Abstract
Electrical Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (EIS) is a technique used to assess passive electrical properties of biological materials. EIS detects physiological and pathological conditions in animal tissues. Recently, the introduction of broadband excitation signals has reduced the measuring time for application techniques such as Electrical Bioimpedance Myography. Therefore, this work is aimed at proposing a prototype by using discrete interval binary sequences (DIBS), which is based on a system that holds a current source, impedance acquisition system, microcontroller and graphical user interface. Measurements between 5 Ω to 5 kΩ had impedance acquisition and phase angle errors of aproximately 2% and were lower than 3 degrees, respectively. Based on a proposed circuit, bioimpedance of the chest muscle (Pectoralis Major) was measured during isotonic exercise (push-up). As a result, our analyses have detected tiredness and fatigue. We have explored and proposed new parameters which assess such conditions, as both the maximum magnitude and tiredness coefficient. These parameters decrease exponentially with consecutive push-ups and were convergent in the majority of the sixteen days of measurement.
1. Introduction
The electrical bioimpedance is the capability that biological materials have to oppose the passage of an electrical current [1]. The intracellular fluids, extracellular fluids and the cell membrane determine the electrical conductivity in biological tissues. These fluids have ions able to move freely, transporting charges [2]. In the medium outside the cell, the most common ions are the sodium () and chlorine () while, in the inside medium, the potassium () is the most abundant one [3]. The cell membrane has small channels that allow the flux of ions between the inside and outside [3]. The bioimpedance depends not only on the tissue physical and chemical structures, like size and shape [4], but also on environmental factors like humidity and temperature.
This technique retrieves information about the Material Under Test (MUT) conditions and is a powerful tool in physiological and pathological analysis [5]. The simplest method to measure the bioimpedance comprises injecting an electrical current or voltage in MUT and measuring the resulting voltage or current [6]; then, the relation V/I is calculated. The measurement of multifrequency bioimpedance is known as Electrical Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (EBIS). Characterization of materials through bioimpedance is a growing topic in biomedical engineering because it can be non-invasive, low-cost and portable [7]. The development of small hardware has become necessary to comply with new applications that demand portable/wearable devices [8].
The standard excitation method in the EBIS uses a series of sine wave signals in different frequencies, and each frequency swaps after a set number of periods [9]. The range is usually between 100 Hz and 10 MHz, depending on the application [10]. This method is efficient because the sine wave power is concentrated in one frequency, leading to a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). However, the time necessary to secure a full spectrum might be too large for some applications [11]. In living beings, there are processes that occur quickly and the traditional EBIS could not monitor them [12]. The fast EBIS also avoids artifacts caused by an MUT involuntary movement, which may lead to changes in the contact interface (electrode–electrolyte) and cause errors during the measurement [13].
The acquisition time in EBIS can be reduced by replacing the standard sequence of sines with a broadband signal. This signal contains many harmonics in a single period, yielding the computation of a complete bioimpedance spectrum in a single period [11]. The usual EBIS broadband signals are the Maximum Length Binary Sequences (MLBS), Chirp, Discrete Interval Binary Sequences (DIBS) and Multisine; however, the best results were obtained using DIBS and Multisine [14].
DIBS are periodic binary sequences with a unique characteristic, the signal level (+1 or −1) can only change within a set interval of time (or its multiples) [14] and the number of points in this sequence must be a power of 2. The power concentrates in some specific harmonics [15], then, by selecting the interval that the signal level can change and the number of changes, one can design DIBS spectra.
The Multisine is the sum of many sine waves; therefore, it has the advantage that the desired harmonics, which are adjustable to any frequency, contain all the power. The waveform amplitude relies on the peak value of each sine wave added [16], thus multisines have a high crest factor (CF—relation between the signal amplitude and the power spectral amplitude). A few modifications enhanced the multisines CF, which reached values down to 1.45 [17]. Furthermore, the distribution of harmonics, how far is one harmonic from another and the pattern of gaps between harmonics, is an important factor regarding the CF of multisines, the binary distribution (harmonics equal to ) leads to lower CF than the logarithmic (harmonics equal to ) [18] and to the equally spaced distributions (harmonics equal to, e.g., ), where n is the harmonic number [19].
An advantageous feature of DIBS and other binary signals is the low CF, around 1.1 and 1.2 [14]. In addition, binary signals are easier to implement in microcontrollers (MCU) and FPGAs than sine waves. When compared to Multisines, multifrequency binary signals may have twice the total power of a multisine with the same amplitude [16], five times more energy [20] and three times less sensitivity to noise [18]. One disadvantage of the binary multifrequency signals is the unequal amplitude of the desired harmonics. Furthermore, the power is not only distributed into the desired harmonics and filtering a binary multifrequency signal leads to distortions and increases the crest factor [16].
Electrical Bioimpedance Myography (EBIM) is a non-invasive application that focuses on the assessment of muscle conditions. Rutkove in 2002 made measurements to understand the mechanisms of impedance changes in neuromuscular diseases [21]. The resistance and reactance depend on the muscle length and cross-sectional area, so one can assume parameters such as muscle mass, shape and tissue quality defines the muscle impedance [22]. One of the major challenges of EBIM is to identify the contributions of each tissue (cutaneous, fat, muscle and bone) in the measurement [23].
There are diverse applications of EBIM in literature, some are: evaluation of paretic muscle changes after stroke [22], fatigue [24,25,26,27], equine muscle diseases [28], detection of muscle activation [29], skeletal muscle injuries [30,31] and identification of many neuromuscular diseases [32].
EBIM researchers generally use manufactured devices [22,26] or build a prototype based on data acquisition cards and other devices [24,29,33]. The works that have characterized the device showed relatively smaller errors, but none of them used broadband excitation, and two could measure in real time [29,33]. Most works that measure EBIM in humans usually focus on arm muscles (biceps brachii and forearm tensor) and have the limitation of measuring only in frequencies smaller than 200 kHz. The ones that measured muscular contraction found converging results, which means an increase in the impedance when the muscle is contracted and a decrease when fatigue is reached.
Researchers are also studying electrodes geometry, materials and positioning to obtain better measurements. Although most EBIM systems use surfaces electrodes, wet (Ag/AgCl) or dry (Metal Plates), these electrodes suffer from misalignment, electrode–skin contact impedance and MUT subcutaneous fat tissue thickness [34]. The distance between the electrodes has a major contribution to the system sensitivity as it changes the depth of current penetration. Through practical and theoretical analyses, for which the results diverged in less than 10%, a group proposed a guideline for electrode positioning [32]. One solution for this setback is the use of minimally invasive needle electrodes [34]; however, this sort of electrode may not be affordable in developing countries due to high prices and lack of suppliers.
The aim of this work is to design a low-cost portable EBIM device for the monitoring of muscle physiological conditions. We describe each stage required in device implementation and how to carefully use the DIBS. Testing known resistive loads allows us to calculate the prototype accuracy error and the standard deviation. By measuring the pectoralis major impedance during isotonic exercises (push-ups), we could see muscular fatigue/exhaustion and propose parameters to identify tiredness.
2. Materials and Methods
The MATLAB toolbox FDIDENT function “dibs” (old version) generated the excitation signal (DIBS). MATLAB functions were also used to analyze and process data (FFT, decimate, smooth), plot graphs and create figures. The printed circuit board, manufactured in a 2-layer copper board, was connected as a shield to the microcontroller (STM32F303ZE-NUCLEO144). All electronic parts had SMD packages, resistors had 1% tolerance, and an external 5 V DC isolated source supplied power.
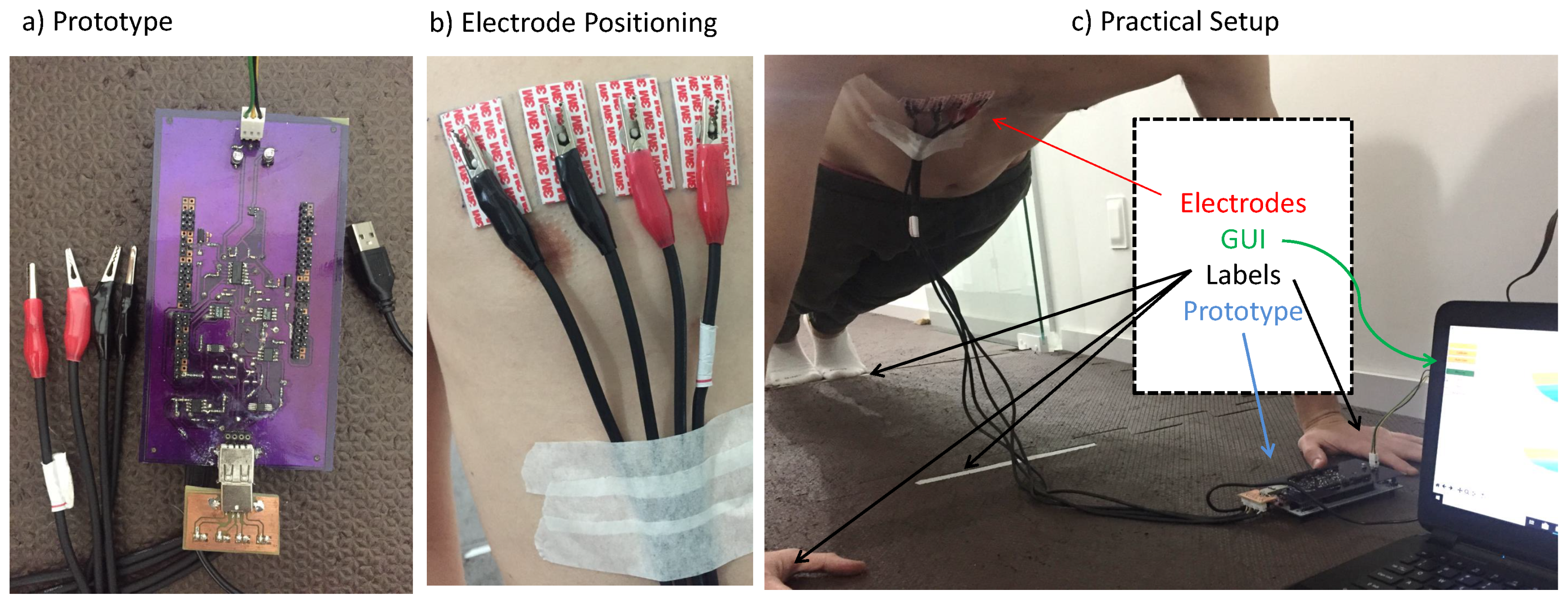
Wet Ag/AgCl electrodes with 1 cm of diameter (2223BRQ, manufactured by 3M) were used. The electrodes displacement was linear and the separation distance between two consecutive electrodes was 3 cm.
The prototype was evaluated by measuring 100 spectra of each one of 25 resistors, between 5 Ω and 5 kΩ, and calculating the error and standard deviation. The real resistance was obtained by measuring each resistor with a 6 digit multimeter (DMM 4050, Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA), in a four wire setup.
After characterizing the prototype, we monitored the Pectoralis Major bioimpedance during a set of isotonic exercises, commonly known as push-ups. This muscle was chosen because it presents lower anisotropy, lower shape distortions during exercise, and simpler electrode alignment compared to Biceps Brachii. One healthy volunteer took part in the experiment (25 years old, 180 cm height, 75 kg). The experiment happened three times a week (Monday–Wednesday–Friday) totaling 16 days. The length of each exercise set was approximately 30 s (≈15 push-ups), this period was defined by previously requesting the volunteer to time how long it took to reach exhaustion. To assure the experiment repeatability, we placed labels onto the floor at the position of hands and foot, marked the electrodes position on the volunteer’s chest skin, and limited the movements amplitude by using a foam block with 25 cm height over the visible label in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Materials and methods.
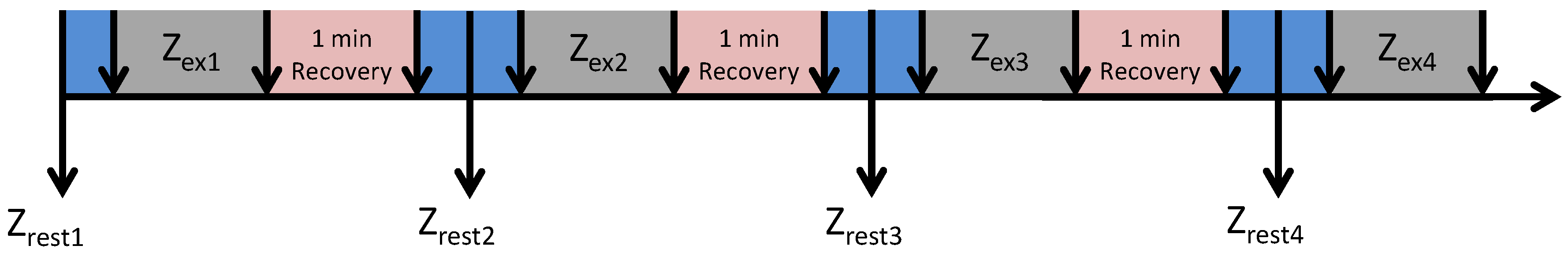
The experiment routine, shown in Figure 2, consists of:
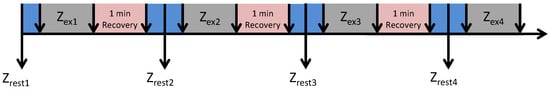
Figure 2.
Measurement routine.
- Measure during rest state (mean of 40 spectra),
- Measure during exercise () (250 spectra),
- Rest (1 min),
- Repeat the items above three more times.
was measured while the volunteer was in the exercise initial position, with arms steady and straights. A trained volunteer controlled the experiment, by proper timing of the rest period, initiating the measurements, saving the data, and observing any discrepancy to the protocol (Figure 2).
In summary, a total of 4 sets of exercises with 30 s duration were monitored by measuring the chest bioimpedance; another 4 measurements happened during rest state, previously to each exercise set.
3. Prototype Design
This section describes a modified version of an electronic prototype designed in [35], all hardware electrical characteristics (current source output impedance, output current vs. load, current and voltage acquisitions output spectra) curves can be seen there.
3.1. DIBS
The designed DIBS has 512 points, updated in a discrete interval () of 0.472 µs, while the update frequency ( kHz) is . The excitation harmonics were distributed linearly in steps of 33.1 kHz between 4.1 () and 1058.8 kHz (), leading to 32 excitation frequencies. We decided to concentrate most harmonics in high frequencies because other works on EBIM measured only in low frequencies. In addition, the bioimpedance values are smaller in high frequencies, leading to smaller SNR, so measuring more points in high frequencies enhances the accuracy. All procedures described in this section were executed in the MATLAB environment.
The DIBS has undesired harmonics that may lead to errors when calculating the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) after the signal acquisition. We simulated the DIBS as a real sampled signal in MATLAB with four different sampling rates, three of them are feasible to implement in our device and the other was an ideal sampling. The number of periods acquired must be an integer and the sampling rate must be a multiple of . The sampling rates were 2.1 MHz, 4.2 MHz, 8.4 MHz and 135.5 MHz and the signal amplitude was 0 and 3.3 V, mimicking a MCU digital output.
