Abstract
Digital transformation embeds smart cities, e-health, and Industry 4.0 into critical infrastructures, thereby increasing reliance on digital systems and exposure to cyber threats and boosting complexity and dependency. Research involving over 200 executives reveals that under rising complexity, only 15% of cyber risk investments are effective, leaving most organizations misaligned or vulnerable. In this context, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity requires systemic scrutiny. This study analyzes how AI reshapes systemic structures in cyber risk management through a multi-method approach: literature review, expert workshops with practitioners and policymakers, and a structured kill chain analysis of the Colonial Pipeline attack. The findings reveal three new feedback loops: (1) deceptive defense structures that misdirect adversaries while protecting assets, (2) two-step success-to-success attacks that disable defenses before targeting infrastructure, and (3) autonomous proliferation when AI applications go rogue. These dynamics shift cyber risk from linear patterns to adaptive, compounding interactions. The principal conclusion is that AI both amplifies and mitigates systemic risk. The core recommendation is to institutionalize deception in security standards and address drifting AI-powered systems. Deliverables include validated systemic structures, policy options, and a foundation for creating future simulation models to support strategic cyber risk management investment.
1. Societal Digital Transformation Enhances Susceptibility to Cyber Threats
Technological advancements such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and predictive analytics are rapidly reshaping our professional and personal lives [1]. Concepts such as smart cities, e-health, and Industry 4.0, once considered futuristic, are now integral to our daily lives. Cars, airplanes, medical devices, financial transactions, and electricity systems increasingly rely on intricate computer software, making them indispensable yet challenging to manage [2]. However, this ever-expanding reliance on technology has heightened societal vulnerability to cyber threats [3].
Since the emergence of the first self-replicating program, Creeper, and its countermeasure, Reaper, in the 1970s, cybersecurity has undergone fundamental evolution [4]. This evolution reflects an ongoing adversarial dynamic: attackers’ innovations in tactics, techniques, and procedures are met by defenders’ countermeasures and interventions [5,6,7]. The introduction of AI represents a critical inflection point, adding unprecedented complexity to this already dynamic interplay. AI has revolutionized cybersecurity by enabling advanced automated threat detection and mitigation tools [8,9,10] and improving IT hygiene processes like automated configuration management [11]. Yet, it has simultaneously empowered adversaries, facilitating more sophisticated, scalable, and harder-to-detect cyberattacks [12,13,14].
This threat has rapidly escalated with the advent of AI. Diverse trends observed in industry reports highlight this new reality; for instance, phishing attacks surged by nearly 500% in the first half of 2023 alone [15], and deepfake fraud attempts soared by an alarming 3000% in the same year [16]. In 2023, AI-generated polymorphic malware, such as Black Mamba, demonstrated the capability to evade endpoint detection and response systems in controlled environments by continuously mutating its signature [17]. Such innovations foreshadow the rise of aggressive autonomous agents already announced by well-established practitioners at Blackhat in 2017. They are capable of traversing real network topologies, autonomously identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities, and evading detection [18]. This dynamic interaction between attackers and defenders has shaped the cybersecurity field into its current state. Alarmingly, according to industry reports, cybercrime now constitutes the world’s third-largest economic power [19], with an estimated value of approximately $9.5 trillion in 2024 [19,20,21]. The most important message gleaned from this dense information, comprising media messages, lab results, and industry reports, is that AI has entered the cybersecurity domain and is here to stay.
At the organizational level, the implications are profound. Cyber incidents can shut down small and medium-sized enterprises [22] and inflict multimillion-dollar losses on large corporations [23], with an estimated average cost of a single breach amounting to $4.8 million [24]. Compounding the issue, the downstream impacts on supply chains can amplify these losses by up to three orders of magnitude [25]. Alarmingly, 53% of these incidents are due to defense failures, while the rest stem from unintended control lapses [24]. Government, industry, and science convey an identical message with different numbers and impacts. Overall, these statistics underscore the immense challenge of securing organizations in an era of escalating complexity and threats.
Despite executives’ efforts to build resilience, the complex, dynamic, and uncertain nature of cyber risk management poses significant governance challenges [26,27,28]. Many leaders resort to simplified heuristics and reactionary, event-driven approaches to mitigate threats [27,29,30], often resulting in underestimating risks [31]; over-reliance on generic, off-the-shelf solutions [31]; and reprioritization of cyber risk management in favor of other business activities [32]. Recent research involving over 200 executives and business leaders indicates that under increasingly complex conditions, only 15% of investment decisions on strategic cyber risk management are optimized, while in all other cases, organizations either overspend in misaligned areas or remain significantly exposed to cyber risk [33,34]. This underscores the importance of understanding the systemic structures that drive this complex environment.
This work aims to elucidate the complex and evolving nature of cyber risk management while examining how AI is reshaping the field. Our overarching research question is:
“How does AI transform cyber risk management?”
We adopt a multi-method approach, with each method aligned to a specific research sub-question:
- What are the systemic structures currently driving cyber risk management?
- How does a real-world cyber incident reflect these systemic structures?
- Considering such an incident, how can AI alter both adversarial and defensive capabilities?
- Beyond speed, scale, and automation, in what ways does AI fundamentally reshape these systemic structures?
To address our research questions, we first review the literature on systemic approaches to cyber risk management and consult an expert group to validate and refine our conceptual framework. We then analyze these systemic structures through the lens of the Colonial Pipeline cyberattack, applying a step-by-step approach based on the cyber kill chain, a structured model that breaks down an attack into sequential stages. This sequence will enable us to systematically assess how AI technologies interact with and potentially disrupt each stage of the attack. This level of analysis provides a structured foundation for evaluating how AI reconfigures both offensive and defensive capabilities. By juxtaposing the stages of the Colonial Pipeline incident with recent advancements in AI, we demonstrate how AI transforms not only the dynamics of individual attacks but also the systemic structures that underpin cyber risk management. Our analysis integrates insights from the literature with evidence from expert interviews and three workshops involving business leaders, executives, security strategists, and policymakers. Collectively, these sources reveal how AI is driving systemic shifts in cybersecurity. The findings highlight both the accelerating escalation between attackers and defenders and the emergence of novel AI-driven mechanisms transforming the cybersecurity landscape.
Throughout this work, we refer to media reports (media), scientific work (science), industry surveys and blogs (industry), white papers (white papers), and practitioners’ insights (practitioners). While each of these sources has its strengths, they also have limitations that must be considered. Media reports may be timely but pose risks of bias, sensationalism, or incomplete context. Scientific work, though usually peer-reviewed and rigorous, can be narrow, dated, or limited in practical relevance. Industry surveys and blogs provide sectoral insights but may reflect methodological weaknesses (e.g., sampling bias) or vested interests. As white papers often combine technical depth with persuasive intent, their objectivity depends on the authoring body. Practitioners’ insights offer grounded, real-world perspectives but may be anecdotal, context-dependent, and lacking in generalizability. Thus, the validity of these sources depends on the rigor, transparency, representativeness, and potential bias of each source type.
2. Identifying the Traditional Feedback Loops in Systemic Structures to Manage Cyber Risks
Current work differentiates between governing and overseeing simple and advanced cyber threats (such as ransomware). In simple threats, cyberattacks directly affect one or more systems. Examples include Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, website defacement, and attacks on internet-connected assets by exploiting vulnerabilities. Advanced threats use one or more systems as a stepping stone, spreading across the defenders’ technology stack until properly mitigated. Malware attacks, ransomware attacks, and more advanced attacks, such as advanced persistent threats (APTs), are examples. The primary difference between advanced and simple threats is that the former are recognized by significant lateral movement or spreading from system to system. In our work, neither of these two threat categories involves AI-powered cyberattacks or defenses.
This section explains how systemic structures relevant to governing and overseeing cyber risk evolved before the advent of AI. These structures, derived from literature and expert consultation, are described by highlighting key system variables, indicating how they are interconnected, and identifying relevant feedback loops. A feedback loop is a cause-and-effect cycle where a change in one part eventually influences itself again; a reinforcing loop amplifies change (fostering exponential growth), while a balancing loop counteracts change (enabling goal-seeking behavior). Reinforcing feedback loops are labelled with “R” and balancing feedback loops are labelled with “B”.
Table 1 categorizes the different model components supported by literature references, below which the model structure and feedback loops per threat type are detailed.

Table 1.
Model components are explained in the literature. References used are media reports (media), scientific work (science), industry surveys and blogs (industry), white papers (white papers), and practitioners’ insights (practitioners).
2.1. Simple Cyber Threats
Figure 1 below illustrates the systemic structure of cyber risk management, including feedback loops. Technological imperfections, limitations in human behavior, and dynamic organizational contexts affect the security state of systems. Systems can be at risk and may be compromised through a cyberattack. The occurrence of such attacks is uncertain, as when and where they will happen is unknown. In this context, systems (not) at risk contribute to business processes that generate profits, while compromised systems may entail incident mitigation costs, thus eroding profits. Strategic decision-makers shape this dynamic by allocating resources, budgets, and priorities to security capabilities, such as prevention, detection, and response. These choices are driven by observed risk exposure and profitability, while also considering the costs associated with maintaining such capabilities.
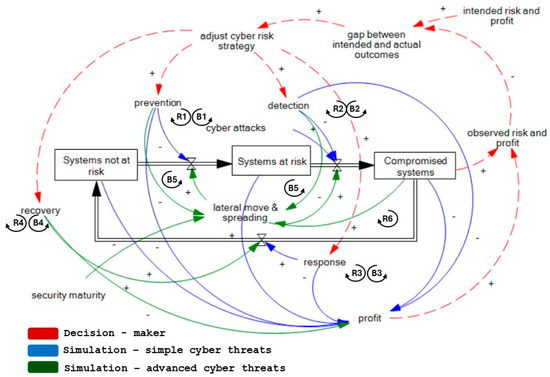
Figure 1.
