How Big Data Analytics Capability Promotes Green Radical Innovation? The Effect of Corporate Environment Ethics in Digital Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
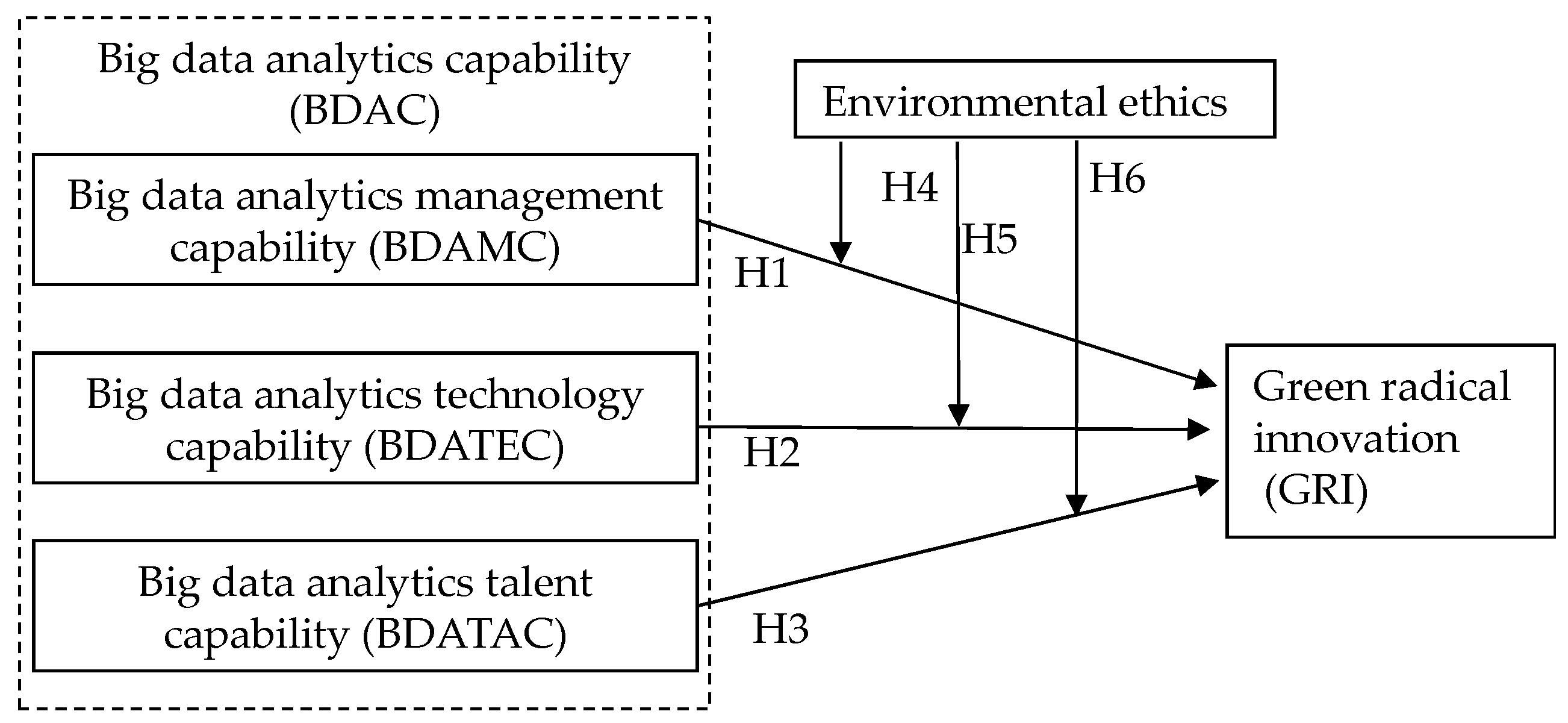
2. Theoretical Background and Hypothesis
2.1. Big Data Analytics Capabilities (BDACs) and Green Radical Innovation (GRI)
2.1.1. Big Data Analytics Management Capability (BDAMC) and GRI
2.1.2. Big Data Analytics Technology Capability (BDATEC) and GRI
2.1.3. Big Data Analytics Talent Capability (BDATAC) and GRI
2.2. The Moderating Effect of Environment Ethics
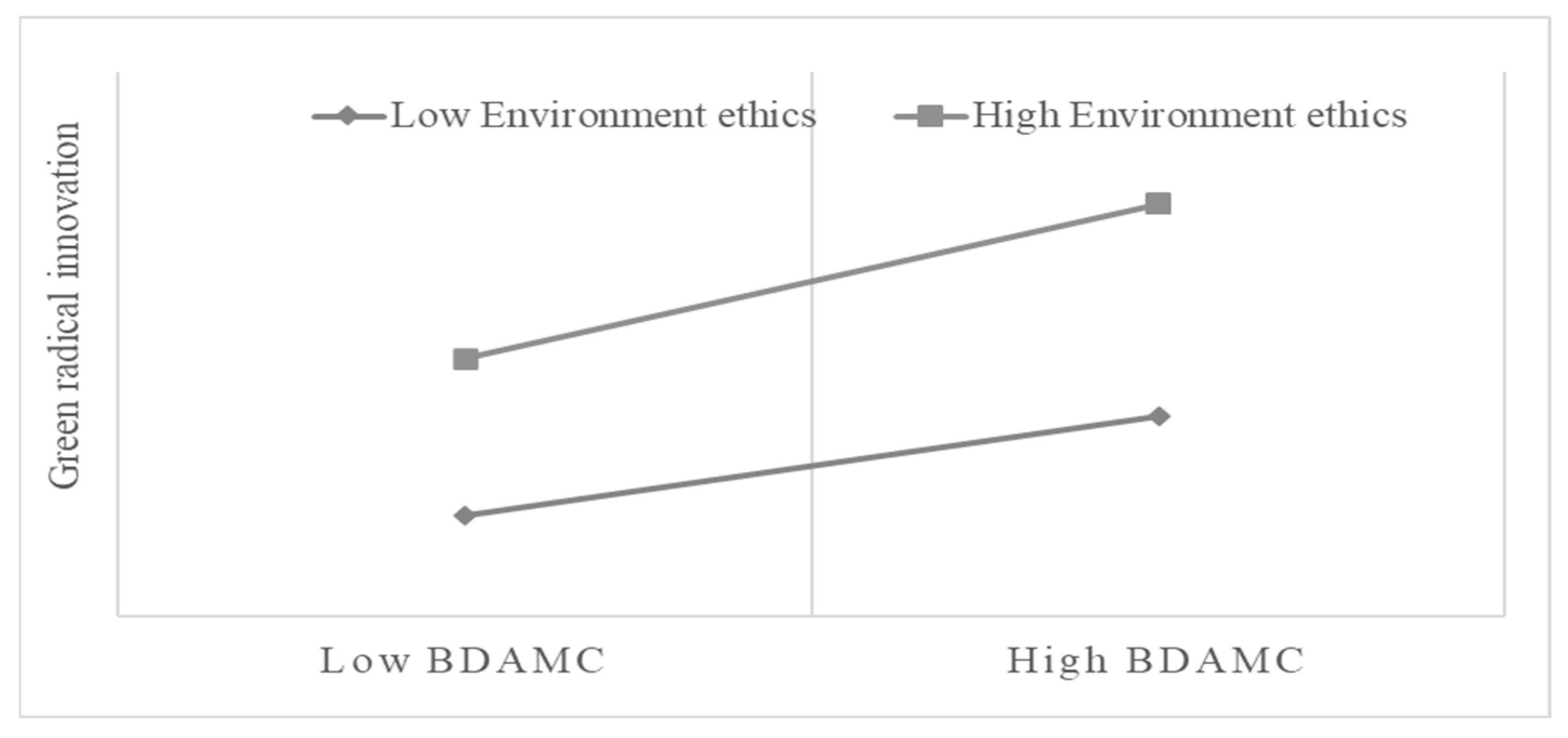
2.2.1. The Moderating Effect of Environmental Ethics on the Relationship Between Big Data Analytics Management Capability (BDAMC) and GRI
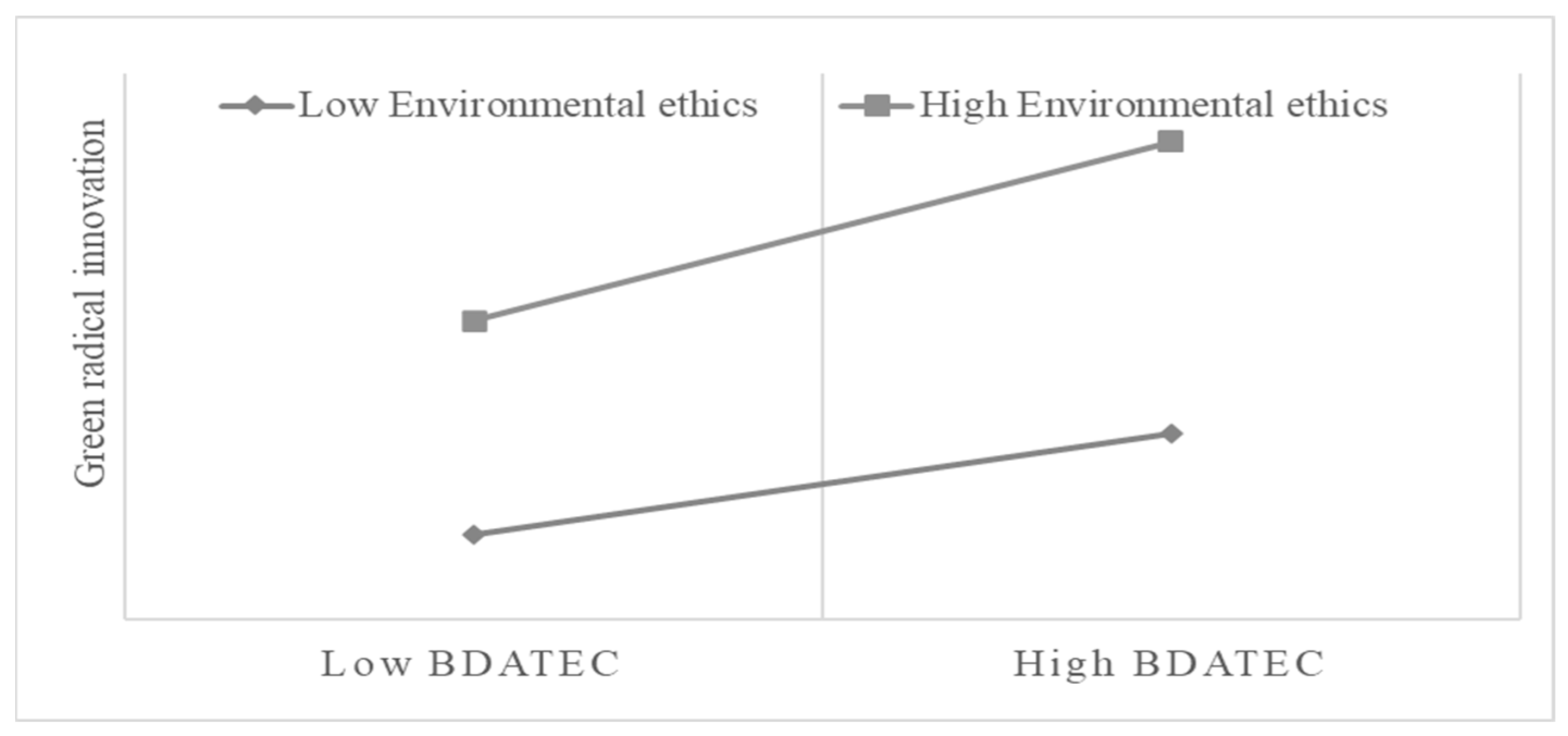
2.2.2. The Moderating Effect of Environmental Ethics on the Relationship Between Big Data Analytics Technology Capability (BDATEC) and GRI
2.2.3. The Moderating Effect of Environmental Ethics on the Relationship Between Big Data Analytics Talent Capability (BDATAC) and GRI
3. Methods
3.1. Research Setting and Data Collection
3.2. Measurement Scales
3.3. Validity and Reliability Testing
3.4. Common Method DeviationTest
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics Results
4.2. Hypotheses Results
4.3. Post-Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Theorical Contribution
5.2. Management Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDA | Big data analytics |
| BDAC | Big data analytics capabilities |
| BDAMC | Big data analytics management capability |
| BDATEC | Big data analytics technology capability |
| BDATAC | Big data analytics talent capability |
| GRI | Green radical innovation |
References
- Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zan, A.; Carayannis, E.G. How Does Coopetition Affect Radical Innovation? The Roles of Internal Knowledge Structure and External Knowledge Integration. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2021, 36, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genin, A.; Ma, W.; Bhagwat, V.; Bernile, G. Board Experiential Diversity and Corporate Radical Innovation. Strateg. Manag. J. 2023, 44, 2634–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, A.W. Can Big Data Analytics Capabilities Promote a Competitive Advantage? Green Radical Innovation, Green Incremental Innovation and Data-Driven Culture in a Moderated Mediation Model. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2022, 28, 1025–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-H. The Determinants of Green Radical and Incremental Innovation Performance: Green Shared Vision, Green Absorptive Capacity, and Green Organizational Ambidexterity. Sustainability 2014, 6, 7787–7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, B.; Halman, J.I.M.; Boes, J.; Voordijk, H.; Dorée, A.G. Procurement and Innovation Risk Management: How a Public Client Managed to Realize a Radical Green Innovation in a Civil Engineering Project. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2022, 28, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, S.F.; Mohr, J.J.; Sengupta, S. Radical Product Innovation Capability: Literature Review, Synthesis, and Illustrative Research Propositions. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2014, 31, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fu, Y.; Sun, X. Green Innovation Efficiency and Multiple Paths of Urban Sustainable Development in China: Multi-Configuration Analysis Based on Urban Innovation Ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, M.U.; Zhang, J.; Le, P.B. Role of Collaborative Culture and Knowledge Management Process for Stimulating Radical and Incremental Innovation: A Comparative Moderation Approach. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2021, 27, 2021–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y. Assessing the Impact of Big Data Analytics Capability on Radical Innovation: Is Business Intelligence Always a Path? J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2024, 35, 1010–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Thurasamy, R. Bridging Big Data Analytics Capability and Competitive Advantage in China’s Agribusiness: The Mediator of Absorptive Capacity. Systems 2025, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Research on the Mechanism of the Role of Big Data Analytic Capabilities on the Growth Performance of Start-up Enterprises: The Mediating Role of Entrepreneurial Opportunity Recognition and Exploitation. Systems 2023, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. How to Improve Firm Performance Using Big Data Analytics Capability and Business Strategy Alignment? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, F.; Demi, S.; Magrini, A.; Marzi, G.; Papa, A. Exploring the Impact of Big Data Analytics Capabilities on Business Model Innovation: The Mediating Role of Entrepreneurial Orientation. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Pan, S. Big Data Analytics Capability and Social Innovation: The Mediating Role of Knowledge Exploration and Exploitation. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, S.H.; Hussain, W.M.H.W.; Khan, J.; Sultan, S.; Ferraris, A. Exploring Data-Driven Innovation: What’s Missing in the Relationship between Big Data Analytics Capabilities and Supply Chain Innovation? Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 333, 799–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Qadir, A.; Ahmad, W.; Rafique, M. Enhancing Organizational Sustainable Innovation Performance through Organizational Readiness for Big Data Analytics. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Khatib, A.W. The Impact of Big Data Analytics Capabilities on Green Supply Chain Performance: Is Green Supply Chain Innovation the Missing Link? Bus. Process Manag. J. 2023, 29, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Jabeen, F.; Rashid, M.; Alshibani, S.M.; Lanteri, A.; Santoro, G. Unraveling the Transformation: The Three-Wave Time-Lagged Study on Big Data Analytics, Green Innovation and Their Impact on Economic and Environmental Performance in Manufacturing SMEs. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Cheng, X. Research on the Impact of Enterprise Big Data Analytics Capability on Ambidextrous Innovation Capability—The Mediating Effect of Agility. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 36, 2242–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. Big Data Analytics Capabilities and Innovation: The Mediating Role of Dynamic Capabilities and Moderating Effect of the Environment. Br. J. Manag. 2019, 30, 272–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. The Role of Information Governance in Big Data Analytics Driven Innovation. Inf. Manag. 2020, 57, 103361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, S. How and When Does Big Data Analytics Capability Boost Innovation Performance? Sustainability 2023, 15, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalef, P.; Krogstie, J. Examining the Interplay between Big Data Analytics and Contextual Factors in Driving Process Innovation Capabilities. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2020, 29, 260–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Honggang, X.; Ahmad, N.; Khan, S.A.R.; Iqbal, M. Big Data Analytics as a Roadmap towards Green Innovation, Competitive Advantage and Environmental Performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 323, 128998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, J.G. Pragmatic Sustainability: Translating Environmental Ethics into Competitive Advantage. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 85, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W. Turning Corporate Environmental Ethics into Firm Performance: The Role of Green Marketing Programs. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2019, 28, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Chen, J.; Del Giudice, M.; El-Kassar, A.-N. Environmental Ethics, Environmental Performance, and Competitive Advantage: Role of Environmental Training. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 146, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federica, L. Big Data, Big Waste? A Reflection on the Environmental Sustainability of Big Data Initiatives. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2020, 26, 1009–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mél, H. Big Data Ecologies. Ephemer. Theory Polit. Organ. 2018, 18, 631–657. [Google Scholar]
