Abstract
Over the past decade, artificial intelligence (AI) has been increasingly used in firm innovation. While AI has contributed to innovation improvement, direct evidence of its effectiveness in radical innovation is limited. This study fills this gap by empirically investigating the impact of AI on radical innovation and how this relationship is shaped by digital foundation and government subsidy from the perspectives of technological synergy and the external institutional environment. Using panel data from Chinese A-share listed firms from 2007 to 2023, this study empirically tests hypotheses through regression analyses. The findings reveal that AI adoption significantly promotes radical innovation, and this relationship is moderated by the characteristics of a firm’s digital foundation (i.e., degree and rate) as well as government subsidy. Specifically, a high degree of digital foundation hinders AI-driven radical innovation, while a fast rate enhances it. In addition, government subsidy strengthens the positive impact of AI adoption on radical innovation. A heterogeneity analysis further shows that both the timing (early vs. late) and pace (fast vs. slow) of AI adoption exert nuanced impacts: firms that adopt AI later and at a slower pace tend to achieve greater gains in radical innovation. This study advances research on radical innovation in the era of intelligence and provides managerial implications regarding the interplay of AI with internal digital foundation and external government subsidy.
1. Introduction
In the intelligent age, embracing AI has become a consensus among businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge [1,2]. However, does investing heavily in AI truly make corporate innovation more radical? The reality appears to be full of contradictions. On the one hand, AI-driven radical innovations are beginning to emerge. We have witnessed AI’s remarkable potential to accelerate new drug development, foster novel material science advancements, and transform cutting-edge product design. For example, Huawei’s “Pangu” AI platform can automatically complete complex core chip design tasks with significantly greater speed and precision than traditional tools, substantially accelerating radical innovation in the semiconductor sector. On the other hand, many firms have found that their AI initiatives fail to yield the expected radical innovation outcomes. For instance, GE invested billions of USD in its smart industrial Internet platform “Predix”, but due to factors like organizational inertia and difficulties in technological integration, the initiative fell short of its intended goals in achieving AI-enabled radical innovation. This phenomenon has drawn increasing attention from both business practitioners and academic researchers. In response, scholars have begun calling for more in-depth and systematic investigations into the relationship between AI and radical innovation in firms [3,4].
Radical innovation originates from the novel recombination of previously unrelated knowledge and is characterized by high complexity and uncertainty [5,6]. AI, with its powerful capabilities in perception, cognition, and autonomous action, is widely expected to facilitate radical innovation by accelerating technological convergence and knowledge creation, as well as enhancing market sensing and demand insight [7,8]. Despite high expectations for AI’s potential to foster radical innovation, existing research primarily focuses on AI’s relationship with green innovation, product and service innovation, or process innovation, or examines its impact on overall enterprise innovation performance or behavior [9,10,11,12]. In contrast, current research provides insufficient theoretical explanation as to whether AI can drive radical innovation outcomes and lacks large-sample empirical validation, noticeably lagging behind radical innovation practice [3]. Furthermore, existing studies tend to view AI adoption as a singular entity, failing to examine how specific adoption characteristics—such as timing and pace of adoption—differentially affect radical innovation [11,13]. Therefore, to bridge this gap and deepen the systematic understanding of AI’s empowerment of enterprise radical innovation, the first core research question posed by this study is: to what extent can enterprise AI adoption promote the emergence of radical innovation outcomes, and do different characteristics of AI adoption (such as adoption timing and pace) have a differential impact on radical innovation?
The TOE framework posits that a firm’s technology adoption and innovation behaviors are jointly influenced by three contextual dimensions: technological (T), organizational (O), and environmental (E) factors [14,15]. Existing studies on the impact of AI have primarily focused on the overall effects of AI technology itself [16]. However, one underexplored perspective is the interaction between AI and organizational-level factors—specifically, a firm’s digital foundation. According to the resource-based view, a firm’s digital foundation is a critical internal contextual factor influencing the realization of AI’s potential [17]. This is because AI technology does not exist or operate in isolation; instead, it is embedded within a firm’s existing digital infrastructure, collaborating with other digital technologies like data platforms, cloud computing, and Internet of Things. Therefore, only examining the independent impact of AI technology might not fully reveal its empowerment pathways within a complex digital ecosystem. Nevertheless, prior research has not yet sufficiently addressed the role of firms’ digital foundation in the process of AI-driven radical innovation [16]. To answer this question, this paper distinguishes and introduces two key dimensions to measure a firm’s digital foundation prior to the systematic introduction of AI technology: (1) the degree of digital foundation, which refers to the completeness of a firm’s digital infrastructure and processes, reflecting its static accumulation of technological resources; and (2) the rate of digital foundation, which refers to the rate at which a firm advances its digital foundational changes, reflecting its dynamic capabilities. We anticipate that a faster pace of digital transformation will foster greater organizational agility and enhance technological integration, thereby supporting the innovative application of AI [18]. However, a highly mature digital foundation, on the other hand, can create path dependency and organizational inertia, potentially hindering the generation and acceptance of radical innovation ideas. Accordingly, this study poses a second core research question: how do the degree and rate of digital foundation moderate the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation?
Beyond internal organizational factors, the external institutional environment also profoundly influences the process of AI-enabled radical innovation. Among these external factors, government subsidies stand out as a crucial policy tool whose role warrants particular attention [19,20]. In the realm of radical innovation, while the integration of AI injects new momentum into firms’ radical innovation efforts, it also introduces new challenges such as technological path uncertainty, algorithmic inexplicability, and systemic integration complexity [21,22]. In this context, external resource support becomes especially critical. Government subsidies are widely expected to share the high sunk costs of frontier exploration and alleviate firms’ concerns about the uncertainty associated with new technologies and radical innovation activities through policy support [23,24]. This, in turn, is anticipated to incentivize firms to more boldly apply AI technologies to frontier radical innovation activities [20]. However, existing research has not yet systematically revealed the contingent role of government subsidies in the “AI adoption—radical innovation” pathway [25,26]. Therefore, to bridge this gap, the third core research question posed by this study is: how do government subsidies moderate the relationship between AI adoption and enterprise radical innovation?
To address the questions outlined above, this study develops a systematic theoretical model integrating AI adoption, organizational-level digital foundation, and external institutional environment-level government subsidies. This model is built upon the resource-based view and the TOE framework. We use data from Chinese A-share listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen stock exchanges spanning from 2007 to 2023. Utilizing panel data regression analysis, we thoroughly examine the direct link between AI adoption and corporate radical innovation. Furthermore, we investigate the moderating roles of digital foundation and government subsidies in this relationship. Finally, the study further explores the nuanced characteristics of AI adoption, with particular attention to the timing (“early vs. late”) and pace (“fast vs. slow”) dimensions.
Our research makes three contributions. First, we offer new insights into the organizational-level boundary conditions of the relationship between AI and radical innovation by examining the interaction between AI and firms’ digital foundation from a technological synergy perspective. Previous research on the impact of AI technology often treats AI as an independent variable, overlooking its synergistic effects with a firm’s digital foundation [7,9]. This oversight may hinder our understanding of the interwoven and integrated nature of diverse technologies within the current digital innovation ecosystem. Our study distinguishes and investigates two key dimensions of digital foundation: its “degree” and “rate”. By analyzing their influence on AI-driven radical innovation activities, we advance knowledge of firms’ radical innovation pathways in the context of multi-technology convergence. Second, our research enriches the study of external contextual effects on the relationship between AI and radical innovation by exploring the role of an external environmental factor—government subsidies. Although government subsidies are widely recognized as a crucial policy tool for promoting technological innovation, empirical evidence on their effectiveness in AI-based radical innovation activities remains very limited [3,19]. By confirming the positive moderating role of government subsidies, this study provides new insights into how policy tools can effectively amplify the innovation potential of AI. Third, by examining the timing (early vs. late) and pace (fast vs. slow) of AI adoption and their differential impacts on radical innovation, we move beyond the traditional perspective that treats AI adoption as a static and unified process, offering more fine-grained empirical evidence from a dynamic lens [25].
