Digital Addiction: Systematic Review of Computer Game Addiction Impact on Adolescent Physical Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
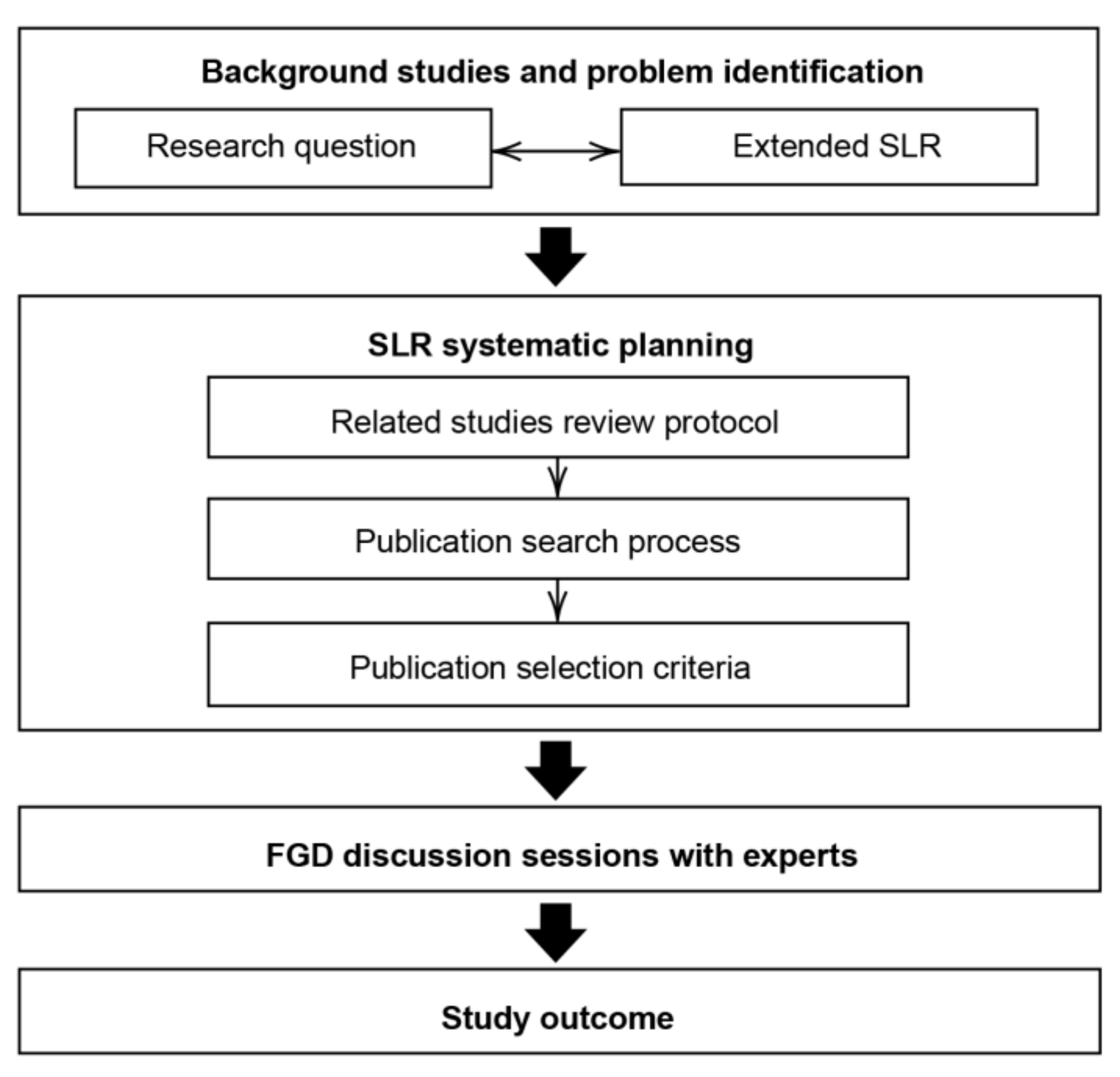
2. Systematic Planning
Research Questions
3. Methodology
3.1. Focus Group Discussion
3.1.1. Group 1: Medical Experts
3.1.2. Group 2: Professional Game Experts
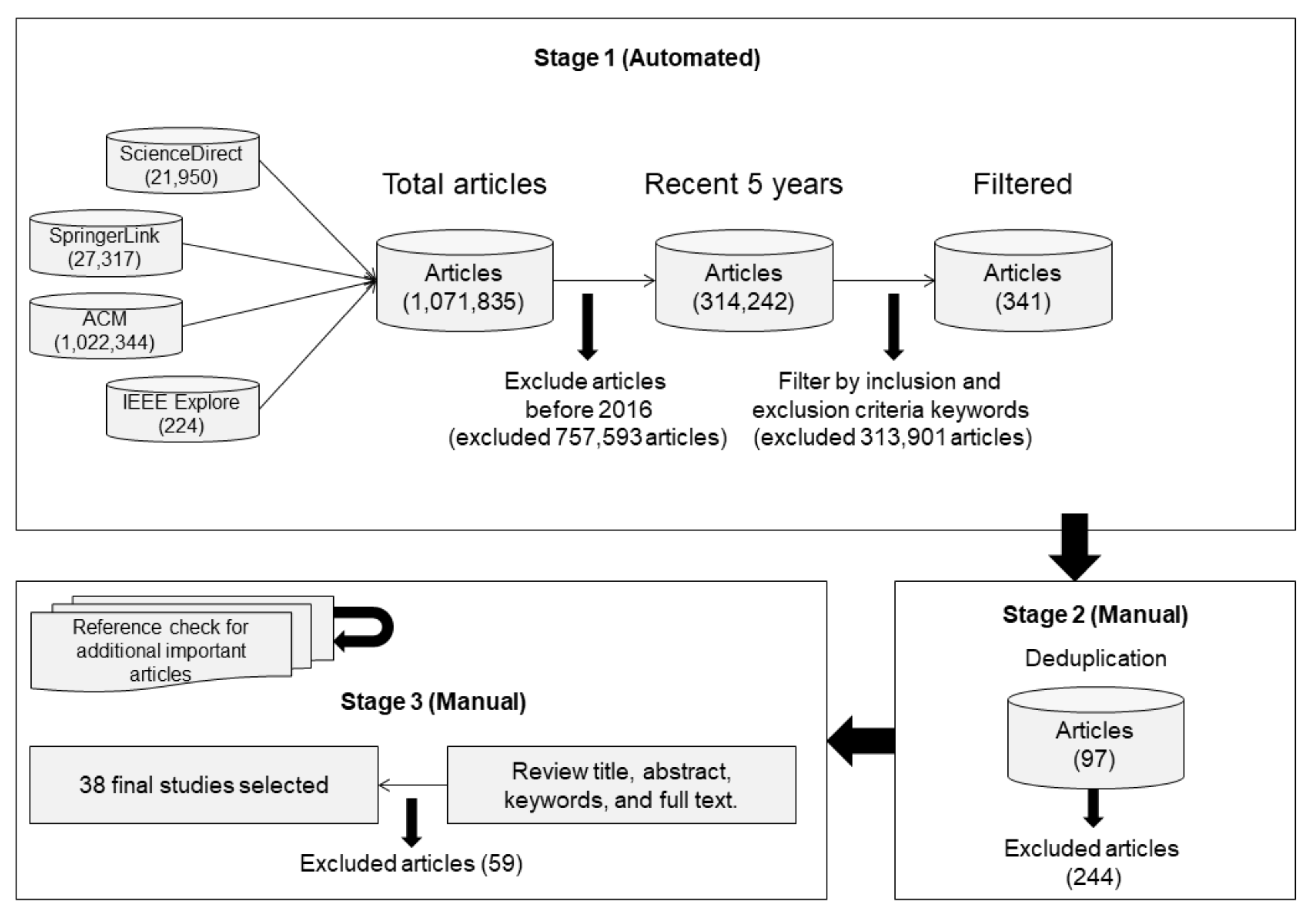
3.2. Literature Search
3.2.1. The Review Protocol
3.2.2. Database and Selection Criteria
3.2.3. Search Strategy
3.2.4. Publication Selection
3.2.5. Data Extraction
3.2.6. Risk of Bias across Studies
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. RQ1: Digital Addiction (DA)
4.1.1. RQ1.0: What Is Addiction?
4.1.2. RQ1.1: What Is DA?
4.1.3. RQ1.2: What Are the Causes of DA?
- Achievers—always aim to achieve the goals set in the computer game (such as ranking higher in levels, reputations, and collection of treasure).
- Explorers—players are primarily interested in the study of the environment of the simulated world (such as geography and physics).
- Socializers—are interested in interacting with another player—either to impose themselves or to promote themselves.
- Killers—keep their interaction alive with other players—they keep communication and role-play active for teamwork.
