Integrating Stakeholder Knowledge Through a Participatory Approach and Semi-Quantitative Analysis for Local Watershed Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
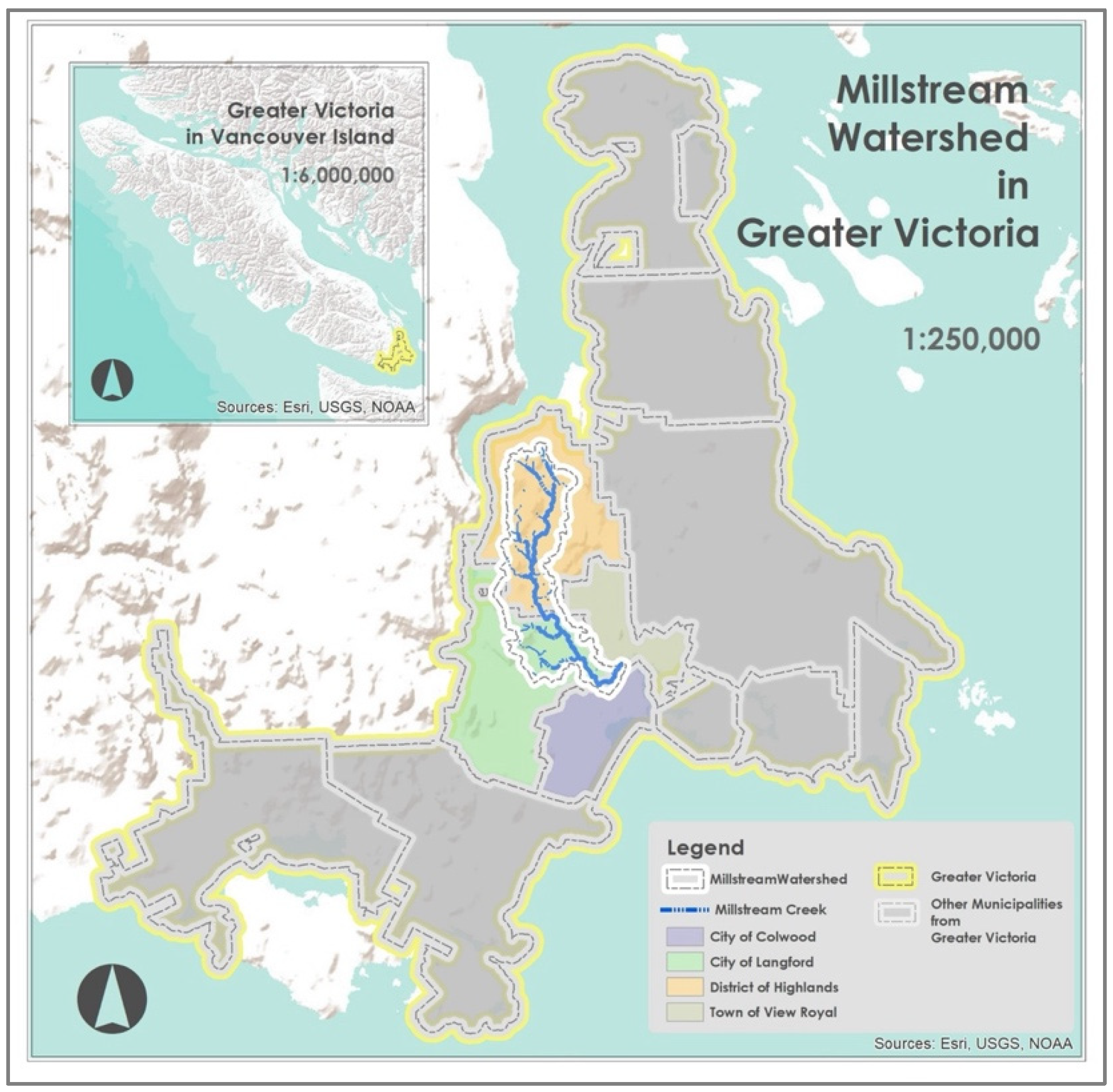
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Fuzzy Cognitive Map Development
2.3. Network and Scenario Analysis
3. Results
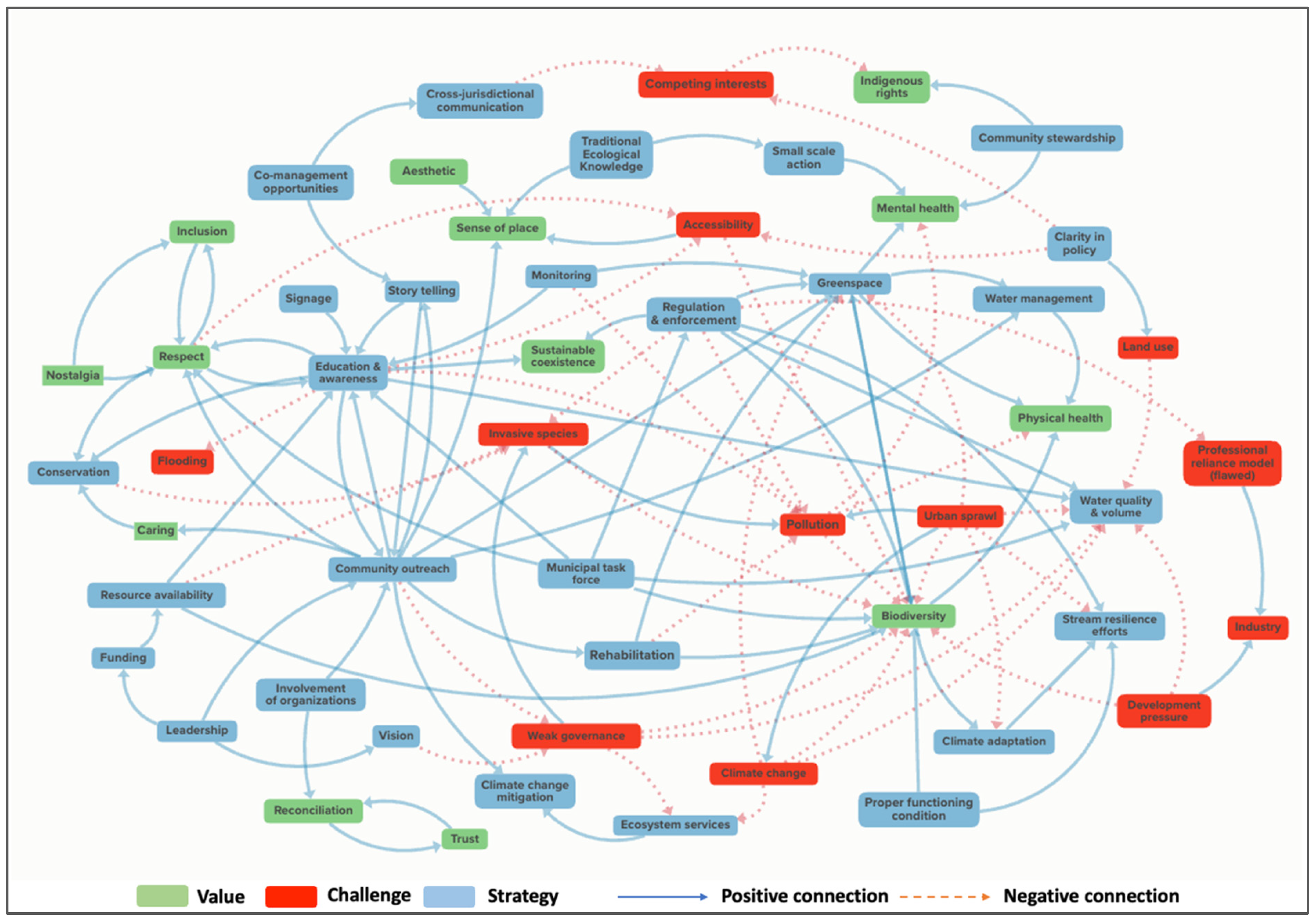
3.1. Systems Components
3.2. Systems Dynamics
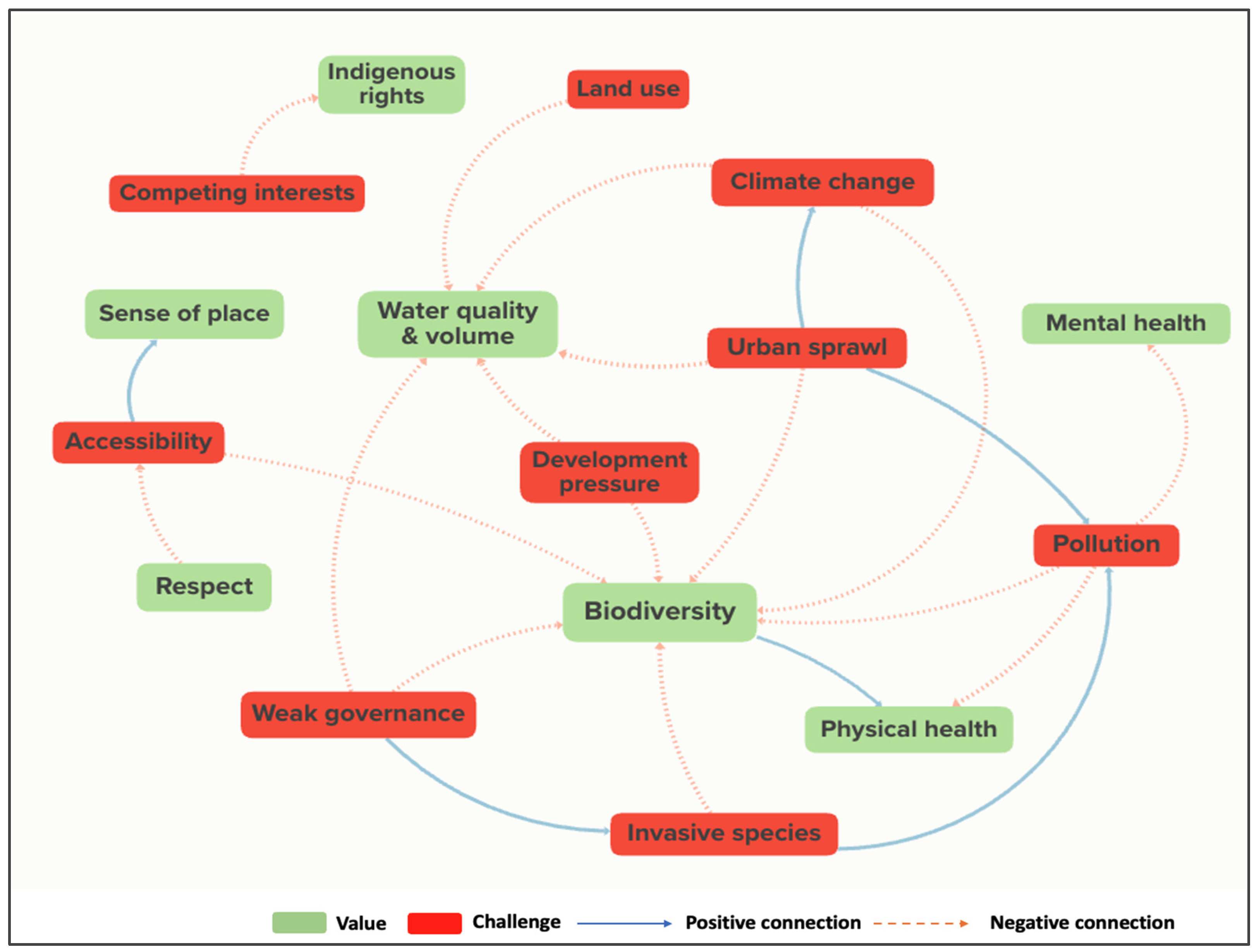
3.2.1. Challenges and Values
3.2.2. Strategies and Challenges
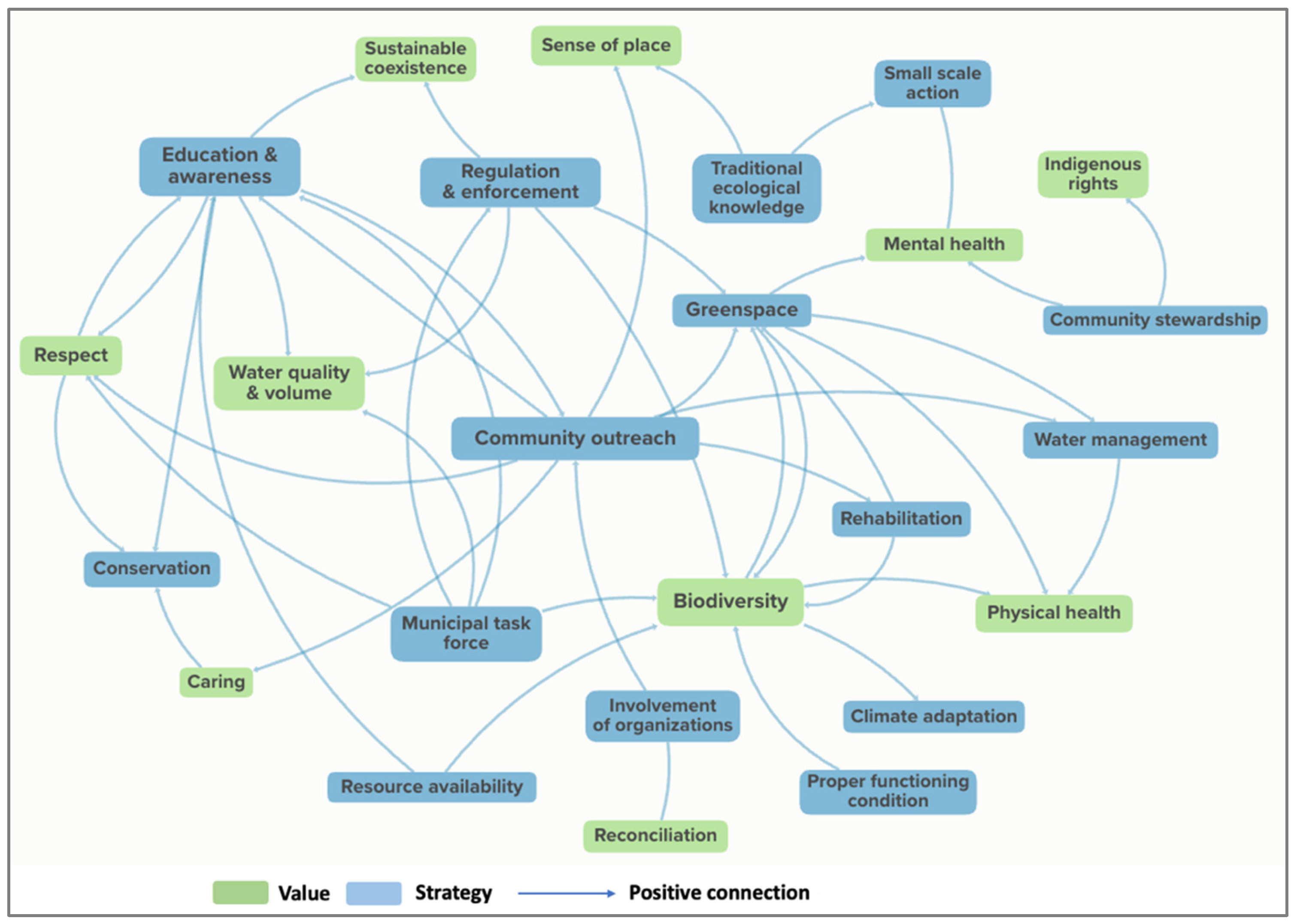
3.2.3. Strategies and Values
3.2.4. Values, Challenges and Strategies
3.3. Scenario Analysis
3.3.1. Engagement-Based Strategies (Community Outreach, Storytelling, Signage, Education)
3.3.2. Governance-Based Strategies (Co-Management, Municipal Task Force, Jurisdictional Communication, Enforcement)
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falkenmark, M. Water and human livelihood resilience: A regional-to-global outlook. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.J.; Benson, W.H. Sustainable Watersheds: Integrating Ecosystem Services and Public Health. Environ. Health Insights 2015, 9s2, EHI.S19586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, D.T. Watershed Ecosystem Goods and Services Sustaining Urban Socioecological Systems: Planning and Management Through Ecological Wisdom. In Ecological Wisdom; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Hallema, D.; Asbjornsen, H. Ecohydrological processes and ecosystservices in the Anthropocene: A review. Ecol. Process. 2017, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.J.; Vaughn, C.C.; Julian, J.P.; García-Llorente, M. Social Demand for Ecosystem Services and Implications for Watershed Management. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Yoneda, Y. Local Temperature Control in Greenhouse Vegetable Production. Hortic. J. 2019, 88, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, I.M. Analysis of the preservation of the watershed as well as the settings in the regulations. Int. J. Humanit. Educ. Soc. Sci. 2022, 1, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, E.; Randhir, T. Effect of climate change on watershed system: A regional analysis. Clim. Change 2008, 89, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Coffey, R.; Stamp, J.; Johnson, T. A Review of Water Quality Responses to Air Temperature and Precipitation Changes 1: Flow, Water Temperature, Saltwater Intrusion. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 55, 824–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, O.; Randhir, T. Spatial and temporal uncertainty in climatic impacts on watershed systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelnour, M.; Gitau, M.W.; Engel, B.A. A Comparison of Streamflow and Baseflow Responses to Land-Use Change and the Variation in Climate Parameters Using SWAT. Water 2020, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kamboj, N.; Kamboj, V. Factors affecting watershed ecosystem: A case study of Mohand Rao watershed in Uttarakhand, India. In Advances in Environmental Pollution Management: Wastewater Impacts and Treatment Technologies; Agro Environ Media—Agriculture and Ennvironmental Science Academy: Haridwar, India, 2020; pp. 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, R.; Hogan, T. Watersheds in watersheds: The fate of the planet’s major river systems in the Great Acceleration. Thesis Elev. 2019, 150, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N.E.; Meybeck, M. Water Quality Degradation Effects on Freshwater Availability: Impacts of Human Activities. Water Int. 2000, 25, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Chamani, R.; Silabi, M.Z.; Tavosi, M.; Katebikord, A.; Darvishan, A.K.; Moosavi, V.; Sadeghi, P.S.; Vafakhah, M.; Rekabdarkolaei, H.M. Watershed health and ecological security zoning throughout Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, M.W.; Morrison, K.E.; Bunch, M.J.; Hallström, L.K.; Neudoerffer, R.C.; Venema, H.D.; Waltner-Toews, D. Towards integrated governance for water, health and social–ecological systems: The watershed governance prism. Glob. Environ. Change 2010, 20, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlas, N.; Ramadan, B.S. Community-based watershed management (CBWM) for climate change adaptation and mitigation: Research trends, gaps, and factors assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Adesina, J.A. Integrated Watershed Management Framework and Groundwater Resources in Africa—A Review of West Africa Sub-Region. Water 2022, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Mang, S.; Cai, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Innes, J.L. Integrated watershed management: Evolution, development and emerging trends. J. For. Res. 2016, 27, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.P.; Sreedevi, T.K.; Reddy, T.S.V.; Venkateshvarlu, B.; Prasad, C.S. Community watersheds for improved livelihoods through consortium approach in drought prone rainfed areas. J. Hydrol. Res. Dev. 2008, 23, 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ffolliott, P.; Baker, M.B.; Edminster, C.; Dillon, M.C.; Mora, K.L. Land Stewardship Through Watershed Management: Perspectives for the 21st Century. 