2. Theoretical Analysis and Hypothesis Development
2.1. Resource-Based View and TOE Framework
The resource-based view of the firm provides the theoretical foundation for constructing our conceptual framework. According to the resource-based view, a firm is a collection of resources and capabilities [27]. Differences in these resources and capabilities lead to variations in firm performance [17,28]. Resources are defined as all assets, capabilities, organizational processes, firm attributes, information, knowledge, and other elements controlled by a firm that enable it to conceive and implement strategies aimed at improving efficiency and effectiveness [17]. Capabilities are considered a specific type of resource, rooted in the dynamic interaction between a firm and its various resources, reflecting the firm’s potential to perform fundamental functional activities and optimize operations [29]. As a unifying theoretical framework for understanding how firms accumulate, utilize, and deploy resources to achieve high performance, the resource-based view has been widely used to explain the determinants of firm innovation performance [30,31]. From this theoretical perspective, AI emerges as a strategic resource possessing rarity, inimitability, and organizational embeddedness, providing crucial support for firms’ radical innovation [3]. AI, through complex computational processes, simulates human-like intelligence (such as perception, prediction, and planning), enabling machines to assist or even surpass human decision-making and innovation capabilities [32,33]. Its highly intelligent, self-learning, and rapidly evolving characteristics mean it can not only optimize existing processes but also inspire fundamental transformations in products, services, and business models [4].
Although AI technology inherently possesses strategic value, the resource-based view posits that the extent to which firms can derive value from such strategic resources largely depends on their internal organizational conditions and external environmental factors [17]. To further identify and examine the key contextual factors influencing AI-driven radical innovation, this study adopts the technology–organization–environment (TOE) framework as a core analytical lens [15]. The central proposition of the TOE framework emphasizes that a firm’s adoption of new technologies and innovation behavior is not determined by a single factor but is instead the result of interactions among three dimensions: technology (T), organization (O), and environment (E) [14,15,34,35]. As a classical theoretical framework for explaining firms’ adoption of new technologies and innovation behavior, the TOE framework aligns well with the research context of AI-driven radical innovation, offering a solid theoretical foundation for our in-depth analysis of how firms integrate internal and external resources to foster such innovation [34,35].
Based on this, and guided by the systemic logic of T–O–E interactions, this study develops an integrated moderation model that incorporates the three TOE dimensions to investigate the formation mechanisms and boundary conditions of AI-driven radical innovation (as shown in Figure 1). Specifically, we focus on key variables across the following three dimensions: In terms of technology (T), AI adoption by firms reflects their access to and deployment of cutting-edge technological resources, which directly form the technological foundation and starting point for disruptive product or service development [4,36]. From the organizational (O) perspective, the degree and rate of digital foundation represent critical organizational capabilities and resource endowments that influence the effectiveness of AI application, determining whether firms can effectively absorb and utilize AI [37]. Regarding the environmental (E) dimension, government subsidies serve as a major external funding source that can alleviate resource constraints and signal policy support, thereby encouraging firms to invest AI resources into high-risk, high-reward exploratory innovation efforts [20].
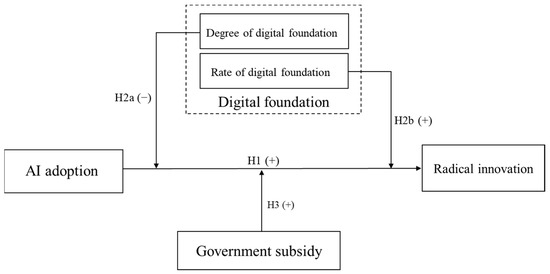
Figure 1.
The theoretical model.
In summary, by integrating the resource-based view with the TOE framework, this study not only enriches the theoretical perspective on the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation but also helps to systematically uncover how key internal and external contextual factors jointly shape the innovation value of AI technologies.
2.2. Relationship Between AI Adoption and Radical Innovation
Radical innovation typically refers to fundamental product, service, or business model transformations achieved through the recombination of formerly unconnected knowledge [3]. It is not merely a linear improvement of existing technologies, but rather a groundbreaking reorganization of previously unrelated knowledge domains that fundamentally alters established technological pathways and reshapes industry competitive landscapes and developmental directions [5,38]. The success of radical innovation relies not only on a firm’s exploratory efforts but also on customer acceptance [39]. Therefore, to achieve the desired knowledge novelty and high customer value, firms must build and develop unique knowledge systems and organizational capabilities.
AI, as a cutting-edge, highly versatile, and pervasive technological resource, provides core empowerment for firms to form difficult-to-imitate, irreplaceable, and valuable combinations of knowledge and capabilities. It is increasingly becoming a key driver of radical innovation. On the one hand, AI ensures the “knowledge novelty” required for radical innovation by promoting technological convergence and knowledge creation [3]. Specifically, AI technologies such as knowledge graphs, natural language processing (NLP), and deep learning can bridge data silos and integrate multi-source heterogeneous information. This allows for the discovery of hidden technological connections and synergistic effects, giving rise to entirely new technological trajectories and solutions [40]. For example, Google’s DeepMind utilized AI to integrate ophthalmic imaging data with biological knowledge bases, developing an automated retinal disease diagnosis system. This not only significantly improved diagnostic efficiency but also represented a revolutionary evolution in the field of computer-assisted diagnosis. On the other hand, AI empowers market sensing and demand insight, supporting the “high customer value” necessary for radical innovation [41]. Through advanced recognition and predictive capabilities, data-driven AI models significantly strengthen a firm’s sensitivity to potential market signals, industry dynamics, and macro-level policy changes, while enhancing its foresight into future trends and innovation opportunities. For instance, Amazon uses AI algorithms to analyze consumer behavior data to accurately predict market demand, subsequently launching the pre-emptive product “Amazon Echo”, successfully opening up and dominating the entirely new smart speaker market. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypothesis:
H1.
AI adoption is positively related to radical innovation.
2.3. The Moderating Impact of Digital Foundation
To reveal the synergistic effects between AI technologies and firms’ digital foundation, this study further divides the digital foundation into two dimensions: degree and rate. The degree of digital foundation reflects the completeness of digital infrastructure and processes. In organizations with a high degree of digital foundation, the positive effect of AI on radical innovation may be constrained by path dependence, organizational inertia, and integration challenges. Such firms have typically established complex digital infrastructures and have formed stable processes and resource allocation paths. As a result, this path dependence can lead to technological lock-in, making firms more inclined to use AI to optimize existing processes rather than driving cross-domain technological recombination [42]. As organizational structures and business processes become increasingly rigid, firms may resist exploring new directions, resulting in organizational inertia [43]. Moreover, integrating emerging AI technologies into mature and complex digital infrastructure often entails unforeseen technical and managerial challenges, which ultimately hinder the application of AI in radical innovation [44]. Therefore, despite possessing stronger technological reserves, firms with a high degree of digital foundation may find the impact of AI on radical innovation constrained by path dependence, organizational inertia, and integration challenges.
In addition, firms with a faster rate of digital foundation development typically demonstrate stronger technological integration capability and organizational agility, which amplify the enabling effect of AI on radical innovation. Rapid digital transformation reflects a dynamic process of accelerated learning, efficient absorption, and deep integration of new technologies [44]. Firms accustomed to fast iteration can embed AI more seamlessly into existing processes and architectures, rather than treating it as a standalone module. This internalized integration capability supports cross-domain knowledge recombination and technological synergy [45]. Moreover, a high transformation rate drives continuous organizational learning to overcome cognitive, behavioral, and business model inertia [43]. This process also fosters organizational agility—reflected in flexible structures, faster decision-making, agile resource allocation, and a culture that embraces experimentation—thereby enabling firms to better identify AI-driven radical innovation opportunities and rapidly mobilize resources to explore and commercialize them in a dynamic competitive landscape. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypotheses:
H2a.
