Abstract
Municipalities often face increasing demand for limited water supplies with few available alternative sources. Under some circumstances, bulk water transport may offer a viable alternative. This case study documents a hypothetical transfer between a water utility district in northern California and urban communities located on the coast of central and southern California. We compare bulk water transport costs to those of constructing a new desalination facility, which is the current plan of many communities for increasing supplies. We find that using water bags to transport fresh water between northern and southern California is in some instances a low-cost alternative to desalination. The choice is constrained, however, by concerns about reliability and, thus, risk. Case-study results demonstrate the challenges of water supply augmentation in water-constrained regions.
1. Introduction
California is facing an unprecedented water crisis. Population continues to increase and environmental water demands are growing, yet a multi-year drought has plagued California since 2009. Although the effects of climate change are unknown, many experts anticipate increased precipitation variability, earlier runoff, and more extreme flood and drought events, all of which create additional challenges for water managers [1]. In response, municipal water agencies in central and southern California have implemented demand-side management and found ways to use existing supply sources more effectively. In some instances, agencies have implemented policies to facilitate local groundwater transfers from existing lower-value uses to higher-value uses. They also continue to seek new water sources to supplement existing supplies. The scarcity value of water in southern California, however, is significant. New water supply sources are difficult to acquire at reasonable cost [2].
Importing water from other regions can be a viable way to increase supplies, though high transaction costs can limit its usefulness [3]. Transfers between water users who are located near each other, rather than far apart, can minimize transportation costs. Such transfers can also minimize impacts on other water users, the environment, and the exporting community. Low-cost transfers have generally been undertaken already though. The challenge for municipal water agency managers in California is thus to find new sources of water, either imported from other regions or previously untapped local supplies, at relatively low cost.
Another important consideration for water managers is risk. Water managers are interested, first and foremost, in the reliability of water sources [4,5,6]. They often prefer to pay a higher price for a more dependable water source than a lower price for one with intermittent availability. Thus new sources must be both financially feasible and sufficiently reliable.
In this paper we consider bulk water transport as a means by which coastal communities in central and southern California could augment existing supplies. In this particular case study, we assume fresh water is pumped into large water bags that are towed behind an oceangoing ship to a destination port. Water bags have been employed by countries around the Mediterranean Sea but have not yet been seriously considered along the western coast of the United States. Over the past 20 years, a number of studies have examined the water balance in California, at either the basin or state level, using integrated hydro-economic models that project demands, available supplies, and the river/canal network through which water is conveyed [2,7,8]. One purpose of these modeling efforts is to evaluate the relative merits of new supply sources.
Here, we take a different approach. To examine the feasibility of a new supply source for central and southern California, namely water bags, we need only compare, on the margin, the cost of meeting new demands with water bag imports to the cost of desalination, the current preferred method for increasing supply. We examine a potential transfer from Humboldt Bay Municipal Water District (HBMWD) in northern California to each of three candidate municipal agencies along the coast of central and southern California. HBMWD has available water as discussed later in the paper. Each potential buyer anticipates demand increases that cannot be met with available supplies, and is therefore actually contemplating ocean-water desalination as a means to augment supply. HBMWD is currently seeking a use for water recently made available by industrial plant closures in its service territory. This is an appealing location for testing the economic feasibility of water bags because the costs and controversy that often plague inter-regional water transfers are minimal. If oceanic bulk water transport is found to be competitive in this case study, it might also be competitive elsewhere.
This paper proceeds as follows. We first describe potential buyers and sellers, as well as factors they are required to consider before implementing a water transfer. We then describe the technology and delivery cost estimates for two new supply sources: bulk water transport and ocean-water desalination. We find that, under certain conditions and for some potential buyers, water bags are a lower-cost means of acquiring water than desalination. We then discuss risk factors and reliability concerns that further influence a water agency’s decision of how best to augment water supply.
2. Market Participants and Water Availability
We identify here the attributes of four water agencies along the California coast for whom participation in a long-distance water transfer might be advantageous. Relevant considerations for potential buyers include current supply portfolio, projected demand increases, and plans for augmenting water supply in the future.
2.1. Humboldt Bay MWD’s Potential Water Exports
HBMWD is located on California’s northwest coast, in Eureka. It provides water to seven wholesale municipal customers in the greater Humboldt Bay area. HBMWD currently delivers between 15.17 and 24.91 million cubic meters (MCM) per year (yr) of treated domestic water to its customers [9]. (1233 cubic meters of water can supply the indoor daily water needs of two families of four for one year). Until recently, HBMWD also sold 82.86 MCM/yr of untreated water to two industrial customers, both pulp mills on the Samoa Peninsula [10]. Both mills ceased operations by 2010. HBMWD is currently seeking a buyer for this water, to avoid having to increase water rates to its other customers, which it will otherwise need to do to completely cover its costs [11]. Furthermore, under California water law, HBMWD may lose their water right to this 82.86 MCM/yr if it does not put the water to use [12].
Importing water from other regions may be a viable way to increase supplies, though three categories of costs limit the potential usefulness of water transfers. The first cost arises from conveyance. Water is a valuable resource, but it is also heavy. The difference in water’s value to sellers (generally agricultural producers of lower-value crops who can reduce water use at relatively low cost by fallowing fields) and to buyers (generally agricultural producers of higher-value crops, municipal utilities, and in some cases environmentally-motivated buyers) must be significant to accommodate high costs of transport [6]. The second cost is third party/environmental impacts. Multiple users rely on the same unit of water as it moves downstream through a watershed, often for a variety of purposes: agriculture, drinking water, recreation, and environmental. Changing the diversion pattern of water can alter its availability to downstream users (third parties) and to the environment (e.g., fish and wildlife habitat). The difficulties of monitoring such impacts, when they are significant or cannot be mitigated, often make transfers infeasible. The third cost category is economic harm to the basin-of-origin because of the export of water. Although neoclassical economics asserts that compensating pecuniary externalities creates market distortions, the political reality is that public outcry typically requires such externalities to be mitigated before transfers can be approved by regulators [13].
