Strategic Resource Extraction and Recycling from Waste: A Pathway to Sustainable Resource Conservation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Object and Sample Collection
2.2. Preparation of the Test Samples
2.3. Test Instrument
2.4. Application of the Economic and Environmental Benefit Model
2.4.1. Economic Benefit Model
2.4.2. Environmental Impact Model
3. Results
3.1. Results Study of Initial and Post-Leachate Products
3.1.1. SEM-EDS Analysis
3.1.2. XRD Analysis Result
3.2. Results Study of Raw Materials
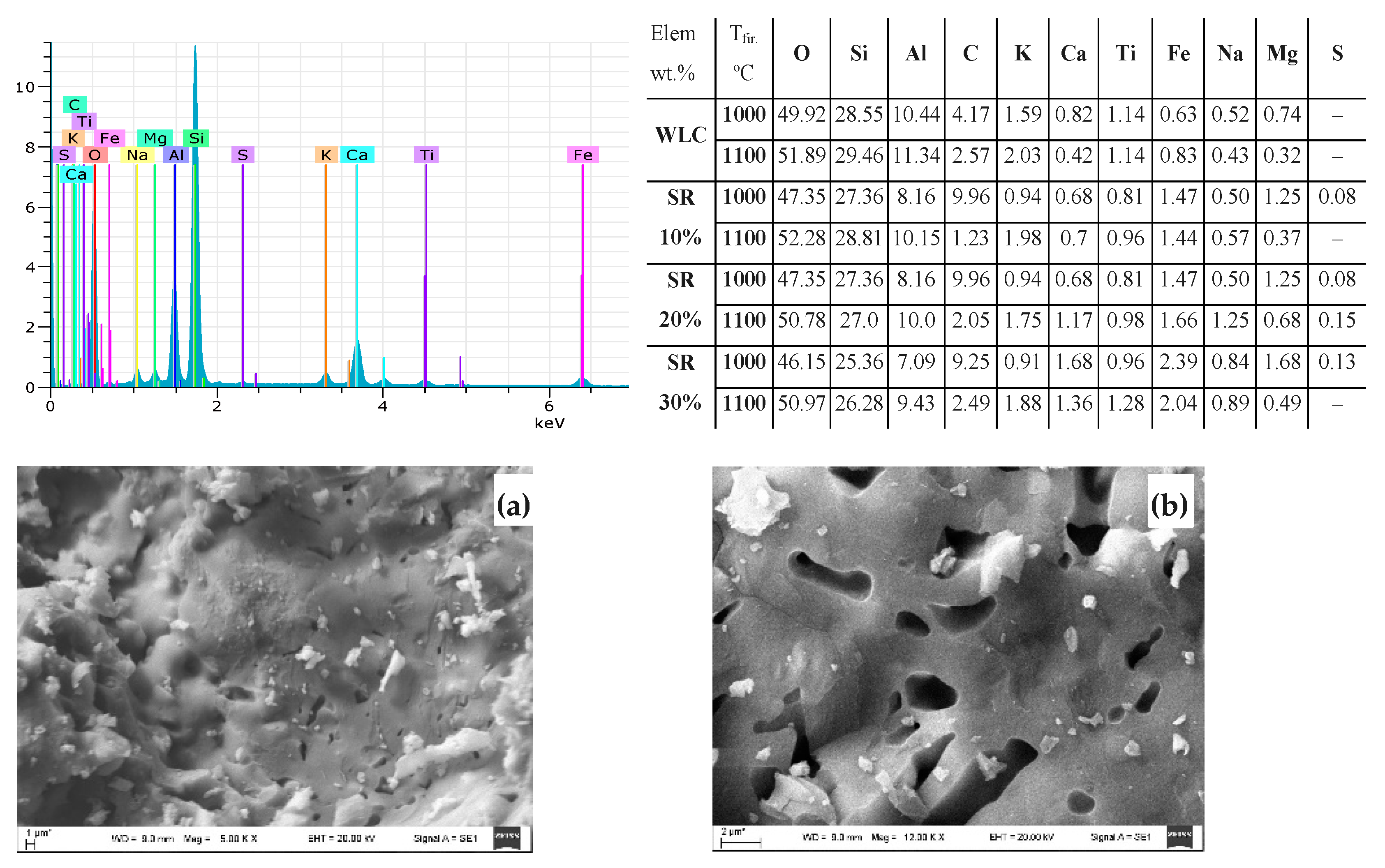
3.2.1. SEM-EDS Analysis of WLC
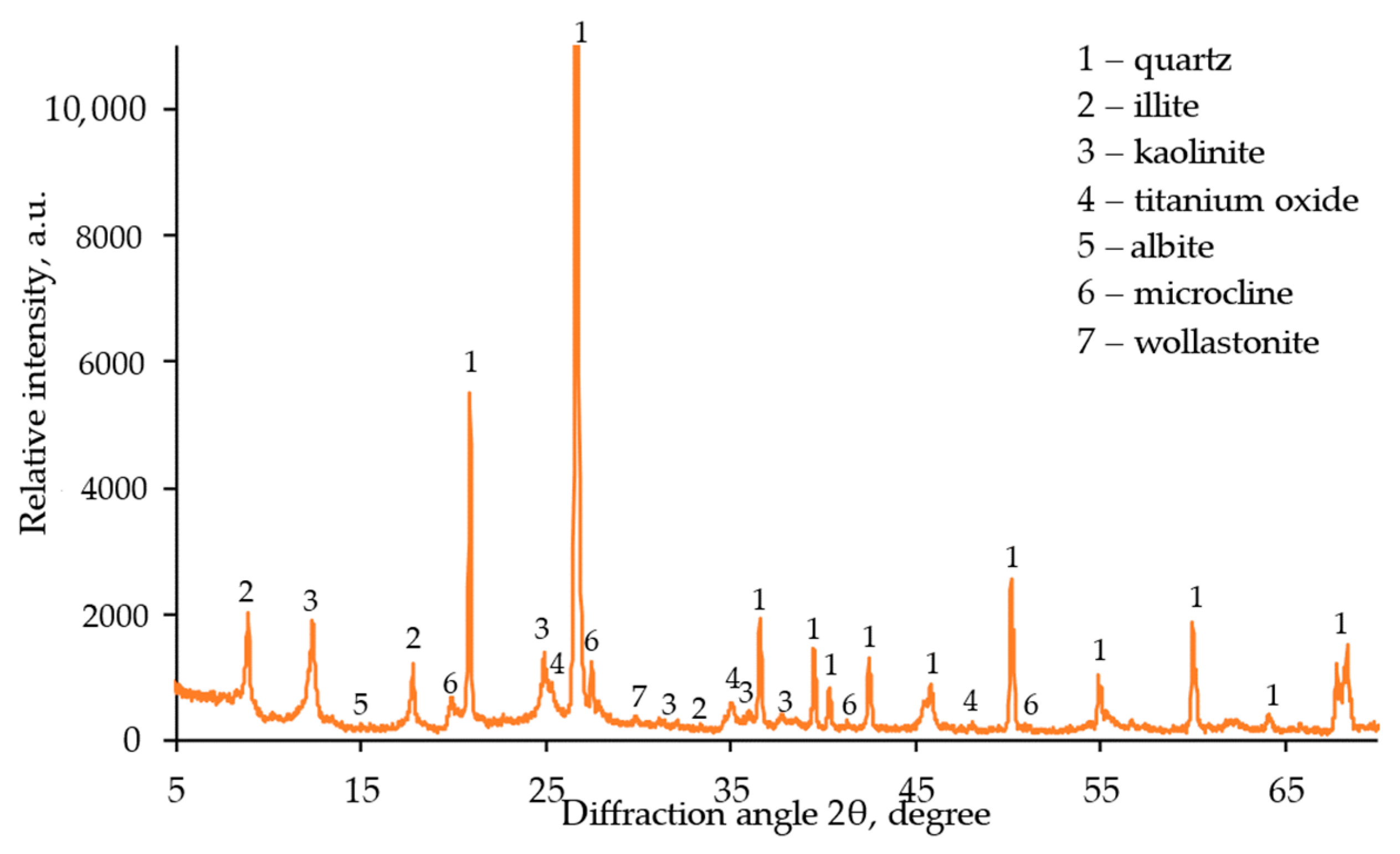
3.2.2. XRD Analysis Result of WLC
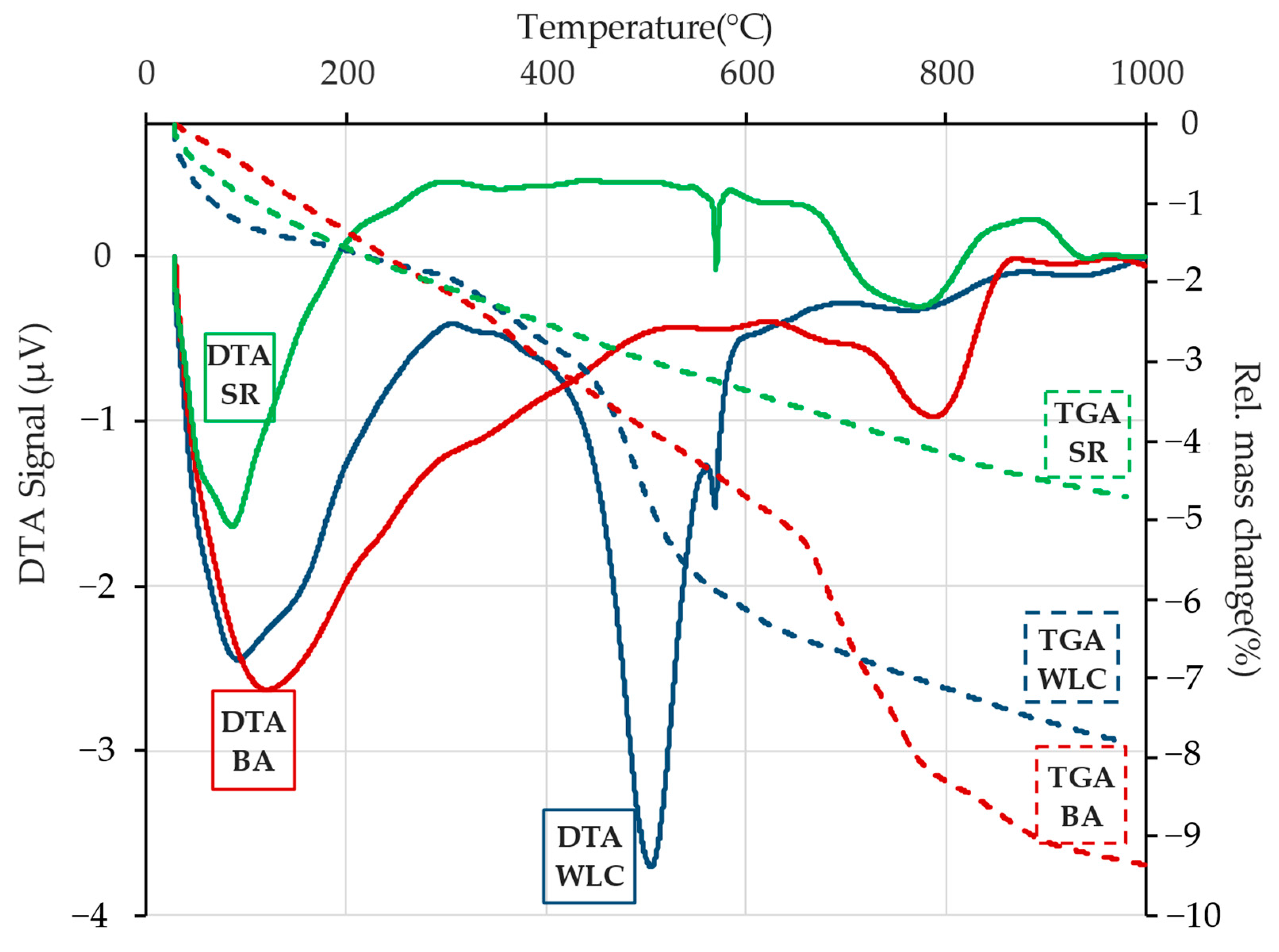
3.2.3. Differential Thermal Analysis Results
3.3. Results Study of Fired Clay Bricks Samples
3.3.1. SEM-EDS Analysis Result of Clay Bricks
3.3.2. FTIR Analysis of Fired Clay Bricks
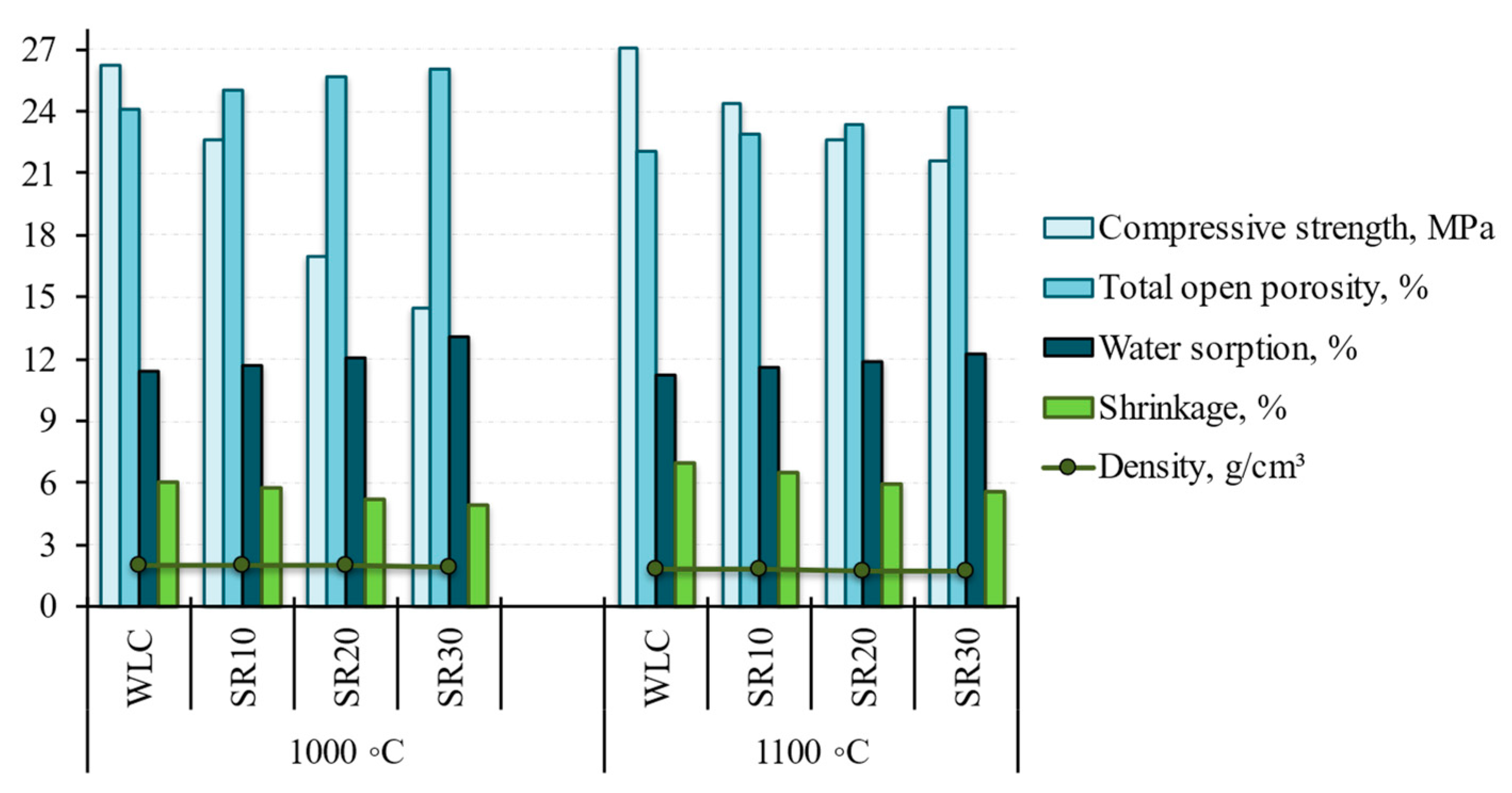