The degree of digital foundation negatively moderates the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation.
H2b.
The rate of digital foundation positively moderates the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation.
2.4. The Moderating Impact of Government Subsidy
In the process of AI-driven radical innovation, beyond the internal organizational factors within firms, the external institutional environment also plays a profound role [17]. Based on the resource-based view, a firm’s innovation potential often remains untapped when it faces shortages of strategic resources [19]. Government subsidies can directly relieve resource constraints for radical innovation by bolstering a firm’s internal resource pool through financial support [20]. Moreover, government subsidies serve as a policy “endorsement”, assisting firms in building a stronger sense of resource security and strategic patience, thereby encouraging the bold mobilization and reallocation of high-value resources. Simultaneously, government subsidies play an important signaling role, enhancing a firm’s ability to secure external strategic resources [46]. As a form of institutional recognition, a government subsidy is a valuable intangible asset—reputational capital. This reputational capital sends positive signals about the firm’s potential to the market, significantly improving its access to scarce resources (e.g., top AI talent, venture capital, strategic partners) from the talent market, capital markets, and collaborative networks. The inflow and integration of these resources further expand the firm’s resource boundaries, ultimately unlocking its potential for radical innovation. Thus, these arguments lead to the following hypothesis:
H3.
Government subsidy positively moderates the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation.
3. Research Design
3.1. Data and Sample
This study focuses on listed companies in China’s Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share markets, covering the sample period from 2007 to 2023. The choice of 2007 as the starting point is based on the following considerations: in 2006, Hinton et al. [47] proposed deep belief networks, which significantly advanced the research and application of deep neural networks and marked the rise of modern deep learning. Since then, AI has entered a new stage of rapid development. In addition, according to the 2019 China Artificial Intelligence Industry Market Outlook Report, China began to gradually establish and improve its statistical system for AI-related fields starting in 2007 [11]. For example, the classification of AI-related patents started to become standardized during this period. Therefore, 2007 was chosen as the starting point of this study to better capture the developmental stages of AI. The annual reports of listed firms used in this study were obtained from Juchao Information Network. Firm-level basic information and financial data were sourced from the China Stock Market & Accounting Research (CSMAR) database. Patent data was obtained from the China National Intellectual Property Administration (NIPA) and the Chinese Research Data Service Platform (CNRDS).
To ensure data quality, the following procedures were applied: (1) Firms in the financial industry were excluded, as their unique accounting standards, regulatory environments, and business models differ substantially from those of non-financial firms. Including such firms would introduce considerable heterogeneity and statistical noise, potentially biasing the results. Therefore, this exclusion ensures the comparability and homogeneity of the sample; (2) Firms designated as ST or *ST in a given year were excluded, as they are subject to special treatment by Chinese stock exchanges due to financial distress or abnormal operations. Their innovation activities are often driven by survival concerns rather than strategic objectives, which may distort behavioral patterns and obscure the relationships under investigation. Thus, this step aims to eliminate extreme outliers and enhance the validity of our empirical findings; (3) Observations with substantial missing data were removed.
3.2. Variable Measurement
3.2.1. Independent Variable
The independent variable in this study is firms’ AI adoption, which refers to a firm’s systematic use of AI technologies as a production tool or strategic resource in its operations, innovation, and decision-making. Given that annual reports are statutory public documents subject to rigorous review by regulatory authorities, their content reflects firms’ strategic priorities, willingness to commit resources, and capability building. Previous studies have also confirmed that AI-related disclosures in annual reports can serve as an effective proxy for firms’ level of AI adoption, especially in data-constrained emerging market contexts [25,48]. We therefore adopt a text analysis approach to construct the key measure of AI adoption. Following the method of Yao et al. [48], we extract AI-related keywords from listed firms’ annual reports using an AI lexicon containing 73 terms (see Appendix A Table A1). The degree of AI adoption is ultimately measured as the natural logarithm of one plus the total number of extracted keywords.
To validate the validity of using the frequency of AI-related terms in annual reports as a proxy for corporate AI adoption, we employed two approaches: First, we examined the correlations among different indicators of AI adoption. We constructed three proxy variables to measure corporate AI adoption: the frequency of AI-related terms in annual reports (AI), the number of AI-related patents (AI_patent), and the investment in AI-related assets (AI_asset). These three indicators capture AI adoption from textual disclosures, asset-level data, and patent data, respectively. Theoretically, if these indicators validly capture “AI adoption,” they should exhibit significant positive correlations with each other. To test this, we conducted Pearson correlation analyses, as shown in Appendix B Table A3. The results indicate that the correlation coefficients between AI and AI_patent and between AI and AI_asset are 0.391 and 0.363, respectively, both significantly positive at the 1% level. This suggests that the three measurement approaches capture corporate AI adoption to a certain extent while also offering distinct informational dimensions. Therefore, these correlation results provide solid empirical support for using the text-based AI indicator as the core explanatory variable in our main model.
Second, following the validation logic proposed by Yao et al. [48], the adoption of AI technologies in firms is typically accompanied by investments in AI-related assets and the generation of technological innovation outputs. Theoretically, if AI-related textual disclosures in annual reports reflect genuine strategic intent—rather than merely symbolic signals or superficial narratives—they should significantly predict actual corporate behaviors in AI-related asset investments and innovation outcomes. To test this, we employed multivariate regression models to examine whether the text-based AI indicator remains a significant predictor of firms’ substantive actions in the AI domain after controlling for other factors. Specifically, we constructed two models: one using the number of AI-related patent applications (AI_patent) as the dependent variable, and the other using the investment in AI-related assets (AI_asset) as the dependent variable. The regression results, as shown in Appendix B Table A4, strongly support our hypothesis: in both models, the AI coefficient is positive and highly significant, confirming that the text-based AI indicator captures not only firms’ strategic focus but also their actual resource investments and innovation outcomes. Therefore, we argue that the AI proxy derived from annual reports is an effective and reliable measure of firms’ actual level of AI adoption.
3.2.2. Dependent Variable
The dependent variable in this study is radical innovation, measured as the natural logarithm of one plus the number of radical innovation patents. Following Gao et al. [19], Grashof and Kopka [3], and Guan and Liu [49], we define radical innovation based on the concept of recombinant innovation, identifying it through novel combinations of technologies in patents. Specifically, we use the first four digits of the IPC codes assigned to each patent to represent its technological components. We extract all four-digit IPC code combinations from patents filed by focal firms each year and compare them with combinations from the previous five years (T–5 to T–1). If a combination does not appear in this five-year window, it is considered novel, and the corresponding patent is classified as a radical innovation. In addition, to avoid measurement overlap between AI adoption and radical innovation, we remove all AI-related patents from the initial pool of radical innovation patents. These patents are identified using the official “Artificial Intelligence Technology Patent Classification Table” from the Patent Classification System for Key Digital Technologies (2023), issued by the China National Intellectual Property Administration. Specifically, we exclude patents whose primary IPC subclass—the first four digits of the IPC code—is explicitly classified as AI technology. This approach mitigates endogeneity concerns stemming from construct contamination, thereby improving construct validity and enabling more rigorous causal inference regarding the impact of AI adoption on radical innovation.
3.2.3. Moderating Variables
This study examines moderating variables from both organizational and environmental levels. Organizational-level moderating variables pertain to a firm’s digital foundation, comprising two dimensions: degree (DF_D) and rate (DF_R). At the environmental level, the moderating variable is government subsidies (Sub).
The measurement of the digital foundation draws upon the research of Zhao et al. [50]. Leveraging their constructed lexicon of 63 foundational digital keywords (see Appendix A Table A2), we applied text analysis to quantify the frequency of these keywords in the annual reports of listed companies. We then took the natural logarithm of this frequency plus one as the indicator for measuring the degree of digital foundation (DF_D). Based on this, we define the rate of digital foundation (DF_R) as the year-over-year growth rate in DF_D.