HBMWD has already explored the possibility of leasing this 82.86 MCM/yr of available water to other public water agencies in need of additional supplies [14]. The potential basin-of-origin impacts of such a transfer are thought to be relatively low. The transfer would occur at the mouth of the river rather than upstream, thereby minimizing environmental impacts and negative effects on other water users. In the absence of third party or environmental impacts, there are, arguably, no negative economic impacts, since the water is not currently used in another sector of the local economy that would be harmed by the water transfer. (One cost of water exports is the foregone cost of not using the water locally in some other economically productive fashion. However, we are unaware of any proposals to use the water locally.) The existing customer base of HBMWD would benefit from a water export because this would generate additional revenues for HBMWD and prevent significant rate hikes. Although the idea of a transfer is not wholly uncontroversial in the basin-of-origin, revenue transfers might be substantial enough to assuage concerns about relinquishing local control of this portion of the basin’s water supply.
2.2. Municipal Water Agencies Seeking New Water Supply Sources
Many municipal water agencies in central and southern California face projected increases in demand, but are unable to expand their existing supply sources. In some instances, decreased flows or environmental restrictions even reduce availability of existing sources. When new water sources are more expensive to acquire than the wholesale average cost of their existing supply base, agencies have an incentive to implement demand-side management policies to encourage consumers to conserve water. Agencies may implement conservation programs (either voluntary or mandatory); or encourage reductions in water use through retail pricing schemes that impose water’s full cost on customers; or require new customers to pay the full cost of new supplies rather than melding their costs with existing, cheaper supplies. For the three municipal water agencies along the coast of central and southern California, we describe next the constraints on their existing sources of supply, and their plans for meeting future excess demand using ocean-water desalination.
Water agencies that provide water for municipal purposes to more than 3000 customers (or that supply more than 3.70 MCM to their customers annually) are required under California law to prepare an urban water management plan (UWMP) every five years [15]. The purpose of UWMPs is to demonstrate that water supplies are sufficient to reliably and efficiently meet existing and future demands. Agency-specific information presented in this paper is derived primarily from the most recent UWMPs of the San Francisco, Santa Cruz, and San Diego municipal water agencies.
2.2.1. San Francisco Public Utilities Commission
The SFPUC provides water to approximately 850,000 retail customers in San Francisco County and an additional 1.75 million customers to the south and east of San Francisco Bay served through wholesale contracts with 27 agencies (Table 1). In an average water year, the SFPUC imports 85% of its water from the Hetch Hetchy Reservoir, in the Upper Tuolumne River Watershed. The balance is from local runoff and groundwater supplies [16]. In dry years, imports from the Tuolumne Watershed increase to 93%.
In 2010, SFPUC delivered 313.81 MCM to its retail and wholesale customers. SFPUC anticipates that its deliveries will need to rise to 363.74 MCM (an increase of 16%) by 2030 to accommodate growing demand. Retail water demand is expected to increase slightly between 2010 and 2030, due to estimated growth in business and industry. SFPUC’s in-city residential customer base is also expected to increase, but residential per capita use is projected to decline, due to SFPUC’s conservation programs and greater compliance with new plumbing codes (e.g., installation of more water-efficient fixtures). (Total consumption and per capita use of water have been declining in San Francisco since the mid-1970s, motivated in part by severe droughts in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Per capita consumption by SFPUC’s retail customers in 2010 was 329.2 liters/day per capita, which is one of the lowest rates in the state.) SFPUC is contractually obligated to provide its wholesale customers with 254.00 MCM/yr through 2018. SFPUC’s wholesale customers have indicated a need for even more water after 2018, but SFPUC has not yet factored this into its demand projections.

Table 1.
Selected water agencies with projected excess demand in Central/Southern California.
| Agency | San Diego | San Francisco | Santa Cruz |
|---|---|---|---|
| End-use and wholesale customers, 2010 | 3.11 million | 2.60 million | 91,000 |
| 2010 Deliveries (MCM) | 697.88 | 313.81 | 13.33 |
| 2030 Projected Population | 3.76 million | 2.99 million | 98,000 |
| 2030 Normal Year Projected Demand (MCM) | 929.68 | 363.74 | 15.31 |
| New Resources Brought On-Line to Meet Projected Demand | Agricultural conservation and transfers; canal lining; purchases through MWD; ocean-water desalination; groundwater storage | Water transfers; ocean-water desalination; additional recycled water, groundwater, and conservation | Conservation; use curtailment in drought years; ocean-water desalination |
| Proposed Desal Facility (MCM) | 69.07 | 69.07 | 3.45 |
| Estimated Desal Costs ($/m3) | 1.77 | 0.31 | 3.22 |
| Distance from HBMWD (nautical·km) | 1048 | 355 | 435 |
| Data Sources | [17] | [16] | [18] |
Note: City of Santa Cruz 2030 population estimate based on a population growth forecast of 8% over 20 years ([18], Appendix I).
A single dry year typically reduces SFPUC’s surface water supplies to 90% of normal year availability. Multiple years of drought have, historically, reduced SFPUC’s surface water supplies to 80% of normal. Groundwater and recycled water supplies are not reduced during drought but are a small portion of SFPUC’s supply system and only available for use in the retail service area. SFPUC is currently exploring ways to strengthen its drought-resilience, such as dry-year supply options offered by water rights holders in the Tuolumne River basin, a groundwater conjunctive-use project, and a regional desalination plant.
2.2.2. City of Santa Cruz Water District
The SCWD serves approximately 91,000 customers. It is supplied entirely by rainfall, surface runoff, and groundwater infiltration, primarily within the San Lorenzo River Watershed. SCWD is isolated from California’s conveyance network and reservoir storage infrastructure by the Santa Cruz Mountains, and consequently does not import water from other parts of California. SCWD anticipates reduced groundwater availability in the future. It does have some surface water storage capacity in Loch Lomond Reservoir, located in the Santa Cruz Mountains.
In 2010, SCWD delivered 13.33 MCM to its retail customers [18]. It projects that these deliveries will rise to 15.31 MCM (an increase of 15%) by 2030. Per capita consumption, however, is expected to decrease through an imposition of additional water restrictions. The latter continue from 2005 and include phased rate increases for residential customers in the city of Santa Cruz. Housing market downturns and the recent economic recession, post-2005, have also reduced water consumption, at least temporarily [18].
