Multidimensional Effectiveness Evaluation of Weapon System-of-Systems Based on Hypernetwork Under Communication Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A generalized multilayer network model that includes information relays is proposed, and based on combat characteristics, a directed multilayer network model is designed to construct a capability matrix for quantifying a WSoS. Unlike existing relay-less network models and adjacency-matrix quantification methods [11,13], under communication-constrained conditions, this approach integrates combat segment capability information by compensating for missing information relay relationships, thereby providing strong data support for networked effectiveness evaluation.
- (2)
- Considering time and probability constraints, a KC generation and analysis method is proposed. Based on this, an effectiveness-evaluation index framework for a WSoS is constructed from the two dimensions of mission tasks and network structure. It includes the effectiveness of both the red force’s (explained later) own structure and its execution of combat tasks. Unlike other methods [15,17,19], KCGA simultaneously considers the time and probability constraints of combat loops and individual combat segments, thereby simplifying the KC generation process. The resulting KC information is more accurate and complete, providing support for the networked effectiveness evaluation of the WSoS.
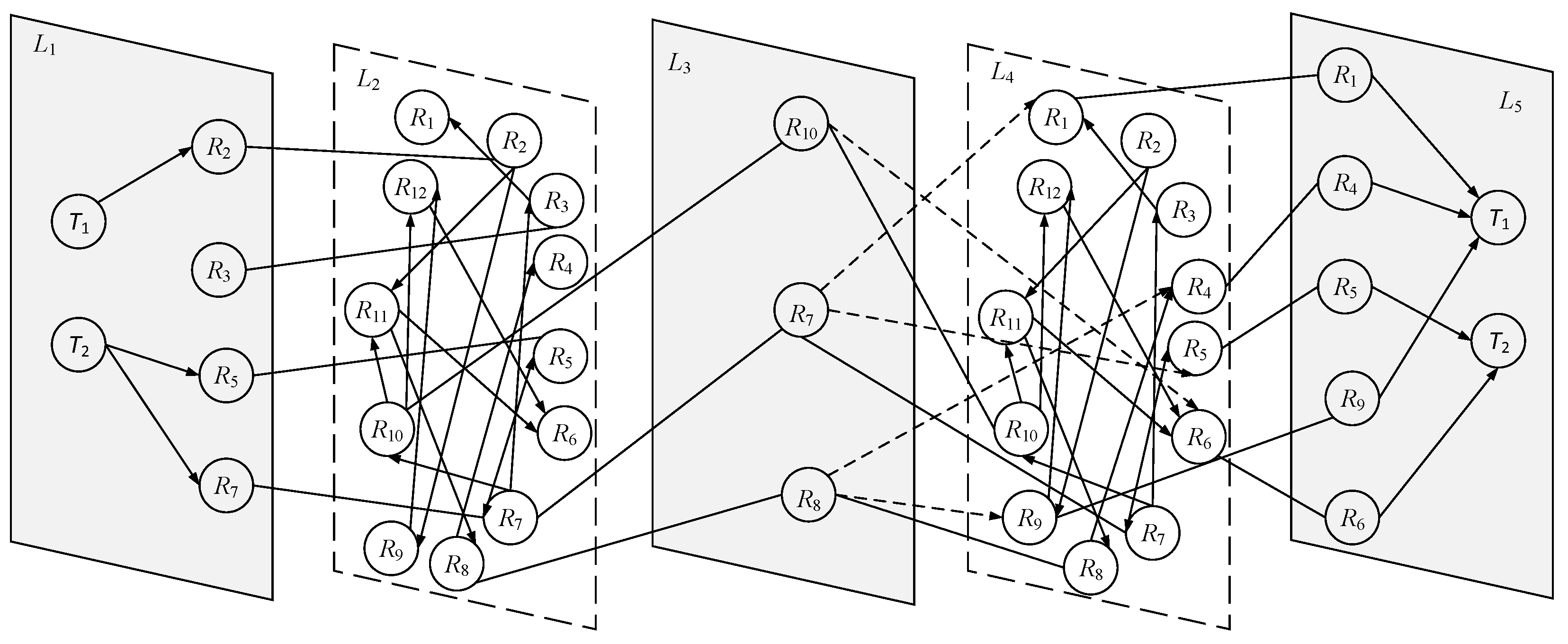
2. Construction of Networked Model for WSoS
2.1. Construction of Supernetwork Model with Information Relays
2.2. Construction of Directed Multilayer Network Model for WSoS
2.3. Directed Multilayer Network Model Capability Matrix Representation
2.3.1. Reconnaissance Layer
2.3.2. Relay Layers and
2.3.3. Command Layer
2.3.4. Strike Layer
3. Networked Effectiveness Evaluation Based on Kill Chains
3.1. Kill Chain and Constraint Construction
3.2. Constraint-Based Kill Chain Generation Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: KCGA |
 |
| Algorithm 2: RCGA |
 |
3.3. Construction of Multidimensional Performance Evaluation Index System
3.3.1. Mission Task Performance
- (1)
- The task completion time () represents the average time required for any of the KCs in the WSoS to successfully strike any enemy target; the smaller this value, the faster the average strike speed on a target. Suppose that there are N KCs for all targets and that target j, i.e., (where ), has KCs: . Then, we have , and is given aswhere represents the total closure time of the KCs for a single target , and represents the average time required to execute task by selecting any one of the KCs. Using the same method, the average task completion time for all targets can be calculated, and by taking the average of all targets, the average time required for selecting any KC to execute any task across all links is obtained.
- (2)
- The task completion probability () represents the average reliability with which any of the KCs in the WSoS can successfully strike any enemy target; the larger this value, the greater the probability of successfully striking a target. We havewhere represents the sum of the closure probabilities of the KCs for a single target , and represents the average reliability of completing task using any one of the KCs. Using the same method, the average reliability for all targets can be calculated, and by taking the average of all targets, the average reliability for selecting any KC to execute any task across all links is obtained.