Following the approach of Wenqi et al. [51], government subsidy is measured as the ratio of the total innovation-related subsidy a firm receives during the period to its total assets. To achieve this, we manually extract and filter data on innovation-related subsidies from the “details of government subsidies” section under “non-operating income” in the notes to financial statements within the annual reports of listed firms.
3.2.4. Control Variables
This study controls for several firm-level variables that may influence corporate radical innovation, specifically including: firm size (Size), measured as the natural logarithm of total assets; firm age (Age), measured as the natural logarithm of the number of years since its establishment; return on assets (ROA), measured by the ratio of net profit to total assets; leverage (Lev), measured by the ratio of total liabilities to total assets; cash flow ratio (Cash), calculated as the net cash flow from operating activities divided by total assets; R&D intensity (RDI), measured as the ratio of R&D expenditure to operating revenue; and whether the chairperson is also CEO (Dual), which equals 1 if the chairperson also serves as the CEO and 0 otherwise.
3.3. Empirical Model
This study employs a fixed effects model based on panel data of Chinese listed companies to examine the impact of AI adoption on radical innovation of firms. The baseline regression model is presented in Equation (1):
The subscripts i and t represent firm and year, respectively. AI denotes the adoption of AI technology, and RI refers to radical innovation. X stands for control variables. and are industry fixed effects and year fixed effects, respectively. is the random disturbance term, and standard errors are clustered at the firm level.
Building upon the baseline regression model (Equation (1)), an interaction term model (Equation (2)) is further constructed to test for moderating effects. The moderating variables, Mod, are represented by the degree of digital foundation (DF_D), the rate of digital foundation (DF_R), and government subsidies (Sub), respectively. The definitions and calculation methods for other variables remain unchanged.
4. Empirical Results and Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Analysis
We used STATA 18.0 to process and analyze the sample data, and the descriptive statistics are presented in Table 1. The results show that for several variables (such as AI, RI, Sub, DF_D, and DF_R), the mean values are higher than the median values, indicating that these variables are right-skewed. For variables like AI, RI, DF_R, and Sub, the standard deviations exceed the means, suggesting significant heterogeneity among the sample firms. The variance inflation factors (VIFs) for all variables are below 3, with an average VIF of 1.44, suggesting that there is no serious multicollinearity problem among the variables.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
4.2. Baseline Regression
Table 2 presents the estimation results of Equation (1). Column (1) shows the regression outcomes controlling for industry and year fixed effects, without including firm-level control variables. The coefficient of AI is 0.0859 and is statistically significant at the 1% level, providing preliminary evidence that AI adoption positively influences the level of corporate radical innovation. In Column (2), a set of firm-level control variables is incorporated. The coefficient of AI remains positive and significant at the 1% level (0.0600), indicating that even after controlling for various firm characteristics, AI adoption continues to significantly enhance corporate radical innovation, thereby supporting Hypothesis 1 (H1).

Table 2.
Baseline regression results.
4.3. Moderating Effect Analysis
Columns (1) and (2) of Table 3 examine the moderating effects of the enterprise’s digital foundation. The results show that the interaction term between AI and the degree of digital foundation (DF_D), denoted as AI × DF_D, has a coefficient of −0.0307, which is significantly negative at the 1% level (p < 0.01). This indicates that a higher degree of digital foundation may actually weaken the positive impact of AI on firms’ radical innovation, supporting Hypothesis 2a (H2a). Column (2) of Table 3 presents the moderating effect of the rate of digital foundation (DF_R). The interaction term AI × DF_R has a coefficient of 0.0402 and is significantly positive at the 10% level (p < 0.1). This suggests that the faster a firm develops its digital foundation, the stronger the positive effect of AI on radical innovation, thereby confirming Hypothesis 2b (H2b). Column (3) of Table 3 shows that the coefficient of AI × Sub is 0.0260, which is significantly positive at the 5% level. This result indicates that government subsidies play a positive moderating role in the relationship between AI and radical innovation, providing support for Hypothesis 3 (H3).

Table 3.
Moderating effect results.
4.4. Endogeneity Checks
4.4.1. Instrumental Variable Regression
We use the average AI level of other firms within the same industry and year as the instrumental variable (denoted as IV1), capturing the peer effects of AI development across firms. The advancement of AI often exhibits industry-level peer influence, with firms tending to align their AI adoption with that of their industry counterparts. Importantly, although this peer firm AI level may reflect broader industry technology dynamics, we argue that it does not directly affect a given firm’s radical innovation activities. Radical innovation, by nature, is characterized by the recombination of previously unrelated knowledge, rather than incremental improvements along existing technological trajectories. In contrast, industry-level knowledge spillovers tend to promote incremental innovation through diffusion and imitation of prevailing technologies, and they are thus less likely to serve as a direct driver of radical breakthroughs. In summary, while peer firm AI adoption may shape the overall technological environment, its direct impact on firm-level radical innovation is limited, supporting the exclusion restriction assumption. Table 4 presents the two-stage least squares (2SLS) estimation results using the instrument. The first-stage regression in Column (1) shows that IV is statistically significant at the 1% level in explaining AI, confirming the instrument’s relevance. Moreover, the Kleibergen–Paap rk LM test is significant at the 1% level, and the Kleibergen–Paap Wald rk F statistic exceeds the 10% critical value of the Stock–Yogo weak identification test, indicating that the instrument does not suffer from under-identification or weak correlation issues. Column (4) presents the second-stage regression results, which show that after controlling for potential endogeneity, the effect of a firm’s AI level on radical innovation remains significantly positive and reaches statistical significance at the 1% level, further validating the important role of AI in promoting corporate radical innovation.

Table 4.
IV-2SLS estimation results.
To further address potential endogeneity concerns and strengthen the causal identification strategy, we additionally introduce an external instrumental variable—namely, the length of optical cable lines at the city level (IV2). The construction and deployment of digital infrastructure, such as optical cable networks, are typically coordinated by local governments and major telecommunications providers, guided by long-term regional development plans rather than by the innovation activities of individual firms. As such, this variable is plausibly exogenous to a given firm’s radical innovation. At the same time, more extensive optical cable infrastructure significantly facilitates the diffusion and application of AI technologies by improving digital connectivity and reducing adoption costs. This makes the variable strongly correlated with a firm’s level of AI adoption. Therefore, this external instrument satisfies both the relevance and exclusion restriction conditions. Column (3) of Table 4 reports the first-stage regression results, showing that city-level cable length is strongly correlated with firm-level AI adoption, with the coefficient being statistically significant at the 1% level. Furthermore, the Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic exceeds the 10% critical value of the Stock–Yogo weak identification test, confirming that the instrument is not weak and satisfies the relevance condition. Column (4) of Table 4 also presents the second-stage results, showing that after controlling for potential endogeneity, AI adoption remains positively and significantly associated with radical innovation at the 1% level. These results collectively support the robustness and validity of our core findings.
4.4.2. Heckman’s Two-Step Method
The adoption of AI may not be random, but rather influenced by factors such as industry characteristics, data infrastructure, and external policy shocks. This selection process could lead to self-selection bias. Furthermore, the research sample consists of companies listed on the Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share markets, excluding some small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in China. Consequently, the sample may not fully represent the overall population, potentially causing sample selection bias. Therefore, this paper uses the Heckman two-stage model to address this issue. In the first stage (Columns 1 and 3 of Table 5), we use a probit model with a dummy variable for radical innovation (RI_dummy) to calculate the inverse Mills ratios, IMR1 and IMR2. In the second stage (Columns 2 and 4), IMR1 and IMR2 are incorporated into their respective regression models to mitigate sample selection bias. The coefficients for both IMR1 (0.9736) and IMR2 (1.1741) are positive and significant at the 1% level, confirming the presence of sample selection bias and justifying the use of the Heckman model. After correcting for this bias, the regression coefficient for AI remains significantly positive at the 1% level in both Column (2) (coefficient = 0.0496) and Column (4) (coefficient = 0.0547). This result indicates that the study’s conclusions remain robust after controlling for sample selection bias.