3.3.3. The Characteristics of Clay Bricks in Terms of Physical and Mechanical Properties
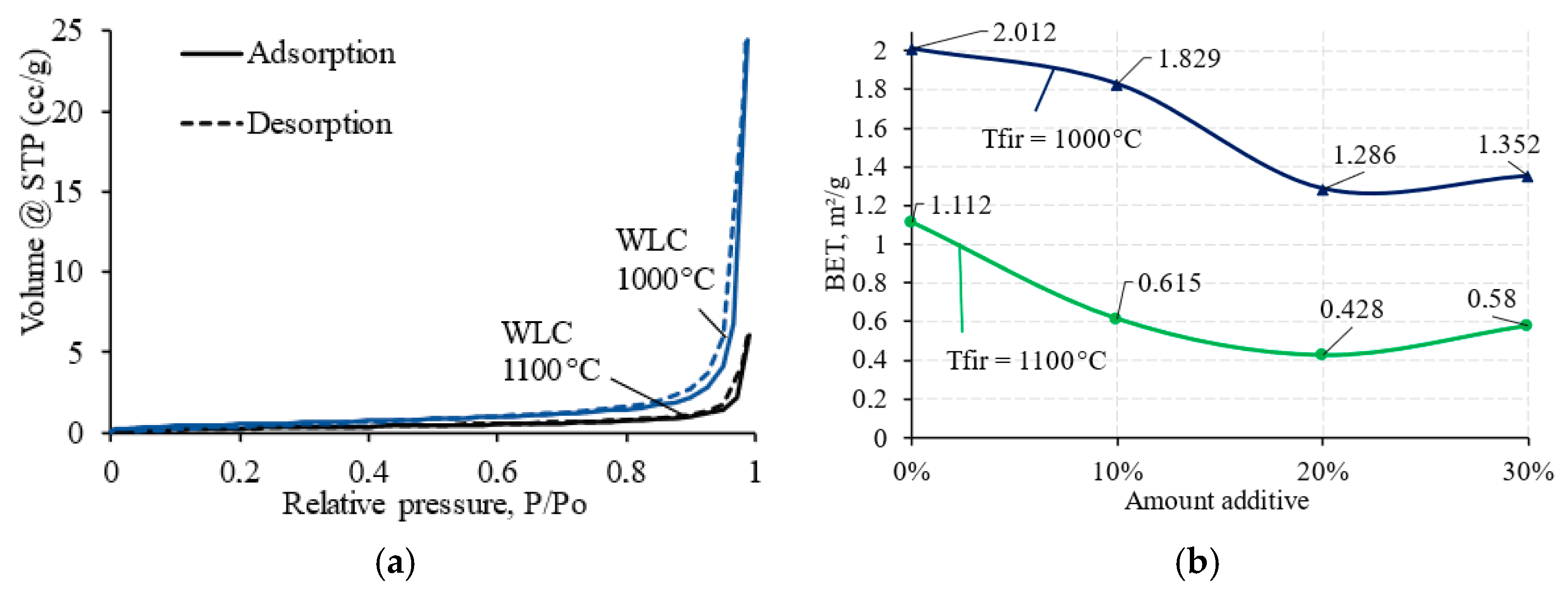
3.3.4. Nitrogen Adsorption Analysis of Clay Bricks
3.3.5. Environmental and Economic Aspects of Calcium Extraction from Bottom Ash and Clay Bricks Production from Solid Residue
- Annual incinerated waste—255,000 tons/year
- BA generated—58,650 tons/year
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) extracted from BA—29,325 tons/year
- Solid residue used as clay replacement in brick production—29,325 tons/year
- Clay needed for 1,000,000 bricks—1500 tons
- BA to the landfill—27,825 tons/year
- Market price of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)—80 USD/ton
- Cost of clay—30 USD/ton
- Processing cost for calcium carbonate extraction—20 USD/ton
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah, M.H.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Anuar, U.H.M.; Marto, A.; Abuelgasim, R. Bottom ash utilization: A review on engineering applications and environmental aspects. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 527, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasenbauer, D.; Huber, F.; Lederer, J.; Quina, M.J.; Blanc-Biscarat, D.; Bogush, A.; Bontempi, E.; Blondeau, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Dahlbo, H. Legal situation and current practice of waste incineration bottom ash utilization in Europe. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 868–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.H.; Nam, B.H.; An, J.; Youn, H. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration (MSWI) Ashes as Construction Materials—A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, H.; Alam, S.R.; Bin-Masud, R.; Prantika, T.R.; Pervez, M.N.; Islam, M.S.; Naddeo, V. A Review on Characteristics, Techniques, and Waste-to-Energy Aspects of Municipal Solid Waste Management: Bangladesh Perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurino, R.; Karamanova, E.; Barbieri, L.; Atanasova-Vladimirova, S.; Andreola, F.; Karamanov, A. New fired bricks based on municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beikmohammadi, M.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H. Analysis of heavy metal, rare, precious, and metallic element content in bottom ash from municipal solid waste incineration in Tehran based on particle size. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerzak, W.; Murzyn, P.; Kuźnia, M.; Magiera, A. Trace elements retention in bottom ashes during coal combustion with hydrated lime additions. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Burke, I.T.; Stewart, D.I. Potential reuse options for biomass combustion ash as affected by the persistent organic pollutants (POPs) content. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 5, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Ash-Incorporated Concrete: One Step towards Environmental Justice. Buildings 