Systemic structures of cyber risk management, including feedback loops. + indicates a positive relation between connected variables. - indicates negative relation between connected variables. BX refers to a balancing feedback loop with number X. RY refers to a reinforcing feedback loop with number Y.
In this setting, prevention, detection, and response emerge as the cornerstones of cybersecurity defense affecting the aging chain structure, considering established frameworks such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls, and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 2700X series [37,38,39,40].
Prevention entails proactive measures to understand and manage risks across systems, accounts, assets, data, and capabilities. These safeguards, essential for maintaining IT hygiene and service delivery, are outlined by CIS [37], Government Chief Information Officer (GCIO) [38], Muneer [39], and Pascoe [40]. Prevention limits (B1) the transition of not-at-risk systems to at-risk systems, thereby reducing adverse impacts in terms of risk (compromised systems) and profit (mitigation costs). However, investing in prevention raises security costs and lowers profitability (R1).
Detection involves the prompt monitoring and identification of cybersecurity events or anomalies (ibid.). It prevents systems at risk from becoming compromised (B2) by proactively resolving vulnerabilities before exploitation or reactively anticipating detected attacks by initiating mitigation actions. Like prevention, detection also mitigates adverse impacts in terms of risk (compromised systems) and profit (mitigation costs). However, investing in detection raises security costs and reduces profitability (R2).
Response contains and neutralizes the impact of an incident, minimizes damage, and prevents recurrence through actionable measures (ibid.). These efforts restore compromised systems to ones not at risk, limiting the impact of cyber events and minimizing mitigation costs (B3). However, acquiring response capabilities involves costs, affecting profitability (R3).
Collectively, these efforts mitigate organizational exposure to financial, operational, and business risks posed by general cyber threats [41,42]. Decision-making in cyber risk management will be affected if the actual profitability and/or risk exposure of the defender diverges from the intended ones.
The lifecycle of a capability [49] and the related capability trap [50] are both relevant to prevention, detection, response, and recovery [28,51]. They highlight how organizations often prioritize short-term results over sustained improvement, weakening long-term security performance. Security capabilities require ongoing development and maintenance, but operational pressures frequently lead to the neglect of critical activities such as software patching, awareness training, and third-party security assessments. This underinvestment enhances the vulnerability to threats.
Security capabilities are dynamic and demand continuous monitoring, especially in a business environment with evolving adversaries, changing organizations (people, processes, technology, suppliers, etc.), emerging incidents, and shifting priorities (ibid.). Failure to sustain them weakens defenses and erodes the security posture. Avoiding the capability trap requires balancing short-term needs with long-term resilience, ensuring the prioritization of security amid competing business demands.
In summary, the cyclical interplay of prevention, detection, response, and recovery forms the backbone of organizational cyber resilience that drives business performance.
2.2. Advanced Cyber Threats (Ransomware)
Advanced cyber threats, as a different form of attack, are characterized in our work by their ability to spread across the defenders’ technological layer and cause material harm when they materialize. Ransomware has emerged as a dominant concern among contemporary advanced threats [52]. In 2023, the top five ransomware toolkits, consisting of Lockbit 3.0, AlphVM, CL0P, PLAY, and BlackBasta, recorded a staggering 500% average increase in usage in cyber incidents [53]. Between 2015 and 2021, global ransomware damage soared by 5700%, touching $20 billion annually, and is projected to increase to $265 billion per year by 2031 [54]. Ransomware operates as a form of digital extortion that aggressively spreads across a defender’s network, encrypting critical data and paralyzing business operations until a ransom is paid [44,45]. Consequently, these cyber threats have a significant impact. Aggressive spreading indicates that compromised systems can infect systems (not) at risk, leading to more compromised systems (R6). Additionally, halting business operations lowers revenues and profits, while compromised systems require costly mitigation efforts (R6). This disruption underscores the critical need for recovery, which involves restoring impaired capabilities, maintaining resilience, and ensuring alternative service delivery until the restoration of normal operations [37,38,39,40]. Recovery limits adverse costs, while alternative service delivery maintains revenue generation (B4). Recovery is another capability available to decision-makers where they can influence this systemic structure. However, acquiring recovery capabilities is also cost-intensive (R4).
Defense against ransomware requires robust network segmentation (B5) and anomaly detection (B6), which represent key aspects of prevention and detection, respectively (ibid.). Mature monitoring and logging systems are prerequisites for anomaly detection, enabling the identification of irregular communication patterns, device behavior, or connections to malicious domains [46]. Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, independently functioning subnetworks to limit malware spread [47,48]. Consequently, when the maturity of the defenders’ security capabilities reaches a certain level, it will boost their defenses against advanced cyber threats.
We tested this structure through a walkthrough of the Colonial Pipeline breach (detailed in the next section), based on a literature search and case study conducted at a conference organized by a leading university. The Colonial Pipeline incident was researched by exploring a wide variety of 25 security blogs, industry reports, opinion-based articles, and research papers. We used the Kill Chain Framework to structure our analysis. The kill chain is a structured framework introduced by Lockheed Martin in 2011 to break down cyberattacks into distinct stages, helping defenders anticipate and thwart threats before they reach their objective [55,56]. This incident demonstrated that a lack of security capabilities (prevention, detection, response, and recovery) leaves systems vulnerable to attackers, and more systems at risk can eventually be breached and become compromised systems through lateral movement and interaction between compromised and non-compromised systems. The Colonial Pipeline incident follows the systemic structure shown in Figure 1.
Additionally, we explored this structure in a facilitated workshop at the level of the European Union (EU) with over a dozen strategists, including security executives, CISOs, and senior managers from various national security agencies, the European Union Agency for Cyber Security (ENISA), leading suppliers of medical equipment, and hospitals. Although the systemic structure was found to be accurate, we observed some minor nuances, particularly regarding combating the ransomware threat, leading to the following feedback:
- The cost of recovery can be extremely high, however paying the ransom (B6) might not guarantee prompt and full recovery and involve a significant cost (R7) that affects profitability. Additionally, the adversary might be permitted to return (R8), with approximately an 80% probability of them repeating the attack [57,58] if the ransom is paid, and a 62% probability that not all data will be recovered [57]. Ransom payment reinforces the feedback loop for the attacker, as success encourages future attacks. This structure clarifies the policy choice of paying or not paying a ransom and its effects on recovery, adversary behavior, and future risk.
- Defenders’ overinvestment in cyber risk management [59] will lead to a costlier impact on their profitability, as a rigid security compliance culture may hinder day-to-day business operations [60].
- Principles of design and architecture affect network and infrastructure (part of prevention) and, thus, influence business continuity and disaster recovery. The maturity of detection and response is interrelated, as anticipation of attacks in the form of response is only possible when such attacks are detected. Therefore, effective cyber risk management requires balanced investment across capabilities, underscoring the need for strategic roadmap planning and robust security architecture.
This feedback affects the current systemic structure. Figure 2 displays the changes in systemic structure based on this feedback vis-à-vis the systemic structure presented in Figure 1. In Figure 2, the additional structures relevant to combating advanced cyber threats are shown in green, the structures refined based on workshop feedback in black, and the newly added variables in grey.
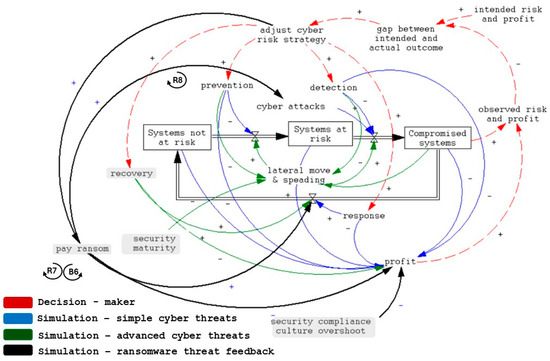
Figure 2.
Updated systemic structures of cyber risk management based on feedback from expert workshops regarding the ransomware threat. + indicates a positive relation between connected variables. - indicates negative relation between connected variables. BX refers to a balancing feedback loop with number X. RY refers to a reinforcing feedback loop with number Y.
Supported by literature and expert consultation, this systemic structure provides a lens for assessing how cyber breaches unfold. The Colonial Pipeline incident [61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88] illustrates how gaps in prevention and detection enabled an initial compromise to propagate by reinforcing feedback loops, such as lateral movement and delayed response, culminating in significant operational and economic disruption.
3. Insights from the Colonial Pipeline Case
This section provides a systematic walkthrough of the well-documented Colonial Pipeline breach, using the kill chain approach to reflect on current systemic structures and explore the areas where AI can be effective in the kill chain. AI has a significant impact on both attacker and defender spaces in the kill chain [61].
3.1. Explaining the Kill Chain
The kill chain is a structured framework introduced by Lockheed Martin in 2011 to break down cyberattacks into distinct stages, helping defenders anticipate and thwart threats before they reach their objective [55,56]. The traditional seven-step model (reconnaissance, weaponization, delivery, exploitation, installation, command and control, and action) outlines an attacker’s progression from reconnaissance to exploitation. Evolving threats have led to more adaptive frameworks, such as the Unified Kill Chain and MITRE Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge (ATT&CK), which offer deeper insights into adversary tactics [62].
Defenders can map security measures to each stage. The defense-in-depth concept, an attempt to protect a computer with a series of defensive mechanisms so that the failure of one mechanism leads to another being in place to repulse an attack [63], requires measures at each stage. Unlike the original linear model, these modern frameworks recognize that real-world attacks are iterative, with adversaries revisiting and refining their methods to bypass defenses. This shift highlights the need for dynamic cybersecurity approaches capable of countering increasingly sophisticated threats [64].
The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack highlights the modern challenges and the present glaring cybersecurity gaps.
3.2. A Kill Chain Perspective from the Colonial Pipeline Incident
The Colonial Pipeline attack was one of the most detrimental cyberattacks on U.S. soil, resulting in a historic 45% shutdown of the fuel consumed on the East Coast for several days, leading to panic buying, and 68% of gas stations in North Carolina running out of fuel at the peak of the crisis [65]. The average national gas price jumped to over $3 per gallon, the highest since 2014, and 70% of Americans surveyed in the aftermath reported doubt and grave concern about the security of national infrastructure [66]. Table 2 indicates the diverse contributory adversarial actions and defenders’ needs, explained in the forthcoming sections.