Table 5.
Heckman’s two-step method results.
4.4.3. Lagged Regression
To address potential reverse causality and account for the delayed effects of AI adoption on corporate radical innovation, we introduce one-year, two-year, and three-year lags for all independent and control variables [52]. As shown in Table 6, the coefficient of our main explanatory variable, AI, remains significantly positive at the 1% level across all three models: one-year lag (coefficient = 0.0590, p < 0.01), two-year lag (coefficient = 0.0587, p < 0.01), and three-year lag (coefficient = 0.0501, p < 0.01). Importantly, the sustained positive effect holds even when we re-run the analysis with alternative proxies for both AI adoption and radical innovation (results omitted for brevity). This suggests that the positive effect of AI on radical innovation is persistent over time and that our main findings are robust.

Table 6.
Lagged regression results.
4.5. Robustness Checks
4.5.1. Change the Measurement of the Independent Variable
To mitigate estimation bias arising from reliance on a single measurement indicator, this study adopts two alternative proxies for AI adoption: AI-related patents and AI-related assets [8]. The identification of AI-related patents is based on classification codes, following the Patent Classification System for Key Digital Technologies (2023) issued by the China National Intellectual Property Administration. Specifically, we use the “Artificial Intelligence Technology Patent Classification Table” from this document to identify patents whose primary classification codes align with the defined AI criteria. The proxy variable AI_patent is constructed as the logarithm of one plus the total number of such patents. For AI-related assets, we extract relevant information from the notes to the financial statements of listed firms. Using keyword filtering, we identify intangible and fixed assets explicitly related to artificial intelligence. The second proxy variable, AI_asset, is then calculated as the ratio of AI-related assets to total assets. The regression results are presented in Columns (1) and (2) of Table 7. The coefficient for the patent-based proxy AI_patent is significantly positive at the 1% level, and the coefficient for the asset-based proxy AI_asset is also significantly positive at the 5% level. These results demonstrate that our main findings remain robust when using alternative measures for AI adoption.

Table 7.
Robustness test results.
4.5.2. Change the Measurement of the Dependent Variable
Previous studies have shown that patents receiving a high number of forward citations typically exhibit greater technological impact and higher radicalness [5,38]. Following the approach of Hesse and Fornahl [5], this study identifies high-impact radical innovations through the following steps. First, we calculate the number of forward citations each patent receives within five years of its application date, excluding self-citations. Then, for each application year, we identify the top 1% most-cited patents as representative of “high-impact innovations” for that year. We then calculate the logarithm of one plus the total number of high-impact patents attributed to each firm and use this as a proxy for radical innovation, labeled RI_new. The results, reported in Column (3) of Table 7, show that the positive effect of AI on RI_new remains statistically significant at the 1% level, consistent with the benchmark regression.
4.5.3. Control for High-Dimensional Fixed Effects
To address the potential interference of unobservable industry-specific factors that vary over time on our baseline estimation results, we further control for industry–year interactive fixed effects. Additionally, province-level factors, such as economic development, specific policies, and the maturity of digital infrastructure, could also influence the relationship between corporate AI adoption and radical innovation. Therefore, we further control for province fixed effects and province–year interactive fixed effects in the model. The estimation results, presented in Column (4) of Table 7, show that the coefficients of AI on firm radical innovation remain significantly positive at the 1% level, thus indicating the robustness of our benchmark findings.
4.5.4. Narrow Study Period
The year 2013 marked a significant turning point in AI development, as breakthroughs in deep learning unveiled AI’s immense potential across various domains. Subsequently, nations worldwide, particularly developed countries, increasingly recognized the transformative impact AI could have on society and the economy, consequently elevating AI development to a strategic priority. Accordingly, we restrict our sample period to 2014–2023, and the regression results, shown in Column (5) of Table 7, remain robust.
5. Heterogeneity Analysis
To explore whether the timing and pace of AI adoption impact radical innovation, this paper further investigates the issues of “early versus late” and “fast versus slow” in AI adoption.
5.1. Timing of AI Adoption: Early and Late
Firms face strategic considerations between being early adopters or late adopters of AI technologies. Early adopters may gain a competitive advantage by leading in technology, accumulating experience, and shaping industry standards. However, they also bear risks such as technological uncertainty and high trial-and-error costs. In contrast, late adopters can learn from the experiences of early movers, avoid technological pitfalls, and catch up with more mature and lower-cost AI solutions, but they may also face the risk of widening gaps due to a weak technological foundation and missed market opportunities.
To examine the impact of AI adoption timing, this study follows the approach of Zhang et al. [53] and uses 2017 as the cutoff year to classify firms into early adopters (those that adopted AI before 2017) and late adopters (those that adopted AI in 2017 or later). The year 2017 was chosen because the State Council of China issued the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan”, elevating AI to a national strategic level. The group regression results, presented in Columns (1) and (2) of Table 8, show that AI adoption significantly promotes radical innovation for both early adopters (coefficient = 0.0242, p < 0.05) and late adopters (coefficient = 0.0691, p < 0.01). A comparison of the coefficients reveals that the effect of AI on radical innovation is greater for late adopters (0.0691) than for early adopters (0.0242). To assess the statistical significance of this difference, we conducted an inter-group coefficient difference test. The results show that this difference is statistically highly significant (p-value = 0.000). Therefore, the marginal effect of AI adoption on radical innovation is more pronounced among late adopters, suggesting that AI offers these firms an opportunity to catch up with early adopters through radical innovation.

Table 8.
Heterogeneity analysis results.
5.2. Pace of AI Adoption: Fast and Slow
The “fast or slow” pace of AI adoption is another crucial dimension of a company’s AI adoption strategy. Firms that adopt AI rapidly are more likely to quickly integrate the technology into operations, thereby strengthening innovation advantages. However, they may also face risks such as organizational disruption or business interruptions due to immature technologies or system incompatibilities. In contrast, firms that adopt AI more slowly may achieve deeper integration between technology and business, forming a stable advantage, but they may also miss market opportunities.
To investigate the impact of the pace of AI adoption, this study draws on the approach of Vermeulen and Barkema [54], who measured the speed of firm internationalization by the average annual number of foreign subsidiaries, and applies a similar logic to construct a measure for AI adoption pace.
Specifically, the measure is calculated by dividing the natural logarithm of one plus the cumulative AI keyword frequency by the cumulative years of AI adoption. The cumulative AI keyword frequency is the total count of AI-related keywords found in a company’s annual reports, starting from the year the firm first mentioned an AI keyword up to the current observation year. The cumulative years of AI adoption refers to the number of years that have passed from the firm’s first mention of an AI keyword up to the current observation year. Based on the 25th and 75th percentiles of this measure, firms are classified into two groups: the “slow adoption group” (below the 25th percentile) and the “fast adoption group” (above the 75th percentile). Grouped regression analyses are then conducted accordingly. As shown in Columns (3) and (4) of Table 8, AI adoption significantly promotes radical innovation in both the fast adoption group (Column 3, coefficient = 0.0361, p < 0.05) and the slow adoption group (Column (4), coefficient = 0.1049, p < 0.01). Notably, the effect is more pronounced in the slow adoption group. A test for the difference in coefficients between the two groups confirms that this difference is statistically significant (p < 0.01). This finding suggests that, compared with a fast adoption approach, a slow adoption strategy may offer firms more time and favorable conditions to achieve deep integration between AI technologies and business operations, thereby more effectively translating AI investment into radical innovation outcomes. Overall, the evidence from heterogeneous analyses indicates substantial potential for AI to drive radical innovation, especially for late adopters and slow adopters.
6. Discussion and Implications
This study investigates the relationship between AI and radical innovation by exploring the moderating roles of the degree and rate of digital foundation and government subsidy. Through rigorous empirical testing of research hypotheses, we provide valuable theoretical and practical implications.
