Adsorptive Findings on Selected Biomasses for Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Biomass
2.1.1. Bulk Density
2.1.2. Proximate Analysis
2.2. Preparation of Adsorbents
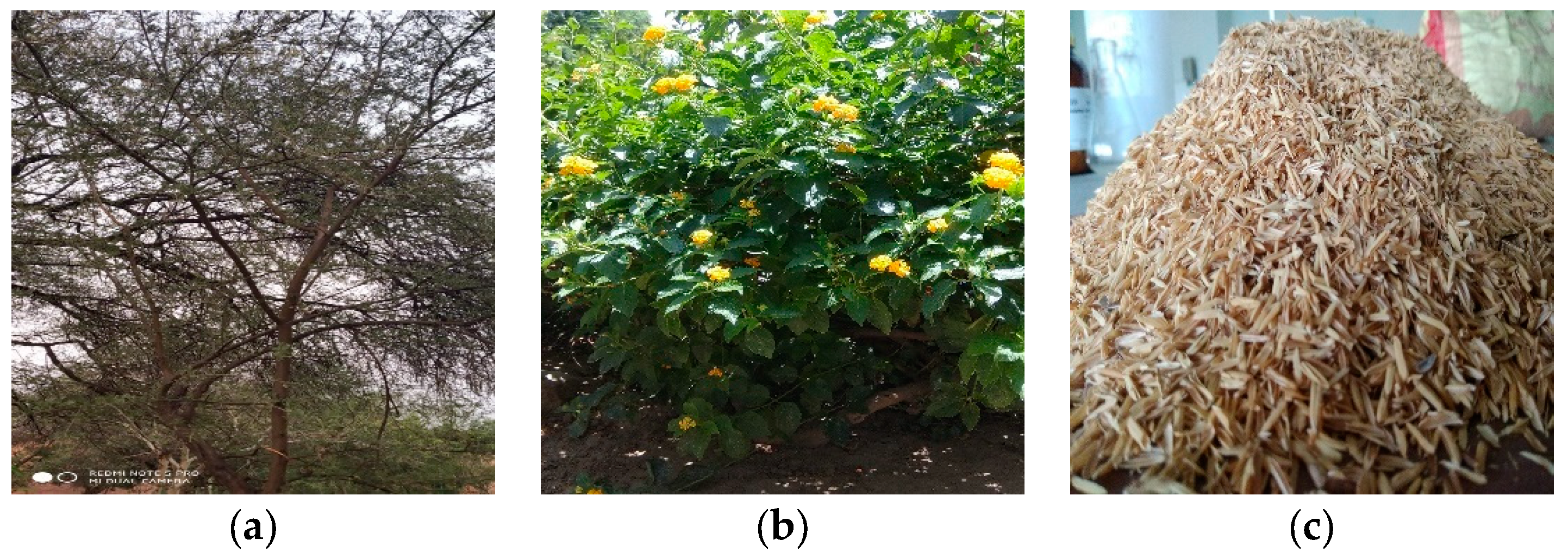
2.2.1. Preparation of Powdered Adsorbent from Raw Biomasses
2.2.2. Preparation of Activated Adsorbent Using Raw Biomasses
2.3. Characterization of Adsorbents
2.4. Batch Experiments
2.5. Mathematical Models for Adsorption Isotherms
2.5.1. Langmuir Isotherm Model
2.5.2. Freundlich Isotherm
2.5.3. Temkin Isotherm
2.6. Mathematical Models for Adsorption Kinetics
2.6.1. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model
2.6.2. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model
2.7. Regeneration of Adsorbents
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Biomasses
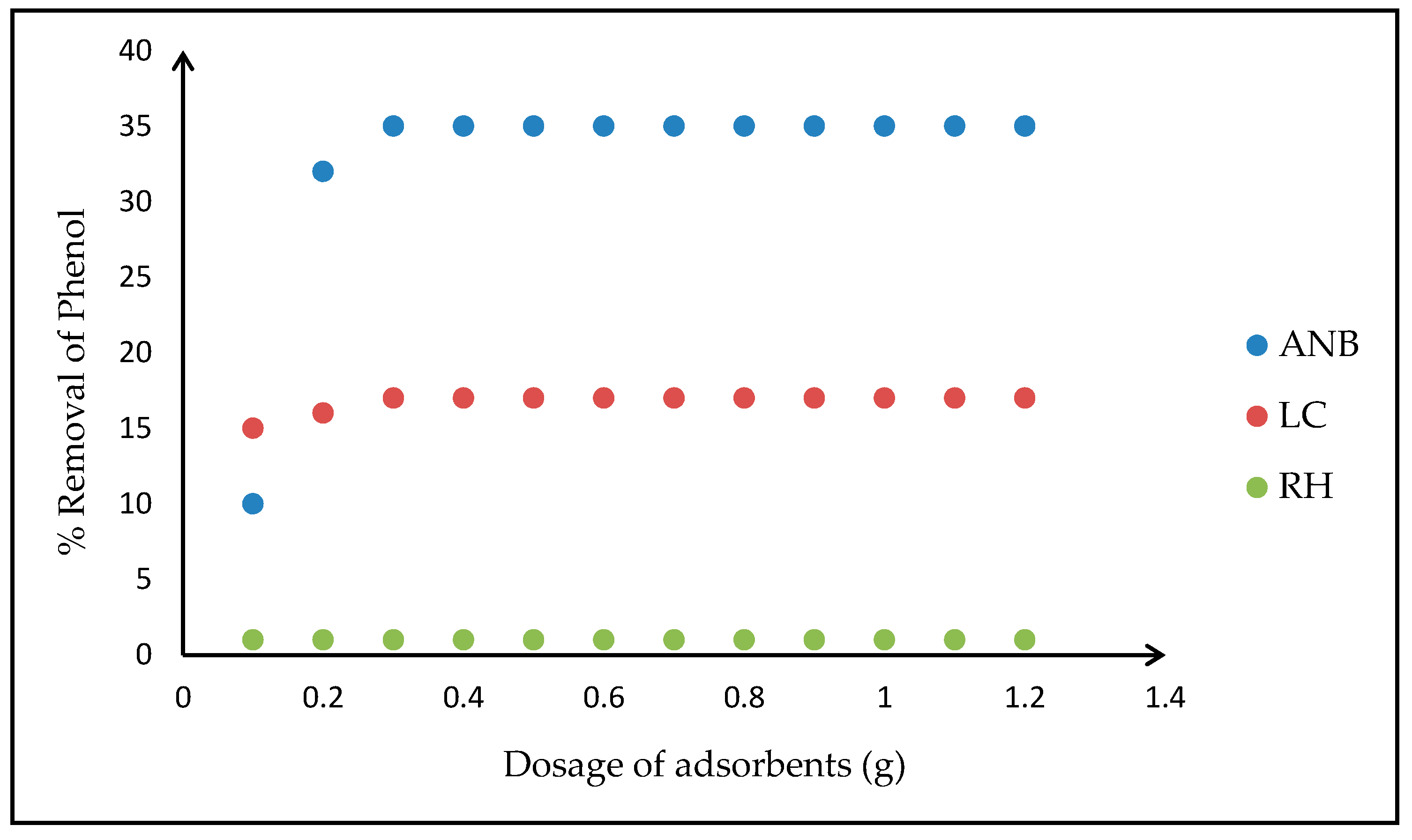
3.2. Characterization and Adsorption Study of Selected Biomasses as Adsorbents
3.3. Characterization of Selected Biomasses after Activation
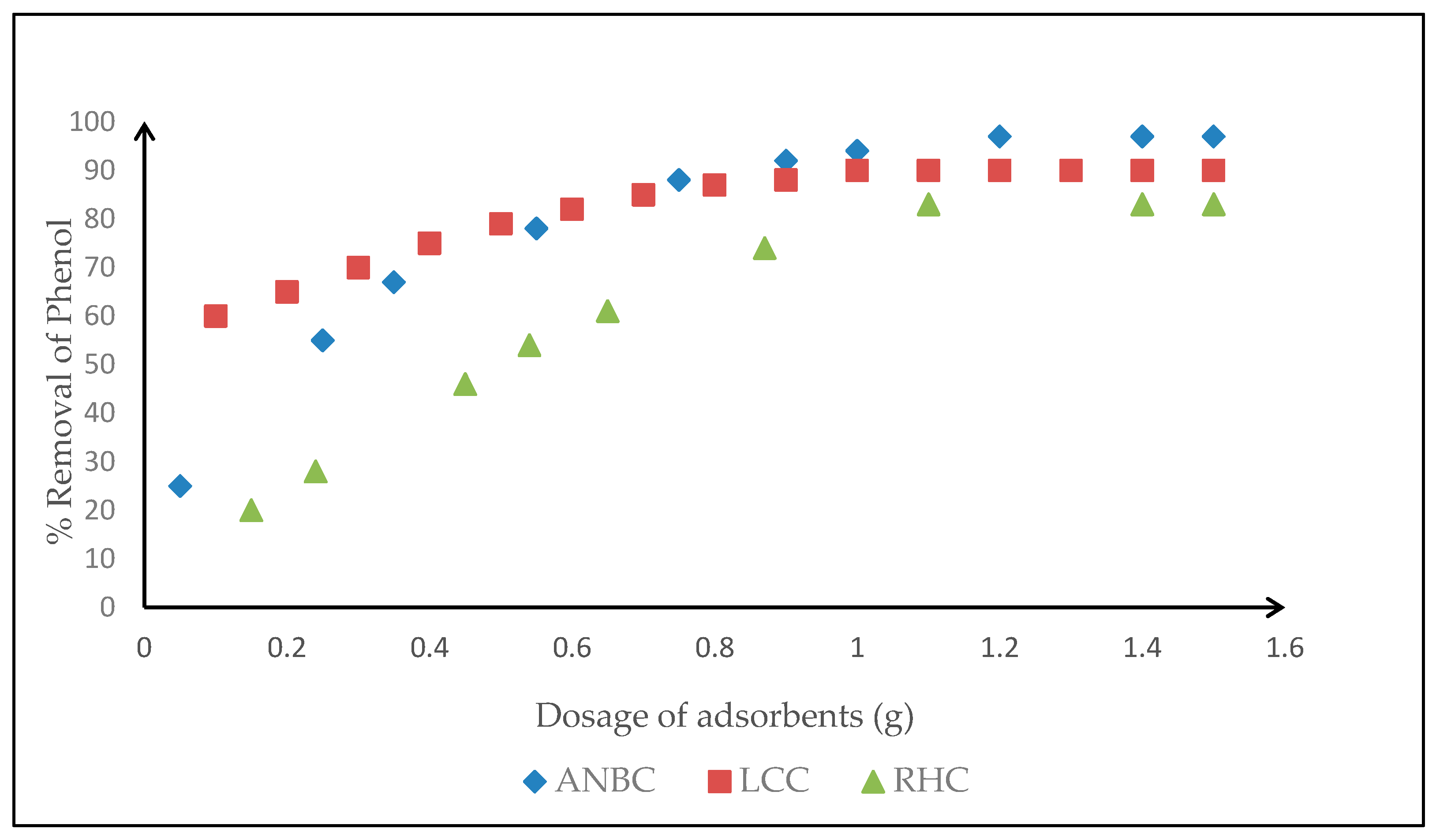
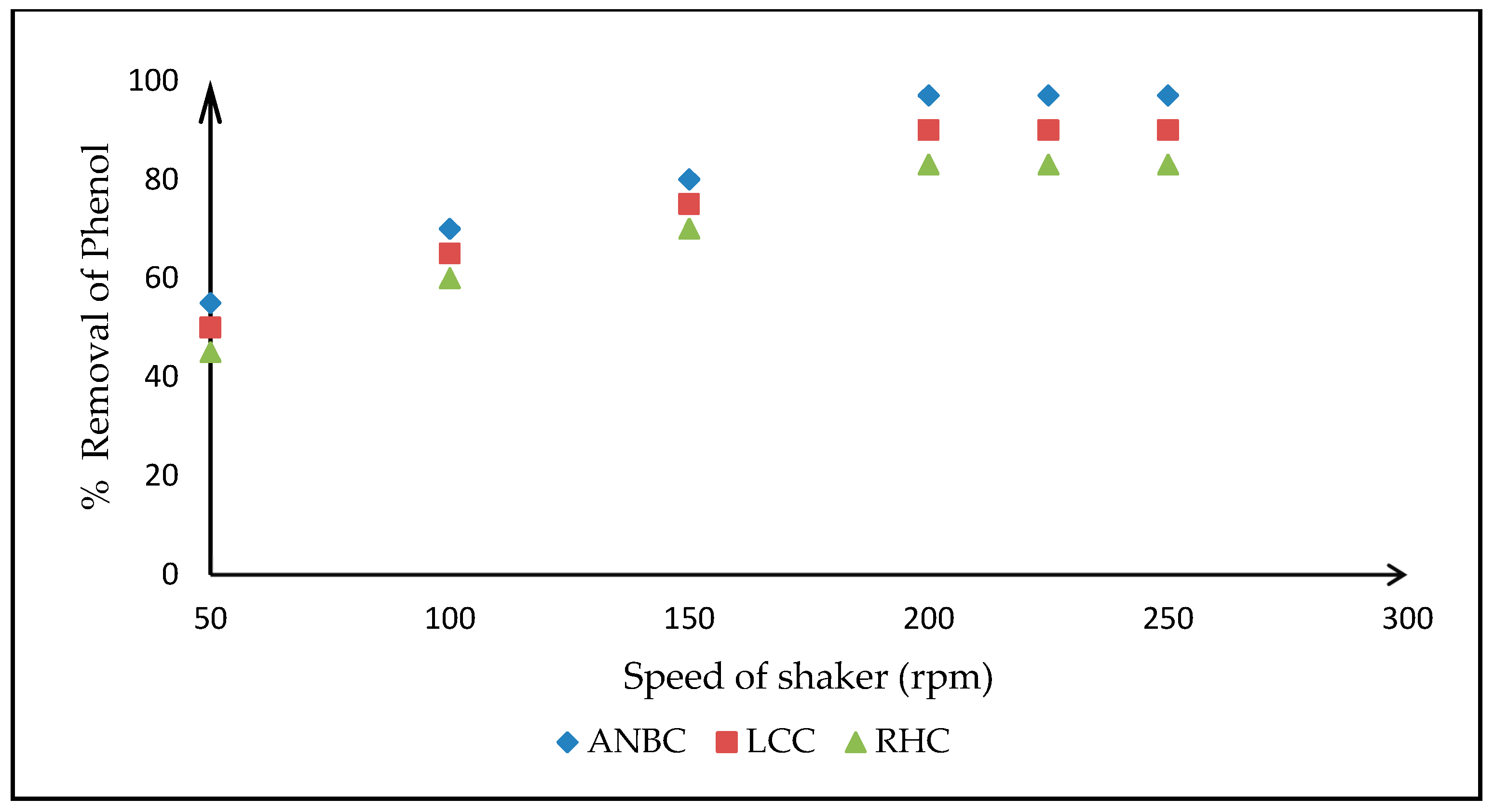
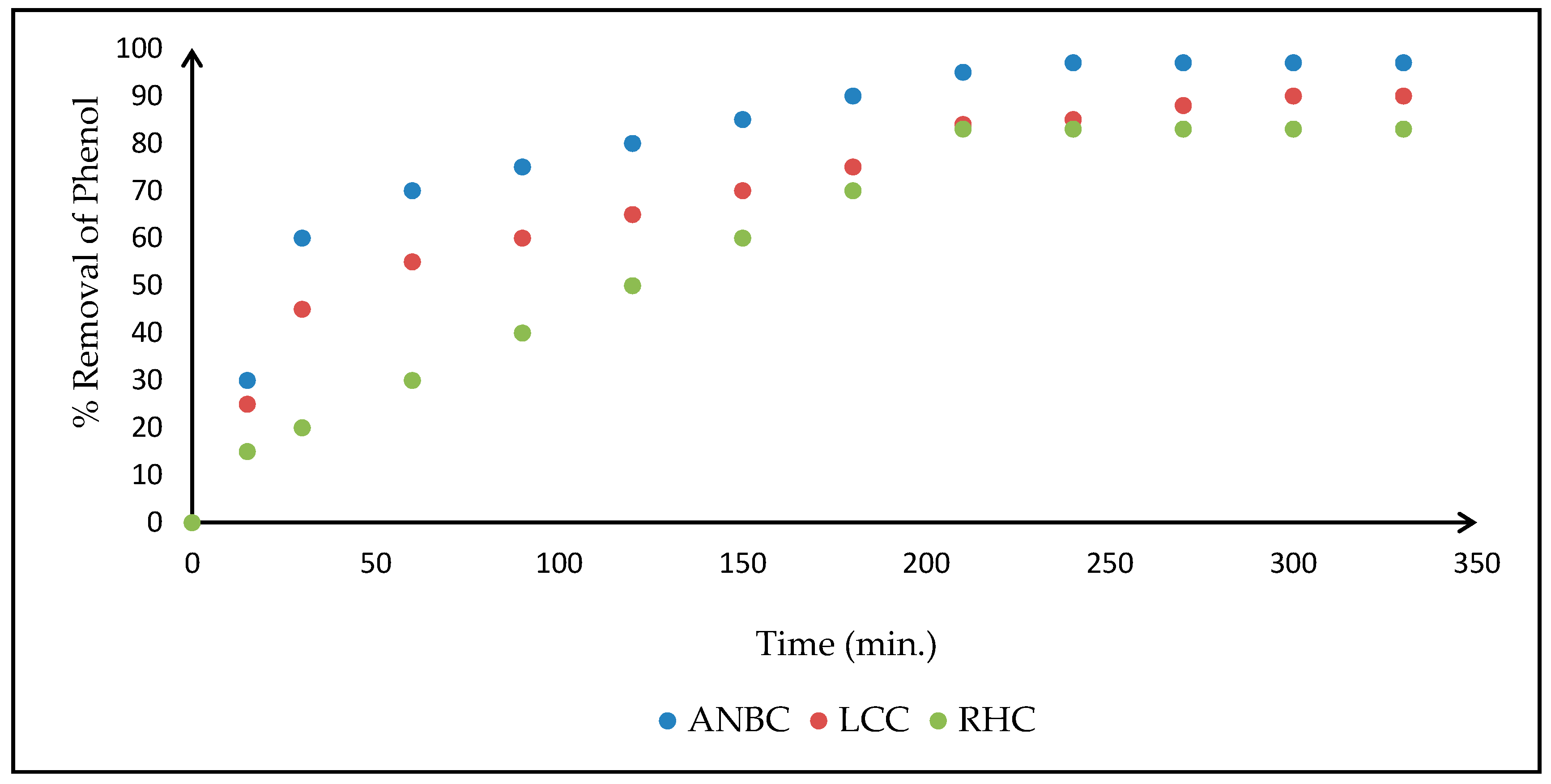
3.4. Adsorption Studies on Activated Biomasses
3.4.1. Effects of Operating Parameters on the Adsorption
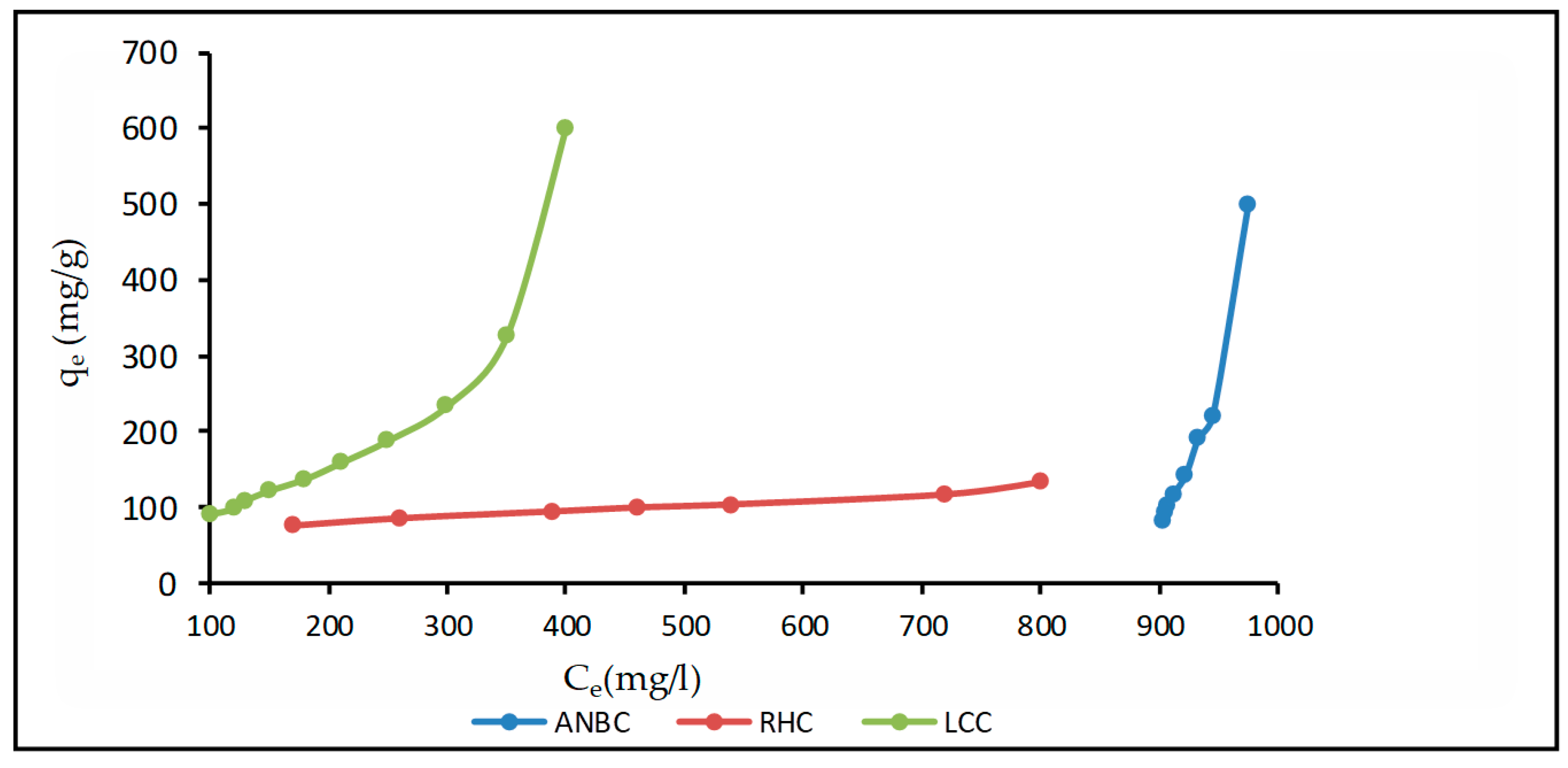
3.4.2. Adsorption Isotherms of Phenol on Activated Biomasses
4. Discussion
4.1. Mathematical Analysis of Adsorption Isotherms
4.2. Mathematical Analysis of Adsorption Kinetics
4.3. Regeneration of Adsorbents
