Unraveling the Drivers of ESG Performance in Chinese Firms: An Explainable Machine-Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Key Determinants of ESG Performance: Financial and Non-Financial Features
2.2. ESG Performance in China
2.3. Machine Learning for ESG Performance Prediction
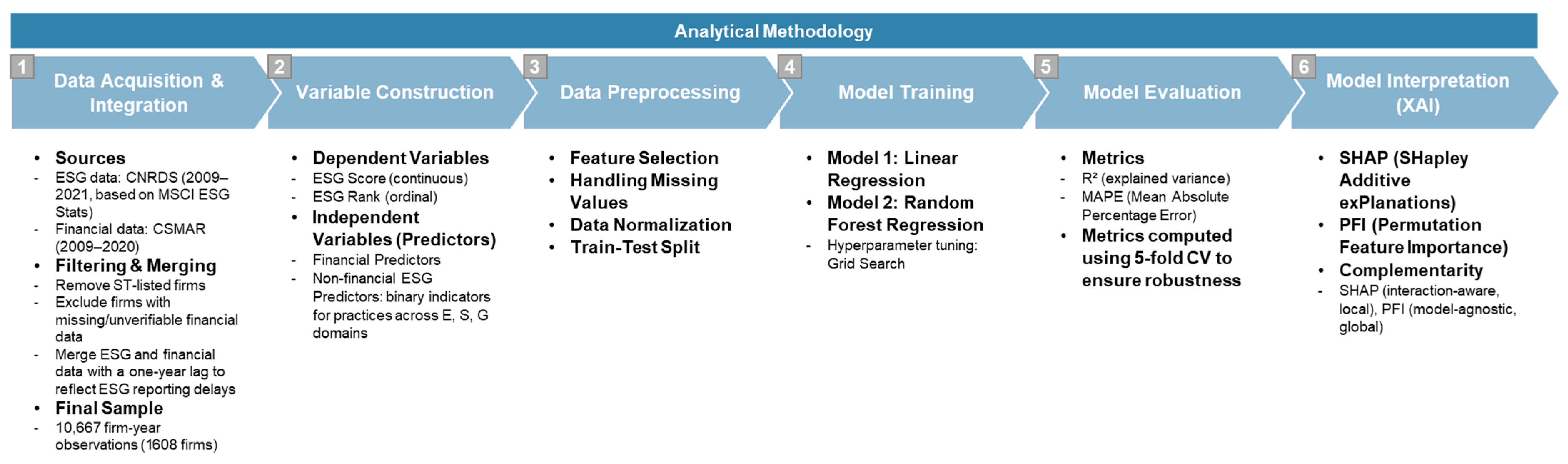
3. Methodology
3.1. Predictive Models
3.2. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)
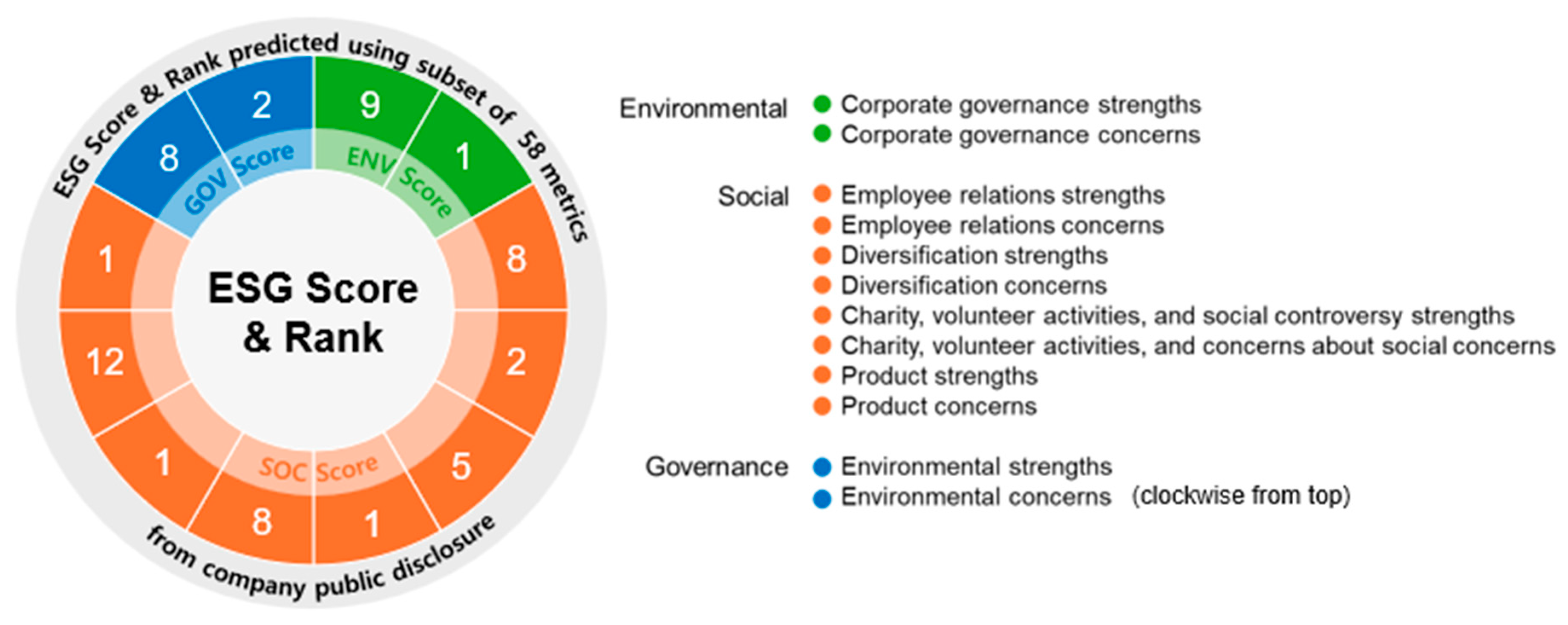
3.3. Data and Variables
3.4. Preprocessing
3.4.1. Feature Selection
3.4.2. Missing Values
4. Result
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Variables Used in the Study
| Variable | Category | Variable | Description | Type | Time | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESG Performance | ESG Score | Annual firm-level ESG scores as reported in CNRDS | Numerical | t | Chinese Research Data Services (CNRDS) | ||
| ESG Rank | Annual firm-level ESG ranks as reported in CNRDS | Numerical | |||||
| Financial Features | Cash | Cash account values as recorded in the China Stock Market and Accounting Research (CSMAR) database | Numerical | t − 1 | China Stock Market and Accounting Research (CSMAR) database | ||
| Inventory | Inventory account values as recorded in the CSMAR database | Numerical | |||||
| Total Assets | Total assets as reported in the CSMAR database | Numerical | |||||
| Total Revenue | Total revenue as reported in the CSMAR database | Numerical | |||||
| Operating Net Cash Flow | Operating net cash flow values as recorded in the CSMAR database | Numerical | |||||
| Return on Total Assets | Return on total assets (ROA) as reported in the CSMAR database | Numerical | |||||
| Non-financial Features | Society | Diversity | Member of the Communist Party of China | Whether there are party members among the directors, supervisors and senior management. 1 if yes, 0 if no. | Binary | t − 1 | Chinese Research Data Services (CNRDS) |
| Female board seats | Women hold four or more board seats. 1 if yes, 0 if no. | Binary | |||||
| Female senior management | The company’s senior management team includes at least one woman. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Innovative human resources projects | Whether the company has innovative human resources programs for people with disabilities/released prisoners, or has a good reputation in hiring people with disabilities and released prisoners. 1 if yes, 0 if no. | Binary | |||||
| No female executives * | 1 if there are no women among the directors, supervisors, or executives, otherwise 0 | Binary | |||||
| Employee relations | Employee participation (stock ownership) | Whether the company strongly encourages employees to participate in or own company ownership through stock options; share in the profits, own shares, share financial information, or participate in making management decisions; or the company has established a compensation incentive mechanism. A value of 1 indicates that the company does so, while a value of 0 indicates that it does not. | Binary | ||||
| Employee benefits | Whether the company has very good retirement and other benefit programs. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Safety management system | Whether the company has adopted a safety production management system. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Safety training | Whether the company has conducted safety production training. 1 if yes, 0 if no. | Binary | |||||
| Occupational safety certification | Whether the company has conducted occupational safety certification. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Professional training | Whether the company provides professional training for employees, 1 if yes, 0 if no. | Binary | |||||
| Employee communication channels | Whether the company has good communication channels for employees to convey their opinions or suggestions to senior management, 1 if yes, 0 if no. | Binary | |||||
| Employee safety disputes * | 1 if the company has recently paid large fines or civil damages for violating employee health and safety guidelines, or if the company has been involved in major health and safety disputes, otherwise 0 | Binary | |||||
| Layoffs * | 1 if the company has carried out a large number of redundancies in recent years, 0 otherwise. | Binary | |||||
| Product quality | Quality system | Whether the company has a product quality management system; if so, 1; if not, 0 | Binary | ||||