6.1. Theoretical Implications
The research findings make several theoretical contributions. First, this study reveals the synergistic effects between AI and digital foundation from the perspective of technological synergy, thereby identifying crucial organizational-level contingency factors for AI-enabled radical innovation. Previous research on technological impacts has largely focused on the independent role of a single type of technology, with less attention paid to the interaction and integration among multiple technologies [3,55]. However, in the context of AI being deeply embedded in firms’ digital ecosystems, AI’s innovative potential often arises from the synergistic interaction of multiple technologies [36,37]. That is, the effectiveness of AI-driven radical innovation is profoundly influenced by firms’ existing digital foundation. To systematically characterize the digital foundation, this study differentiates and measures it across two key dimensions: extent and rate. By investigating their moderating effects in the process of AI-enabled radical innovation, this study enriches the literature on the interaction between AI and firms’ digital foundation and extends theoretical research on radical innovation in the context of technology integration.
Second, this study enriches the research on the external contextual effects in the relationship between AI and radical innovation by investigating the moderating role of government subsidy. While government subsidy is widely acknowledged as a key policy tool for promoting technological innovation, the existing literature rarely addresses its role in AI-driven innovation [19,20]. Our findings demonstrate that government subsidy, as both a vital external financial support and a strong policy signal, positively moderates the effect of AI on firm radical innovation. This result highlights the importance of governmental support in shaping the realization of AI-driven radical innovation potential, offering new empirical evidence for understanding how the macro-institutional environment influences AI-driven radical innovation.
Third, this study transcends the traditional perspective that treats AI adoption as a static, monolithic phenomenon, thereby deepening our understanding of its underlying complexity. Recognizing that AI adoption is an ongoing and dynamic process, this study focuses on how this dynamism contributes to differences in radical innovation performance, rather than attributing such differences solely to static changes. While prior research has acknowledged AI’s overall contribution to firm performance and innovation outcomes, it often overlooks the inherent complexity of the AI adoption process itself [16,56]. In particular, limited attention has been paid to how dynamic adoption characteristics—such as timing and pace—affect radical innovation. Grounded in the resource-based view, our study not only examines the overall impact of AI on radical innovation but also investigates the heterogeneous effects of adoption timing (early vs. late) and pace (fast vs. slow). This nuanced insight reveals distinct patterns in how AI adoption paths shape firms’ radical innovation outcomes.
6.2. Practical Implications
Our research findings offer several insights for managers seeking to achieve radical innovation success in the intelligent age.
First, the research findings indicate that the effective adoption of AI is a crucial prerequisite for successful radical innovation. For example, Huawei’s “Pangu” AI platform demonstrates how embedding AI into the core innovation strategy—aligned closely with the firm’s overall development and innovation objectives—can lead to breakthrough results in complex domains such as semiconductor design. In contrast, GE’s “Predix” case shows that even substantial AI investments may fail if technological integration and strategic synergy are lacking. Therefore, managers should focus on three key areas to strengthen their ability to leverage AI for radical innovation: One, integrate AI into the radical innovation strategy. Managers should view AI as a strategic asset driving business transformation and radical innovation, ensuring that the AI strategy is highly synergistic with the firm’s overall development strategy and innovation strategy. Two, build a unique combination of AI resources and capabilities. This involves investing in advanced AI technology platforms and tools, strengthening cross-departmental data integration and technological collaboration, and attracting and cultivating interdisciplinary talents equipped with AI knowledge. Three, foster an agile and inclusive organizational environment. This necessitates promoting agile organizational structural changes and cultivating an innovation culture that encourages experimentation and tolerates failure, thereby creating a supportive ecosystem for exploratory AI applications and the emergence of radical innovation.
Second, managers should pay close attention to the moderating roles of organizational digital foundation and government subsidy in the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation. Our findings suggest that for firms with a highly mature digital foundation, excessive reliance on existing systems can lead to path dependency, mirroring the integration challenges faced in GE’s “Predix” project. Such firms should instead maintain flexibility by regularly upgrading systems and encouraging cross-functional learning. Given that a faster transformation rate often indicates higher organizational agility and technological integration capabilities, managers should accelerate digital iteration by continuously optimizing organizational processes and flexibly allocating resources, thereby creating favorable conditions for the innovative application of AI technologies. Meanwhile, managers should actively seek and secure government subsidies, viewing them as an important means to alleviate resource constraints and attract high-quality external resources.
Third, by analyzing the heterogeneity in the timing and pace of AI adoption, this study provides valuable insights for managerial decision-making regarding AI adoption strategies. In terms of timing, our results show a notable late mover advantage. For instance, in emerging technology sectors such as new materials, late adopters can use mature AI solutions to leapfrog early movers in radical innovation output. Managers in such firms should actively deploy AI to capitalize on this catch-up potential. Early adopters, on the other hand, must guard against technological lock-in by continuously renewing AI infrastructure, investing in complementary capabilities, and fostering organizational adaptability. Regarding adoption pace, the evidence supports the notion that “slow and steady wins the race”: slower adopters benefit from extended integration time, allowing deeper technology–organization alignment and knowledge accumulation. Fast adopters must ensure that rapid deployment is coupled with rigorous integration quality checks, robust talent development, and systematic knowledge management.
Fourth, the findings of this study offer crucial insights for government departments in formulating policies that support AI-driven radical innovation. Firstly, subsidy mechanisms should be optimized. Policy instruments should prioritize projects addressing critical AI technologies or pursuing high-risk, high-potential radical innovations, such as those seen in frontier drug discovery or advanced semiconductor design. Secondly, the science and technology innovation ecosystem should be continuously optimized. The government should persistently strengthen the construction of new digital infrastructure, build innovation platforms that integrate industry, academia, research, and application, and enhance intellectual property protection. Thirdly, differentiated support strategies should be formulated. For late-adopting enterprises, specialized subsidies and talent training should be implemented to encourage them to leverage AI for innovative breakthroughs. For early-adopting enterprises, relevant incentive mechanisms should be improved to guide them in breaking existing path dependencies and boldly pursuing radical innovation attempts. For fast AI adopters, policies should guide them to prioritize integration quality and avoid the potential pitfalls of rushing implementation. For slow-adopting enterprises, support should be provided to solidify their technological and organizational foundations, thereby creating conditions for the continuous emergence of radical innovations.
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
This study has several limitations that warrant further exploration and extension in future research. First, the construction of AI adoption and digital foundation indicators in this study primarily relies on textual analysis of annual reports from listed firms. Although this method is widely adopted in the existing literature, annual report information inherently possesses a certain selective disclosure tendency [3]. Future research could introduce other proxy variables, such as job posting information, announcements of technology procurement and collaboration, and field survey data, to enhance the accuracy and objectivity of measurement. Second, this study uses patent data to measure radical innovation. While patents are a crucial indicator of technological innovation, they may fall short in capturing non-technological dimensions of radical innovation, such as business model innovation and service innovation [5,19]. Future research could combine methods like text mining-based content analysis to build a more comprehensive radical innovation measurement. Third, the sample of this study is limited to Chinese firms, which may constrain the generalizability of the findings. Future studies could expand the sample to include firms from more countries, especially developed economies with a higher degree of digital transformation, to examine the cross-national applicability and robustness of the findings. Finally, this study mainly examines the boundary conditions of the AI–radical innovation relationship but does not explore the potential mediating mechanisms. Future research could further investigate the mediating pathways through which AI enables radical innovation, thus advancing our understanding of how AI can be transformed into radical innovation outcomes.
