RRAM Random Number Generator Based on Train of Pulses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
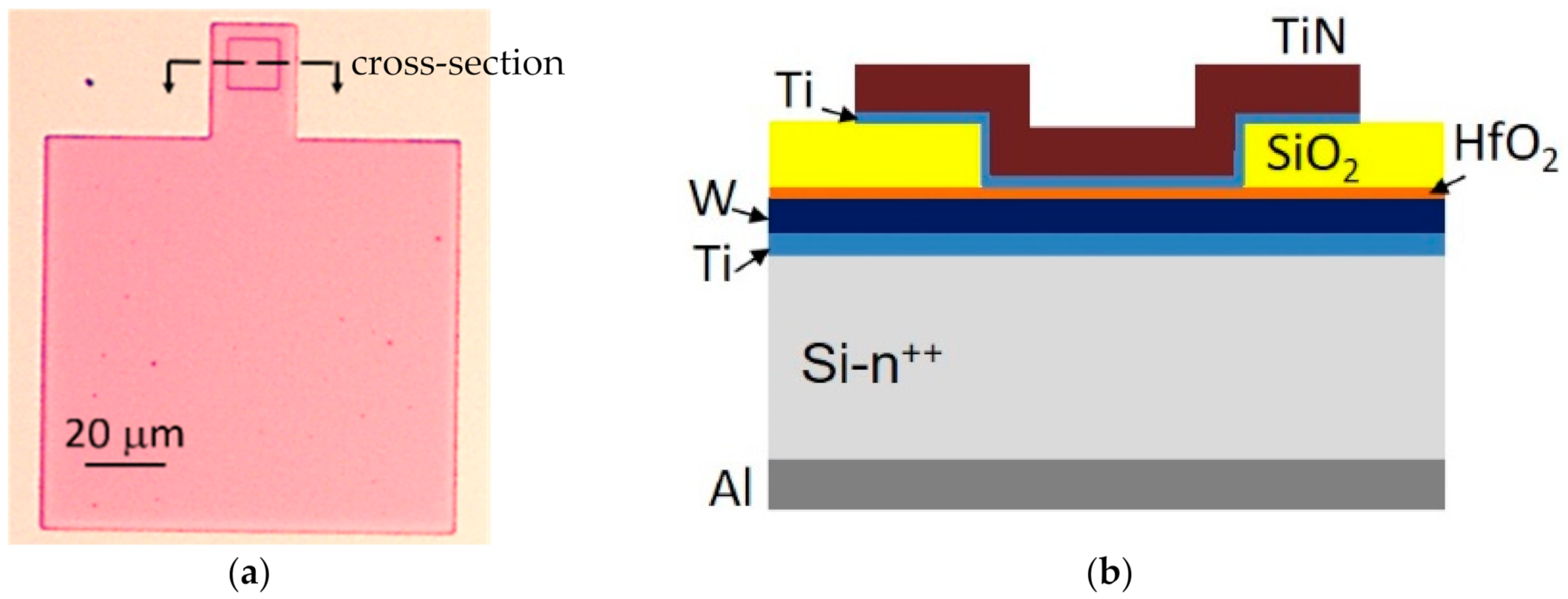
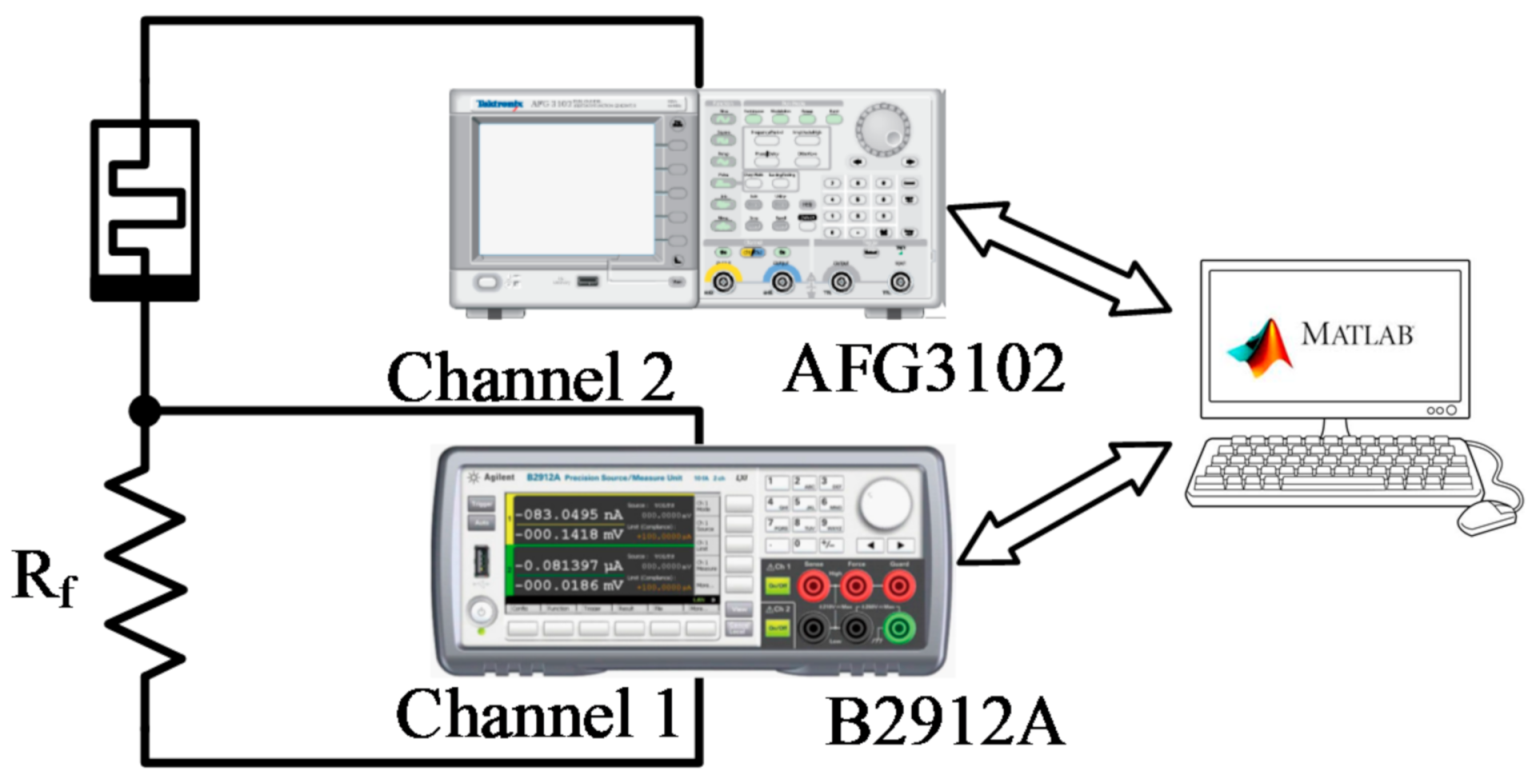
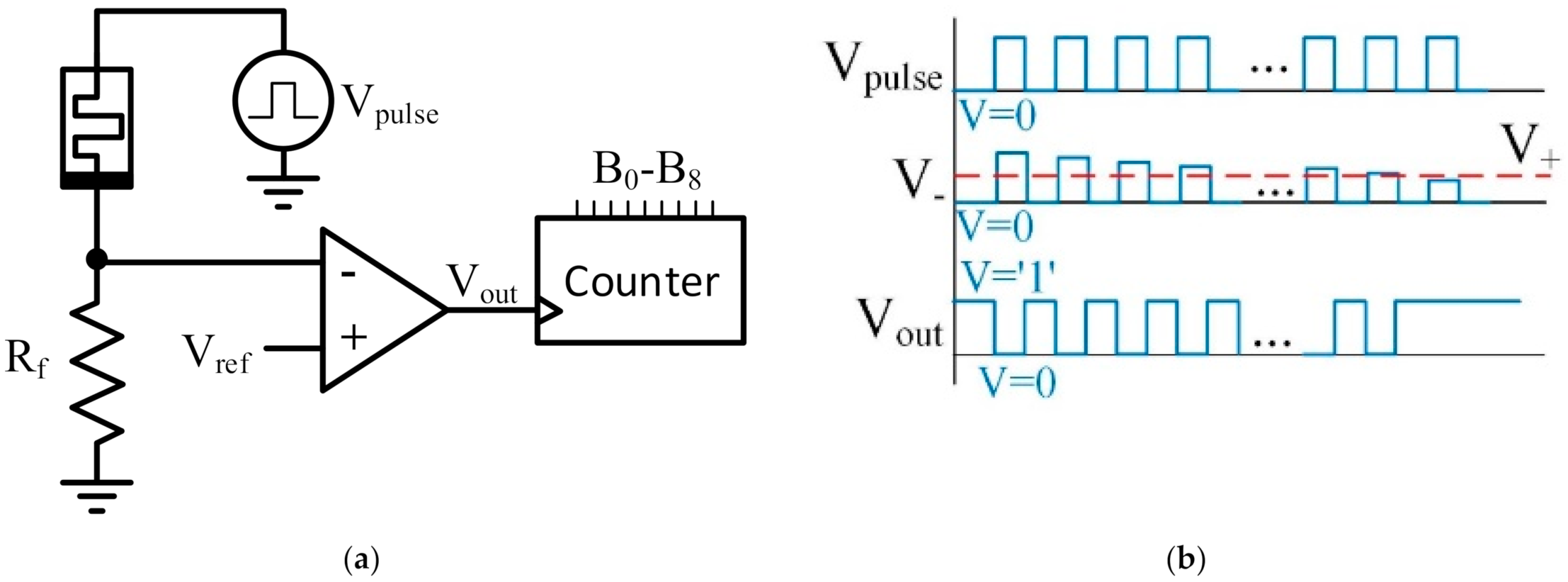
2. Experimental Set-Up
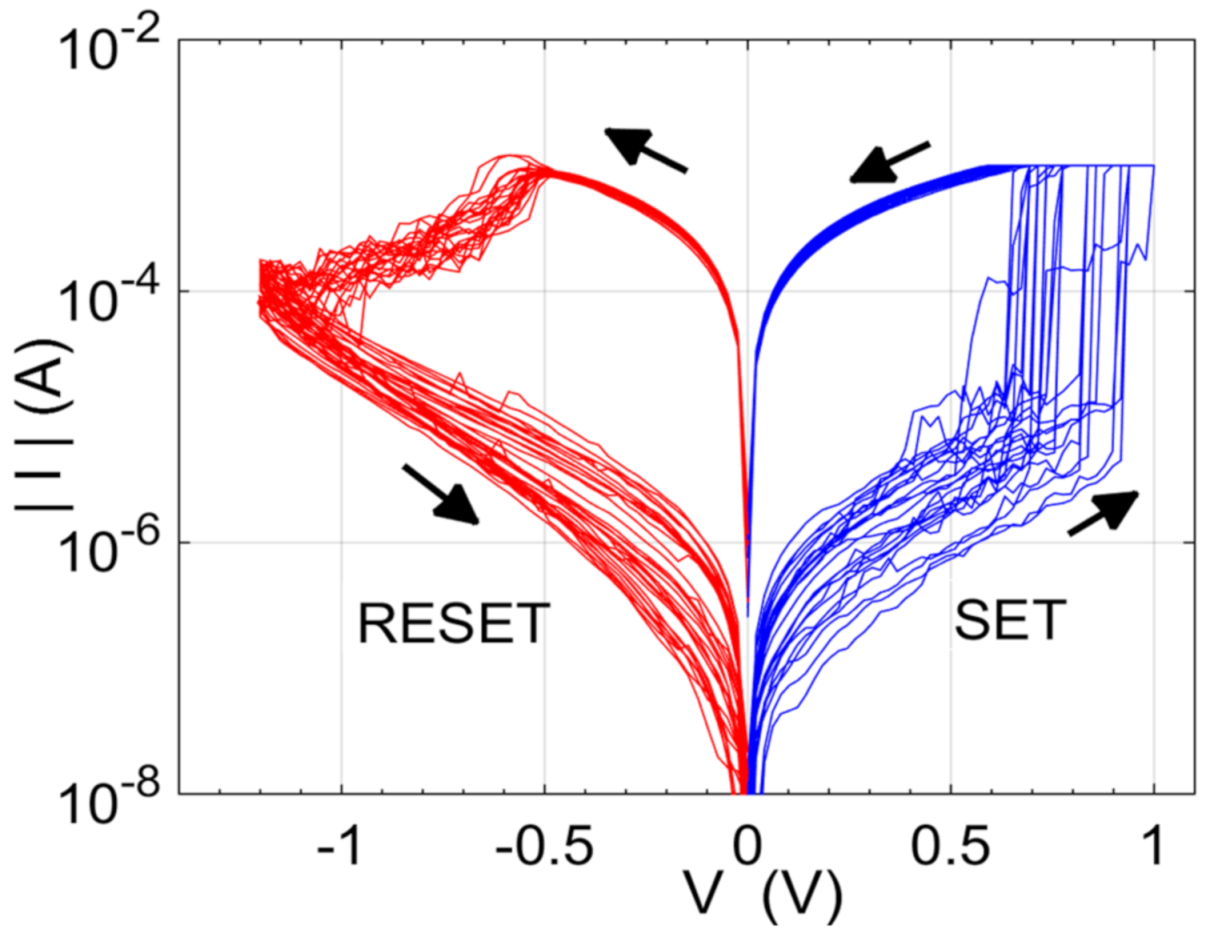
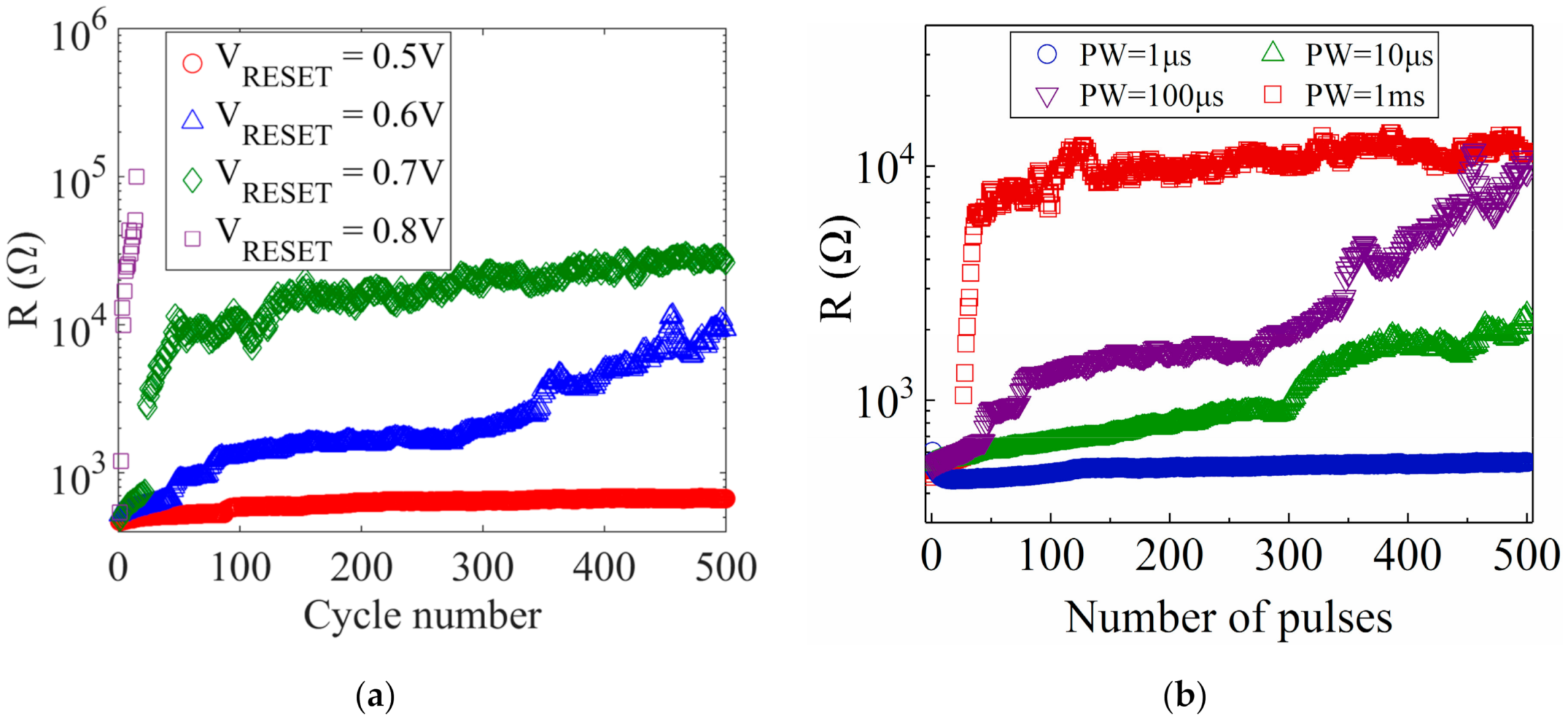
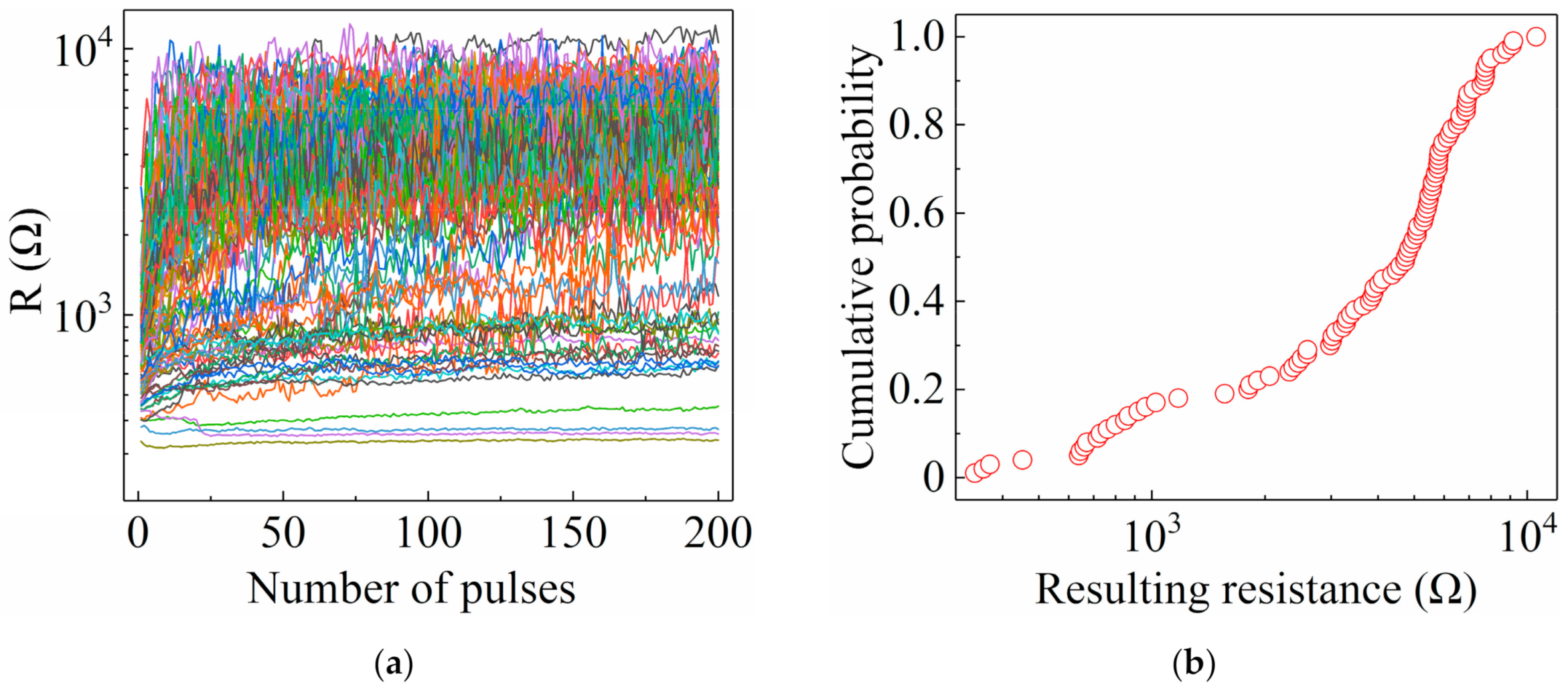
3. Resistance Variability under Pulse Programming
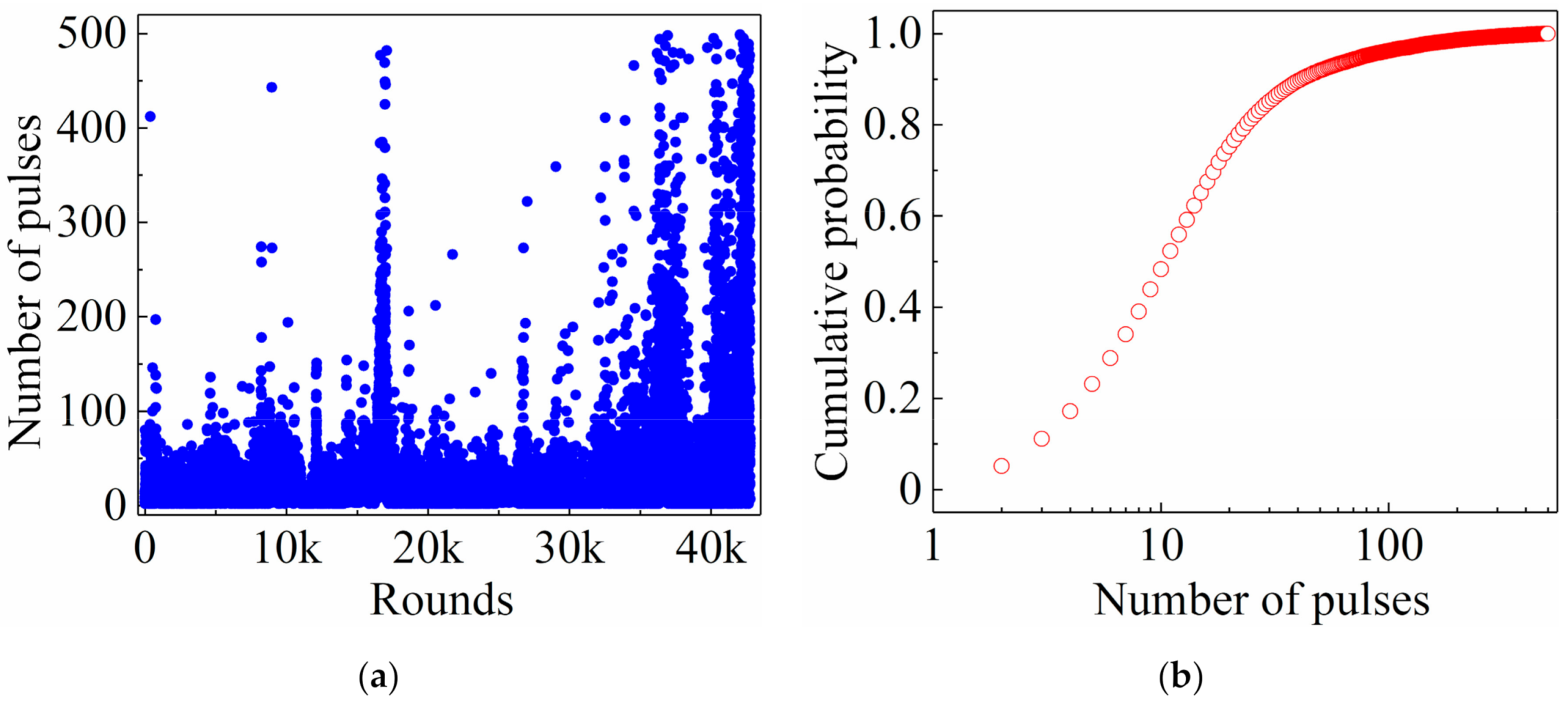
4. Random Number Generator Proposal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, H.; Peris-Lopez, P.; Tapiador, J.E.; San Millan, E. A New TRNG Based on Coherent Sampling With Self-Timed Rings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Leest, V.; Maes, R.; Schrijen, G.-J.; Tuyls, P. Hardware Intrinsic Security to Protect Value in the Mobile Market. In ISSE 2014 Securing Electronic Business Processes, Proceedings of the 2014: Information Security Solutions Europe Conference, Brussels, Belgium, 14–15 October 2014; Reimer, H., Pohlmann, N., Schneider, W., Eds.; Springer Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2014; pp. 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunar, B.; Martin, W.J.; Stinson, D.R. A Provably Secure True Random Number Generator with Built-In Tolerance to Active Attacks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2007, 56, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.; Germani, L.; Luzzi, R.; Trifiletti, A.; Varanonuovo, M. A high-speed oscillator-based truly random number source for cryptographic applications on a smart card IC. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2003, 52, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brederlow, R.; Prakash, R.; Paulus, C.; Thewes, R. A low-power true random number generator using random telegraph noise of single oxide-traps. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 February 2006; pp. 1666–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, S.; Satake, H.; Tanamoto, T.; Ohba, R.; Uchida, K.; Fujita, S. Physical random number generator based on MOS structure after soft breakdown. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits. 2004, 39, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.H.; Gao, B.; Deng, N.; Lu, Z.; Haukness, B.; Bronner, G.; Qian, H. Resistive random access memory for future information processing system. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1770–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D. Brain-inspired computing with resistive switching memory (RRAM): Devices, synapses and neural networks. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 190, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Satat, G.; Wald, N.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. Memristor-Based Material Implication (IMPLY) Logic: Design Principles and Methodologies. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2014, 22, 2054–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cordero, G.; González, M.B.; Campabadal, F.; Jiménez-Molinos, F.; Roldán, J.B. A new technique to analyze RTN signals in resistive memories. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 215, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Lin, C.-C.; Tseng, T.-Y. Switching Failure Mechanism in Zinc Peroxide-Based Programmable Metallization Cell. Nanoscale. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.D.; Li, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Xue, K.H.; Miao, X.S. Enhancement of DC/AC resistive switching performance in AlOx memristor by two-technique bilayer approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 173504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, J.; Karri, R.; Wendt, J.B.; Potkonjak, M.; McDonald, N.; Rose, G.S.; Wysocki, B. Nano meets security: Exploring nanoelectronic devices for security applications. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Belkin, D.; Savel’ev, S.E.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Joshi, S.; Midya, R.; Li, C.; Rao, M.; et al. A novel true random number generator based on a stochastic diffusive memristor. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postel-Pellerin, J.; Bazzi, H.; Aziza, H.; Canet, P.; Moreau, M.; Della Marca, V.; Harb, A. True random number generation exploiting SET voltage variability in resistive RAM memory arrays. In Proceedings of the 2019 19th Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium (NVMTS), Durham, NC, USA, 28–30 October 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambou, B.; Telesca, D.; Assiri, S.; Garrett, M.; Jain, S.; Partridge, M. TRNGs from Pre-Formed ReRAM Arrays. Cryptography 2021, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatti, S.; Ambrogio, S.; Carboni, R.; Milo, V.; Wang, Z.; Calderoni, A.; Ramaswamy, N.; Ielmini, D. Physical Unbiased Generation of Random Numbers With Coupled Resistive Switching Devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2016, 63, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Yin, M.; Xu, C.; Lu, X.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, R. High-speed true random number generation based on paired memristors for security electronics. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 455202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, H.; Postel-Pellerin, J.; Bazzi, H.; Canet, P.; Moreau, M.; Della Marca, V.; Harb, A. True Random Number Generator Integration in a Resistive RAM Memory Array Using Input Current Limitation. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2020, 19, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Shen, W.C.; Tseng, Y.-H.; King, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-J. A Contact-Resistive Random-Access-Memory-Based True Random Number Generator. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 33, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, R.; Ghosh, S.; Katkoori, S. CSRO-Based Reconfigurable True Random Number Generator Using RRAM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2018, 26, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Nili, H.; Truong, N.D.; Ahmed, T.; Yang, J.; Jeong, D.S.; Sriram, S.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Ippolito, S.; Chun, H.; et al. Nano-Intrinsic True Random Number Generation: A Device to Data Study. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2019, 66, 2615–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larentis, S.; Nardi, F.; Balatti, S.; Gilmer, D.C.; Ielmini, D. Resistive switching by voltage-driven ion migration in bipolar RRAM—Part II: Modeling. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2012, 59, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, E. Compact model for the major and minor hysteretic I-V loops in nonlinear memristive devices. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2015, 14, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblador, S.; Gonzalez, M.B.; Campabadal, F. Investigation of the multilevel capability of TiN/Ti/HfO2/W resistive switching devices by sweep and pulse programming. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187–188, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, H.; Ossorio, O.G.; Dueñas, S.; Castán, H. Controlling the intermediate conductance states in RRAM devices for synaptic applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 215, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassham III, L.E.; Rukhin, A.L.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.R.; Smid, M.E.; Barker, E.B.; Leigh, S.D.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.L.; et al. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Technical Report for National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
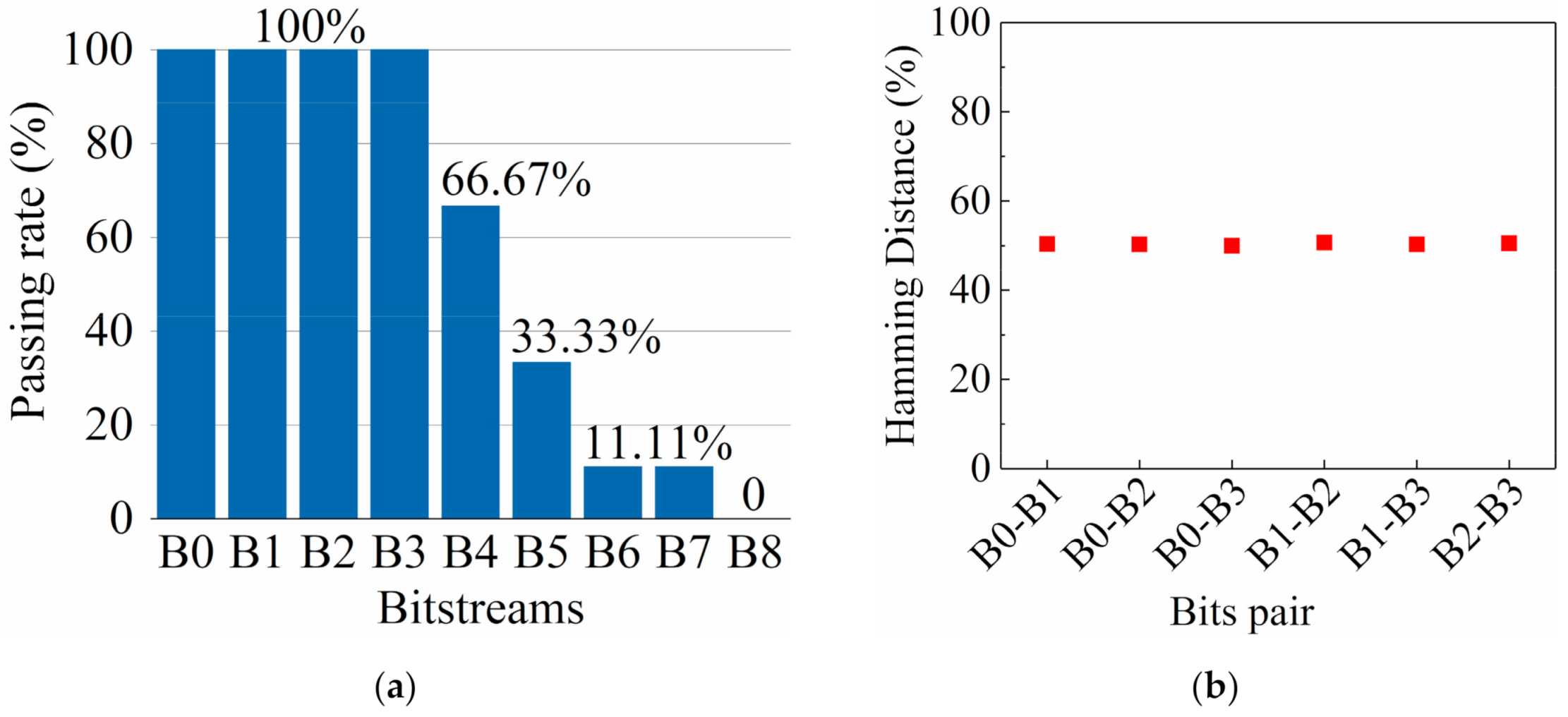
| Test | B0 | B1 | B2 | B3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-value | P-value | P-value | P-value | |
| Frequency | 0.82340 | 0.87983 | 0.05831 | 0.57935 |
| Block frequency | 0.03699 | 0.63301 | 0.09892 | 0.23719 |
| Runs | 0.45817 | 0.78983 | 0.10153 | 0.69051 |
| Longest run of ones | 0.46035 | 0.76249 | 0.96569 | 0.72316 |
