Abstract
The ultimate goal of China’s tourism industry is to create a flourishing sector that brings happiness. It is of immense theoretical and practical importance to investigate the impact of tourism development (TD) on urban welfare (UW) and uncover its spatial spillover characteristics from a macro perspective. Utilizing panel data from 41 cities in the Yangtze River Delta region from 2000 to 2021, this study applies the spatial panel Durbin model to explore the direct and spillover effects of TD on UW. The results show that TD significantly boosts UW in both local and neighboring areas, with the spillover effects taking a dominant position in the total effects. Examining the sub-dimensions of UW, the local welfare effects of TD primarily stem from economic welfare, whereas the spillover effects are characterized by the “three-wheel drive” of economic, social, and environmental welfare. This study can provide practical insights into the coordinated and sustainable development of the regional tourism industry.
1. Introduction
As a manifestation of happiness, benefit, and well-being, welfare is an important symbol of a civilization’s progress and modernization [1]. With the passage of time, people have gradually realized that the ultimate objective of social and economic development is not the expansion of production scale or the growth of gross product but rather the improvement of the level of people’s welfare. The report of the twentieth CPC National Congress emphasized the necessity of upholding and enhancing people’s welfare throughout the development process. With the purpose of creating pleasant experiences and good memories [2], the tourism industry is characterized by high input–output efficiency, low employment thresholds, ecological friendliness, and strong driving force [3,4], which is recognized as an emerging sunrise industry in the new era aiming to meet residents’ material and spiritual needs while enhancing people’s well-being [5,6]. In 2013, President Xi Jinping highlighted that tourism is an important indicator of the improvement of people’s living standards. In 2016, Premier Li Keqiang put forth that tourism, culture, sports, health, and pension constitute the five happiness industries. Moreover, in 2018, the National Tourism Work Conference elevated tourism to the status of the “leading industry” among the five happiness industries. Within the context of constructing a modern and high-level welfare state, China’s tourism industry bears a special significance and mission. However, in practical terms, the welfare effects of the tourism industry are frequently called into question. The agglomeration of the tourism industry has led to a series of issues, including rising prices, traffic congestion, frequent conflicts, and the marginalization of local residents in destinations, which have been subject to repeated criticism [7]. In the face of controversy, only through a scientific understanding of the impact of tourism development on urban welfare can we clear up doubts and implement precise measures to fully release the industrial value of tourism to promote the goal of a “Happy China”.
Welfare has consistently been a central focus of cutting-edge economic theories globally. It has evolved from the initial concept of “relief for the poor” to a comprehensive notion that encompasses the three dimensions of economy, society, and environment [8]. This comprehensive view includes both material and immaterial aspects, such as income, consumption, housing, employment, education, ecology, and security, integrating subjective happiness experiences with objective utility acquisition [9]. With the deepening and broadening of the connotation of welfare, scholars have introduced it into the field of tourism studies. For a considerable period, the discussion surrounding the connection between tourism and welfare has primarily focused on the micro-level analysis of whether tourists can derive happiness from their travel experiences. This includes the research on the disparities between various types of tourism activities in generating blissful tourism experiences [10,11,12], the pathways to enhancing blissful tourism for tourism consumer groups with distinct characteristics [13,14,15], and the mechanism behind generating tourism happiness experiences [2,16,17]. Under the wave of the massification and popularization of tourism activities, the studies above have laid a solid foundation for the rational cognition of whether tourism possesses the attributes of a happiness industry. However, they have neglected a more macroscopic research perspective of whether tourism development can boost the overall level of welfare in the region. In light of this, academics have begun to recognize the welfare effects of tourism development from this perspective. Based on theoretical derivation and empirical tests, relevant scholars have found that the high-quality development of tourism can play a crucial role in boosting regional economic growth [18], urbanization [19], social employment [20], and green development [21]. They have also analyzed its positive impacts on major national strategies such as poverty alleviation [3], rural revitalization [22], and common prosperity [23]. Moreover, economic development, stable employment, environmental enhancement, and reduction of the wealth gap are precisely the necessary processes for improving the welfare level. Furthermore, in recent years, researchers in the field have measured the level of regional livelihood welfare by constructing a comprehensive evaluation index system, thus achieving a direct quantitative correlation between the tourism system and the welfare system. Zhu et al. [24] utilized a coupled coordination model and found that the coordination coefficient between the provincial tourism industry and residents’ livelihood in China has steadily increased, although the overall level remains moderate. Wang et al. [25] explored the dynamic response relationship between tourism development and people’s well-being in Chinese provinces based on the Panel Vector Autoregression model (PVAR). They discovered that the two systems exhibit a mutually beneficial “win-win” effect, where tourism development serves as an important driving force for people’s well-being while also being subject to the counteraction of people’s well-being. Ma et al. [7] made attempts at the county level and, through panel regression modeling, discovered that the agglomeration of the tourism industry in 24 districts in western Hunan has a predominantly negative impact on overall human well-being, with regional and temporal variations. It is evident that a consensus conclusion has not been reached in related research. Further refinement is needed in the analysis of the spatio-temporal correlation and the influence mechanisms between the tourism system and the welfare system.