Historically, SCWD has focused on demand conservation and restriction to address supply-demand imbalance. In the future, SCWD might partner with a local golf course to exchange the District’s recycled water for the golf course’s treated water, as a means to supplement treated supplies. The exchanged water would mitigate SCWD’s need to comply with ESA restrictions pertaining to instream flows for anadromous fish. In addition to the exchanged recycled water and continued conservation, SCWD’s primary plan for water supply augmentation is construction of a desalination plant [18].
2.2.3. San Diego County Water Authority
SDCWA is a wholesale provider of water to 24 member agencies, who collectively serve 3.11 million retail customers. SDCWA obtains its water supplies from several sources, including member agencies’ local groundwater and surface sources, water transfers (e.g., from the Imperial Irrigation District), canal linings (All-American and Coachella Canal Lining Projects), and recycled water for both non-potable and potable purposes.
In 2010, SDCWA delivered 697.88 MCM to its wholesale customers [17]. SDCWA anticipates that demand for supplemental water from member agencies will increase to 929.68 MCM by 2030. This is cause for concern since, in 2010, total local sources delivered just 11% of the water used in the service area. SDCWA is seeking to increase local supplies through more efficient use of the 25 San Diego County reservoirs [17].
One of SDCWA’s primary water supply sources is the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California (MWD). MWD serves 26 wholesale customers in southern California, including SDCWA. MWD’s member agencies may request as much water as they like from MWD. MWD then provides its member agencies with a certain amount of water at the average supply cost of its two primary sources: State Water Project supplies from northern California and the Colorado River. However, MWD charges a higher rate for any additional supplies it must develop on behalf of a member agency [19]. MWD provides incentives to its member agencies to reduce their demand for conventional sources by developing alternative supplies, for example desalination plants, recycling and groundwater recovery as well as curtailing demand via conservation. SDCWA can obtain dry-year supplemental waters, both intra and extra-regionally, by withdrawing from district reservoirs and groundwater sources, and increasing the recycling of water. SDCWA also plans to augment its supply portfolio through desalination.
3. Case Study
The three water agencies described above seek supplemental water sources either in all years or during extended dry periods. The HBMWD’s 82.86 MCM of available water is enough to meet the needs of approximately 500,000 people each year. Although this is a small percentage of the millions of people who live along the central and south coasts of California, it is a significant portion of any single agency’s customer base, and a large percentage of any one of these agencies’ shortfalls. (For example, the 82.86 MCM from HBMWD would meet 15% and 20% of San Diego and San Francisco water needs respectively, and would more than exceed SCWD’s entire annual demand.) The question remains how the cost of desalination, as the base case for augmenting the agencies’ supply portfolios, compares to the costs of delivering water to the agencies by water bags.
3.1. Water Supply Augmentation through Ocean-Water Desalination
The three buyer agencies described above are all in the planning stages of constructing desalination facilities to meet projected demand. Use of seawater and brackish desalination has been expanding over the past few decades, due to increasing stresses on other water sources and technological advances that have decreased desalination’s power consumption and equipment costs. Nonetheless, it remains a capital and energy-intensive process. As of 2002 (the most recent year for which comprehensive statistics are available), over 15,000 industrial-scale desalination units worldwide had been installed or contracted, with a capacity of over 11,713.5 MCM/yr. Nearly 60% of this capacity was for seawater desalination [20].
No industrial-scale desalination plants are currently operating in California. At least 20 communities and water utilities in California are considering desalination for supply augmentation, though many of these are only at the conceptual or planning stages [21]. The preferred technology for the low and medium capacity systems under consideration in California is reverse osmosis (RO), as opposed to other membrane processes or thermal distillation methods. RO has lower costs than thermal methods, due primarily to lower energy consumption and recent advances in membrane technology [22]. RO accounts for over 50% of installed desalination capacity worldwide [23].
Calculating RO desalination costs involves a number of interrelated factors, many of which vary by site (e.g., source water, energy source), technology (e.g., capital, plant life, operations and maintenance), and plant capacity. Higher feed water temperatures can also increase costs significantly [24]. Desalination cost estimates also vary because of inconsistent methods for reporting costs. For example, studies rarely report with any degree of specificity which costs are included or excluded from the analysis. Land cost and pretreatment costs are often completely ignored [25].
Despite inconsistencies across studies, [22] were able to synthesize estimates of desalination costs from the literature, based on type of feed water, desalination method, energy source, and capacity of the desalting plant. Cost estimates vary considerably by these factors but still clearly indicate increasing economies of size (i.e., larger desalination plants have lower average cost). They report cost estimates of $1.62 to $5.09/m3 for a small RO plant (between 91.24 and 365 TCM/yr capacity where TCM is thousand cubic meters); estimates of $0.61 to $2.11/m3 for a medium-sized RO plant (between 5473 and 21,891 TCM/yr capacity); and estimates from $0.58 to $0.86/m3 for a larger RO plant (between 36,486 and 79,763 TCM/yr capacity). Other cost estimates from the literature fall within these ranges [26,27]. Desalination costs have also been declining over time. The average cost of desalination in 1970 was $32.02/m3, whereas in the early 2000s it had declined to $1.30/m3. Projected costs for larger RO plants proposed in the early 2000s in Florida and Israel were even lower, approximately $0.69/m3 [20].
Desalination costs generally consist of capital and annual operating charges. For capital costs, we assume a 30-year project life with amortization at 4.77% over the project lifetime. The rate is based on a Municipal Revenue Bond Index, which reflects 25 different revenue bonds that all mature in 30 years [28]. (The average rating is similar to Moody’s A1 and Standard and Poor’s A-plus bond ratings. The 4.77% is from 2013, the last year for which bond data are available, and what we consider the “base year”.) Operating costs are estimated on a per annum basis (US$2013). The sum of amortized capital costs and annual operating costs is then divided by the project yield (m3/yr) to determine the unit cost per m3/yr (US$2013) [29]. Using these methods, we can construct cost estimates for each of the desalination projects being contemplated or planned by the three water agencies (Table 2).

Table 2.