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhuvaneshwari, S.; Hettiarachchi, H.; Meegoda, J.N. Crop Residue Burning in India: Policy Challenges and Potential Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bnapurmath, N.R.; Yaliwal, V.S.; Adaganti, S.Y.; Halewadimath, S.S. Power Generation from Renewable Energy Sources Derived from Biodiesel and Low Energy Content Producer Gas for Rural Electrification. In Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation; Debabreta, B., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 151–194. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, P.V.R.; Rao, T.R.; Grover, P.D. Biomass Thermo-Chemical Characterisation, 3rd ed.; Chemical Engineering Department, IIT Delhi: Delhi, India, 2002; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A. Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, M.; Apaydin-Varol, E.; Putin, A.E. Adsorptive removal of phenol from aqueous solutions on activated carbon prepared from tobacco residues: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard Mater. 2011, 189, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A. Removal of Mn (II) from water using chemically modified banana peels as an efficient adsorbent. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Radi, N.; Ahmed, Z.; Aklaim, A.F. The use of sawdust as a by-product adsorbent of an organic pollutant from wastewater: Adsorption of maximum blue dye. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2014, 12, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Namasivayam, C.; Sangeetha, D. Recycling of agricultural solid waste, coir pith: Removal of anions, heavy metals, organics and dyes from water by adsorption onto ZnCl2 activated coir pith carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, G.D.; Clayton, F.E. Patty’s Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Dursun, G.; Cicek, H.; Dursun, A.Y. Adsorption of aqueous phenol solution by using carbonized beet pulp. J. Hazard Mater. 