Time and space are intrinsic attributes of tourism [26]. Against the backdrop of the deepening development concepts of “regional integration” and “all-for-one tourism”, the topic of spatial externalities in tourism development has drawn considerable attention. Considering the comprehensive driving force of the tourism industry in conjunction with the spatial extension of tourism flows, the academic community has come to realize that the tourism economy is not an “island economy” [27]. The development of tourism in a particular location will inevitably be influenced by its neighboring regions. Relevant researchers have confirmed the spatial spillover of tourism development itself through empirical cases [28]. Furthermore, they have explored the spatial spillover of tourism development on economic growth [26,29] and the construction of ecological civilization [30,31]. Therefore, do the aforementioned industrial characteristics result in spatial spillovers from tourism development to urban welfare? What are the pathways and details of such spatial spillovers? These are the crucial questions this paper addresses.
In summary, existing studies have explored the relationship between tourism and well-being in a variety of ways, fully justifying the attributes of tourism as a happy industry. However, not much of the literature has quantitatively explored the multidimensional impacts of tourism development on urban welfare levels at the macro level, with rare in-depth analyses of the impact mechanisms and spatial spillovers. The Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region, which encompasses Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui Provinces, comprising a total of 41 cities, is one of the most economically dynamic regions in China. It boasts robust innovation capacity, a well-developed tourism industry, and a high level of welfare. In the new century, especially since the 18th CPC National Congress, the integration process of the YRD region has accelerated in all aspects. Notably, the spatial correlation characteristic of tourism development has become increasingly prominent in this region. In light of this, by focusing on the YRD region as a case study, this paper examined the direct and spillover effects of tourism development on urban welfare using the spatial panel Durbin model. Furthermore, it unveiled the mechanism and pathways of this impact through a three-dimensional decomposition of urban welfare. The ultimate goal is to offer practical insights to facilitate the coordinated and sustainable development of the regional tourism industry.
2. Theoretical Analysis and Hypotheses
Urban welfare is intricately linked to the overall quality of life of residents and the sustainable development of society [32], possessing profound theoretical significance and practical relevance. In a narrow sense, urban welfare refers to a variety of government-run public goods as well as transfers for specific groups [33], with a focus on emphasizing the universality and equity of urban public services. In a broad sense, urban welfare refers to the subjective experiences and objective enjoyment of the general public towards the terminal outcomes of urban economic and social development [8]. It is a generalized concept that encompasses the three major dimensions of economy, society, and environment, involving many areas of daily life, such as clothing, food, housing, transportation, education, employment, medical care, and culture. This paper argues that the narrow concept of urban welfare does not match the philosophical logic of “comprehensive human development” in the new era. Therefore, based on the theory of sustainable development, this study adopts the concept of broad urban welfare to analyze the impact of tourism development on urban welfare and its spatial spillover mechanism from the three-dimensional perspectives of economy, society, and environment. The theoretical framework is shown in Figure 1.