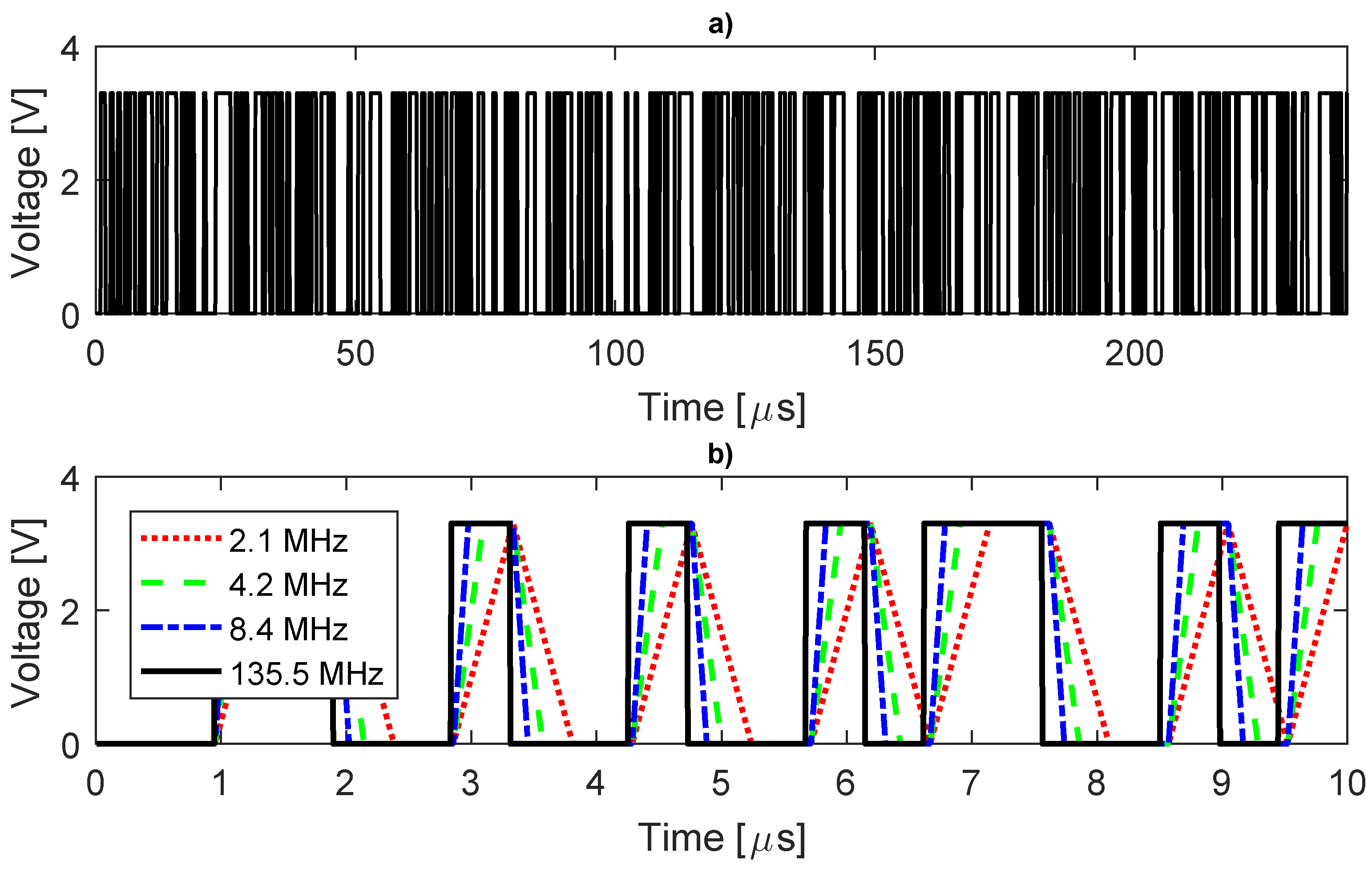
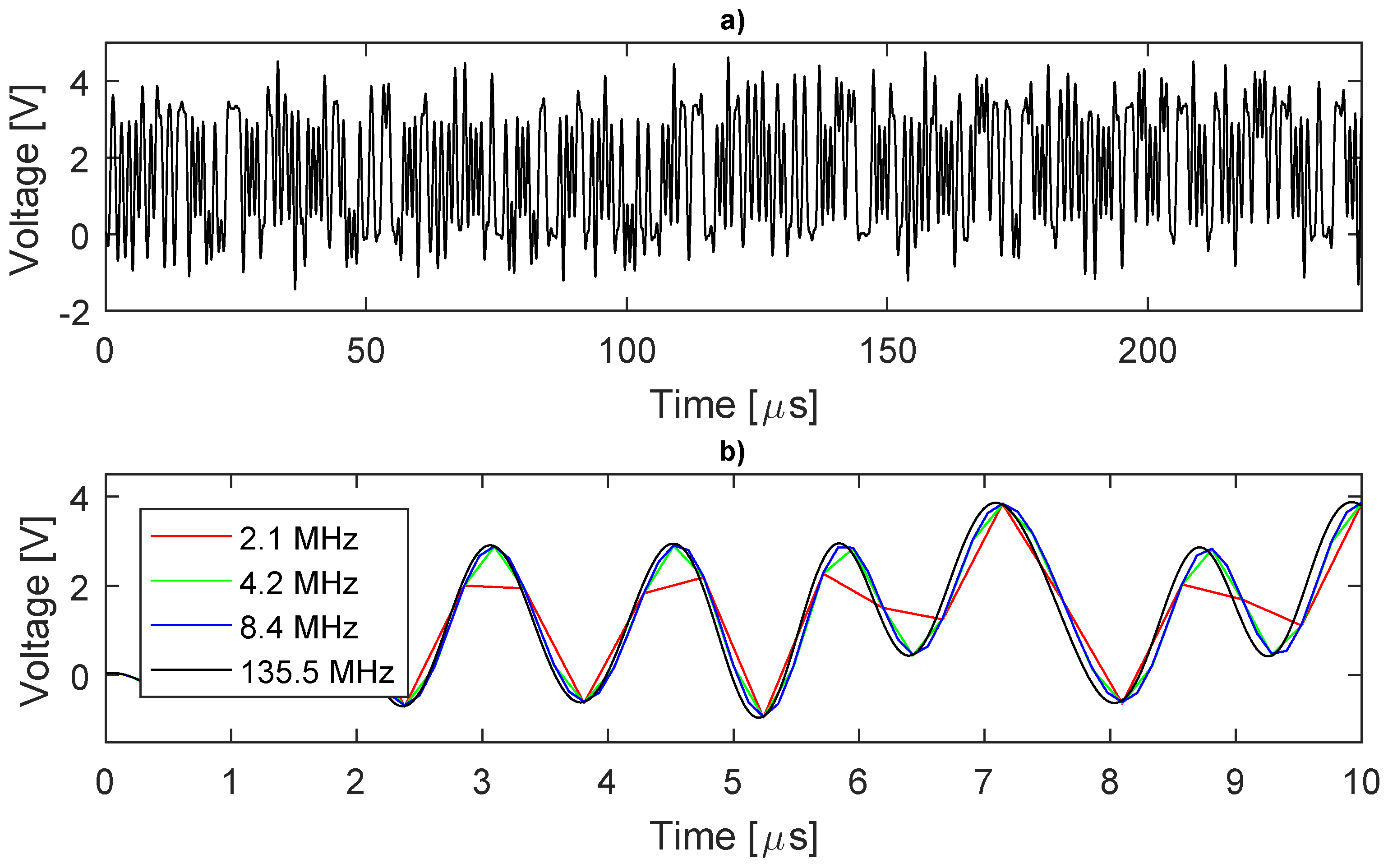
In Figure 3a, the complete waveform of the “ideal” DIBS (135.5 MHz) is shown, while, in Figure 3b, one can observe the waveform generated by each sampling rate. The curves with small sampling rates have an almost triangular shape instead of rectangular; however, to assess the sampling quality, we must calculate the FFT, as shown in Figure 4.
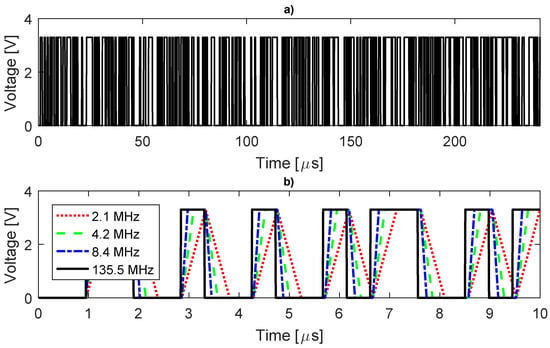
Figure 3.
DIBS waveform. (a) complete period (135.5 MHz); (b) part of the waveform for different sampling.
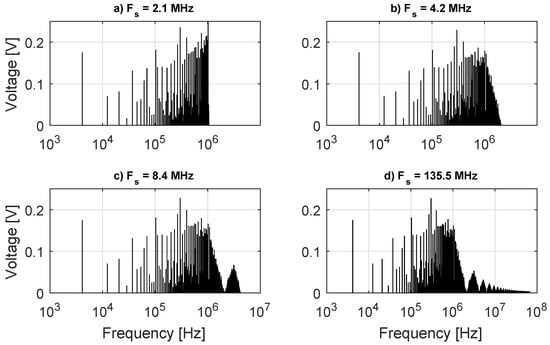
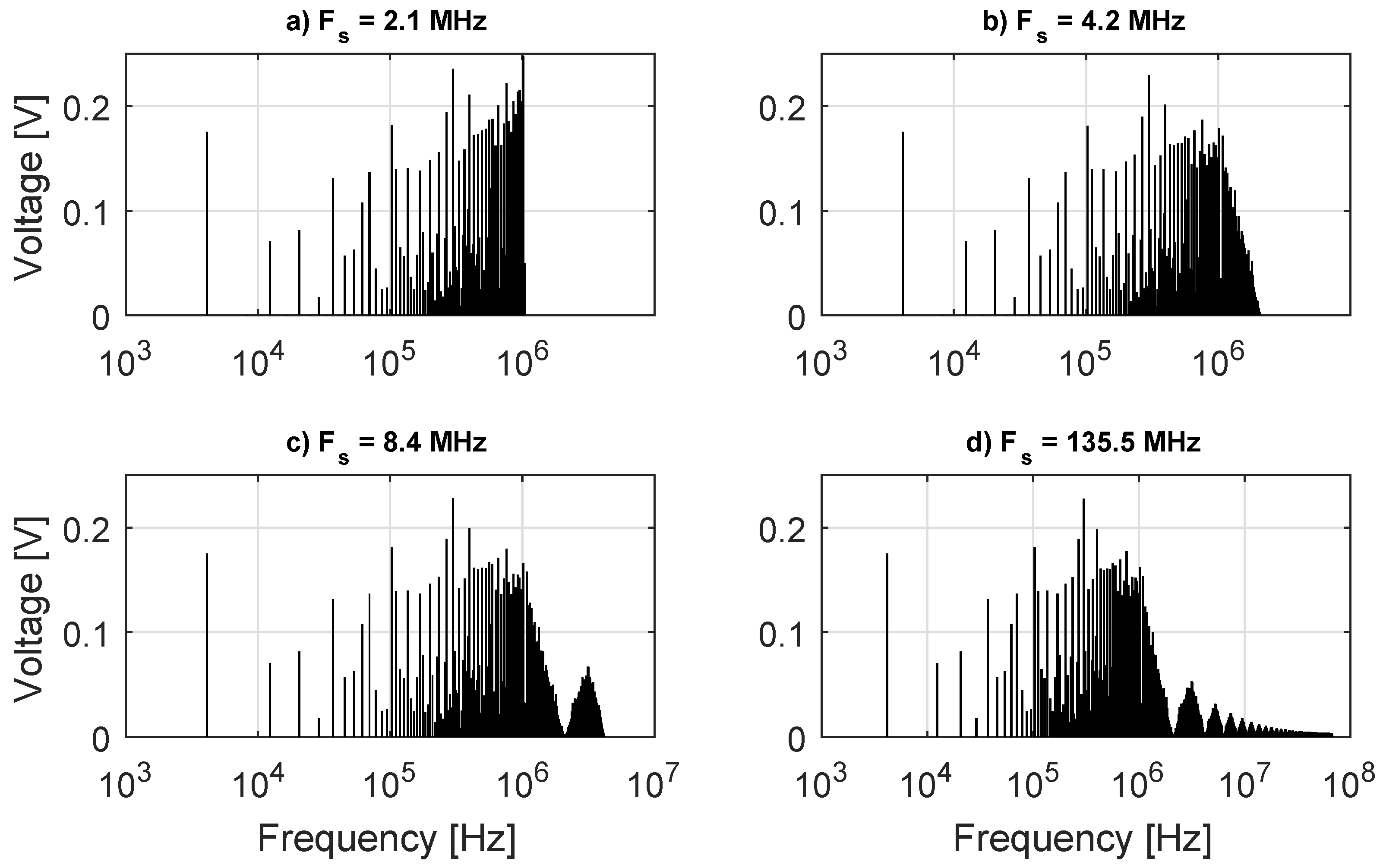
Figure 4.
Complete DIBS FFT for four sampling rates.
In Figure 4, the behavior of the spectrum generated by the FFT on each sampling can be seen. In Figure 4d, the case closest to an ideal sampling, the DIBS spectrum, has high frequency lobes centered at the odd harmonics of the . The first lobe is approximately on 3.1 MHz, so considering that Nyquist frequency of 2.1 and 4.2 MHz sampling is below the lobe frequency, then an aliasing error appears. The same happens for the higher frequencies lobes with the 8.4 MHz sampling. One can see the desired harmonics measured on each sampling rate in Figure 5a.
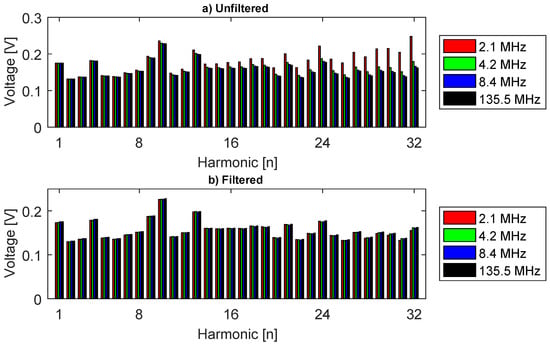
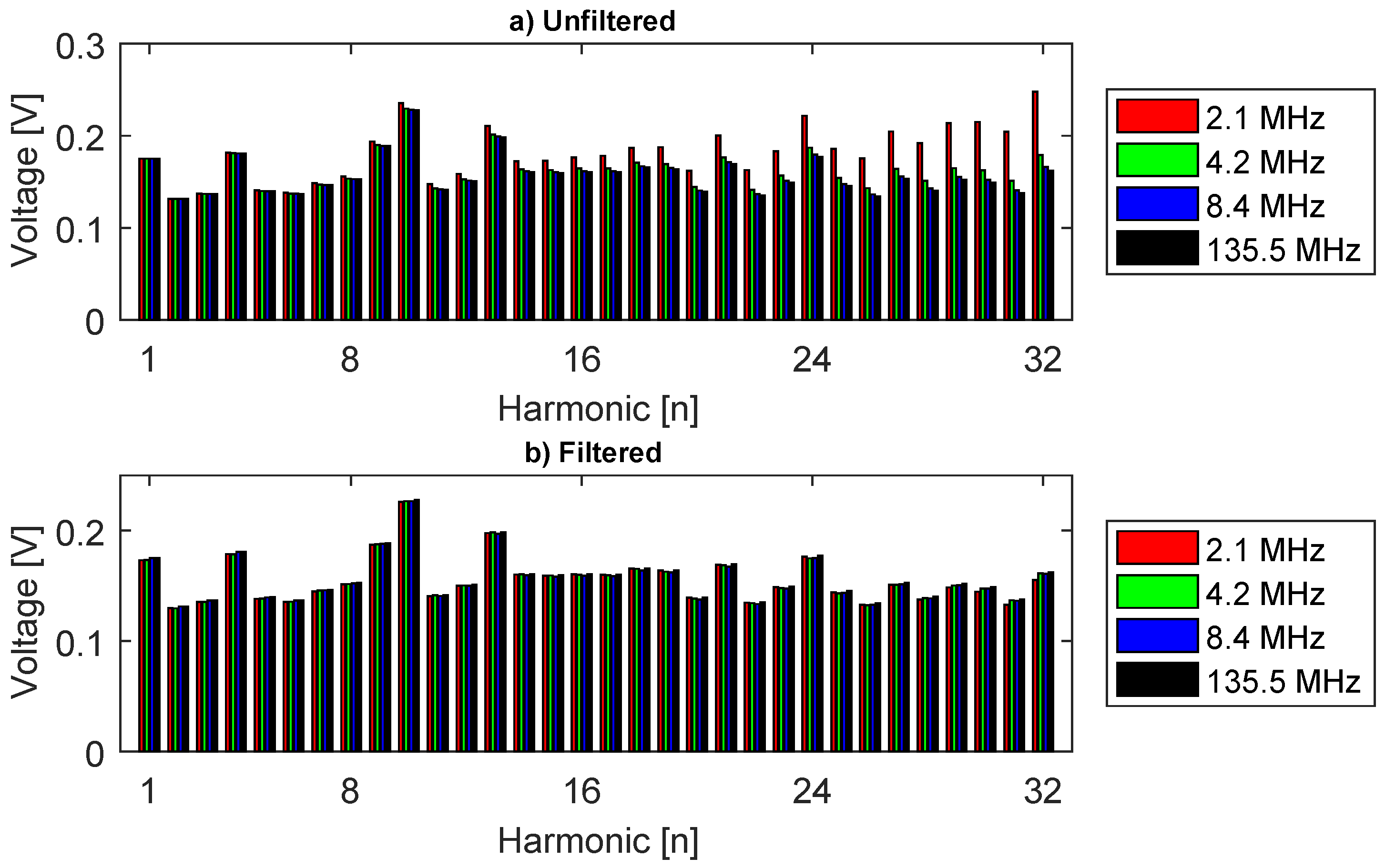
Figure 5.
