Economic Activities and Management Issues for the Environment: An Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) and STIRPAT Analysis in Turkey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Model
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Data
4.2. Unit Root Test
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
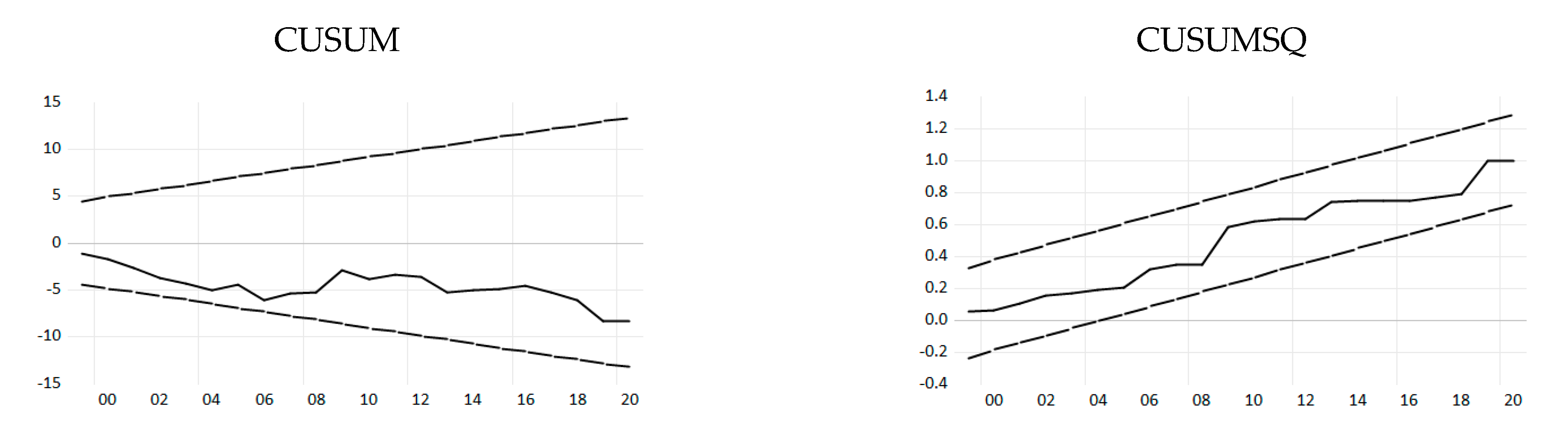
Appendix A. Stability Diagnostics of the STIRPAT Model
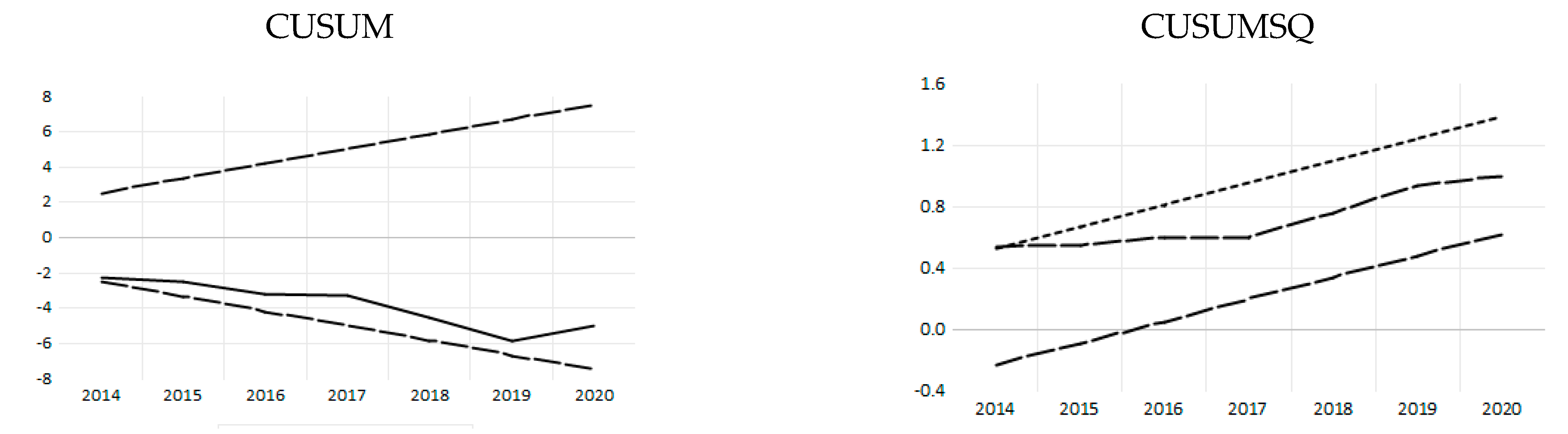
Appendix B. Stability Diagnostics of the EKC Model
References
- Uğurlu, E. Greenhouse Gases Emissions and Alternative Energy in the Middle East. In Climate Change and Energy Dynamics in the Middle East: Modeling and Simulation-Based Solutions; Qudrat-Ullah, H., Kayal, A.A., Eds.; Understanding Complex Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 259–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurlu, E. Renewable Energy Strategies for Sustainable Development in the European Union. In Renewable Energy: International Perspectives on Sustainability; Kurochkin, D., Shabliy, E.V., Shittu, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurlu, E. Renewale Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation. In Energy Policy Advancement: Climate Change Mitigation and International Environmental Justice; Kurochkin, D., Crawford, M.J., Shabliy, E.V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers—Global Warming of 1.5 °C. 2022. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/chapter/spm/ (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Levine, N. Antiurbanization: An Implicit Development Policy in Turkey. J. Dev. Areas 1980, 14, 513–538. [Google Scholar]
- TURKSTAT. Adrese Dayalı Nüfus Kayıt Sistemi Sonuçları. 2022. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Adrese-Dayali-Nufus-Kayit-Sistemi-Sonuclari-2021-45500 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A. Effects of population and affluence on CO2 emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayotou, T. Demystifying the environmental Kuznets curve: Turning a black box into a policy tool. Environ. Dev. Econ. 1997, 2, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Payne, J.E. CO2 emissions, energy usage, and output in Central America. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 3282–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, P.C. I=PBAT. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 40, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A. Rethinking the Environmental Impacts of Population, Affluence and Technology. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 1994, 1, 277–300. [Google Scholar]
- Haseeb, M.; Hassan, S.; Azam, M. Rural–urban transformation, energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emissions using STRIPAT model for BRICS countries. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.I. Environmental Kuznets Curve. In Encyclopedia of Energy; Cleveland, C.J., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, M. Analysis of The COVID-19 Impact on Electricity Consumption and Production. Sak. Univ. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 3, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K. Renewable energy consumption, urbanization, financial development, income and CO2 emissions in Turkey: Testing EKC hypothesis with structural breaks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K. The influence of coal and noncarbohydrate energy consumption on CO2 emissions: Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Turkey. Energy 2018, 160, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölük, G.; Mert, M. The renewable energy, growth and environmental Kuznets curve in Turkey: An ARDL approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozgor, G.; Can, M. Export product diversification and the environmental Kuznets curve: Evidence from Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21594–21603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgin, C.; Öztunalı, O. Environmental Kuznets Curve for the Informal Sector of Turkey (1950–2009). Panoeconomicus 2014, 61, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, N.Ç. CO2 Emission, Energy Consumption, and Economic Growth for Turkey: Evidence from a Cointegration Test with a Structural Break. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2014, 9, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, F.; Koçak, E.; Bulut, Ü. The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: A revisited Environmental Kuznets Curve approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, E.; Şarkgüneşi, A. The impact of foreign direct investment on CO2 emissions in Turkey: New evidence from cointegration and bootstrap causality analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, M.C.; Ekinci, A.; Sakarya, B. The impact of output volatility on CO2 emissions in Turkey: Testing EKC hypothesis with Fourier stationarity test. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3008–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbostancı, E.; Türüt-Aşık, S.; Tunç, G.İ. The relationship between income and environment in Turkey: Is there an environmental Kuznets curve? Energy Policy 2009, 37, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katircioğlu, S.; Katircioğlu, S. Testing the role of urban development in the conventional Environmental Kuznets Curve: Evidence from Turkey. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2018, 25, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, B.M.; Katircioglu, S.; Gokmenoglu, K.K. The moderating role of informal economy on financial development induced ekc hypothesis in turkey. Energy Environ. 2022, 33, 1203–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alola, A.A.; Donve, U.T. Environmental implication of coal and oil energy utilization in Turkey: Is the EKC hypothesis related to energy? Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2021, 32, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.M.; Azam, M. Evaluating the impact of GDP per capita on environmental degradation for G-20 economies: Does N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve exist? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 11103–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katircioğlu, S.T.; Taşpinar, N. Testing the moderating role of financial development in an environmental Kuznets curve: Empirical evidence from Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Apergis, N.; Shahbaz, M. A revisit of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Turkey: New evidence from bootstrap rolling window causality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32381–32394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özokcu, S.; Özdemir, Ö. Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Acaravci, A. CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 3220–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A. Çevresel Kuznets Eğrisi Hipotezinin Türkiye İçin İncelenmesi: Stirpat Modelinden Bulgular. Cumhur. Üniversitesi İktisadi Ve İdari Bilim. Derg. 2018, 19, 268–283. [Google Scholar]
- Çağlar, A.E. Türkiye’de çevresel Kuznets Eğrisi hipotezinin araştırılmasında çevresel patentlerin rolü: Genişletilmiş ARDL ile kanıtlar. Ömer Halisdemir Üniversitesi İktisadi Ve İdari Bilim. Fakültesi Derg. 2022, 15, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraç, Ş.; Yağlikara, A. The Impact of Globalization and Financial Development on Environment within the Context of STIRPAT Model: The Case of Turkey. Anadolu Üniversitesi Sos. Bilim. Derg. 2019, 19, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, A.; Ali, G. Investigation of key contributors of CO2 emissions in extended STIRPAT model for newly industrialized countries: A dynamic common correlated estimator (DCCE) approach. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topdağ, D.; Acar, T.; Çeli, İ.E. Estimation of the Global-Scale Ecological Footprint within the Framework of STIRPAT Models: The Quantile Regression Approach. İstanbul İktisat Derg. 2020, 70, 339–358. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Wang, S.; Marinova, D.; Zhao, D.; Hong, J. Impacts of urbanization and real economic development on CO2 emissions in non-high income countries: Empirical research based on the extended STIRPAT model. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 952–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yan, R.; Cai, W. An extended STIRPAT model-based methodology for evaluating the driving forces affecting carbon emissions in existing public building sector: Evidence from China in 2000–2015. Nat Hazards. 2017, 89, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadorsky, P. Trade and energy consumption in the Middle East. Energy Econ. 2011, 33, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, B. What are the carbon emissions elasticities for income and population? Bridging STIRPAT and EKC via robust heterogeneous panel estimates. Glob. Environ. Change 2015, 31, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xia, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, S. What matters for carbon emissions in regional sectors? A China study of extended STIRPAT model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Basu, S.; Pal, P. Examining the driving forces in moving toward a low carbon society: An extended STIRPAT analysis for a fast growing vast economy. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2017, 19, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shackman, J.; Liu, X. Carbon emission flow in the power industry and provincial CO2 emissions: Evidence from cross-provincial secondary energy trading in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zarzoso, I.; Maruotti, A. The impact of urbanization on CO2 emissions: Evidence from developing countries. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Salim, R.; Apergis, N. Agriculture, trade openness and emissions: An empirical analysis and policy options. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2016, 60, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürlük, S.; Karaer, F. Türkiye’de Ekonomik Büyüme ile Çevre Kirliliği İlişkisinin İncelenmesi. Tarım Ekon. Derg. 2004, 10, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Başar, S.; Temurlenk, M.S. Çevreye Uyarlanmiş Kuznets Eğrisi: Türkiye Üzerine Bir Uygulama. Atatürk Üniversitesi İktisadi Ve İdari Bilim. Derg. 2010, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Omay, R.E. The Relationship between Environment and Income: Regression Spline Approach. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2013, 3, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Acaravci, A.; Ozturk, I. On the relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Europe. Energy 2010, 35, 5412–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, T.; Beşer, M.K.; Alola, A.A. Environmental sustainability statement of economic regimes with energy intensity and urbanization in Turkey: A threshold regression approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42533–42546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, P.R.; Holdren, J.P. Impact of population growth. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 1971, 26, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmami, M.; Ben-Salha, O. An empirical analysis of the determinants of CO2 emissions in GCC countries. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2020, 27, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Ulucak, R.; Dogan, E. Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: The role of ecological footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 29387–29396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Group. Türkiye Country Climate and Development Report; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/37521 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- IEA. Global Energy Review: CO2 Emissions in 2021—Analysis. 2021. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-co2-emissions-in-2021-2 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- IEA. Global Energy Review 2021 Assessing the Effects of Economic Recoveries on Global Energy Demand and CO2 Emissions in 2021; IEA: Paris, France, 2021; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-energy-review-2021/co2-emissions (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Eurostat. CO2 Emissions from Energy Use Up by More Than 6% in 2021. 2021. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-eurostat-news/-/ddn-20220624-1 (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the Estimators for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Likelihood Ratio Statistics for Autoregressive Time Series with a Unit Root. Econometrica 1981, 49, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C.B.; Perron, P. Testing for a Unit Root in Time Series Regression. Biometrika 1988, 75, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R.J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J. Appl. Econom. 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumik, L.C.; Ridwan, M. Impact of FDI, industrialization, and education on the environment in Argentina: ARDL approach. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumik, L.C.; Rahman, M.H.; Hossain, M.S. Investigating the subsistence of Environmental Kuznets Curve in the midst of economic development, population, and energy consumption in Bangladesh: Imminent of ARDL model. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, W.; Abdullah, A.; Azam, M. Re-visiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for Malaysia: Fresh evidence from ARDL bounds testing approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesma-Martín, D.; Puente-Ajovín, M. The Environmental Kuznets Curve at the thermoelectricity-water nexus: Empirical evidence from Spain. Water Resour. Econ. 2022, 39, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodyma, K.; Papież, M.; Śmiech, S. Revisiting the Environmental Kuznets Curve in the European Union countries. Energy 2022, 241, 122899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, D.H.; Nhan, T.N.; Ho, C.M.; Nguyen, T.C. Does the Kuznets curve apply for financial development and environmental degradation in the Asia-Pacific region? Heliyon 2021, 7, e06708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S.; Celebi, A.; Ozdeser, H.; Sancar, N. Modelling the impact of energy consumption and environmental sanity in Turkey: A STIRPAT framework. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 120, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Cho, H.C. Research on the relationship between urban public infrastructure, CO2 emission and economic growth in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 7361–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, P.; Lample, L.; Miguel, J.A.; Salvador, M. Co-Movements between Eu Ets and the Energy Markets: A Var-Dcc-Garch Approach. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, H. The environmental Kuznets curve in Asia: The case of Sulphur and carbon emissions. Asia Pac. Dev. J. 2013, 19, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis on CO2 Emissions: Evidence for China. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, A.; Takman, J.; Uddin, G.S.; Ahmed, A. The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: An empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5848–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljadani, A.; Toumi, H.; Toumi, S.; Hsini, M.; Jallali, B. Investigation of the N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve for COVID-19 mitigation in the KSA. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 29681–29700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehzad, K.; Zeraibi, A.; Zaman, U. Testing the N-shaped environmental Kuznets Curve in Algeria: An imperious role of natural resources and economic globalization. Resour. Policy 2022, 77, 102700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Tanveer, M.; Furqan, M. Investigating the N-Shaped Energy-Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy. 2021, 11, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R. Dynamic Conditional Correlation: A Simple Class of Multivariate Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity Models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2002, 20, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.D. Macroeconomics and ARCH; Working Paper Series; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Definition | Unit | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual total production-based emissions of carbon dioxide () | Million tonnes | (GitHub) 1 | |
| Environmental and resource productivity (energy productivity) | % | OECD | |
| GDP (growth) | % | World Bank | |
| Y | GDP per capita | Constant (TRL) | World Bank |
| TR | The sum of imports and exports | % of GDP | World Bank |
| FDI | Foreign direct investment, net inflows | % of GDP | World Bank |
| ES | Total energy supply | Petajoule (PJ.) | World Energy Statistics |
| FEC | Total final consumption | Petajoule (PJ.) | World Energy Statistics |
| URB | Urban population (% of the total population) | (% of the total population) | World Bank |
| LCO2 | LEP | LES | LFDI | LFEC | LTR | LURB | LY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 5.57 | 3.40 | 8.20 | −0.06 | 7.93 | 3.25 | 4.21 | 9.52 |
| Median | 5.57 | 3.40 | 8.16 | 0.15 | 7.91 | 3.29 | 4.21 | 9.51 |
| Maximum | 6.06 | 3.83 | 8.72 | 1.28 | 8.43 | 3.66 | 4.33 | 9.97 |
| Minimum | 5.02 | 2.85 | 7.65 | −1.18 | 7.43 | 2.81 | 4.08 | 9.14 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.73 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.27 |
| Skewness | −0.09 | −0.24 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.001 | −0.32 | −0.09 | 0.26 |
| Kurtosis | 1.69 | 2.00 | 1.79 | 1.69 | 1.77 | 2.42 | 1.75 | 1.69 |
| ADF | PP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Intercept | Intercept and Trend | Intercept | Intercept and Trend |
| LCO2 | −2.62 (0) * | −2.13 (0) | −5.68 (20) *** | −1.87 (8) |
| CO2 | −6.20 (0) *** | −5.47 (1) *** | −6.20 (0) *** | −8.48 (15) *** |
| CO2 | 0.56 (0) | −2.61 (0) | 3.19 (40) | −2.46 (7) |
| CO2 | −5.64 (1) *** | −5.68 (1) *** | −7.12 (39) *** | −11.97 (39) *** |
| LFEC | −1.04 (1) | −3.89 (0) ** | −1.50 (35) | −3.85 (2) ** |
| −8.39 (0) *** | −8.38 (0) *** | −2.01 (16) *** | −18.12 (23) *** | |
| LFDI | −1.97 (0) | −2.71 (0) | −1.84 (5) | −2.66 (3) |
| −6.14 (0) *** | −6.02 (0) *** | −10.5 (27) *** | −10.66 (27) *** | |
| ULRB | −4.30 (9) *** | −2.69 (9) | −6.78 (5) *** | −6.85 (4) *** |
| L | 0.07 (9) | −4.58 (7) *** | −0.56 (7) | −2.63 (0) |
| −3.50 (8) *** | −3.44 (8) ** | −6.98 (4) *** | −6.87 (4) *** | |
| LEP | −1.82 (0) | −1.46 (0) | −1.78 (1) | −1.35 (2) |
| −6.25 (0) *** | −4.37 (7) *** | −6.29 (3) *** | −7.57 (7) *** | |
| LES | −1.04 (0) | −3.08 (0) | −1.90 (9) | −2.88 (4) |
| ES | −6.77 (0) *** | −6.85 (0) *** | −7.30 (6) *** | −8.56 (8) *** |
| LFDI | −2.97 (0) ** | −4.02 (0) *** | −3.03 (5) ** | −4.04 (1) *** |