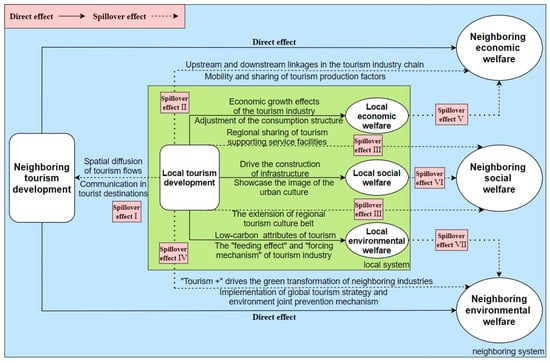
Figure 1.
The impact and spatial spillover mechanism of tourism development on urban welfare. Note: The green background represents the local system, the light blue background represents the neighboring system, and the pink background represents spillover effects.
2.1. Local Welfare Effects of TD
Based on the three-dimensional connotation of urban welfare in the broad sense, this paper reveals the direct impact of tourism development on local urban welfare from economic, social, and environmental perspectives. (1) Economic welfare effects of TD. Established research substantiates that tourism can bolster the economic growth of a destination by generating foreign exchange earnings, stimulating domestic demand, attracting investments, and fostering industry integration, among other benefits [18,34]. While GDP growth cannot be directly equated with an increase in residents’ income consumption levels, a robust material foundation is a crucial cornerstone for enhancing economic welfare [9]. Moreover, with the flourishing growth of mass tourism, travel activities have become an important symbol of people’s pursuit of a better life [5]. Consequently, tourism expenditure has secured its position within the total expenses of residents, exerting a profound impact on the reduction of household Engel’s coefficient and the adjustment of consumption structure. (2) Social welfare effects of TD. Firstly, as a labor-intensive sector, the development of tourism and its associated service industries offers a substantial number of employment opportunities in the respective regions, thereby contributing to overall job creation [20,35]. Secondly, well-maintained and comprehensive public facilities serve as the backbone for the smooth functioning of the tourism sector. Tourism destinations strive to provide tourists with comprehensive and comfortable facilities and services while simultaneously enhancing convenience for local residents [36]. Thirdly, in the backdrop of the deepening concept of “cultural and tourism integration”, tourism stands out as a crucial factor in burnishing a city’s cultural appeal [37], which plays a vital role in safeguarding and promoting the traditional culture. The rich cultural ambiance will subtly impact residents’ growth, character development, emotional enrichment, and even their quality of life. (3) Environmental welfare effect of TD. To begin with, the development of tourism inevitably consumes resources and generates a certain degree of environmental pollution. However, tourism income can provide financial support for the restoration and protection of the environment [38], ultimately serving to “feed back” into the environment. Additionally, the United Nations recognizes tourism as a pivotal sector in driving the global economic transition from “brown” to “green” [39], with the industry itself possessing attributes of resource conservation and environmental friendliness. The establishment of forest parks, wetland parks, and water conservancy scenic areas influenced by tourism can enhance carbon sink accumulation and support the goal of achieving “carbon neutrality” [40,41]. Moreover, the progression of tourism demands a healthy ecological environment as its foundation, necessitating higher environmental standards at destinations and compelling destination governments to implement strict environmental regulations [42]. Lastly, the emergence of ecotourism, forest health tourism, and other innovative tourism forms provides residents with opportunities to escape the urban hustle and enjoy environmental welfare.
