Novel Chymotrypsin Purified and Biochemically Characterized from Digestive Organs of Bigfin Reef Squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Squid and Crude Enzyme Extract
2.3. Chymotrypsin Purification
2.4. Chymotrypsin Activity Assay
2.5. Protein Concentration Measurement
2.6. Determination of Optimal Activity and Stability of Chymotrypsin
2.6.1. Optimum pH and Temperature
2.6.2. pH and Thermal Stabilities
2.7. Determination of Inhibition against Chymotrypsin
2.8. Determination of Kinetics of Chymotrypsin
2.9. SDS-PAGE and Native-PAGE
2.10. Molecular Weight Measurement
2.11. Measurement of N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequence
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
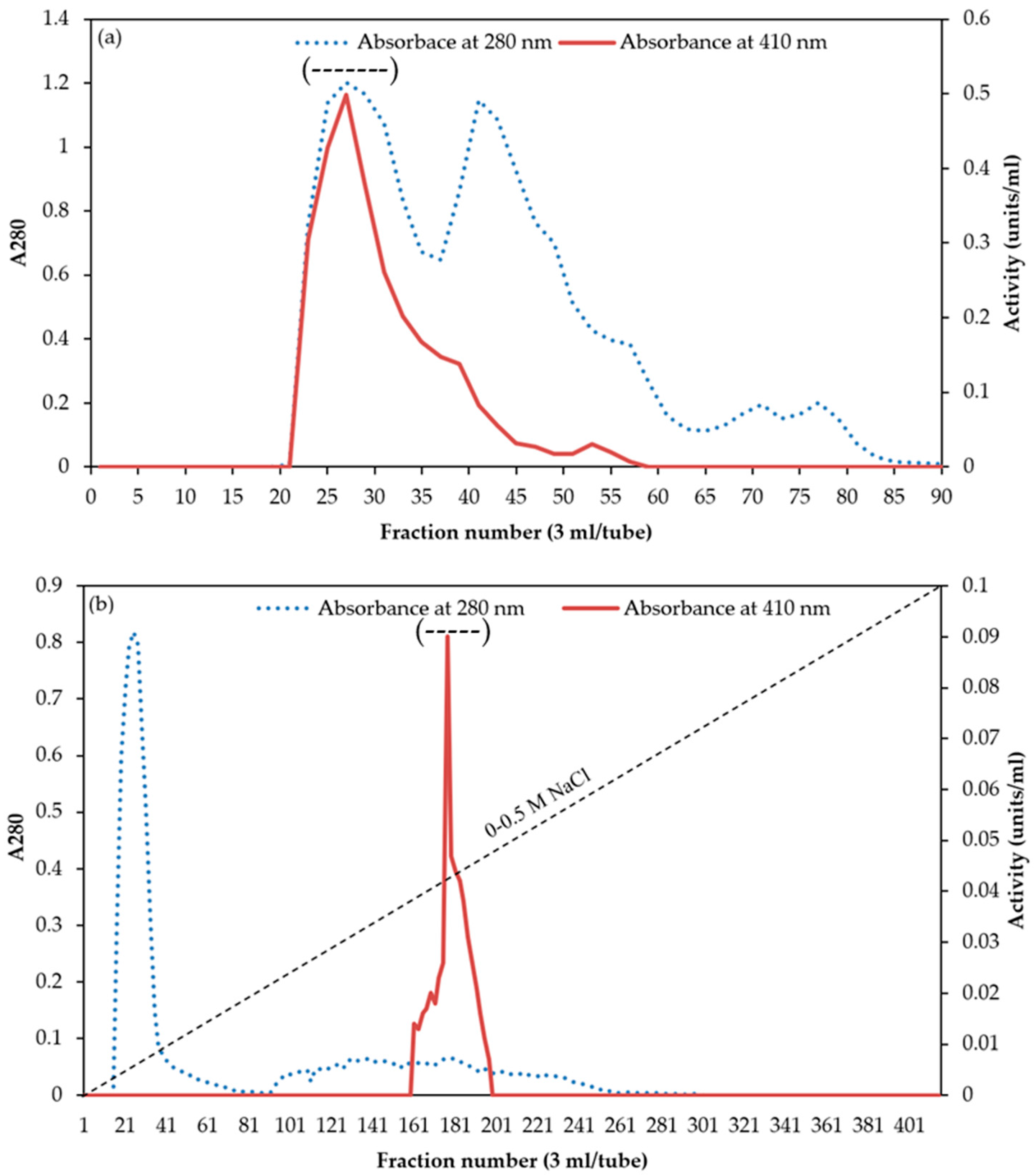
3.1. Purification of Chymotrypsin
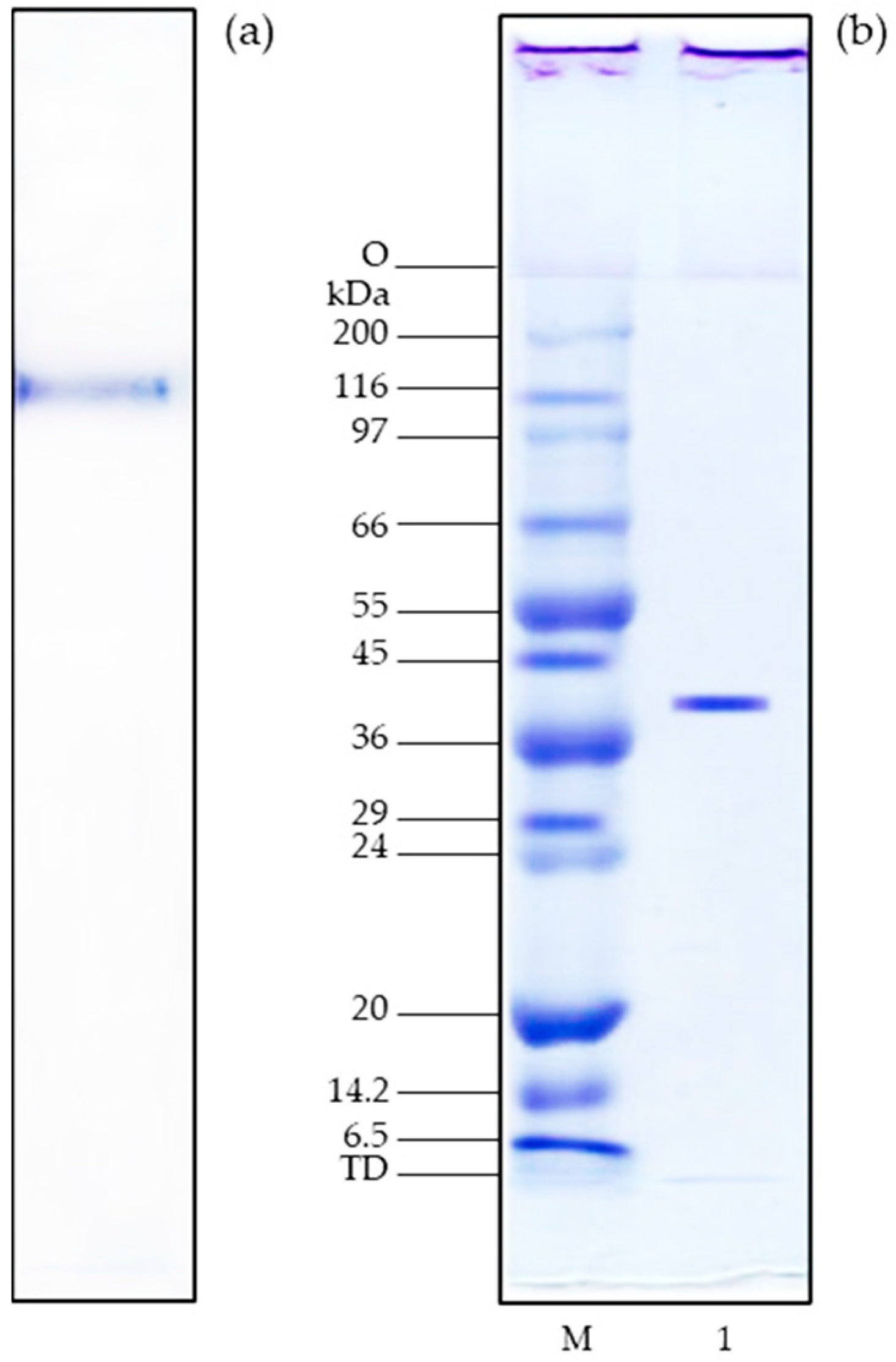
3.2. Native- and SDS-PAGE
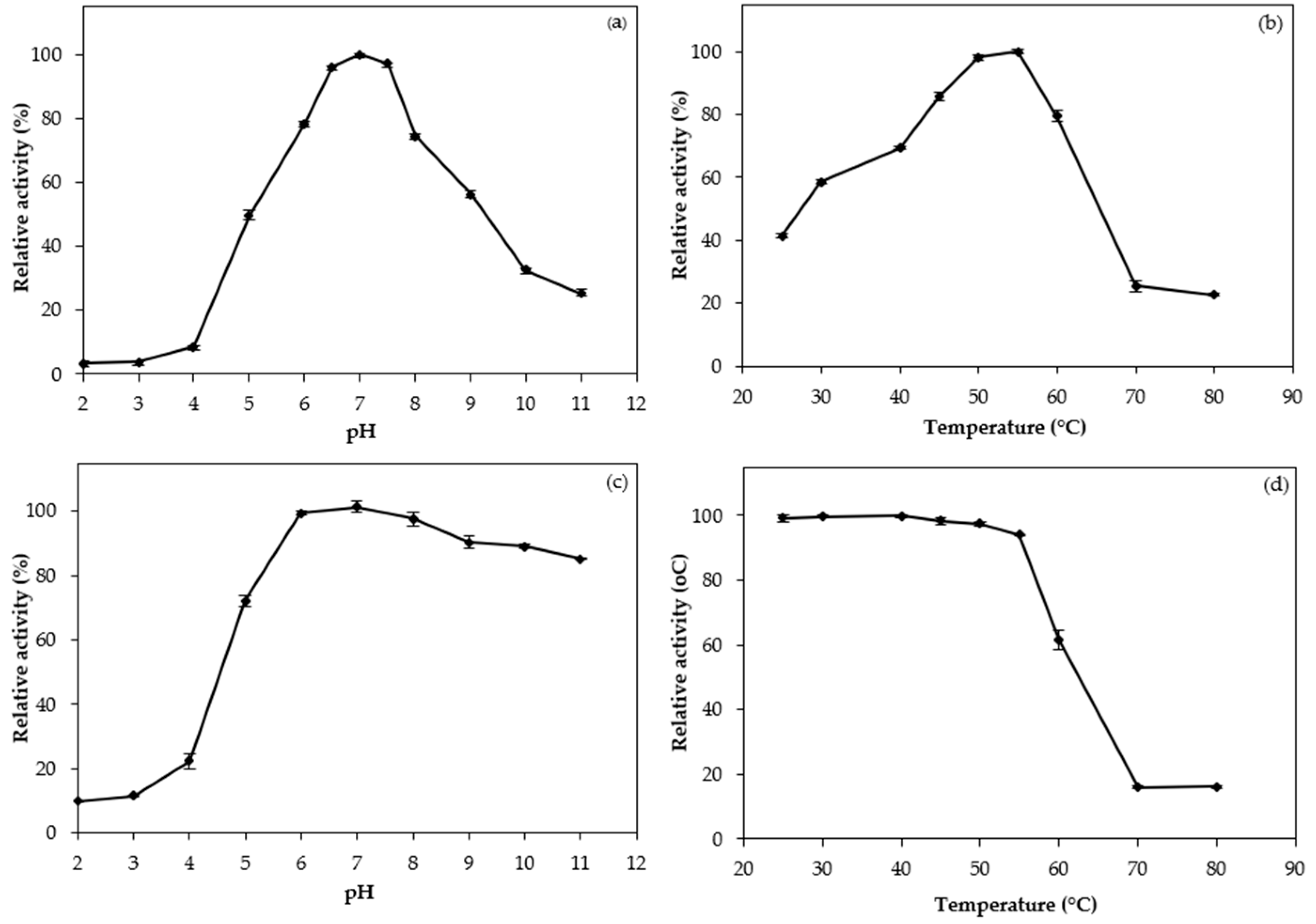
3.3. pH and Temperature Profiles
3.4. pH and Thermal Stabilities
3.5. Influence of Protease Inhibitors
3.6. Kinetics Studies
3.7. N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequence
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, P.G.; Turk, P.E.; Yang, W.T.; Hanlon, R.T. Biological characteristics and biomedical applications of the squid Sepioteuthis lessoniana cultured through multiple generations. Biol. Bull. 1994, 186, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-García, L.E.; Tovar-Romírez, D.; Rosas, C.; Campa-Córdova, Á.I.; Mazón-Suástegui, J.M. Digestive enzymes of the California two-spot octopus, Octopus bimaculoides (Pickford and McConnaughey, 1994). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 215, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, P.; Fracalossi, D.M.; Chimal, M.E.; Sánchez, A.; Rosas, C. Digestive enzymes and timing of digestion in Octopus vulgaris type II. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 16, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jivaluk, J.; Nabhitabhata, J.; Nateewathana, A.; Watprasit, P. Description of Thai type of bigfin reef squid, Sepioteuthis lessoniana, hatchling with note on comparison to Japanese types. Phuket Mar. Biol. Cent. Res. Bull. 2005, 66, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Semmens, J.M. Changes in the digestive gland of the loliginid squid Sepioteuthis lessoniana (Lesson 1830) associated with feeding. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2002, 274, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satjarak, J.; Klomklao, S.; Suanyuk, N.; Thongprajukaew, K. Biochemical characterization of protein-digesting enzymes from viscera of bigfin reef squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana) and implications for in vitro protein digestibility. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2023, 57, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balti, R.; Bougherra, F.; Bougatef, A.; Hayet, B.K.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Dhulster, P.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Chymotrypsin from the hepatopancreas of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) with high activity in the hydrolysis of long chain peptide substrates: Purification and biochemical characterization. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete-del-Toro, M.A.; García-Carreño, F.L.; Hernández-Cortés, P.; Molnár, T.; Gráf, L. Biochemical characterisation of chymotrypsin from the midgut gland of yellowleg shrimp, Penaeus californiensis. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Cortés, P.; Whitaker, J.R.; García-Carreño, F.L. Purification and characterization of chymotrypsin from Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea: Decapoda). J. Food Biochem. 1997, 21, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Yañez, F.J.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Lugo-Sanchez, M.E.; Garcia-Sanchez, G.; Quintero-Reyes, I.E. Biochemical characterization of an isoform of chymotrypsin from the viscera of Monterey sardine (Sardinops sagax caerulea), and comparison with bovine chymotrypsin. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Simpson, B.K.; Saeki, H. Trypsins from yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albocores) spleen: Purification and characterization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 144, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonsin, T.; Simpson, B.K.