| After-sales service | Whether the company is constantly improving its aftersales service; if so, 1; if not, 0 | Binary | |||||
| Customer satisfaction survey | Whether the company has conducted a customer satisfaction survey, so 1, no 0 | Binary | |||||
| Quality awards | Whether the company has obtained certifications and honors in terms of product quality, so 1, no 0 | Binary | |||||
| Anti-corruption measures | Whether the company has anticommercial bribery measures or anticorruption measures. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Strategy shared | Whether the company has established a strategy sharing mechanism and platform with its business partners, including long-term strategic cooperation agreements, shared experimental bases, shared databases, and stable communication and exchange platforms. | Binary | |||||
| Integrity in business philosophy | Whether the company has the concept and system guarantee of integrity management and fair competition. | Binary | |||||
| Number of patents | The total number of patents independently and jointly obtained by the company in the current year | Numerical | |||||
| Product dispute * | Whether the company has recently been involved in major disputes or regulatory actions due to product or service safety issues, and has paid substantial fines or civil damages. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Governance | Charity, volunteer activities and social controversies | Supporting education | Whether the company has supported education, such as starting a school, donating to Project Hope, sponsoring poor students, etc. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||
| Supporting charity | Whether the company has projects that support charitable giving. For example, the company establishes its own charitable foundation, or cooperates with other organizations to promote charitable causes. A value of 1 indicates that the company has such projects, while a value of 0 indicates that it does not. | Binary | |||||
| Volunteer activities | Whether the company has outstanding volunteer activities. A value of 1 indicates that the company has such activities, while a value of 0 indicates that it does not. | Binary | |||||
| International assistance | Whether the company has provided aid to foreign countries. A value of 1 indicates that the company has such activities, while a value of 0 indicates that it does not. | Binary | |||||
| Employment generation | Whether the company has policies or measures to promote employment and has implemented them accordingly. A value of 1 indicates that the company has implemented such policies or measures, while a value of 0 indicates that the company has not. | Binary | |||||
| Boost the local economy | Whether the company’s operations contribute to the economic development of the local community, as well as policies and measures that drive local economic development, such as localized procurement policies and localized employment policies. | Binary | |||||
| Total amount of donations | The total amount of charitable donations (unit: 10,000 RMB) | Numerical | |||||
| Financing disputes * | Whether the company has disputes and controversies over loans or investments, 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Governance | CSR column | Whether the company homepage has a CSR column, 1 for yes, 0 for no | Binary | ||||
| CSR report pages | The total number of CSR report pages (unit: pages) | Numerical | |||||
| CSR leader agency | Whether the company has established a CSR leadership organization or a clear CSR department in charge, 1 for yes, 0 for no | Binary | |||||
| CSR vision | Whether the company has a concept, vision or values of being responsible for the economy, society and the environment. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| CSR training | CSR training has been carried out. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Reliability guarantee | Reliability assurance of CSR report. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Accounting irregularities * | If there are accounting violations, 1 if present, 0 if not | Binary | |||||
| Environment | Environmental performance | Environmentally beneficial products | Whether the company has developed or used innovative environmentally beneficial products, equipment or technologies. A value of 1 indicates that the company has done so; a value of 0 indicates that it has not | Binary | |||