4.1.4. RQ1.3: How Does DA Impact an Addict?
4.1.5. RQ1.4: How Does the Withdrawal of the Addictive Substance Impact an Addict?
4.2. RQ2: Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD)
4.2.1. RQ2.0: What Is IGD?
4.2.2. RQ2.1: What Are the Causes of Computer Game Addiction?
4.2.3. RQ2.2: What Are the Effects of Excessive Computer Gaming/IGD?
4.2.4. RQ2.3: Is IGD Diagnosable and Curable?
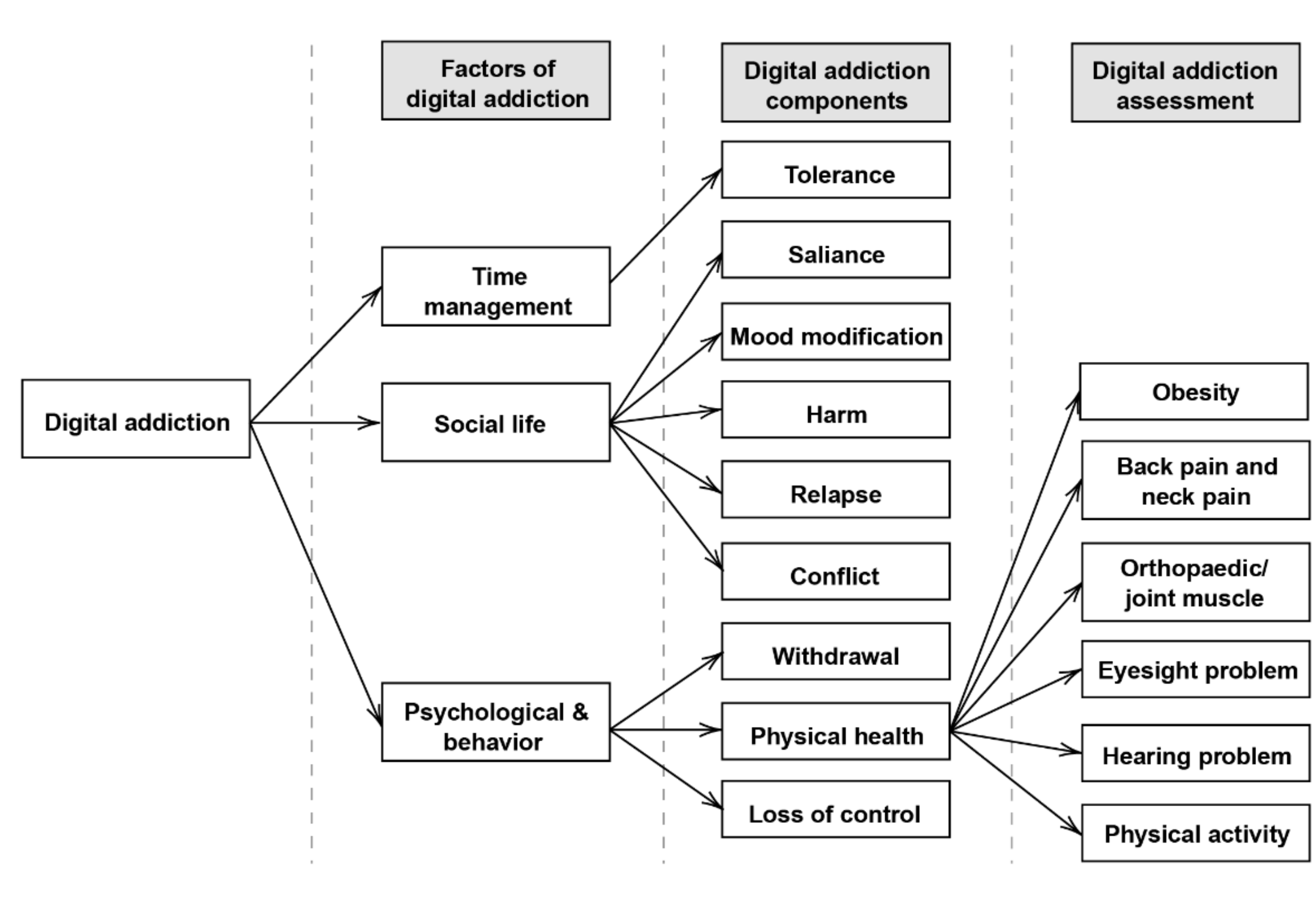
4.3. RQ3: What Are the Factors of DA in Computer Games Which Influence Malaysian Adolescents?
- Time management—most computer gamers tend to spend extensive hours playing computer games, and they often spend late nights online with their gaming community. This situation raises concerns, as spending too much time on computer games affects the gamer’s personal and professional life as a result.
- Social life—social life is related to the relationship of the individual with family, friends, and their surrounding community. The five DA components related to the DA factor of social life will become a part of the personal lives of gamers. For instance, salience causes gamers to consider playing a game as an essential part of life. Mood modification lets gamers have mood swings and tend to spend more time playing games in their room. Relapse causes gaming behavior to become an addiction and keep repeating the gaming sessions. Harm causes gamers to think and behave aggressively with people around them, as aggression is a part of a computer game—MMOGs. Conflict is a situation where gamers challenge each other online, which, if brought into real-life, may cause harm and danger to other people.
- Psychological and behavior—Physical and behavioral components of addiction include physical health, loss of control, and withdrawal. Physical health, as mentioned before, is a situation where gamers have issues with their health physically, such as neck and back pain. Loss of control includes mood swings, and withdrawal is the behavior changes of the addict when they are withdrawn from the addictive substance.
4.4. RQ4: What Are the Components of DA in Computer Games Which Influence Malaysian Adolescents?
4.5. RQ5: What Are the Consequences of Computer Game Addiction on Adolescent Physical Health?
- Obesity—computer games addiction may cause adolescents to gain weight and become obese as gamers tend to continue eating while playing computer games, and at the same time, have no active physical movement to burn the added calories.
- Back pain and neck pain—an extensive computer gaming period may cause gamers to have back and neck pain, as they tend to sit in the same position for hours while playing computer games.
- Orthopaedic/joint muscle—Some might have orthopedic/joint problems, called gamer’s thumb, or hand injuries due to spending an excessive amount of time using a mouse and keyboard.
- Eyesight problems—excessive computer gaming and the use of screens negatively impact eyesight. A study by Lee et al. [54] has specifically focused on the effect of excessive computer gaming on binocular vision. The result suggests that excessive and constant gaming activity on computers causes both the weakening of visual functions and ocular and physical fatigue.
- Hearing problems—computer gamers may also have reduced hearing ability, as they are used to listening to loud noises using their headphones. Some of the noises include loud sound effects, such as shooting, explosions, engines roaring, and other loud sound effects that are designed to immerse gamers into the gaming world.