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Yoshida, A.; Osatomi, K.; Klomklao, S. Anionic trypsin from the spleen of albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga): Purification, biochemical properties and its application for proteolytic degradation of fish muscle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungruangsak-Torrissen, K.; Moss, R.; Andresen, L.H.; Berg, A.; Waagbø, R. Different expressions of trypsin and chymotrypsin in relation to growth in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 32, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineweaver, H.; Burk, D. The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H. Principle and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Groppe, J.C.; Morse, D.E. Molluscan chymotrypsin-like protease; structure, localization and substrate specificity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 305, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leth-Larsen, R.; Ásgeirsson, B.; Thórólfsson, M.; Nørregaard-Madsen, M.; Højrup, P. Structure of chymotrypsin variant B from Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1297, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez-Rios, E.; Coto-Arriola, O.; Villalba-Villalba, A.G.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Lopez-Corona, B.E.; Torres-Arreola, W. Chymotrypsin isolation from jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) hepatopancreas: Partial characterization and effect on muscle collagen. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibo-Verdugo, B.; Rogo-Arreola, L.; Navarrete-del-Toro, M.A.; García-Carreño, F. A chymotrypsin from the digestive tract of California spiny lobster, Panulirus interruptus: Purification and biochemical characterization. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chevalier, P.; Sellos, D.; Van Wormhoudt, A. Purification and partial characterization of chymotrypsin-like proteases from the digestive gland of the scallop Pecten maximus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 110, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjánsson, M.M.; Nielsen, H.H. Purification and characterization of two chymotrypsin-like proteases from the pyloric caeca of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 101, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkloff, H.; Ronnestad, I. Effects