Manufacturing Supply Chain Resilience Amid Global Value Chain Reconfiguration: An Enhanced Bibliometric–Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Framework
2.1. GVCs
2.2. SCR and MSCR
2.3. Linking Value Chains and Supply Chains
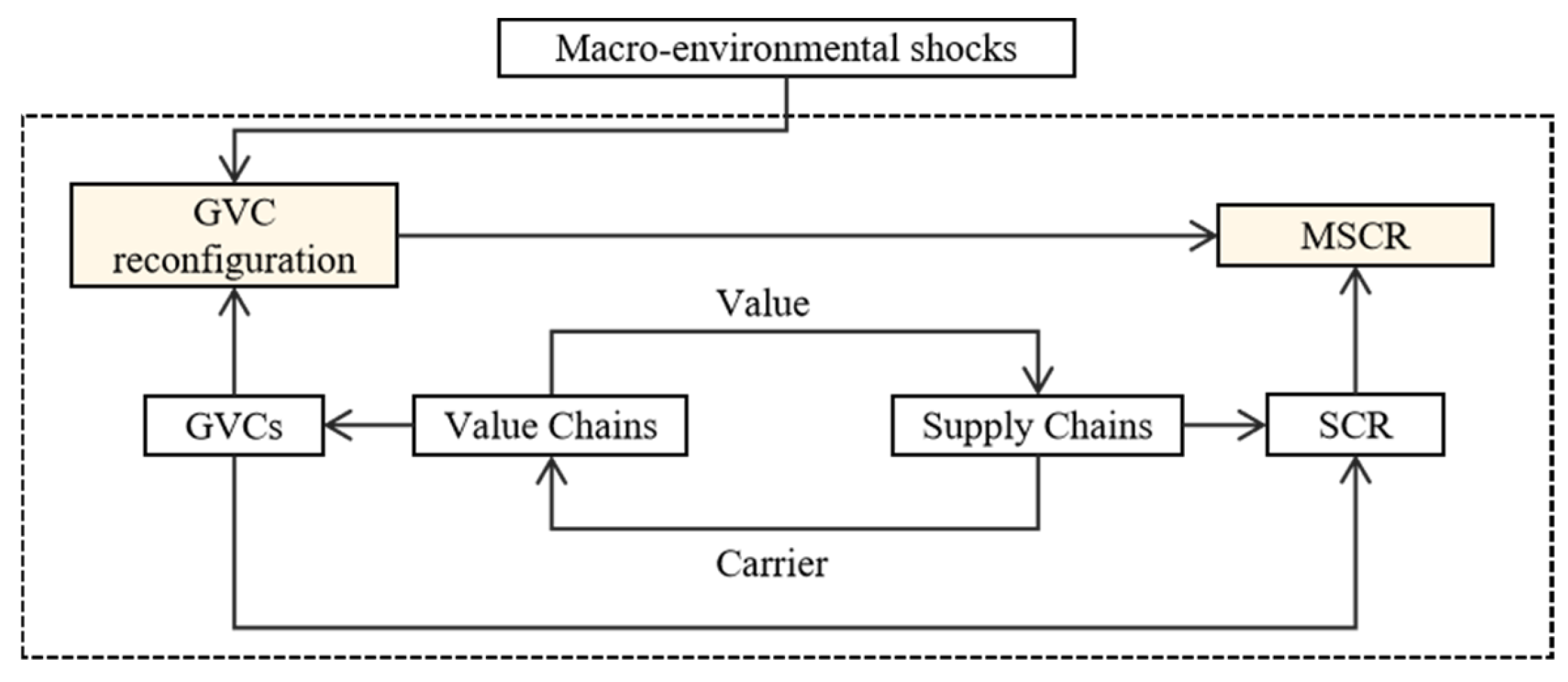
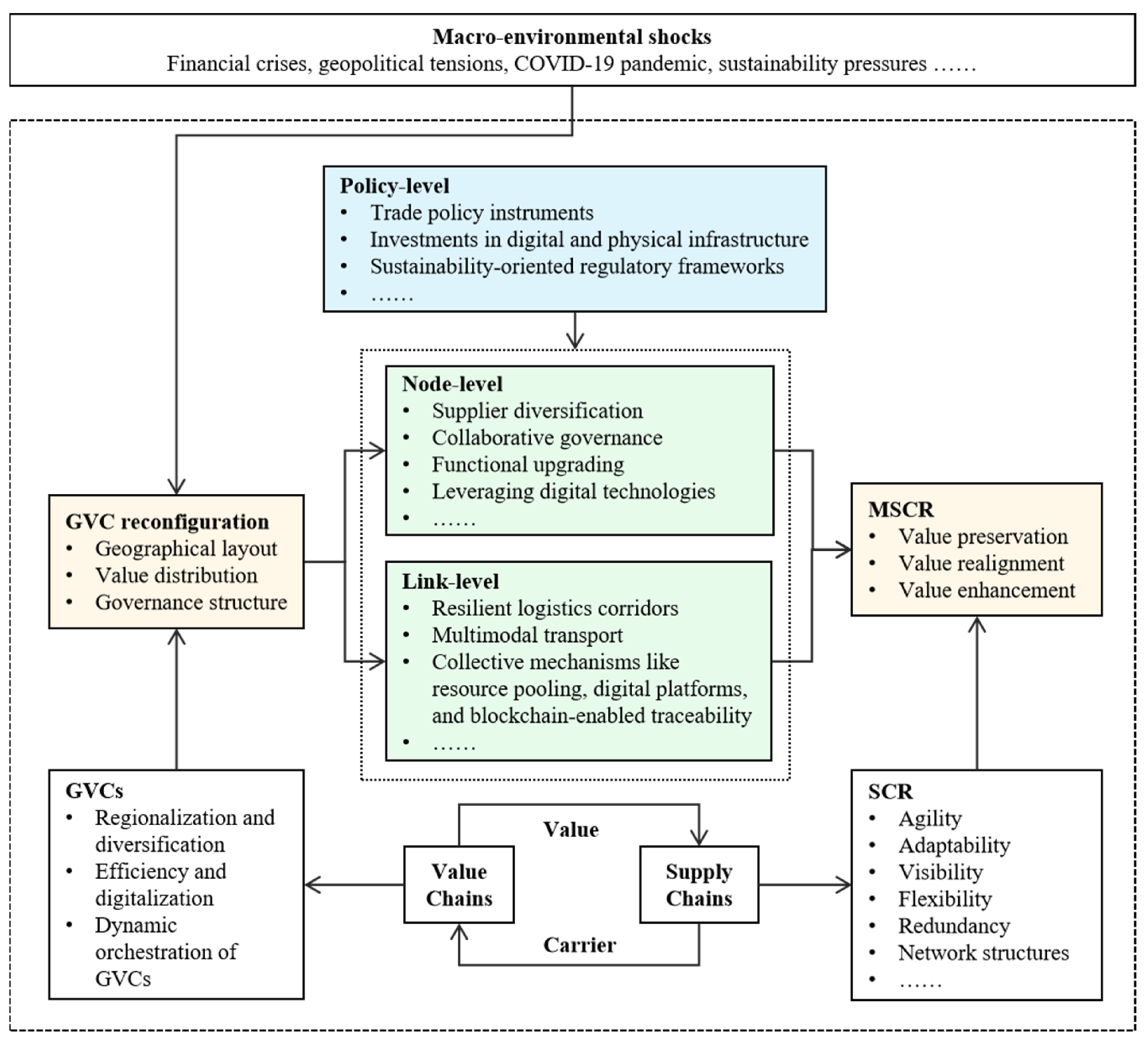
2.4. The MSCR Within the GVC Framework
3. Methodology
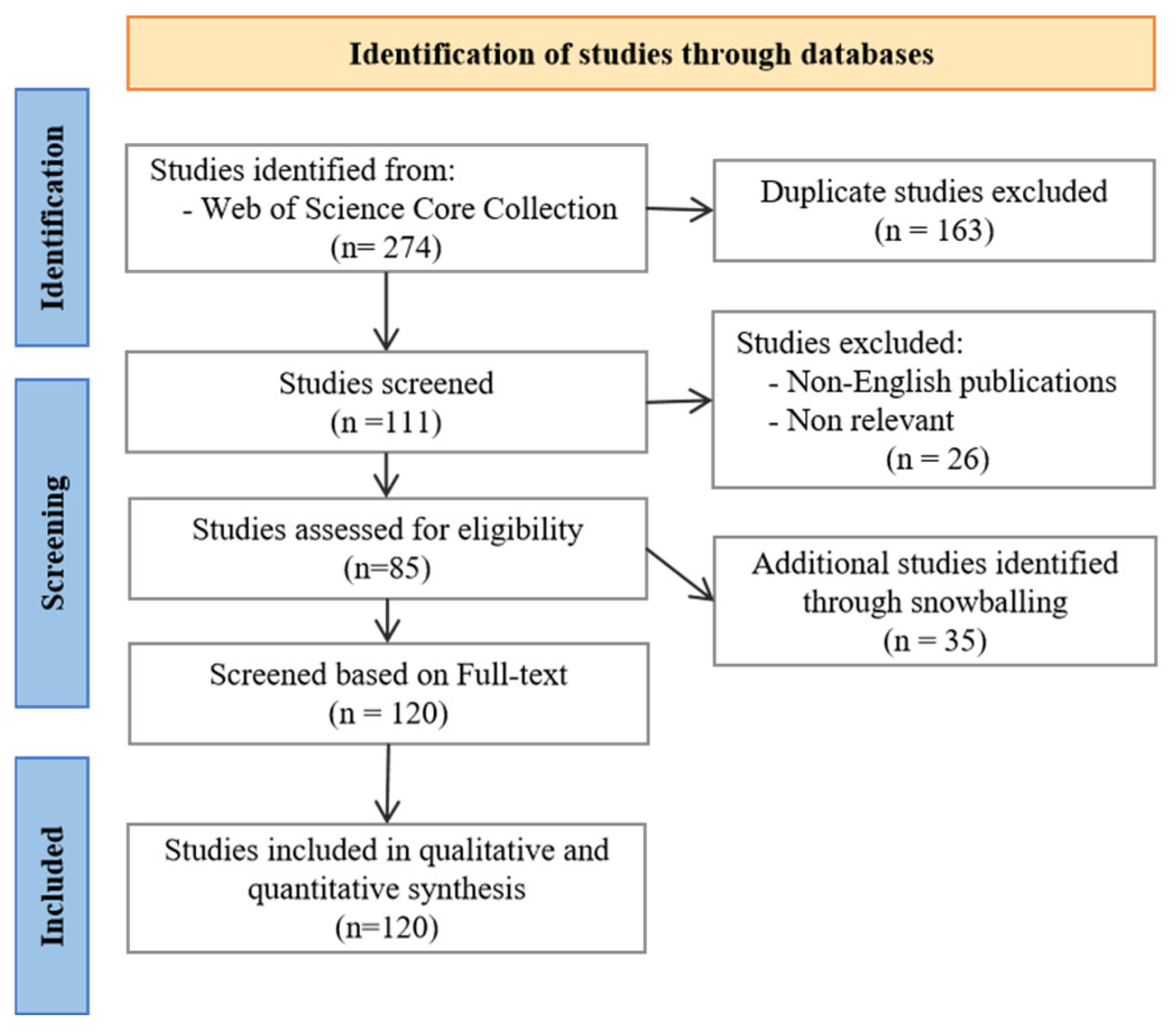
3.1. Planning Phase
3.2. Conducting Phase
3.3. Reporting Phase
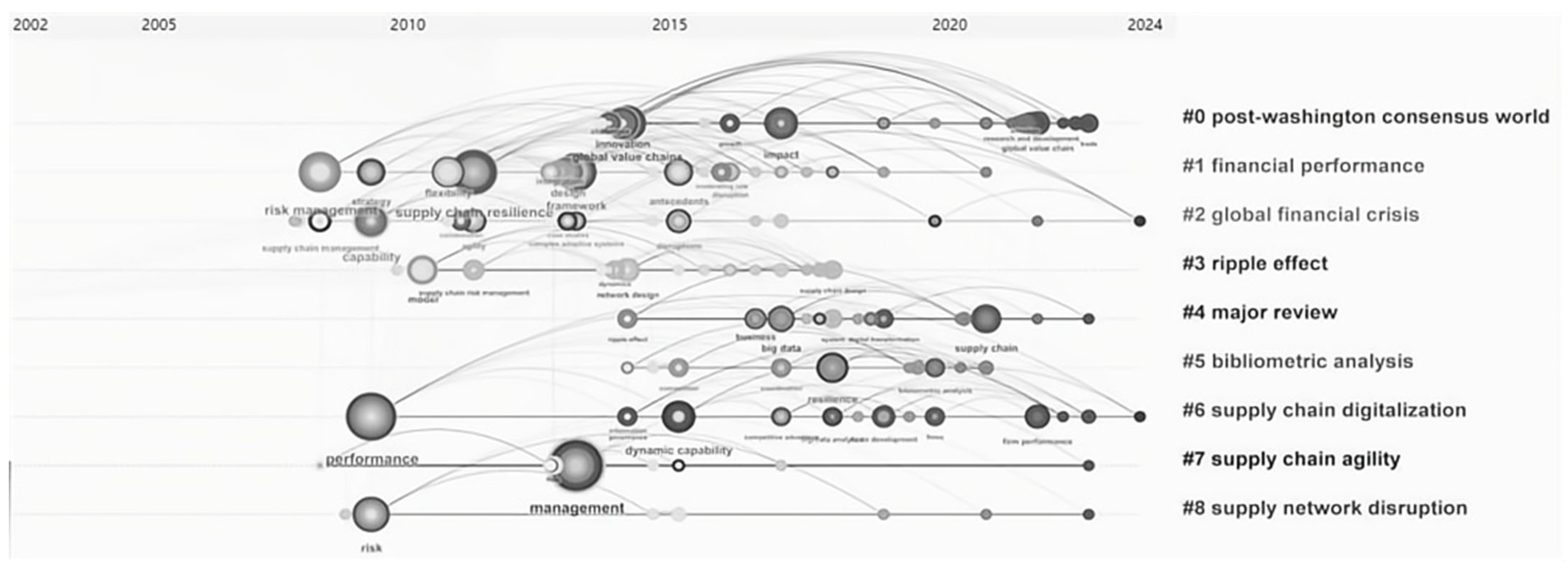
4. Results of the Bibliometric Analysis
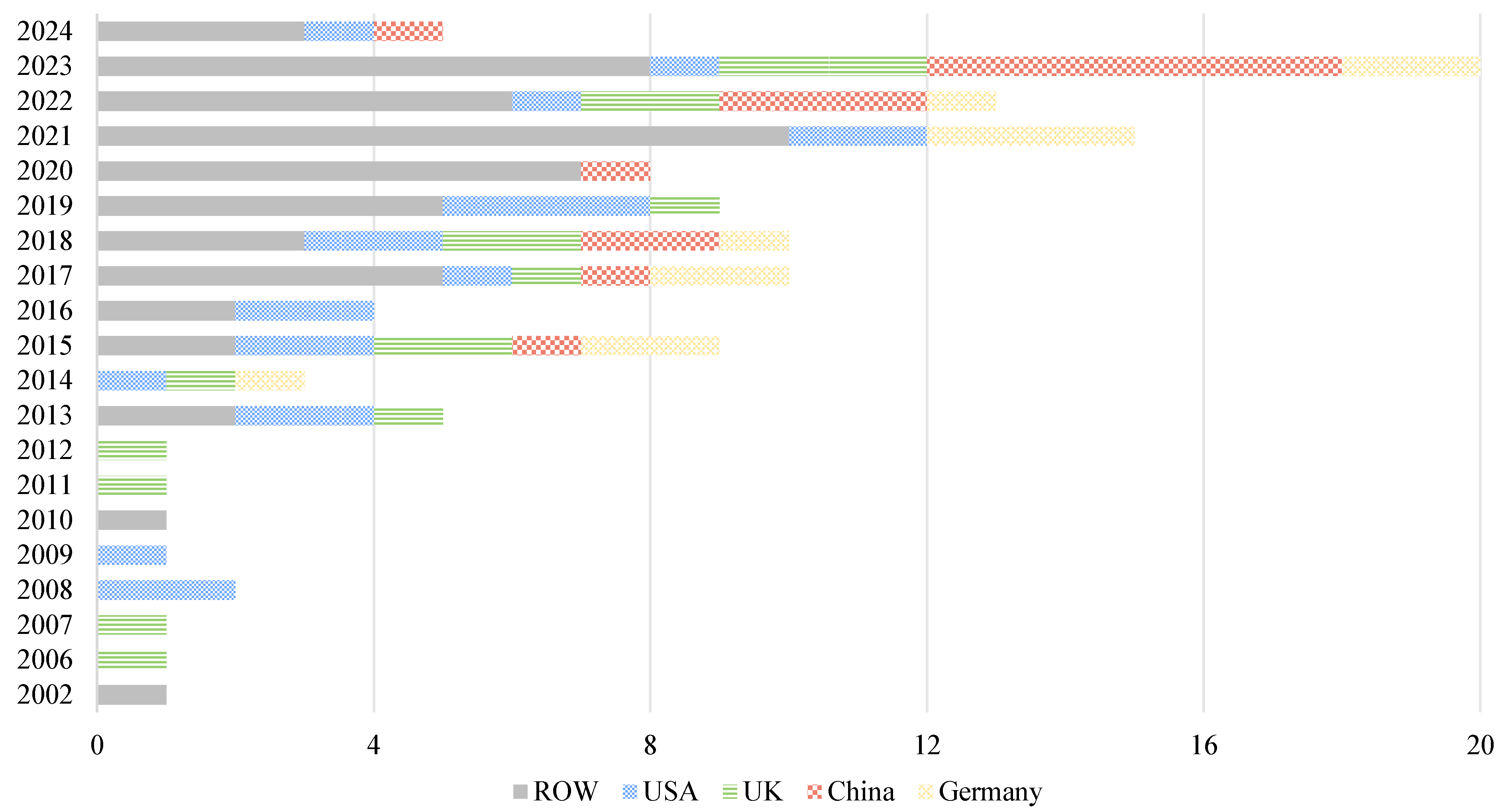
4.1. Descriptive Results Analysis
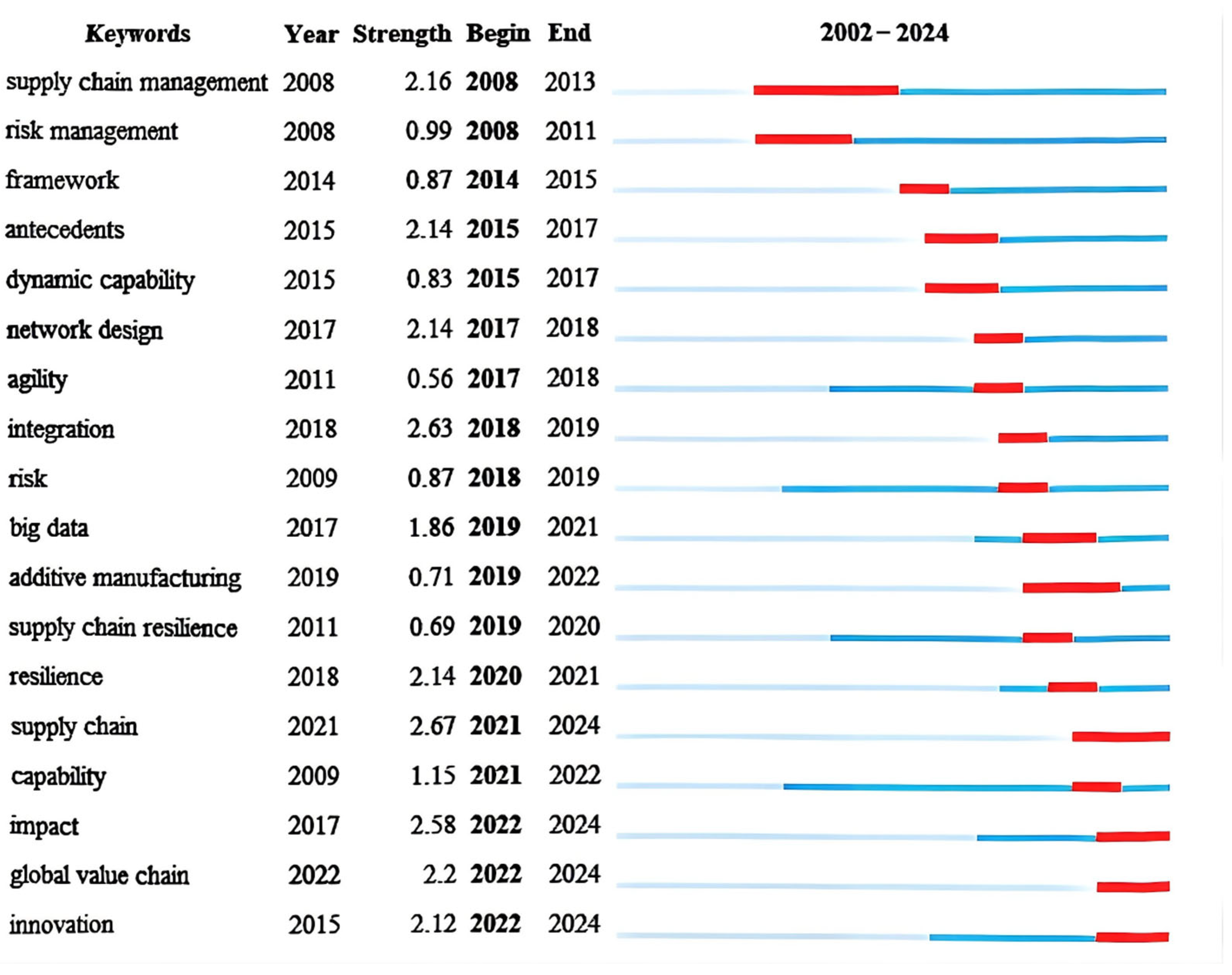
4.2. Trend Analysis
4.2.1. General Trend Analysis
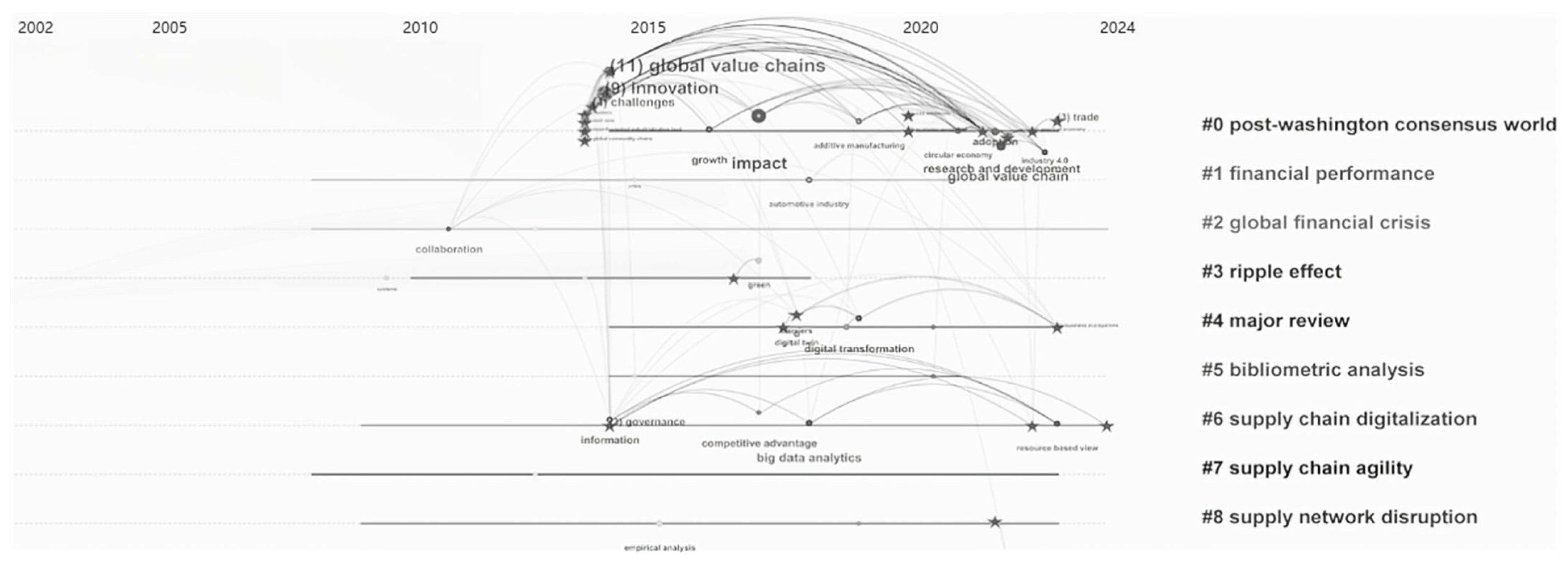
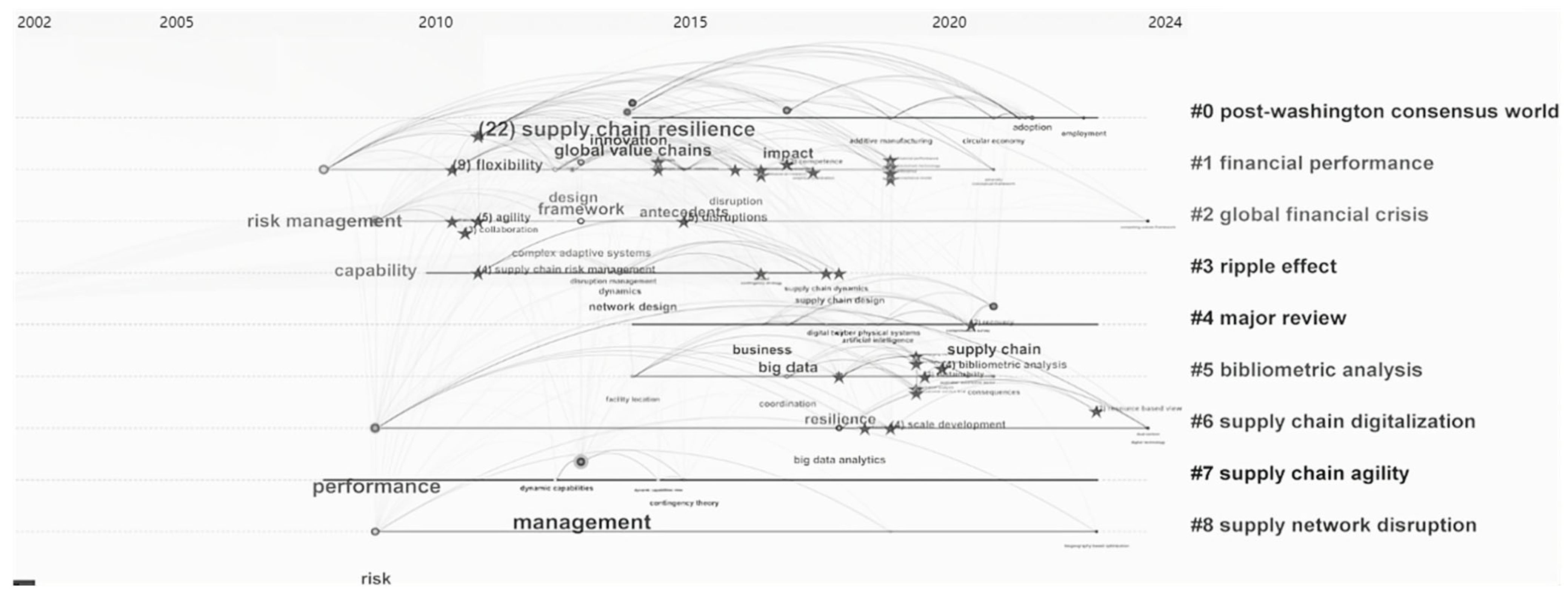
4.2.2. Research Trends on GVC and SCR
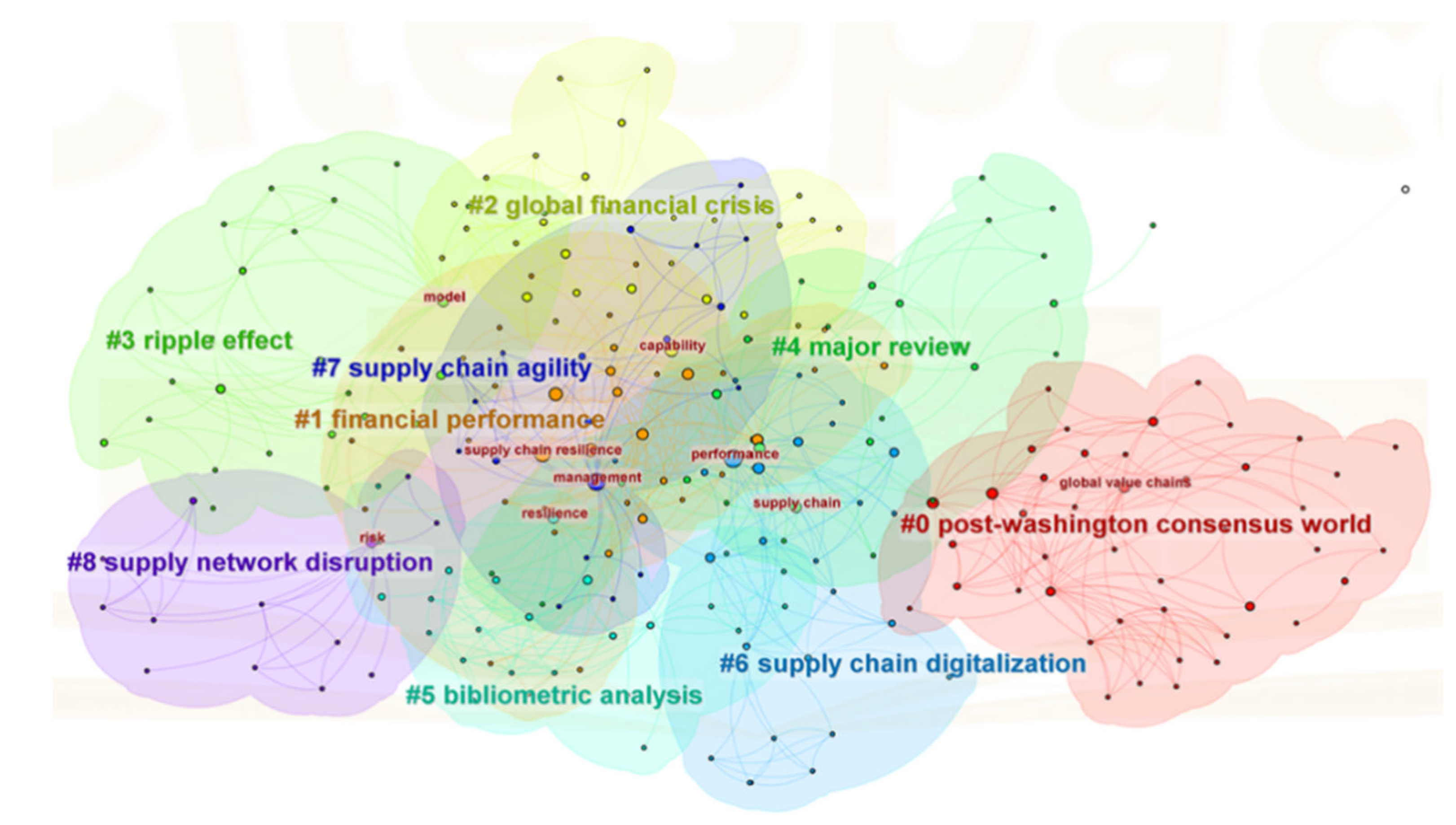
5. Systematic Review of the Clusters
5.1. Macro-Environmental Shocks Driving GVC Reconfiguration (Clusters 0 and 2)
5.2. The Impact of GVC Reconfiguration on SCR (Clusters 1, 3, and 8)
5.3. Manufacturing Practices and Strategic Responses (Clusters 4–7)
6. Discussion
6.1. Main Implications
6.1.1. Theoretical Implications
6.1.2. Methodological Implications
6.1.3. Managerial Implications
6.2. Future Research Directions
6.2.1. Firm-Level GVC Participation and Resilience Capability Enhancement
6.2.2. Inter-Firm Collaboration and Multi-Level Network Resilience
6.2.3. Integrative Modeling of Macro-Micro Linkages and Multi-Disciplinary Integration
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Reference | Year | Focus | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Williams et al. [95] | 2008 | Supply chain security and research agenda | Literature review and categorization of existing research |
| Hohenstein et al. [12] | 2015 | Phenomenon of SCR | Systematic literature review |
| Tukamuhabwa et al. [11] | 2015 | Definition and theoretical foundations of SCR | Literature review |
| Hosseini et al. [26] | 2016 | Definitions and measurement of system resilience | Classification |
| Kamalahmadi & Parast [13] | 2016 | Enterprise and SCR principles | Literature survey |
| Ali et al. [8] | 2017 | SCR constructs | Systematic literature review with concept mapping framework |
| Ivanov et al. [9] | 2017 | Disruption recovery in supply chains | Literature review |
| Dolgui et al. [68] | 2018 | Ripple effect in supply chains | Literature review and classification |
| Ghobakhloo [50] | 2018 | Review of SC digitalization and Industry 4.0 | Systematic literature review |
| Wan et al. [27] | 2018 | Resilience in transportation systems | Systematic review |
| Ali & Gölgeci [23] | 2019 | SCR research trends | Systematic review + VOS viewer co-occurrence analysis |
| Frank et al. [77] | 2019 | Industry 4.0 in manufacturing | Conceptual review and empirical synthesis |
| Bešinović [28] | 2020 | Railway transport resilience | Literature review |
| De Marchi et al. [33] | 2020 | Evolution of GVCs in international business | Systematic review and quantitative content analysis |
| Dolgui et al. [3] | 2020 | Supply chain adaptation to ever changing environments | Literature analysis along with tertiary studies |
| Kano et al. [31] | 2020 | Multi-disciplinary review of GVCs | Literature review |
| Xu et al. [24] | 2020 | Disruption risks in supply chain management | Bibliometric analysis |
| Aldrighetti et al. [5] | 2021 | Supply chain network design under disruption risks | Systematic literature review |
| Cohen & Kouvelis [56] | 2021 | “Triple A & R” framework for defining excellence capabilities in global supply chains | Literature review |
| Hillmann & Guenther [42] | 2021 | Organizational resilience as construct and its measurement | Systematic literature review |
| Goyal & Kumar [29] | 2021 | SCR and performance | Systematic review and bibliometric review |
| Wieland [4] | 2021 | Supply chain based on panarchy theory | Literature review |
| Zheng et al. [19] | 2021 | Applications of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing and SCR | Systematic literature review |
| Katsaliaki et al. [10] | 2022 | Supply chain disruptions and resilience | Literature review |
| Nguyen et al. [18] | 2022 | Digital twin and physical internet in SC | Literature review and bibliometric analysis |
| Chen et al. [25] | 2023 | Uncertainty analysis and optimization in supply chain management | Systematic review and bibliometric analysis |
| Hokmabadi et al. [20] | 2024 | SMEs/startups resilience through digital transformation | Systematic review |
Appendix B
| ID | Silhouette | Label | Top Terms (LLR) | Top Terms (LSl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.861 | Post-Washington consensus world | post-Washington consensus world (37.57, 1.0 × 10−4); episodic supply chain (33.33, 1.0 × 10−4); COVID-19 pandemic (29.1, 1.0 × 10−4); firm-level evidence (29.1, 1.0 × 10−4); emerging economies (29.1, 1.0 × 10−4) | global value chain; post-Washington consensus world; episodic supply chain; firm-level evidence; advanced digitalization | global supply chain; early evidence; foreign subsidiaries; value creation; episodic supply chain |