- Physical inactivity—computer gamers tend to spend more time playing computer games in a room instead of going for outdoor activities.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Authors | Factors of DA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Management | Social Life | Psychological Behavior | ||
| 1 | Ko CH, Yen JY, Chen CC, Chen SH, Yen CF. 2005 | x | x | x |
| 2 | Chan PA, Rabinowitz T. 2006 | x | x | |
| 3 | Kim EJ, Namkoong K, Ku T, Kim SJ. 2008 | x | x | |
| 4 | Lemmens JS, Valknburg PM, Peter J. 2009 | x | x | x |
| 5 | Lemmens JS, Valknburg PM, Peter J. 2009a | x | x | x |
| 6 | Skoric MM, Teo LLC, Neo RL. 2009 | x | x | |
| 7 | Rehbein F, Psych G, Kleimann M, Mediasci G, Mößle T. 2010 | x | x | x |
| 8 | Thomas NJ, Martin FH. 2010 | x | x | x |
| 9 | Rehbein F, Psych G, Kleimann M, Mediasci G, Mößle T. 2010a | x | x | x |
| 10 | Thomas NJ, Martin FH. 2010a | x | x | x |
| 11 | van Rooij AJ, Schoenmakers TM, van de Eijnden RJ, van de Mheen D. 2010 | x | x | |
| 12 | Lemmens JS, Valknburg PM, Peter J, 2011 | x | x | x |
| 13 | Lemmens JS, Valknburg PM, Peter J, 2011a | x | x | x |
| 14 | Lemmens JS, Valknburg PM, Peter J, 2011b | x | x | x |
| 15 | Van Rooij AJ, Schoenmakers TM, Van de Eijnden RJ, Van de Mheen D. 2011 | x | x | |
| 16 | Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. 2011 | x | x | |
| 17 | Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. 2011a | x | x | x |
| 18 | Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. 2012 | x | x | x |
| 19 | Kuss DJ. 2013 | x | x | x |
| 20 | King DL, Haagsma MC, Delfabbro PH, Gradisar M, Griffiths MD. 2013 | x | x | x |
| 21 | Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD, Binder JF. 2013 | x | x | x |
| 22 | Lee ZW, Cheung CM, Chan TK. 2015 | x | x | x |
| 23 | Li W, O’Brien JE, Snyder SM, Howard MO. 2015 | x | x | x |
| 24 | Brunborg GS, Hanss D, Mentzoni RA, Pallesen S. 2015 | x | x | x |
| 25 | Andreassen CS. 2015 | x | x | x |
| 26 | You S, Kim E, Lee D. 2017 | x | ||
| 27 | Taylor T. 2016 | x | x | x |
| 28 | Khan A, Muqtadir R. 2016 | x | x | x |
| 29 | Smohai M, Urbán R, Griffiths MD, Király O, Mirnics Z, Vargha A, Demetrovics Z. 2017 | x | x | x |
| 30 | Taylor T. 2016a | x | x | x |
| 31 | King DL, Kaptsis D, Delfabbro PH, Gradisar M. 2016 | x | x | |
| 32 | Lee WY. 2015 | x | x | x |
| 33 | Monacis L, Palo VD, Griffiths MD, Sinatra M. 2016 | x | x | x |
| 34 | King DL, Herd MC, Delfabbro PH. 2017 | x | ||
| 35 | Kwok SW, Lee PH, Lee RL. 2017 | x | x | x |
| 36 | Krossbakken E, Pallesen S, Molde H, Mentzoni RA, Finserås TR. 2017 | x | x | x |
| 37 | Hawi NS, Samaha M. 2017 | x | x | x |
| 38 | Kesici A, Tunç NF. 2018 | x | x | x |
References
- Caplan, S.; Williams, D.; Yee, N. Problematic Internet use and psychosocial well-being among MMO players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2009, 25, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R. Digital Motivation, Digital Addiction and Responsibility Requirements. In Proceedings of the 2018 1st International Workshop on Affective Computing for Requirements Engineering (AffectRE), Banff, AB, Canada, 21 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhu, P.A.; SarojVerma. Role of Internet Addiction in Mental Health Problems of College Students. Psychol. Behav. Sci. Int. J. 2017, 2, 555–591. [Google Scholar]
- Shirinkam, M.S.; Shahsavarani, A.M.; Toroghi, L.M.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Sattari, K. Internet addiction antecendants: Self-control as a predictor. Int. J. Med Res. Health Sci. 2016, 5, 115–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yeap, J.A.L.; Ramayah, T.; Kurnia, S.; Halim, H.A.; Ahmad, N.H. The assessment of Internet addiction among university students: Some findings from a focus group. Teh. Vjesn. 2015, 22, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.; Freire, R.; Zugliani, M.; Cirillo, P.; Santos, H.H.; Nardi, A.E.; King, A.L.S. Treatment outcomes in patients with Internet Addiction and anxiety. MedicalExpress 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keele, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; EBSE: Goyang City, Korea, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, Y.A.; Ahmad, M.N.; Ahmad, N.; Zakaria, N.H. Social media for knowledge-sharing: A systematic literature review. Telemat. Inform. 2019, 37, 72–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Prisma Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Pontes, H.M. Chaos and confusion in DSM-5 diagnosis of Internet Gaming Disorder: Issues, concerns, and recommendations for clarity in the field. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehenbauer-Baum, M.; Fohringer, M. Towards classification criteria for Internet Gaming Disorder: Debunking differences between addiction and high engagement in a German sample of World of Warcraft players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 45, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrobai, A.; McAlaney, J.; Dogan, H.; Phalp, K.; Ali, R. Exploring the requirements and design of persuasive intervention technology to combat digital addiction. In Human-Centered and Error-Resilient Systems Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 130–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tzavela, E.C.; Karakitsou, C.; Halapi, E.; Tsitsika, A.K. Adolescent digital profiles: A process-based typology of highly engaged Internet users. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 69, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Internet Users Survey 2018; Suruhanjaya Komunikasi dan Multimedia Malaysia: Cyberjaya, Malaysia, 2018.