| Spectral DFT | 0.16787 | 0.59143 | 0.39501 | 0.06316 |
| Non-overlapping template a | 0.53067 | 0.47208 | 0.47176 | 0.50414 |
| Serial 1 | 0.06643 | 0.47075 | 0.03791 | 0.67948 |
| Serial 2 | 0.11829 | 0.71713 | 0.29277 | 0.80299 |
| Approximate entropy | 0.08384 | 0.28695 | 0.18705 | 0.23089 |
| Cumulative sum (forward) | 0.94112 | 0.58962 | 0.01683 | 0.60898 |
| Cumulative sum (reverse) | 0.76293 | 0.72926 | 0.05127 | 0.23647 |
| Work | Entropy Source | # of RRAMs | RRAM Integration | Extra Circuitry | # of Random Bits | NIST Passed | Post-Processing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | Switching delay | 1 | Single cell | Comparator, AND and counter | 6 | 15/15 | No |
| [15] | Probabilistic switching | 1 | 1T-1R (7 × 7 array) | Comparator | 1 | 11/15 | No |
| [16] | Inter-device variability | 2 | 2 Mbit array | Comparator | 1 | 10/10 | XOR |
| [17] | Switching delay | 2 | Single cell | Comparator | 1 | 9/15 | Von Neumann |
| [18] | Inter- and intra-device switching variability. | 2 | 1 × 2 array | Comparator | 1 | 12/15 | Von Neumann |
| [19] | RRAM switching current | 1 | 7 × 7 array | Comparator | 1 | 12/15 | XOR |
| [20] | RTN | 1 | Single cell | Comparator and D Flip-flop | 1 | 5/15 | No |
| [21] | RTN and intra-device switching variability | 1 | 1T-1R (Simulation) | Ring oscillator and D Flip-flop. | 1 | 12/12 | No |
