Application of Metallic Iron and Ferrates in Water and Wastewater Treatment for Cr(VI) and Organic Contaminants Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setups for Fe0-Based Treatment
2.2. Setups for Ferrate-Based Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Iron-Induced Cr(VI) Removal from Natural Water
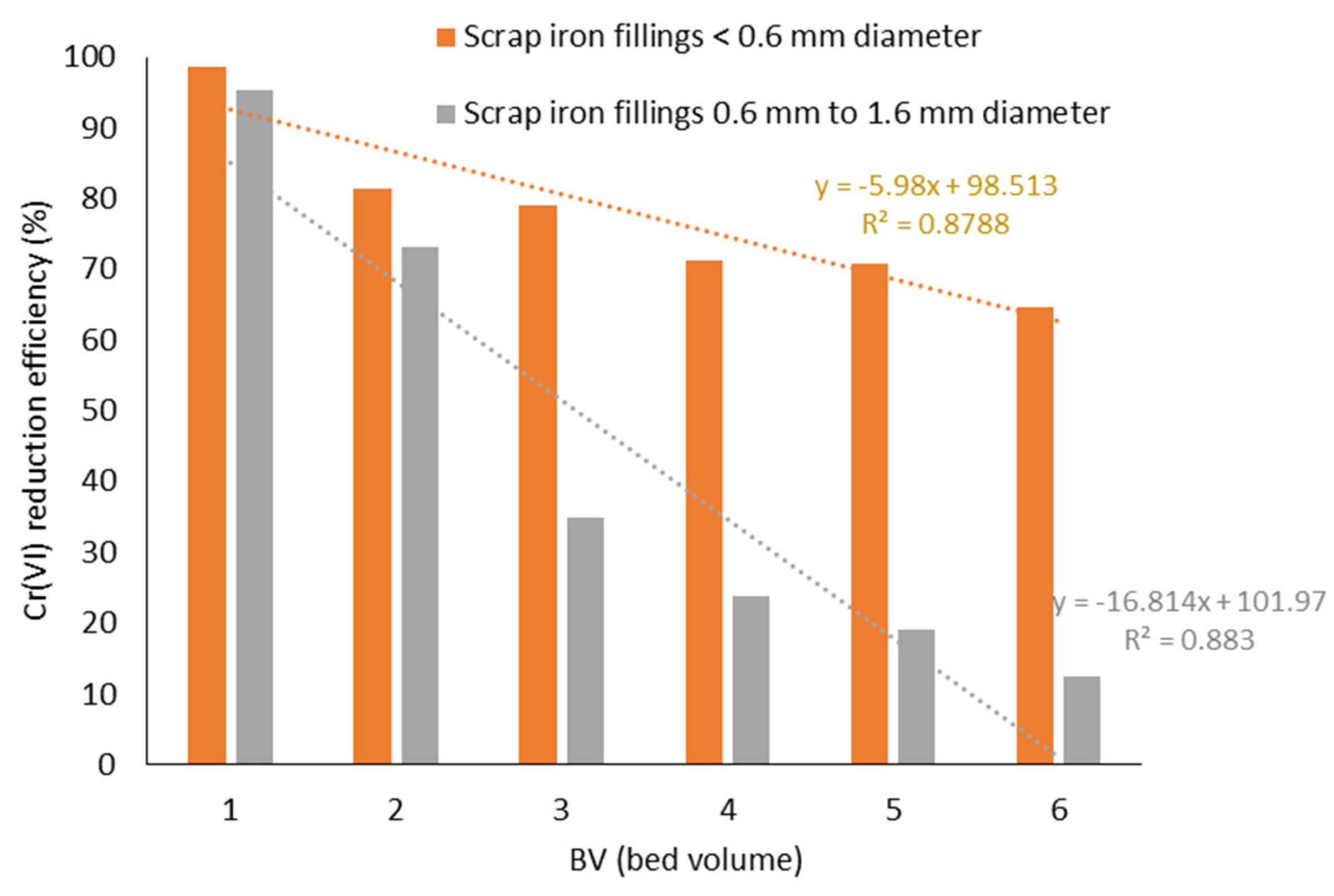
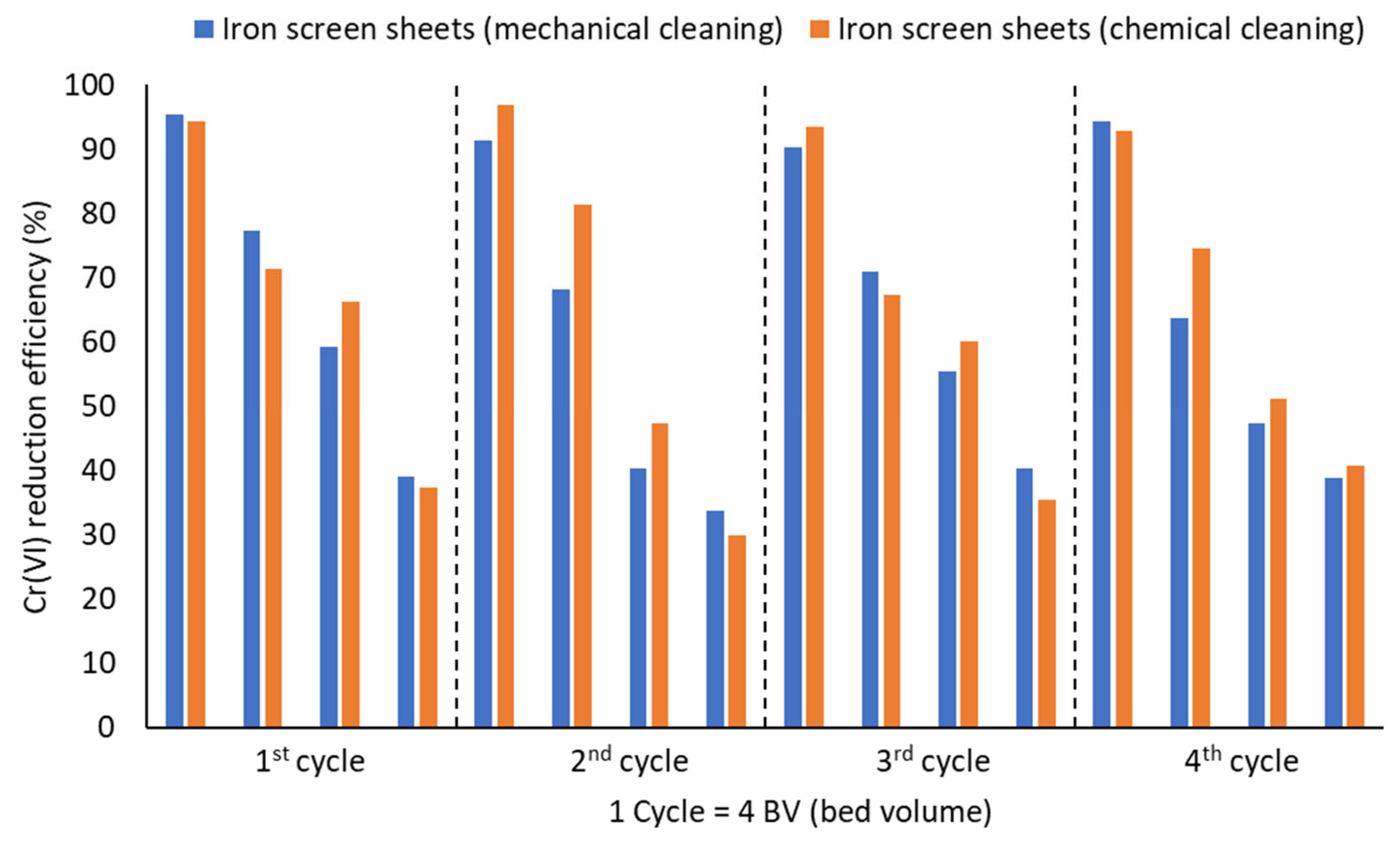
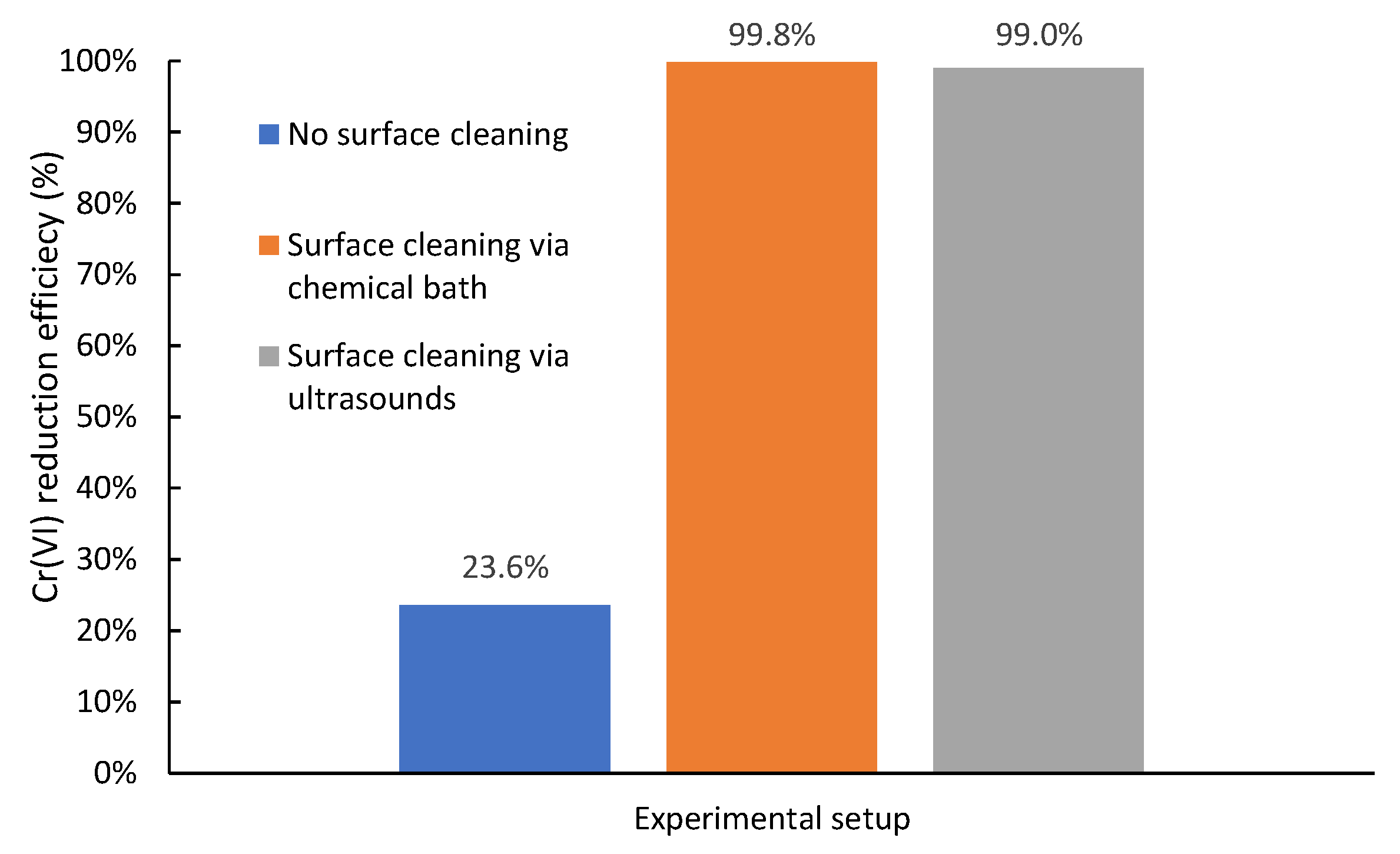
3.1.1. Effect of Iron Coating and Surface Passivation on Cr(VI) Reduction
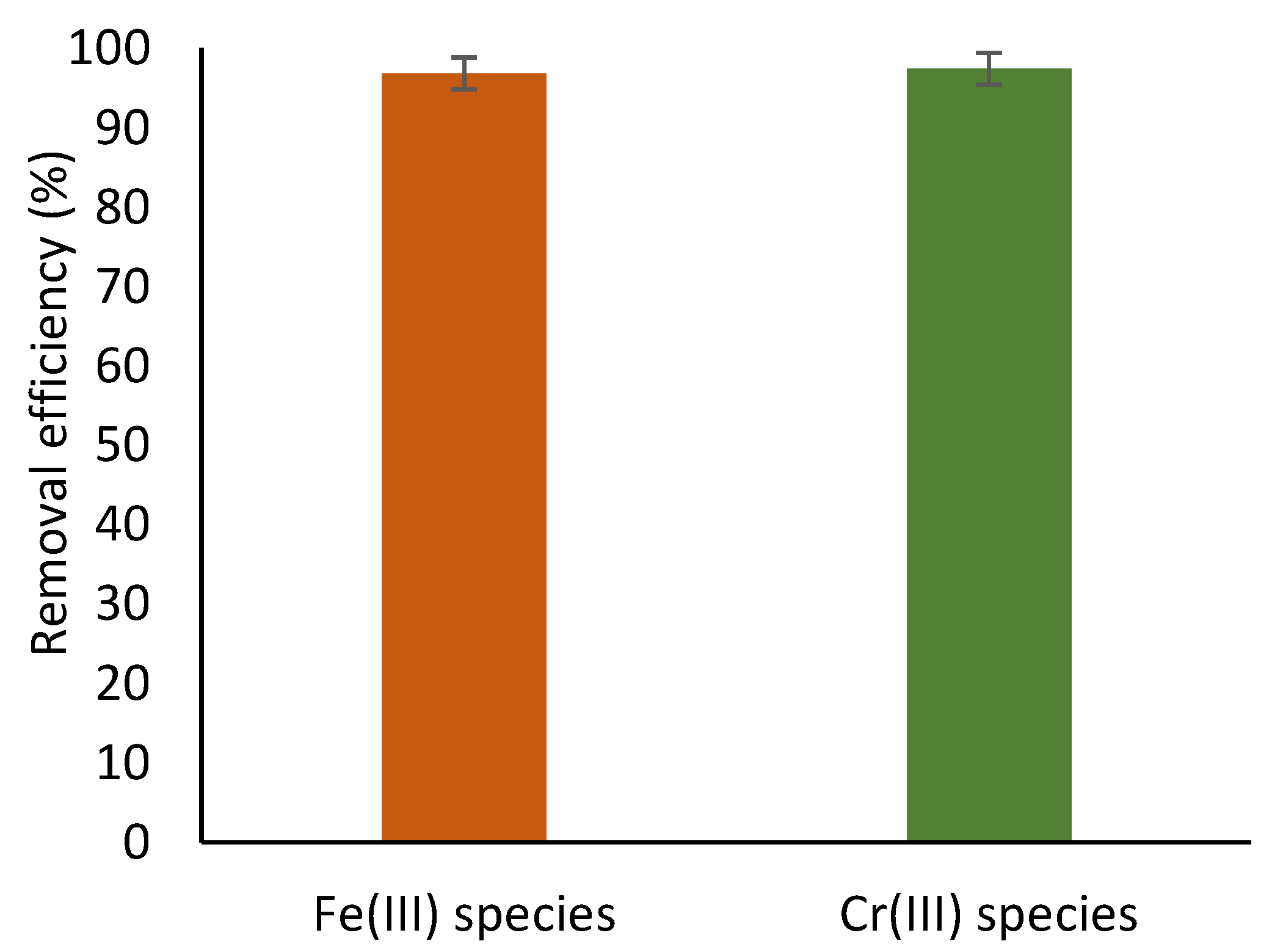
3.1.2. Removal of Precipitants
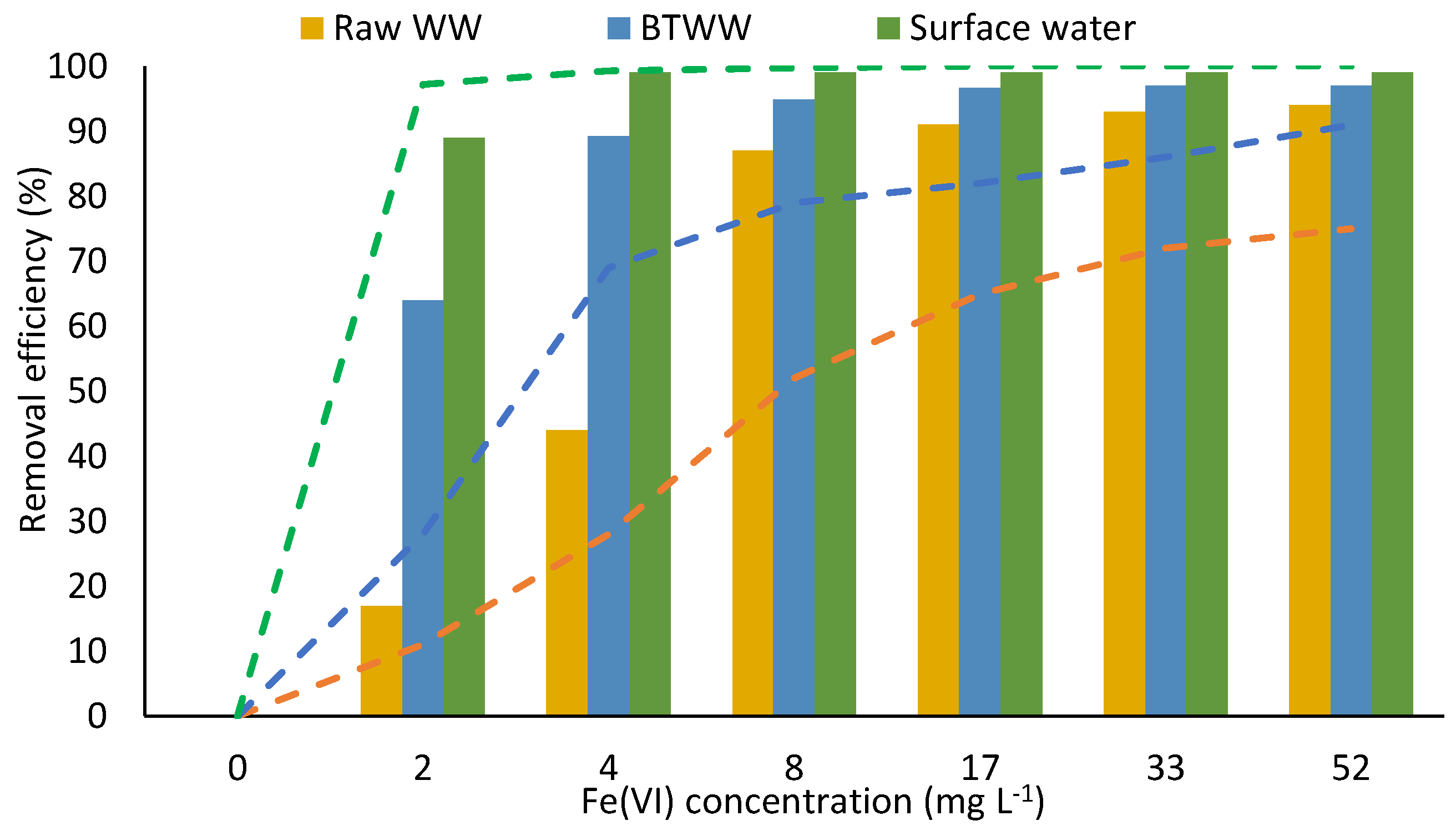
3.2. Ferrates for the Removal of Organic Compounds from Water and Wastewater
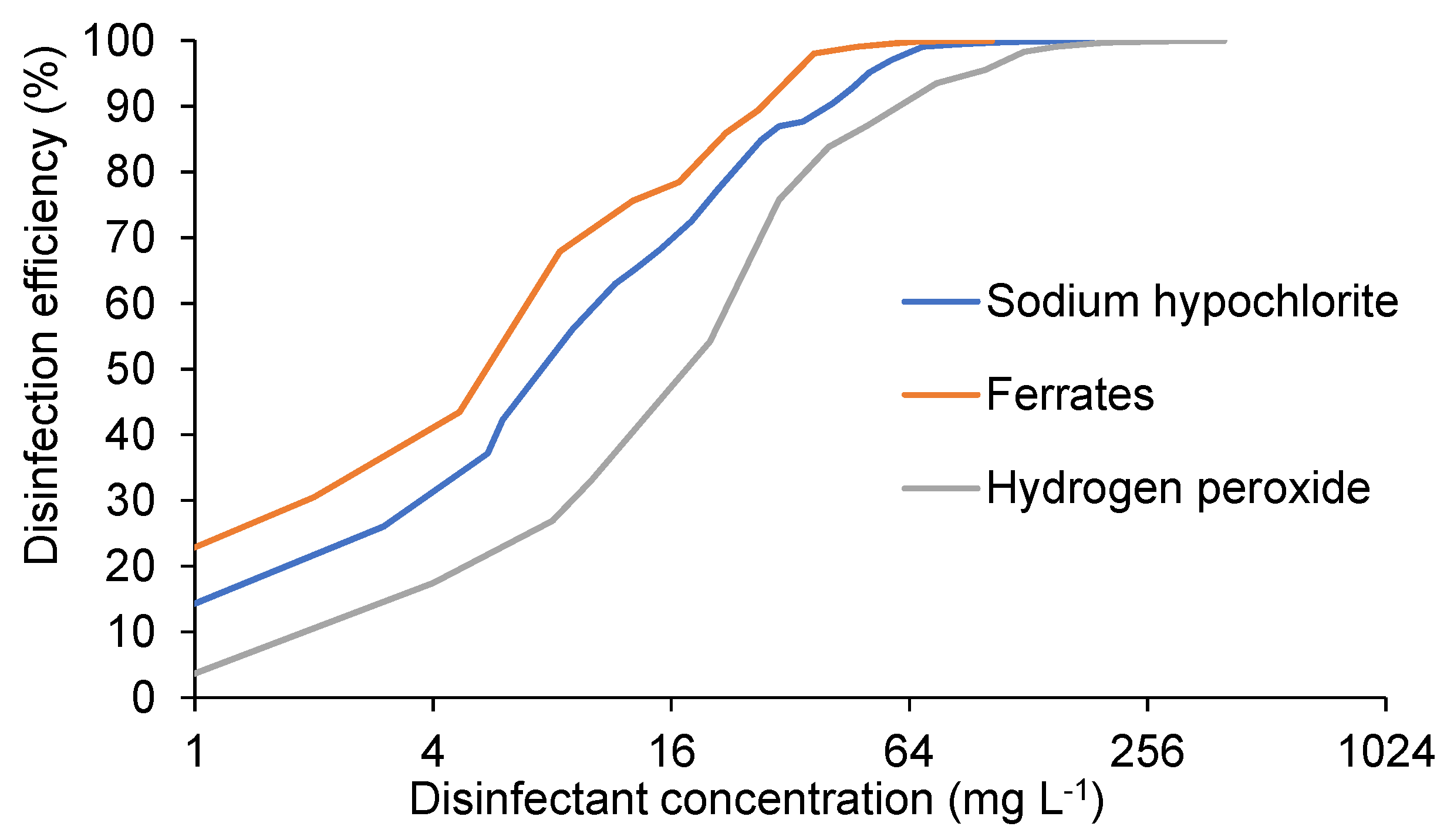
3.3. Ferrates for Water and Wastewater Disinfection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, J.P.; Nicklow, J.W. In situ permeable reactive barriers for groundwater contamination. Soil. Sediment. Contam. 2002, 11, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.D.; Demond, A.H. Long-term performance of zero-valent iron permeable reactive barriers: A critical review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 24, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, J.; Lo, I.M.C.; He, D.; Dong, H. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: The development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res. 2015, 45, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, R.; Birke, V. Permeable Reactive Barrier: Sustainable Groundwater Remediation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; 333p, ISBN 978-1-4822-2448-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Khan, A.