Desalination costs by water district.
| San Diego SDCWA | San Francisco SFPUC | Santa Cruz SCWD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Capital Cost ($millions) | 1003 | 168.5 | 120 |
| Annual Capital Payment ($millions) | 63.5 | 10.68 | 7.60 |
| Annual Operating Costs ($millions) | 58.86 | 11.39 | 3.82 |
| Annual Total Payments ($millions) | 122.41 | 22.07 | 11.42 |
| Expected Plant Yield (MCM/yr) | 69.07 | 69.07 | 3.45 |
| Annual Per-Unit Cost ($/m3) | 1.77 | 0.32 | 3.31 |
| Data Sources | [17] | [16] | [18] |
Notes: All values are in 2013 US dollars. Calculations assume an annual interest rate of 4.77% over a 30-year loan life (annual payments).
The regional desalination project contemplated by SFPUC is a joint venture with four other Bay Area water agencies. It would increase supply reliability within the region, provide a source of water during emergencies and extended droughts, and allow other facilities to be taken out of service for maintenance or repairs. The project would produce a maximum of 69.07 MCM/yr [16]. SFPUC anticipates taking delivery of 12.3 MCM/yr [30], with the remaining going to the other project partners. The unit cost to SFPUC for the new facility is estimated to be $0.32 per m3/yr (Table 2).
SCWD and the neighboring Soquel Creek Water District are also pursuing development of a desalination plant. The maximum operating capacity of the plant will initially be 3.45 MCM/yr, with the potential to increase capacity to 6.17 MCM/yr in the future [31]. The plant would serve as a backup water source to the City of Santa Cruz during drought years. During non-drought years, Soquel Creek Water District would run the plant at less than full capacity (approximately 2.22 MCM/yr) to recharge groundwater aquifers and thus prevent seawater intrusion [18]. In the future, the City of Santa Cruz may also need to use desalination plant output during non-drought years, particularly if existing surface water supplies must be curtailed to improve habitat conditions for endangered species [18]. Santa Cruz anticipates using 59% of the yields from the desalination facility and will consequently pay 59% of the capital costs [31]. Cost of the desalination plant is estimated to be $3.22 per m3.
SDCWA is pursuing purchase of 69.07 MCM/yr from the Carlsbad Desalination Project, owned by a private company called Poseidon Resources [32]. The project is not yet operational but is fully permitted. SDCWA considers this a “verifiable” water source. Desalinated water from the Carlsbad Desalination Project is estimated to cost $1.77 m3/yr (Table 2). SDCWA is also in the planning stages for two other regional seawater desalination projects, one of them situated in Mexico [17].
Table 2 summarizes desalination costs. These estimates fall generally within the bounds, by facility size/yield, that [22] report. Per-unit cost estimates vary widely, however, due to differences in the scale of proposed facilities and ensuing water yield.
3.2. Bulk Water Transport
In bulk water transport, a closed container or bag transports water from source to end-use. At sea, the bag approach requires towing by an oceangoing tugboat. Transportation costs are therefore a key feature of the variable cost for this form of bulk water transport. Variable cost also depends upon distance conveyed, fuel costs for the tugboat, and the number of bags (volume of water) that can be transported [33].
Aquarius Water Transportation Company has been delivering 65,3184 kg and 1,814,400 kg bags of water from the mainland to the Greek Islands since 1997 [34]. Norwegian Nordic Water Company has been testing bags of various sizes. Since 2000, they have implemented a 19,000 m3 polyester fabric bag to convey water from Turkey to Cyprus [34]. While these companies have focused on designing optimally sized bags, other entrepreneurs are exploring the benefits and costs of towing several bags behind the same tugboat. Terry Spragg, in particular, has developed a means of connecting bags in a train-like fashion. Each bag holds 17,000 m3 of water [33,34].
Although such examples demonstrate the technical feasibility of water bags, their commercial success has so far been limited. This raises the question, “Is water bag technology economically feasible in the California context?” We use engineering and cost information provided by Terry G. Spragg & Associates, regarding the Spragg Bag, as a starting point for analyzing this question [19].
The delivered cost of water, via oceanic transport using the Spragg technology, comprises four components: transportation (tugboat chartering, fuel); operational (dockside fees and maintenance, loading/unloading labor); capital (water bags, loading/unloading facilities); and the cost of water. We assume a baseline diesel fuel cost of $1.06/liter [35], and a 20-bag maximum for a water bag “train”. Each tug thus transports a maximum of 349 TCM of water and is approximately 3.06 km in length. We assume HBMWD that will charge $0.05/m3 for the freshwater transported by water bag [11]. Water bag delivery quantity is set equal to the amount of water each agency otherwise proposes to acquire from desalination, though this amount is capped at 82.86 MCM, which is the water quantity that HBMWD has available to market.
Table 3 provides delivery cost estimates for the water bag approach for the three potential buyer agencies described above. The total cost of providing a cubic meter of water via water bags ranges from a low of $0.44/m3 for SFPUC to a high of $2.06/m3 for SCWD, with SDCWA facing a cost of $0.74/m3. Differences between delivery costs across SFPUC, SCWD, and SDCWA can largely be attributed to differences in yields and capital costs. Fuel and other variable costs increase with increased distance from the source. Total capital costs for SDCWA and SFPUC are higher than those of SCWD because the quantity transferred to SDCWA and SFPUC would require the use of two loading facilities. Per-unit capital costs for SDCWA and SFPUC are lower than those of SCWD, however, due to size economies. We also observe scale economies in distance. The greater the distance, the larger the proportion of fuel in the per-unit cost.
Before comparing our cost estimates for water bags to those for desalination, we compare them first to one other cost estimate in the literature, for a similar water bag technology. The United States Bureau of Reclamation (USBR) recently conducted a long-term assessment of water supply and demand in the Colorado River Basin [36]. USBR undertook this basin study in response to concerns that water shortages were probable in many locations throughout the Colorado River Basin under a broad range of possible supply and demand scenarios. (Southern California receives 5429.6 MCM/yr from the Colorado River Basin.) They determined that 246.60 MCM/yr of water could be delivered to San Diego in water bags at a cost of $2.19/m3 [37]. The USBR assumes a bag capacity of 49,320 m3 (we use a bag capacity of 17,015 m3 but assume that multiple bags can be towed behind a single tug) and sources the water 3226 nautical km from San Diego, in Alaska (we source the water from Humboldt Bay, which is 1048 nautical km from San Diego).