2002. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Land-stewardship-through-watershed-management%3A-for-Ffolliott-Baker/9eaea67d50f2a62712959e2a69b64b8cc2b423e5 (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Chandrakar, B.; Dewangan, N.P.; Verma, S.; Mishra, A. Empowering Community for River Basin Management. In Urban Hydrology, Watershed Management and Socio-Economic Aspects; Sarma, A.K., Singh, V.P., Kartha, S.A., Bhattacharjya, R.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolavalli, S.; Kerr, J. Scaling Up Participatory Watershed Development in India. Dev. Change 2022, 33, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiavi, A.N.; Vafakhah, M.; Sadeghi, S.H. Comparative applicability of MCDM-SWOT based techniques for developing integrated watershed management framework. Nat. Resour. Model. 2023, 36, e12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supangat, A.B.; Basuki, T.M.; Indrajaya, Y.; Setiawan, O.; Wahyuningrum, N.; Purwanto; Putra, P.B.; Savitri, E.; Indrawati, D.R.; Auliyani, D.; et al. Sustainable Management for Healthy and Productive Watersheds in Indonesia. Land 2023, 12, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worte, C. Integrated watershed management and Ontario’s conservation authorities. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 33, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrubsole, D.; Walters, D.; Veale, B.; Mitchell, B. Integrated Water Resources Management in Canada: The experience of watershed agencies. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, Y.; Kebede, B.; Kuma, T. Assessing the role of community participation in integrated watershed management in Dandi Lake watershed Dandi district, West Showa, Oromia, Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnychuk, N.; Jatel, N.; Sears, A.L.W. Integrated water resource management and British Columbia’s Okanagan Basin Water Board. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, B.H.; Siregar, C.A.; Dharmawan, I.W.S.; Sukmana, A.; Pratiwi; Pramono, I.B.; Basuki, T.M.; Nugroho, H.Y.S.H.; Supangat, A.B.; Purwanto; et al. A Review on Sustainability of Watershed Management in Indonesia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freebairn, L.; Atkinson, J.-A.; Kelly, P.M.; McDonnell, G.; Rychetnik, L. Decision makers’ experience of participatory dynamic simulation modelling: Methods for public health policy. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginger, C. Integrating knowledge, interests and values through modelling in participatory processes: Dimensions of legitimacy. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2014, 57, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T.; Partington, D.; Ticehurst, J.; Croke, B.F.W.; Jakeman, A.J. A socio-environmental model for exploring sustainable water management futures: Participatory and collaborative modelling in the Lower Campaspe catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 28, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor, G.B.; Palomo, I.; Santiago, C.A.L.; Oteros-Rozas, E.; Hill, J. Assessing stakeholders’ perceptions and values towards social-ecological systems using participatory methods. Ecol. Process. 2014, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, Q.H.; Chan, E.M.; Spangler, K.R.; Weinberger, K.R.; Lane, K.J.; Errett, N.A.; Hess, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Wellenius, G.A.; Nori-Sarma, A. Examining the Optimal Placement of Cooling Centers to Serve Populations at High Risk of Extreme Heat Exposure in 81 US Cities. Public Health Rep. 2023, 138, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.K.; Fisher, K.T.; Dickson, M.E.; Thrush, S.F.; Le Heron, R. Improving ecosystem service frameworks to address wicked problems. Ecol. Soc. 2015, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskrey, S.A.; Mount, N.J.; Thorne, C.R. Doing flood risk modelling differently: Evaluating the potential for participatory techniques to broaden flood risk management decision-making. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, R.; Castilla-Rho, J.; Bennison, G.; Bridgart, R.; Prats, C.; Claro, E. Participatory and Integrated Modelling under Contentious Water Use in Semiarid Basins. Hydrology 2022, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbrook-Johnson, P.; Penn, A. Participatory systems mapping for complex energy policy evaluation. Evaluation 2021, 27, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, G.; Miskolczi, P. Dynamics of participation: System dynamics and participation—An empirical review. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2019, 36, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quimby, B.; Beresford, M. Participatory Modeling: A Methodology for Engaging Stakeholder Knowledge and Participation in Social Science Research. Field Methods 2023, 35, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, J.B.; Berke, P.R. Urban Nexus Science for Future Cities: Focus on the Energy-Water-Food-X Nexus. Curr. Sustain. Energy Rep. 2017, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.V. Systems-thinking for environmental policy coherence: Stakeholder knowledge, fuzzy logic, and causal reasoning. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 136, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.A.; Gray, S.; De Kok, J.L.; Helfgott, A.E.R.; O’Dwyer, B.; Jordan, R.; Nyaki, A. Using fuzzy cognitive mapping as a participatory approach to analyze change, preferred states, and perceived resilience of social-ecological systems. Ecol. Soc. 2015, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliadou, A.; Santoro, F.; Nader, M.R.; Dagher, M.A.; Al Indary, S.; Salloum, B.A. Prioritising coastal zone management issues through fuzzy cognitive mapping approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 97, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluchinotta, I.; Esposito, D.; Camarda, D. Fuzzy cognitive mapping to support multi-agent decisions in development of urban policymaking. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olazabal, M.; Pascual, U. Use of fuzzy cognitive maps to study urban resilience and transformation. Environ. Innov. Soc. Transit. 2016, 18, 18–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotir, J.H.; Jagustovic, R.; Papachristos, G.; Zougmore, R.B.; Kessler, A.; Reynolds, M.; Ouedraogo, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Aziz, A.A.; Johnstone, R. Field experiences and lessons learned from applying participatory system dynamics modelling to sustainable water and agri-food systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, R.; Seidl, R.; Nickel, D.; Büttner, H. Global change impacts on the Upper Danube Catchment (Central Europe): A study of participatory modeling. Reg. Environ. Change 2015, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Newell, R.; Veerkamp, C.G.; Issac, J. Millstream Watershed Visualization Project: Identifying Watershed Issues, Values and Strategies Using Participatory Modelling and Participatory Mapping. ResearchGate. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/383305057_Millstream_Watershed_Visualization_Project_Identifying_watershed_issues_values_and_strategies_using_participatory_modelling_and_participatory_mapping (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Peninsula Streams Society. Available online: https://peninsulastreams.ca/ (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- The Land