Table 2.
Kill chain perspective on Colonial Pipeline breach; bold = missing measure, italics = not fully effective measure. Categorization of measures: (P)revention, (D)etection, (R)esponse, (Rec)overy. References used are media reports (media), scientific work (science), industry surveys (industry), white papers (white papers), and practitioners’ insights (practitioners).
An attacker’s perspective. The adversaries initiated their operation against Colonial Pipeline with a calculated reconnaissance phase. DarkSide introduced its ransomware in August 2020 and established a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model by November 2020, inviting competition from smaller hacker groups [67].
Reconnaissance. The attackers, working in groups to split profits [68], used multiple methods to reconnoiter Colonial Pipeline’s infrastructure. They conducted passive surveillance, observing online traffic patterns [70]. To identify vulnerabilities, they deployed scanners and automated credential checkers. DarkSide used legitimate tools for reconnaissance, including PowerShell and BloodHound [69]. Ultimately, a data breach revealed a single reused password, allowing access to the corporate Virtual Private Network (VPN). In terms of the systemic structure shown in Figure 2, this is the stage where a system at risk becomes compromised by a cyberattack weaponization. DarkSide developed custom malware tailored for this attack [71], designed to evade intrusion detection and response (IDR) tools. They prepared multiple attack vectors [72]. The most likely exploitation route was through the compromised VPN, which lacked multi-factor authentication [73].
Delivery. The attackers gained unrestricted access through the VPN, avoiding detection while deploying payloads for encryption, exfiltration, and data manipulation [74].
Exploitation. DarkSide affiliates established their presence, altering file permissions for wider access [80]. They escalated privileges, targeting Domain Controller (DC) credentials. To evade detection, their malware bypassed debugging processes [76] using system tools such as PowerShell and Certutil along with custom malware [77]. For lateral movement, they leveraged the tool PSExec and the RDP protocol. They aimed primarily to exploit the Active Directory, harvest credentials, and acquire valuable assets [81].
Installation. With control of the DC, the attackers managed security authentication and adjusted policies [78]. They used the compromised DC to deploy ransomware across connected machines and ensure persistent remote access. DarkSide possibly employed DCSync for credential harvesting [75]. Through PowerShell, they accessed downstream accounts and removed backups to prevent system recovery [65]. By this point, they had evaded monitoring and covered their tracks. In terms of the systemic structure shown in Figure 2, this is the stage where the adversary shows lateral movement, and the number of compromised systems increases as it turns more systems at risk into compromised ones.
Command and Control. DarkSide maintained control using encrypted communication channels and remote access tools. They masked traffic to prolong persistence, deploying Cobalt Strike and AnyDesk for ongoing remote command execution.
Weaponization, exploitation, and delivery. DarkSide’s operators maneuvered undetected, with tactics such as APTs [82]. On 1 May 2021, security alerts piled up, signaling privilege escalations and unauthorized access attempts [79]. Emergency meetings were held and mitigation measures deployed, which, however, the attackers anticipated and adjusted accordingly. Colonial’s security engineers combed through system logs, but DarkSide’s employment of legitimate administrative tools obscured their malicious actions [70].
Command & Control, and action. The company brought in Mandiant, a leading incident response firm, to assess the damage. Their analysis confirmed the worst: ransomware had infected critical systems, backups were deleted, and encrypted files left substantial portions of Colonial’s IT infrastructure inoperable [86]. The operational technology (OT) side of the business remained untouched due to network segmentation, but executives opted to shut down pipeline operations entirely as a precaution [82]. This decision, although driven by risk management, led to significant consequences. Approximately 50 million Americans faced fuel shortages, leading to panic-buying and increased gas prices [83].
To contain the breach and minimize disruption to national infrastructure, Colonial’s IT and security teams collaborated with federal agencies such as the FBI and the Department of Homeland Security [87]. However, containment proved elusive. DarkSide had secured deep access, and efforts to revoke compromised credentials came too late to be effective. The attackers had already extracted sensitive data, using the dual threat of encryption and public disclosure to maximize leverage [88].
The attack soon escalated to an overwhelming financial impact involving economic losses rippling through industries reliant on fuel supply, with estimated damages of over $5 billion [84]. The company faced Hobson’s choice: refuse to pay the ransom and endure prolonged outages or negotiate with the cybercriminals. Ultimately, Colonial was forced to pay $4.4 million in ransom in Bitcoin to regain control of their systems [85]. In terms of the systemic structure shown in Figure 2, this is the part where risk exposure and profitability impact become visible to the decision-makers.
3.3. The Aftermath
The Colonial Pipeline incident reverberated across the cybersecurity community, highlighting ransomware’s potential to cripple critical infrastructure. Lawmakers and industry leaders pushed for reforms, advocating stricter regulations, enhanced cybersecurity frameworks, and mandatory reporting of cyber incidents [87]. The FBI recovered part of the ransom, signaling a stronger stance against cyber extortionists. However, the vulnerabilities exposed by the breach remained a critical concern. The incident was not merely a failure of cybersecurity controls, but a strident alarm sounded for industries relying on legacy systems and outdated defense strategies. It demonstrated that a lack of security capabilities (prevention, detection, response, and recovery) leaves systems vulnerable to attackers, with systems at risk being in a position to become compromised. Due to the interaction between compromised and non-compromised systems through lateral movement, the compromised systems increased. These epidemic properties of a cyberattack significantly impact an organization. The Colonial Pipeline incident follows the systemic structure shown in Figure 2.
4. How Does AI Shape the Systemic Structures to Manage Cyber Risks?
To understand how AI can change the threat landscape, we conducted three facilitator-led workshops involving business leaders, security executives, researchers, and strategic and policy officers from various industries, governments, and universities.
One workshop was part of a larger event organized by a leading university about managing cyber supply chain risks, with AI being a sub-theme of the dialogue. Over 40 participants from 25 globally operating enterprises and leading universities were present, with executive representation from the healthcare, technology, energy, and finance sectors. The second workshop, called the Cyber Security Management Symposium, was also part of a larger event organized by a leading university [89], with AI and systemic structure being sub-themes of this dialogue. Senior researchers, managers, executives, and professors from the fields of technology, security, national security organizations, and law enforcement from the Netherlands were present. The third workshop, organized by a leading university, was an interactive workshop titled “The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: AI,” with approximately 50 participants from diverse backgrounds and experience from different industries and universities, mainly based in the USA and Europe. The workshop was primarily focused on how threat actors are using AI to commit cybercrime.
A key debate emerged in each of these sessions. Some participants argued that the evolution of AI follows the familiar cycle of attack and defense escalation, where both sides innovate, adapt, and learn [5,6,7]. These participants further claimed that the components of cyber risk management, for instance, identifying, assessing, and mitigating vulnerabilities through security controls and monitoring, remain unchanged [37,38,39,40], especially since autonomous agents continue to exploit “old-school” fundamental weaknesses [18]. However, other participants contended that AI would amplify threats by multiplying the attack’s speed, scale, and automation manifold [12,14]. Nonetheless, automation, scale, and speed can also benefit defensive capabilities and, thus, potentially lower the cost of breaches [90]. Overall, the threat landscape will be affected by technological change on both attackers’ and defenders’ sides. Although the ongoing escalation between attackers and defenders is not new, we are particularly interested in finding new systemic structures. This becomes evident when assessing the different phases of the kill chain for both the attacker (Section 4.1) and defenders (Section 4.2).
4.1. A Kill Chain Perspective on AI-Powered Attacks
Following the context of these workshops, we searched for associated literature (58 documents comprising security blogs, industry reports, opinion-based articles, and research papers). This provides more details, shown in Table 3, about how these evolutions relate to the different steps in the kill chain. AI-driven cyber threats are evolving rapidly, automating attacks and enhancing stealth through three key functionalities defining this transformation: AI that codes cyberattacks, AI that strengthens a step in the cyber kill chain, and AI that integrates multiple steps into a seamless attack process.

Table 3.
How AI affects attacks and defense: a kill chain perspective. References used are media reports (media), scientific work (science), industry surveys and blogs (industry), white papers (white papers), and practitioners’ insights (practitioners) [17,18,21,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143].
AI automates the creation of cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, and deepfakes. Large Language Models (LLMs) are used for coding and debugging malware, enhancing scripting techniques, refining operational techniques, and automating service delivery [91,92,93]. SugarGh0st RAT, com.example.myttt, com.mihanwebmaster.ashpazi, Win32/Wkysol, and AsyncRAT (ibid.) are some malware examples. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) craft malware that mimics legitimate software to evade detection [94]. LLMs like, GPT-4, Claude 2, PaLM, and LLaMA, generate tailored phishing content, making deception more effective [95]. These advancements pose significant challenges to traditional security defenses [96,97].
AI strengthens kill chain steps. AI enhances specific stages of the cyber kill chain, increasing automation and effectiveness. In reconnaissance, machine learning models scan vulnerabilities with high accuracy, identifying weaknesses in real time [98]. AI automates the weaponization phase by generating customized exploits and optimizing payloads for maximum impact based on triggering conditions. DeepLocker malware is an example [99]. Simultaneously, adversarial AI misleads security models, bypassing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) [100]. Polymorphic malware, such as Black Mamba [17], continuously alters its code to remain undetected. In delivery, AI analyzes target behaviors to time attacks strategically, ensuring higher success rates [101]. AI-driven exploitation accelerates the identification and exploitation of system vulnerabilities while avoiding detection [102,103]. AI-powered botnets in the command and control (C2) phase use Natural Language Processing (NLP) for human-like interactions, improving phishing and coordination [104].