Table 3.
Water bag delivery costs.
| Agency | Units | San Diego SDCWA | San Francisco SFPUC | Santa Cruz SCWD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | m3/yr | 69,074,936 | 69,074,936 | 3,453,747 |
| Number of tugs | 9 | 5 | 1 | |
| Number of bags per trip | 20 | 20 | 14 | |
| Number of trips per year | 203 | 36 | 14 | |
| Water cost | $/m3 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Fuel cost | $/m3 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.11 |
| Other variable costs | $/m3 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.21 |
| Capital cost | $/m3 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 1.68 |
| Total per-unit cost | $/m3 | 0.74 | 0.44 | 2.06 |
| Fuel as % of per-unit cost | % | 26% | 15% | 5% |
| Total capital costs | $in millions | 106 | 148 | 58 |
Notes: Maximum tug length is 20 water bags and fuel cost is $4.00/gallon. Other variable cost includes O&M (loading/unloading labor, moorage) and transportation (chartered ocean/harbor tugs and labor) costs. Capital cost includes loading/unloading facilities and water bags.
Our water bag cost estimate for delivery to San Diego is 0.74/m3, which falls significantly below the USBR estimate of $2.19/m3 [37]. This is logical, as our model sources the water from northern California rather than Alaska, and we assume that more water can be transported behind a single tug. Note that the per-unit cost estimate for SCWD is quite high relative to the other two estimates in Table 3, and somewhat similar to the USBR estimate. If SCWD requested more water, it would have more delivered units over which to spread fixed capital costs.
If we restrict our model based on the Spragg technology to deliver only 49 TCM per tug (rather than the 340 TCM per tug represented in Table 3) over a distance of 3226 rather than 1048 nautical·km, we calculate a per-unit cost of $8.05/m3, significantly higher than the USBR estimate. How much water would need to be delivered from Alaska per tug, using our model based on the Spragg technology, to reduce the per-unit costs to the USBR estimate of $2.19/m3. A tug would need to tow approximately 222 TCM to spread the capital costs over sufficient units to lower the per-unit cost to $2.19/m3. These estimates suggest that the Spragg technology may be more capital-intensive than the water bag technology assessed by USBR. The Spragg technology may thus be more appropriate for shorter distances and instances where scale economies reduce allow capital costs to be spread over more units, than the technology assessed by USBR.
Water source, and distance between source and use point, are clearly important factors influencing the cost of a unit of water delivered by water bag. Next, we provide a sensitivity analysis of key cost drivers, followed by a cost comparison of water bags and desalination. This sets the stage for a discussion of reliability concerns that water managers have when comparing two potential sources, especially unconventional ones such as desalination and water bag transport.
3.3. Cost-Effectiveness of Water Bags versus Desalination
Whereas capital investment is the major component of desalination costs for SDCWA and SCWD (and nearly so for SFPUC), operating costs are the major component of water bag costs for all three agencies. To further explore this phenomenon for water bags, Figure 1 reports results of sensitivity analysis on different tug length restrictions and fuel prices. Number of bags towed behind one tug boat varies from 20 (baseline), 10, and 5 bags per trip per tug. This range arises from possible state limits on length of towed vessels. Diesel fuel prices range from $1.06 (baseline), $1.59, and $2.11 per liter.
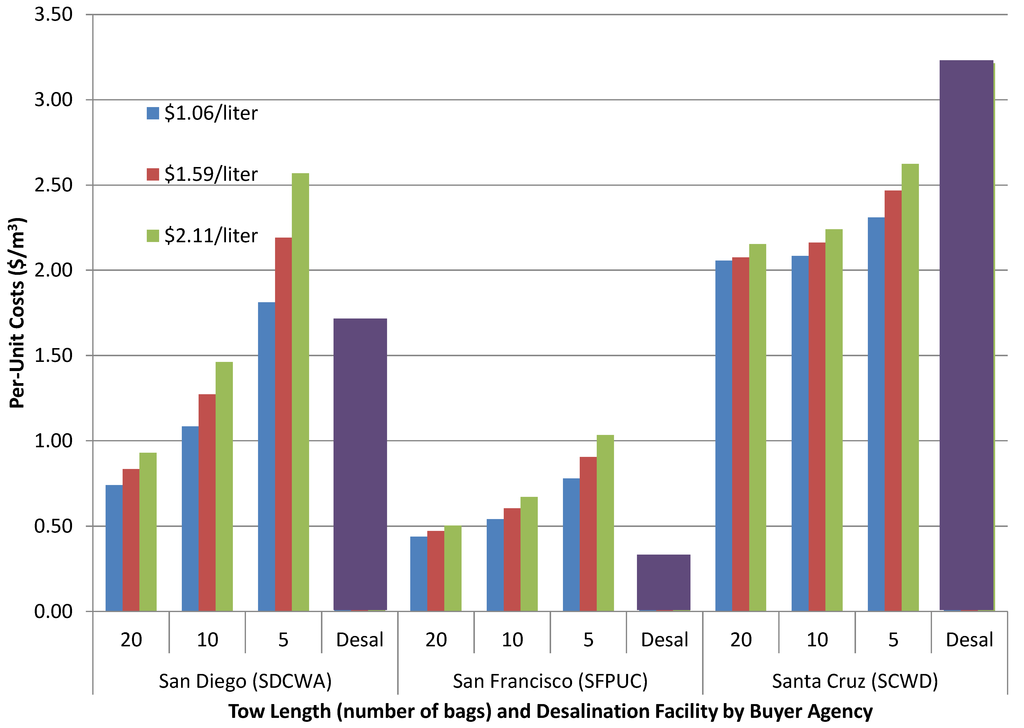
Figure 1.
Sensitivity analysis on water bag tow length and fuel prices, as compared to desalination ($/m3, US$2013).