| 1 | 0.678 | Financial performance | financial performance (32.17, 1.0 × 10−4); dynamism disruption orientation (32.17, 1.0 × 10−4); major finding (29.66, 1.0 × 10−4); future research (29.66, 1.0 × 10−4); liner shipping industry (24.66, 1.0 × 10−4) | supply chain resilience; supply chain; financial performance; dynamic capabilities perspective; major finding|production system; further study; theoretical foundation; digital transformation; strategic supplier relationship |
| 2 | 0.849 | Global financial crisis | global financial crisis (36.54, 1.0 × 10−4); empirical study (36.54, 1.0 × 10−4); social-ecological perspective (31.9, 1.0 × 10−4); supply network resilience capabilities (31.9, 1.0 × 10−4); multitier supply chain management (27.28, 1.0 × 10−4) | supply chain resilience; empirical study; global financial crisis; social-ecological perspective; supply network resilience capabilities|multifaceted effect; supply chain agility; chain disruption; Chinese manufacturing supply chain; supply base complexity |
| 3 | 0.817 | Ripple effect | ripple effect (37.19, 1.0 × 10−4); disruption management (29.57, 1.0 × 10−4); marrying supply chain sustainability (22.04, 1.0 × 10−4); sustainable supply chain design (14.6, 0.001); sustainability analysis (14.6, 0.001) | supply chain; ripple effect; disruption management; marrying supply chain sustainability; disruption risk|marrying supply chain sustainability; supply chain; disruption risk; recent literature; ripple effect |
| 4 | 0.799 | Major review | major review (30.26, 1.0 × 10−4); future research agenda (30.26, 1.0 × 10−4); supply chain disruption (30.26, 1.0 × 10−4); manufacturing companies (25.15, 1.0 × 10−4); manufacturing context (20.07, 1.0 × 10−4) | major review; supply chain disruption; future research agenda; manufacturing companies; facing GVC challenge | manufacturing context; systematic literature review; UK construction value chain; risk distribution; steel reuse |
| 5 | 0.832 | Bibliometric analysis | bibliometric analysis (50.79, 1.0 × 10−4); literature review (31.35, 1.0 × 10−4); supply chain management (31.35, 1.0 × 10−4); value dynamics (24.98, 1.0 × 10−4); kingpins bottleneck (24.98, 1.0 × 10−4) | bibliometric analysis; disruption risk; literature review; supply chain management; value dynamics|supply chain; transformative supply chain management; value dynamics; disruption risk; supply chain management |
| 6 | 0.796 | Supply chain digitalization | supply chain digitalization (21.47, 1.0 × 10−4); multimediation model (21.47, 1.0 × 10−4); government effectiveness (18.39, 1.0 × 10−4); dynamic digital capabilities (18.39, 1.0 × 10−4); enabling role (15.38, 1.0 × 10−4) | multimediation model; supply chain digitalization; government effectiveness; dynamic digital capabilities; supply chain integration|supply chain resilience; moderating effect; supply chain; big data analytics capability; building supply chain resilience |
| 7 | 0.854 | Supply chain agility | supply chain agility (39.77, 1.0 × 10−4); moderating effect (30.04, 1.0 × 10−4); structural equation model (25.2, 1.0 × 10−4); product complexity (21, 1.0 × 10−4); supply chain adaptability (21, 1.0 × 10−4) | supply chain; supply chain agility; moderating effect; dynamic capabilities perspective; structural equation model|managing cyber; exploratory analysis; information risk; supply chain risk; COVID-19 pandemic driving |
| 8 | 0.865 | Supply network disruption | supply network disruption (26.08, 1.0 × 10−4);structural perspective (26.08, 1.0 × 10−4); medium-sized firm (17.21, 1.0 × 10−4); internal social capital (17.21, 1.0 × 10−4); chain disruption (11.72, 0.001) | supply network disruption; structural perspective; medium-sized firm; supply chain resilience; internal social capital|medium-sized firm; internal social capital; chain disruption; supply chain resilience; supply network disruption |
| ID | Label | Reference | Focus | Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Post-Washington consensus world | Gereffi [28] | Global value chains in the post-Washington consensus era | Conceptual analysis |
| Calza et al. [17] | Digitalization and resilience in developing and emerging economies | Empirical analysis | ||
| Shih & Lin [34] | Manufacturing upgrading and co-location in the COVID-19 era | Empirical analysis | ||
| Phillips et al. [36] | GVC reconfiguration under COVID-19 and geopolitical tensions | Case-based conceptual and policy analysis | ||
| Li et al. [99] | China’s embodied CO2 emissions and value added in GVCs | Structural path analysis | ||
| 1 | Financial performance | Chowdhury & Quaddus [15] | A scale for measuring SCR | Qualitative field study + quantitative survey |
| Yu et al. [78] | Dynamism, disruption orientation and financial performance | Empirical survey analysis | ||
| Hillmann & Guenther [42] | Organizational resilience as construct and its measurement | Systematic literature review | ||
| Kamalahmadi & Parast [13] | Enterprise and SCR principles | Literature survey | ||
| Ali et al. [8] | SCR constructs | Systematic literature review with concept mapping framework | ||
| 2 | Global financial crisis | Jüttner & Maklan [44] | SCR in the global financial crisis | Empirical Study |
| Tukamuhabwa et al. [84] | SCR in a developing country context | Case study | ||
| Statsenko et al. [79] | Post-crisis supply chain adaptation from a socio-ecological perspective | Qualitative multiple case study | ||
| Ambulkar et al. [97] | Firm resilience under disruption | Empirical analysis | ||
| Delbufalo [88] | Effects of supply base complexity on agility and resilience | Empirical analysis | ||