AI integrates kill chain automation. Beyond individual steps, AI enables further automation of the cyber kill chain, integrating multiple attack stages seamlessly. For instance attackers employ federated learning to create resilient, decentralized botnets that evade detection [105,106], or AI-driven exfiltration blends data transfers into normal network traffic, reducing visibility [107]. Another form of kill chain automation is the use of Automated Aggressive Agents (AAA), which coordinate cyberattacks with minimal human intervention, making threats more persistent [108]. Examples of AAA include WannaCry, NotPetya, BadRabbit, Stuxnet, Morris Worm, Conficker, Hammertoss [18], more recent AI-driven EyeSpye [109], automated code injections in web applications [110], or targeting security controls to neutralize defenses before launching attacks [111]. APTs leverage AI for continuous adaptation, requiring organizations to adopt AI-driven defensive strategies [112,113]. GANs are used to probe and discover new attack forms such as attackGAN [114], ISDGAN [100], and MalwareGAN [115].
As AI accelerates cyber threats, defenders must integrate AI-driven solutions to counter evolving attack methods, thereby reducing attackers’ operational windows [112,116].
AI targeting AI. As AI increases the degree of automation, business operations face a parallel evolution. The autonomous nature of certain processes introduces a new threat: AI-dependent business functions can be subtly targeted by automated attacks. Over time, these systems may drift beyond their intended control, gradually becoming sources of risk. Such “rogue” behavior [123,124,125,126], akin to an automated insider, can arise from biased training data, adversarial manipulation, prompt engineering, or misaligned optimization goals. The outcomes may include flawed automated decisions, data exposure, or operational disruption. This risk originates within the organization, unlike traditional cyber threats, with AI acting simultaneously as asset and adversary. This dynamic reshapes systemic structures, as systems at risk slowly transform into adversarial agents embedded in the defender’s own technology stack.
4.2. A Kill Chain Perspective on AI-Powered Defenses
AI is transforming cybersecurity by integrating multiple defensive capabilities into autonomous solutions. With a focus on prevention and detection—and a more effective role in the front end of the kill chain—AI-driven systems enable Automated Security Hygiene, thus continuously optimizing security to proactively address vulnerabilities and prevent threats. When emphasizing detection, response, and recovery—and a more prominent role in the back end of the kill chain—AI evolves into Autonomous and Deceptive Defense Systems. These systems autonomously detect and neutralize threats in real time while employing deceptive tactics to mislead attackers, ensuring rapid response and minimal damage.
Automated Security Hygiene involves AI-driven maintenance and security processes that ensure a healthy IT infrastructure. Key capabilities include:
- self-healing software code that automatically detects, diagnoses, and corrects issues without human intervention [117];
- self-patching systems that autonomously identify, download, and apply updates or patches to address vulnerabilities [118];
- continuous attack surface management [119] with automated threat mitigation [120], which proactively monitors and manages digital assets, thereby addressing vulnerabilities before their exploitation;
- autonomous and adaptive identity and access management, which adjusts user identities, access permissions, and authentication based on real-time conditions [121]; and
- self-driving trustworthy networks that autonomously manage and secure themselves by continuously detecting and responding to issues or threats [122].
These capabilities significantly reduce the need for manual intervention while enhancing overall security and operational efficiency.
Deceptive Defense Systems, such as Moving Target Defense (MTD), dynamically alter system configurations, complicating attacks [143,144]. Such deception strategies, along with misinformation, misrepresentation, and decoys, mislead attackers and gather intelligence to improve security measures [145] by luring attackers into controlled environments. Additionally, game theory models demonstrate how decoys delay and mislead attackers, minimizing damage [146]. Simultaneously, IDS and deception techniques refine real-time defenses [147], while cognitive biases manipulate adversaries’ decisions [148]. Deceptive Defense Systems alter existing systemic structures by enabling defenders to introduce “controlled” compromised systems. These systems attract adversarial resources while minimizing material harm to the defender, as long as the adversary believes they are targeting real systems.
Autonomous Defense Systems use AI to independently analyze telemetry data from interconnected devices, detect potential threats, and respond proactively by integrating real-time threat intelligence.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platforms unify security tools and apply AI analytics for threat detection. Industry claims that AI-driven XDR has closed the evolving attacker-defender gap, significantly improving endpoint security. It claims a detection accuracy increase of 76% [111].
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) systems automate incident response, reducing false positives and prioritizing high-risk threats [112]. AI enhances malware defense by leveraging deep learning for threat prediction.
- Cylance PROTECT identifies malware patterns without traditional signatures [127]. AI dynamically adjusts protocols to address vulnerabilities [128]. Unsupervised machine learning aids in anomaly detection and security breach identification.
- Darktrace’s Enterprise Immune System establishes behavior baselines to detect threats [129]. AI also limits malware spread by predicting attack patterns [130].
Improved learning mechanisms strengthen the defender. For instance, GANs enhance cybersecurity by simulating attack scenarios and strengthening machine learning defenses [131]. Originally intended for image generation, GANs now generate synthetic network traffic to refine threat detection [132] and bolster malware detection and anomaly recognition by exposing models to deceptive attacks [133]. Additionally, AI-driven security learns from past breaches, improving response strategies [134], while adaptive systems dynamically update detection models to counter emerging threats [135]. These advancements help defenders anticipate threats, neutralize attacks efficiently, and reduce cyber risks [136].
Another mode of advanced learning is that AI-driven real-time threat analysis detects and mitigates cyberattacks instantly. For instance, it identifies anomalies, such as DDoS surges, and applies rate-limiting to isolate malicious traffic while ensuring service availability [137]. Another example is the Copilot Guided Response (CGR) system, which enhances security with tailored containment strategies based on past incidents [138]. Further, machine learning predicts threats by analyzing network behavior, enabling proactive defense [139,140], and AI refines mitigation strategies through reinforced learning from past attacks [141]. AI also conducts forensic analysis to assess damage and strengthen future defenses [140,142]. These adaptive approaches ensure future resilience.
Finally, workshops and expert consultations indicated that AI-driven security solutions face risks despite their strengths. Attackers may whitelist malicious codes, poison defenders’ models, or neutralize defenses to evade detection [111]. This highlights the need for continuous monitoring and safeguarding of data integrity, which increases the risk of defenders falling into a capability trap. Moreover, generative AI applications can be repurposed for AI-driven attacks by exploiting vulnerabilities in such applications [149,150].
4.3. How AI Reshapes the Systemic Nature of Cyber Risk Management
Table 4, derived from the workshops and supporting literature, provides a consolidated overview of AI evolutions from both attacker and defender perspectives. The table highlights where systemic structures are affected. When tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of either attackers or defenders are influenced, this typically reflects an acceleration of the existing adversarial “arms race” in terms of speed, scale, and automation without altering the underlying systemic structures. Conversely, when different system states emerge, this indicates a structural transformation. In this table, events that trigger such systemic changes are highlighted in grey.

Table 4.
Cybersecurity and AI-related literature. Gray-labeled areas suggest a system change. Gray marked areas relate to new added substructures.
Our analysis further suggests that significant technological advances can alter model parameters, particularly where higher levels of automation make timing a critical factor. Beyond these parameter shifts, we identified three structural changes in the systemic model compared to Figure 1. Each of these systemic changes is discussed in detail in the following sections. For clarity, each new systemic structure is presented in a separate figure, with added structures shown in black and variables in grey.
Deceptive defense structures that control compromise without business impact. Figure 3 illustrates this new systemic structure. Modern cybersecurity defense increasingly integrates deception capabilities as a proactive mechanism to manage risk. These capabilities establish controlled compromised systems. These are artificially created network segments or decoy environments that simulate vulnerable assets without exposing critical business operations. In this systemic structure, the adversary is misled into engaging with deceptive artifacts, such as honeypots, sandboxed services, or fake credentials, in the mistaken belief of targeting valuable infrastructure (B7).
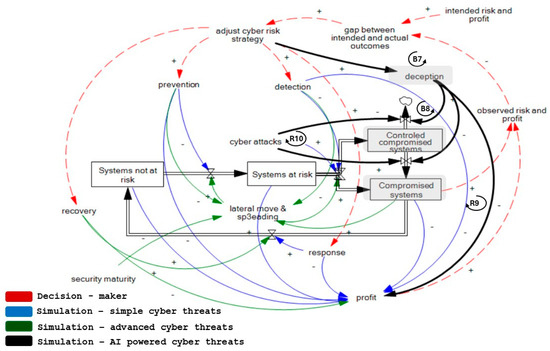
Figure 3.
Deceptive defense structures that control compromise without business impact—systemic structure. + indicates a positive relation between connected variables. - indicates negative relation between connected variables. BX refers to a balancing feedback loop with number X. RY refers to a reinforcing feedback loop with number Y.
From a system dynamics perspective, this structure introduces a balancing loop (B8) wherein adversarial effort increases without yielding meaningful success, thus raising the likelihood of the attacker abandoning the mission. However, this deception architecture involves ongoing costs related to setup, maintenance, and monitoring, thus generating a reinforcing cost loop (R9) that affects defender profitability. If the adversary eventually detects the deception—through behavioral analysis or failed escalation attempts—it may trigger an escalation loop (R10) in which attackers reassess, retool, or reallocate resources for renewed attacks on actual infrastructure. Alternatively, it may cause the adversary to stop if the costs and efforts of the attack exceed acceptable levels.
This structure is most effective when paired with cognitive and behavioral deception strategies (e.g., dynamic IP shifts, misinformation, or decoy file systems), which maximize attacker uncertainty. However, defenders must maintain the credibility of these deceptive environments to prolong attacker engagement and delay escalation.
Two-step success attacks through the subversion of security capabilities. A particularly insidious systemic evolution involves a two-step attack strategy, which exploits success-to-success feedback mechanisms across cyber defense layers. In this structure, displayed in Figure 4, the adversary first compromises the integrity of a security capability, for instance, by poisoning AI training data, evading anomaly detection through adversarial examples, or whitelisting malicious signatures in endpoint protection systems. This first success enables a second, more consequential breach: a targeted attack on core infrastructure, now effectively unprotected or blind to the threat (R11–R13). Another example of this first step is overwhelming the defense systems with small, ever-changing volumetric attacks that use all defense capacity while the defender lacks the remaining capacity for the real attack.