of temperature on feedinf and digestive processes in fish. Temperature 2020, 7, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonsin, T.; Simpson, B.K.; Visessanguan, W.; Yoshida, A.; Klomklao, S. Optimal immobilization of trypsin from the spleen of albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) and its characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DelMar, E.G.; Largman, C.; Brodrick, J.W.; Geokas, M.C. A sensitive new substrate for chymotrypsin. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 99, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, T.; Gertler, A.; Birk, Y. Pancreatic proteolytic enzymes from carp (Cyprinus carpio) I. purification and physical properties of trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase and carboxypeptidase B. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1981, 69, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellos, D.; Van Wormhoudt, A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA that encodes a serine protease with chymotryptic and collagenolytic activities in the hepatopancreas of the shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Crustacea, Decapoda). FEBS Lett. 1992, 309, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danwattananusorn, T.; Kondo, H.; Aoki, T.; Hirono, I. Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of a chymotrypsin-like serine protease from kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicas. Fish Sci. 2009, 75, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.K.; Sun, L.C.; Cai, Q.F.; Liu, G.M.; Yoshida, A.; Osatomi, K.; Cao, M.J. Biochemical characterization of chymotrypsins from the hepatopancreas of Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2010, 58, 8069–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Srivastava, A.S.; Kurokawa, T. cDNA cloning and phylogenetic analysis of pancreatic serine proteases from Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 131, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.J.; Weng, C.F. Developmental regulation of gastric pepsin and pancreatic serine protease in larvae of the euryhaline teleost, Oreochromis mossambicus. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Purification Step | Total Activity (U) | Total Protein (mg) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Yield (%) | Purity (fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude enzyme extract | 1942 | 1298 | 1.5 | 100 | 1 |