| Measures to reduce the three wastes | Whether the company’s policies, measures or technologies to reduce emissions of waste gas, waste water, waste residue and greenhouse gases. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Circular economy | Whether the company’s policies and measures to use renewable energy or adopt a circular economy. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Energy saving | Whether the company has policies, measures or technologies to conserve energy. 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Green office | Whether the company has green office policies or measures, 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Environmental certification | Whether the company’s environmental management system is ISO 14001 [73] certified, 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Environmental recognition | Whether the company has received environmental recognition or other positive evaluations, 1 if yes, 0 if no | Binary | |||||
| Environmental penalties * | if the company has been penalized for environmental violations, 1 is given; if not, 0 | Binary | |||||
| Pollutant emissions * | if the company has pollutant emissions, 1 is given; if not, 0 | Binary | |||||
Appendix A.2. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Techniques Applied
References
- Heinzer, I.; Mezzanzanica, A. Does a Company’s ESG Score Have a Measurable Impact on Its Market Value? Deloitte 2023. Available online: https://www.deloitte.com/ch/en/services/financial-advisory/research/does-a-company-esg-score-have-a-measurable-impact-on-its-market-value.html (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Lloyd, S. Adoption of Global Sustainability Disclosure Standards Gains Steam Around the World. Thomson Reuters. 2024. Available online: https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en-us/posts/esg/forum-global-sustainability-disclosure-standards/ (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Chen, S.; Fan, M. ESG ratings and corporate success: Analyzing the environmental governance impact on Chinese companies’ performance. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1371616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchiello, A.F.; Marrazza, F.; Perdichizzi, S. Non-financial disclosure regulation and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance: The case of EU and US firms. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porteous, A.H.; Rammohan, S.V.; Lee, H. Carrots or Sticks? Improving Social and Environmental Compliance at Suppliers Through Incentives and Penalties. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2015, 24, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villena, V.H. The Missing Link? The Strategic Role of Procurement in Building Sustainable Supply Networks. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2019, 28, 1149–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kemenade, A.; Shukla, A.; Jin, Y.; McCafferty, G.; Lim, H.; Simms, A. ESG Priorities in China: How Companies in China Are Approaching ESG. Economist Impact. 2023. Available online: https://www.fidelity.com.cn/media/PDF/esg/esg-priorities-in-china-en.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Tian, Y. Will Informal Institutions Affect ESG Rating Divergence? Evidence from Chinese Confucian Culture. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Yang, L. Shaping Corporate ESG Performance: Role of Social Trust in China’s Capital Market. China Financ. Rev. Int. 2024, 14, 34–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lin, H.; Han, W.; Wu, H. ESG in China: A Review of Practice and Research, and Future Research Avenues. China J. Account. Res. 2023, 16, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhong, M. Do ESG Ratings of Chinese Firms Converge or Diverge? A Comparative Analysis Based on Multiple Domestic and International Ratings. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, F.; Kölbel, J.; Rigobon, R. Aggregate confusion: The divergence of ESG ratings. Rev. Financ. 2022, 26, 1315–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.A.; Khalil, R.; Khalil, M.K. Environmental, social and governance (ESG)-augmented investments in innovation and firms’ value: A fixed effects panel regression of Asian economies. China Financ. Rev. Int. 2024, 14, 76–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, F.; Migliavacca, M. The determinants of ESG rating in the financial industry: The same old story or a different tale? Sustainability 2020, 12, 6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, R.; Paolone, F.; Cucari, N.; Dezi, L. Non-financial strategy disclosure and environmental, social and governance score: Insight from a configurational approach. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friede, G.; Busch, T.; Bassen, A. ESG and financial performance: Aggregated evidence from more than 2000 empirical studies. J. Sustain. Financ. Invest. 2015, 5, 210–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlitzky, M.; Schmidt, F.; Rynes, S. Corporate Social and Financial Performance: A Meta-analysis. Organ. Stud. 2003, 24, 403–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Elahi, E.; Khalid, Z.; Sun, X.; Sun, F. Environmental, Social and Governance Performance: Analysis of CEO Power and Corporate Risk. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, A.; Cimino, A.; Longo, F.; Solina, V.; Verteramo, S. The Impact of ESG Practices in Industry with a Focus on Carbon Emissions: Insights and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasiotis, I.; Gouopoulos, D.; Konstantios, D.; Ratsika, V. ESG Reputational Risk, Corporate Payouts and Firm Value. Br. J. Manag. 2024, 35, 871–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, M.; Lagasio, V.; Porretta, P. Be good to be wise: Environmental, Social, and Governance awareness as a potential credit risk mitigation factor. J. Int. Financ. Manag. Account. 2022, 33, 522–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandella, P.; Sergi, B.S.; Sironi, E. Corporate social responsibility performance and the cost of capital in BRICS countries. The problem of selectivity using environmental, social and governance scores. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, S.; Tron, A.; Colantoni, F.; Savio, R. Sustainability Disclosure and IPO Performance: Exploring the Impact of ESG Reporting. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-García, C.; Marchante-Lara, M.; Benavides-Chicón, C.G. Towards sustainable development: Environmental innovation, cleaner production performance, and reputation. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Li, X. ESG performance and corporate value: Analysis from the stakeholders’ perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1084632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, H. How does corporate ESG performance affect sustainable development: A green innovation perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1170582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Loh, L.; Wu, W. How do Environmental, Social and Governance Initiatives Affect Innovative Performance for Corporate Sustainability? Sustainability 2020, 12, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Mohd. Zobair, S.A.; Sobhani, F.A.; Siddik, A.B. Does ESG Impact Firms’ Sustainability Performance? The Mediating Effect of Innovation Performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellyn, K.B.; Muller-Kahle, M. ESG leaders or laggards? A configurational analysis of ESG performance. Bus. Soc. 2023, 63, 1149–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisin, A.; Kushnir, A.; Koryakov, A.G.; Fomenko, N.L.; Shchukina, T.V. Financial stability in companies with high ESG scores: Evidence from North America using the Ohlson O-score. Sustainability 2022, 14, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beji, R.; Yousfi, O.; Lukil, N.; Omri, A. Board Diversity and Corporate Social Responsibility: Empirical Evidence from France. J. Bus. Ethics 2021, 173, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Kilic, M.; Uyar, A.; Karaman, A. Drivers and Value-Relevance of CSR Performance in the Logistics Sector: A Cross-Country Firm-Level Investigation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-García, L.; Zorio-Grima, A.; García-Benau, M.A. Stakeholder Engagement, Corporate Social Responsibility and Integrated Reporting: An Exploratory Study. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2013, 22, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayegh, M.F.; Abdul Rahman, R.; Homayoun, S. Corporate Economic, Environmental, and Social Sustainability Performance Transformation through ESG Disclosure. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. The Consequences of Mandatory Corporate Sustainability Reporting. In The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility: Psychological and Organizational Perspectives; McWilliams, A., Siegel, D., Wright, C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; Chapter 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokuwaduge, C.S.D.S.; Heenetigala, K. Integrating Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Disclosure for a Sustainable Development: An Australian Study. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barko, T.; Cremers, M.; Renneboog, L. Shareholder Engagement on Environmental, Social, and Governance Performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 180, 777–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Pan, C.-H.; Statman, M. Why Do Countries Matter So Much in Corporate Social Performance? J. Corp. Financ. 2016, 41, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, R.; Ali, H.; Mohamed, E. The Sustainable Development Goals and Corporate Sustainability Performance: Mapping, Extent and Determinants. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Lv, X. Institutional pressures and firms’ environmental management behavior: The moderating role of slack resources. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 66, 2513–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Yang, Z. Board Group Faultlines, Slack Resource, and Corporate Carbon Performance. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmouda, A.M.O.; Orzes, G.; Sauer, P.C.; Molinaro, M. Determinants of Environmental, Social and Governance Scores: Evidence from the Electric Power Supply Chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 471, 143372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, J.L.; Hoffman, A.J. Exceptional Boards: Environmental Experience and Positive Deviance from Institutional Norms. J. Organ. Behav. 2013, 34, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haniffa, R.M.; Cooke, T.E. The Impact of Culture and Governance on Corporate Social Reporting. J. Account. Public Policy 2005, 24, 391–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooneeapen, O.; Abhayawansa, S.; Mamode Khan, N. The Influence of the Country Governance Environment on Corporate Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Performance. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2022, 13, 953–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Hung, M.; Wang, Y. The Effect of Mandatory CSR Disclosure on Firm Profitability and Social Externalities: Evidence from China. J. Account. Econ. 2018, 65, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Mendes-Da-Silva, W.; Orsato, R.J. Sensitive Industries Produce Better ESG Performance: Evidence from Emerging Markets. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 150, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Khan, M.A.; Mazliham, M.S.; Alam, M.M.; Aman, N.; Abbas, K. Applying artificial intelligence techniques for predicting the environment, social, and governance (ESG) pillar score based on balance sheet and income statement data: A case of non-financial companies of USA, UK, and Germany. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 975487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, V.; D’Ecclesia, R.; Levantesi, S. Fundamental ratios as predictors of ESG scores: A machine learning approach. Decis. Econ. Financ. 2021, 44, 1087–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, A.; Taglialatela, J.; Testa, F.; Iraldo, F. Determinants of Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) Performance: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 456, 142213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortas, E.; Álvarez, I.; Zubeltzu, E. Firms’ Board Independence and Corporate Social Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vitto, A.; Marazzina, D.; Stocco, D. ESG ratings explainability through machine learning techniques. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.K.; Wang, J.; Angel, V.; Luo, M. China’s ESG Scorecard: A Predictive Machine Learning Model. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2024, 31, 3468–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Liao, K. Rowing or Crowding? The Nonlinear Effects of State-Owned Capital Participation on ESG Performance in Private Enterprises. Econ. Anal. Policy 2025, 87, 790–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, D. Is the ESG Performance of State-Owned Enterprises Becoming a Pivotal Role?