Excitation harmonics for different sampling rates (a) original; (b) filtered.
An ideal low-pass filter (cutoff = 1 MHz) was created and applied to the 135.5 MHz sampled spectrum, the inverse FFT was calculated to obtain the waveform. Therefore, the filtered 135.5 MHz sampled signal was decimated to obtain the waveform for the others sampling rates (2.1, 4.2 and 8.4 MHz), and the FFT of those signals were calculated. The 32 excitation harmonics for each sampling are shown in Figure 5, where Figure 5a shows the unfiltered harmonics and Figure 5b shows the filtered harmonics.
The three unfiltered real sampling (Figure 5a) show large errors compared to the ideal ones (135.5 MHz), and only the first five harmonics are free of errors when using the 2.1 MHz sampling rate, while the first 11 harmonics are suitable when using 8.4 MHz sampling. The 32nd harmonic has the largest errors, as high as 33% for the 2.1 MHz sampling rate. However, the errors fall drastically when using the filter and the biggest one appears at the harmonic 32 for the 2.1 MHz, 4.3%. However, the decimation function used in MATLAB has inbuilt filters that might have created little distortions to the waveform, leading to these small errors in the spectra.
Once it is proved that the MCU can acquire the data correctly when using a low-pass filter, we must assess the waveform modification created by this filter to comply with the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measuring range (0 to 3.3). Figure 6a shows a full period of the ideal filtered DIBS, the signal is not binary anymore and its amplitude has increased, indicating that the CF has degraded, while in Figure 6b it shows part of the DIBS waveform using different samples.
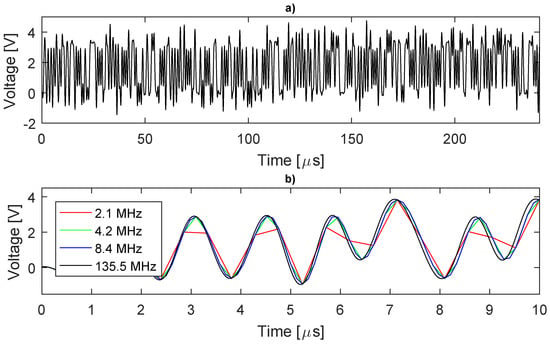
Figure 6.
Filtered DIBS waveform. (a) complete period (135.5 MHz); (b) part of the waveform for different sampling.
The results shown in these sections were obtained through simulations, and no practical results are displayed. In order to evaluate results of a practical DIBS implementation, we would need a oscilloscope or data acquisition board that allows setting the sampling rate to multiples of . The low-pass filter simulated in MATLAB, in practice, is an integrated circuit, which we discuss in the next sections. This filter cannot be implemented digitally in the microcontroller because it must serve as an anti-aliasing filter.
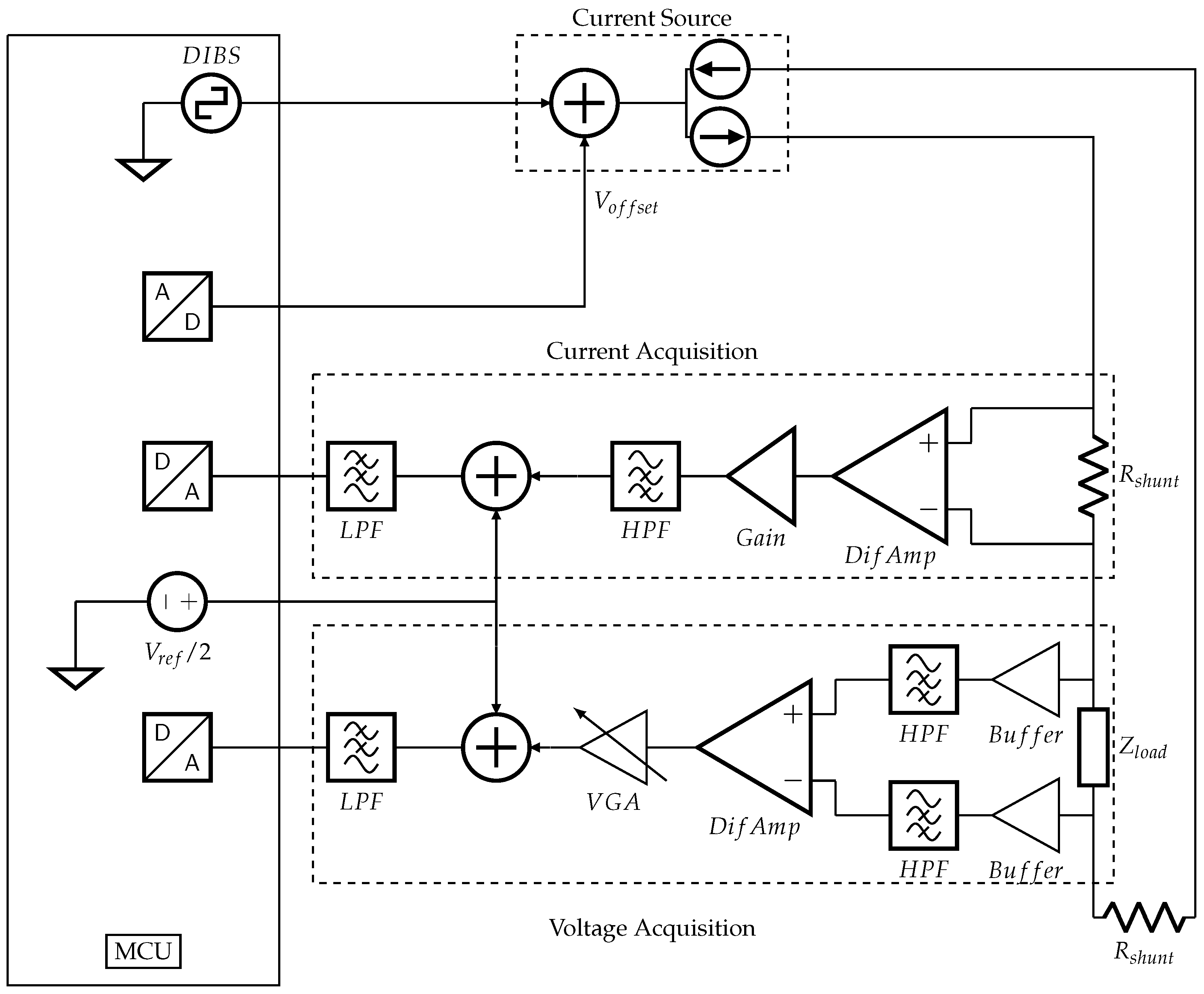
3.2. System Concept
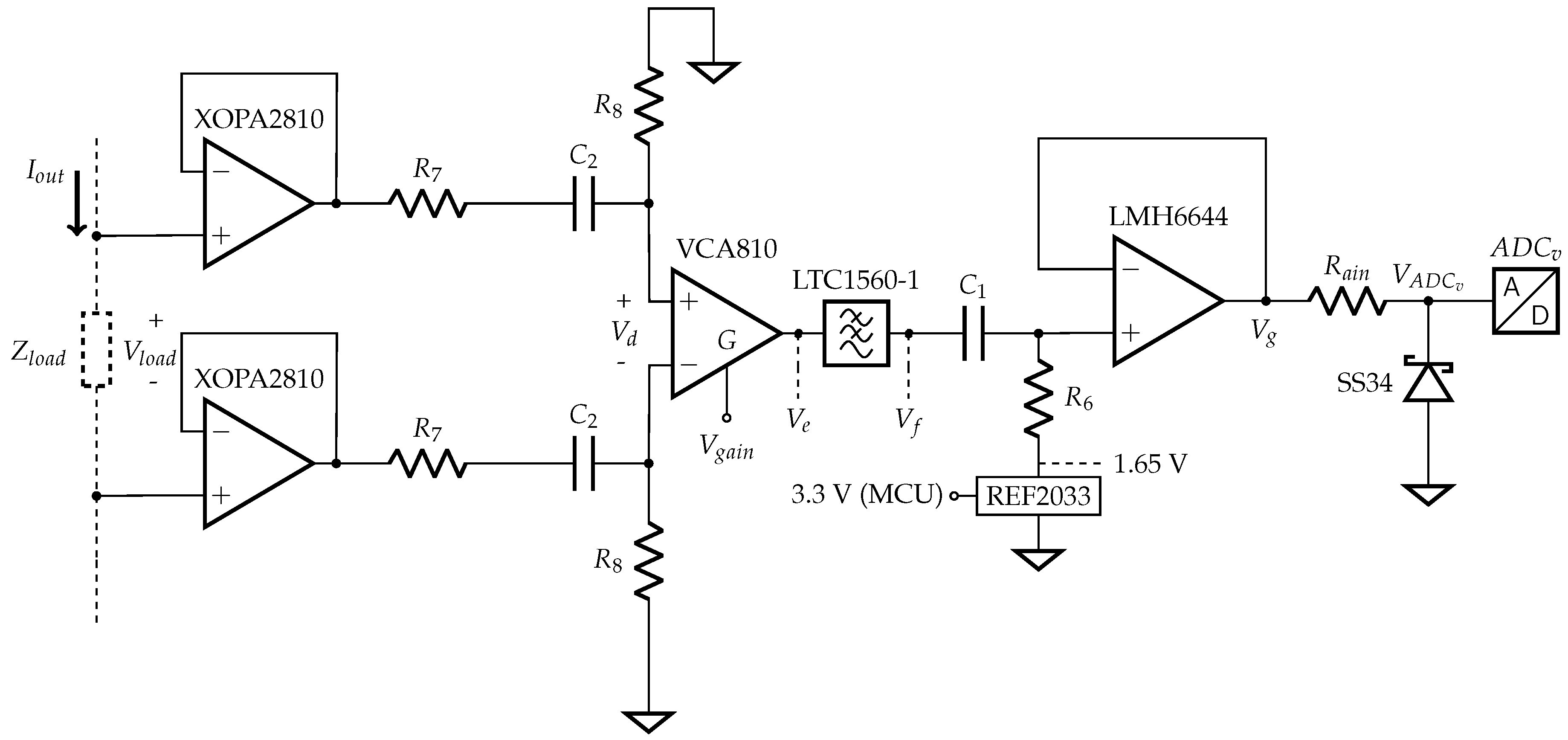
A simple block diagram of the proposed system is shown in Figure 7, while the next subsections explain each stage. is the MCU digital output DIBS waveform, is an analog voltage ranging from 0 to 3.3 V, generated by a digital to analog converter, is a shunt resistor, are difference amplifiers, are high-pass filters, are low-pass filters, is the microcontroller operating voltage (3.3 V), and is a variable gain amplifier.
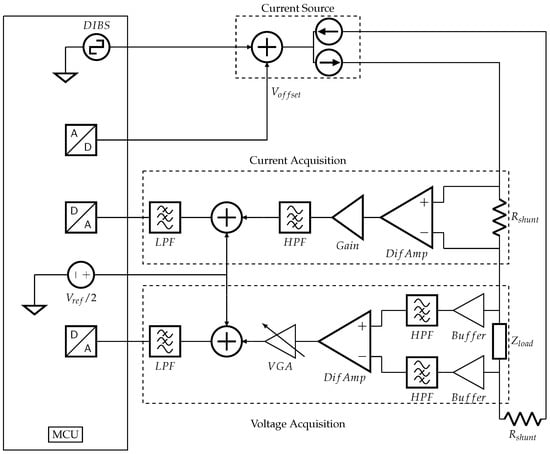
Figure 7.
Simplified block diagram of an EBIM system.
3.3. Current Source
The proposed system has a current source to excite the MUT, thus assuring maximum resolution and health safety. The Enhanced Howland Current Sources (EHCS) [36] and its modifications (mirrored [37], load-in-the-loop [38], NIC [39], GIC [40], lead-lag [36], and differential [41]) are the preferred current sources in bioimpedance measurements because they show higher cost–benefit (regarding number of active components, stability, output impedance, output compliance and output common mode) than other circuits. Nevertheless, alternative current sources exist, it can be simpler than the EHCS [42] or even integrated [37].
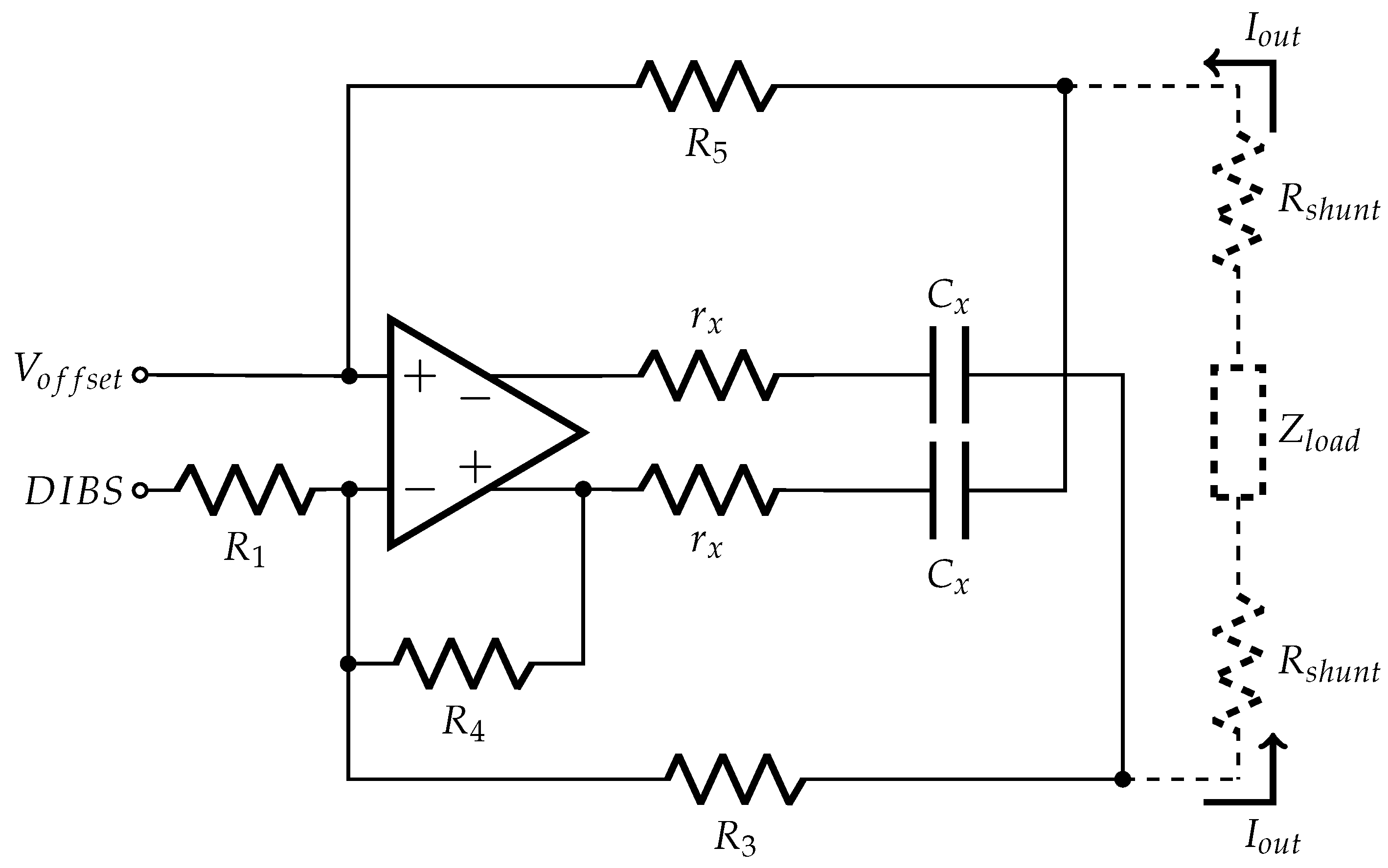
The modified EHCS used in this work (Figure 8) has a symmetric output that reduces the Load Common Mode Voltage (LCMV) and increases the output swing compared to the standard EHCS [43]. The common mode voltage is a well-known artifact generated in differential measurements, while the output compliance relates to the maximum voltage that the circuit can supply to the load. Because the current is constant, the load can only increase to the point that the operational amplifier output saturates. By using a highly symmetric source, we could center the signal at the reference (ground), so the LCMV is close to 0 V and the swing is doubled in relation to the standard EHCS and other grounded-load topologies [43]. This happens because, on these grounded-load current sources, all the load voltage drop is on the output node, while in a symmetric current source the load voltage is split equally to both outputs [43]. For example, on a standard EHCS with 1 mA output and a 1 kΩ load, the voltage on the output is 1 V, while in the proposed topology the voltage at each output is 0.5 V with reverse polarity. Furthermore, highly symmetric current excitation allows identical electrode polarization on the monitoring electrodes, which reduces measurement artifacts [41]. However, because there is a current acquisition stage that uses a shunt resistor (), another resistor with the same value must be added to the opposite pole of the load (), yielding output symmetry.