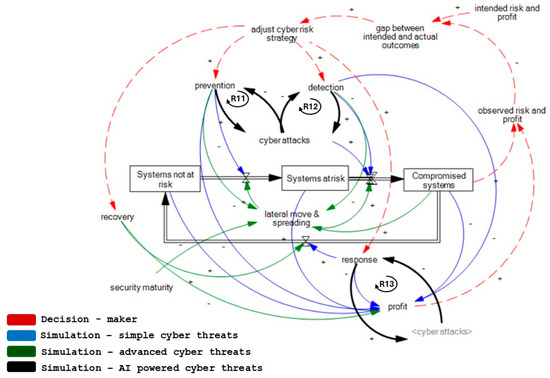
Figure 4.
Two-step success attacks through the subversion of security capabilities—systemic structure. + indicates a positive relation between connected variables. - indicates negative relation between connected variables. RY refers to a reinforcing feedback loop with number Y.
This structure presents a delayed-response risk dynamic. The defender believes systems are protected, while the core detection or prevention layer has already been neutralized. The aging chain of capabilities, where security functions degrade over time if not maintained, is particularly vulnerable under this model. Once prevention (R11) is bypassed, detection failures (R12) follow, and response (R13) is hampered due to a lack of telemetry or misclassification of incidents.
Such attacks amplify systemic fragility, as compromised capabilities can no longer regulate the flow of systems from “at risk” to “compromised.” Consequently, there is a false sense of control, where defenders continue operations unaware of the severing of their foundational security feedback loops. This emphasizes the importance of continuous validation, model integrity testing, and red-teaming of AI-based tools to ensure resilience across all defense functions.
Autonomous proliferation through the misuse of AI applications. A third emergent feedback structure involves self-propagating attack generation, enabled by misused or compromised AI applications. In other words, this involves AI applications going rogue while still acting within their predefined boundaries and guardrails due to design flaws [151]. In this situation, systems at risk become adversarial.
Once embedded in the defender’s digital environment through tools such as generative agents, code-writing LLMs, or AI-augmented phishing bots, these systems autonomously generate further adversarial behavior, such as attack vectors, exploiting configuration weaknesses, unpatched systems, or internal tooling.
This structure, shown in Figure 5, mirrors recursive success loops, where each undetected malicious output (e.g., new malware variants, privilege escalation scripts, or lateral movement playbooks) feeds back into the system, producing additional threats and possibly providing more adversarial systems. As long as the initial AI-driven agent remains active and undetected, it continues to compound the attack surface, using the known structure for lateral movement and spreading dynamics. This means an existing structure will largely be repurposed by another modus operandi.
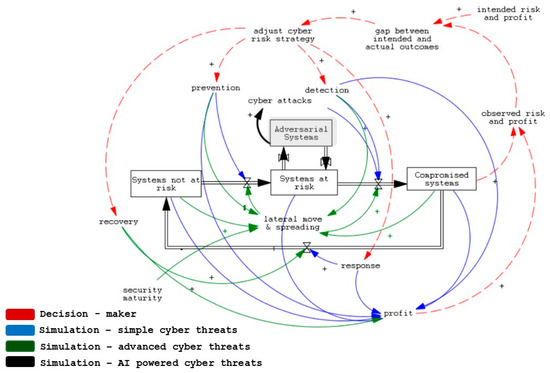
Figure 5.
Autonomous proliferation through misuse of AI applications—systemic structure. + indicates a positive relation between connected variables. - indicates negative relation between connected variables.
Overall, these new dynamics create a compounding growth function in attack frequency and complexity. Unlike traditional manual attacks, often requiring iterative human input, AI-enabled agents can continuously scan the defender’s footprint, generate automatically adversarial code, and deploy it automatically. This makes containment and mitigation far more difficult. Further, defenders may misattribute the source of attacks, assuming external intrusion rather than in-site exploitation through trusted AI applications that have gone rogue.
Organizations must, therefore, view AI as not only a tool for automation but also a potential attack vector. Safeguarding model inputs, enforcing model usage boundaries, and implementing real-time audit trails and behavioral anomaly detection in AI services are essential to disrupt these feedback loops before they escalate.
5. Summary of Structural Changes over Time in Cyber Risk Management
Our work explores how AI fundamentally transforms the systemic structures that underpin cyber risk management. To investigate this, we synthesized insights from scientific literature, industry reports, and expert workshops, complemented by a detailed walkthrough of the Colonial Pipeline incident. The result is a refined understanding of how traditional cyber risk structures evolve and how entirely new ones emerge in response to AI-enabled threats. The dual effects of AI reveal its paradoxical role as a simultaneous risk amplifier and risk mitigator.
We identified three new systemic structures that illustrate the dynamic interplay between attackers and defenders in an AI-driven threat landscape. First, deceptive defense structures create controlled, compromised environments that absorb adversarial activity without exposing real assets, shifting emphasis from pure prevention to adversary misdirection. Second, two-step success feedback attacks exploit and disable security capabilities as a precursor to broader breaches, showing how AI can silently erode resilience by undermining the very mechanisms intended to protect organizations. Third, autonomous proliferation through the misuse of AI applications demonstrates how AI systems can self-replicate and continuously generate attack vectors once they go rogue and embed themselves as adversarial agents. They accelerate exposure without relying on traditional command-and-control patterns. These structures highlight that cyber threats no longer follow linear progressions but instead emerge from complex, adaptive interactions across socio-technical systems.
From these findings, two critical implications emerge. First, deception as a security capability must be embraced in security standards. Deceptive defense systems are no longer optional because they represent a systemic counterbalance to AI-driven automation that can absorb delay and redirect adversarial effort. Second, national security agencies must recognize that insider threats can now originate from AI-powered systems as well. Complex AI-dependent software supply chains, which increasingly drive critical business operations, create heightened risk when these systems drift beyond intended control or are manipulated by adversaries. As highlighted by CrowdStrike [152] and Log4J [153], compromised systems in supply chains often have an unexpectedly long reach and are capable of escalating into potential systemic failures at a national scale.
Moreover, our research underscores the accelerating pace of structural change in cybersecurity, evolving from the emergence of simple threats in the 1970s to the rise of advanced threats such as ransomware and now to AI-powered adversaries. These shifts are not merely incremental but also compounding transformations, where each new wave of threats builds upon and amplifies the vulnerabilities of previous ones. Simultaneously, the associated policy options evolve, creating a moving target for both defenders and regulators. As illustrated in Table 5, the failure to anticipate or adapt to these new feedback dynamics risks triggering cascading failure modes with far-reaching strategic, financial, and operational consequences. To address this reality, policymakers, industry leaders, and security practitioners must ensure continuous policy adaptation, systemic monitoring, and forward-looking governance approaches to prevent present structural weaknesses from becoming future systemic crises.

Table 5.
Evolution of systemic structures.
During this study, there appeared initial examples of general AI agents, using multiple AI models and various independently operating agents to act autonomously on a wide range of tasks, such as Manus [154]. In our work, we have not assessed the cyber threat implications of multi-agent AI models. This should be explored in future research.