—Based on the Empirical Evidence from Chinese Listed Firms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, M.; Wang, H. ESG Rating Disagreement and Stock Returns: Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2024, 91, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Sadiq, M.; Tye, W.B.; Zhang, J. The Impact of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Rating Disparities on Corporate Risk: The Mediating Role of Financing Constraints. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Hsu, B.-W. Empirical study of ESG score prediction through machine learning—A case of non-financial companies in Taiwan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.S.A.; Masrom, S.; Rahman, R.A.; Ibrahim, R.; Gilal, A.R. Genetic programming based automated machine learning in classifying ESG performances. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 59612–59629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.K. The pertinence of incorporating ESG ratings to make investment decisions: A quantitative analysis using machine learning. J. Sustain. Financ. Invest. 2024, 14, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.; Joo, H.; Choi, H.; Cheon, M. Proposing an Integrated Approach to Analyzing ESG Data via Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.07874. [Google Scholar]
- Shapley, L.S. Stochastic Games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1953, 39, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.G.; Lee, S.I. Consistent Individualized Feature Attribution for Tree Ensembles. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Lin, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q. Provincial industrial policy and corporate emissions: Evidence from China. J. Int. Financ. Manag. Account. 2025; forthcoming. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jifm.12229 (accessed on 29 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Jia, F.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Fernandes, K. The impact of corporate social responsibility decoupling on financial performance: The role of customer structure and operational slack. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2023, 43, 1859–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Wang, K.; Sueyoshi, T.; Wang, D.D. ESG: Research progress and future prospects. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsi, T.; Turgut, G. Boardroom Diversity and Its Effect on Social Performance: Conceptualization and Empirical Evidence. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 112, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayssi, M.; Dah, M.; Jizi, M. Women on Boards, Sustainability Reporting and Firm Performance. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2016, 7, 376–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomka-Gołębiowska, A.; De Masi, S.; Zambelli, S.; Paci, A. Towards Higher Sustainability: If You Want Something Done, Ask a Chairwoman. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 58, 104308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarmuji, I.; Maelah, R.; Tarmuji, N.H. The impact of environmental, social and governance practices (ESG) on economic performance: Evidence from ESG score. Int. J. Trade Econ. Financ. 2016, 7, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14001; Environmental Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
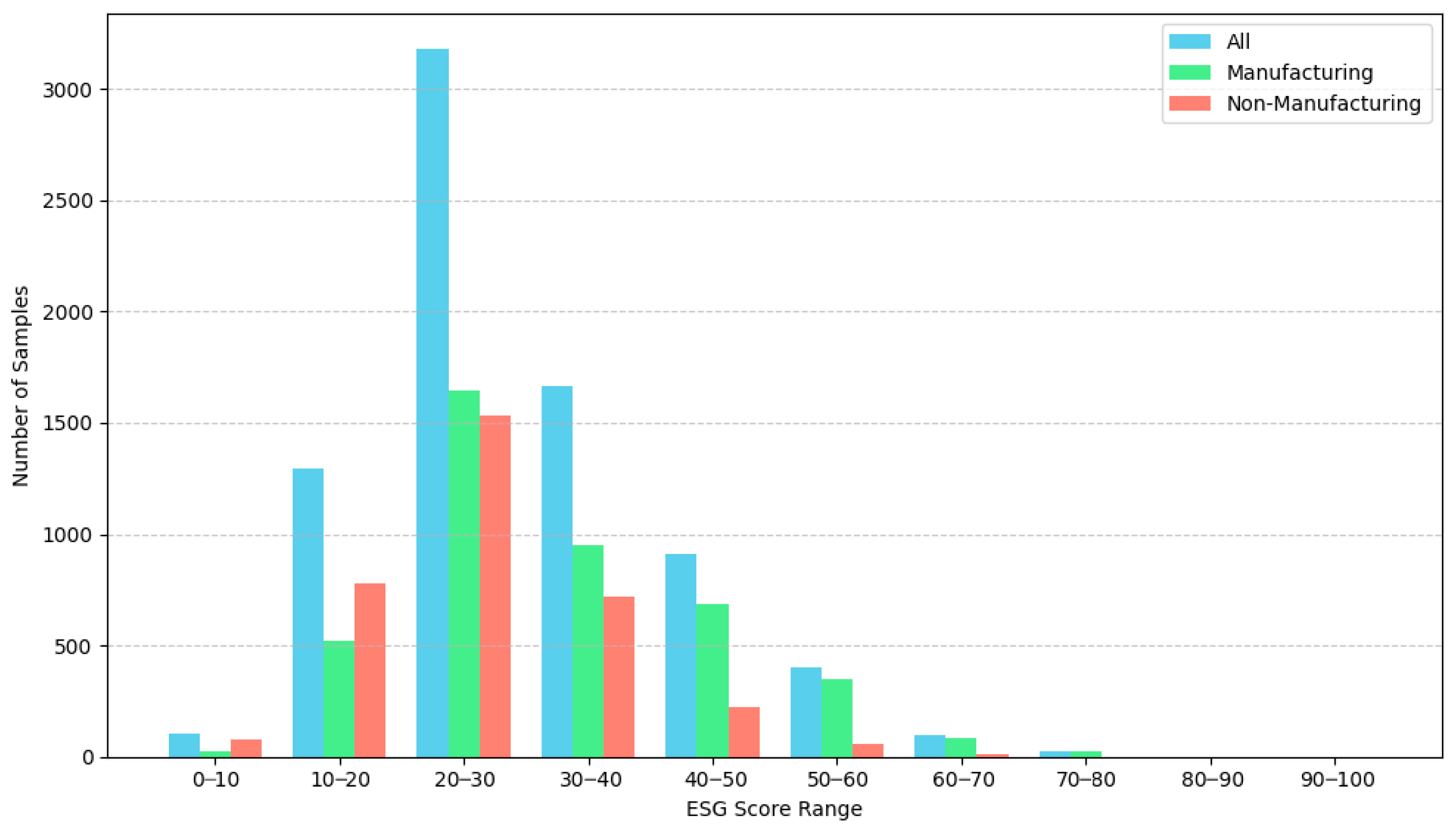
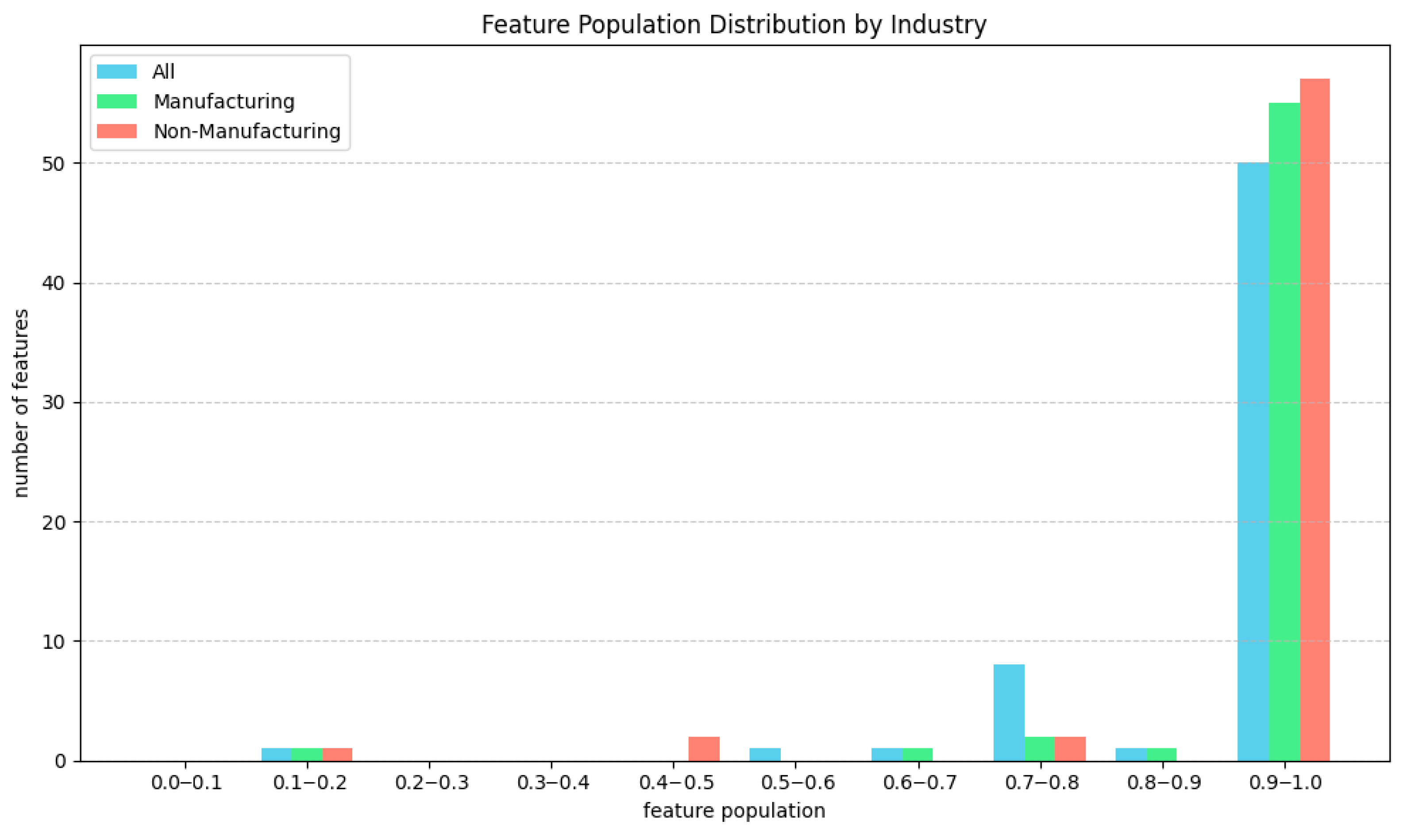

| Features (Financial) | Features (Non-Financial) | Samples-Total | Samples-Train (80%) | Samples-Test (20%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 6 | 48 | 6447 | 5158 | 1289 |
| Manufacturing | 6 | 48 | 3333 | 2666 | 667 |
| Non-manufacturing | 6 | 48 | 3114 | 2491 | 623 |
| ESG Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Mean Absolute SHAP | Permutation Feature Importance | ||||
| 1 | Number of patents | S | 1.74266 | Number of patents | S | 0.422643 |
| 2 | Total Assets | F | 0.855732 | CSR training | F | 0.167886 |
| 3 | Pollutant emissions | E | 0.832052 | Pollutant emissions | E | 0.163459 |
| 4 | CSR training | G | 0.779826 | Total Assets | G | 0.160654 |
| 5 | Total amount of donations | S | 0.674143 | Inventory | S | 0.149073 |
| 6 | Member of the Communist Party of China | S | 0.661451 | Total amount of donations | S | 0.143337 |
| 7 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | E | 0.646329 | Cash | E | 0.126472 |
| 8 | Inventory | F | 0.599417 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | F | 0.125692 |