2005, 125, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anku, W.W.; Mamo, M.A.; Govender, P.P. Phenolic Compounds in Water: Sources, Reactivity, Toxicity and Treatment Methods. In Phenolic Compounds; Hernadez, M.S., Tenango, M.P., Mateos, R.G., Eds.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2017; pp. 420–443. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Sharma, D.K. Adsorption of phenol from wastewater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Din, A.T.; Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.L. Batch adsorption of phenol onto physiochemical-activated coconut shell. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 161, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinakis, A.S.; Elia, L.; Halvadakis, C.P. Removal of total phenols from olive- mill wastewater using an agricultural by-product, olive pomace. J. Hazard Mater. 2008, 160, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamed, Y.A. Adsorption kinetics and performance of packed bed adsorber for phenol removal using activated carbon from date’s stones. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 170, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.L.; Wu, K.T.; Juang, R.S. Kinetic studies on the adsorption of phenol, 4-chlorophenol, and 2, 4-dichlorophenol from water using activated carbons. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, D.N.; Vanjara, A.K. Removal of phenol from wastewater using sawdust, polymerized sawdust and sawdust carbon. Int. J. Chem. Technol. 2004, 11, 5–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, N.; Fakhruddin, A.N.M. Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions using rice-straw as an adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B. Characterisation of Biomass/Agro Residues and Application of Selected Biomass for Sorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions. Ph.D. Thesis, SLIET, Longowal, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gottipati, R. Preparation and Characterisation of Microporous Activated Carbon from Biomass and its Application in the Removal of Chromium (VI) from Aqueous Phase. Ph.D. Thesis, NIT, Rourkela, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, H.; Lu, X.; Tang, J.; Xu, X. Removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution using the rice husk carbons prepared by the physical activation process. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, F.; Gao, J.; Wu, S.; Qin, Y. Preparation of activated carbons for SO2 adsorption by CO2 and steam activation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ould-Idriss, A.; Stitou, M.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, C.; Marcias-Garcia, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Gomez-Serrano, V. Preparation of activated carbons from olive-tree wood revisited. II. Physical activation with air. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Cai, X. Significance of the carbonization of volatile pyrolytic products on the properties of activated carbons from phosphoric acid activation of lignocellulosic material. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Wu, P.H.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Preparation of activated carbons from unburnt coal in bottom ash with KOH activation for liquid-phase adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P. Biomass Characterisation and the Application of Biomass Char for Sorption of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions. Ph.D. Thesis, IIT, Delhi, India, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, P. Rice husk as an adsorbent for phenol removal. J. Sci. Nat. 2011, 2, 593–596. [Google Scholar]
- Chilton, N.; Jack, N.; Losso, N.; Wayne, E.; Marshall, R. Freundlich adsorption isotherm of agricultural by-product based powdered activated carbon in the geosmin water system. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 85, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, T.W.; Chakravorti, R.K. Pore and Solid diffusion models for the fixed-bed adsorbent. Aiche J. 1974, 2, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Ahmad, S.; Toheed, A.; Ahmad, J. A Potential of Rice- Husks for Antimony Removal. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2000, 52, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.; Murthy, Z.V.P.; Jha, B.K. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by chemically modified seaweed. Cryptomeria indica. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, M.S.; Li, H.Y. Adsorption Behavior of Reactive Dye in Aqueous Solution on Chemical Cross-Linked Chitosan Beads. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P. Application of agro-residues based activated carbon as adsorbents for phenol sequestration from aqueous streams: A Review. In Re-Use and Recycling of Materials: Solid Waste Management and Water Treatment; Nzihou, A., Thomas, S., Kalarikkal, N., Jibin, K.P., Eds.; Rivers Publishers: Lange Geer, Denmark, 2019; pp. 189–213. [Google Scholar]
- Dass, B.; Jha, P. Batch adsorption of phenol by improved acacia nilotica branches char: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic studies. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 8, 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- Mahvi, A.H.; Maleki, A.; Eslami, A. Potential of Rice Husk and Rice Husk Ash for Phenol Removal in Aqueous Systems. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2004, 1, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, L.; Deventer, J.S.J.V.; Landi, W.M. Factors affecting the mechanism of the adsorption of arsenic species on activated carbon. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawski, W.; Warszawski, A.; Ratajczak, W.; Porebski, T.; Capala, W.; Ostrowska, I. Removal of phenol from wastewater by different separation techniques. Desalination 2014, 163, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, A.; Magaril, E.; Magaril, R.; Panepinto, D.; Ravina, M.; Zanetti, M.R. Towards Circular Economy: Evaluation of Sewage Sludge Biogas Solutions. Resources 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RL Value | Type of Process |
|---|---|
| RL = 0 | Irreversible |