- (3)
- The KC task matching degree (TMD) describes the matching relationship between the average quality of KCs assigned to each target and the importance of the target. If the target node being struck is considered more important and the probability of successfully striking the target is greater, then the KC TMD is higher; conversely, the TMD is lower. We havewhere represents the sum of the closure probabilities of all KCs assigned to target , and represents the sum of the closure probabilities of all KCs in the WSoS; the ratio of these two values gives the average quality of KCs assigned to the target. Meanwhile, represents the importance weight of target , and represents the sum of the importance weights of all targets in the WSoS; the ratio of these two values gives the average importance of target . The smaller the difference between these two values, the more balanced the KC allocation, and the higher the KC TMD for task . The average of all targets gives the overall average matching degree between the KC average quality and the target importance for all targets.
3.3.2. Network Structure Performance
- (1)
- Survivability. The risk of the WSoS represents mainly the impact on the entire kill web after a friendly node is attacked; the fewer the KCs lost by the targets when a friendly node is destroyed and unable to participate in the WSoS’s interaction, the lower the risk. We havewhere N represents the number of KCs before destruction, and represents the number of remaining KCs after equipment is destroyed; the difference between these two values is the number of KCs lost. Using the same method, the number of KCs lost after the destruction of all equipment can be calculated, and the average of these values gives the average number of KCs lost when a particular piece of equipment is destroyed in the supernetwork.
- (2)
- Redundancy. Given by , this characterizes mainly the degree of diversification of available strike means for a target in the WSoS, as given byThe specific evaluation approach is to calculate the average number N of KCs that can be formed by a multilayer network for m targets. The more KCs that there are, the stronger the redundancy; conversely, the fewer the KCs, the weaker the redundancy.
- (3)
- Communication efficiency. The network communication efficiency of the WSoS refers to the ability of various constituent systems within the operational system to seek, acquire, and provide information and services to other systems based on combat needs. The more elements in the communication adjacency matrix that have the value 1, the greater the communication efficiency. Therefore, the spectral norm can be chosen as the evaluation matrix norm for the connectivity matrix, as given byHere, represents the spectral norm when is a fully connected matrix (all elements are 1), and the ratio of these two values represents the degree of connectivity in the current state compared to the optimal connectivity state.