Variable fuel prices and concerns about fuel prices that trend upwards may be an issue, especially over longer distances. SDCWA and SFPUC are linear in fuel costs: every 25-cent increase in per-liter fuel costs leads to a per-unit cost increase of 4.7 cents/m3 for SDCWA and 1.6 cents/m3 for SFPUC respectively. Santa Cruz follows a different pattern. At lower fuel prices, the cost-minimizing tug length is not the maximum tug length. At higher fuel prices, the cost-minimizing tug length is higher, which increases capital costs (more bags must be purchased) and decreases per-unit variable costs (fewer trips per year). Thus increasing fuel price by 25 cents on a base rate of $1.06/liter increases unit cost to Santa Cruz by 1.3 cents/m3 whereas increasing fuel price by 25 cents on a base rate of $2.11/liter increases unit cost by 7.4 cents/m3.
Per-unit cost is less sensitive to fuel price than it is to tug length, though this is less true for longer distances. Tug length matters more over long distances because on the margin, it is less costly to add one more bag to a tug than it is to run a new tug.
In sum, under no fuel price and tug length combinations are water bags lower-cost than desalination for San Francisco. For Santa Cruz, the cost of desalination is sufficiently high that all fuel price and tug length combinations point to water bags as the lower-cost water source. For San Diego, water bags are lower-cost than desalination only at higher tug lengths.
4. Incorporating Reliability
Reliability of new water supplies is a significant consideration for municipal water district managers. Reliability is the extent to which fluctuations in supply can be maintained within a defined range. In a survey of federal, regional, and private water suppliers, reliability was identified as the most important water supply attribute; quality and cost were second and third most important [4].
Thus cost alone is not a sufficient basis for choosing how best to augment water supply. A simple unit cost comparison does not take into account the environmental, reliability, and cost attributes risks of different water sources. For example, water managers would prefer to know with certainty how much water a supply source will yield, and at what cost, under different water year types. Even better would be to know the likelihood that a particular water year type will occur. However, even when the relationships between, for example, water year type and availability of a supply source are relatively well understood and probabilities can be assigned to all possible outcomes, the resulting comparison would be between two “expected value” estimates. Such an analysis would fail to incorporate the importance of risk management to a water manager’s decision-making process.
If such probability distributions of possible outcomes were known, one could also compare the minimum and maximum supply availability, percentiles, and downside risks (e.g., the probability of a supply shortfall) of two different supply sources, as well as the expected values. Such detailed information is often not available but we recognize the importance of such information to water managers.
The authors of [5] explore how a water manager might weigh the costs and benefits of alternative water supply sources. They apply methods from portfolio finance theory to the problem of water supply augmentation. They modify the least-cost approach method to incorporate reliability. For example, they begin by assuming a water agency must meet a certain level of demand with a specific level of reliability (for example, all demands can be met 9 years out of 10). The agency compares several different portfolio compositions (i.e., different combinations of water supply sources), and chooses the one that meets the required specifications at lowest cost. (Specific water quality targets could also be included as an additional dimension in the least-cost approach [5].) This approach recognizes the importance of considering how the risk profile of a new supply source complements or detracts from the risk profile of existing sources. [5] note that differences in sources’ yield, quality, and reliability affect the overall risk profile of a water supply portfolio. It is therefore essential to assess the variance and correlation between sources. The approach advocated by [5] is consequently a comparison of water supply portfolios rather than single supply sources. This type of analysis allows for the possibility that a higher-cost water source could bring to the water supply portfolio a sufficiently different set of risks, (and perhaps a higher water reliability) than existing sources, that its addition would be advantageous.
Following are major sources of risk that water managers might consider when they seek to expand supply. Agency-specific examples are provided to generate insights about the ability of different water sources to contribute to a well-balanced water supply portfolio.
4.1. Yield Risk
Climate variability causes significant variation in water availability for many water sources; this is especially true for surface water. All three buyer agencies rely heavily on surface water supplies, either imported (San Francisco from Hetch Hetchy Reservoir, and San Diego from MWD) or native (Santa Cruz). All three buyer agencies project that supplies are adequate to meet demand in 2030, at least in a normal water year or a single-year drought. However, multiple dry years become problematic because their water supply portfolios and available storage capacity cannot withstand more than one or two years of limited surface water supplies.
From the perspective of climate-generated yield risk, both water bags and desalination would complement the agencies’ supply portfolios. Desalination is not subject to climate risk directly in terms of sea/brackish water availability. Indirectly, however, disruption of desalination production may arise from climatic changes effecting hydro-generated energy. The cost to customers (and to public agency employees) of such supply (yield) disruptions is often far greater than the cost of improving system reliability [4].
Similarly, the surface water that HBMWD seeks to market is from a different hydrologic region then the buyer agencies. Non-climate yield risks could also affect water bags and desalination, though. Damage to bags in transit, for example, or at loading/unloading facilities could affect yields [38]. Periods of non-operation due to maintenance outages could affect yields at desalination plants. Other sources of yield risk faced by water agencies include changes in environmental and water quality regulations, and changes in public opinion regarding, for example, recycled water [4,5].
It is noteworthy that drought or other natural disaster emergencies may be beneficially served by bag deliveries. The bag system offers a worthwhile means for water managers to diversify their water supply portfolios. The political economy/institutional constraints that may exist are relevant but not confining. Bag delivery for emergencies and drought scenarios may be grounds to permit a variance on the maximum bag number towed or the length of the chain of bags.
4.2. Cost Risk
There is significant uncertainty around the desalination and water bag costs reported in Figure 1. For example, SFPUC reports proposed desalination yields ranging from 12.33 to 69.07 MCM/yr [16]. Additionally, water bag transport is sensitive to fuel costs, distance between loading and off-loading points, the number of bags towed, and bond rates for capital financing purposes, as discussed above.