| 0 < RL < 1 | Favorable |
| RL = 1 | Linear |
| RL > 1 | Unfavorable |
| Biomass | FC (%) | Ash (%) | VM (%) | Bulk Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANB | 25.00 | 2.50 | 72.50 | 210.0 |
| Bagasse | 15.10 | 4.90 | 80.00 | 65.0 |
| Corn Cob | 19.01 | 2.00 | 78.99 | 170.0 |
| Cotton Stalk | 20.55 | 4.45 | 75.00 | 100.0 |
| GNS | 22.01 | 6.75 | 71.24 | 95.0 |
| LC | 23.50 | 12.30 | 64.20 | 250.0 |
| RH | 20.00 | 18.00 | 62.00 | 110.0 |
| Rice Straw | 15.33 | 20.66 | 64.01 | 60.0 |
| Saw Dust | 19.44 | 3.00 | 77.56 | 275.0 |
| Wheat Straw | 18.00 | 9.88 | 72.12 | 50.0 |
| Properties | ANB | LC | RH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ash Content on dry basis (%) | 2.50 | 12.30 | 18 |
| Fixed Carbon on dry basis (%) | 25.00 | 23.50 | 20 |
| Volatile Matter on dry basis (%) | 72.50 | 64.20 | 62 |
| Iodine Number | 485 | 70.0 | 10.1 |
| BET Surface Area (m2g−1) | 50 | 46.4 | 35.5 |
| Particle Size (µm) | 300 | 180 | 300 |
| Methylene Blue Adsorption (mg/g) | 40 | 5.8 | 0.45 |
| Properties | ANBC | LCC | RHC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ash Content on a dry basis (%) | 1.0 | 5.0 | 4.80 |
| Fixed Carbon on a dry basis (%) | 87.0 | 85.0 | 84.20 |
| Volatile Matter on a dry basis (%) | 12.0 | 10.0 | 11.00 |
| pH of slurry | 6.5 (1.2%) | 7.5 (1.0%) | 6.8 (1.1%) |
| Phenol Number (g) | 0.8 | 1.0 | - |
| Iodine Number | 870 | 325 | 750 |
| BET Surface Area (m2g−1) | 450 | 151 | 301 |
| Particle Size (µm) | 45 | 42.3 | 25.3 |
| Methylene Blue Adsorption (mg/g) | 155 | 50.1 | 55.5 |
| Equilibrium Constants | ANBC | LCC | RHC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | |||