2021, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, C.; Kang, S.; Siddique, R.; Tangchirapat, W. Properties of ultra-high performance concrete and conventional concrete with coal bottom ash as aggregate replacement and nanoadditives: A review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 62, 0323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, X.; Struble, L.J.; Yang, E.H. Characterization of calcium-containing phases in alkali-activated municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash binder through chemical extraction and deconvoluted Fourier transform infrared spectra. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Z.; Lin, H.-H.; Tang, Y.-C.; Shen, Y.-H. Recovery of Calcium from Reaction Fly Ash. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkelund, G.M.; Skevi, L.; Ottosen, L.M. Electrodialytically treated MSWI fly ash use in clay bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitak, I.; Baltušnikas, A.; Kalpokaitė-Dičkuvienė, R.; Kriukiene, R.; Denafas, G. Experimental study effect of bottom ash and temperature of firing on the properties, microstructure and pore size distribution of clay bricks: A Lithuania point of view. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LST EN 772-13:2003; Methods of Test for Masonry Units—Part 13: Determination of Net and Gross Dry Density of Masonry Units (Except for Natural Stone). Lietuvos Standartizacijos Tarnyba: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2003.
- SIST EN 772-21:2011; Methods of Test for Masonry Units—Part 21: Determination of Water Absorption of Clay and Calcium Silicate Masonry Units by Cold Water Absorption. Slovenian Institute for Standardization: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2011.
- LST EN 772-1:2003; Methods of Test for Masonry Units—Part 1: Determination of Compressive Strength. Lietuvos Standartizacijos Tarnyba: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2003.