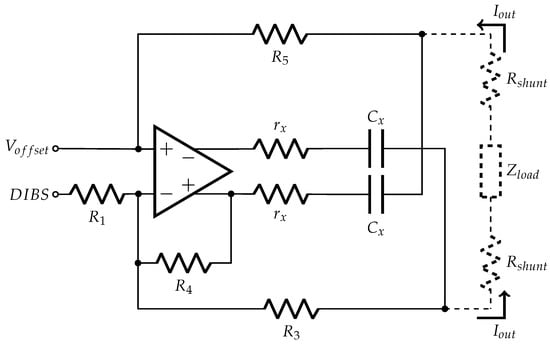
Figure 8.
EHCS with symmetric output.
Like in the standard EHCS [36], a few resistor conditions must be imposed to the circuit behave as a current source, those conditions are, and . Hence, Equation (1) describes the output current as a function of the input voltage and resistors, considering that the operational amplifier open-loop gain is infinite. The capacitors were not included in the equations:
The DIBS amplitude is 3.3 Vpp at the MCU output voltage and the output current is 1 mApp; therefore, the transconductance gain must be 1/3300 S. The chosen resistors values are kΩ, kΩ, kΩ, kΩ, the operational amplifier is the AD8132, and the amplifier common-mode pin is grounded. The effective transconductance gain at the inverting input is 0.305 × 10−3 S, while at the non-inverting input is 2.305 × 10−3 S. must be 0.218 V to compensate the DC level of 1.65 in the DIBS. Those conditions lead to an output current amplitude of 0.503 mAp with 0 V DC level. However, and the resistors are not exact, and the operational amplifier output has a DC offset. Consequently, a DC level may appear at the current source output and cause electric shock, burns and electrode oxidoreduction. To avoid such problems, the capacitor F is placed in series with , thus the effective DC level was smaller than 30 mV.
For the sake of brevity, the output impedance, output current amplitude, and output current phase graphs are not showed in this paper, only on [35,43]. However, we can mention that the output impedance varied between 300 kΩ (low frequencies) and 50 kΩ (1 MHz). The low output impedance led to a decrease of 10% on the output current in 1 MHz when loaded with 5 kΩ, while, for loads that are smaller than 1 kΩ, the variation was smaller than 2%. The output current phase angle varied up to 30 degrees depending on the load and frequency. Nevertheless, the current was measured so these changes that depend on the load and frequency are monitored, avoiding measurement errors. The maximum load allowed without saturation was approximately 9 kΩ.
3.4. Current Acquisition
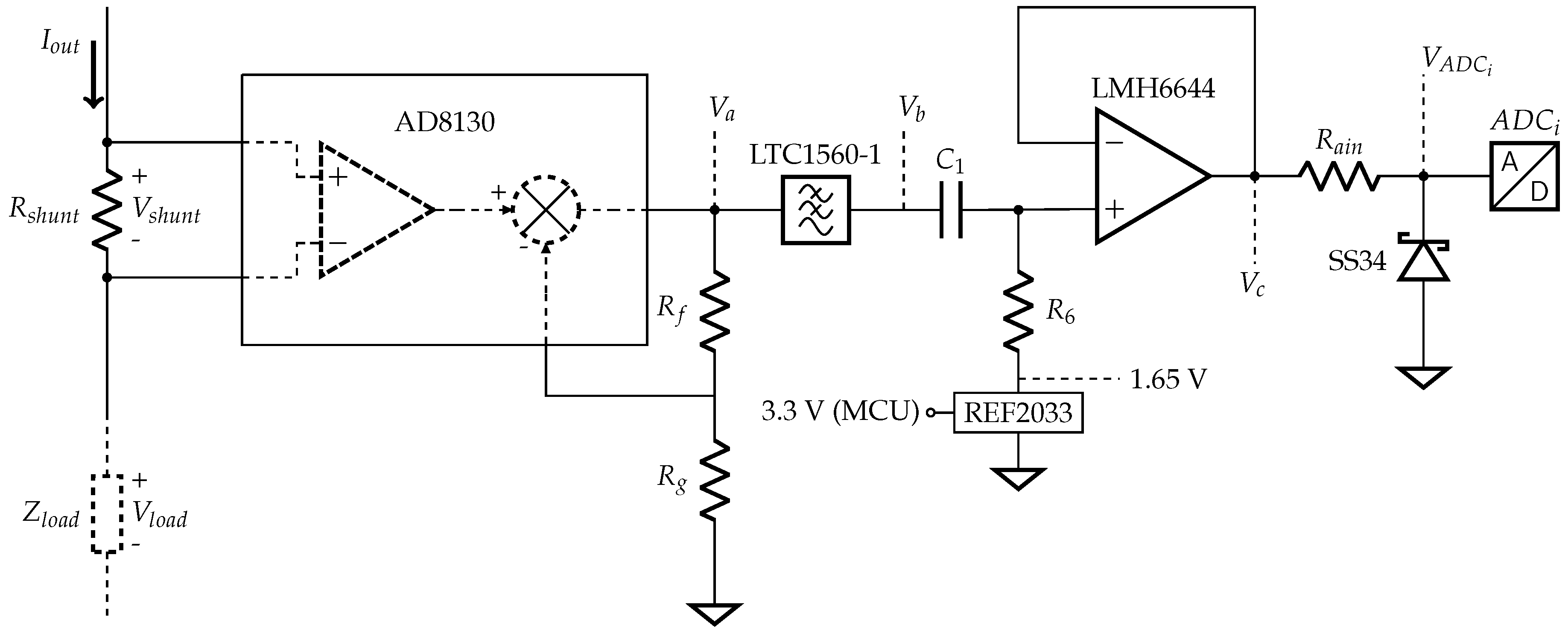
The current acquisition is mainly necessary for ensuring an accurate bioimpedance phase measurement because the current source phase delay is not constant along the frequency range [44,45,46]. In the following subsections, we discuss the implementation of the block from Figure 7 into the circuit of Figure 9.
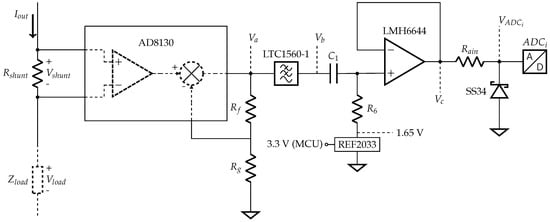
Figure 9.
Current acquisition circuit schematic.
3.4.1. , and
The first stage of the current acquisition is a shunt resistor () and a difference amplifier. They act like a current-to-voltage converter, where the resistor value defines part of the gain. must be small enough to not interfere in the current source swing but large enough to guarantee a high SNR. The difference amplifier must have high input impedance and sufficient bandwidth to amplify , which needs to constantly comply with the ADC dynamic range in all frequencies. The difference amplifier chosen was the AD8130 that has an input impedance of 6 MΩ // 3 pF, and Ω.
As the current can be considered constant within the load range expected, the current acquisition does not need a variable gain stage. Two external resistors set the AD8130 gain to 6.1, kΩ and kΩ, hence the total transimpedance gain is given by the difference amplifier gain and the shunt resistor, thus . In addition, although the ADC8130 input impedance is relatively low, it measures a very low resistor, and, even when the device is loaded with 5 kΩ, the error (0.2 mV, simulated in Spice) is smaller than 1 LSB (0.8 mV) from the 12-bit ADC.
3.4.2. Filtering and Offset
The LTC1560-1, a 1 MHz, 5th order, low-noise, elliptic low-pass filter (), filters to ensure no alias artifacts. nF and kΩ forms a high-pass filter () to eliminate DC level, the cutoff is 5 kHz. The reference is 1.65 V in order to center the signal on the ADC measuring range. The last stage (buffer) is necessary to match the ADC input impedance, while limits the current on the Schottky diode (SS34, Vishay, Malvern, PA, USA) that protects the ADC against negative voltages. From the STM32F303ZE datasheet, the maximum allowed is 220 Ω; otherwise, impedance mismatch will lead to artifacts.
3.5. Voltage Acquisition
The voltage acquisition is the most important stage in an EBIM system because the load is unknown and then requires variable gain; moreover, the measured signal amplitude can be as low as the noise amplitude. Like in the current acquisition section, the blocks of Figure 7 are compared to the implemented circuit shown in Figure 10.
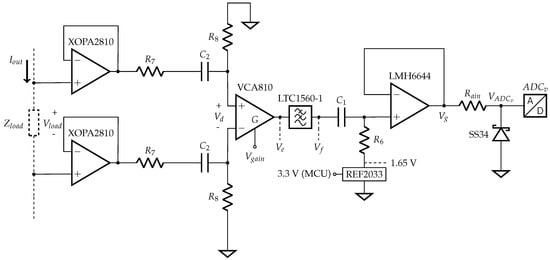
Figure 10.
Voltage acquisition circuit schematic.
3.5.1. Buffer and
The load is unknown and connected to the device through cables; therefore, the circuit needs a very high input impedance. The XOPA2810 is the operational amplifier in both input buffers, providing an input impedance of 1 TΩ.
After the buffer, an RC attenuator eliminates DC voltages from electrode polarization. The attenuation is necessary to comply with the maximum input voltage of the next stage (VCA810) in the load range accepted (5 Ω to 5 kΩ). The cutoff frequency is 5 kHz and the attenuation is approximately 10, the parts’ values are , and nF.
3.5.2. and
The difference amplifier computes the load voltage drop, converting the differential signal into a single-ended. The voltage measured depends not only on the MUT itself but also on the electrode material, geometry and position. Thus, the voltage acquisition gain must vary to adapt the signal amplitude to the ADC dynamic range and ensure high resolution. The VCA810 is a difference amplifier with a controllable gain of −40 to 40 dB, while , which ranges from 0 to −2 V, controls the gain.
3.5.3. Filtering and Offset
The further stages are identical to the corresponding ones in the current acquisition.
3.6. Firmware
The MCU used is the STM32F303ZE within the development board NUCLEO-144. In the next subsections, we discuss briefly some of the firmware features.
3.6.1. Signal Generation
The DIBS generation routine uses the memory, a direct memory access (DMA) channel, the timer and one full GPIO register. The 512 DIBS points form an array in the memory, the timer runs in up-count mode and the compared value is 34, and, when the timer reaches 34, it generates a DMA trigger event. Hence, the DIBS update frequency is defined by the relation between the clock frequency and the compare value ( MHz). The DMA, set in the circular mode, transfers data from the memory to the GPIO register BSRR (Bit Set Reset Register), which updates the digital output.
3.6.2. Data Acquisition
The setup was the same for both voltage and current acquisition, comprised by the memory, the ADC and a DMA channel, all parts are inbuilt in the STM32F303ZE-NUCLEO144. We used one separate ADC for current measurement and another one for voltage measurement, instead of using separate channels of the same ADC. The ADC runs in continuous mode and the sampling frequency is set by the relation between the clock frequency (72 MHz) and the number of clock cycles necessary for a full conversion (17). Once the conversion is complete, the ADC generates an event that triggers the DMA, which transfers the output to a position of an array within the memory. One must recall that the highest frequency of interest is MHz, thus .
This MCU has four ADCs and allows for using them in an interleaved mode, so two ADCs function together to double the sampling frequency. We tested the ADCs in both normal and interleaved modes, and the normal one showed better results. When doubling the sampling frequency () but keeping the same number of points captured (due to memory limit), the FFT resolution is halved; then, the system becomes more vulnerable to noise between FFT bins and errors are increased. In addition, the interleaved ADC technique has problems with unmatched-gain error and conversion delay mismatches between the two interleaved ADCs.
3.6.3. Communication
To communicate with the Graphical User Interface (GUI), we used a USART protocol with MBED libraries, and the baud rate was 230,400. The same USB connector shared the roles of powering the MCU, programming the firmware and communicating with the interface. In practice, the CPU is trapped in the main loop waiting for one of the three triggers via USART. The autogain routine computes and sets the voltage acquisition gain. The evaluation measurement acquires and sends to the GUI all measured points by both ADCs. It is a slow process and requires two seconds to complete; this feature’s main purpose is to assist in device development because it retrieves both current and voltage acquisitions waveform and full spectra. Then, one can use this information to analyze other device characteristics, such as noise and THD. The fast measurement measures current and voltage, computes the FFT and send to GUI only the 32 desired harmonics data (absolute and phase), with a speed of 8 spectra per second.
3.7. GUI
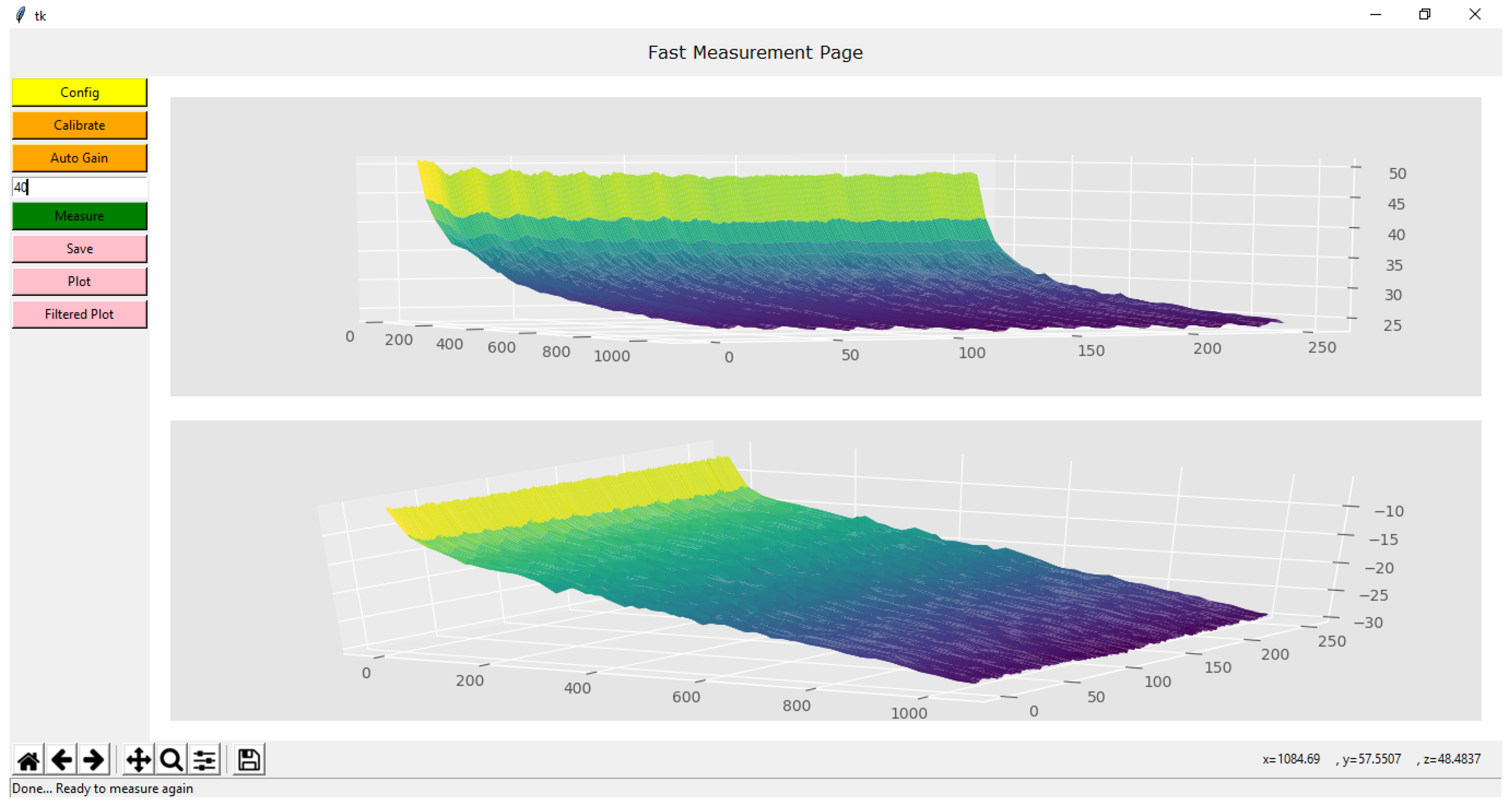
The GUI shown in Figure 11 was created in Python, and some of the libraries used are: tkinter to create the interface itself, scipy to calculate and process the data, matplotlib to plot the graphs and pyserial to establish the serial communication. Besides measuring and plotting the original data, the GUI can save the outputs in a .txt file or as an image in .png, .jpg or .eps. The filtered plot uses an image Gaussian filter to reduce noise.