| Q0 (mg/g) | - | 16.49 | 135.13 |
| b (L/mg) | - | 13.95 | 0.007 |
| RL | 0.067 | 1.0 | - |
| R2 | - | 0.95 | 0.88 |
| Freundlich | |||
| k | - | 0.31 | 13.52 |
| n | - | 0.84 | 3.06 |
| R2 | - | 0.90 | 0.95 |
| Temkin | |||
| A (L/g) | 0.001 | - | 0.05 |
| b 1(J mol−1) | 0.82 | - | 76 |
| R2 | 0.99 | - | 0.90 |
| Kinetic Constants | ANBC | LCC | RHC |
|---|---|---|---|
| First order kinetics | |||
| qe (mg/g) | 68.93 | 85.43 | 78.72 |
| k1 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.009 |
| R2 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| Second order kinetics | |||
| qe (mg/g) | 90.91 | 103.09 | - |
| h (mg/g min) | 2.50 | 1.84 | - |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | - |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jha, P. Adsorptive Findings on Selected Biomasses for Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions. Resources 2019, 8, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040180
Jha P. Adsorptive Findings on Selected Biomasses for Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions. Resources. 2019; 8(4):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040180
Chicago/Turabian StyleJha, Pushpa. 2019. "Adsorptive Findings on Selected Biomasses for Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions" Resources 8, no. 4: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040180
APA StyleJha, P. (2019). Adsorptive Findings on Selected Biomasses for Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions. Resources, 8(4), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040180