| Ammonium sulfate precipitation (0–40% w/v) | 1305 | 170 | 7.7 | 67 | 5 |
| Sephacryl S-200 | 733 | 38 | 19 | 38 | 13 |
| DEAE-Sepharose | 111 | 1.8 | 62 | 5.7 | 41 |
| Inhibitors | Concentration | Remaining Activity (%) * |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 100.00 ± 1.60 e | |
| E-64 | 0.1 mM | 98.60 ± 0.15 e |
| N-ethylmaleimide | 1 mM | 97.56 ± 1.80 de |
| Soybean trypsin inhibitor | 1.0 g/L | 89.23 ± 3.70 c |
| TLCK | 5 mM | 97.49 ± 0.50 de |
| TPCK | 5 mM | 27.59 ± 0.28 b |
| Benzamidine | 5 mM | 98.60 ± 0.80 e |
| PMSF | 1 mM | 9.05 ± 0.98 a |
| Pepstatin A | 0.01 mM | 94.99 ± 1.19 d |
| EDTA | 2 mM | 98.83 ± 0.88 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Satjarak, J.; Klomklao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Thongprajukaew, K. Novel Chymotrypsin Purified and Biochemically Characterized from Digestive Organs of Bigfin Reef Squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana). Resources 2024, 13, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13050067
Satjarak J, Klomklao S, Zhang Y, Thongprajukaew K. Novel Chymotrypsin Purified and Biochemically Characterized from Digestive Organs of Bigfin Reef Squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana). Resources. 2024; 13(5):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13050067
Chicago/Turabian StyleSatjarak, Jirapan, Sappasith Klomklao, Yi Zhang, and Karun Thongprajukaew. 2024. "Novel Chymotrypsin Purified and Biochemically Characterized from Digestive Organs of Bigfin Reef Squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana)" Resources 13, no. 5: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13050067
APA StyleSatjarak, J., Klomklao, S., Zhang, Y., & Thongprajukaew, K. (2024). Novel Chymotrypsin Purified and Biochemically Characterized from Digestive Organs of Bigfin Reef Squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana). Resources, 13(5), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13050067