Infrastructure and facility financing are also sensitive to the cost of issuing bonds to cover capital expenses. Changes in the bond rate affect desalination and water bag costs differently because of the relatively capital-intensive nature of the desalination technology. Decreasing the annual bond rate by one percentage point (from the base rate of 4.77% to 3.77%) decreases water bag capital costs by between 3.72% and 4.76% for the three buyer agencies. This represents a decrease in total cost of between 1.31% and 3.75% for the buyer agencies, depending on how significant a proportion of water bag costs are capital-related. The same change in the bond rate (4.77% to 3.77%) results in an 11.25% reduction in desalination capital costs for all water districts. Similarly total desalination costs fell by between 5.44% and 7.49%. Financing costs for the desalination plants are more responsive to changes in bond rate than water bag financing. In reality, the municipal revenue bond rates used here varied in amount by 0.76 percentage points between 2010 and 2013 [28]. Differences in financing capital costs may vary across types of technology supplying the water as well as across project location or jurisdiction. The variability in financing costs for both is risky.
One additional source of cost risk for water bags is exposure to market risk at the end of the project horizon. The project life of the water bag approach is 10 years, whereas the desalination time horizon is 30. After 10 years, new water bags would need to be purchased and contracts potentially re-negotiated. On the other hand, the shorter life span of the water bag technology may be a benefit to a potential buyer who prefers to keep their future water supply options open.
Although new technologies are often relatively costly, it is often the case that they have benefits in terms of higher reliability (e.g., desalination) or flexibility (e.g., water bags) than conventional water sources.
4.3. Environmental/Regulatory Risk
The regulations and permit approvals needed to bring a new water supply source on line can be significant. This is especially true for relatively new technologies such as water bags and desalination facilities. Furthermore, environmental and public opinion objections to water exports from a basin-of-origin pose a risk for all inter-regional water transfers, regardless of whether the water is transported by water bag or more conventional means. Such concerns are less of an issue for the HBMWD, for the reasons discussed before, but permitting is still a hurdle.
Importing water from other states would likely introduce additional hurdles. However, freshwater imports from Alaska might be relatively easy to achieve, from a regulatory perspective. Alaska legislation (1992) allows for bulk water transport. This is due, in part, to the fact that Alaska discharges approximately 1,233,000 MCM/yr into the Pacific. Permitting would be simply a matter of negotiating with rights holders in the state [38].
Desalination permitting for input and effluent outtake points could also be a point of local contention. SCWD, for example, has ongoing wildlife habitat (anadromous fish) constraints that make their permitting process highly sensitive to state and federal regulations and regulatory actions. Although SDCWA has successfully permitted its Carlsbad facility, it has two other desalination facilities in the beginning stages of planning that are not yet permitted [17].
4.4. New Technology/Adoption Risk
Water manager preferences for new water supply technologies affect both water bags and desalination. Because more information is available about the feasibility, operation and success of desalination, water agencies are likely to prefer it to the more experimental water bag technology. This might even be true when the cost estimates (per m3) are lower for water bags than for desalination, as is true for SCWD, and in some cases SDCWA. One example of new technology adoption risk, for water bags, is uncertainty about whether water bag “trains”—i.e., multiple water bag arrays—are seaworthy along the Pacific Coast of North America and elsewhere, beyond the Mediterranean Sea. As mentioned previously, water bags may also be damaged at both loading and offloading points.
A subtler example of new technology risk stems from uncertainty about location-specific logistics and capacity. Our water bag case study relies on water supplies from HBWMD. If conditions at the acquisition point are unsuitable for filling multiple bags, other water sources may be required. We assume HBMWD water is loaded at Humboldt Bay. Conditions there may limit the number of bags that can be towed behind a single tug, which would increase costs. Such location-specific uncertainties would ideally be resolved before a project is implemented, but implementation of new technologies can often result in unforeseen challenges and costly mistakes.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The three case-study water districts in central and southern California differ in several relevant characteristics: distance to the water source in northern California; current and expected demands; entities they partner with; and diversity of their existing water supply portfolios. This analysis suggests that, in some instances, water bags may be a more affordable means than desalination of delivering water to regions with excess demand. Santa Cruz and, under some assumptions regarding tug length, San Diego, would find water bag technology cost-effective relative to desalination. Once the risk issues raised in the previous section are taken into account, perhaps only Santa Cruz would find water bags a beneficial addition to its water supply portfolio.
In USBR’s evaluation of 30 different water supply augmentation options for southern California, importation via water bags did not rank sufficiently high (based on for example, low water yield, high cost, low technical feasibility, and high implementation risk) to justify serious consideration [37]. However, the scope and perspective of USBR’s study is quite different from the individual water agencies we have chosen to model. Consider Santa Cruz (SCWD) as an example. For a small agency with only intermittent excess demand at relatively close proximity to the supply source, water bags may be a viable alternative to existing technologies.
Whether water bags are cost-effective in other situations will hinge primarily on two factors: the technical feasibility of water bags (i.e., structural integrity of larger tows), and the location-specific cost estimates for water bags versus desalination. Such costs vary widely, depending on site-specific circumstances, thus making it difficult to directly apply the results of our case study to a new location with very different characteristics.
Arguments about the variability and uncertainty of using water bags in new situations are persuasive; they are a significant part of the reason why water bags have not yet been adopted more widely. However, this analysis demonstrates that, in some instances, water bags may be sufficiently lower-cost than desalination to potentially offset at least some of the adoption risks. The risks associated with using water bag technology are not the same as the risks associated with other supply sources. This suggests that water bags might have a place in a water supply portfolio, where risk minimization through diversification is a goal.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Scott Miller and Dannele Peck of the University of Wyoming for helpful comments. Andrew Hodges is grateful for financial support from NOAA Western Water Assessment and the University of Wyoming Agricultural Experiment Station.
Author Contributions
The authors shared equally in the tasks of data gathering, literature synthesis, analysis, and manuscript preparation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- California Department of Water Resources. Managing an Uncertain Future: Climate Change Adaptation Strategies for California’s Water. Available online: www.water.ca.gov/climatechange/articles.cfm (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- Jenkins, M.W.; Lund, J.R.; Howitt, R.E.; Draper, A.J.; Msangi, S.M.; Tanaka, S.K.; Ritzema, R.S.; Marques, G.F. Optimization of California’s water supply system: Results and insights. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R. Why are there so few transactions among water users? Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1986, 68, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, D.; Ingram, H.; Rayner, S. Maintaining the status quo: How institutional norms and practices create conservative water organizations. Tex. Law Rev. 2005, 83, 2027–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, G.; Kasower, S. The Portfolio Approach to Water Supply: Some Examples and Guidance for Planners. Available online: http://www.waterboards.ca.gov/water_issues/programs/grants_loans/water_recycling/docs/econ_tskfrce/10.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2014).