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7290–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makota, S.; Nde-Tchoupe, A.I.; Mwakabona, H.T. Metallic iron for water treatment: Leaving the valley of confusion. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4177–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C.; Makota, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Rescuing Fe0 remediation research from its systemic flaws. Res. Rev. Insights 2017, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwakabona, H.T.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Njau, K.N.; Noubactep, C.; Wydra, K.D. Metallic iron for safe drinking water provision: Considering a lost knowledge. Water Res. 2017, 117, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, E.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Mwakabona, H.T.; Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Noubactep, C.; Njau, K.N.; Wydra, K.D. Making Fe0-based filters a universal solution for safe drinking water provision. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Gwenzi, W.; Ruppert, H.; Noubactep, C. Designing the Next Generation of Fe0-Based Filters for Decentralized Safe Drinking Water Treatment: A Conceptual Framework. Processes 2020, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ileri, B.; Ayyildiz, O.; Apaydin, O. Ultrasound-assisted activation of zero-valent magnesium for nitrate denitrification: Identification of reaction by-products and pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Feng, M.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zhou, H.-C.; Jinadatha, C.; Manoli, K.; Smith, M.F.; Luque, R.; Ma, X.; Huang, C.-H. Reactive high-valent iron intermediates in enhancing treatment of water by ferrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Umairi, A.R.; How, Z.T.; El-Din, M.G. Enhanced primary treatment during wet weather flow using ferrate as a coagulant, coagulant aid and disinfectant. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Sumita; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, C.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Pang, W. A Review of Research Progress in the Preparation and Application of Ferrate(VI). Water 2023, 15, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, J.-Q. Synergistic Effect of Ferrate with Various Water Processing Techniques—A Review. Water 2022, 14, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shao, B.; Qiao, J.; Guan, X. Application of Fe(VI) in abating contaminants in water: State of art and knowledge gaps. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou-Eliopoulos, M.; Megremi, I. Contamination of the Soil–Groundwater–Crop System: Environmental Risk and Opportunities. Minerals 2021, 11, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioptsias, C.; Samiotis, G.; Lefteri, L. Cr(VI) Leached from Lignite Fly Ash—Assessment of Groundwater Contamination Risk. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2020, 231, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatidou, C.; Samiotis, G.; Batsi, A.; Amanatidou, E. Correlation of hexavalent chromium concentration to groundwater hydrochemical zones chemistry. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100672. [Google Scholar]
- Samiotis, G.; Ziagova, M.G.; Amanatidou, E. Wastewater substrate disinfection for cyanobacteria cultivation as tertiary treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 8746–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, J.M.; Thompson, G.W.; Ockerman, L.T. Oxidation of chromium(III) with potassium ferrate(VI). Anal. Chem. 1950, 22, 1426–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standards Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Amanatidou, E.; Trikoilidou, E.; Tsikritzis, L.; Katsiouli, F. Uncertainty in spectrophotometric analysis—“Error propagation break up”, a novel statistical method for uncertainty management. Talanta 2011, 85, 2385–2390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amanatidou, E.; Trikoilidou, E.; Samiotis, G.; Benetis, N.P.; Taousanidis, N. An easy uncertainty evaluation of the COD titrimetric analysis in correlation with quality control and validation data. Method applicability region. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 4204–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidou, K.; Bakouros, L.; Mitrakas, M. Techno-Economic Evaluation of Iron and Aluminum Coagulants on Se(IV) Removal. Water 2020, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, D.L.; Chan, P.G. Reduction of hexavalent chromium by ferrous iron. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.E. Surface reactions of chromium in soils and waters. Geoderma 1995, 67, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Hug, S.J. Kinetics and pH Dependence of Chromium(VI) Reduction by Iron(II). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 34, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.D.; Puls, R.W. Natural Attenuation of Hexavalent Chromium in Groundwater and Soils; EPA Ground Water Issue; EPA/540/5-94/505; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington D.C., USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gheju, M. Progress in Understanding the Mechanism of CrVI Removal in Fe0-Based Filtration Systems. Water 2018, 10, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, A.D.; Tare, V.; Bose, P. Extent of oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) under various conditions pertaining to natural environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, K.N.; Fullston, D.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Surface modification for stability of nano-sizes silica colloids. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2007, 315, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remoundaki, E.; Hatzikioseyian, A.; Tsezos, M. A systematic study of chromium solubility in the presence of organic matter: Consequences for the treatment of chromium-containing wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Causal Analysis/Diagnosis Decision Information System (CADDIS). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/caddis (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse; Metcalf & Eddy Inc.: Boston, MA, USA; McGraw Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sulistyo, H.; Sediawan, W.B.; Sarto, S.; Yusuf, Y.; Nainggolan, R. Water Treatment by Coagulation-Flocculation Using Ferric Sulphate as Coagulant. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 12, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidou, E.; Samiotis, G.; Trikoilidou, E.; Pekridis, G.; Tsikritzis, L. Complete solids retention activated sludge process. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanatidou, E.; Samiotis, G.; Trikoilidou, E.; Tsikritzis, L. Particulate organics degradation and sludge minimization in aerobic, complete SRT bioreactors. Water Res. 2014, 94, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokarovtseva, I.G.; Belyaev, I.N.; Semenyakova, L.V. Oxygen compounds of iron (VI), (V) and (IV). Russ. Chem. Rev. 1972, 41, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, S.J.; Cantelli, M.; De Luca, M.A. Ferrate vs. traditional coagulants in the treatment of combined industrial wastes. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzewicz, P.; Drobniewska, A.; Sikorska, K.; Nałęcz-Jawecki, G. Analytical and ecotoxicological studies on degradation of fluoxetine and fluvoxamine by potassium ferrate. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3265–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaude, L.; Laszlo, P. A novel oxidizing reagent based on potassium ferrate(VI). J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 6360–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzaki, S.; Urano, H.; Yamada, S. Effect of pH on the Efficacy of Sodium Hypochlorite Solution as Cleaning and Bactericidal Agents. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 2007, 58, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.R.G.; Crastechini, E.; Feitosa, F.A.; Pucci, C.R.; Borges, A.B. Influence of pH on the effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide whitening. Oper. Dent. 2014, 39, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Lloyd, B. Progress in the development and use of ferrate(VI) salt as an oxidant and coagulant for water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.Z.; Graham, N. A study of the preparation and reactivity of potassium ferrate. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry-Chase, A.; Tewari, B.B. Use to Ferrate (VI) a green chemical for the environmental remediation. Rev. Boliv. Quim. 2013, 30, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.I.; Dore, M.H.I.; Singh, R.G.; Achari, G.; Khaleghi-Moghadam, A. Cost scenarios for small drinking water treatment technologies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 3628–3638. [Google Scholar]
| Material | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Iron wool | Wire diameter (mm) = 0.06 Specific weight (g/m) = 0.0076 Specific surface area (m2/m) = 0.00038 |
| Iron wire | Wire diameter (mm) = 1 Specific weight (g/m) = 0.0076 Specific surface area (m2/m) = 0.00314 |
| Iron screen | Wire diameter (mm) = 0.1 Specific weight (kg/m2) = 0.255488 Specific surface area (m2/m2) = 0.00041867 |
| Scrap iron chips | Wire diameter (mm) = 1 Specific weight (g/m) = 0.0076 Specific surface area (m2/m) = 0.031557 |
| Scrap iron fillings | Mesh (mm) = 0.6–1.6 and <0.6 Specific weight (kg/L) = 1884 and 1271.25 Specific surface area (m2/kg) = 80.7 and 111.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samiotis, G.; Stimoniaris, A.; Ristanis, I.; Kemmou, L.; Mavromatidou, C.; Amanatidou, E. Application of Metallic Iron and Ferrates in Water and Wastewater Treatment for Cr(VI) and Organic Contaminants Removal. Resources 2023, 12, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12030039
Samiotis G, Stimoniaris A, Ristanis I, Kemmou L, Mavromatidou C, Amanatidou E. Application of Metallic Iron and Ferrates in Water and Wastewater Treatment for Cr(VI) and Organic Contaminants Removal. Resources. 2023; 12(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamiotis, Georgios, Adam Stimoniaris, Ilias Ristanis, Liana Kemmou, Charoula Mavromatidou, and Elisavet Amanatidou. 2023. "Application of Metallic Iron and Ferrates in Water and Wastewater Treatment for Cr(VI) and Organic Contaminants Removal" Resources 12, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12030039
APA StyleSamiotis, G., Stimoniaris, A., Ristanis, I., Kemmou, L., Mavromatidou, C., & Amanatidou, E. (2023). Application of Metallic Iron and Ferrates in Water and Wastewater Treatment for Cr(VI) and Organic Contaminants Removal. Resources, 12(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12030039