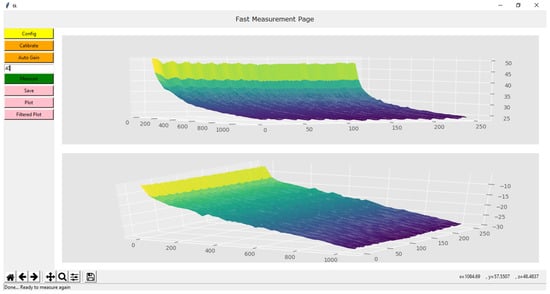
Figure 11.
Example of an EBIM measurement using the GUI.
There is an in-built calibration and an external one. The internal calibration was created by measuring resistors and finding equations that relate the absolute impedance, frequency and phase angle. The external calibration (which the button can be seen in Figure 11) uses as reference an external 100 Ω resistor, and normalizes the measured spectra over an ideal 100 Ω spectrum.
3.8. Instrument Characterization
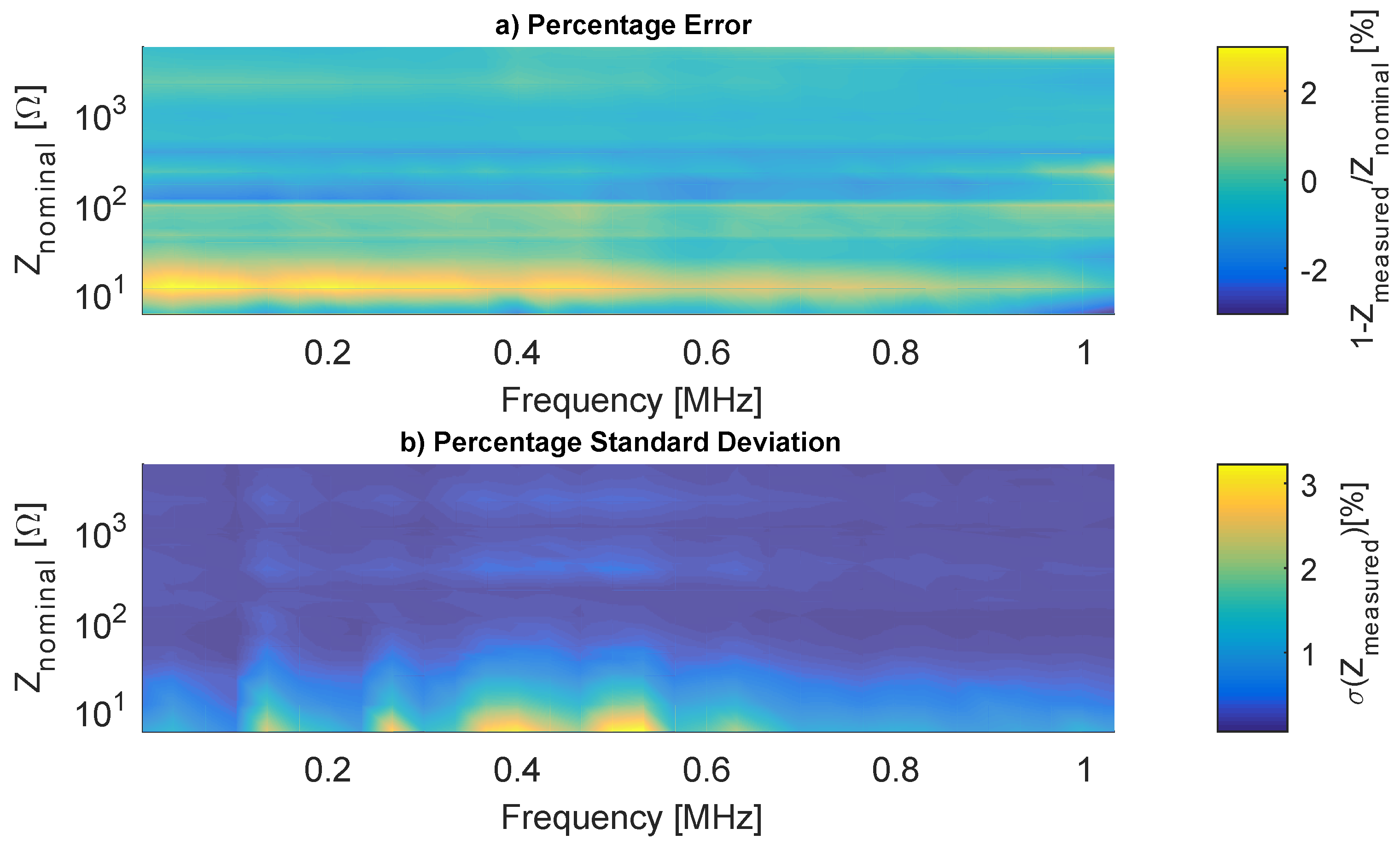
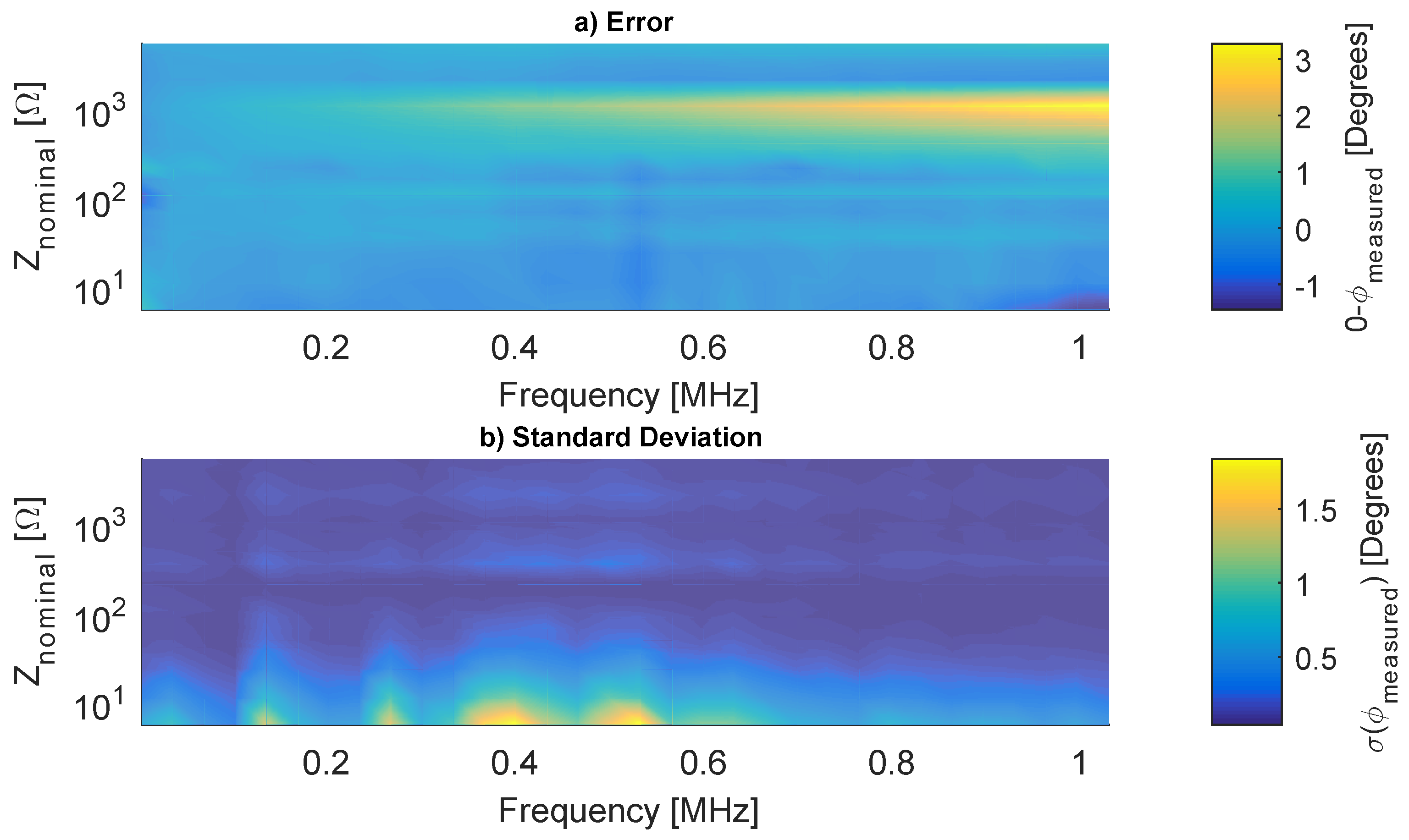
The system was evaluated with 25 loads between 5 Ω and 5 kΩ, the results are the mean and the standard deviation of 100 spectra for each load. Figure 12 and Figure 13 show the magnitude and phase accuracy, respectively.
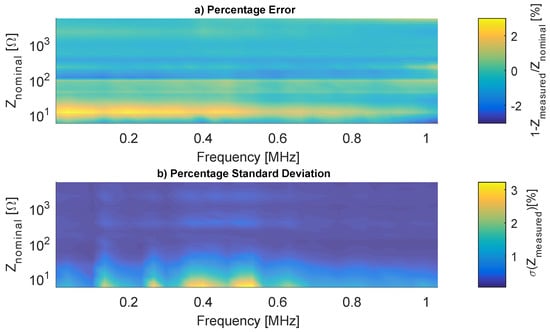
Figure 12.
Measured Z modulus percentage errors.
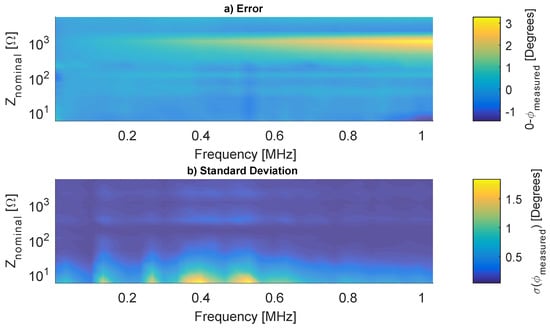
Figure 13.
Measured Z phase angle errors.
The maximum magnitude percentage error is 2% for loads in the region of 10 Ω and 150 Ω, mainly in low frequencies. The maximum Standard Deviation (StD) is 3% for loads smaller than 10 Ω, near 300 kHz and 500 kHz. The lower resolution explains the larger errors in the region of 10 Ω because, even with the VCA810 maximum gain (40 dB), the voltage at the ADC input is still relatively low. Furthermore, this load region is more susceptible to the noise artifacts (smaller SNR), and the high StD for small loads corroborates with this supposition.
The phase error is smaller than 2° for most loads, but, in high frequencies and close to 1 kΩ, the error reaches 3°. The phase StD varies from 0° to 1.5°, and general behavior is similar to the magnitude. A poor calibration fitting close to 1 kΩ explains the absolute error, while the StD is mainly due to noise.
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of
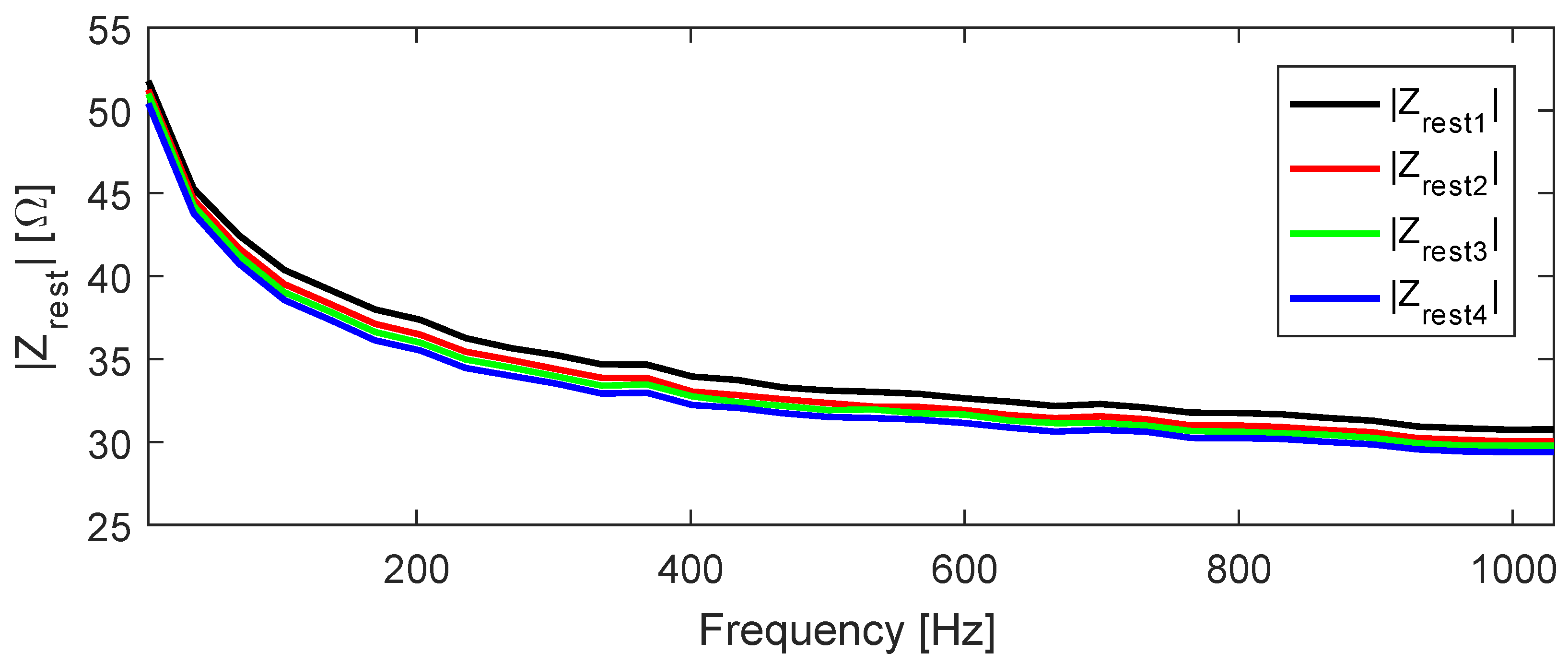
Figure 14 shows the for day 14; refer to Figure 2 for understanding the measurement routine. The bioimpedance magnitude ranged from 51.8 to 30.8 Ω in , it decreased after each session of exercises, and in the bioimpedance ranged from 50.4 to 29.4 Ω. The bioimpedance drop between and on this day was 1.4 Ω, for both highest and lowest frequencies.