- Ardito, L.; Raby, S.; Albino, V.; Bertoldi, B. The Duality of Digital and Environmental Orientations in the Context of SMEs: Implications for Innovation Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Despeisse, M.; Johansson, B. Environmental Sustainability of Digitalization in Manufacturing: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Zhu, Q.S. Digitalization and the Greening of Supply Chains. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 121, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.B.; Ketchen, D.J., Jr.; Wright, M. Resource-Based Theory and the Value Creation Framework. J. Manag. 2021, 47, 1936–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.S. A Resource-Based Perspective on Information Technology Capability and Firm Performance: An Empirical Investigation. MIS Q. 2000, 24, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Motamarri, S.; Hani, U.; Shams, R.; Fernando, M.; Mohiuddin Babu, M.; Ning Shen, K. Building Dynamic Service Analytics Capabilities for the Digital Marketplace. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 118, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidgen, R.; Shaw, S.; Grant, D.B. Management Challenges in Creating Value from Business Analytics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 261, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.M.; Herhausen, D.; Troilo, G.; Rossi, A. How and When Do Big Data Investments Pay off? The Role of Marketing Affordances and Service Innovation. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 790–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.J.; Wamba, S.F.; Akter, S.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. Modelling Quality Dynamics, Business Value and Firm Performance in a Big Data Analytics Environment. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 5011–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Dubey, R.; Wamba, S.F.; Childe, S.J.; Hazen, B.; Akter, S. Big Data and Predictive Analytics for Supply Chain and Organizational Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Drave, V.A.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Ismagilova, E. Achieving Superior Organizational Performance via Big Data Predictive Analytics: A Dynamic Capability View. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 90, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Blome, C.; Papadopoulos, T. Big Data and Predictive Analytics and Manufacturing Performance: Integrating Institutional Theory, Resource-Based View and Big Data Culture. Br. J. Manag. 2019, 30, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, A.; Mazzoleni, A.; Devalle, A.; Couturier, J. Big Data Analytics Capabilities and Knowledge Management: Impact on Firm Performance. Manag. Decis. 2019, 57, 1923–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte-Real, N.; Ruivo, P.; Oliveira, T. Leveraging Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics Initiatives in European and American Firms: Is Data Quality a Way to Extract Business Value? Inf. Manag. 2020, 57, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, U.; Shamim, S.; Khan, Z.; Zia, N.U.; Shariq, S.M.; Khan, M.N. Big Data Analytics Capability and Decision-Making: The Role of Data-Driven Insight on Circular Economy Performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 168, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, M.; Tatoglu, E.; Kilic, H.S.; Zaim, S.; Delen, D. Big Data Analytics Capabilities and Firm Performance: An Integrated MCDM Approach. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 114, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Wu, K.; Gao, L.; Shang, H. Intellectual Property Protection as Catalyst for Radical Technological Innovation in National Research Program Teams through Innovation Milieu and Group Potentials. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, F.; Marzi, G.; Demi, S.; Faraoni, M. The Big Data-Business Strategy Interconnection: A Grand Challenge for Knowledge Management. A Review and Future Perspectives. J. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 24, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côrte-Real, N.; Oliveira, T.; Ruivo, P. Assessing Business Value of Big Data Analytics in European Firms. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremel, C.; Herterich, M.; Wulf, J.; Waizmann, J.; Brenner, W. How AUDI AG Established Big Data Analytics in Its Digital Transformation. MIS Q. Exec. 2017, 16, 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- LaValle, S.; Lesser, E.; Shockley, R.; Hopkins, M.S.; Kruschwitz, N. Big Data, Analytics and the Path from Insights to Value. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2010, 52, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Byrd, T.A. Big Data Analytics: Understanding Its Capabilities and Potential Benefits for Healthcare Organizations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2018, 126, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.; Raguseo, E.; Solazzo, G.; Pigni, F. Strategic Business Value from Big Data Analytics: An Empirical Analysis of the Mediating Effects of Value Creation Mechanisms. Inf. Manag. 2022, 59, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. How Does Corporate Social Responsibility Contribute to Innovation Performance? The Moderating Role of Social Media Strategic Capability and Big Data Analytics Capability. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2023, 28, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, M.H.; Chang, V.; Batool, A.; Wah, T.Y. Big Data Reduction Framework for Value Creation in Sustainable Enterprises. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-H. The Influence of Corporate Environmental Ethics on Competitive Advantage: The Mediation Role of Green Innovation. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 104, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q. Do Corporate Environmental Ethics Influence Firms’ Green Practice? The Mediating Role of Green Innovation and the Moderating Role of Personal Ties. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 122054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Abbass, K.; Li, D. Advancing Eco-Excellence: Integrating Stakeholders’ Pressures, Environmental Awareness, and Ethics for Green Innovation and Performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, J.; Abid, N.; Sarwar, H.; Veneziani, M. Environmental Ethics, Green Innovation, and Sustainable Performance: Exploring the Role of Environmental Leadership and Environmental Strategy. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ma, Y.; Fan, X.; Peng, X. Corporate Environmental Ethics and Employee’s Green Creativity? The Perspective of Environmental Commitment. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023, 30, 1856–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, S.; Marabelli, M. Strategic Opportunities (and Challenges) of Algorithmic Decision-Making: A Call for Action on the Long-Term Societal Effects of ‘Datification’. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2015, 24, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, A.; Zare, J. Beyond Technological Capabilities: The Mediating Effects of Analytics Culture and Absorptive Capacity on Big Data Analytics Value Creation in Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 7147–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graafland, J. Competition in Technology and Innovation, Motivation Crowding, and Environmental Policy. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Ashfaq, M.; Asiaei, K.; Shahzad, K. Green Intellectual Capital and Green Business Strategy: The Role of Green Absorptive Capacity. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 4907–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack-Polay, D.; Rahman, M.; Billah, M.M.; Al-Sabbahy, H.Z. Big Data Analytics and Sustainable Textile Manufacturing: Decision-Making about the Applications of Biotechnologies in Developing Countries. Manag. Decis. 