| 3 | Ripple effect | Ivanov et al. [46] | Trade-off “efficiency-flexibility-resilience” in ripple effect propagation | Quantitative analysis |
| Ivanov et al. [69] | SC dynamics and disruption propagation | Quantitative analysis and empirical analysis | ||
| Fahimnia & Jabbarzadeh [103] | Integration of sustainability and resilience in supply chains | Multi-objective optimization model | ||
| Jabbarzadeh [70] | Resilient and sustainable supply chain design | A stochastic bi-objective optimization model | ||
| Scheibe & Blackhurst [71] | Disruption propagation, systemic risk and accident theory | Theory case study | ||
| 4 | Major review | Ghobakhloo [50] | Review of SC digitalization and Industry 4.0 | Systematic literature review |
| Aldrighetti et al. [5] | SCN design under disruption risks | Systematic literature review | ||
| Nguyen et al. [18] | Digital twin and physical internet in SC | Literature review and bibliometric analysis | ||
| Zheng et al. [19] | Applications of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing and SCR | Systematic literature review | ||
| Frank et al. [77] | Industry 4.0 in manufacturing | Conceptual review and empirical synthesis | ||
| 5 | Bibliometric analysis | Xu et al. [24] | Disruption risks in supply chain management | Bibliometric analysis |
| Wieland [4] | Supply chain based on panarchy theory | Literature review | ||
| Cohen & Kouvelis [56] | “Triple A & R” framework for defining excellence capabilities in global supply chains | Literature review | ||
| Goyal & Kumar [29] | SCR and performance | Systematic review and bibliometric review | ||
| Free & Hecimovic [48] | Neoliberal globalization policies and global supply chains | Case study | ||
| 6 | Supply chain digitalization | Zhao et al. [60] | Impact of supply chain digitalization on SCR and performance | Survey and questionnaire |
| Brusset & Teller [14] | Supply chain capabilities, risks, and resilience | Survey and empirical study | ||
| Dubey et al. [75] | SC digital transformation and resilience | Multi-method approach | ||
| Ali & Gölgeci [23] | SCR research trends | Systematic review and VOS viewer co-occurrence analysis | ||
| Munir et al. [76] | Supply chain integration and supply chain risk management | Empirical study | ||
| 7 | Supply chain agility | Blome et al. [74] | Antecedents of SC agility and its effect on performance | Empirical survey |
| Eckstein et al. [73] | SC agility, adaptability, and product complexity | Empirical study | ||
| Gunasekaran et al. [102] | Big data and predictive analytics and supply chain and organizational performance | Empirical survey | ||
| Aman & Seuring [93] | SCR approaches in emerging economies | Survey + SCOR-based quantitative analysis | ||
| Van Hoek & Dobrzykowski [80] | Supply chain risks and COVID-19 pandemic and reshoring considerations | Case study | ||
| 8 | Supply network disruption | Kim & Chen [45] | Supply network disruption and resilience | Qualitative research |
| Kawa & Światowiec-Szczepańska [52] | Logistics value and customer satisfaction in e-commerce | Survey and empirical study | ||
| Chen et al. [25] | Uncertainty analysis and optimization in supply chain management | Systematic review and bibliometric analysis | ||
| Dolgui et al. [68] | Ripple effect in supply chains | Literature review and classification | ||
| Hohenstein et al. [12] | Phenomenon of SCR | Systematic literature review |
References
- Gereffi, G.; Humphrey, J.; Sturgeon, T. The Governance of Global Value Chains. Rev. Int. Polit. Econ. 2005, 12, 78–104. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, R. The World Trade Organization and the Future of Multilateralism. J. Econ. Perspect. 2016, 30, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Sokolov, B. Reconfigurable Supply Chain: The X-Network. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 4138–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A. Dancing the Supply Chain: Toward Transformative Supply Chain Management. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 57, 58–73. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrighetti, R.; Battini, D.; Ivanov, D.; Zennaro, I. Costs of Resilience and Disruptions in Supply Chain Network Design Models: A Review and Future Research Directions. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 235, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ndubisi, N.O.; Venkatesh, M. Manufacturing and Service Supply Chain Resilience to the COVID-19 Outbreak: Lessons Learned from the Automobile and Airline Industries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 163, 120447. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Dellana, S.; Falasca, M. Risk Management Maturity and Robustness in the Chinese Manufacturing Supply Chain: A Comparison Study Across Organisational Cultures. Int. J. Logist. 2024, 27, 2813–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Mahfouz, A.; Arisha, A. Analysing Supply Chain Resilience: Integrating the Constructs in a Concept Mapping Framework via a Systematic Literature Review. Supply Chain Manag. 