4. Experimental Study
4.1. Scenarios
4.2. Basic Experimental Results
4.3. Comparison of Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
DURC Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashraf, N. The paradox of cyber warfare and clausewitz’s conception of war. NUST J. Int. Peace Stab. 2025, 8, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.G.; Xia, Z.C.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhu, L.Q.; Dai, L.H.; Xu, R.T.; Sun, G.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Xu, W.T. Research on visual simulation for complex weapon equipment interoperability based on MBSE. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 13463–13482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, R.; Fu, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, P. Research on security authentication methods for unmanned aerial vehicle systems in mosaic warfare scenarios. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Guidance, Navigation and Control, Changsha, China, 9–11 August 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cui, C.; Zhong, J. Mission reliability modeling and evaluation for reconfigurable unmanned weapon system-of-systems based on effective operation loop. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 34, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R. J; Ning, G.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Li, M.H.; Li, J.C.; Yang, K.W.; Lou, Z.Y. CSoS-STRE: A combat system-of-system space-time resilience enhancement framework. Front. Eng. Manag. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Jiang, J. Research on the selection and application of weapons portfolio considering threats. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Big Data and Information Analytics (BigDIA), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 25–28 October 2024; pp. 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Sheng, M.; Zhao, N.; Tang, J.; Niyato, D.; Wong, K.-K. When UAV meets IRS: Expanding air-ground networks via passive reflection. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, N.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.A. Air-ground integrated sensing and communications: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2023, 61, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cares, J.R. An Information Age Combat Model; Alidade, Inc.: Newport, PR, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, A.H. Measuring the agility of networked military forces. J. Battlef. Technol. 2006, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, S.; Dou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, K. An approach for weapon system-of-systems scheme generation based on a supernetwork granular analysis. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 11, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Yin, S.Y.; Li, L.F.; Cui, W.W.; Hong, D.P. Resilience metric and dynamic assessment of unmanned system-of-systems considering cooperative reconfiguration strategies. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2024, 74, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y. Research on functional robustness of heterogeneous combat networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2018, 13, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, J. Research on disintegration of combat networks under incomplete information. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Melbourne, Australia, 17–20 October 2021; pp. 784–791. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K. Research on networked description and modeling methods of armament system-of-systems. J. Syst. Manag. 2012, 21, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Han, J. Distributed combat system of systems network modeling. J. Networks 2013, 8, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, T. Complex network-based resilience capability assessment for a combat system of systems. Systems 2024, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Pang, B.; Li, S.; Li, N.; Guo, P.; Fan, C.; Li, W. Evaluation method and optimization strategies of resilience for air & space defense system of systems based on kill network theory and improved self-information quantity. Def. Technol. 2023, 21, 219–239. [Google Scholar]
- Bundy, A.; Wallen, L. Breadth-first search. In Catalogue of Artificial Intelligence Tools; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, E.; Hatano, N.; Benzi, M. The physics of communicability in complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2012, 514, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, M. Algebraic connectivity of graphs. Czechoslov. Math. J. 1973, 23, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.; Killingback, T.; Sundaram, B.; Wang, Z. Attack robustness and centrality of complex networks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Barahona, M.; Tan, Y.-J.; Deng, H.-Z. Natural connectivity of complex networks. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2010, 27, 078902. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Barahona, M.; Tan, Y.-J.; Deng, H.-Z. Spectral measure of structural robustness in complex networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern.-A Syst. Humans 2011, 41, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, M.; Lamb, D.; Odat, E.; Taleb-Bendiab, A. Distributed redundancy and robustness in complex systems. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2011, 77, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Anderson, R. An experimental evaluation of robustness of networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2013, 7, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deller, S.; Rabadi, G.; Tolk, A.; Bowling, S.R. Organizing for improved effectiveness in networked operations. In Operations Research for Unmanned Systems; Cares, J.R., Dickmann, J.Q., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 255–270. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, T. Network-based metric for measuring combat effectiveness. Def. Sci. J. 2014, 64, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Xu, D.-L.; Chen, Y.-W. Weapon system capability assessment under uncertainty based on the evidential reasoning approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 13773–13784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, P.; Hu, T.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J. Research on invulnerability of combat net model based on complex networks. J. Syst. Simul. 2011, 23, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, X.; Pan, C. Hierarchical evolution model of command and control network based on hypernetwork. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 5860461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ge, B.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y. Meta-path based heterogeneous combat network link prediction. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 482, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shang, B.; Song, B.; Ke, E.; Wang, Y. Contribution evaluation of aviation armament sys-tem-of-systems based on operation loop. Acta Aeronaut. Et Astronaut. Sin. 2022, 43, 224958. [Google Scholar]



| Type | Name | Description | Entity Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | Target type node | Enemy combat entity | Anti damage; counter reconnaissance; threat |
| S | Reconnaissance type node | Our equipment with reconnaissance, surveillance, and other functions | Communication; reconnaissance; identification |
| C | Communication type node | Responsible for relaying and transmitting information | Communication |
| D | Command type node | Our command platforms, command posts, or command centers responsible for war command | Communication; information processing |
| I | Influence type node | A weapon platform or weapon system that causes damage or severe disruption to enemy targets | Communication; firepower strike |
| Indicator Type | Indicator Decomposition | Key Quantitative Parameters | Indicator Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network structure performance | Survivability | N | Number of KCs |
| Number of KCs after is destroyed | |||
| Redundancy | N | Number of KCs | |
| Communication efficiency | Adjacency matrix of relay layer | ||
| Mission task performance | Task kill chain matching degree | Closure probability of each kill chain | |
| Importance of each target | |||
| Task completion time | Closure time of each kill chain | ||
| Task completion probability | Closure probability of each kill chain |
| a Reconnaissance layer’s adjacency matrix | b Reconnaissance layer’s closure probability capability matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 0 | 0.92 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| c Reconnaissance layer’s closure time capability matrix | d Strike layer’s adjacency matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| null | 7 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | 8 | null | 9 | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| e Strike layer’s closure probability capability matrix | f Strike layer’s closure time capability matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.84 | 0 | 0 | 0.92 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | null | null | 35 | null | null | null | null | 51 | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | 28 | 42 | null | null | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| g Command layer’s adjacency matrix | h Command layer’s closure probability capability matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.82 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.87 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.94 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.92 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.98 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| i Command layer’s closure time capability matrix | j Relay layer’s adjacency matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| 8 | null | null | null | 7 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | 9 | null | null | null | null | 10 | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | 7 | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| k Relay layer’s closure probability capability matrix | l Relay layer’s closure time capability matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.84 | 0 | 0.82 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 8 | null | 5 | null | ||||||||