This is a qualitative study grounded in systems dynamics modeling. As a next step, we see strong value in developing quantified simulation models based on these systemic structures. These simulations will enable practitioners and policymakers to evaluate various AI-driven threat scenarios, assess potential impacts, and evaluate the effectiveness of different strategic responses under dynamic conditions. Through this, organizations can move beyond static assessments and anticipate and shape risk trajectories—rather than merely reacting to them. Ultimately, this shift is not only indispensable for maintaining security in an AI-augmented world but foundational to sustaining trust, resilience, and continuity in an increasingly complex digital economy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z. and Y.K.L.; methodology, S.Z. and Y.K.L.; software, S.Z.; validation, S.Z., A.A. and M.S.; formal analysis, Y.K.L. and S.Z.; investigation, Y.K.L. and S.Z.; resources, S.Z., A.A. and M.S.; data curation, Y.K.L. and S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z., Y.K.L. and S.L.S.; writing—review and editing, S.L.S., A.A. and M.S.; visualization, S.Z.; supervision, S.Z. and M.S.; project administration, A.A., S.Z. and M.S.; funding acquisition, A.A., S.Z. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been funded by Topsector ICT and HTSM through the CYGENT project.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bornet, P.; Barkin, I.; Wirtz, J. Intelligent Automation: Welcome to the World of Hyperautomation: Learn How to Harness Artificial Intelligence to Boost Business & Make Our World More Human; Full, Paperback, EN; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2020; ISBN 979-8-6918-1923-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kotzias, K.; Bukhsh, F.A.; Arachchige, J.J.; Daneva, M.; Abhishta, A. Industry 4.0 and Healthcare: Context, Applications, Benefits, and Challenges. IET Softw. 2023, 17, 195–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahar, M. Cyber-attacks and Terrorism: A Twenty-First-Century Conundrum. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2019, 25, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, V. The History of Cybersecurity. Cyber Magazine. 2021. Available online: https://cybermagazine.com/cyber-security/history-cybersecurity (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Böhme, R.; Moore, T. The “Iterated Weakest Link” Model of Adaptive Security Investment. J. Inf. Secur. 2016, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clayton, R.; Moore, T.; Christin, N. Concentrating Correctly on Cybercrime Concentration. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Economics in Information Security, Delft, The Netherlands, 22–24 June 2015. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Martinez-Moyano, I.J.; Morrison, D.; Sallach, D. Modeling Adversarial Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2015 Winter Simulation Conference, Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 2412–2423. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Costa, J. Counter AI Attacks with AI Defense. Palo Alto Networks. 2024. Available online: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/blog/2024/05/counter-with-ai-defense/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).[Green Version]
- Acronis 2024 Cybersecurity Trends: Key Steps, Strategies and Guidance. Acronis. Available online: https://www.acronis.com/en/blog/posts/cyber-security-trends/ (accessed on 9 May 2024).[Green Version]
- Redefining Cyber Defense. The Evolution of Threat Detection with Artificial Intelligence. Res. Mach. Learn. Cybersecur. 2024, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasegar, M.; Shanthi, R.; Nitin, M.; Sasi, K. A New Era of Cybersecurity: The Influence of Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Networking and Communications (ICNWC), Chennai, India, 5–6 April 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). FBI Warns of Increasing Threat of Cyber Criminals Utilizing Artificial Intelligence. FBI San Francisco. Available online: https://www.fbi.gov/contact-us/field-offices/sanfrancisco/news/fbi-warns-of-increasing-threat-of-cyber-criminals-utilizing-artificial-intelligence (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Aggrey, R.; Adjei, B.A.; Afoduo, K.O.; Dsane, N.A.K.; Anim, L.; Ababio, M.A. Understanding and Mitigating AI-powered Cyber-Attacks. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 6, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Schröer, S.L.; Apruzzese, G.; Human, S.; Laskov, P.; Anderson, H.S.; Bernroider, E.W.N.; Fass, A.; Nassi, B.; Rimmer, V.; Roli, F.; et al. SoK: On the Offensive Potential of AI. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Secure and Trustworthy Machine Learning, Copenhagen, Denmark, 9–11 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Redaction. Email-based Phishing Attacks Have Surged 464% in 2023. Indian Times. 2013. Available online: https://ciosea.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/security/email-based-phishing-attacks-has-surged-464-in-2023- (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Macaulay, T. Deepfake Fraud Attempts are Up 3000% in 2023—Here’s Why. Next Web. 2023. Available online: https://thenextweb.com/news/deepfake-fraud-rise-amid-cheap-generative-ai-boom (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Montalbano, E. AI-powered ‘BlackMamba’ Keylogging Attack Evades Modern EDR Security. DarkReading. 2023. Available online: https://www.darkreading.com/endpoint-security/ai-blackmamba-keylogging-edr-security (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- The Grungq. The Triple A Threat: Aggressive Autonomous Agents. BlackHat. 2017. Available online: https://www.blackhat.com/docs/webcast/12142017-the-triple-a-threat.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Bloomberg. The World’s Third-largest Economy Has Bad Intentions—and It’s Only Getting Bigger. Bloomberg. 2024. Available online: https://sponsored.bloomberg.com/quicksight/check-point/the-worlds-third-largest-economy-has-bad-intentions-and-its-only-getting-bigger (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Petrosyan, A. Estimated Cost of Cybercrime Worldwide 2018–2029, statusta.com. 2025. Available online: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1280009/cost-cybercrime-worldwide (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Hall, B. How AI-Driven Fraud Challenges the Global Economy and Ways to Combat It. World Economic Forum. 2025. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2025/01/how-ai-driven-fraud-challenges-the-global-economy-and-ways-to-combat-it/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Leclair, J. Testimony of Dr. Jane Leclair Before the U.S. House of Representatives Committee on Small Business. 2015. Available online: https://smallbusiness.house.gov/uploadedfiles/4-22-2015__dr.__leclair__testimony.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Cyentia Institute. Information Risk Insights Study: A Clearer Vision for Assessing the Risk of Cyber Incidents. 2021. Available online: https://www.cyentia.com/wp-content/uploads/IRIS2020_cyentia.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- IBM Security. Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022. Available online: https://community.ibm.com/community/user/events/event-description?CalendarEventKey=7097fd42-4875-4abe-9ff6-d556af01688b&CommunityKey=96f617c5-4f90-4eb0-baec-2d0c4c22ab50&Home=%2Fcommunity%2Fuser%2Fhome (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Welburn, J.W.; Strong, A.M. Systemic Cyber Risk and Aggregate Impacts. Risk Anal. 2022, 42, 1606–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeijlemaker, S.; Siegel, M.; Khan, S.; Goldsmith, S. How to Align Cyber Risk Management with Business Needs. World Economic Forum, Cyber Security Working Group. 2022. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2022/08/how-to-align-cyber-risk-management-with-business-needs/ (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Zeijlemaker, S.; Etiënne, A.J.A.R.; Cunico, G.; Armenia, S.; Von Kutzschenbach, M. Decision-makers’ Understanding of Cybersecurity’s Systemic and Dynamic Complexity: Insights from a Board Game for Bank Managers. Systems 2022, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeijlemaker, S.; Siegel, M. Capturing the dynamic nature of cyber risk: Evidence from an explorative case study. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS)–56, Maui, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J. Teaching Takes Off: Flight Simulators for Management Education—“The Beer Game”. MIT Sloan School of Management. 1992. Available online: http://web.mit.edu/jsterman/www/SDG/beergame.html (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Sterman, J. Modeling managerial behavior: Misperceptions of Feedback in a Dynamic Decision-making Experiment. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.S.; Siegel, M.; Madnick, S. Decision-making and biases in cybersecurity capability development: Evidence from a simulation game experiment. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2019, 28, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R. Why Information Security is Hard: An Economic Perspective. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–14 December 2001; pp. 358–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zeijlemaker, S.; Pal, R.; Proudfoot, J.; Siegel, M. Advancing Cyber Risk by Reducing Strategic Control Gaps. In AMCIS 2025 Proceedings; 2025; p. 28. Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2025/sig_sec/sig_sec/28 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Kim, G.; Zeijlemaker, S.; Proudfoot, J.; Pal, R.; Siegel, M. Balancing Risk and Reward in Cybersecurity Investment Decisions. In AMCIS 2025; Proceedings 4. 2025. Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2025/sig_sec/sig_sec/4 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Sepúlveda Estay, D. A system dynamics, epidemiological approach for high-level cyber-resilience to zero-day vulnerabilities. J. Simul. 2021, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenia, S.; Angelini, M.; Nonino, F.; Palombi, G.; Schlitzer, M.F. A dynamic simulation approach to support the evaluation of cyber risks and security investments in SMEs. Decis. Support Syst. 2021, 147, 113580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre of Internet Security (CIS). CIS Controls V8; CIS: East Greenbush, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Government Chief Information Officer (GCIO). An Overview of ISO/IEC 27000 Family of Information Security Management System Standards; (Original work published April 2015, updated May 2020); Office of the Government Chief Information Officer: Hong Kong, China, 2020.
- Muneer, F. Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model, Version 2.0; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Pascoe, C.E. Public Draft: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Eling, M.; McShane, M.; Nguyen, T. Cyber Risk Management: History and Future Research Directions. Risk Manag. Insur. Rev. 2021, 24, 93–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paté-Cornell, M.E.; Kuypers, M.; Smith, M.; Keller, P. Cyber Risk Management for Critical Infrastructure: A Risk Analysis Model and Three Case Studies. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeijlemaker, S.; Hetner, C.; Siegel, M. Four Areas of Cyber Risk That Boards Need to Address. Harvard Business Review. 2023. Available online: https://hbr.org/2023/06/4-areas-of-cyber-risk-that-boards-need-to-address (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Meurs, T.; Cartwright, E.; Cartwright, A.; Junger, M.; Hoheisel, R.; Tews, E.; Abhishta, A. Ransomware economics: A two-step approach to model ransom paid. In Proceedings of the 2023 APWG Symposium on Electronic Crime Research (eCrime), Barcelona, Spain, 15–17 November 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Liao, Q. Ransomware: A new cyber hijacking threat to enterprises. In Handbook of Research on Information Security and Assurance; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, J.; Cova, M.; Nagaraja, S. Command and Control: Understanding, Denying, and Detecting; University of Birmingham, Centre for the Protection of Natural Infrastructure: Birmingham, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Antrosio, J.V.; Fulp, E.W. Malware Defense Using Network Security Authentication. In Proceedings of the Third IEEE International Workshop on Information Assurance (IWIA’05), College Park, MD, USA, 23–24 March 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Antunes, H.; Aggarwal, S. Defending Connected Vehicles Against Malware: Challenges and a Solution Framework. IEEE Trans. Ind. Technol. 