2020, 58, 1699–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Wu, S.; Funk, R.J. Regulation and Innovation Revisited: How Restrictive Environments Can Promote Destabilizing New Technologies. Organ. Sci. 2024, 36, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, S.; Chen, J. Bridging Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow: Ceo Temporal Focus, Environmental Dynamism, and Rate of New Product Introduction. Acad. Manag. J. 2014, 57, 1810–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, R.; Chadee, D.; Best, P. Managing Change toward Environmental Sustainability: A Conceptual Model in Small and Medium Enterprises. Organ. Environ. 2018, 31, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, A.W.; Valeri, M. Can Intellectual Capital Promote the Competitive Advantage? Service Innovation and Big Data Analytics Capabilities in a Moderated Mediation Model. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2022, 27, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, J. The Deconcentration of Major Suppliers and Corporate Green Innovation in the Context of Knowledge Diffusion: Moderating Effects of Trust and Human Capital Quality. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 11758–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etse, D.; McMurray, A.; Muenjohn, N. The Effect of Regulation on Sustainable Procurement: Organisational Leadership and Culture as Mediators. J. Bus. Ethics 2022, 177, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassar, A.-N.; Singh, S.K. Green Innovation and Organizational Performance: The Influence of Big Data and the Moderating Role of Management Commitment and HR Practices. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Waris, I.; Bhutto, M.Y. Understanding the Nexus among Big Data Analytics Capabilities, Green Dynamic Capabilities, Supply Chain Agility and Green Competitive Advantage: The Moderating Effect of Supply Chain Innovativeness. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2024, 35, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rialti, R.; Zollo, L.; Ferraris, A.; Alon, I. Big Data Analytics Capabilities and Performance: Evidence from a Moderated Multi-Mediation Model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 149, 119781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C. Data-Driven Supply Chain Orientation and Innovation: The Role of Capabilities and Information Complexity. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Kiani, A.; Rashid, M. Is Data the Key to Sustainability? The Roles of Big Data Analytics, Green Innovation, and Organizational Identity in Gaining Green Competitive Advantage. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2023, 37, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, M.; Madan, R.; Joha, A.; Sivarajah, U. Ethical Framework for Artificial Intelligence and Digital Technologies. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2022, 62, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinenko, V.; Bowbrick, I.; Naumov, I.; Zaitseva, Z. Global Guidelines and Requirements for Professional Competencies of Natural Resource Extraction Engineers: Implications for ESG Principles and Sustainable Development Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Demosthenes, P. Real-World Data: A Brief Review of the Methods, Applications, Challenges and Opportunities. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2022, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.; Mendes, G.; Ayala, N.; Ghezzi, A. Servitization and Industry 4.0 Convergence in the Digital Transformation of Product Firms: A Business Model Innovation Perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 141, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguseo, E. Big Data Technologies: An Empirical Investigation on Their Adoption, Benefits and Risks for Companies. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 38, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinings, B.; Gegenhuber, T.; Greenwood, R. Digital Innovation and Transformation: An Institutional Perspective. Inf. Organ. 2018, 28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G. Understanding Digital Transformation: A Review and a Research Agenda. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2019, 28, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Development of Green Business Strategies through Green Dynamic Capabilities and Environmental Regulation: Empirical Evidence from the Construction Sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 438, 140826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Category | Frequency | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Respondent Position | Chairman/general manager and executives | 65 | 22.34 |