2.2. Spatial Spillover Mechanism of TD on Neighboring UW
The spillover effect of TD on neighboring UW is primarily manifested in the following four aspects: (1) The spatial spillover effect of TD on itself (spillover effect Ⅰ). This refers to local tourism development stimulating tourism growth in neighboring cities. This spatial positive externality is, on the one hand, attributed to the spatial diffusion effects of tourism flows. Motivations for multi-destination travel by tourists, joint marketing among neighboring tourism destinations, and well-developed transportation networks may lead to the diffusion of tourism flows to neighboring cities [27,43], thereby driving tourism development in those cities. On the other hand, it is also imputed to the exchange and mutual learning of tourism development experiences. When significant progress is achieved in the tourism industry of a specific area, the approaches used to exploit tourism resources there often hold substantial reference value for neighboring areas [44]. (2) The spatial spillover effect of TD on economic welfare (spillover effect Ⅱ). Firstly, this is achieved through the spatial spillover effect of tourism development on itself, where the tourism development in one area drives the development of tourism in neighboring areas, directly affecting the economic welfare levels of those neighboring areas. Secondly, it relies on the regional linkage of the upstream and downstream sectors of the tourism industry chain. As demand for tourism products incrementally increases, a single city often falls short of supplying all the necessary resources for its tourism sector’s growth, necessitating the support of related industries in neighboring areas [24]. These supporting industries will directly affect the economic development and economic welfare of neighboring cities. Thirdly, it relies on the flow and sharing of regional tourism production factors. The development of tourism requires production factors such as capital, labor, technology, and information, some of which will move to neighboring areas along with the tourism flow [45], thereby influencing the economic system of neighboring cities. (3) The spatial spillover effect of TD on social welfare (spillover effect Ⅲ). Initially, this is realized through the spatial spillover effect of tourism development on itself, facilitating the transmission of social welfare effects. Moreover, this capitalizes on the regional sharing of tourism-supporting facilities. Airports, transportation networks, and other high-quality public service infrastructures developed to cater to tourists at destinations can also serve neighboring areas [30], thus enhancing the living standards for residents in those localities. Additionally, it hinges on the extension of regional tourism cultural belts. Certain tourist attractions are spread across cities in a ribbon-like spatial pattern, like the Grand Canal National Cultural Park. Implementing systematic linear development in such areas is beneficial for consolidating regional cultural resources, emphasizing unique regional cultural characteristics, boosting the region’s overall visibility, and ultimately fostering the development of local and neighboring residents’ sense of identity [46]. (4) The spatial spillover effect of TD on environmental welfare (spillover effect Ⅳ). Firstly, the transmission of the environmental welfare effect is accomplished by utilizing the spatial spillover of tourism development on itself. Furthermore, in the context of inter-regional cooperation through forms such as “tourism+” and “+tourism”, the green and environmentally friendly attributes of the tourism industry can be seamlessly integrated into agriculture and manufacturing sectors of neighboring areas through industry linkages [30], thus generating a synergistic “fusion effect”. This integration not only yields complementary advantages but also contributes to the eco-friendly transformation of the neighboring industries. Lastly, guided by the “all-for-one tourism” concept, regional environmental joint prevention and control mechanisms transcend administrative barriers, promoting the improvement of environmental welfare in neighboring areas.
Moreover, the spatial spillover effects of economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare on themselves (spillover effects Ⅴ, Ⅵ, Ⅶ) will further transmit the impact of TD on local UW to neighboring areas. The spillover effects Ⅰ–Ⅶ complement each other and accumulate layer by layer, collectively delineating the spatial spillover network of the welfare effects of TD.
2.3. Theoretical Hypotheses
This paper primarily focuses on three core research questions. Firstly, does tourism development at the macro level significantly promote urban welfare levels? Secondly, how does tourism development influence urban welfare levels? What specific impacts does it have on economic welfare (UW_ECO), social welfare (UW_SOC), and environmental welfare (UW_ENV) subsystems? Thirdly, within the context of regional integration, does tourism development generate spatial spillover effects on urban welfare? Building upon the theoretical analysis above, this paper proposes the following hypotheses regarding the research questions:
Hypothesis 1.
TD has a positive impact on local UW.
Hypothesis 1a.
TD has a positive impact on local UW_ECO.
Hypothesis 1b.
TD has a positive impact on local UW_SOC.
Hypothesis 1c.
TD has a positive impact on local UW_ENV.
Hypothesis 2.
TD generates positive spatial spillover effects on neighboring UW.
Hypothesis 2a.
TD generates positive spatial spillover effects on neighboring UW_ECO.
Hypothesis 2b.
TD generates positive spatial spillover effects on neighboring UW_SOC.
Hypothesis 2c.
TD generates positive spatial spillover effects on neighboring UW_ENV.