| 9 | Supporting charity | G | 0.588065 | Member of the Communist Party of China | G | 0.124322 |
| 10 | Cash | F | 0.583546 | Total Revenue | F | 0.119035 |
| 11 | Operating Net Cash Flow | F | 0.523641 | Operating Net Cash Flow | F | 0.1154 |
| 12 | CSR report pages | G | 0.489355 | CSR report pages | G | 0.115086 |
| 13 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.477658 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.112074 |
| 14 | Total Revenue | F | 0.444592 | Supporting charity | F | 0.0984276 |
| 15 | Employment generation | G | 0.331092 | CSR column | G | 0.0415728 |
| 16 | CSR column | G | 0.276555 | Employment generation | G | 0.0395218 |
| 17 | Environmental certification | E | 0.274086 | Safety management system | E | 0.0341658 |
| 18 | Environmental recognition | E | 0.200331 | Quality system | E | 0.0300699 |
| 19 | Quality system | S | 0.184208 | Environmental recognition | S | 0.0233895 |
| 20 | Safety management system | S | 0.181707 | Environmental certification | S | 0.0199159 |
| 21 | Safety training | S | 0.178463 | Financing disputes | S | 0.0184858 |
| 22 | Quality awards | S | 0.160327 | Female senior management | S | 0.0183731 |
| 23 | Number of patents | S | 1.74266 | Safety training | S | 0.0172071 |
| 24 | Total Assets | F | 0.855732 | Supporting education | F | 0.0161966 |
| 25 | Pollutant emissions | E | 0.832052 | Employee communication channels | E | 0.0161184 |
| ESG Rank | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Mean Absolute SHAP | Permutation Feature Importance | ||||
| 1 | Member of the Communist Party of China | S | 111.517 | Member of the Communist Party of China | S | 0.305326 |
| 2 | CSR training | G | 69.6411 | Quality system | G | 0.228257 |
| 3 | Quality system | S | 68.4796 | Number of patents | S | 0.19466 |
| 4 | Number of patents | S | 65.9659 | Inventory | S | 0.15933 |
| 5 | Total amount of donations | G | 58.131 | Total Revenue | G | 0.156924 |
| 6 | Inventory | F | 56.6408 | Total Assets | F | 0.155962 |
| 7 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | E | 55.2762 | CSR training | E | 0.154597 |
| 8 | Cash | F | 55.2046 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.154056 |
| 9 | Total Revenue | F | 55.2001 | Total amount of donations | F | 0.146728 |
| 10 | Total Assets | F | 54.7308 | Cash | F | 0.143121 |
| 11 | Return on Total Asset | F | 52.5459 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | F | 0.133377 |
| 12 | Pollutant emissions | E | 51.2728 | Operating Net Cash Flow | E | 0.130985 |
| 13 | Employee participation (stock ownership) | S | 44.0143 | Pollutant emissions | S | 0.106161 |
| 14 | Operating Net Cash Flow | F | 42.9649 | CSR report pages | F | 0.067136 |
| 15 | Employee benefits | S | 32.78 | Employee participation (stock ownership) | S | 0.064002 |
| 16 | Supporting charity | G | 28.2561 | Supporting charity | G | 0.054323 |
| 17 | CSR report pages | G | 24.1889 | Employee benefits | G | 0.053619 |
| 18 | Volunteer activities | G | 19.7836 | Strategy shared | G | 0.030886 |
| 19 | Energy saving | E | 16.1273 | Energy saving | E | 0.025813 |
| 20 | Circular economy | E | 14.5797 | Green office | E | 0.022999 |
| 21 | Green office | E | 12.7173 | Circular economy | E | 0.02092 |
| 22 | CSR leader agency | G | 12.2752 | Volunteer activities | G | 0.020497 |
| 23 | Strategy shared | S | 12.1109 | Environmentally beneficial products | S | 0.016302 |
| 24 | Integrity in business philosophy | S | 10.464 | CSR leader agency | S | 0.015167 |
| 25 | After-sales service | S | 10.3301 | Female senior management | S | 0.014861 |
| ESG Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Manufacturing Firms | Non-Manufacturing Firms | ||||
| 1 | Number of patents | S | 2.11471 | Number of patents | S | 1.63427 |
| 2 | Supporting charity | G | 1.20173 | CSR report pages | G | 0.87808 |
| 3 | Operating Net Cash Flow | F | 1.0444 | Total amount of donations | F | 0.620057 |
| 4 | Member of the Communist Party of China | S | 0.896692 | Total Revenue | S | 0.61991 |
| 5 | Total amount of donations | G | 0.829836 | Inventory | G | 0.53834 |
| 6 | Cash | F | 0.804307 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.518472 |
| 7 | CSR report pages | G | 0.713684 | CSR training | G | 0.467066 |
| 8 | CSR training | G | 0.699526 | Cash | G | 0.41838 |
| 9 | Inventory | F | 0.579346 | Total Assets | F | 0.371522 |
| 10 | Pollutant emissions | E | 0.457653 | Operating Net Cash Flow | E | 0.353452 |