| [22] | RTN | 2 | Single cell | Comparator and DAC | 1 | 15/15 | Von Neumann |
| This work | Intra-device RESET switching variability | 1 | Single cell | Comparator and counter | 4 | 9/9 | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.; Arumí, D.; Manich, S.; Gómez-Pau, Á.; Rodríguez-Montañés, R.; González, M.B.; Campabadal, F.; Fang, L. RRAM Random Number Generator Based on Train of Pulses. Electronics 2021, 10, 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10151831
Yang B, Arumí D, Manich S, Gómez-Pau Á, Rodríguez-Montañés R, González MB, Campabadal F, Fang L. RRAM Random Number Generator Based on Train of Pulses. Electronics. 2021; 10(15):1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10151831
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Binbin, Daniel Arumí, Salvador Manich, Álvaro Gómez-Pau, Rosa Rodríguez-Montañés, Mireia Bargalló González, Francesca Campabadal, and Liang Fang. 2021. "RRAM Random Number Generator Based on Train of Pulses" Electronics 10, no. 15: 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10151831
APA StyleYang, B., Arumí, D., Manich, S., Gómez-Pau, Á., Rodríguez-Montañés, R., González, M. B., Campabadal, F., & Fang, L. (2021). RRAM Random Number Generator Based on Train of Pulses. Electronics, 10(15), 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10151831