3. Methodology and Data Sources
3.1. Measurement of TD and UW
3.1.1. Construction of Evaluation Index System
Following the principles of science, comparability, and data availability, an evaluation index system for the level of tourism development was constructed. This system, based on reference to the studies of Wang et al. [47], Zhao et al. [26], and Wang et al. [38], encompasses three key dimensions: tourism economic benefits, tourism industry status, and tourism reception capacity (Table 1). Tourism economic benefits directly reflect the outcomes of regional tourism development, which are represented by total tourism revenue and the number of tourists. Tourism industry status indicates the level of government emphasis on tourism development, measured by the proportion of total tourism revenue to the added value of the tertiary industry and the share of the tertiary industry’s added value in GDP. Tourism reception capacity is essential for ensuring the smooth functioning of the tourism system, evaluated through the quantity of star-rated hotels, the count of scenic spots rated 3A or higher, and the number of travel agencies.

Table 1.
Indicator system for evaluating tourism development and urban welfare.
Currently, the academic community and international organizations primarily follow three paths to evaluate and measure urban welfare: firstly, economic welfare based on GDP and its refined indicators such as Net Economic Welfare [48] and Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare [49]. Secondly, composite indicators developed from Amartya Sen’s capability approach, with the Human Development Index (HDI) proposed by the United Nations Development Programme—comprising per capita GDP, life expectancy, and adult literacy rate—as a notable example [50]. Thirdly, a comprehensive evaluation system constructed from multi-dimensional indicators that encompass income, consumption, safety, housing, education, leisure, and the ecological environment [8,9,38]. In consideration of the practicalities of regional development and data accessibility, this paper selected 38 secondary indicators from economic, social, and environmental perspectives to conduct a thorough assessment of urban welfare (Table 1). This evaluation framework covers numerous domains intimately connected to the daily lives of the populace, including income savings, consumption structure, price levels, healthcare, employment, education, social security, infrastructure, ecological construction, and environmental governance. It is capable of more holistically reflecting the material and non-material aspirations of people for a better quality of life.
3.1.2. Data Source and Processing
Taking the 41 cities in the YRD region as the research unit, the study period was determined as 2000 to 2021 based on data accessibility and economic development stages. The data for the assessment index system were sourced from the following origins: Shanghai Statistical Yearbook (2001–2022), Anhui Statistical Yearbook (2001–2022), Zhejiang Statistical Yearbook (2001–2022), Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook (2001–2022), China Environmental Statistical Yearbook (2001–2022), China City Statistical Yearbook (2001–2022), Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development from 2000 to 2021, and Statistical Bulletin on Urban Health from 2000 to 2021. To mitigate the impact of extreme data points on the outcomes, each indicator was characterized using per capita, per unit area values, or proportions. Economic data were all standardized based on the year 2000. It is important to note that due to administrative changes in Chaohu City in 2011, data before 2011 were aggregated by county and added to the three cities of Hefei, Wuhu, and Ma’anshan. Additionally, for cities with missing indicators in certain years, SPSS interpolation method was used to supplement and enhance the data.
Considering the potential collinearity among evaluation indicators that might affect the accuracy of the measurement results [51], the principal component analysis method was used to separately calculate the scores for tourism development, economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare. To address the issue of some scores being negative, the minimum–maximum normalization method was employed to map the original scores to the range of 0 to 1. Finally, referring to the research of Hu et al. [8], the urban welfare level was measured using a weighted approach based on Formula (1).
where , , , and , respectively, denote urban welfare, economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare.
3.2. The Construction of Spatial Panel Econometric Models
3.2.1. The Setting of Spatial Weight Matrix
The spatial weight matrix is not only a quantitative representation of the geographical effects among observed individuals [52] but also a fundamental prerequisite for constructing spatial econometric models [53]. Currently, in academia, spatial weight matrices are mainly set based on geographic proximity, geographic distance, and economic distance [54]. The traditional first-order geographic adjacent weight matrix assumes that only directly adjacent spatial units are related, while slightly more distant spatial entities do not influence each other, which does not align with the essential characteristics of spatial movement in tourism flows [26]. Hence, in this paper, the K-nearest spatial weight matrix was selected to incorporate the attributes of geographic proximity while also accounting for the influence of tourism at slightly greater distances. The value of K was set to 4 and 5 for comparative study (denoted as knn4 and knn5). Additionally, this study introduced geographic distance weight matrix and economic–geographic distance nested matrix in the robustness test section to ensure the reliability of the research results through multiple spatial operation paradigms.