2017, 22, 16–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B.; Ivanova, M. Literature Review on Disruption Recovery in the Supply Chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 6158–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaliaki, K.; Galetsi, P.; Kumar, S. Supply Chain Disruptions and Resilience: A Major Review and Future Research Agenda. Ann. Oper. Res. 2022, 319, 965–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukamuhabwa, B.R.; Stevenson, M.; Busby, J.; Zorzini, M. Supply Chain Resilience: Definition, Review and Theoretical Foundations for Further Study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 5592–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenstein, N.O.; Feisel, E.; Hartmann, E.; Giunipero, L.R. Research on the Phenomenon of Supply Chain Resilience: A Systematic Review and Paths for Further Investigation. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2015, 45, 90–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalahmadi, M.; Parast, M.M. A Review of the Literature on the Principles of Enterprise and Supply Chain Resilience: Major Findings and Directions for Future Research. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 171, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusset, X.; Teller, C. Supply Chain Capabilities, Risks, and Resilience. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 184, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Paul, S.K. Applications of Industry 4.0 Technologies in Supply Chain Resilience: An Empirical Study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107739. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, R.; Bryde, D.J.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Papadopoulos, T.; Foropon, C.; Roubaud, D. Humanitarian Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Prod. Plan. Control 2020, 31, 637–657. [Google Scholar]
- Calza, E.; Lavopa, A.; Zagato, L. Advanced Digitalisation and Resilience During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Firm-Level Evidence From Developing and Emerging Economies. Ind. Innov. 2023, 30, 864–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Duong, Q.H.; Nguyen, T.V.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, L. Knowledge Mapping of Digital Twin and Physical Internet in Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 244, 108381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Ardolino, M.; Bacchetti, A.; Perona, M. The Applications of Industry 4.0 Technologies in Manufacturing Context: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 1922–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokmabadi, H.; Rezvani, S.M.H.S.; de Matos, C.A. Business Resilience for Small and Medium Enterprises and Startups by Digital Transformation and the Role of Marketing Capabilities—A Systematic Review. Systems 2024, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Gao, K. The Impact of Industrial Robots on the ESG Rate of Downstream Enterprises in the Context of Supply Chain. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 262, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi-Nouri, B.; Rohaninejad, M.; Hanzálek, Z.; Foumani, M. A Batch Production Scheduling Problem in a Reconfigurable Hybrid Manufacturing-Remanufacturing System. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 204, 111099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Gölgeci, I. Where Is Supply Chain Resilience Research Heading? A Systematic and Co-Occurrence Analysis. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2019, 49, 793–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, X.T.; Feng, L.P.; Yang, W.T. Disruption Risks in Supply Chain Management: A Literature Review Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 3508–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dong, T.; Peng, J.; Ralescu, D. Uncertainty Analysis and Optimization Modeling With Application to Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Review. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Barker, K.; Ramirez-Marquez, J.E. A Review of Definitions and Measures of System Resilience. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 145, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.P.; Yang, Z.L.; Zhang, D.; Yan, X.P.; Fan, S.Q. Resilience in Transportation Systems: A Systematic Review and Future Directions. Transp. Rev. 2018, 38, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bešinović, N. Resilience in Railway Transport Systems: A Literature Review and Research Agenda. Transp. Rev. 2020, 40, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, K.; Kumar, S. Financial Literacy: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. The Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, L.; Tsang, E.W.K.; Yeung, H.W.C. Global Value Chains: A Review of the Multi-Disciplinary Literature. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2020, 51, 577–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereffi, G. Global Value Chains in a Post-Washington Consensus World. Rev. Int. Polit. Econ. 2014, 21, 9–37. [Google Scholar]