Conservancy of BC. Available online: https://conservancy.bc.ca/ (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Kok, K. The potential of Fuzzy Cognitive Maps for semi-quantitative scenario development, with an example from Brazil. Glob. Environ. Change 2009, 19, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, E.I.; Hatwágner, M.F.; Buruzs, A.; Kóczy, L.T. A concept reduction approach for fuzzy cognitive map models in decision making and management. Neurocomputing 2017, 232, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourhir, A. Scoping review of the potentials of fuzzy cognitive maps as a modeling approach for integrated environmental assessment and management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 135, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.A.; Gray, S.; Cox, L.J.; Henly-Shepard, S. Mental Modeler: A Fuzzy-Logic Cognitive Mapping Modeling Tool for Adaptive Environmental Management. In Proceedings of the 2013 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Wailea, HI, USA, 7–10 January 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, S.; Salmeron, J.L. Benchmarking main activation functions in fuzzy cognitive maps. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 5221–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasov, O.; Chervanyov, I. Intangible nature use: «informal sector» in environmental sciences. Ukr. Geogr. J. 2021, 2, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.A.; Dempster, F.L.; Hawkins, J.I.; Johnston, R.J.; Boxall, P.C.; Rolfe, J.; Kragt, M.E.; Burton, M.P.; Pannell, D.J. Valuing non-market economic impacts from natural hazards. Nat. Hazards 2019, 99, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riper, C.J.; Kyle, G.T. Capturing multiple values of ecosystem services shaped by environmental worldviews: A spatial analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, C.M.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Kabisch, N.; Berry, P.; Breil, M.; Nita, M.R.; Geneletti, D.; Calfapietra, C. A framework for assessing and implementing the co-benefits of nature-based solutions in urban areas. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 77, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.; Lawler, J.; Lowe, C.; Thompson, L.; Hinckley, T.; Kim, S.-H.; Bolton, S.; Meschke, S.; Olden, J.D.; Voss, J. Case studies in co-benefits approaches to climate change mitigation and adaptation. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2017, 60, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawska, A. The Role of Public Awareness Campaigns in Sustainable Development. Econ. Environ. Stud. 2017, 17, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelús, C.; Middendorf, G. Ecological literacy: The educational foundation necessary for informed public decision making. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 330–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cureg, M.C.; Bagunu, A.M.; van Weerd, M.; Balbas, M.G.; Soler, D.; van der Ploeg, J. A longitudinal evaluation of the Communication, Education and Public Awareness (CEPA) campaign for the Philippine crocodile Crocodylus mindorensis in northern Luzon, Philippines. Int. Zoo Yearb. 2016, 50, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, H.Y.S.H.; Sallata, M.K.; Allo, M.K.; Wahyuningrum, N.; Supangat, A.B.; Setiawan, O.; Njurumana, G.N.; Isnan, W.; Auliyani, D.; Ansari, F.; et al. Incorporating Traditional Knowledge into Science-Based Sociotechnical Measures in Upper Watershed Management: Theoretical Framework, Existing Practices and the Way Forward. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, F.; Caković, M.; Dragović, N.; Jovanović, N.; Rončević, V.; Živanović, N.; Zlatić, M. Current Trends and Future Perspectives of Integrated Watershed Management. S.-East Eur. For. 2024, 15, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeski, J.C.L.; Trindade, L.d.L. Lacunas de governança da água nas bacias hidrográficas da Vertente Atlântica do Estado de Santa Catarina. Eng. Sanit. E Ambient. 2023, 28, e20220231-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Issac, J.; Newell, R. Integrating Stakeholder Knowledge Through a Participatory Approach and Semi-Quantitative Analysis for Local Watershed Management. Systems 2025, 13, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050364
Issac J, Newell R. Integrating Stakeholder Knowledge Through a Participatory Approach and Semi-Quantitative Analysis for Local Watershed Management. Systems. 2025; 13(5):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050364
Chicago/Turabian StyleIssac, Jofri, and Robert Newell. 2025. "Integrating Stakeholder Knowledge Through a Participatory Approach and Semi-Quantitative Analysis for Local Watershed Management" Systems 13, no. 5: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050364
APA StyleIssac, J., & Newell, R. (2025). Integrating Stakeholder Knowledge Through a Participatory Approach and Semi-Quantitative Analysis for Local Watershed Management. Systems, 13(5), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050364