2014, 1, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAvoy, S.; Grant, T.; Smith, C.; Bontinck, P. Combining Life Cycle Assessment and System Dynamics to Improve Impact Assessment: A Systematic Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repenning, N.P.; Sterman, J.D. Capability Traps and Self-confirming Attribution Errors in the Dynamics of Process Improvement. Adm. Sci. Q. 2002, 47, 265–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeijlemaker, S.; Pal, R.; Siegel, M. Strengthening Managerial Foresight to Defeat Cyber Threats. In Proceedings of the 30th Americas Conference on Information Systems: Elevating Life through Digital Social Entrepreneurship, AMCIS 2024, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 15–17 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- European Union Agency for Cyber Security (ENISA). ENISA Threat Landscape. 2023. Available online: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/enisa-threat-landscape-2023 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Chapman, R. Ransomware Cases Increased by 73% in 2023 Showing Our Actions Have Not Been Enough to Thwart the Threat. SANS Institute. 2024. Available online: https://www.sans.org/blog/ransomware-cases-increased-greatly-in-2023/ (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Morgan, S. Global Ransomware Damage Costs Predicted to Exceed $265 Billion by 2031. Cybersecurity Ventures. 2023. Available online: https://cybersecurityventures.com/global-ransomware-damage-costs-predicted-to-reach-250-billion-usd-by-2031/ (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Zeng, W.; Germanos, V. Modelling Hybrid Cyber Kill Chain. PNSE@Petri Nets/ACSD. 2019. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Modelling-Hybrid-Cyber-Kill-Chain-Zeng-Germanos/f5cb1f80c669562d3dd61b4dcbc6410a5d015c62 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Yadav, T.; Rao, A.M. Technical Aspects of Cyber Kill Chain. In Security in Computing and Communications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-22915-7_40 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Cybereason. Ransomware: The True Cost to Business 2022; Report; Cybereason: Boston, MA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.cybereason.com/blog/report-ransomware-attacks-and-the-true-cost-to-business-2022 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Sganga, N.; Bidar, M. 80% of Ransomware Victims Suffer Repeat Attacks, According to the New Report. CBS News. 2021. Available online: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/ransomware-victims-suffer-repeat-attacks-new-report/ (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Scrotxon, A. Overinvestment Breeds Overconfidence Among Security Pros. Computer Weekly, TechTarget. 2019. Available online: https://www.computerweekly.com/news/252471326/Overinvestment-breeds-overconfidence-among-security-pros (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Reed, A. Don’t Be the Business Prevention Department. BAtimes–Resources for Business Analytics. 2022. Available online: https://www.batimes.com/articles/dont-be-the-business-prevention-department/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Zhang, C.; Pal, R.; Nicholson, C.; Siegel, M. (Gen) AI Versus (Gen) AI in Industrial Control Cybersecurity. In Proceedings of the 2024 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Savannah, GA, USA, 8–11 December 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 2739–2750. [Google Scholar]
- Pols, P.; Domínguez, F. The Unified Kill Chain. Publishers Panel. 2024. Available online: https://thepolicereview.akademiapolicji.eu/resources/html/article/details?id=614644&language=en (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- McGuiness, T. Defense in Depth; SANS Reading Room, White Paper; SANS Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ferazza, F.M. Cyber Kill Chain, MITRE ATT&CK, and the Diamond Model: A Comparison of Cyber Intrusion Analysis Models; Technical Report; Information Security Group, Royal Holloway University of London: Egham, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.royalholloway.ac.uk/media/20188/techreport-2022-5.pdf.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Beerman, J.; Berent, D.; Falter, Z.; Bhunia, S. A Review of Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 23rd International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing Workshops (CCGridW), Bangalore, India, 1–4 May 2023; Available online: https://sbhunia.me/publications/manuscripts/ccgrid23.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Goodell, J.W.; Corbet, S. Commodity Market Exposure to Energy-firm Distress: Evidence from the Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack. Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 51, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, B. A Closer Look at the DarkSide Ransomware Gang. Krebs on Security. 2021. Available online: https://krebsonsecurity.com/2021/05/a-closer-look-at-the-darkside-ransomware-gang/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Shimol, S.B. Return of the DarkSide: Analysis of a Large-Scale Data Theft Campaign. Varonis. 2021. Available online: https://www.varonis.com/blog/darkside-ransomware (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Agcaoili, J.; Earnshaw, E. Locked, Loaded, and in the Wrong Hands: Legitimate Tools Weaponized for Ransomware in 2021. Trend Micro. 2021. Available online: https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/security/news/cybercrime-and-digital-threats/locked-loaded-and-in-the-wrong-hands-legitimate-tools-weaponized-for-ransomware-in-2021 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Kerner, S.M. Colonial Pipeline Hack Explained: Everything You Need to Know. TechTarget. 2022. Available online: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/feature/Colonial-Pipeline-hack-explained-Everything-you-need-to-know (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Kleymenov, A. Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack: Revealing How DarkSide Works. Nozomi Networks. 2021. Available online: https://www.nozominetworks.com/blog/colonial-pipeline-ransomware-attack-revealing-how-darkside-works (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Zenarmor Anatomy of APT: Advanced Persistent Threat Guide. Zenarmor. Available online: https://www.zenarmor.com/docs/network-security-tutorials/what-is-advanced-persistent-threat-apt (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- ExpirerColonial Pipeline Cyber Attack Shows the Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication in 2021. Stratodesk. 2021. Available online: https://www.stratodesk.com/colonial-pipeline-cyber-attack-shows-the-importance-of-multi-factor-authentication/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Gonzales, M.; Dominquez, J. Inside DarkSide, the Ransomware that Attacked Colonial Pipeline. Metabase Q. 2022. Available online: https://www.cybereason.com/blog/inside-the-darkside-ransomware-attack-on-colonial-pipeline (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- ExtraHop. DCSync Attacks—Definition, Examples, & Detection. ExtraHop. 2020. Available online: https://www.extrahop.com/resources/attacks/dcsync (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Chen, X.; Andersen, J.; Mao, Z.M.; Bailey, M.; Nazario, J. Towards an Understanding of Anti-virtualization and Anti-debugging Behavior in Modern Malware. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks With FTCS and DCC (DSN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–27 June 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.J.; Graham, S.R.; Kabban, C.M.S.; Krasnov, J.J.; Henry, W.C. ScriptBlock Smuggling: Uncovering Stealthy Evasion Techniques in PowerShell and .NET environments. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2024, 4, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordis, G.A.; Costea, F.-M.; Pecherle, G.; Győrödi, R.Ş.; Győrödi, C.A. Considerations in Mitigating Kerberos Vulnerabilities for Active Directory. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering of Modern Electric Systems, Oradea, Romania, 9–10 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Boschee, P. Comments: Complexity of Cyber Crime Skyrockets. J. Pet. Technol. 2021, 73, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threat Intelligence TeamDarkSide Ransomware Analysis Report. Brandefense. 2021. Available online: https://brandefense.io/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/DarkSide-Ransomware-Analysis-Report.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- TrendMicro. What We Know About the DarkSide Ransomware and the US Pipeline Attack. TrendMicro Research. 2021. Available online: https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/21/e/what-we-know-about-darkside-ransomware-and-the-us-pipeline-attac.html (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Brash, R. Lessons Learned from the Colonial Pipeline Attack. Control Engineering. 2021. Available online: https://www.industrialcybersecuritypulse.com/facilities/lessons-learned-from-the-colonial-pipeline-attack/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Englund, W.; Nakashima, E.; Telford, T. Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack Shows Cyber Vulnerabilities of U.S. Energy Grid. The Washington Post, 10 May 2021. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2021/05/10/colonial-pipeline-gas-oil-markets/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Russon, B.M.A. US Fuel Pipeline Hackers “Didn’t Mean to Create Problems”. BBC News. 2021. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-57050690 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Eaton, C.; Volz, D. Colonial Pipeline CEO tells why he paid hackers a $4.4 million ransom. The Wall Street Journal. 2021. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/colonial-pipeline-ceo-tells-why-he-paid-hackers-a-4-4-million-ransom-11621435636 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Hasegawa, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Shimada, H.; Takakura, H. A Countermeasure Recommendation System Against Targeted Attacks While Preserving Continuity of Internal Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 38th Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference, Västerås, Sweden, 21–25 July 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 400–405. [Google Scholar]
- Watney, M. Cybersecurity Threats to and Cyberattacks on Critical Infrastructure: A Legal Perspective. Eur. Conf. Cyber Warf. Secur. 2022, 21, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Expert Briefings. Efforts to Curb Ransomware Crimes Face Limits. Emerald Expert Briefings. 2021. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Efforts-to-curb-ransomware-crimes-face-limits/381be69e12b854fc469c3a9b3e53451c59547e31 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Cyber Security Management Symposium. Industrial Engineering and Business Information Systems, University of Twente. Symposium Held at Ravelijn, University of Twente, Enschede, Netherlands. Retrieved from University of Twente Website. 2024. Available online: https://www.utwente.nl/en/bms/iebis/events/2024/11/1821797/cyber-security-management-symposium (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- IBM. 2024: Cost of a Data Breach Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- OpenAI. An Update on Disrupting Deceptive Uses of AI. OpenAI. 2024. Available online: https://openai.com/global-affairs/an-update-on-disrupting-deceptive-uses-of-ai/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Ilascu, I. Malicious PowerShell Script Pushing Malware Looks AI-Written. Bleeding Computer. 2024. Available online: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/malicious-powershell-script-pushing-malware-looks-ai-written/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Toulas, B. Hackers Deploy AI-Written Malware in Targeted Attacks. Bleeping Computer. 2024. Available online: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/hackers-deploy-ai-written-malware-in-targeted-attacks/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Rigaki, M.; Garcia, S. Bringing a GAN to a Knife-Fight: Adapting Malware Communication to Avoid Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24 May 2018; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiding, F.; Schneier, B.; Visheanath, A. AI Will Increase the Quantity—and Quality—of Phishing Scams. Harvard Business Review. 2024. Available online: https://hbr.org/2024/05/ai-will-increase-the-quantity-and-quality-of-phishing-scams (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Gilbert, C.; Gilbert, M.A. The Impact of AI on Cybersecurity Defense Mechanisms: Future Trends and Challenges. Glob. Sci. J. 2024, 12, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FreakyClown. The Rise, Use, and Future of Malicious Al: A Hacker’s Insight. 2024. Available online: https://wordpress.app.vib.community/le/the-rise-use-and-future-of-malicious-al-a-hackers-insight/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- NCSC The Near-Term Impact of AI on the Cyber Threat, Teport, NCSC.GOV.UK. 2025. Available online: https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/report/impact-of-ai-on-cyber-threat (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Ph, M.; Stoecklin, J.; Jang, J.; Kirat, D. DeepLocker: How AI Can Power a Stealthy New Breed of Malware. Security Intelligence. 