- De Marchi, V.; Di Maria, E.; Golini, R.; Perri, A. Nurturing International Business Research Through Global Value Chains Literature: A Review and Discussion of Future Research Opportunities. Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.Y.; Lin, C.A. Co-Location With Marketing Value Activities as Manufacturing Upgrading in a COVID-19 Outbreak Era. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 148, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereffi, G.; Pananond, P.; Pedersen, T. Resilience Decoded: The Role of Firms, Global Value Chains, and the State in COVID-19 Medical Supplies. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2022, 64, 46–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.; Roehrich, J.K.; Kapletia, D.; Alexander, E. Global Value Chain Reconfiguration and COVID-19: Investigating the Case for More Resilient Redistributed Models of Production. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2022, 64, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleticha, P. Who Benefits From Global Value Chain Participation? Does Functional Specialization Matter? Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2021, 58, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttke, T. Global Value Chains and Local Inter-Industry Linkages: South Africa’s Participation in the Automotive GVC. J. Dev. Stud. 2023, 59, 153–169. [Google Scholar]
- Blažek, J.; Lypianin, A. What Drives the Economic Performance of Suppliers in Global Value Chains/Global Production Networks—Tier, Ownership, Size, Specialization, or Region? Norsk Geogr. Tidsskr. 2022, 76, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Meindl, P.; Kalra, D.V. Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Scholten, K.; Stevenson, M.; van Donk, D.P. Dealing With the Unpredictable: Supply Chain Resilience. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2019, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmann, J.; Guenther, E. Organizational Resilience: A Valuable Construct for Management Research? Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2021, 23, 7–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Blackhurst, J.V.; Choi, T.M. Toward Supply Chain Viability Theory: From Lessons Learned Through COVID-19 Pandemic to Viable Ecosystems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 2402–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, U.; Maklan, S. Supply Chain Resilience in the Global Financial Crisis: An Empirical Study. Supply Chain Manag. 2011, 16, 246–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Chen, Y.S.; Linderman, K. Supply Network Disruption and Resilience: A Network Structural Perspective. J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 33–34, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Sokolov, B.; Dolgui, A. The Ripple Effect in Supply Chains: Trade-Off ‘Efficiency-Flexibility-Resilience’ in Disruption Management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 2154–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.; de Ruyter, A.; Hearne, D.; Ortega-Argilés, R. Shocks, Resilience and Regional Industry Policy: Brexit and the Automotive Sector in Two Midlands Regions. Reg. Stud. 2023, 57, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, C.; Hecimovic, A. Global Supply Chains After COVID-19: The End of the Road for Neoliberal Globalisation? Account. Audit. Account. J. 2021, 34, 58–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ghouri, A.M.; Akhtar, P.; Venkatesh, V.G.; Ashraf, A.; Arsenyan, G.; Tarba, S.Y.; Khan, Z. Enhancing Supply Chain Innovation and Operational Agility Through Knowledge Acquisition From the Social Media: A Microfoundational Approach. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 12777–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. The Future of Manufacturing Industry: A Strategic Roadmap Toward Industry 4.0. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 910–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holweg, M.; Helo, P. Defining Value Chain Architectures: Linking Strategic Value Creation to Operational Supply Chain Design. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawa, A.; Światowiec-Szczepańska, J. Logistics as a Value in E-Commerce and Its Influence on Satisfaction in Industries: A Multilevel Analysis. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2021, 36, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Li, G.Y.; Han, P.H.; Osen, O.; Zhang, H.X. Impacts of COVID-19 on Ship Behaviours in Port Area: An AIS Data-Based Pattern Recognition Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25127–25138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.D.R.; D’Agosto, M.D.A. Value Chain Analysis Applied to the Scrap Tire Reverse Logistics Chain: An Applied Study of Co-Processing in the Cement Industry. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 78, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereffi, G. Global value chains and international development policy: Bringing firms, networks and policy-engaged scholarship back in. J Int Bus Policy. 2019, 2, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.A.; Kouvelis, P. Revisit of AAA Excellence of Global Value Chains: Robustness, Resilience, and Realignment. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2021, 30, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Choi, B.; Jimenez, A. Early Evidence on How Industry 4.0 Reshapes MNEs’ Global Value Chains: The Role of Value Creation Versus Value Capturing by Headquarters and Foreign Subsidiaries. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2023, 54, 599–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Green Innovation Risk Index Screening Under the Global Value Chain Based on the Group Decision Characteristic Root Method. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1208497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.L.; Hou, Y.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Si, S.B.; Wei, Y.X. Transforming Digital Value Chain Ecosystems for Dual-Carbon Target: An Exploration of the BDS-RAS Framework. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 188, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.Y.; Hong, J.T.; Lau, K.H. Impact of Supply Chain Digitalization on Supply Chain Resilience and Performance: A Multi-Mediation Model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 259, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, G.; Balzano, M.; Caputo, A.; Pellegrini, M.M. Guidelines for Bibliometric-Systematic Literature Reviews: 10 Steps to Combine Analysis, Synthesis and Theory Development. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2025, 27, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, G.; Balzano, M.; Marchiori, D. K-Alpha Calculator–Krippendorff’s Alpha Calculator: A User-Friendly Tool for Computing Krippendorff’s Alpha Inter-Rater Reliability Coefficient. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranfield, D.; Denyer, D.; Smart, P. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence—Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 2003, 14, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilubi, I.; Haasis, H.D. Supply Chain Risk Management Research: Avenues for Further Studies. Int. J. Supply Chain Oper. Resil. 2016, 2, 75–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wee, B. Accessible Accessibility Research Challenges. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 51, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarzani, H.; Fahimnia, B.; Bell, M.; Sarkis, J. Greening Ports and Maritime Logistics: A Review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and Visualizing Emerging Trends and Transient Patterns in Scientific Literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Sokolov, B. Ripple Effect in the Supply Chain: An Analysis and Recent Literature. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D. Revealing Interfaces of Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainability: A Simulation Study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 3507–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarzadeh, A.; Fahimnia, B.; Sabouhi, F. Resilient and Sustainable Supply Chain Design: Sustainability Analysis Under Disruption Risks. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 5945–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibe, K.P.; Blackhurst, J. Supply Chain Disruption Propagation: A Systemic Risk and Normal Accident Theory Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Stecke, K.E.; Li, D.N. The Evolution of Production Systems From Industry 2.0 Through Industry 4.0. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, D.; Goellner, M.; Blome, C.; Henke, M. The Performance Impact of Supply Chain Agility and Supply Chain Adaptability: The Moderating Effect of Product Complexity. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 3028–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, C.; Schoenherr, T.; Rexhausen, D. Antecedents and Enablers of Supply Chain Agility and Its Effect on Performance: A Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 1295–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Bryde, D.J.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Graham, G.; Foropon, C.; Papadopoulos, T. Dynamic Digital Capabilities and Supply Chain Resilience: The Role of Government Effectiveness. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2023, 258, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Jajja, M.S.S.; Chatha, K.A.; Farooq, S. Supply Chain Risk Management and Operational Performance: The Enabling Role of Supply Chain Integration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 227, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.G.; Dalenogare, L.S.; Ayala, N.F. Industry 4.0 Technologies: Implementation Patterns in Manufacturing Companies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 210, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.T.; Jacobs, M.A.; Chavez, R.; Yang, J.H. Dynamism, Disruption Orientation, and Resilience in the Supply Chain and the Impacts on Financial Performance: A Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 218, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, L.; Jayasinghe, R.S.; Soosay, C. Supply Network Resilience Capabilities: A Social–Ecological Perspective. Supply Chain Manag. 2024, 29, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoek, R.; Dobrzykowski, D. Towards More Balanced Sourcing Strategies—Are Supply Chain Risks Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic Driving Reshoring Considerations? Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 26, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öberg, C. Episodic Supply Chains at Times of Disruption. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 27, 312–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.; Han, N. Understanding the Relationships Between Global Supply Chain Risk and Supply Chain Resilience: The Role of Mitigating Strategies. Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 26, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colicchia, C.; Creazza, A.; Menachof, D.A. Managing Cyber and Information Risks in Supply Chains: Insights From an Exploratory Analysis. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 24, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukamuhabwa, B.; Stevenson, M.; Busby, J. Supply Chain Resilience in a Developing Country Context: A Case Study on the Interconnectedness of Threats, Strategies and Outcomes. Supply Chain Manag. 2017, 22, 486–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, K.; Schilder, S. The Role of Collaboration in Supply Chain Resilience. Supply Chain Manag. 2015, 20, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Pettit, S.J.; Beresford, A.K.C. An Assessment of the Integration of Seaports Into Supply Chains Using a Structural Equation Model. Supply Chain Manag. 2013, 18, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Fan, X.; He, M.K. Analysis on the Effects of Global Supply Chain Reconfiguration on China’s High-End Equipment Manufacturing Industry. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2023, 54, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbufalo, E. Disentangling the Multifaceted Effects of Supply Base Complexity on Supply Chain Agility and Resilience. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2022, 52, 700–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunant, C.F.; Drewniok, M.P.; Sansom, M.; Corbey, S.; Cullen, J.M.; Allwood, J.M. Options to Make Steel Reuse Profitable: An Analysis of Cost and Risk Distribution Across the UK Construction Value Chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.; Crespi, F.; Marin, G.; Paglialunga, E. Eco-Innovation, Sustainable Supply Chains and Environmental Performance in European Industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 155, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stindt, D. A Generic Planning Approach for Sustainable Supply Chain Management—How to Integrate Concepts and Methods to Address the Issues of Sustainability? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.; Ravi, V. Supplier Selection in Resilient Supply Chains: A Grey Relational Analysis Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, S.; Seuring, S. Analysing Developing Countries Approaches of Supply Chain Resilience to COVID-19. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2023, 34, 909–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarov, S.Y.; Holcomb, M.C. Understanding the Concept of Supply Chain Resilience. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2009, 20, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, Z.; Lueg, J.E.; LeMay, S.A. Supply Chain Security: An Overview and Research Agenda. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2008, 19, 254–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, M.; Oke, A. Antecedents of Supply Chain Visibility in Retail Supply Chains: A Resource-Based Theory Perspective. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambulkar, S.; Blackhurst, J.; Grawe, S. Firm’s Resilience to Supply Chain Disruptions: Scale Development and Empirical Examination. J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 33–34, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobides, M.G.; Tae, C.J. Kingpins, Bottlenecks, and Value Dynamics Along a Sector. Organ. Sci. 2015, 26, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.P.; Wu, S.M.; Li, S.T. Weighing China’s Embodied CO2 Emissions and Value Added Under Global Value Chains: Trends, Characteristics, and Paths. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115302. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, C.N.; Dang, H. COVID-19 in America: Global Supply Chain Reconsidered. World Econ. 2023, 46, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhofen, D.M.; El-Sahli, Z.; Kneller, R. Estimating the Effects of the Container Revolution on World Trade. J. Int. Econ. 2016, 98, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Dubey, R.; Wamba, S.F.; Childe, S.J.; Hazen, B.; Akter, S. Big Data and Predictive Analytics for Supply Chain and Organizational Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Jabbarzadeh, A. Marrying Supply Chain Sustainability and Resilience: A Match Made in Heaven. Transp. Res. Part E 2016, 91, 306–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, V.H.; Foo, P.Y.; Cham, T.H.; Hew, T.S.; Tan, G.W.H.; Ooi, K.B. Big Data Analytics Capability in Building Supply Chain Resilience: The Moderating Effect of Innovation-Focused Complementary Assets. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2024, 124, 1203–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.A.; Singh, R.K.; Mishra, R.; Bag, S. Application of Blockchain Technology for Sustainability Development in Agricultural Supply Chain: Justification Framework. Oper. Manag. Res. 2022, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Veelenturf, L.P. The Strategic Role of Logistics in the Industry 4.0 Era. Transp. Res. Part E 2019, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Min, H. Blockchain Technology for Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, K.; Boualam, B.; Martin, J. Are Clusters Resilient? Evidence From Canadian Textile Industries. J. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 20, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, A.; Tucker, C. Digital Economics. J. Econ. Lit. 2019, 57, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Póoa, A.P.; Pinto, J.M. Resilient Supply Chains—Robustness and Dynamics in the Context of Industrial Gas Supply Chains. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 179, 108435. [Google Scholar]