| Department manager | 73 | 25.09 | |
| Big data business supervisor | 153 | 52.58 | |
| Firm Age | Less than 1 year | 2 | 0.69 |
| 1–5 years | 27 | 9.28 | |
| 5–10 years | 63 | 21.65 | |
| 10–15 years | 59 | 20.27 | |
| More than 15 years | 140 | 48.11 | |
| Firm Size | 300 employees or less | 138 | 47.42 |
| 301–1000 employees | 42 | 14.43 | |
| 1001–2000 employees | 35 | 12.03 | |
| 2001–5000 employees | 28 | 9.62 | |
| More than 500 employees | 48 | 16.49 | |
| Firm Nature | Sino-foreign joint venture enterprises | 53 | 18.21 |
| State-owned and collective enterprises | 98 | 33.68 | |
| Foreign enterprises | 8 | 2.75 | |
| Private enterprises | 132 | 45.36 | |
| Firm Geographic Location | Eastern region | 184 | 63.23 |
| Central region | 51 | 17.53 | |
| Western region | 56 | 19.24 |
| Variable | Items | Loadings |
|---|---|---|
| BDAMC [9,12] | 1. Our firm strategically uses big data analytics to identify innovation opportunities. | 0.857 |
| 2. Our firm has made adequate preparations to utilize and introduce big data analytics capabilities. | 0.535 | |
| 3. Our firm formalizes and systematizes the big data analytics planning process. | 0.812 | |
| 4. Our firm frequently adjusts its big data analytics plans to better adapt to changes. | 0.507 | |
| 5. When making investment decisions in big data analytics, our firm considers and estimates its impact on employee productivity. | 0.825 | |
| 6. When making investment decisions in big data analytics, our firm considers and predicts whether these investments will significantly enhance user decision-making efficiency. | 0.818 | |
| 7. When making investment decisions in big data analytics, our firm estimates the additional training costs incurred by users due to this decision. | 0.860 | |
| 8. When making investment decisions in big data analytics, our firm predicts how much time managers will need to supervise this change. | 0.598 | |
| 9. Business analysts and frontline employees frequently meet formally and informally to discuss important issues. | 0.819 | |
| 10. Business analysts and frontline employees often participate in cross-functional meetings. | 0.892 | |
| 11. Analysts and frontline staff can work harmoniously together. | 0.901 | |
| 12. Consensus is reached between business analysts and frontline personnel, facilitating the sharing of ideas for managers and executors to utilize available knowledge. | 0.883 | |
| 13. In our firm, responsibilities for the development of big data analytics are clearly defined. | 0.907 | |
| 14. Our firm is confident in the appropriate evaluation of big data analytics project proposals. | 0.911 | |
| 15. Our firm continuously monitors the effectiveness of its big data analytics capabilities. | 0.568 | |
| 16. The analytics department is clear about its performance standards. | 0.871 | |
| BDATEC [9,12] | 1. Our firm possesses the best big data analytics systems compared to competitors. | 0.837 |
| 2. All remote, branch, and mobile offices are connected to the central office for analysis. | 0.898 | |
| 3. Our firm utilizes open system network mechanisms to enhance analytical connectivity. | 0.874 | |
| 4. In analytical discussions, our firm perceives no identifiable communication bottlenecks internally. | 0.623 | |
| 5. Software applications can be easily transferred and processed across multiple analytical platforms. | 0.927 | |
| 6. The user interface provides transparent access to all platforms and applications. | 0.833 | |
| 7. Analytically driven information is comprehensively shared within our firm. | 0.705 | |
| 8. Our firm provides numerous analytical interfaces or information entry points for external users. | 0.702 | |