3.2.2. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation
The “First Law of Geography” posits that there is a correlation between geographic elements, with closer distances exhibiting stronger spatial correlations. Typically, spatial autocorrelation describes the spatial attributes of a single geographic element. However, bivariate spatial autocorrelation, which examines the spatial relationships between two geographic elements, is more applicable for capturing spatial associations effectively [55]. Building upon the analysis of the spatial autocorrelation characteristics of tourism development and urban welfare, respectively, using univariate global Moran’s I, this study delved into the spatial correlation features between the two through bivariate global Moran’s I. The calculation formula for bivariate global Moran’s I is as follows [56]:
where represents the bivariate Moran’s I coefficient; and are the observed values of different geographical attributes for spatial units i and j, respectively; n is the total sample size; is the sample variance; is the predefined K-nearest spatial weight matrix.
3.2.3. Selection of Model Variables
Dependent variable: Initially, the level of urban welfare (UW) is set as the dependent variable. To further analyze the pathways through which tourism development influences urban welfare, the dependent variable is then replaced with the sub-dimensions of urban welfare, namely economic welfare (UW_ECO), social welfare (UW_SOC), and environmental welfare (UW_ENV).
Core explanatory variable: The level of tourism development (TD), determined by establishing a comprehensive evaluation index system and calculated utilizing PCA.
Control Variables: (1) Economic development (ED), represented by per capita GDP. Economic growth serves as the primary driver behind the enhancement of urban welfare. However, the associated resource consumption and environmental pollution may also lead to a scenario where the area reaches a “welfare threshold” [57,58]. (2) Population agglomeration (PA). Population density serves as a proxy variable for population agglomeration [9]. On the one hand, population agglomeration facilitates the formation of economies of scale; on the other hand, it may also lead to negative livelihood issues such as traffic congestion and price increases [59]. (3) Government intervention (GI), indicated by the ratio of government expenditure to GDP. Through fiscal measures, the government fulfills its role in macroeconomic regulation, thereby influencing regional economic and social development along with the establishment of people’s welfare [60,61]. (4) Innovation capacity (IC). Advanced science and technology play a pivotal role in societal advancement, positively impacting economic productivity and driving the eco-friendly transformation of industries [62]. This capacity is quantified by the number of patent grants [9]. (5) Foreign direct investment (FDI). The relationship between the degree of foreign economic engagement and urban welfare encompasses both a “pollution haven” effect and technology spillover [63,64]. While foreign direct investment can relocate pollution to host countries, it also facilitates the dissemination of new technologies and concepts from abroad. The amount of foreign direct investment serves as a proxy variable [65]. (6) Environmental regulation (ER). Stringent environmental regulation policies can effectively curb pollutant emissions [21,66], compelling the optimization of regional industrial structures and, consequently, fostering improvements in environmental and urban welfare. Given the data availability at the municipal level, the compliance rate of industrial wastewater is utilized as a metric. Variable selection and explanations are provided in Table 2.

Table 2.
Description of variables and basis for selection.
3.2.4. Spatial Panel Durbin Model
The spatial panel Durbin model (SPDM) is a significant model for exploring the spatial correlation of geographical factors [67]. It encompasses the spatial lag terms of both the explanatory variables and the dependent variable, making it a comprehensive form of the spatial panel lag model (SPLM) and the spatial panel error model (SPEM) [55]. This study utilized the SPDM to unveil the spatial spillover effects of tourism development on urban welfare and its sub-dimensions, followed by a spatial effect decomposition. Furthermore, to ensure the soundness of model selection, the analysis also employed LM test, LR test, Hausman test, and Wald test for validation in the subsequent sections. The expression of the SPDM is as follows [68]:
where represents the K-nearest spatial weight matrix; denotes the spatial regression coefficient of the dependent variable; and stand for the regression coefficients of the core explanatory variable and control variable; and represent the spatial regression estimation coefficients of the core explanatory variable and control variables; signifies the set of control variables; and represent time effects and spatial effects; denotes the error term.