- Hower, J.C.; Berti, D.; Winkler, C.R.; Qian, D.; Briot, N.J. High-Resolution Transmission. Electron Microscopy Study of a Powder River Basin Coal-Derived Fly Ash. Minerals 2022, 12, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, J.C.T.; Ramos, V.H.S.; Oliveira, H.A.; Oliveira, R.M.P.B.; Jesus, E. Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solutions Using Clay from Calumbi Geological Formation, N. Sra. Socorro, SE State, Brazil. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 912, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conconi, M.S.; Morosi, M.; Maggi, J.; Zalba, P.E.; Cravero, F.; Rendtorff, N.M. Thermal behavior (TG-DTA-TMA), sintering and properties of a kaolinitic clay from Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Cerâmica 2019, 65, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, L.F.; Freitas, M.E.; Grillet, A.-C.; Mendes, N.; Woloszyn, M. Microstructural Characterization of Porous Clay-Based Ceramic Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utpalendu, K.; Manika, P. Specific surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales. Eur. Assoc. Geosci. Eng. Geophys. Prospect. 2013, 61, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, A.I. Nanomaterials, Nanostructures, Nanotechnologies; Fizmatlit: Moskow, Russia, 2005; 416p. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M. Physical adsorption characterization of nanoporous materials. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2010, 82, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigm, M.; Vecino, X.; Valderrama, C.; Sirés, I.; Cortina, J.-L. Waste-to-energy bottom ash management: Copper recovery by electrowinning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Yue, D. Calcium leaching characteristics in landfill leachate collection systems from bottom ash of municipal solid waste incineration. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polettini, A.; Pomi, R. The leaching behavior of incinerator bottom ash as affected by accelerated ageing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 113, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, F.-G.; Scholz, P. Assessment of the Long-Term Leaching Behavior of Incineration Bottom Ash: A Study of Two Waste Incinerators in Germany. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shimaoka, T.; Saffarzadeh, A.; Takahashi, F. Mineralogical characterization of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash with an emphasis on heavy metal-bearing phases. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, P.; Su, L.; Cai, G. Mechanical properties and microscopic characteristics of fly ash-slag composite backfill. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliu, I. Comparative analysis of the compressive strengths of clay and sandcrete blocks for low-cost housing. J. Eng. Archit. 2021, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Notes. (9a) Specifications for and Classification of Brick. Available online: https://www.gobrick.com/resources/technical-notes (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- SIST EN 771-1:2011+A1:2015; Specification for Masonry Units—Part 1: Clay Masonry Units. Slovenian Institute for Standardization: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2011.
- Bruno, M.; Abis, M.; Kuchta, K.; Simon, F.-G.; Grönholm, R.; Hoppe, M.; Fiore, S. Material flow, economic and environmental assessment of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash recycling potential in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zuo, J.; Chang, R.; Zillante, G.; Li, L.; Carbone, A. Effectiveness of solid waste management policies in Australia: An Exploratory Study. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; de Brito, J.; Lynn, C.J.; Dhir, R.K. Environmental impacts of the use of bottom ashes from municipal solid waste incineration: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margallo, M.; Aldaco, R.; Irabien, Á. Environmental management of bottom ash from municipal solid waste incineration based on a life cycle assessment approach. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.A.; Marashdeh, M.W. Clay-based bricks’ rich illite mineral for gamma-ray shielding applications: An experimental evaluation of the effect of pressure rates on gamma-ray attenuation parameters. Open Chem. 2023, 21, 20230167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.L. Mineralogical Study of Historical Bricks of Patan, Nepal Using XRD and FTIR Analysis. Int. J. Adv. Res. Chem. Sci. 2017, 4, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitak, I.; Sholokhova, A.; Baltušnikas, A.; Kriūkienė, R. Strategic Resource Extraction and Recycling from Waste: A Pathway to Sustainable Resource Conservation. Resources 2025, 14, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14010001
Pitak I, Sholokhova A, Baltušnikas A, Kriūkienė R. Strategic Resource Extraction and Recycling from Waste: A Pathway to Sustainable Resource Conservation. Resources. 2025; 14(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14010001
Chicago/Turabian StylePitak, Inna, Anastasiia Sholokhova, Arūnas Baltušnikas, and Rita Kriūkienė. 2025. "Strategic Resource Extraction and Recycling from Waste: A Pathway to Sustainable Resource Conservation" Resources 14, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14010001
APA StylePitak, I., Sholokhova, A., Baltušnikas, A., & Kriūkienė, R. (2025). Strategic Resource Extraction and Recycling from Waste: A Pathway to Sustainable Resource Conservation. Resources, 14(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14010001