| 11 | Total Assets | F | 0.450299 | Member of the Communist Party of China | F | 0.265095 |
| 12 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.442602 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | F | 0.251654 |
| 13 | Total Revenue | F | 0.361372 | Financing disputes | F | 0.236631 |
| 14 | Female senior management | S | 0.322558 | Occupational safety certification | S | 0.217014 |
| 15 | CSR column | G | 0.302507 | CSR column | G | 0.18826 |
| 16 | CSR vision | G | 0.297468 | Environmentally beneficial products | G | 0.182068 |
| 17 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | E | 0.297438 | Safety management system | E | 0.170876 |
| 18 | Environmental recognition | E | 0.24509 | CSR vision | E | 0.169513 |
| 19 | Employment generation | G | 0.223482 | Environmental certification | G | 0.164461 |
| 20 | Environmentally beneficial products | E | 0.209439 | No female executives | E | 0.158087 |
| 21 | Employee benefits | S | 0.198984 | Supporting education | S | 0.154673 |
| 22 | Supporting education | G | 0.158466 | Strategy shared | G | 0.148178 |
| 23 | Boost the local economy | G | 0.153876 | Safety training | G | 0.14809 |
| 24 | Safety training | S | 0.135864 | Supporting charity | S | 0.130331 |
| 25 | Strategy shared | S | 0.122036 | Employee participation (stock ownership) | S | 0.127808 |
| ESG Rank | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Manufacturing Firms | Non-Manufacturing Firms | ||||
| 1 | Number of patents | S | 2.11471 | Number of patents | S | 1.63427 |
| 2 | Supporting charity | G | 1.20173 | CSR report pages | G | 0.87808 |
| 3 | Operating Net Cash Flow | F | 1.0444 | Total amount of donations | F | 0.620057 |
| 4 | Member of the Communist Party of China | S | 0.896692 | Total Revenue | S | 0.61991 |
| 5 | Total amount of donations | G | 0.829836 | Inventory | G | 0.53834 |
| 6 | Cash | F | 0.804307 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.518472 |
| 7 | CSR report pages | G | 0.713684 | CSR training | G | 0.467066 |
| 8 | CSR training | G | 0.699526 | Cash | G | 0.41838 |
| 9 | Inventory | F | 0.579346 | Total Assets | F | 0.371522 |
| 10 | Pollutant emissions | E | 0.457653 | Operating Net Cash Flow | E | 0.353452 |
| 11 | Total Assets | F | 0.450299 | Member of the Communist Party of China | F | 0.265095 |
| 12 | Return on Total Asset | F | 0.442602 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | F | 0.251654 |
| 13 | Total Revenue | F | 0.361372 | Financing disputes | F | 0.236631 |
| 14 | Female senior management | S | 0.322558 | Occupational safety certification | S | 0.217014 |
| 15 | CSR column | G | 0.302507 | CSR column | G | 0.18826 |
| 16 | CSR vision | G | 0.297468 | Environmentally beneficial products | G | 0.182068 |
| 17 | Measures to reduce the three wastes | E | 0.297438 | Safety management system | E | 0.170876 |
| 18 | Environmental recognition | E | 0.24509 | CSR vision | E | 0.169513 |
| 19 | Employment generation | G | 0.223482 | Environmental certification | G | 0.164461 |
| 20 | Environmentally beneficial products | E | 0.209439 | No female executives | E | 0.158087 |
| 21 | Employee benefits | S | 0.198984 | Supporting education | S | 0.154673 |
| 22 | Supporting education | G | 0.158466 | Strategy shared | G | 0.148178 |
| 23 | Boost the local economy | G | 0.153876 | Safety training | G | 0.14809 |
| 24 | Safety training | S | 0.135864 | Supporting charity | S | 0.130331 |
| 25 | Strategy shared | S | 0.122036 | Employee participation (stock ownership) | S | 0.127808 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Lee, M. Unraveling the Drivers of ESG Performance in Chinese Firms: An Explainable Machine-Learning Approach. Systems 2025, 13, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070578
Kim H, Lee M. Unraveling the Drivers of ESG Performance in Chinese Firms: An Explainable Machine-Learning Approach. Systems. 2025; 13(7):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070578
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyojin, and Myounggu Lee. 2025. "Unraveling the Drivers of ESG Performance in Chinese Firms: An Explainable Machine-Learning Approach" Systems 13, no. 7: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070578
APA StyleKim, H., & Lee, M. (2025). Unraveling the Drivers of ESG Performance in Chinese Firms: An Explainable Machine-Learning Approach. Systems, 13(7), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070578