4. Results
4.1. The Measurement Results of TD and UW
4.1.1. Temporal Evolution Characteristics
Based on principal component analysis, the levels of TD and UW in the Yangtze River Delta region from 2000 to 2021 were calculated (Figure 2). Overall, the tourism industry in the entire region witnessed rapid development. Between 2000 and 2019, the TD level increased from 0.062 to 0.318, displaying an impressive average annual growth rate of 8.99%, with only minor fluctuation in 2003 due to the impact of the SARS epidemic. Throughout this period, the YRD region firmly grasped significant opportunities in mass tourism, “all-for-one tourism”, “cultural and tourism integration”, and “integrated regional tourism development”, facilitating a remarkable shift in the tourism industry from “small, weak, and fragmented” to “scaled, specialized, and high-end”. Between 2020 and 2021, the rampant spread of the COVID-19 pandemic brought the tourism industry into a harsh winter, with the TD level plummeting significantly to 0.286.
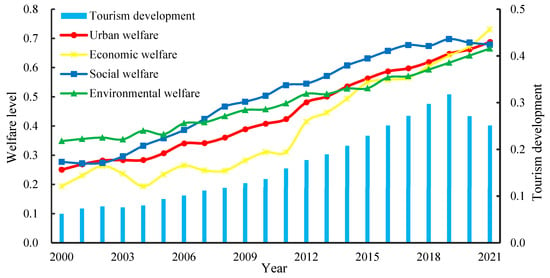
Figure 2.
Temporal evolution characteristics of tourism development and urban welfare.
Between 2000 and 2021, the level of UW across the region exhibited a remarkable upward trend, surging from 0.251 to 0.688, with an average annual growth rate of 4.92%. This surge reflected a substantial enhancement in residents’ sense of happiness, fulfillment, and satisfaction since the beginning of the new century, showcasing the effective transformation of the region’s economic and social development outcomes. In terms of the sub-dimensions of UW, Economic welfare increased rapidly at an average annual rate of 6.52%, indicating the continuous improvement in residents’ income, consumption levels, and the progressive refinement of market mechanisms. It is worth mentioning that economic welfare experienced significant fluctuations before 2012, being sensitive to events like the financial crisis and SARS. However, from 2013 to 2021, its resilience gradually strengthened, showing a positive trend of linear growth. Social welfare steadily grew at an average annual rate of 4.34%, primarily benefiting from the rapid development of regional infrastructure, healthcare, employment, and education, among other livelihood initiatives. The growth rate of environmental welfare was the slowest, characterized by prolonged stagnation. This was primarily attributed to the continuous high levels of industrial pollution emissions in the YRD region and the inherent disadvantage of forests and green space coverage. Moreover, the “once-in-fifty-years” haze that occurred around 2013 further impeded the effective rising of environmental welfare.
4.1.2. Spatial Evolution Patterns
The TD and UW levels in the Yangtze River Delta region were categorized into five levels: high, relatively high, medium, relatively low, and low. The spatial visualization of three cross-sections for the years 2000, 2010, and 2021 was conducted using ArcGIS 10.7 software (Figure 3).
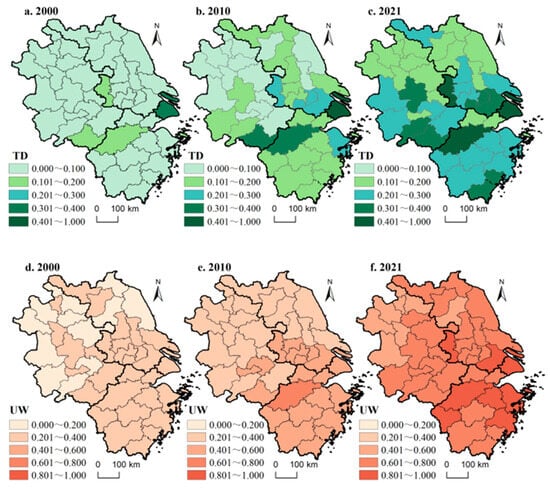
Figure 3.
