Dopamine-Sensing Characteristics and Mechanism by Using N2/O2 Annealing in Pt/Ti/n-Si Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sensor Fabrication Procedure and Measurement
2.1. Material Deposition
2.2. Sensing Area Patterned by Lithography
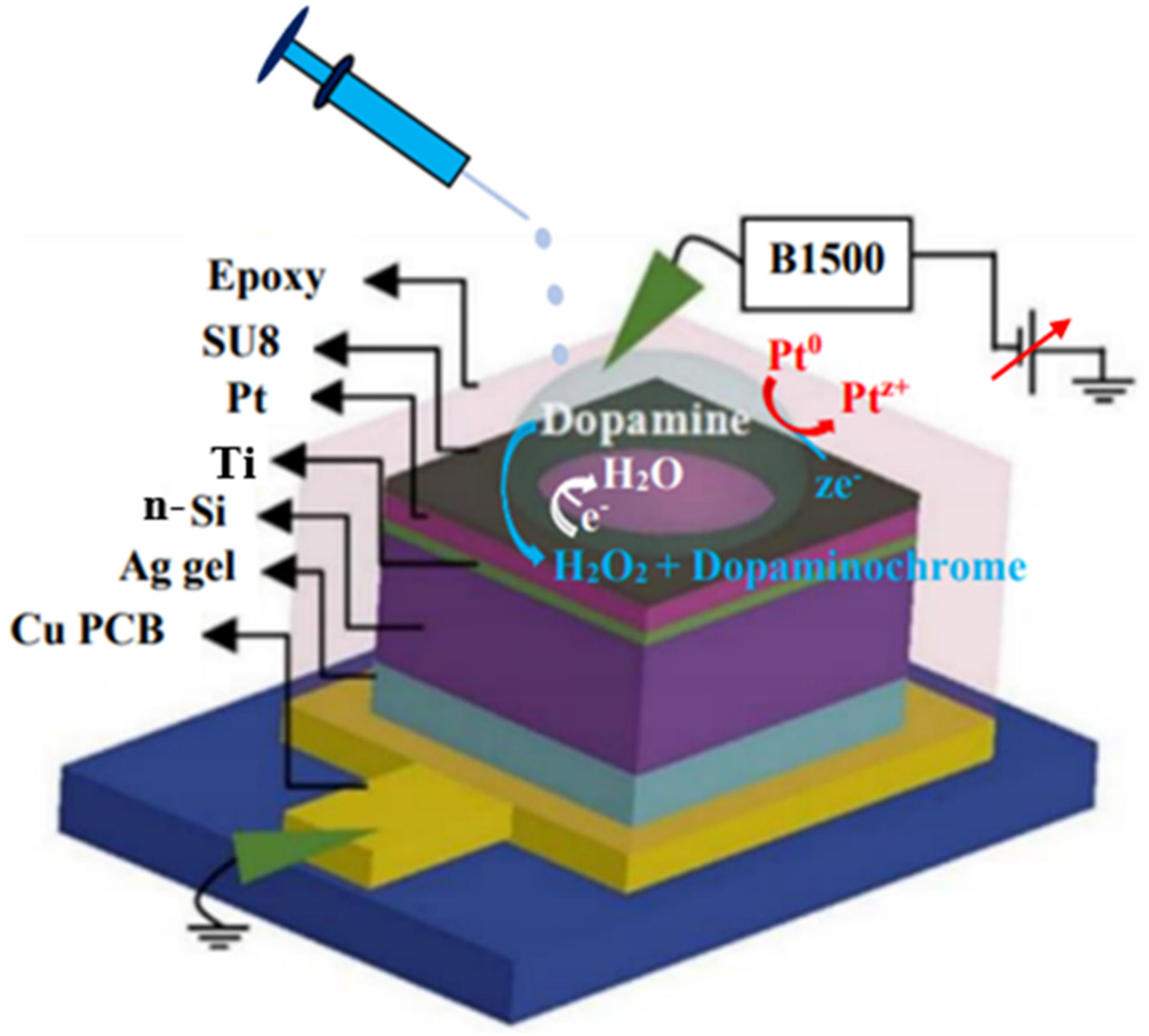
2.3. Sensor Structure and Measurement Procedure
2.4. Details of Materials and Preparation of the Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
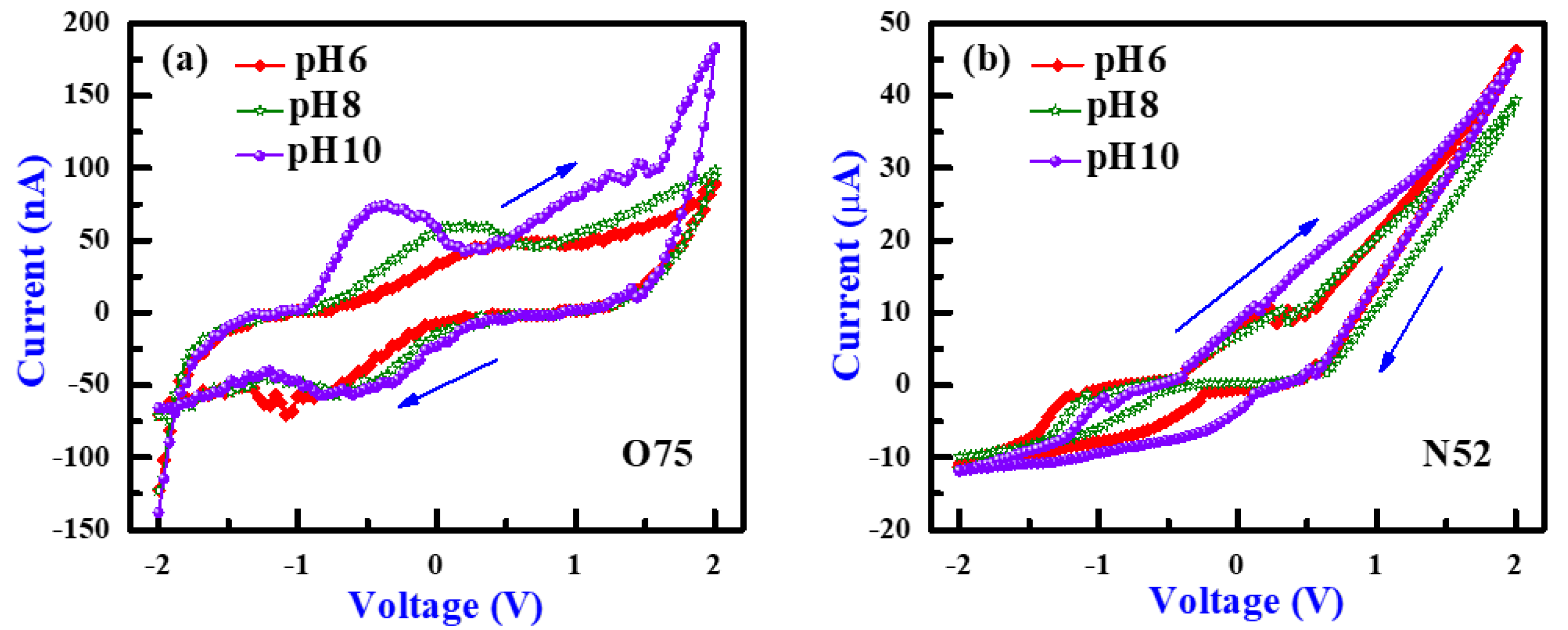
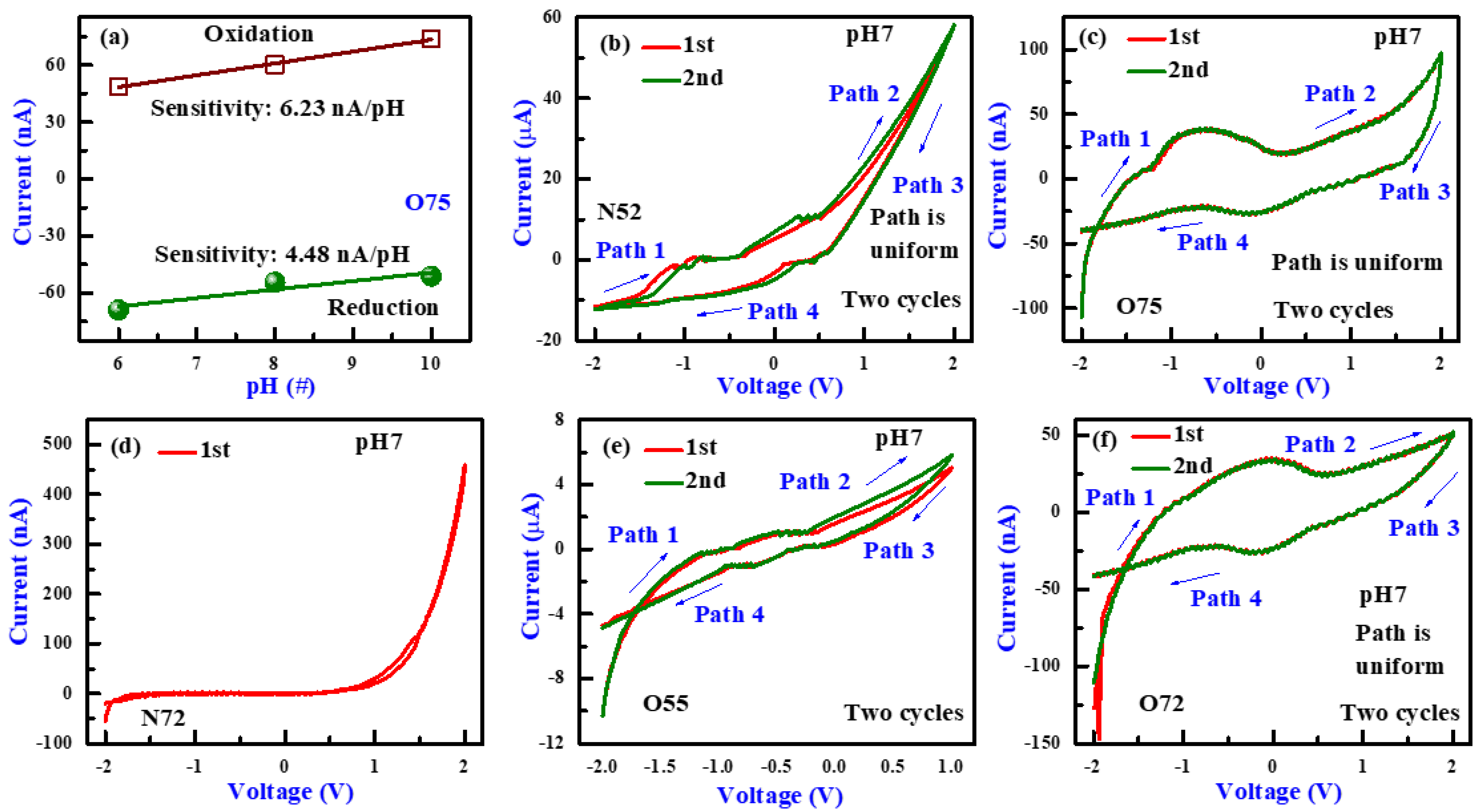
3.1. PH Sensing and I-V Sweeping Characteristics
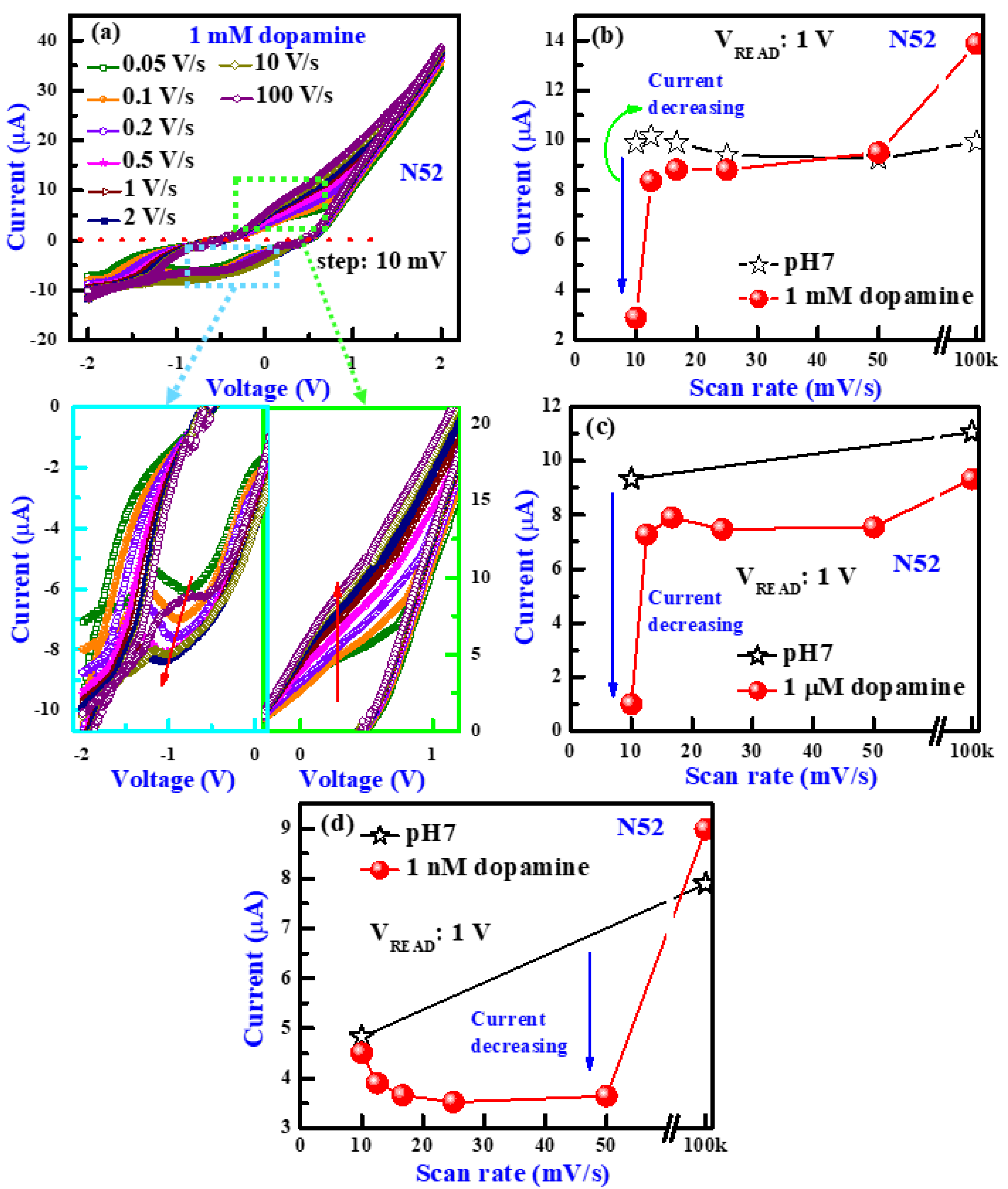
3.2. Scan Rate Dependence
3.3. I-V Characteristics of Dopamine Sensing
3.4. Scan Rate-Dependent Dopamine Sensing
3.5. Low Concentration Dopamine Detection
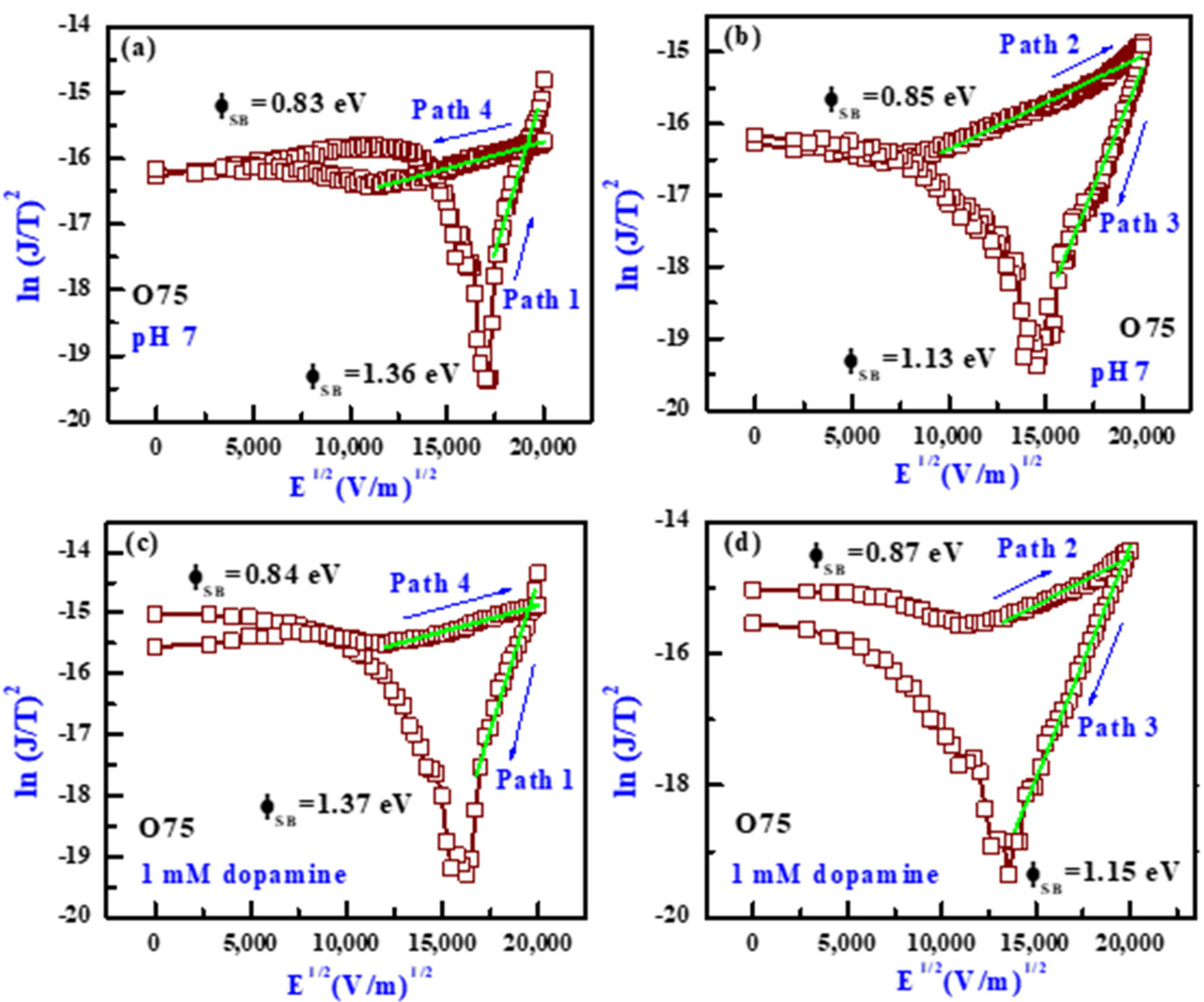
3.6. Transport and Dopamine-Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roy, A.; Chen, Y.P.; Qiu, J.T.; Maikap, S. Sarcosine prostate cancer biomarker detection by controlling oxygen in NiOx membrane on vertical silicon nanowires in electrolyte–insulator–nanowire structure. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8064–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjardi, H.R.Z. Electrochemical sensing of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using carbon paste electrode modified with molybdenum Schiff base complex/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate. Iran. Chem. Commun. 2018, 6, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, A.; Panda, S.; Yesodha, S.K. Physiological level and selective electrochemical sensing of dopamine by a solution processable graphene and its enhanced sensing property in general. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 256, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Chen, X.J.; Li, W.T.; Zhou, W.H.; Guo, X.C.; Kang, W.Y.; Kou, D.X.; Zhou, Z.J.; Meng, Y.N.; Tian, Q.W.; et al. ZnO nanotubes supported molecularly imprinted polymers arrays as sensing materials for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Talanta 2018, 176, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.K.; Lavon, A.; Shmulevich, O.; Yoav, H.B. The effect of loading carbon nanotubes onto chitosan films on electrochemical dopamine sensing in the presence of biological interference. Talanta 2018, 181, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, P.; Wang, N.; Lin, M. Voltammetric sensing of dopamine based on a nanoneedle array consisting of NiCo2S4 hollow core-shells on a nickel foam. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Chen, D.; Zhang, S.; Luan, F.; Chen, L. Reduced graphene oxide functionalized with a CoS2/ionic liquid composite and decorated with gold nanoparticles for voltammetric sensing of dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, M.; Sun, P.; Han, D.; Niu, L.; Cui, G. Hierarchical bi-continuous Pt decorated nanoporous Au-Sn alloy on carbon fiber paper for ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid simultaneous sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Oh, J.; Kim, S.G.; Jang, J. Highly sensitive and selective field-effect transistor nonenzyme dopamine sensors based on Pt/conducting polymer hybrid nanoparticles. Small 2015, 11, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang QWu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L. PtNi bimetallic nanoparticles loaded MoS2 nanosheets: Preparation and electrochemical sensing application for the detection of dopamine and uric acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1055, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xian, H.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Permselectivity and dopamine detection with Pt electrodes covered with PAA-modified porous silicate film. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, H19–H24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, J.; Sha, R.; Badhulika, S. A ruthenium (IV) disulfide based non-enzymatic sensor for selective and sensitive amperometric determination of dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, K.C.F.; Bonacin, J.A. Preferential coordination of ruthenium complex as an electroactive self-assembled monolayer on gold substrate and its application in sensing of dopamine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 99, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakkthivel, P.; Chen, S.M. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid and dopamine in the presence of uric acid on ruthenium oxide modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, T.; Mariani, F.; Scavetta, E.; Schuhmann, W.; Andronescu, C. Reduced-graphene-oxide-based needle-type field-effect transistor for dopamine sensing. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 1922–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Hung, C.H.; Lo, Y.R.; Lee, C.C.; Su, C.J.; Lin, H.C.; Ko, F.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Yang, Y.S. Ultrasensitive detection of dopamine using a polysilicon nanowire field-effect transistor. Chem. Commun. 2008, 5749–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Elbaz, J.; Gill, R.; Zayats, M.; Willner, I. Analysis of dopamine and tyrosinase activity on ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (ISFET) devices. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 7288–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalini, S.; Leonardi, F.; Cramer, T.; Biscarini, F. Organic field-effect transistor for label-free dopamine sensing. Org. Electron. 2013, 14, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rithesh, R.D.; Sudarsanakumar, C. Surface plasmon resonance-based fiber optic dopamine sensor using BSA-gold cluster/polymer composites. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 5598–5602. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.A.; Lakshminarayanan, V.; Ramamurthy, S.S. Platinum nanoparticles decorated graphene-modified glassy carbon electrode toward the electrochemical determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and paracetamol. C. R. Chim. 2019, 22, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, J. Synthesis of Au@Pt nanoflowers supported on graphene oxide for enhanced electrochemical sensing of dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 817, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Zhao, C.; Gui, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z. Reduced graphene oxide/nile blue/gold nanoparticles complex modified glassy carbon electrode used as a sensitive and label-free aptasensor for ratiometric electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1025, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Faisal, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Jalalah, M.; Alsareii, S.A. Development of an amperometric biosensor for dopamine using novel mesoporous silicon nanoparticles fabricated via a facile stain etching approach. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2022, 135, 114952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlinger, E.; Jameson, R.F.; Linert, W. Spontaneous autoxidation of dopamine. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1995, 2, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccarato, F.; Toscano, P.; Alexandre, A. Dopamine-derived dopaminochrome promotes H2O2 release at mitochondrial complex I. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15587–15594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Maikap, S.; Tzeng, P.J.; Qiu, J.T. Sensing characteristics of dopamine using Pt/n-Si structure. Vacuum 2020, 172, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.C. A review on conduction mechanisms in dielectric films. Ann. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 578168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, A.C.; Ping, A.T.; Khan, M.A.; Chen, Q.; Yang, J.W.; Adesida, I. Schottky barrier properties of various metals on n-type GaN. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1996, 11, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | Thickness in nm | Post-Deposition Annealing (PDA) for 10 Min | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | N2 (2.5 slm) | O2 (2.5 slm) | ||||
| 2 | 5 | Temperatures (°C) | Temperatures (°C) | |||
| 500 | 700 | 500 | 700 | |||
| N52 | √ | √ | ||||
| N72 | √ | √ | ||||
| O72 | √ | √ | ||||
| O55 | √ | √ | ||||
| O75 | √ | √ | ||||
| Electrode | Minimum Detection (nm) | Method | Substance (pH) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt@NP-AuSn/Ni/CFP | 130 | DPV | 7 | Yang et al. [8] |
| PtNi@MoS2 | 100 | CV, DPV | 7.4 | Ma et al. [10] |
| PAA-SNFs/Pt | 1.7 | DPV | 7.6 | Wang et al. [11] |
| GPtNPs-GCE | 5 | DPV | 7.4 | Kumar et al. [20] |
| Au@Pt/GO/GCE | 0.11 | CV | 7.0 | Yang et al. [21] |
| Pt/Ti/n-Si | 0.001 | I-V | 7 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-P.; Roy, A.; Wu, P.-H.; Huang, S.-Y.; Maikap, S. Dopamine-Sensing Characteristics and Mechanism by Using N2/O2 Annealing in Pt/Ti/n-Si Structure. Electronics 2021, 10, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243146
Chen Y-P, Roy A, Wu P-H, Huang S-Y, Maikap S. Dopamine-Sensing Characteristics and Mechanism by Using N2/O2 Annealing in Pt/Ti/n-Si Structure. Electronics. 2021; 10(24):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243146
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Pin, Anisha Roy, Ping-Hsuan Wu, Shih-Yin Huang, and Siddheswar Maikap. 2021. "Dopamine-Sensing Characteristics and Mechanism by Using N2/O2 Annealing in Pt/Ti/n-Si Structure" Electronics 10, no. 24: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243146
APA StyleChen, Y.-P., Roy, A., Wu, P.-H., Huang, S.-Y., & Maikap, S. (2021). Dopamine-Sensing Characteristics and Mechanism by Using N2/O2 Annealing in Pt/Ti/n-Si Structure. Electronics, 10(24), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243146