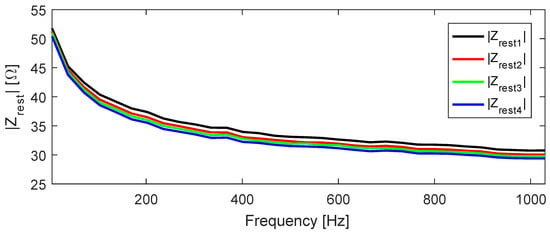
Figure 14.
Measured for day 14.
In 15 of the 16 measurement days, was larger than ; in the only case that this behavior was not verified, showed unfeasible values. We believe that a bad contact in one electrode caused the issue. However, both and were larger than , and this result is consistent with the ones from the other days; then, there is no need to exclude all data from this date.
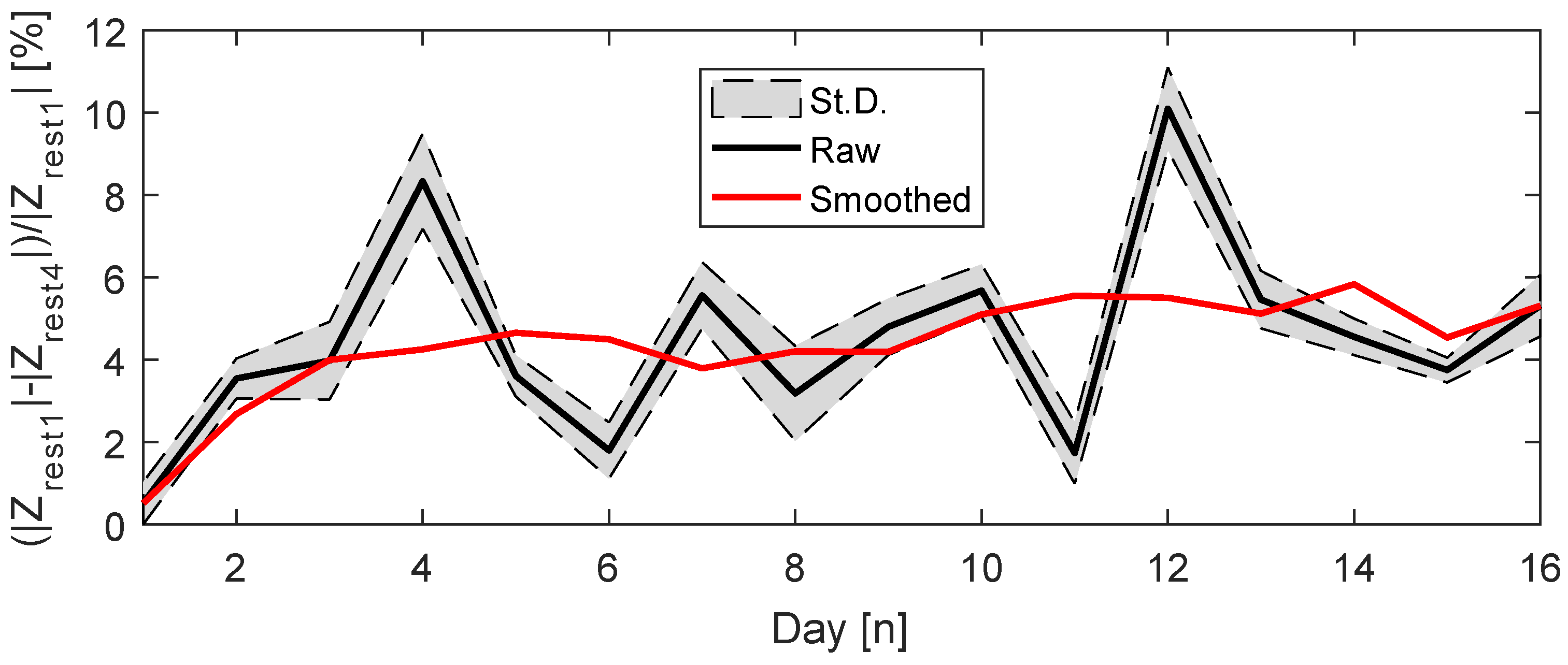
The percentage change between and was calculated for each day of exercise. This computation is the mean of for all frequencies, and the standard deviation retrieves how much the percentage difference of varied in regard to each frequency. For day 16, replaced the discarded .
The percentage variation is not linear, as Figure 15 raw data exhibits. In some cases, one can observe large changes from one day to the next one, like on days 11 to 12; however, in other moments, small variations were perceived such as on days 13 to 15. This points to the hypothesis that muscle conditions are susceptible to other factors, and a linear improvement cannot be expected during regular practice of exercises. This sort of information is relevant for the rehabilitation process of people with muscular diseases.
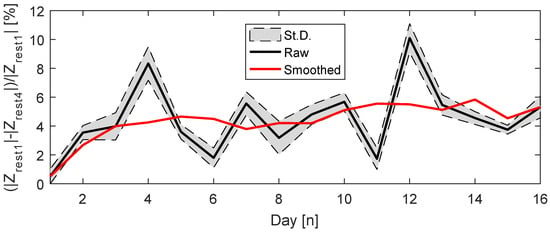
Figure 15.
Percentage variation of .
However, by examining the smoothed data, one can observe an increase in the variation along the experiment period. This analysis used the MATLAB inbuilt smooth function, which applies a moving average algorithm. The first day of measurements showed the smallest variation, less than 1%, while day 12 showed the opposite, close to 10%. The standard deviation was smaller than 1%, thus the change is almost equal for every frequency measured.
One can assume that, on the last days of measurements, the musculature would be stronger and the volunteer better trained, so the fatigue and exhaustion would take longer to happen. Through the results of Figure 15, this enhancement in the musculature might translate to a larger difference between and .
4.2. Analysis of
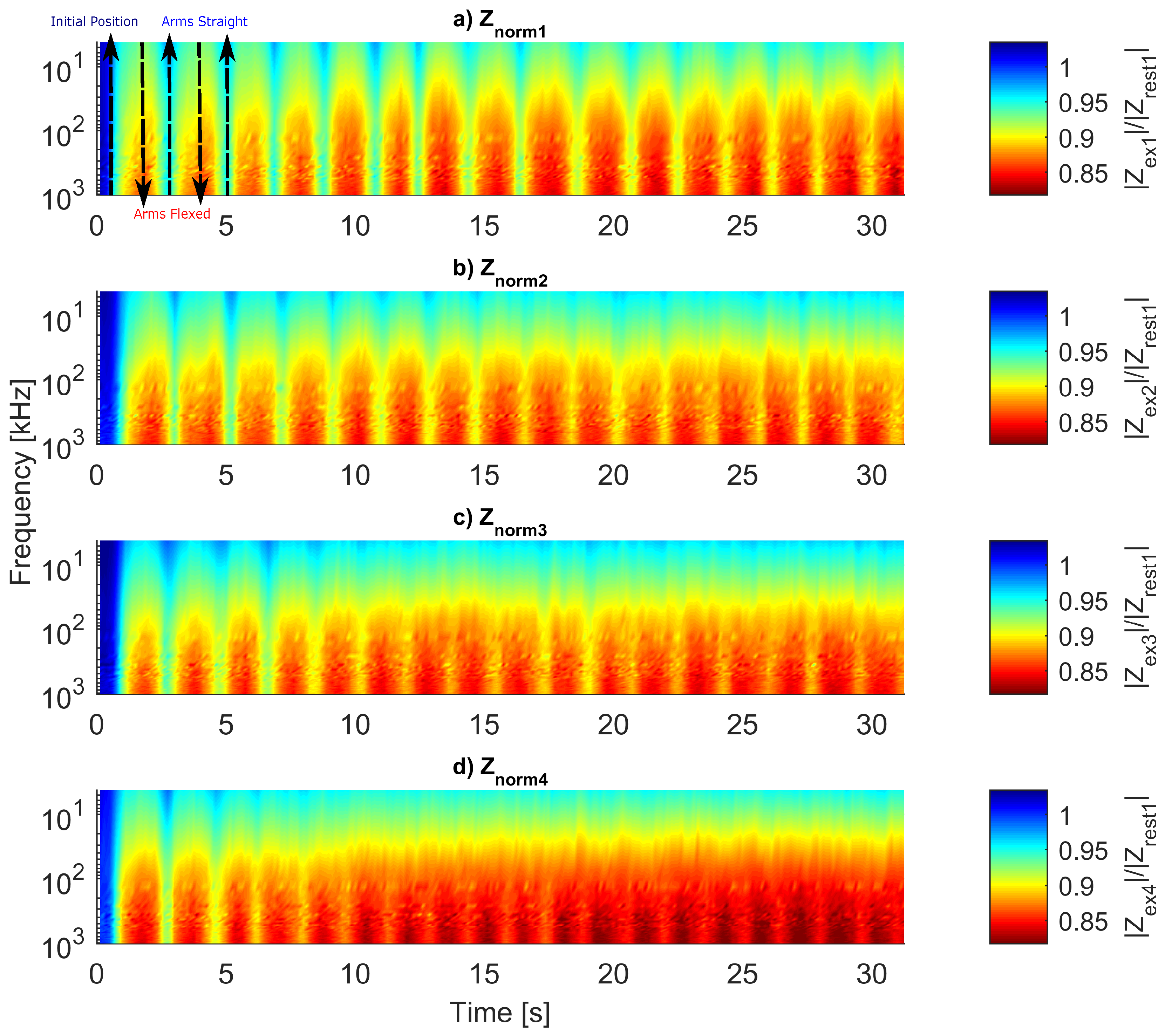
A visual comparison between the four measured in a day is achieved with normalized spectra. Thus, we divided every spectrum of by from the same day. Figure 16 displays the normalized ().
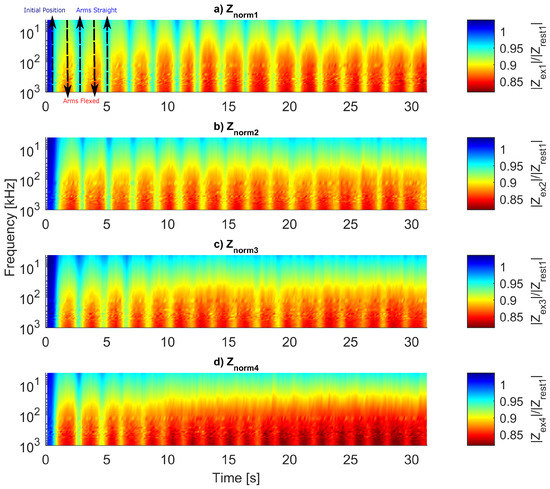
Figure 16.
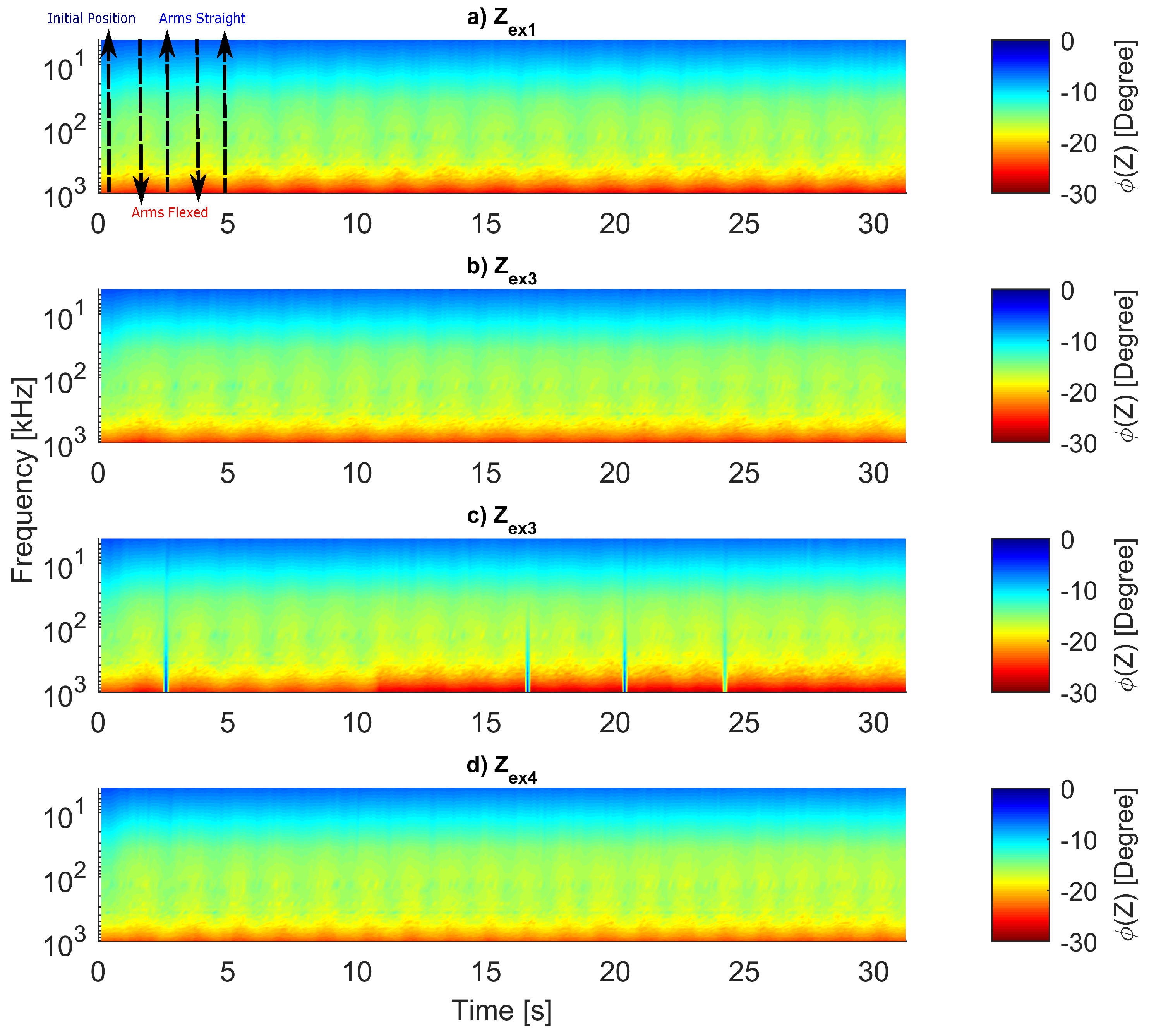
normalized with .
In the first spectrum, the volunteer is in the position so is close to 1. As the exercise starts, falls until the arms are flexed and the chest reaches the block (predefined push-up limit). Then, rises until the arms get almost straight again.
The plot shows that the musculature changes throughout the exercise are differentiable in the whole spectrum. However, in the plot, after the third push-up (n = 50), the movements become harder to visually distinguish, mainly in frequencies lower than 500 kHz.
The bioimpedance decrease for each set of exercises is evident. For all , the first push-up showed large changes between flexed and extended position, but, for the last push-up, the alternations are smaller. Furthermore, one can notice the influence of the resting time between two sessions of —for example, contrasting the last push-up from to the first one of . Although the muscle could recover from the set , it is already tired and the impedance variations fade quickly, becoming unclear in .