| 9. Reusable software modules are widely utilized in the development of new analytical models. | 0.880 | |
| 10. End-users can create their own analytical applications using object-oriented tools. | 0.892 | |
| 11. Our firm employs object-oriented techniques to reduce development time when creating new analytical applications. | 0.845 | |
| 12. The applicability of applications meets various needs during analytical tasks. | 0.504 | |
| BDATAC [9,12] | 1. Our firm′s analysts possess high technical skills in coding. | 0.791 |
| 2. Our firm′s analysts are highly capable in managing the entire project lifecycle. | 0.859 | |
| 3. Our firm′s analysts are very skilled in data and network management and maintenance. | 0.704 | |
| 4. The decision-support systems established by our firm′s analysts are highly efficient. | 0.800 | |
| 5. Our firm′s analysts have a profound understanding of technological trends. | 0.535 | |
| 6. Our firm′s analysts demonstrate strong learning abilities for new technologies. | 0.848 | |
| 7. Our firm′s analysts are well aware of the key factors for organizational success. | 0.840 | |
| 8. Our firm′s analysts clearly understand that big data analytics is viewed as a tool. | 0.848 | |
| 9. Our firm′s analysts have a deep understanding of organizational policies and plans. | 0.791 | |
| 10. Our firm′s analysts can adeptly interpret business issues and develop appropriate technological solutions. | 0.520 | |
| 11. Our firm′s analysts have a strong understanding of business functions. | 0.827 | |
| 12. Our firm′s analysts are well-informed about the business environment. | 0.863 | |
| 13. Our firm′s analysts excel in planning, organizing, and leading projects. | 0.870 | |
| 14. Our firm′s analysts are adept at planning and conducting work in a collaborative environment. | 0.572 | |
| 15. Our firm′s analysts possess strong teaching abilities. | 0.891 | |
| 16. Our firm′s analysts maintain close contact with clients and establish good customer relationships. | 0.862 | |
| Environmental Ethics [55,59] | 1. Our firm has clear and specific environmental policies. | 0.781 |
| 2. Our firm′s budget planning includes considerations for environmental investments or procurement. | 0.903 | |
| 3. Our firm integrates its environmental planning, vision, or mission into its marketing activities. | 0.738 | |
| 4. Our firm incorporates its environmental planning, vision, or mission into its corporate culture. | 0.902 | |
| GRI [3,5] | 1. Our firm develops a new generation of eco-friendly innovations in its products and services. | 0.918 |
| 2. Our firm is implementing significant organizational changes to align with its focus on green innovations. | 0.789 | |
| 3. Our firm is also interested in offering unprecedented experiences in green technology. | 0.912 | |
| 4. Our firm emphasizes new radical environmental thought. | 0.814 | |
| 5. Our firm establishes innovative green distribution channels. | 0.962 |
| Variables | KMO | Alpha | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDAMC | 0.890 | 0.853 | 0.964 | 0.636 |
| BDATEC | 0.900 | 0.842 | 0.955 | 0.645 |
| BDATAC | 0.917 | 0.875 | 0.962 | 0.617 |
| Environmental ethics | 0.857 | 0.789 | 0.901 | 0.696 |
| GRI | 0.853 | 0.769 | 0.945 | 0.777 |
| Fit | χ2/df | RMSEA | SRMR | CFI | TLI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Single-factor model | BDAMC + BDATEC + BDATAC + EE + GRI | 1.446 | 0.039 | 0.043 | 0.903 | 0.899 |
| 2 | Two-factor model | BDAMC + BDATEC + BDATAC + EE; GRI | 1.423 | 0.038 | 0.043 | 0.908 | 0.905 |
| 3 | Three-factor model | BDAMC + BDATEC + BDATAC; EE; GRI | 1.415 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.91 | 0.906 |
| 4 | Four-factor model | BDAMC + BDATEC; BDATAC; EE; GRI | 1.411 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.911 | 0.907 |
| 5 | Five-factor model | BDAMC; BDATEC; BDATAC; EE; GRI | 1.410 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.912 | 0.907 |
| Criteria | <5 | <0.08 | <0.08 | >0.9 | >0.9 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 2 | 0.605 *** | 1 | 3.96 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.616 *** | 0.825 *** | 1 | 4.33 | |||||
| 4 | 0.632 *** | 0.824 *** | 0.837 *** | 1 | 4.34 | ||||