- Aziz, A. RM10m Allocation for eSports a Great Start, Says MDec. 2018. Available online: https://www.theedgemarkets.com/article/rm10m-allocation-esports-great-start-says-mdec (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Cunningham, G.B.; Fairley, S.; Ferkins, L.; Kerwin, S.; Lock, D.; Shaw, S.; Wicker, P. eSport: Construct specifications and implications for sport management. Sport Manag. Rev. 2018, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, T.S. Internet Addiction among M’sians Has Reached Alarming Rate: Jailani. 2017. Available online: https://www.thesundaily.my/archive/internet-addiction-among-msians-has-reached-alarming-rate-jailani-BUARCH512374 (accessed on 23 September 2018).
- Daily, T.S. Internet Addiction Can Dominate Lives of Children: Rosmah. 2017. Available online: https://www.thesundaily.my/archive/internet-addiction-can-dominate-lives-children-rosmah-LTARCH495320 (accessed on 22 July 2018).
- Kapahi, A.; Ling, C.S.; Ramadass, S.; Abdullah, N. Internet addiction in Malaysia causes and effects. iBusiness 2013, 5, 33745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, H.M.; Griffiths, M.D. Internet addiction disorder and Internet gaming disorder are not the same. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 2014, 5, e124. [Google Scholar]
- Király, O.; Sleczka, P.; Pontes, H.M.; Urbán, R.; Griffiths, M.D.; Demetrovics, Z. Validation of the ten-item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10) and evaluation of the nine DSM-5 Internet Gaming Disorder criteria. Addict. Behav. 2017, 64, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.L.; Kaptsis, D.; Delfabbro, P.H.; Gradisar, M. Craving for Internet games? Withdrawal symptoms from an 84-h abstinence from massively multiplayer online gaming. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 62, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartle, R.A. Design principles. Mult. Soc. Asp. Digit. Gaming 2013, 3, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.W. Effect of parental neglect on smartphone addiction in adolescents in South Korea. Child Abus. Negl. 2018, 77, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-P.; Wu, J.Y.-W.; You, J.; Hu, W.-H.; Yen, C.-F. Prevalence of Internet addiction and its risk and protective factors in a representative sample of senior high school students in Taiwan. J. Adolesc. 2018, 62, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansz, J.; Martens, L. Gaming at a LAN event: The social context of playing video games. New Media Soc. 2005, 7, 333–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.S.; Malesky, L.A., Jr. Problematic usage among highly-engaged players of massively multiplayer online role playing games. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.-A.; Lee, J.; Jung, H.Y.; Sohn, B.K.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, D.; Choi, J.-S. Changes of quality of life and cognitive function in individuals with Internet Gaming Disorder: A 6-month follow-up. Medicine 2016, 95, e5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, P.K.H.; Chan, V.W.Y.; Chan, S.W.; Lau, J.T.F. The role of social support on emotion dysregulation and Internet addiction among Chinese adolescents: A structural equation model. Addict. Behav. 2018, 82, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, R.A.; Aziz, N.A.; Jalil, M.T.A. Impact of online games among undergraduate students. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing Informatics, Cheonan, Korea, 25–27 April 2017; pp. 523–532. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, M.J.; Jeong, J.-E.; Chun, J.-W.; Cho, H.; Jung, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.J. Predictors and patterns of problematic {Internet} game use using a decision tree model. J. Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-L.; Chen, C.-Y. An exploration of the tendency to online game addiction due to user’s liking of design features. Asian J. Health Inf. Sci. 2008, 3, 38–51. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, D.; Bhang, S.-Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Kweon, Y.S.; Lee, S.