| LY | 0.41 (0) | −2.26 (0) | 1.20 (6) | −2.26 (0) |
| −6.61 (0) *** | −4.09 (5) *** | −6.96 (5) *** | −7.61 (6) *** | |
| 0.59 (0) | −2.02 (0) | 1.67 (7) | −2.02 (0) | |
| −6.48 (0) *** | −4.10 (5) *** | −6.72 (5) *** | −7.77 (7) *** | |
| 0.78 (0) | −1.79 (0) | 2.05 (7) | −1.78 (1) | |
| −6.34 (0) *** | −4.09 (5) *** | −6.47 (5) *** | −7.61 (7) *** | |
| MODEL 1 ARDL (1,0,0,0,2,0,1) | |
|---|---|
| Coefficient | Long-Run Coefficient Dependent Variable: Log CO2 |
| 0.26 (1.73) | |
| LY | 0.23 (1.85) ** |
| LFDI | −0.009 (−0.89) |
| LFEC | 1.17 (5.57) *** |
| LEP | −0.14 (−4.72) *** |
| LTR | −0.017 (−0.39) |
| LURB | −1.34 (−1.82) * |
| a | −0.73 (−9.11) *** |
| F-bounds | 39.60 upper bound of 1%: 3.99 |
| 1.44 prob: 0.25 | |
| 0.40 prob: 0.52 | |
| CUSUM | Stable in full period |
| CUSUMQ | Stable in full period |
| MODEL 1 ARDL (4,2,2,2,1,1,2,2) | |
|---|---|
| Coefficient | Long-Run Coefficient Dependent Variable: Log CO2 |
| −33.95 (−2.53) ** | |
| LY | 117.75 (2.36) ** |
| −11.49 (−2.18) ** | |
| 0.35 (2.02) ** | |
| LTR | 0.01 (0.30) |
| LFEC | 0.76 (2.13) ** |
| g | −0.04 (−1.99) * |
| LES | −0.30 (−1.1) |
| a | −1.27 (−4.67) *** |
| F-bounds | 3.33 upper bound of 5%: 3.21 |
| F = 3.09 (prob = 0.09) | |
| F = 0.02 (prob: 0.86) | |
| CUSUM | Stable |
| CUSUMSQ | Stable |
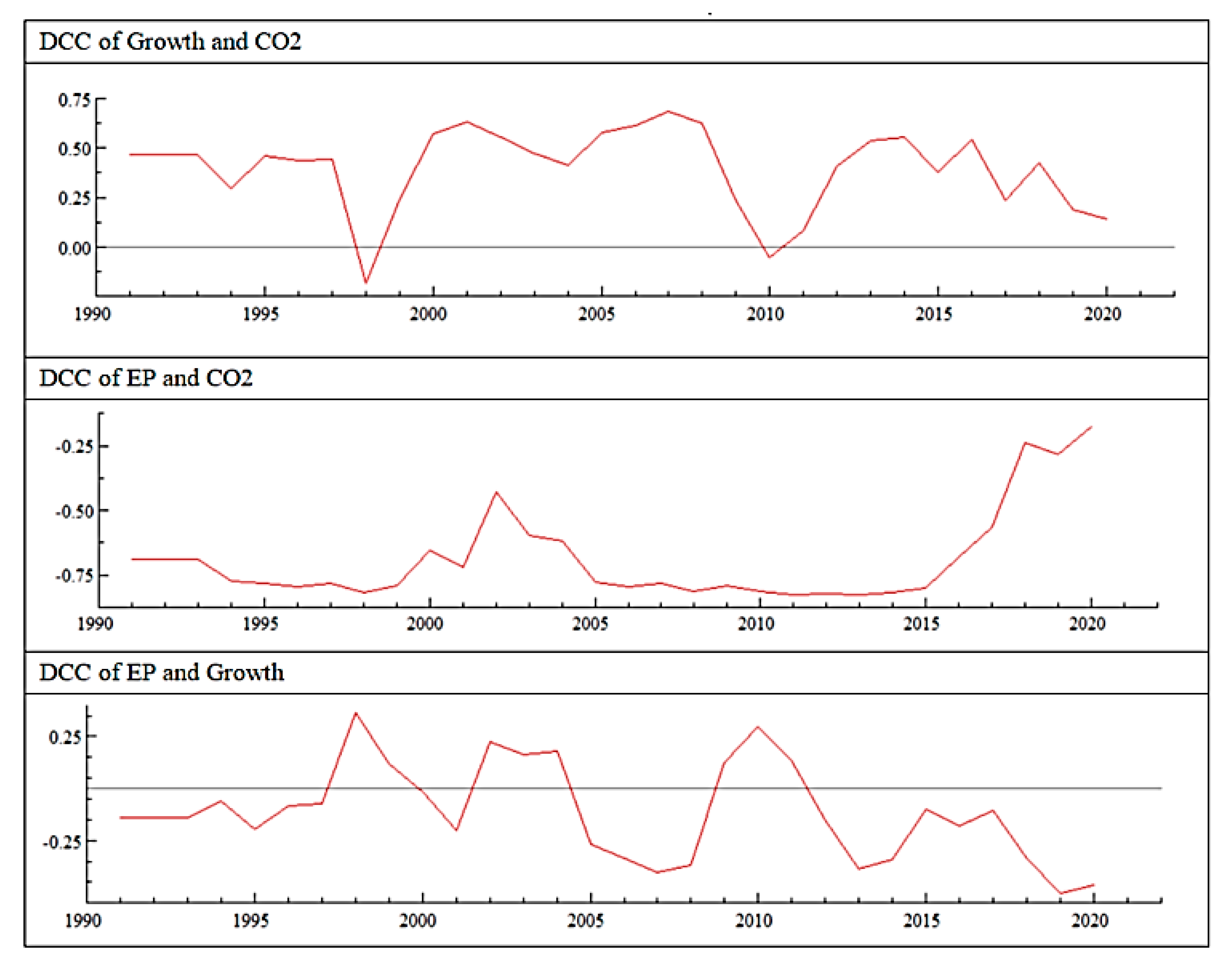
| Parameters | Coefficient (t-Value) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCC (1,1) | alfa | 0.259 *** (2.81) | ||
| beta | 0.67 *** (5.48) | |||
| 0.51 ** (2.40) | ||||
| −0.55 * (−1.77) | ||||
| 0.09 (0.34) | ||||
| Autocorrelation and heteroskedasticity test | ||||
| Parameters | Q | p-values | p-values | |
| Hosing (5) | 53.40 | 0.13 | 57.23 | 0.79 |
| Hosking (10) | 107.1 | 0.08 | 82.03 | 0.51 |
| Li-McLeod (5) | 54.07 | 0.126 | 59.61 | 0.097 |
| Li-McLeod (10) | 108.32 | 0.081 | 88.21 | 0.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojaghlou, M.; Ugurlu, E.; Kadłubek, M.; Thalassinos, E. Economic Activities and Management Issues for the Environment: An Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) and STIRPAT Analysis in Turkey. Resources 2023, 12, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12050057
Ojaghlou M, Ugurlu E, Kadłubek M, Thalassinos E. Economic Activities and Management Issues for the Environment: An Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) and STIRPAT Analysis in Turkey. Resources. 2023; 12(5):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12050057
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjaghlou, Mortaza, Erginbay Ugurlu, Marta Kadłubek, and Eleftherios Thalassinos. 2023. "Economic Activities and Management Issues for the Environment: An Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) and STIRPAT Analysis in Turkey" Resources 12, no. 5: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12050057
APA StyleOjaghlou, M., Ugurlu, E., Kadłubek, M., & Thalassinos, E. (2023). Economic Activities and Management Issues for the Environment: An Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) and STIRPAT Analysis in Turkey. Resources, 12(5), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12050057