- Hansen, K.; Howitt, R.; Williams, J. Water trades in the western United States: Risk, speculation, and property rights. In Water Trading and Global Water Scarcity: International Perspectives; Maestu, J., Ed.; RFF Press Water Policy Series: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Booker, J.F.; Young, R.A. Modeling intrastate and interstate markets for Colorado River water resources. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1994, 26, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, F.; Pulido-Velazquez, M. Economic costs of sustaining water supplies: Findings from the Rio Grande. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 2883–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzler and Kelly Consulting Engineers. Humboldt County General Plan: Water Resources Technical Report (Draft); Prepared for the County of Humboldt Community Development Division; Eureka, CA, USA, 2007, pp. 1–83. Available online: http://humboldtgov.org/DocumentCenter/Home/View/1865 (accessed on 25 July 2014).
- Stillwater Sciences. Mad River Watershed Assessment. Available online: http://www.waterboards.ca.gov/northcoast/water_issues/programs/tmdls/mad_river/pdf/120329/FINAL_PDF_MRWA.PDF (accessed on 25 July 2014).
- Rische, C.; Humboldt Bay Municipal Water District, Eureka, CA USA. Personal communication, 18 January 2013.
- Getches, D.H. Water Law in a Nutshell, 4th ed.; Thomson/Reuters: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hanak, E. Stopping the drain: Third party responses to California’s water market. Contemp. Econ. Policy 2005, 23, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humboldt Bay Municipal Water District. Water Resource Planning, Implementation Plan to Evaluate and Advance Recommended Water Use Options. Available online: http://www.water.ca.gov/urbanwatermanagement/2010uwmps/Humboldt%20Bay%20Municipal%20WD/Appendix%20C%20-%20WRP%20Implementation%20Plan%20-%20Final%20Draft%20%28to%20Board%20on%20April%2014,%202011%29.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- California Urban Water Management Planning Act 1983, California Water Code Division 6, Part 2.6, Sections 10610 through 10656. 21 September 1983.
- San Francisco Public Utilities Commission. 2010 Urban Water Management Plan. Available online: http://www.sfwater.org/Modules/ShowDocument.aspx?documentID=1055 (accessed on 2 December 2013).
- San Diego County Water Authority Water Resources Department (SDCWA). 2010 Urban Water Management Plan. Available online: http://www.sdcwa.org/sites/default/files/files/water-management/2010UWMPfinal.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2013).
- City of Santa Cruz Water Department. 2010 Urban Water Management Plan. Available online: http://www.cityofsantacruz.com/Modules/ShowDocument.aspx?documentid=24687 (accessed on 3 December 2013).
- Hodges, A.J. The Economics of Bulk Water Transport in Southern California. Master’s Thesis, University of Wyoming, Laramie, Wyoming, 12 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tol, R.S.J. Evaluating the cost of desalination and water transport. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalination Tracker. Glob. Water Intell. 2014, 15, 43–54.
- Karagiannis, I.; Soldatos, P. Water desalination cost literature: Review and assessment. Desalination 2008, 223, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.; Bohn, P.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.; Marinas, B.; Mayes, A. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, L.; Lawler, D.; Freeman, B.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayet, M. Solar desalination by membrane distillation: Dispersion in energy consumption analysis and water production (a review). Desalination 2013, 308, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, N. Distillation plant development and cost update. Desalination 2001, 136, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorenza, G.; Sharma, V.; Braccio, G. Techno-economic evaluation of a solar powered water desalination plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 2217–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondbuyer Indexes: Revenue Bond Index 2010–2013. Available online: http://www.bondbuyer.com/apps/custom/msa_search.php?product=bbi_averages (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- Cooley, H.; Ajami, N. Key Issue for Seawater Desalination in California: Cost and Financing; Pacific Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 2012. Available online: http://pacinst.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/21/2013/02/financing_final_report3.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- Bay Area Regional Desalination Project: Pilot Testing, Appendix I Full-Scale Cost Estimates; Prepared by M. Lee Corporation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010; Available online: http://www.regionaldesal.com/downloads/Final%20Pilot%20Study%20Report%202/BARDP%20Pilot%20Report%20APPENDIX%20I%20Mar%2010%20Cost%20Estimates.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- City of Santa Cruz and Soquel Creek Water District. Agreement Endorsing Recommendations of Joint Task Force on Seawater Desalination Facility. Available online: http://www.scwd2desal.org/documents/Draft_EIR/Appendices/AppendixP.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2014).
- San Diego County Water Authority. Seawater Desalination: The Carlsbad Desalination Project. Available online: http://www.sdcwa.org/sites/default/files/desal-carlsbad-fs.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2014).
- Haddad, M.; Mizyed, N. Non-conventional options for water supply augmentation in the Middle East: A case study. Water Int. 2004, 29, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, M.; Clarke, T. Blue Gold: The Fight to Stop the Corporate Theft of the World’s Water; The New Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Economic Fisheries Information Network. West Coast and Alaska Marine Fuel Prices 2011–2013; Pacific States Marine Fisheries Commission: Portland, OR, 2013. Available online: http://www.psmfc.org/efin/docs/2013FuelPriceReport.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2014).
- United States Bureau of Reclamation. Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study, Executive Summary. Available online: http://www.usbr.gov/lc/region/programs/crbstudy/finalreport/Executive%20Summary/CRBS_Executive_Summary_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2013).
- United States Bureau of Reclamation. Colorado River Basin Water Supply and Demand Study, Appendix F4: Option Characterization—Importation. Available online: http://www.usbr.gov/lc/region/programs/crbstudy/finalreport/Executive%20Summary/CRBS_Executive_Summary_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2013).
- Quinlan, B.; Thompson, G. Technical Evaluation of Options for Long-Term Augmentation of the Colorado River System: Water Imports Using Ocean Routes. Available online: https://www.usbr.gov/lc/region/programs/crbstudy/longtermaugmentationrpt.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).