| 5 | 0.493 *** | 0.603 *** | 0.619 *** | 0.627 *** | 1 | 1.76 | |||
| 6 | 0.098 * | 0.120 ** | 0.035 | 0.110 * | 0.044 | 1 | 1.41 | ||
| 7 | 0.076 | 0.082 | 0.026 | 0.09 | 0.009 | 0.303 *** | 1 | 1.11 | |
| 8 | −0.155 *** | −0.124 ** | −0.142 ** | −0.144 ** | −0.131 ** | 0.442 *** | 0.131 ** | 1 | 1.31 |
| Mean | 3.348 | 3.318 | 3.258 | 3.316 | 3.369 | 2.333 | 3.732 | 2.789 | 4.058 |
| S.D. | 0.727 | 0.622 | 0.674 | 0.658 | 0.741 | 1.537 | 0.904 | 0.892 | 1.064 |
| Variables | Model Base | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDAMC | H1 | 0.212 ** | 0.192 * | 0.192 * | 0.197 * | 0.192 * | |
| (1.997) | (1.816) | (1.827) | (1.861) | (1.827) | |||
| BDATEC | H2 | 0.231 ** | 0.215 ** | 0.229 ** | 0.210 ** | 0.237 ** | |
| (2.305) | (2.139) | (2.292) | (2.095) | (2.353) | |||
| BDATAC | H3 | 0.279 *** | 0.250 ** | 0.235 ** | 0.252 ** | 0.221 ** | |
| (2.644) | (2.361) | (2.234) | (2.392) | (2.091) | |||
| BDAMC × Environmental ethics | H4 | 0.105 * | −0.155 | ||||
| (1.665) | (−1.140) | ||||||
| BDATEC × Environmental ethics | H5 | 0.151 *** | 0.296 ** | ||||
| (2.724) | (2.204) | ||||||
| BDATAC × Environmental ethics | H6 | 0.120 ** | −0.031 | ||||
| (2.076) | (−0.220) | ||||||
| Environmental ethics | 0.094 | 0.100 * | 0.095 | 0.114 * | |||
| (1.588) | (1.716) | (1.611) | (1.920) | ||||
| R&D | 0.009 | 0.018 | 0.026 | 0.025 | 0.026 | 0.024 | |
| (0.184) | (0.415) | (0.609) | (0.596) | (0.619) | (0.569) | ||
| Firm age | −0.100 ** | −0.064 * | −0.058 | −0.051 | −0.057 | −0.048 | |
| (−2.376) | (−1.789) | (−1.628) | (−1.441) | (−1.595) | (−1.346) | ||
| Firm size | 0.074 ** | 0.040 | 0.042 | 0.040 | 0.040 | 0.036 | |
| (2.471) | (1.551) | (1.632) | (1.560) | (1.565) | (1.400) | ||
| Firm nature | 0.039 | 0.051 ** | 0.045 * | 0.043 * | 0.044 * | 0.044 * | |
| (1.333) | (2.030) | (1.825) | (1.728) | (1.782) | (1.782) | ||
| Is high-tech firm | 0.257 ** | −0.011 | 0.009 | 0.025 | 0.008 | 0.021 | |
| (2.429) | (−0.119) | (0.099) | (0.267) | (0.084) | (0.224) | ||
| Industry type | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control | |
| Constant | 3.007 *** | 0.879 *** | 0.723 ** | 0.685 ** | 0.721 ** | 0.666 ** | |
| (10.143) | (2.718) | (2.190) | (2.089) | (2.188) | (2.026) | ||
| Observations | 291 | 291 | 291 | 291 | 291 | 291 | |
| Adj R-squared | 0.204 | 0.427 | 0.435 | 0.444 | 0.438 | 0.444 | |
| F | 7.745 | 16.44 | 14.96 | 15.50 | 15.13 | 13.87 |
| Coeff | t | p | [95% Conf. Interval] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| βBDAMC×Environmental ethics = βBDATEC×Environmental ethics | −0.450 | −1.98 | 0.048 | [−0.897, −0.003] |
| βBDAMC×Environmental ethics = βBDATAC×Environmental ethics | −0.124 | −0.55 | 0.590 | [−577, 0.329] |
| βBDATEC×Environmental ethics = βBDATAC×Environmental ethics | 0.326 | 1.35 | 0.178 | [−150, 0.802] |
| Hypothesis | Results |
|---|---|
| Direct effect H1: BDAMC→GRI | Supported |
| H2: BDATEC→GRI | Supported |
| H3: BDATAC→GRI | Supported |
| Moderating effect H4: Environmental ethics × BDAMC→GRI | Supported |
| H5: Environmental ethics × BDATEC→GRI | Supported |
| H6: Environmental ethics × BDATAC→GRI | Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Li, X.; Ruan, G. How Big Data Analytics Capability Promotes Green Radical Innovation? The Effect of Corporate Environment Ethics in Digital Era. Systems 2025, 13, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050370
Wu W, Li X, Ruan G. How Big Data Analytics Capability Promotes Green Radical Innovation? The Effect of Corporate Environment Ethics in Digital Era. Systems. 2025; 13(5):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050370
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Weiwei, Xue Li, and Guowei Ruan. 2025. "How Big Data Analytics Capability Promotes Green Radical Innovation? The Effect of Corporate Environment Ethics in Digital Era" Systems 13, no. 5: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050370
APA StyleWu, W., Li, X., & Ruan, G. (2025). How Big Data Analytics Capability Promotes Green Radical Innovation? The Effect of Corporate Environment Ethics in Digital Era. Systems, 13(5), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050370