6.4. Conclusions
The main findings are as follows: (1) AI adoption significantly promotes radical innovation. This conclusion remains robust even after accounting for potential endogeneity and conducting a series of robustness checks; (2) In firms with a higher degree of digital foundation, the marginal benefits of AI in driving radical innovation are diminished, possibly due to path dependence, organizational inertia, and high coordination costs. In contrast, the rate of digital foundation positively moderates this relationship, indicating that a rapid digitalization process enhances firms’ technological integration capabilities and organizational agility, thereby amplifying AI’s potential to drive radical innovation; (3) As an external environmental factor, government subsidies positively moderate the relationship between AI adoption and radical innovation; and (4) Heterogeneity analysis further reveals the heterogeneous effects of differentiated characteristics of AI adoption on radical innovation. The results show that AI adoption has a more pronounced effect on radical innovation in late mover firms compared with early adopters, highlighting AI’s potential in enabling catch-up and leapfrogging in innovation. Furthermore, this study finds that firms adopting AI at a slower pace are more effective in driving radical innovation development. This suggests that the relatively ample time allows enterprises to conduct deeper technological integration and more comprehensive knowledge accumulation, which is particularly crucial for achieving radical innovation. In summary, while emphasizing AI technology as a core driver of radical innovation, this study also deeply reveals how firms’ own digital foundation and the external policy environment jointly shape the ultimate effectiveness of AI-driven innovation. These findings not only enrich radical innovation theory in the context of the digital intelligence era but also provide valuable insights for enterprises on how to strategically deploy AI to gain a sustainable competitive advantage.
Author Contributions
Z.W.: Writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, supervision, funding acquisition, conceptualization. X.Z.: Writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology. X.S.: Writing—original draft, formal analysis, investigation, visualization, data curation. J.H.: Writing—review and editing, visualization, investigation, data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Grant No: HUST: 2020WKYXZX008; and the Excellent Youth Fund of the Hunan Provincial Department of Education, Grant No: 24B0195.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. AI and Digital Foundation Dictionary

Table A1.
AI dictionary.
Table A1.
AI dictionary.
| AI Dictionary | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Artificial Intelligence | 26 | AI Chip | 50 | Human–Machine Collaboration |
| 2 | Computer Vision | 27 | Deep Learning | 51 | Smart Agriculture |
| 3 | Image Recognition | 28 | Feature Recognition | 52 | Smart Speaker |
| 4 | Knowledge Graph | 29 | Smart Insurance | 53 | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) |
| 5 | Intelligent Education | 30 | Smart Retail | 54 | Question Answering System |
| 6 | Augmented Reality | 31 | Smart Healthcare | 55 | Reinforcement Learning |
| 7 | Smart Government | 32 | Intelligent Transportation | 56 | Big Data Analytics |
| 8 | Feature Extraction | 33 | Smart Home | 57 | Natural Language Processing (NLP) |
| 9 | Business Intelligence | 34 | Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) | 58 | Big Data Management |
| 10 | Smart Elderly Care | 35 | Big Data Risk Management | 59 | Intelligent Computing |
| 11 | Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 36 | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | 60 | Language Interaction |
| 12 | Knowledge Representation | 37 | Wearable Products | 61 | Machine Learning |
| 13 | Pattern Recognition | 38 | Big Data Platform | 62 | Biometric Recognition |
| 14 | Internet of Things (IoT) | 39 | Augmented Intelligence | 63 | Speech Recognition |
| 15 | Human–Machine Dialogue | 40 | Big Data Operations | 64 | Intelligent Supervision |
| 16 | AI Products | 41 | Edge Computing | 65 | Robo-Advisor |
| 17 | Human–Computer Interaction (HCI) | 42 | Cloud Computing | 66 | Intelligent Speech |
| 18 | Data Mining | 43 | Deep Neural Network (DNN) | 67 | Voiceprint Recognition |
| 19 | Smart Banking | 44 | Machine Translation | 68 | Face Recognition |
| 20 | Intelligent Customer Service | 45 | Neural Network | 69 | Intelligent Agent |
| 21 | Virtual Reality (VR) | 46 | Speech Synthesis | 70 | Big Data Processing |
| 22 | Autonomous Driving | 47 | Big Data Marketing | 71 | Distributed Computing |
| 23 | Unmanned Driving | 48 | Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) | 72 | Smart Sensor |
| 24 | Smart Finance | 49 | Intelligent Chip | 73 | Smart Environmental Protection |
| 25 | Intelligent Search | ||||

Table A2.
Digital foundation dictionary.
Table A2.
Digital foundation dictionary.
| Digital Foundation Dictionary | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Management | 22 | Internet of Things (IoT) | 43 | 5G |
| 2 | Data Mining | 23 | Mobile Internet | 44 | Online to Offline |
| 3 | Data Network | 24 | Industrial Internet | 45 | Online and Offline |
| 4 | Data Platform | 25 | Connected Industry | 46 | O2O |
| 5 | Data Center | 26 | Internet Solutions | 47 | B2B |
| 6 | Data Science | 27 | Internet Technology | 48 | C2C |
| 7 | Digital Control | 28 | Internet Thinking | 49 | B2C |
| 8 | Digital Technology | 29 | Internet Action | 50 | C2B |
| 9 | Digital Communication | 30 | Internet Business | 51 | Information Sharing |
| 10 | Digital Network | 31 | Internet Mobile | 52 | Information Management |
| 11 | Digital Intelligence | 32 | Internet Application | 53 | Information Integration |
| 12 | Digital Terminal | 33 | Internet Marketing | 54 | Information Software |
| 13 | Digital Marketing | 34 | Internet Strategy | 55 | Information System |
| 14 | Digitalization | 35 | Internet Platform | 56 | Information Network |
| 15 | Big Data | 36 | Internet Model | 57 | Information Terminal |
| 16 | Cloud Computing | 37 | Internet Business Model | 58 | Information Center |
| 17 | Cloud IT | 38 | Internet Ecosystem | 59 | Informatization |
| 18 | Cloud Ecosystem | 39 | E-commerce | 60 | Networking |
| 19 | Cloud Services | 40 | Online retail | 61 | Industrial Communication |
| 20 | Cloud Platform | 41 | Internet | 62 | Industrial Information |
| 21 | Blockchain | 42 | Internet Plus | 63 | Virtual Reality |
Appendix B. Construct Validity Test of AI Adoption

Table A3.
Pearson correlation test.
Table A3.
Pearson correlation test.
| VARIABLES | AI | AI_invest | AI_patent |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI | 1.000 | ||
| AI_invest | 0.363 *** | 1.000 | |
| AI_patent | 0.391 *** | 0.233 *** | 1.000 |
Note(s): *** p < 0.01.

Table A4.
Regression results for the AI indicators.
Table A4.
Regression results for the AI indicators.
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Variables | AI_invest | AI_patent |
| AI | 0.0014 *** | 0.2832 *** |
| (0.0002) | (0.0196) | |
| Size | 0.0000 | 0.1970 *** |
| (0.0001) | (0.0220) | |
| Lev | 0.0010 | 0.1835 ** |
| (0.0008) | (0.0802) | |
| ROA | −0.0060 *** | 0.7921 *** |
| (0.0018) | (0.1762) | |
| Age | 0.0007 | −0.0943 |
| (0.0006) | (0.0649) | |
| Cash | 0.0068 *** | 0.2270 |
| (0.0016) | (0.1695) | |
| RDI | 0.0003 *** | 0.0493 *** |
| (0.0000) | (0.0047) | |
| Dual | −0.0004 * | −0.0094 |
| (0.0002) | (0.0305) | |
| _cons | −0.0009 | −4.2825 *** |
| (0.0032) | (0.5247) | |
| Industry FE | Yes | Yes |
| Year FE | Yes | Yes |
| N | 19,823 | 22,292 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.2218 | 0.2619 |
Note(s): Robust standard errors in parentheses; *** p < 0.01, ** p < 0.05, * p < 0.1.