-K.; Potenza, M.N. The validation of Implicit Association Test measures for smartphone and Internet addiction in at-risk children and adolescents. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaal, Y.; Billieux, J.; Thorens, G.; Khan, R.; Louati, Y.; Scarlatti, E.; Theintz, F.; Lederrey, J.; Van Der Linden, M.; Zullino, D. French validation of the Internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhaimin, M.; Aziz, N.; Ariffin, M. Problematic of Massively Multiplayer Online Game Addiction in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Reliable Information and Communication Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–24 June 2018; pp. 749–760. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, N.; Iida, H.; Ariffin, M.; Akhir, E.A.P.; Sugathan, S.K. Massively Multiplayer Online Game (MMOG) impact towards Malaysian youth’s time management, social life and psychology. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 1754–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.-S.; Chiou, W.-B. Why are adolescents addicted to online gaming? An interview study in Taiwan. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, E.Y.; Hong, Y.R. Factors Influencing Internet Game Addiction in Middle School Students. Med. Leg. Update 2020, 20, 2167–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Adiele, I.; Olatokun, W. Prevalence and determinants of Internet addiction among adolescents. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 31, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Zainal, N. Exploratory Study on Internet Addiction among Varsity Students in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Commerce, e-Administration, e-Society, e-Education, and e-Technology (e-CASE &e-TECH 2011), Tokyo, Japan, 19–21 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shubnikova, E.G.; Khuziakhmetov, A.N.; Khanolainen, D.P. Internet-addiction of adolescents: Diagnostic problems and pedagogical prevention in the educational environment. Eur. J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 13, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.T.; Yasuoka, J.; Poudel, K.C.; Otsuka, K.; Jimba, M. Massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPG): Association between its addiction, self-control and mental disorders among young people in Vietnam. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2013, 59, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krossbakken, E.; Pallesen, S.; Molde, H.; Mentzoni, R.A.; Finserås, T.R. Not good enough? Further comments to the wording, meaning, and the conceptualization of Internet Gaming Disorder: Commentary on: Chaos and confusion in DSM-5 diagnosis of Internet Gaming Disorder: Issues, concerns, and recommendations for clarit. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, N. Motivations for Play in Online Games. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.L.; Herd, M.C.E.; Delfabbro, P.H. Motivational components of tolerance in Internet Gaming Disorder. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 78, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-J.; Ting, C.-C. The role of flow experience in cyber-game addiction. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2003, 6, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, T.; Gentile, D.A.; Bricolo, F.; Serpelloni, G.; Gulamoydeen, F. A conceptual review of research on the pathological use of computers, video games, and the Internet. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 748–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Allen, J.; Anderson, C.A. Satisfaction and frustration of basic psychological needs in the real world and in video games predict {Internet Gaming Disorder} scores and well-being. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 84, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.; Nam, T.-H.; Hwang, M.H. Attachment style, stressful events, and Internet gaming addiction in Korean university students. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2020, 154, 109724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.I.; Mahmud, I.; Ramayah, T.; Alfarraj, O.; Alalwan, N. Extending the theory of planned behavior (TPB) to explain online game playing among Malaysian undergraduate students. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norliah, K.; Safiah, S.; Izharrudin, Z.; Kamalrudin, M.; Hassan, M.A.; Mohamed, S. Internet Usage Pattern and Types of {Internet} Users among Malaysian University Students. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 12, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, Z.; Lee, C.W. Internet addiction and depression among college students in Malaysia. Int. Med, J. 2017, 24, 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, R. Internet addiction update: Diagnostic criteria, assessment and prevalence. Neuropsychiatry 2017, 7, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Cho, H.G.; Moon, B.-Y.; Kim, S.-Y.; Yu, D.-S. Effects of prolonged continuous computer gaming on physical and ocular symptoms and binocular vision functions in young healthy individuals. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ID | Research Question | Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| RQ1 | Digital addiction (DA) | To answer research questions regarding DA. |
| RQ1.0 | What is addiction? | To get a clear definition of the term “addiction” |
| RQ1.1 | What is DA? | To get a clear definition of DA. |
| RQ1.2 | What are the causes of DA? | To explore the possible causes of DA. |
| RQ1.3 | How does DA impact an addict? | To explain the impact of DA on an addict. |
| RQ1.4 | How does the withdrawal of the addictive substance impact an addict? | To understand how the withdrawal of the addictive substance impacts an addict. |
| RQ2 | Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) | To answer research questions regarding IGD. |
| RQ2.0 | What is IGD? | To define IGD. |
| RQ2.1 | What are the causes of computer game addiction? | To explore the possible cause of computer game addiction. |
| RQ2.2 | What are the effects of excessive computer gaming/IGD? | To explain the impact of excessive computer gaming on the addict. |
| RQ2.3 | Is IGD diagnosable and curable? | To explore the possible chances of curing IGD. |
| RQ3 | What are the factors of DA in computer games which influence Malaysian adolescents? | To explore the DA factors in computer games among Malaysian adolescents. |
| RQ4 | What are the components of DA in computer games which influence Malaysian adolescents? | To explore the DA components among Malaysian adolescents. |
| RQ5 | What are the consequences of computer game addiction on adolescent physical health? | To explore the impact of computer game addiction on the physical health of an adolescent. |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
|
|
| Keyword | Database (Last Retrieved) | Full Query Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| Digital addiction | ScienceDirect (21 Nov. 2020) | General query: digital addiction Title, abstract, keywords: “physical health” AND “adolescent” Year published: 2016−2020 |
| SpringerLink (21 Nov. 2020) | Using Advanced Search: Query: {“Digital addiction” AND (“physical health AND adolescent”)} Year published: 2016–2020 | |
| ACM DL (21 Nov. 2020) | “query”: { Title:(Digital addiction) AND Fulltext:(Digital addiction) AND Fulltext:(physical health) AND Fulltext:(adolescent) } “filter”: { Publication Date: (01/01/2016 TO 12/31/2020), ACM Content: DL, NOT VirtualContent: true } | |
| IEEE Xplore (21 Nov. 2020) | General query: digital addiction Filter: Selection based on title suitability | |
| Computer game addiction | ScienceDirect (21 Nov. 2020) | General query: computer game addiction Title, abstract, keywords: “physical health” AND “adolescent” Year published: 2016–2020 |
| SpringerLink (21 Nov. 2020) | Using Advanced Search: Query: {“Computer game addiction” AND (“physical health AND adolescent”)} Year published: 2016–2020 | |
| ACM DL (21 Nov. 2020) | “query”: { Title:(Computer game addiction) AND Fulltext:(Computer game addiction) AND Fulltext:(physical health) AND Fulltext:(adolescent) } “filter”: { Publication Date: (01/01/2016 TO 12/31/2020), ACM Content: DL, NOT VirtualContent: true } | |
| IEEE Xplore (21 Nov. 2020) | General query: computer game addiction Filter: Selection based on title suitability | |