- El Hamdi, S.; Abouabdellah, A. Logistics: Impact of Industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Gu, B.M.; Chen, J.H. Enablers for Maritime Supply Chain Resilience During Pandemic: An Integrated MCDM Approach. Transp. Res. Part A 2023, 175, 103777. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, C.F.; Ku, C.C.; Lu, Y.Y. Ensemble Learning for Demand Forecast of After-Market Spare Parts to Empower Data-Driven Value Chain and an Empirical Study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 185, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, X.M.; Pan, Y. Global Industrial Chain Resilience Research: Theory and Measurement. Systems 2023, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, T.J.; Croxton, K.L.; Fiksel, J. The Evolution of Resilience in Supply Chain Management: A Retrospective on Ensuring Supply Chain Resilience. J. Bus. Logist. 2019, 40, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Search Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Boolean operations | OR, AND, NOT |
| Search scope | Topic: title, abstract, and indexing |
| Language | English |
| Time limit | January 2002 to December 2024 |
| Database | Web of Science Core Collection |
| Keywords | “global value chain” OR “value chain” AND “supply chain resilience” OR “SCR” OR “supply chain uncertainty” OR “supply chain vulnerability” OR “supply chain disruption” OR “robust supply chain” AND “Manufacturing” OR “industry” |
| Source | Freq. | References |
|---|---|---|
| International Journal of Production Research | 14 | Dolgui et al. [3]; Ivanov et al. [9]; Tukamuhabwa et al. [11]; Zheng et al. [19]; Xu et al. [24]; Ivanov et al. [43]; Ivanov et al. [46]; Dolgui et al. [68]; Ivanov [69]; Jabbarzadeh et al. [70]; Scheibe & Blackhurst [71]; Yin et al. [72]; Eckstein et al. [73]; Blome et al. [74] |
| International Journal of Production Economics | 11 | Aldrighetti et al. [5]; Kamalahmadi & Parast [13]; Brusset & Teller [14]; Chowdhury & Quaddus [15]; Nguyen et al. [18]; Holweg & Helo [51]; Zhao et al. [60]; Dubey et al. [75]; Munir et al. [76]; Frank et al. [77]; Yu et al. [78] |
| Supply Chain Management: An International Journal | 10 | Ali et al. [8]; Jüttner & Maklan [44]; Van Hoek & Dobrzykowski [79]; Statsenko et al. [80]; Öberg [81]; Um & Han [82]; Colicchia et al. [83]; Tukamuhabwa et al. [84]; Scholten & Schilder [85]; Woo et al. [86] |
| International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management | 4 | Hohenstein et al. [12]; Ali & Gölgeci [23]; Zhang et al. [87]; Delbufalo [88] |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 4 | Dunant et al. [89]; Costantini et al. [90]; Stindt [91]; Rajesh & Ravi [92] |
| The International Journal of Logistics Management | 3 | Aman & Seuring [93]; Ponomarov & Holcomb [94]; Williams et al. [95] |
| Journal of Operations Management | 3 | Kim et al. [45]; Barratt & Oke [96]; Ambulkar et al. [97] |
| Theory | Focus Within SCR Research | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAS | Ripple effects, systemic contagion, adaptive behaviors | Limited managerial guidance | Statsenko & Jayasinghe [79]; Tukamuhabwa et al. [84] |
| Dynamic Capabilities | Sensing, seizing, and transforming capabilities for turbulence adaptation | Underemphasis on initial resources and contextual constraints | Eckstein et al. [73]; Blome et al. [74]; Yu et al. [78] |
| RBV | Deployment of VRIN resources (strategic inventory, backup suppliers, redundant capacity) for resilience | Neglect of systemic network effects | Barratt & Oke [96]; Gunasekaran et al. [102] |
| Social Network | Disruption propagation across network nodes; resilience shaped by structural, relational, and cognitive social capital | Underplayed firm-level capabilities; selective node vulnerability impacts | Dolgui et al. [3]; Ivanov et al. [43]; Kim et al. [45] |
| GVC | Linking firm-level resilience with systemic reconfiguration across global production networks | Requires integration with micro- and meso-level theories | Gereffi et al. [35]; Blažek & Lypianin [39]; Delbufalo [88]; Ambulkar et al. [97] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q. Manufacturing Supply Chain Resilience Amid Global Value Chain Reconfiguration: An Enhanced Bibliometric–Systematic Literature Review. Systems 2025, 13, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100873
Li Y, Xia X, Wang C, Huang Q. Manufacturing Supply Chain Resilience Amid Global Value Chain Reconfiguration: An Enhanced Bibliometric–Systematic Literature Review. Systems. 2025; 13(10):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yan, Xinxin Xia, Cong Wang, and Qingbo Huang. 2025. "Manufacturing Supply Chain Resilience Amid Global Value Chain Reconfiguration: An Enhanced Bibliometric–Systematic Literature Review" Systems 13, no. 10: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100873
APA StyleLi, Y., Xia, X., Wang, C., & Huang, Q. (2025). Manufacturing Supply Chain Resilience Amid Global Value Chain Reconfiguration: An Enhanced Bibliometric–Systematic Literature Review. Systems, 13(10), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13100873