References
- Muhlroth, C.; Grottke, M. Artificial Intelligence in Innovation: How to Spot Emerging Trends and Technologies. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022, 69, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, Y. Do Artificial Intelligence Capabilities Impact Sustainability-Oriented Innovation Performance: Exploring the Role of Green Intellectual Capital and Learning Orientation. J. Intellect. Cap. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grashof, N.; Kopka, A. Artificial Intelligence and Radical Innovation: An Opportunity for All Companies? Small Bus. Econ. 2023, 61, 771–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Laurell, C.; Ots, M.; Sandström, C. Digital Innovation and the Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Firms’ Research and Development—Automation or Augmentation, Exploration or Exploitation? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 179, 121636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, K.; Fornahl, D. Essential Ingredients for Radical Innovations? The Role of (Un-)Related Variety and External Linkages in Germany. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2020, 99, 1165–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, U.; Barbieri, N.; Ramaciotti, L.; Iannantuono, D. The Division of Labour between Academia and Industry for the Generation of Radical Inventions. J. Technol. Transf. 2020, 45, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, H.; Forrest, J.Y.-L.; Yang, B. Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Technological Innovation: Evidence from the Panel Data of China’s Manufacturing Sectors. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 158, 120142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D. Does Artificial Intelligence Drive Technology Convergence? Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Companies. Technol. Soc. 2024, 79, 102715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babina, T.; Fedyk, A.; He, A.; Hodson, J. Artificial Intelligence, Firm Growth, and Product Innovation. J. Financ. Econ. 2024, 151, 103745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöcher, K.; Alt, R. AI and Robotics in the European Restaurant Sector: Assessing Potentials for Process Innovation in a High-Contact Service Industry. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, X.; Yang, S. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Corporate Green Innovation: Can “Increasing Quantity” and “Improving Quality” Go Hand in Hand? J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mariani, M. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Capabilities and the R&D Performance of Organizations: The Moderating Role of Environmental Dynamism. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 11522–11532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, Y.; Fosso Wamba, S. Artificial Intelligence and Adaptive Response to Market Changes: A Strategy to Enhance Firm Performance and Innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 174, 114500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, S.S. Social Commerce Adoption Using TOE Framework: An Empirical Investigation of Saudi Arabian SMEs. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornatzky, L.G.; Fleischer, M. The Processes of Technological Innovation; Lexington Books: Lexington, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.L.; Candi, M. Artificial Intelligence and Innovation Management: Charting the Evolving Landscape. Technovation 2024, 136, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, K.; Mao, H.; Liang, T. Is Faster Really Better? The Impact of Digital Transformation Speed on Firm Financial Distress: Based on the Cost-Benefit Perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 179, 114703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Can Public R&D Subsidy Facilitate Firms’ Exploratory Innovation? The Heterogeneous Effects between Central and Local Subsidy Programs. Res. Policy 2021, 50, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Wang, S.; Zheng, B.; Wu, X. R&D Subsidies and Radical Innovation: Innovative Mindset and Competition Matter. Systems 2025, 13, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, A.; Giones, F.; Werle, M. The AI Digital Revolution in Innovation: A Conceptual Framework of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for the Management of Innovation. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekic, Z.; Füller, J. Managing Innovation in the Era of AI. Technol. Soc. 2023, 73, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sahut, J.-M.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Hikkerova, L. The Effects of Government Subsidies on the Sustainable Innovation of University-Industry Collaboration. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 174, 121233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, F. Government Subsidies, R&D Investment and Innovation Performance: Analysis from Pharmaceutical Sector in China. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2021, 33, 535–553. [Google Scholar]
- Bahoo, S.; Cucculelli, M.; Qamar, D. Artificial Intelligence and Corporate Innovation: A Review and Research Agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 188, 122264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, N.; Wincent, J.; Parida, V.; Gassmann, O. Artificial Intelligence and Innovation Management: A Review, Framework, and Research Agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 162, 120392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernerfelt, B. A Resource-Based View of the Firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlenkova, I.V.; Samaha, S.A.; Palmatier, R.W. Resource-Based Theory in Marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2014, 42, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M.; Martin, J.A. Dynamic Capabilities: What Are They? Strateg. Manag. J. 2000, 21, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, M.; Gordon, S.R. Understanding the Influence of Information Systems Competencies on Process Innovation: A Resource-Based View. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2007, 16, 353–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terziovski, M. Innovation Practice and Its Performance Implications in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in the Manufacturing Sector: A Resource-Based View. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, M.A. Artificial Intelligence: A Very Short Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, D.M.; Hunt, R.A.; Rady, J.; Manocha, P.; Jin, J.h. Are the Futures Computable? Knightian Uncertainty and Artificial Intelligence. Acad. Manage. Rev. 2024, 50, 415–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wael Al-Khatib, A. Drivers of Generative Artificial Intelligence to Fostering Exploitative and Exploratory Innovation: A TOE Framework. Technol. Soc. 2023, 75, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, T. Digital Transformation and Innovation Performance of China’s Manufacturers? A Configurational Approach. Technol. Soc. 2023, 75, 102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietronudo, M.C.; Croidieu, G.; Schiavone, F. A Solution Looking for Problems? A Systematic Literature Review of the Rationalizing Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Decision-Making in Innovation Management. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 182, 121828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yousaf, Z.; Grigorescu, A.; Popovici, N. Harnessing Digital Foundations and Artificial Intelligence Synergies: Unraveling the Role of Digital Platforms, Artificial Intelligence, and Strategic Adaptability in Organizational Innovativeness. J. Innov. Knowl. 2025, 10, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmakers, W.; Duysters, G. The Technological Origins of Radical Inventions. Res. Policy 2010, 39, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberius, V.; Schwarzer, H.; Roig-Dobón, S. Radical Innovations: Between Established Knowledge and Future Research Opportunities. J. Innov. Knowl. 2021, 6, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, S.; Fomina, K. Combining Human and Artificial Intelligence: Hybrid Problem-Solving in Organizations. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2025, 50, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, E.; Belitski, M.; Braga, A.; Savoie, R. Enhancing Knowledge Spillover of Innovation through Artificial Intelligence: An Empirical Investigation. J. Technol. Transf. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, W.; Gartland, M.; Stack, M. Old Habits Die Hard:Path Dependency and Behavioral Lock-In. J. Econ. Issues 2004, 38, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaganer, E.; Gregory, R.W.; Sarker, S. A Process for Managing Digital Transformation: An Organizational Inertia Perspective. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2023, 24, 1005–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.M.; Scheepers, H.; Lui, A.K.H.; Ngai, E.W.T. The Implementation of Artificial Intelligence in Organizations: A Systematic Literature Review. Inf. Manag. 2023, 60, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunke, S.; Weerawardena, J.; McColl-Kennedy, J.R. The Central Role of Knowledge Integration Capability in Service Innovation-Based Competitive Strategy. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2019, 76, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeing, P. The Allocation and Effectiveness of China’s R&D Subsidies—Evidence from Listed Firms. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 1774–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.-W. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, K.; Guo, L.; Feng, X. How does artificial intelligence improve firm productivity? based on the perspective of labor skill structure adjustment. Manag. World 2024, 40, 101–116, 133, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Liu, N. Exploitative and Exploratory Innovations in Knowledge Network and Collaboration Network: A Patent Analysis in the Technological Field of Nano-Energy. Res. Policy 2016, 45, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Li, X. How Does Digital Transformation Affect Total Factor Productivity of Firms? Financ. Trade Econ. 2021, 42, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenqi, D.; Khurshid, A.; Rauf, A.; Calin, A.C. Government Subsidies’ Influence on Corporate Social Responsibility of Private Firms in a Competitive Environment. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ren, X.; Shi, Y. AI Adoption Rate and Corporate Green Innovation Efficiency: Evidence from Chinese Energy Companies. Energy Econ. 2024, 132, 107499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Lu, C.; Lin, X. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Adoption on Firm Competitive Advantage. Sci. Res. Manag. 2025, 46, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; Barkema, H. Pace, Rhythm, and Scope: Process Dependence in Building a Profitable Multinational Corporation. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Machado, I.; Magrelli, V.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial Intelligence in Innovation Research: A Systematic Review, Conceptual Framework, and Future Research Directions. Technovation 2023, 122, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, Y.; Papagiannidis, S. Artificial Intelligence as an Enabler for Innovation: A Review and Future Research Agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 183, 121852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).