| Internet game addiction | ScienceDirect (21 Nov. 2020) | General query: Internet game addiction Title, abstract, keywords: “physical health” AND adolescent" Year published: 2016–2020 |
| SpringerLink (21 Nov. 2020) | Using Advanced Search: Query: {“Internet game addiction” AND (“physical health AND adolescent”)} Year published: 2016–2020 | |
| ACM DL (21 Nov. 2020) | “query”: { Title:(Internet game addiction) AND Fulltext:(Internet game addiction) AND Fulltext:(physical health) AND Fulltext:(adolescent) } “filter”: { Publication Date: (01/01/2016 TO 12/31/2020), ACM Content: DL, NOT VirtualContent: true } | |
| IEEE Xplore (21 Nov. 2020) | General query: internet game addiction Filter: Selection based on title suitability |
| Type of Bias | Methods Used to Avoid Bias |
|---|---|
| Interview bias |
|
| Citation bias |
|
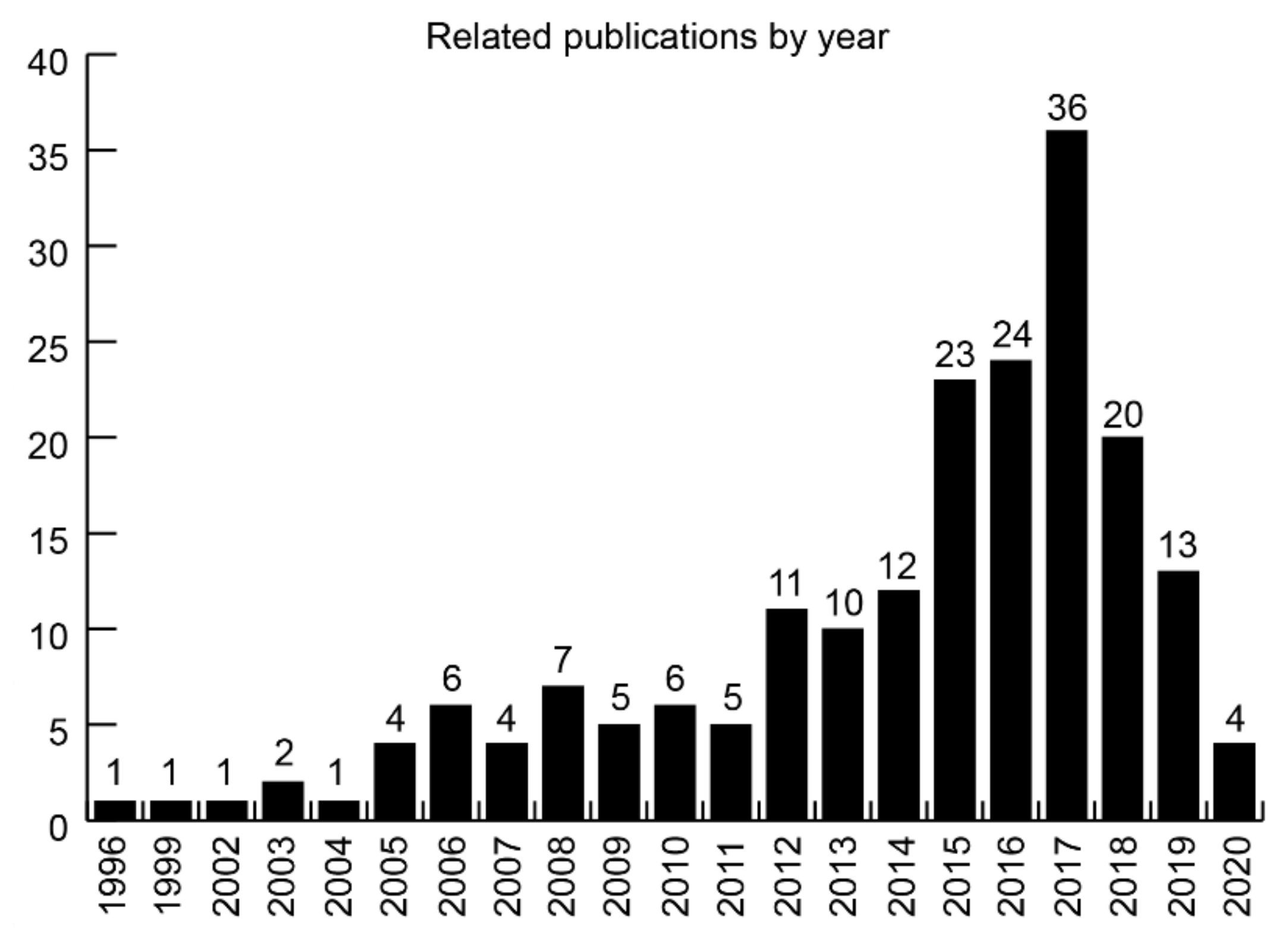
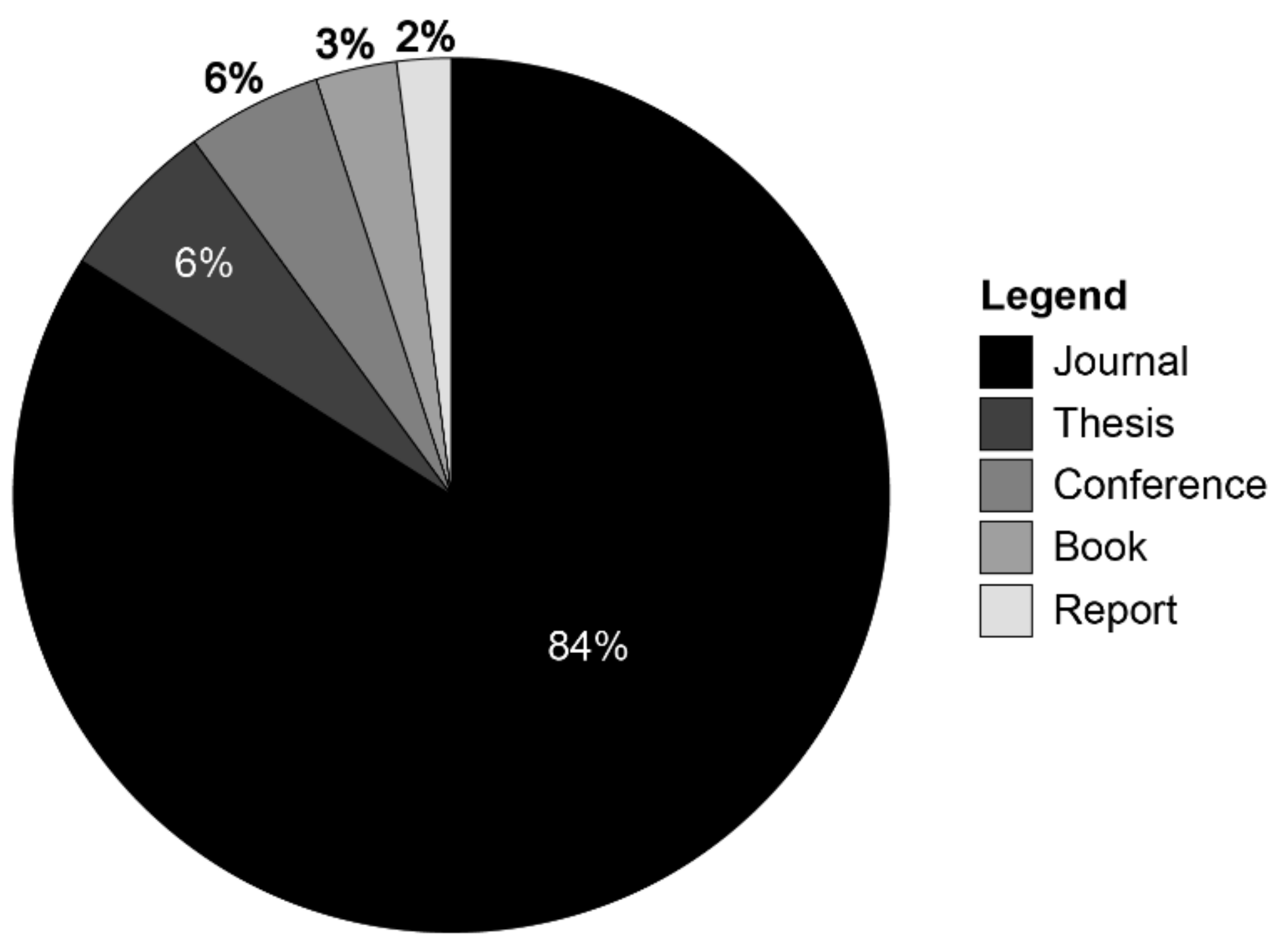
| Year | Type of Identified Publications | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Journal | Thesis | Conference | Book | Report | ||
| 1996 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 1999 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| 2002 | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| 2003 | 2 | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| 2004 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| 2005 | 3 | - | - | 1 | - | 4 |
| 2006 | 4 | 2 | - | - | - | 6 |
| 2007 | 3 | - | 1 | - | - | 4 |
| 2008 | 6 | - | - | - | 1 | 7 |
| 2009 | 5 | - | - | - | - | 5 |
| 2010 | 5 | - | 1 | - | - | 6 |
| 2011 | 4 | - | - | - | 1 | 5 |
| 2012 | 7 | 2 | - | 2 | - | 11 |
| 2013 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | 10 |
| 2014 | 11 | - | 1 | - | - | 12 |
| 2015 | 20 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 23 |
| 2016 | 19 | 1 | 3 | 1 | - | 24 |
| 2017 | 31 | 3 | 1 | - | 1 | 36 |
| 2018 | 19 | - | 1 | - | - | 20 |
| 2019 | 12 | - | 1 | - | - | 13 |
| 2020 | 4 | - | - | - | - | 4 |
| Total | 164 | 11 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 196 |
| Factor of DA | Description of Activities | Consequences on Physical Health |
|---|---|---|
| Psychological behavior | Playing computer games is a sedentary activity. Gamers tend to spend time playing games indoors instead of performing outdoor activities. Hence, they are prone to the risk of obesity, especially when they eat while playing computer games. | Obesity |
| Prolonged physical immobility will lead to muscle pain such as back and neck pain. | Back pain and neck pain | |
| Using a mouse and keyboard for a long time causes muscle problems in fingers and hands. | Orthopaedic/ joint muscle | |
| Having a long on-screen time can cause dry eyes and eyesight problems. | Eyesight problem | |
| Continuous exposure to loud noise from headphones can reduce hearing ability. | Hearing problem | |
| Computer gamers tend to have much less physical activity than other people as they spend more time playing computer games in a room. | Physical inactivity |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziz, N.; Nordin, M.J.; Abdulkadir, S.J.; Salih, M.M.M. Digital Addiction: Systematic Review of Computer Game Addiction Impact on Adolescent Physical Health. Electronics 2021, 10, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10090996
Aziz N, Nordin MJ, Abdulkadir SJ, Salih MMM. Digital Addiction: Systematic Review of Computer Game Addiction Impact on Adolescent Physical Health. Electronics. 2021; 10(9):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10090996
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziz, Norshakirah, Md Jan Nordin, Said Jadid Abdulkadir, and Muhammad Muhaimin M. Salih. 2021. "Digital Addiction: Systematic Review of Computer Game Addiction Impact on Adolescent Physical Health" Electronics 10, no. 9: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10090996
APA StyleAziz, N., Nordin, M. J., Abdulkadir, S. J., & Salih, M. M. M. (2021). Digital Addiction: Systematic Review of Computer Game Addiction Impact on Adolescent Physical Health. Electronics, 10(9), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10090996






