Behavior of Sludge Dewaterability and Nutrient Contents after Treatment with Cellulose-Based Flocculants with Combined PTS and Catalytic Behavior of Sludge towards Tetracycline Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
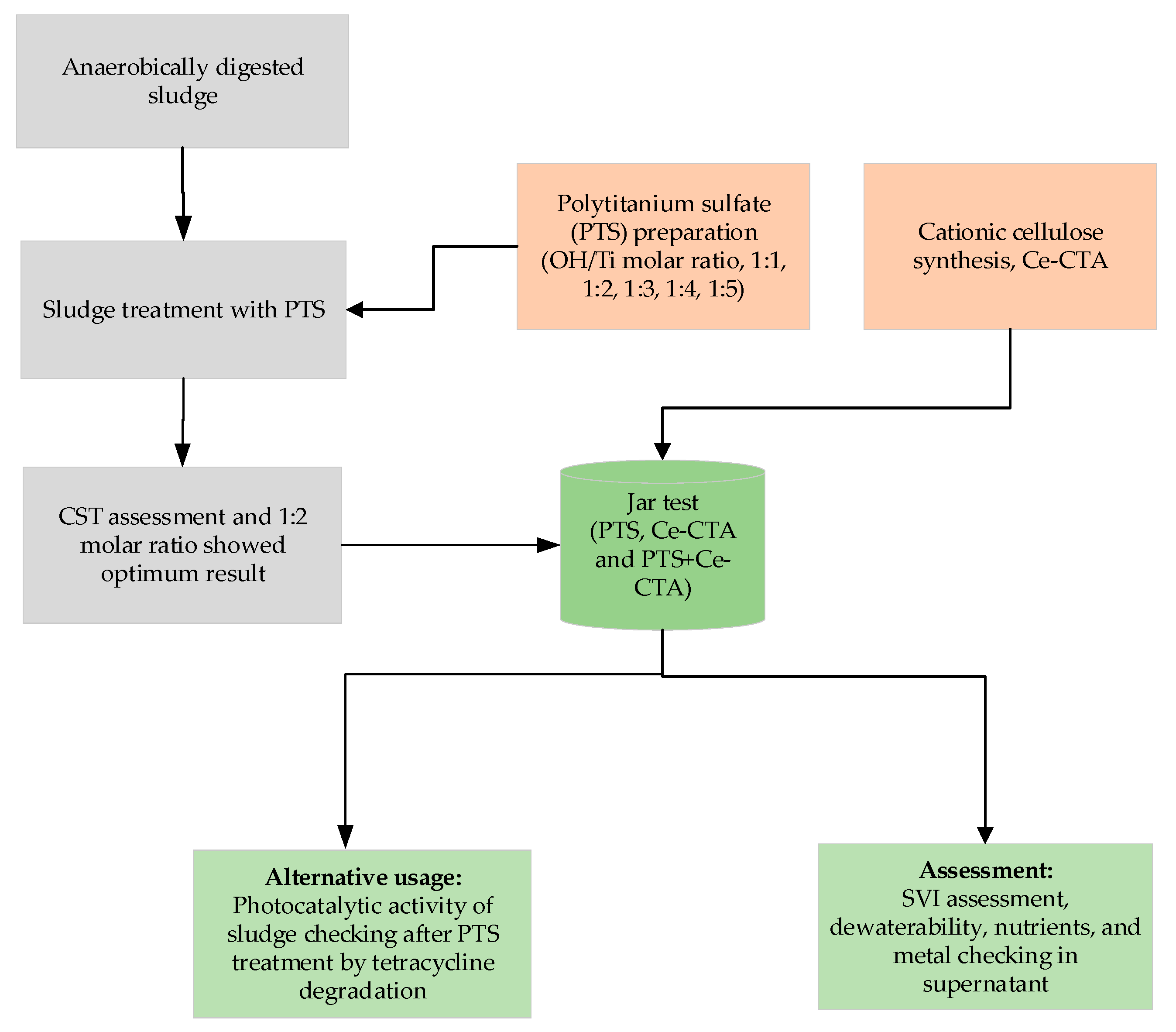
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cationic Cellulose and Poly Titanium Sulfate Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Sludge Conditioning
2.4. Sludge Volume Index (SVI)
2.5. CST Measurement of Sludge after PTS Treatment
2.6. EPS Extraction
2.7. Heavy Metal and Phosphorus Assessment
2.8. Sludge Pyrolysis and Photocatalytic Activity Assessment
2.9. XRD and FTIR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sludge Treatment with PTS and Ce-CTA
3.2. Sludge Dewaterability Check after Coagulation–Flocculation
3.3. Heavy Metals Concentration before and after Treatment
3.4. Nutrient Content after PTS and Ce-CTA Treatment
3.5. Photocatalytic Activity of Sludge after Coagulation–Flocculation
4. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, D.; Sun, M.; Bao, B.; Chen, J.; Luo, H.; Li, J. Rethinking the timing of flocculant addition during activated sludge dewatering. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyrycz, M.; Ochowiak, M.; Krupińska, A.; Włodarczak, S.; Matuszak, M. A review of flocculants as an efficient method for increasing the efficiency of municipal sludge dewatering: Mechanisms, performances, influencing factors and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Meng, C.; Wang, D. Wastewater sludge dewaterability enhancement using hydroxyl aluminum conditioning: Role of aluminum speciation. Water Res. 2016, 105, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Cao, B.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Ma, T.; Xia, H. Improvement of wastewater sludge dewatering performance using titanium salt coagulants (TSCs) in combination with magnetic nano-particles: Significance of titanium speciation. Water Res. 2017, 110, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Comprehensive insights into the inorganic coagulants on sludge dewatering: Comparing aluminium and iron salts. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1534–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbabaei Kootenaei, F.; Mehrdadi, N.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.; Amini Rad, H.; Hasanlou, H.; Mahmoudnia, A. Improvement of Sludge Dewatering by Ultrasonic Pretreatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Cai, A.; Chen, M.; Sun, H.; Xu, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Deng, J. A comparison of oxidation and re-flocculation behaviors of Fe2+/PAA and Fe2+/H2O2 treatments for enhancing sludge dewatering: A mechanism study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Deng, J.; Ye, C.; Cai, A.; Ruan, S.; Chen, M.; Li, X. Fe(II)-activated sodium percarbonate for improving sludge dewaterability: Experimental and theoretical investigation combined with the evaluation of subsequent utilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hernando, M.; Simón, F.X.; Labanda, J.; Llorens, J. Effect of ultrasound, thermal and alkali treatments on the rheological profile and water distribution of waste activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowla, D.; Tran, H.N.; Allen, D.G. A review of the properties of biosludge and its relevance to enhanced dewatering processes. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 58, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Ma, T.; Bai, R. Enhancement of activated sludge dewatering performance by combined composite enzymatic lysis and chemical re-flocculation with inorganic coagulants: Kinetics of enzymatic reaction and re-flocculation morphology. Water Res. 2015, 83, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Li, X.-Y. Polymerized titanium salts for municipal wastewater preliminary treatment followed by further purification via crossflow filtration for water reuse. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Huang, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, S. Potential of titanium coagulants for water and wastewater treatment: Current status and future perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Kim, S.; Shon, H.K.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kim, S.D.; Cho, J.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, J.B.; Park, H.J.; et al. Aquatic toxicity evaluation of TiO2 nanoparticle produced from sludge of TiCl4 flocculation of wastewater and seawater. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, S.C. Low levels of aluminum can lead to behavioral and morphological changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease and age-related neurodegeneration. Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, R. Correlation of physicochemical properties and sludge dewaterability under chemical conditioning using inorganic coagulants. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, H.; Li, A. A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment. Water Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzer, L. Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Flocculants and Performance Tests. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2016; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Ida, S.; Eva, T. Removal of heavy metals during primary treatment of municipal wastewater and possibilities of enhanced removal: A review. Water 2021, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsi, V.; Sarathy, S.R.; Walton, J.R.; Watson, I.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Santoro, D. Enhancing sludge dewaterability and phosphate removal through a novel chemical dosing strategy using ferric chloride and hydrogen peroxide. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-B.; Li, M.; Liu, J.-W.; Xu, W.; Cheng, S.-H.; Zhao, H.-Z. Molecular insights into the mechanism and the efficiency-structure relationship of phosphorus removal by coagulation. Water Res. 2018, 147, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melia, P.M.; Cundy, A.B.; Sohi, S.P.; Hooda, P.S.; Busquets, R. Trends in the recovery of phosphorus in bioavailable forms from wastewater. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Ren, J.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Sludge dewaterability of a starch-based flocculant and its combined usage with ferric chloride. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA/AWWA/WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 541, ISBN 9780875532356. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, T.; Ding, M.; Lu, C.; Cui, J.; Shen, K.; Xu, H. Dewatering of drinking water treatment sludge using the Fenton-like process induced by electro-osmosis. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 293, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L. Influences of extracellular polymeric substances on the dewaterability of sewage sludge during bioleaching. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, J.; Qian, G.; Wang, A. pH dependent phosphorus release from waste activated sludge: Contributions of phosphorus speciation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumky, J.; Visigalli, S.; Turolla, A.; Gelmi, E.; Necibi, C.; Gronchi, P.; Sillanpää, M.; Canziani, R. Electro-dewatering treatment of sludge: Assessment of the influence on relevant indicators for disposal in agriculture. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 268, 110689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Coagulation performance and flocs properties of a new composite coagulant: Polytitanium–silicate–sulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejimofor, M.I.; Ezemagu, I.G.; Menkiti, M.C. Physiochemical, Instrumental and thermal characterization of the post coagulation sludge from paint industrial wastewater treatment. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, M.; Chandra Dey, S.; Rashid, T.U.; Ashaduzzaman, M.; Shamsuddin, S.M. Solar Assisted Photocatalytic Degradation of Reactive Azo Dyes in Presence of Anatase Titanium Dioxide. Int. J. Latest Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 2, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer, J.; Strk, A.; Kiefer, A.L.; Glade, H. Infrared spectroscopic analysis of the inorganic deposits from water in domestic and technical heat exchangers. Energies 2018, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, M.W.; Peterson, B.N.; Nottoli, T.; McCulloch, J.M.; Jinkerson, R.E.; Boyle, N.R.; Posewitz, M.C. Effectiveness of cationically modified cellulose polymers for dewatering algae. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrahim, B.; Abderrahman, E.; Mohamed, A.; Fatima, T.; Abdesselam, T.; Krim, O. Kinetic Thermal Degradation of Cellulose, Polybutylene Succinate and a Green Composite: Comparative Study. World J. Environ. Eng. 2015, 3, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Boyacioglu, E. Evaluation of the performance of titanium and zirconium salts as coagulants in industrial wastewater treatment: Pollutant removal, sludge production, and sludge characteristics. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masihi, H.; Badalians Gholikandi, G. Using acidic-modified bentonite for anaerobically digested sludge conditioning and dewatering. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Gu, M.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, N. Insights into the enhancement of waste activated sludge dewaterability using sodium dichloroisocyanurate and dodecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride: Performance, mechanism, and implication. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.; Jin, R.; Liu, G.; Dong, B.; Zhou, J.; Xing, D. Improving waste activated sludge dewaterability with sodium periodate pre-oxidation on extracellular polymeric substances. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Guan, Z. Analysis of the relationship of extracellular polymeric substances to the dewaterability and rheological properties of sludge treated by acidification and anaerobic mesophilic digestion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, J.I.; Stephenson, T. Effect of influent organic content on digested sludge extracellular polymer content and dewaterability. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3620–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, A.; Mizerna, K.; Bożym, M. An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, A.; Hamid, A.; Muhammad, N.; Naseer, A.; Ghauri, M.; Iqbal, J.; Rafiq, S.; Shah, N.S. Cellulose-based Materials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater—An Overview. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fu, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, M.; Jin, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y. Recent Development in Sludge Biochar-Based Catalysts for Advanced Oxidation Processes of Wastewater. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monea, M.C.; Löhr, D.K.; Meyer, C.; Preyl, V.; Xiao, J.; Steinmetz, H.; Schönberger, H.; Drenkova-Tuhtan, A. Comparing the leaching behavior of phosphorus, aluminum and iron from post-precipitated tertiary sludge and anaerobically digested sewage sludge aiming at phosphorus recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanyan, A.; Kafa, N.; Konstantinidis, V.; Shin, S.G.; Vyrides, I. Phosphorus dissolution from dewatered anaerobic sludge: Effect of pHs, microorganisms, and sequential extraction. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carliell-Marquet, C.; Smith, J.; Oikonomidis, I.; Wheatley, A. Inorganic profiles of chemical phosphorus removal sludge. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Water Manag. 2010, 163, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhong, C.; Yin, K.; Peng, S.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, G. Alkaline solubilization of excess mixed sludge and the recovery of released phosphorus as magnesium ammonium phosphate. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilfert, P.; Mandalidis, A.; Dugulan, A.I.; Goubitz, K.; Korving, L.; Temmink, H.; Witkamp, G.J.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Vivianite as an important iron phosphate precipitate in sewage treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 104, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

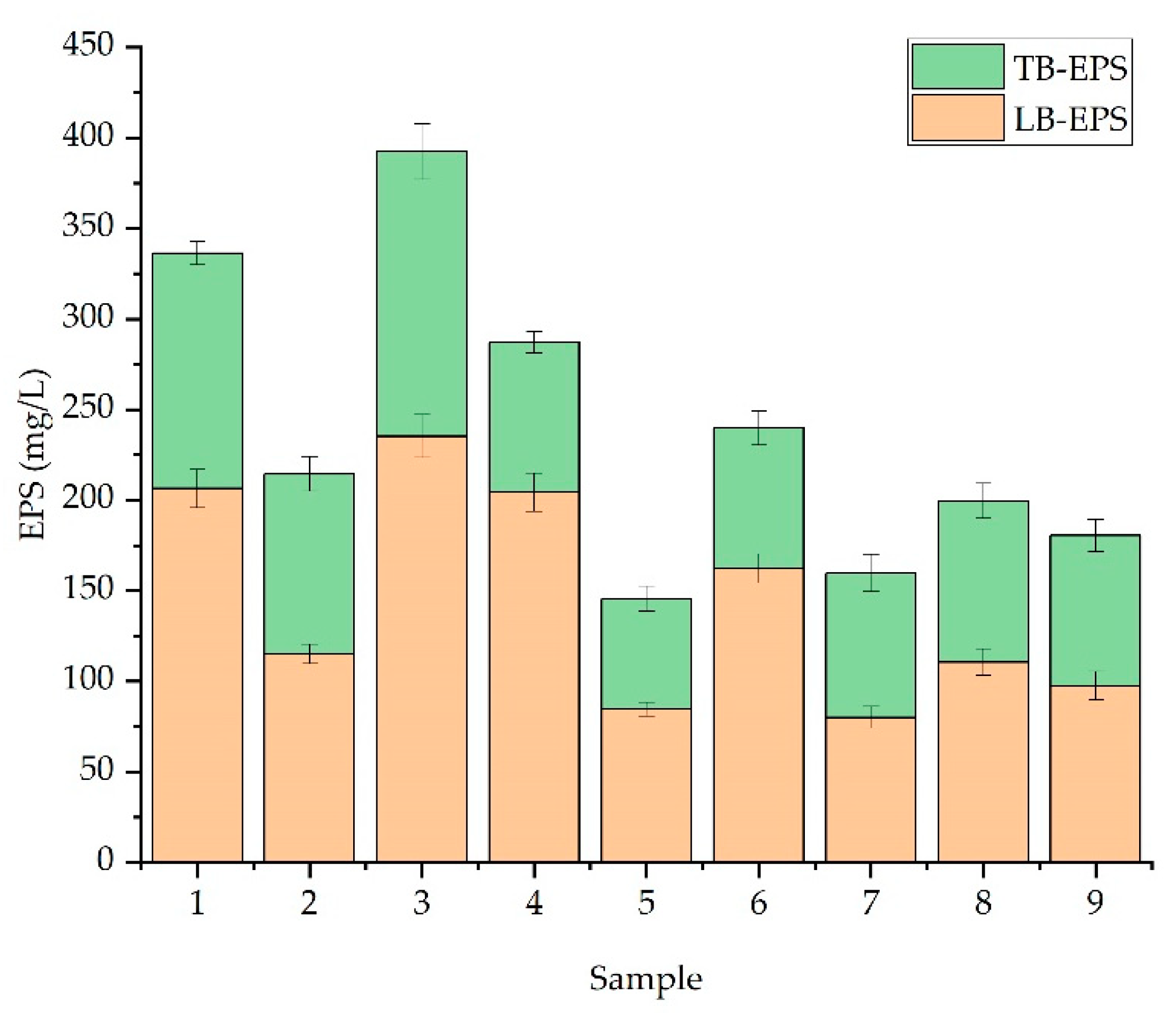



| Sample No. | Nitrate (ppm) | Phosphate (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (pH 3) | 5.063 ± 0.5 | 15 ± 2.05 |
| Sample 2 (pH 3) | 5.063 ± 0.43 | 9 ± 1.01 |
| Sample 3 (pH 3) | 5.314 ± 0.32 | 18 ± 3.05 |
| Sample 4 (pH 6) | 5.328 ± 0.31 | × |
| Sample 5 (pH 6) | × | × |
| Sample 6 (pH 6) | × | × |
| Sample 7 (pH 9) | 5.031 ± 0.51 | × |
| Sample 8 (pH 9) | × | × |
| Sample 9 (pH 9) | × | × |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rumky, J.; Bandina, E.; Repo, E. Behavior of Sludge Dewaterability and Nutrient Contents after Treatment with Cellulose-Based Flocculants with Combined PTS and Catalytic Behavior of Sludge towards Tetracycline Degradation. Resources 2023, 12, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12020017
Rumky J, Bandina E, Repo E. Behavior of Sludge Dewaterability and Nutrient Contents after Treatment with Cellulose-Based Flocculants with Combined PTS and Catalytic Behavior of Sludge towards Tetracycline Degradation. Resources. 2023; 12(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleRumky, Jannatul, Ekaterina Bandina, and Eveliina Repo. 2023. "Behavior of Sludge Dewaterability and Nutrient Contents after Treatment with Cellulose-Based Flocculants with Combined PTS and Catalytic Behavior of Sludge towards Tetracycline Degradation" Resources 12, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12020017
APA StyleRumky, J., Bandina, E., & Repo, E. (2023). Behavior of Sludge Dewaterability and Nutrient Contents after Treatment with Cellulose-Based Flocculants with Combined PTS and Catalytic Behavior of Sludge towards Tetracycline Degradation. Resources, 12(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12020017