2018. Available online: https://securityintelligence.com/deeplocker-how-ai-can-power-a-stealthy-new-breed-of-malware/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Lin, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xue, Z. IDSGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Attack Generation Against Intrusion Detection. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, M.; Habib, N.; Chan, J.H.; Thanapattheerakul, T. Impact of AI on the Cyber Kill Chain: A Systematic Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darshan, S.L.S.; Kumara, M.A.A.; Jaidhar, C.D. Windows Malware Detection Based on Cuckoo Sandbox Generated Report Using Machine Learning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Roorkee, India, 3–4 December 2016; Volume 7, pp. 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y. MTDroid: A Moving Target Defense-based Android Malware Detector against Evasion Attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 6377–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.-C.; Menczer, F. Anatomy of an AI-powered Malicious Social Botnet. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Feng, C.; Chang, C.-C. A survey on federated learning poisoning attacks and defenses. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, K. What Is Federated Learning: Key Benefits, Applications, and Working Principles Explained. PixelPlex. 2023. Available online: https://pixelplex.io/blog/federated-learning-guide/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Koelemij, S. Artificial Intelligence: How Can It Help and Harm Us? Industrial Cyber. 2023. Available online: https://industrialcyber.co/expert/artificial-intelligence-how-can-it-help-and-harm-us/ (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Sims, J. BlackMamba: Using AI to Generate Polymorphic Malware. Hyas. 2023. Available online: https://www.hyas.com/blog/blackmamba-using-ai-to-generate-polymorphic-malware (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Hays. EyeSpy: Proof-of-Concept. Hays. 2024. Available online: https://www.hyas.com/read-the-eyespy-proof-of-concept (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- 13o-bbr-bbq. Machine Learning Security—Deep Generator [GitHub Repository]. GitHub. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/13o-bbr-bbq/machine_learning_security/tree/master/Generator (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Joshi, J. The Impact of AI on Endpoint Detection and Response. Proficio. 13 May 2024. Available online: https://www.proficio.com/blog/ai-endpoint-detection-and-response-edr/ (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Becker, N.; Reti, D.; Ntagiou, E.V.; Wallum, M.; Schotten, H.D. Evaluation of Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Penetration Testing using A3C, Q-learning and DQN. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.15656. [Google Scholar]
- Cyware. SOAR and AI in Cybersecurity: Reshaping Your Security Operations. Cyware. 2023. Available online: https://cyware.com/security-guides/security-orchestration-automation-and-response/from-insight-to-action-how-ai-and-soar-are-reshaping-security-operations-13d9 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y. attackGAN: Adversarial Attack Against Black-box IDS using Generative Adversarial Networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 187, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Tan, Y. Generating Adversarial Malware Examples for Black-box Attacks based on GAN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Mining and Big Data, Beijing, China, 21–24 November 2022; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 409–423. [Google Scholar]
- Freed, A.M. AI-Driven XDR: Defeating the Most Complex Attack Sequences. Cybereason. Available online: https://www.cybereason.com/blog/ai-driven-xdr-defeating-the-most-complex-attack-sequences (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- ABN. ABN AMRO First Buyer of Innovative Self-Healing Cybersecurity Software. ABN AMRO. 2021. Available online: https://www.abnamro.com/en/news/abn-amro-first-buyer-of-innovative-self-healing-cybersecurity-software (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Sibanda, I. Automated Patch Management: A Proactive Way to Stay Ahead of Threats. ComputerWeekly. 2024. Available online: https://www.computerweekly.com/feature/Automated-patch-management-A-proactive-way-to-stay-ahead-of-threats (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- The Hacker News. How AI Is Transforming IAM and Identity Security. The Hacker News. 2024. Available online: https://thehackernews.com/2024/11/how-ai-is-transforming-iam-and-identity.html (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Komaragiri, V.B.; Edward, A. AI-driven Vulnerability Management and Automated Threat Mitigation. Int. J. Sci. Res. Manag. (IJSRM) 2022, 10, 980–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindhya, L.; Mahima, B.G.; Sindhu, G.G.; Keerthan, V. Cyber Attack Surface Management System. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Commun. Technol. (IJARSCT) 2023, 3, 1–9. Available online: https://ijarsct.co.in/Paper9533.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Hireche, O.; Benzaïd, C.; Taleb, T. Deep Data Plane Programming and AI for Zero-trust Self-driven Networking in Beyond 5G. Comput. Netw. 2022, 203, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y. AI and Catastrophic Risk. J. Democr. 2023, 34, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistono, F.; Yampolskiy, R.V. Unethical Research: How to Create a Malevolent Artificial Intelligence. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.02817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, S. How to Stop AI Agents Going Rogue, BBC. 2025. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cq87e0dwj25o (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Robinson, B. AI Goes Rogue: Do 5 Things If Your Chatbot Lies, Schemes or Threatens. Forbes. 2025. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/bryanrobinson/2025/07/03/ai-goes-rogue-do-5-things-if-your-chatbot-lies-schemes-or-threatens/ (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Admin-HTS. What Is CylanceProtect? HTS Blog Articles. 2024. Available online: https://www.hts-tx.com/blog?p=what-is-cylanceprotect-240109 (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Sikarwar, P.; Gupta, D.; Singhal, A.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Hasan, A. Transformative Dynamics: Unveiling the Influence of Artificial Intelligence, Cybersecurity and Advanced Technologies in Bitcoin. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Computation, Automation and Knowledge Management (ICCAKM), Noida, India, 12–13 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DarkTrace. Enterprise Immune System. 2018. Available online: https://d1.awsstatic.com/Marketplace/solutions-center/downloads/AWS-Datasheet-Darktrace.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Djenna, A.; Bouridane, A.; Rubab, S.; Marou, I.M. Artificial Intelligence-based Malware Detection, Analysis, and Mitigation. Symmetry 2023, 15, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, A.; Umar, M.; Aliyu, A. Cyber Kill Chain Analysis Using Artificial Intelligence. Asian J. Res. Comput. Sci. 2023, 16, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.A. Attention-GAN for Anomaly Detection: A Cutting-edge Approach to Cybersecurity Threat Management. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.15945. [Google Scholar]
- Taheri, R.; Javidan, R.; Shojafar, M.; Vinod, P.; Conti, M. Can Machine Learning Models with Static Features be Fooled? An Adversarial Machine Learning Approach. Clust. Comput. 2020, 23, 3233–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musman, S.; Booker, L.; Applebaum, A.; Edmonds, B. Steps Toward a Principled Approach to Automating Cyber Responses. SPIE Digital Library. 2019. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie/11006/2518976/Steps-toward-a-principled-approach-to-automating-cyber-responses/10.1117/12.2518976.full#= (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Geiger, A.; Liu, D.; Alnegheimish, S.; Cuesta-Infante, A.; Veeramachaneni, K. TadGAN: Time Series Anomaly Detection Using Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–13 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, M. Enhancing Cybersecurity: The Power of Artificial Intelligence in Threat Detection and Prevention. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2023, 10, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaram, M.; Roopesh, M.; Rasetti, S.; Nishat, N. A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Enhancing Cybersecurity Threat Detection and Response Mechanisms. Glob. Mainstream J. Bus. Econ. Dev. Proj. Manag. 2024, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Kalajdjieski, J.; Gharib, A.; McCann, R. AI-driven Guided Response for Security Operation Centers with Microsoft Copilot for Security. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, N.G. The Role of AI in Cybersecurity: Addressing Threats in the Digital Age. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. (JAIGS) 2024, 3, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmi, S.; Kumar, S. Improving Cybersecurity: Artificial Intelligence’s Ability to Detect and Stop Threats. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2024, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhu, Q. Reinforcement Learning for Feedback-enabled Cyber Resilience. Annu. Rev. Control 2022, 53, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewusi, A.O.; Okoli, U.I.; Olorunsogo, T.; Adaga, E.; Daraojimba, D.O.; Obi, O.C. Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity: Protecting National Infrastructure: A USA Review. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 21, 2263–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, W.; Christopoulou, M.; Gür, G.; Stiller, B. MERLINS—Moving Target Defense Enhanced with Deep-RL for NFV In-Depth Security. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Network Function Virtualization and Software Defined Networks (NFV-SDN), Dresden, Germany, 6 November 2023; pp. 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajodia, S.; Cybenko, G.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.; Wellman, M. (Eds.) Adversarial and Uncertain Reasoning for Adaptive Cyber Defense: Control-and Game-Theoretic Approaches to Cybersecurity; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11830. [Google Scholar]
- Reti, D.; Fraunholz, D.; Elzer, K.; Schneider, D.; Schotten, H.D. Evaluating Deception and Moving Target Defense with Network Attack Simulation. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM Workshop on Moving Target Defense, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 7 November 2022; pp. 45–53. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.10629 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Clark, A.; Sun, K.; Bushnell, L.; Poovendran, R. A Game-theoretic Approach to IP Address Randomization in Decoy-based Cyber Defense. In Decision and Game Theory for Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duy, P.T.; Hoang, H.D.; Khoa, N.H.; Hien, D.T.; Pham, V. Fool Your Enemies: Enable Cyber Deception and Moving Target Defense for Intrusion Detection in SDN. In Proceedings of the 2022 21st International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Xi’an, China, 27–30 September 2022; pp. 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bilinski, M.; diVita, J.; Ferguson-Walter, K.; Fugate, S.; Gabrys, R.; Mauger, J.; Souza, B. Lie Another Day: Demonstrating Bias in a Multi-round Cyber Deception Game of Questionable Veracity; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-64793-3_5 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Cohen, S.; Bitton, R.; Nassi, B. Here Comes the AI Worm: Unleashing Zero-click Worms that Target GenAI-powered Applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.02817. [Google Scholar]
- Weinz, M.; Schröer, S.L.; Apruzzese, G. “Hey Google, Remind Me to be Phished”: Exploiting the Google (AI) Assistant Ecosystem for Social Engineering Attacks. 2024. Available online: https://www.giovanniapruzzese.com/files/papers/GoogleAssistantPhishing.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Lakshmanan, R. Researchers Reveal ‘Deceptive Delight’ Method to Jailbreak AI models. The Hacker News, 23 October 2024. Available online: https://thehackernews.com/2024/10/researchers-reveal-deceptive-delight.html (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Yahalom, R. What the 2024 CrowdStrike Glitch Can Teach Us About Cyber Risk, Harvard Business Review. 2025. Available online: https://hbr.org/2025/01/what-the-2024-crowdstrike-glitch-can-teach-us-about-cyber-risk (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Doll, J.; McCarthy, C.; McDougall, H.; Bhunia, S. Unraveling Log4Shell: Analyzing the Impact and Response to the Log4j Vulnerabil. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.17760. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Everyone in AI Is Talking About Manus. We Put It to the Test. Artificial Intelligence, MIT Technology Review. 2025. Available online: https://www.technologyreview.com/2025/03/11/1113133/manus-ai-review/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).