099 | 1.1892 | 0.7777 | 0.7353 | 0.724 | 0.7159 | 0.6649 | |
| −3.56 dB | SNR | 3.0834 | 1.0235 | 2.0647 | 3.7093 | 3.8175 | 3.9327 | 4.5942 |
| MSE | 0.9235 | 2.6333 | 1.6485 | 1.0566 | 1.0077 | 1.0029 | 0.8043 | |
| −8 dB | SNR | 0.6377 | 0.3380 | 0.5647 | 1.8885 | 2.0183 | 2.0942 | 2.9838 |
| MSE | 1.1294 | 4.6011 | 3.3930 | 1.6247 | 1.5141 | 1.5134 | 1.0025 |
| Signal to Noise Ratio | Parameter | Improved EMD Algorithm | Heuristic Threshold | Minimaxi Threshold | Lifting Wavelet Threshold | Wavelet Entropy Soft Threshold | Lifting Wavelet Decomposition Wavelet Entropy Soft Threshold | PSO-VMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.44 dB | SNR | 3.8410 | 3.5747 | 5.6157 | 5.8679 | 5.8219 | 5.9898 | 6.3891 |
| MSE | 0.8099 | 1.1892 | 0.7777 | 0.7353 | 0.724 | 0.7159 | 0.6649 | |
| −3.56 dB | SNR | 3.0834 | 1.0235 | 2.0647 | 3.7093 | 3.8175 | 3.9327 | 4.5942 |
| MSE | 0.9235 | 2.6333 | 1.6485 | 1.0566 | 1.0077 | 1.0029 | 0.8043 | |
| −8 dB | SNR | 0.6377 | 0.3380 | 0.5647 | 1.8885 | 2.0183 | 2.0942 | 2.9838 |
| MSE | 1.1294 | 4.6011 | 3.3930 | 1.6247 | 1.5141 | 1.5134 | 1.0025 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Chen, X.-j.; Zhu, M.-y. A 1/f Noise Detection Method for IGBT Devices Based on PSO-VMD. Electronics 2022, 11, 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11111722
Wu J, Chen X-j, Zhu M-y. A 1/f Noise Detection Method for IGBT Devices Based on PSO-VMD. Electronics. 2022; 11(11):1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11111722
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jie, Xiao-juan Chen, and Mei-yue Zhu. 2022. "A 1/f Noise Detection Method for IGBT Devices Based on PSO-VMD" Electronics 11, no. 11: 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11111722
APA StyleWu, J., Chen, X.-j., & Zhu, M.-y. (2022). A 1/f Noise Detection Method for IGBT Devices Based on PSO-VMD. Electronics, 11(11), 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11111722