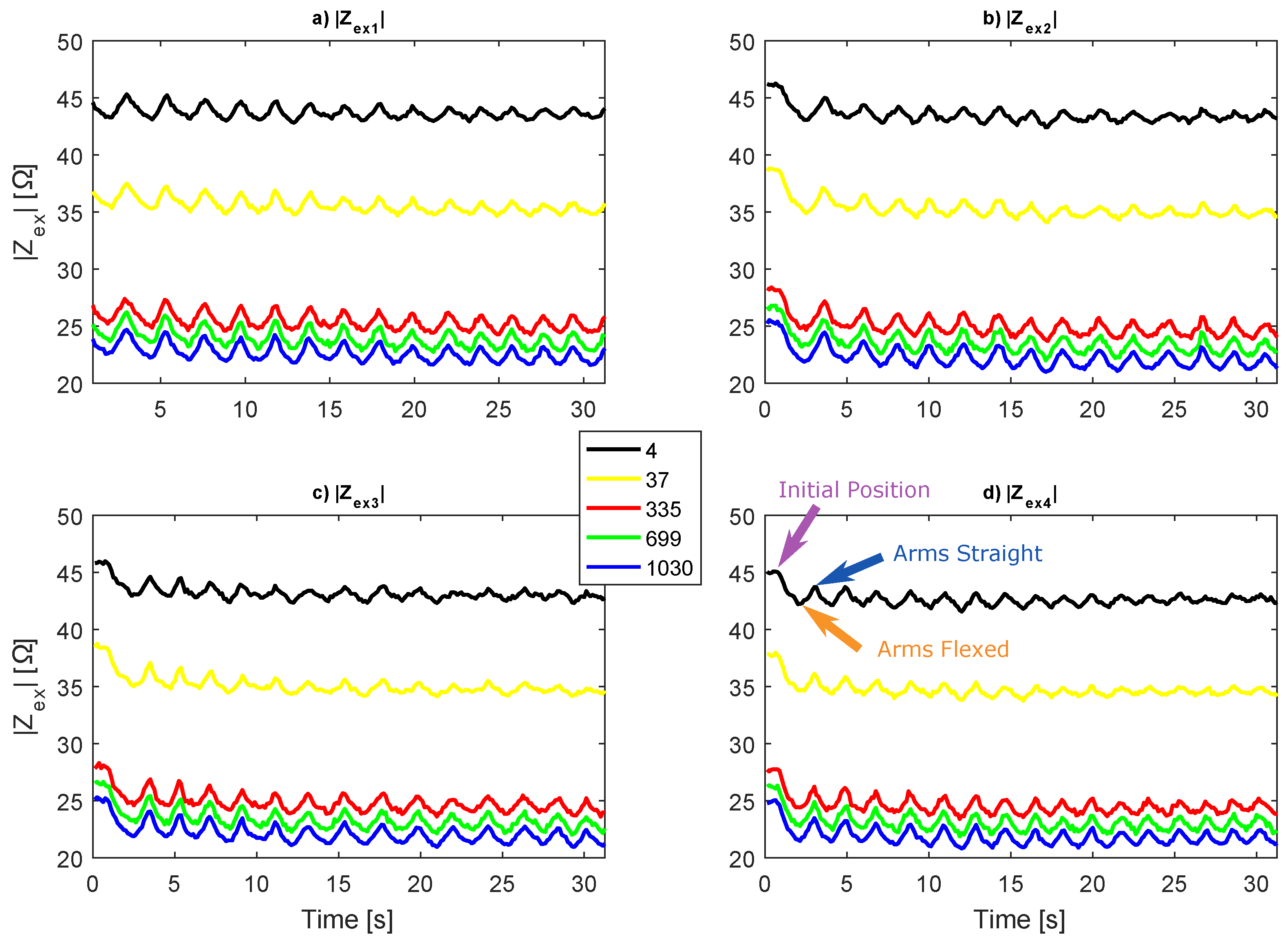
Another way to investigate is through the originally measured bioimpedance magnitude; however, plotting it as surfaces (as Figure 16) is not possible. The variations produced by the push-up (in Ω) are too small in relation to the impedance baseline, which derives from (see Figure 14), hence the color change is imperceptible. Therefore, Figure 17 shows in only five frequencies (4 kHz, 37 kHz, 335 kHz, 699 kHz and 1030 kHz).
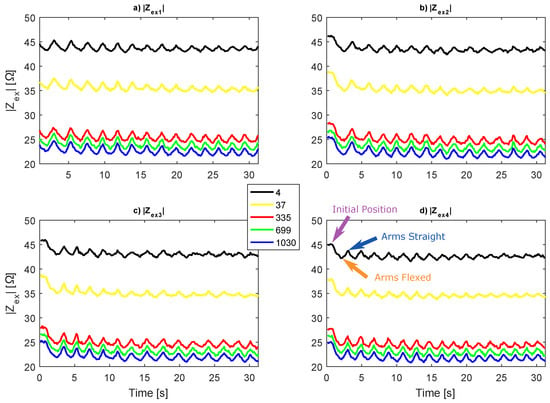
Figure 17.
Original measured in five frequencies.
In agreement with the plots of Figure 16, the graphs from Figure 17 exhibit that, as more exercise is done, the bioimpedance alternations are smaller. Moreover, in lower frequencies, the variations fade faster. The curves in 4 kHz show undersized impedance changes in the last five seconds, while, in 1030 kHz, the variations remain considerably high. Another relevant observation is that the impedance baseline shows a small decrease as the exercises follows, just like the decrease showed in Figure 14 for the . Therefore, the decrease in was monitored by , confirming the results obtained in analysis.
For both and , not only is the bioimpedance magnitude measured, but also the phase angle. The φ is shown in Figure 18, while φ is not analyzed. The φ is not affected by the exercises, both baseline and single frequency variations, which drastically changed in the magnitude measurement, are not relevant in this case. Therefore, tiredness cannot be monitored just by the phase angle. However, the variations decreased over time, and the exercise movements become less distinguishable through the magnitude analysis. Then, because the variations of φ are constant, it can identify when a complete push-up occurred through maximum and minimum values.
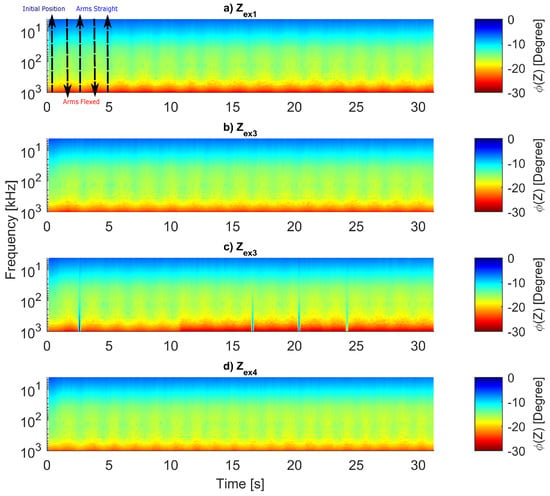
Figure 18.
phase angle.
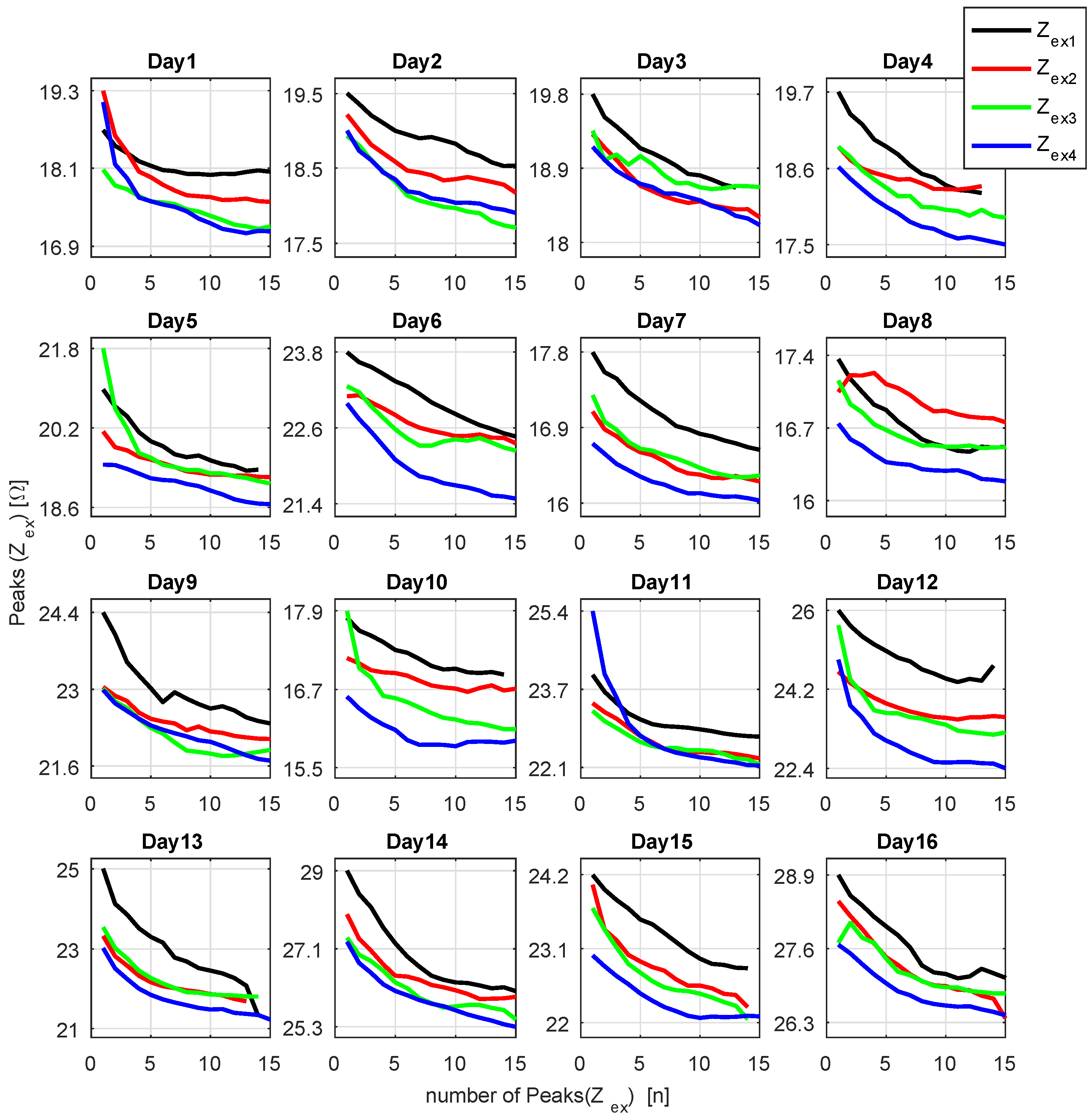
The peaks and valleys of φ in 300 kHz (most sensitive frequency) were found by using a MATLAB algorithm. Once the peaks and valleys positions are known through φ, the value of in these positions of push-ups can also be obtained. In summary, the bioimpedance magnitude assesses tiredness and fatigue, while the phase angle retrieves the bend during the push-up (arms straight or flexed). The positions of peaks and valleys led to two analyses: the first uses the proper peak values and the second refers to valleys as reference. The results of these analysis are shown in Figure 19 and Figure 20, respectively.
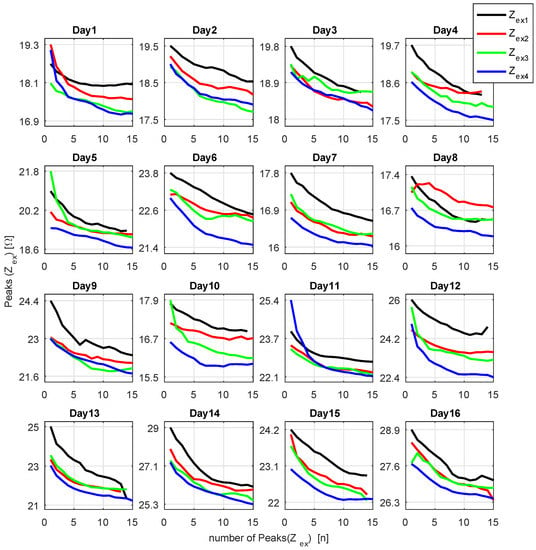
Figure 19.
Variation of peak values in 1030 kHz.
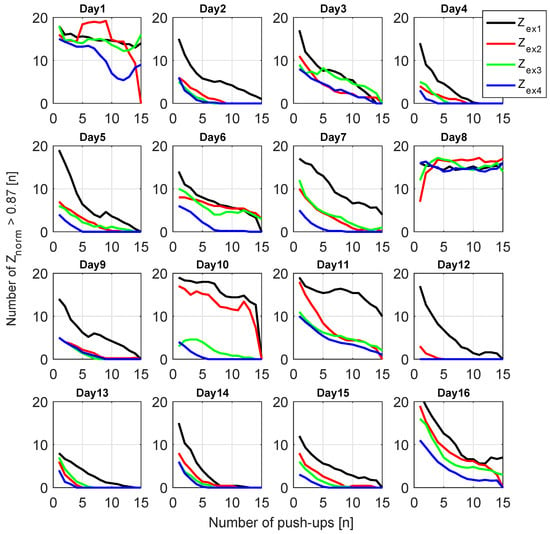
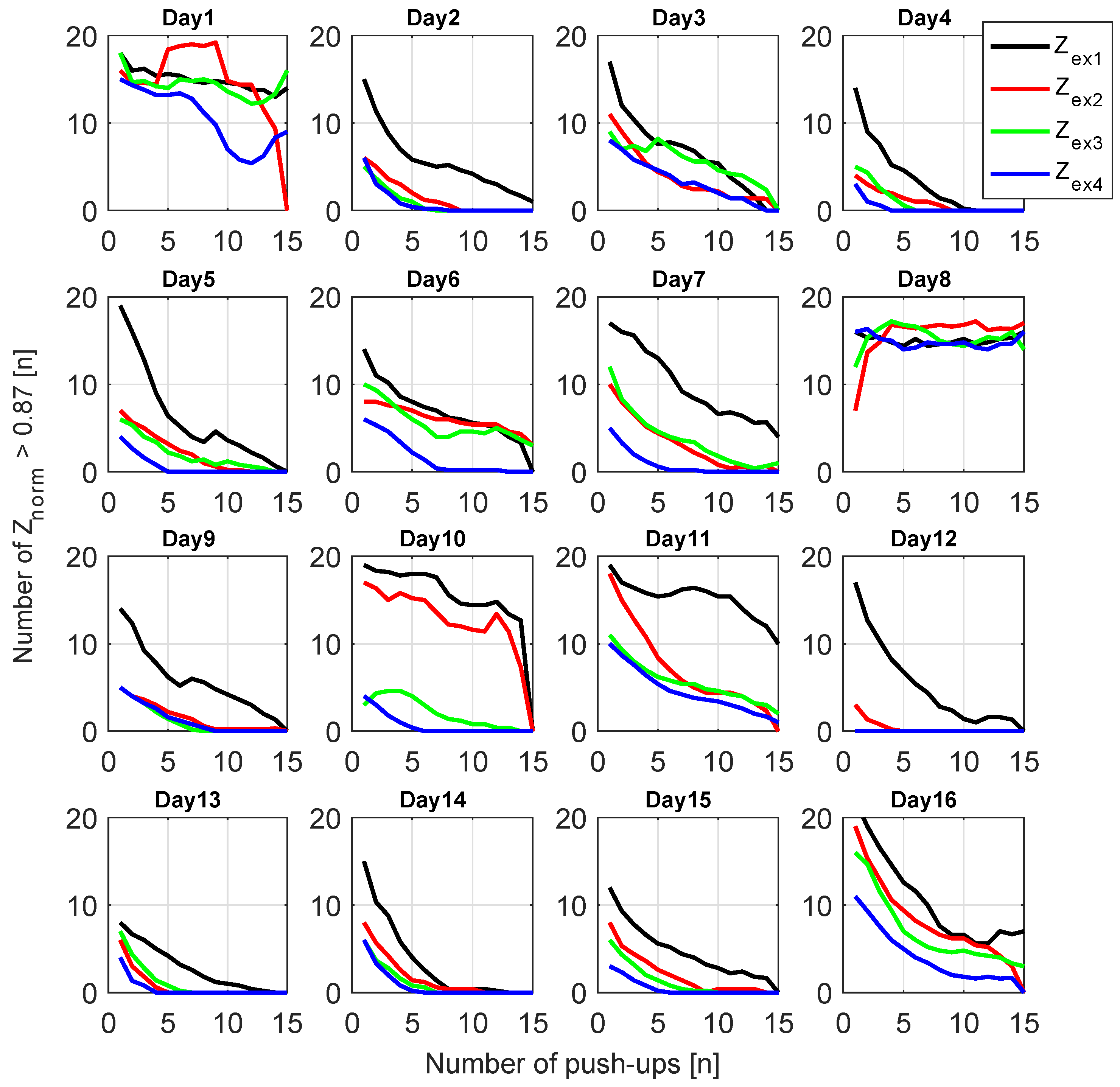
Figure 20.
Number of measured data between two valleys of that are smaller than CF (0.87).