| 0.91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | null | 6 | null | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0.77 | 0 | 0.87 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.79 | 0 | 0 | null | null | 3 | null | 4 | null | null | null | null | 7 | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.84 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | 6 | null | null | null | null | 7 | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.89 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 4 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.92 | 0.78 | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | null | 10 | 8 | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | 11 | null | 9 | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.73 | 0 | 0.82 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | null | null | null | null | null | 8 | null | 8 | null | null | null | null | ||||||||
| Scenario | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Kill Chain | Time [s] | Probability | Kill Chain | Time [s] | Probability |
| →→→→ | 53 | 0.38 | ||||
| →→→→→→ | 91 | 0.37 | ||||
| →→→→ | 61 | 0.5 | →→→→→→ | 86 | 0.24 | |
| →→→→ | 79 | 0.5 | →→→→ | 48 | 0.55 | |
| →→→→→ | 86 | 0.53 | ||||
| →→→→→ | 81 | 0.34 | ||||
| II | →→→→→ | 71 | 0.5 | →→→→ | 53 | 0.38 |
| →→→→→→ | 91 | 0.37 | ||||
| →→→→→→ | 77 | 0.42 | →→→→→→ | 86 | 0.24 | |
| →→→→→ | 89 | 0.51 | →→→→ | 48 | 0.55 | |
| →→→→→→ | 95 | 0.43 | →→→→→ | 86 | 0.53 | |
| →→→→→ | 81 | 0.34 | ||||
| Scenario | Kill-Chain Count | Task Matching Degree | Task Completion Time | Task Completion Probability | Anti-Destructiveness | Agility | Communication Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 8 | 0.94 | 72.1 | 0.45 | 2.33 | 4 | 0.19 |
| II | 10 | 0.92 | 78.58 | 0.43 | 3.25 | 5 | 0.17 |
| Scenario | Kill Chain Count | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kill Chain Structure | Time [s] | Probability | Kill Chain Structure | Time [s] | Probability | |||
| [15] | I | 3 | →→→→ | 61 | 0.5 | →→→→ | 53 | 0.38 |
| →→→→ | 79 | 0.5 | ||||||
| II | 1 | ∅ | ∅ | ∅ | →→→→ | 53 | 0.38 | |
| [17] | I | 4 | /(2) | / | / | /(2) | / | / |
| II | 2 | /(0) | / | / | /(2) | / | / | |
| [19] | I | 14 | →→→→ | 53 | 0.38 | |||
| →→→→ | 61 | 0.5 | →→→→ →→ | 91 | 0.37 | |||
| →→→→ →→ | 77 | 0.42 | →→→→ →→→→→ | 108 | 0.2 | |||
| →→→→ → | 71 | 0.5 | →→→→ →→ | 86 | 0.24 | |||
| →→→→ | 79 | 0.5 | →→→→ | 48 | 0.55 | |||
| →→→→ →→ | 95 | 0.43 | →→→→ → | 86 | 0.53 | |||
| →→→→ → | 89 | 0.51 | →→→→ →→→→ | 103 | 0.29 | |||
| →→→→ → | 81 | 0.34 | ||||||
| II | 12 | →→→→ | 53 | 0.38 | ||||
| →→→→ →→ | 91 | 0.37 | ||||||
| →→→→ →→ | 77 | 0.42 | →→→→ →→→→→ | 108 | 0.2 | |||
| →→→→ → | 71 | 0.5 | →→→→ →→ | 86 | 0.24 | |||
| →→→→ →→ | 95 | 0.43 | →→→→ | 48 | 0.55 | |||
| →→→→ → | 89 | 0.51 | →→→→ → | 86 | 0.53 | |||
| →→→→ →→→→ | 103 | 0.29 | ||||||
| →→→→ → | 81 | 0.34 | ||||||
| Scenario | Kill Chain Count | Task Matching Degree | Task Completion Time | Task Completion Probability | Anti-Destructiveness | Agility | Communication Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCGA | I | 8 | 0.94 | 72.1 | 0.45 | 2.33 | 4 | 0.19 |
| II | 10 | 0.92 | 78.58 | 0.43 | 3.25 | 5 | 0.17 | |
| [15] | I | 3 | 0.63 | 61.5 | 0.44 | 0.67 | 1.5 | 0.19 |
| II | 1 | 0.65 | null | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.5 | 0.17 | |
| [17] | I | 4 | / | / | / | 0.83 | 2 | 0.19 |
| II | 2 | / | / | / | 0.33 | 1 | 0.17 | |
| [19] | I | 14 | 0.85 | 80.3 | 0.42 | 5 | 7 | 0.19 |
| II | 12 | 0.96 | 82.5 | 0.41 | 4.5 | 6 | 0.17 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Song, S. Multidimensional Effectiveness Evaluation of Weapon System-of-Systems Based on Hypernetwork Under Communication Constraints. Systems 2025, 13, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100928
Wang N, Zhang Y, Song S. Multidimensional Effectiveness Evaluation of Weapon System-of-Systems Based on Hypernetwork Under Communication Constraints. Systems. 2025; 13(10):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100928
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ningning, Yuchen Zhang, and Shenmin Song. 2025. "Multidimensional Effectiveness Evaluation of Weapon System-of-Systems Based on Hypernetwork Under Communication Constraints" Systems 13, no. 10: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100928
APA StyleWang, N., Zhang, Y., & Song, S. (2025). Multidimensional Effectiveness Evaluation of Weapon System-of-Systems Based on Hypernetwork Under Communication Constraints. Systems, 13(10), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100928