The peaks in 1030 kHz, from the 16 experiment dates, were plotted in relation to the number of push-ups (Figure 19). All curves decreased exponentially over the course of the exercise, the base value also decreased from one session to the next. The bioimpedance range was not constant and each date revealed unique values, the highest impedances occurred on day 14, between 25.3 Ω and 29 Ω, while the smallest range is shown on day 8, 16.3 to 17.4 Ω. One can observe that in most cases ; this condition corresponds to the behavior verified in (Figure 14).
By contrasting the measurements, we could create a few hypotheses. On most days, the difference between and was larger than and also larger than . This phenomenon can be explained by the body warming up, and consequently increasing the temperature, the blood flow and the muscle oxygenation. Meanwhile, the distance from to and varied, yielding the supposition that, when is closer to than to , the volunteer was in better physical condition, had a better performance and was less tired. However, this assumption must be further investigated on experiments with more volunteers in order to be confirmed.
The slope of might be another indicator of fatigue. For example, in , the peaks only reached a constant value on days 1, 8 and 12. Nevertheless, in , the peak value stabilized on days 1, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 16. Therefore, we can suppose that, when the curve reaches a constant value, this means that the muscle is exhausted. On the other hand, we could not find any correlation between the curve slope and a presumed improvement on the volunteer performance.
Additionally, we propose a procedure to identify tiredness through at 1 MHz. This method uses two parameters: the first is the tiredness coefficient (TC), empirically set to 0.87, and the second is the “number of Greater than the Tiredness Coefficient (ZnGTC)” between consecutive valleys. This supposition stems from the principle that, when decreases to a certain value (TC), it indicates an exhausted musculature. The volunteer was consulted on all test dates to assess when he felt tired, leading to the identification of a corresponding , which is TC. Thus, the obtainment of ZnGTC contrives counting the number of spectra above the TC, and revolves, that when ZnGTC is zero, one should cease the exercise because the muscle reached a high tiredness level. The results of ZnGTC analysis are shown in Figure 20.
The chosen TC led to feasible results in 14 of the 16 experiment days; only on days 1 and 8 could the parameter not show the expected changes. For the days that the technique worked, ZnGTC decreased exponentially, never reached 0 before the 10th push-up, while reached 0 usually around the 5th push-up. The reasons why the method failed on those two days are not straightforward, but one hypothesis is that a bad electrode contact or misplacement could be responsible for this error. Although the methodology was carefully followed and the electrodes and cables were fixed onto the skin with extra tape, undesired motion of these parts during the exercise could still happen.
The benefit of using ZnGTC over the peak values is that these are normalized values (); then, it does not depend on only, which varies uncontrollably from day to day. Furthermore, it is sensitive to impedance changes from push-ups and to variation on the baseline. The drawback is that this method will only work for cyclic exercises because it depends on the peak values to identify each push-up. Moreover, it is affected by artifacts in both and .
5. Discussion
In this work, we developed an EBIM prototype based on a broadband excitation signal (DIBS) to monitor muscle physiological conditions; the range of operation for impedance is 5 Ω to 5 kΩ. DIBS excitation reduces the complexity of the hardware compared to the multisine technique because it does not require a fast digital-to-analog converter or a Direct Digital Synthesizers (DDS). The DIBS versatility allows for configuring the spectrum shape by the user; however, unwanted high-frequency harmonics are inevitable and generate artifacts during the acquisition of the signal. Low-pass filters solve this issue, although this solution increases the natural low Crest Factor of binary signals.
Our prototype measures 8 spectra per second, while systems with higher impedance spectrum per second rate (≈3000) already exist [47]. However, such high speed is unwanted in this case; it would lead to a higher amount of data and increase the system complexity unnecessarily. The main reason for using a broadband excitation was avoiding artifacts during a spectrum acquisition, due to exercise motion.
The designed current source has low output common-mode; this improves accuracy in measurements by providing equal polarization on the monitoring electrodes, and also increases output compliance. The system is simplified by adding a current acquisition stage because it allows a lower output impedance of the current source. The voltage acquisition main features are the high input impedance, DC coupling to eliminate any electrode polarization and variable gain. Both current and voltage acquisition have a high-quality low-pass filter to avoid alias artifacts. The interface created in Python allows freedom for further developments once it has a vast number of libraries. Moreover, the GUI can plot results or save it as an image or data. The system presented maximum errors of ±2% and a maximum StD of 3% in the magnitude (Figure 12). The phase angle maximum error was 3° in a narrow load range, and the StD was always smaller than 1.5° (Figure 13).
The device closest to ours was the one of Ibrahim et al. [33]. They developed a prototype to measure bioimpedance from 1 Ω to 120 Ω with a quadratic mean error smaller than 0.07. The frequency range is 4 to 120 kHz, and the measuring time of one spectrum is 150 ms, while the time to measure a single frequency is 4.7 ms. They measured biceps activity during a bending motion that led to variations smaller than 10 Ω, and also plotted the output in a spectrogram.
Our measurements of (Figure 14) converges with the ones from [25], where, after a set of exercises, the bioimpedance magnitude spectrum decreases for all frequencies. A drop in the bioimpedance real part when reaching fatigue was also reported in [22,24]. Albeit our project evaluated only one volunteer, the protocol (Figure 2) was repeated 16 times, and the outcomes for all days were consistent. We further plotted the variation of to for all exercise days (Figure 15). The raw data showed dispersion, but this is expected since the muscle performance depends on many factors [48]. However, the standard deviation showed close values on all dates, and the smoothed data displayed an increase in during these days. This can possibly indicate an enhancement in muscle conditions as a consequence of training, but this assumption must be deeply explored in future works.
The (Figure 16) can be our most significant contribution to assess fatigue; the color scale reveals the muscle tiring process. During the protocol execution (Figure 2), each push-up can be clearly defined in the graphs a and b from Figure 16; in Figure 16c, the color variations start to fade, and finally, in Figure 16d, one cannot define such movements below 500 kHz. The φ peaks and valleys showed constant values (Figure 18); hence, this parameter is not sensitive to fatigue. However, it could be used to identify the push-up initial and final positions.
The largest difference between peaks and valleys of φ appears in 300 kHz, so this frequency can be considered as the most reliable due to higher SNR. Low frequencies in (Figure 16) and (Figure 17) are less sensitive to exercise motion; consequently, 1 MHz was chosen to be analyzed more deeply. However, we cannot claim that only this selected frequency needs to be measured because understanding why low frequencies could not sense movements after some time might lead to new information about the process of tiring.
Two methods were proposed to assess fatigue: the first used the peaks magnitude and the second used a parameter called ZnGTC. Both show decreasing exponential shape as the push-ups follow (Figure 19 and Figure 20); this may indicate that, after a certain amount of consecutive exercises, the bioimpedance magnitude tends to be constant. We believe that, when the curves reach constant values, the peaks do not vary anymore or, once the ZnGTC is zero, one should cease the exercise due to fatigue.
The methodology presented some setbacks, due to electrodes and exercise repeatability. The electrodes were disposable and had to be replaced every exercise day, and although their positions were marked onto the skin, variations are unavoidable. Furthermore, the electrode linear configuration is sensitive to anisotropy, and we could only fix hand and foot positions, but the elbow and shoulder could change, which alters the muscle fibers’ direction. The use of concentric and microneedle electrodes shall eliminate those problems.
6. Conclusions
The proposed prototype can measure the changes of bioimpedance in the chest muscle (Pectoralis Major) during isotonic exercises. Although the prototype had relatively high accuracy errors of %, the precision and resolution are enough to identify variations of less than 1 Ω. Our device was designed to reduce complexity in both hardware and software in Electrical Bioimpedance Myography; this system can be used as a portable instrument due to reduced size and high versatility.
The bioimpedance magnitude was used to propose parameters and plots that can be used as a diagnostic tool to identify fatigue and tiredness. Although the bioimpedance phase angle is not sensitive to fatigue, it could still be used to identify the push-up period. As future works, we intend to keep developing the device to enhance accuracy, increase communications and processing speed. In addition, new concentric and microneedle electrodes must be designed for this application. We are looking for physicians to assist us in improving the methodology and increasing the number of volunteers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.S.; Supervision, P.B.-F.; Validation, K.M.; Writing—review & editing, J.G.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank UDESC for the scholarship. We are especially grateful to the reviewers for their contributions to help us improve our paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MUT | Material Under Test |
| EBIS | Electrical Bioimpedance Spectroscopy |
| EBIM | Electrical Bioimpedance Myography |
| DIBS | Discrete Interval Binary Sequences |
| Impedance measured during exercise | |
| Impedance measured during rest (Mean of 40 spectra) | |
| φ | Phase angle of |
| TC | Tiredness Coefficient |
| ZnGTC | number of Greater than the Tiredness Coefficient |
References
- Grimnes, S.; Martinsen, Ø.G. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 488. [Google Scholar]
- Buendía Lopez, R. Improvements in Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Data Analysis: Artefact Correction, Cole Parameters, and Body Fluid Estimation. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH—Royal Institute of Technology and University of Alcalá, Stockholm, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gouaux, E.; MacKinnon, R. Principles of selective ion transport in channels and pumps. Science 2005, 310, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abtahi, F. Aspects of Electrical Bioimpedance Spectrum Estimation. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bera, T.K. Bioelectrical Impedance Methods for Noninvasive Health Monitoring: A review. J. Med. Eng. 2013, 2014, 381251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atefi, S.R. Electrical Bioimpedance Cerebral Monitoring: From Hypothesis and Simulation to First Experimental Evidence in Stroke Patients. Ph.D. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology KTH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasaraghavan, V. Bioimpedance Spectroscopy of Breast Cancer Cells: A Microsystems Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Garcia, P.; Maldonado, A.; Yufera, A.; Huertas, G.; Rueda, A.; Huertas, J.L. Towards Bio-Impedance Based Labs: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Design of Circuits and Integrated Systems (DCIS 2015), Estoril, Portugal, 25–27 November 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, O.; Land, R.; Min, M.; Annus, P.; Rist, M.; Reidla, M. Improved impedance analyzer with binary excitation signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing (WISP 2015), Siena, Italy, 15–17 May 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertemes-Filho, P. Tissue Characterisation using an Impedance Spectroscopy Probe. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Min, M.; Paavle, T.; Annus, P.; Land, R. Rectangular wave excitation in wideband bioimpedance spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA 2009), Cetraro, Italy, 29–30 May 2009; pp. 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Ojarand, J.; Martens, O.; Paavle, T.; Land, R.; Annus, P.; Rist, M.; Reidla, M.; Parve, T. Binary signals in impedance spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Jäckel, H. Continuous monitoring of electrode—Skin impedance mismatch during bioelectric recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Vandersteen, G.; Bragos, R.; Schoukens, J. Basics of broadband impedance spectroscopy measurements using periodic excitations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, K.R.; Tan, A.H.; Barker, H.A.; Chong, B. A survey of readily accessible perturbation signals for system identification in the frequency domain. Control Eng. Pract. 2005, 13, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojarand, J.; Rist, M.; Min, M. Comparison of excitation signals and methods for a wideband bioimpedance measurement. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Taipei, Taiwan, 23–26 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojarand, J.; Min, M.; Annus, P. Crest factor optimization of the multisine waveform for bioimpedance spectroscopy. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land, R.; Cahill, B.P.; Parve, T.; Annus, P.; Min, M. Improvements in design of spectra of multisine and binary excitation signals for multi-frequency bioimpedance measurement. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 4038–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojarand, J.; Annus, P.; Min, M.; Gorev, M.; Ellervee, P. Optimization of multisine excitation for a bioimpedance measurement device. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC) Proceedings, Montevideo, Uruguay, 12–15 May 2014; pp. 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojarand, J.; Land, R.; Min, M. Comparison of spectrally sparse excitation signals for fast bioimpedance spectroscopy: In the context of cytometry. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications Proceedings (MeMeA 2012), Budapest, Hungary, 18–19 May 2012; pp. 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkove, S.B. Electrical impedance myography: Background, current state, and future directions. Muscle Nerve 2009, 40, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, L.; Shin, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, P. Electrical impedance myography for evaluating paretic muscle changes after stroke. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkove, S.B.; Pacheck, A.; Sanchez, B. Sensitivity distribution simulations of surface electrode configurations for electrical impedance myography. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.; Romano, M.; Bifulco, P.; Cesarelli, M. Study of muscular tissue in different physiological conditions using electrical impedance spectroscopy measurements. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 34, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Freeborn, T.J. Biceps tissue bioimpedance changes from isotonic exercise-induced fatigue at different intensities. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4, 025037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeborn, T.J.; Bohannan, G.W. Changes of Fractional-Order Model Parameters in Biceps Tissue from Fatiguing Exercise. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shin, H.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, P. Localized electrical impedance myography of the biceps brachii muscle during different levels of isometric contraction and fatigue. Sensors 2016, 16, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.P.; Elbrønd, V.S.; Riis-Olesen, K.; Bartels, E.M. Multi-frequency bioimpedance in equine muscle assessment. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, C.; Kim, S.; Jong Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, D.E. Detection of muscle activation through multi-electrode sensing using electrical stimulation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 275, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescolarde, L.; Yanguas, J.; Lukaski, H.; Alomar, X.; Rosell-Ferrer, J.; Rodas, G. Effects of muscle injury severity on localized bioimpedance measurements. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, B.; Iyer, S.R.; Li, J.; Kapur, K.; Xu, S.; Rutkove, S.B.; Lovering, R.M. Non-invasive assessment of muscle injury in healthy and dystrophic animals with electrical impedance myography. Muscle Nerve 2017, 56, E85–E94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, B.; Pacheck, A.; Rutkove, S.B. Guidelines to electrode positioning for human and animal electrical impedance myography research. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, B.; Hall, D.A.; Jafari, R. Bio-impedance spectroscopy (BIS) measurement system for wearable devices. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Torino, Italy, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Rutkove, S.B.; Sanchez, B. Recording characteristics of electrical impedance myography needle electrodes. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 1748–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtoli, V.G. Desenvolvimento de um Medidor de Bioimpedância Rápido Utilizando Discrete Interval Binary Sequences (DIBS). Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina, Joinville, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, A.S.; Fox, R.M.; Sadleir, R.J. Biocompatible, high precision, wideband, improved howland current source with lead-lag compensation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 7, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Rahal, M.; Demosthenous, A.; Bayford, R.H. Comparison of a new integrated current source with the modified howland circuit for EIT applications. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcelles, K.F.; Sirtoli, V.G.; Bertemes-Filho, P.; Vincence, V.C. Howland current source for high impedance load applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 114705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, P.B.; Lima, R.G.; Tanaka, H. A current source using a negative impedance converter (NIC) for electrical impedance tomography (EIT). In Proceedings of the 17th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering, São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 10–14 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, T.R.; Chatwin, C.R.; Huber, N.; Zarafshani, A.; Tunstall, B.; Wang, W. Comparison of Howland and General Impedance Converter (GIC) circuit based current sources for bio-impedance measurements. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 224, 012167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliquett, U.; Schönfeldt, M.; Barthel, A.; Frense, D.; Nacke, T. Offset-free bidirectional current source for impedance measurement. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 224, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.M.; Yang, G.Z. Smart wireless headphone for cardiovascular and stress monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 14th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN 2017), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 9–12 May 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtoli, V.G.; Morcelles, K.F.; Vincence, V.C. Design of current sources for load common mode optimization. J. Electr. Bioimpedance 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassanos, P.; Constantinou, L.; Triantis, I.F.; Demosthenous, A. An integrated analog readout for multi-frequency bioimpedance measurements. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, P.J.; Neshatvar, N.; Demosthenous, A. A sinusoidal current driver with an extended frequency range and multifrequency operation for bioimpedance applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2015, 9, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassanos, P.; Yang, G.Z. A CMOS programmable phase shifter for compensating synchronous detection bioimpedance systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 24th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Batumi, Georgia, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusche, R.; Malhotra, A.; Ryschka, M.; Ardelt, G.; Klimach, P.; Kaufmann, S. A FPGA-Based Broadband EIT System for Complex Bioimpedance Measurements—Design and Performance Estimation. Electronics 2015, 4, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoka, R.M.; Stuart, D.G. Neurobiology of muscle fatigue. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 72, 1631–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).