Spatial evolution patterns of tourism development and urban welfare. (a), (b), (c) respectively represent the spatial patterns of tourism development levels in the years 2000, 2010, and 2021; (d), (e), (f) respectively represent the spatial patterns of urban welfare levels in the years 2000, 2010, and 2021.
Based on Figure 3a–c: In the year 2000, TD in the YRD region was generally at a low level, with only Shanghai, Huangshan, Hangzhou, and Nanjing having an index higher than 0.1. By 2010, significant growth was observed in the region’s tourism sector, with numerous cities in Zhejiang Province, southern Jiangsu, and southern Anhui transitioning from low to medium or relatively low levels, indicating an initial trend of “higher in the south and lower in the north”. Impacted by the pandemic, the tourism industry faced challenges in 2021. Nevertheless, the TD levels of various cities remained significantly higher than those in 2010. Cities at medium and relatively high levels expanded rapidly across the region, accounting for a cumulative proportion of 58.54%. Meanwhile, there was a substantial reduction in cities at relatively low levels, primarily concentrated in western Anhui and northern Jiangsu regions. In general, the tourism development in the YRD region exhibited a pattern of “high in the southeast and low in the northwest”, as well as a characteristic of dual-core distribution. Cities such as Shanghai, Suzhou, and Nanjing formed the first tourism core area along the Yangtze River, mainly benefiting from their substantial market scale and well-established reception systems. Meanwhile, cities like Chizhou and Huangshan, along with Hangzhou, developed a second high-value aggregation area in the southern Anhui and northern Zhejiang regions, primarily relying on world-class tourism resources such as Jiuhua Mountain and Yellow Mountain, as well as government emphasis on the tourism industry.
According to Figure 3d–f, in the year 2000, the UW level of cities in the YRD region was predominantly low and relatively low, accounting for 29.27% and 70.73%, respectively. By 2010, there was a significant improvement in the overall UW level of the region, with 48.78% of cities reaching a medium or higher level. Notably, Hangzhou city stood out with the most prominent index.
As of 2021, only Lu’an, Fuyang, Huainan, Bozhou, Huaibei, Suzhou, and Huai’an remained at a medium welfare level, while the indices of other cities exceeded 0.6, resulting in a proportion of high-welfare cities reaching 21.95%. Overall, the UW levels of cities in the YRD region also followed a “dual-core driven” pattern, with higher levels in the south and lower levels in the north. Shanghai and Suzhou formed the first core welfare area at the mouth of the Yangtze River, depending on their strong material economic foundation. Meanwhile, cities such as Hangzhou and Zhoushan generated the second high-value welfare area in northern Zhejiang through their harmonious development of economy, society, and ecological environment.
The spatial evolution of urban welfare is dominated by its internal economic, social, and environmental welfare systems. Given the limitations in article length, this study selected the average economic, social, and environmental welfare of each city from 2000 to 2021 as samples for visualization. Employing the natural breaks method in ArcGIS 10.7 software, the data were divided into five categories to further analyze the spatial distribution characteristics of different dimensions of welfare (Figure 4). Overall, there was a significant spatial mismatch between the levels of economic, social, and environmental welfare in the YRD region. The high-value economic welfare areas were mainly concentrated in the economically developed central cities across the region, forming a “Z”-shaped zone that connected the Yangtze River Basin and the Hangzhou Bay area. This pattern of high-value economic welfare areas evolved in a “core-periphery” fashion, gradually spreading out to the surrounding regions. The spatial pattern of social welfare closely mirrored the economic welfare landscape, with Zhejiang Province taking a leading position in social welfare levels, which was mainly attributed to its effective measures in civil affairs services and social security in recent years, such as the implementation of the “run once only” reform. The distribution of environmental welfare showed a distinct pattern, where high-value cities were predominantly located in areas blessed with superior natural resources and lower levels of pollution, such as western Zhejiang and southern Anhui. Conversely, cities that were economically and socially advanced, such as Shanghai, Nanjing, Jiaxing, and Wuxi, appeared to be somewhat deficient in environmental welfare.
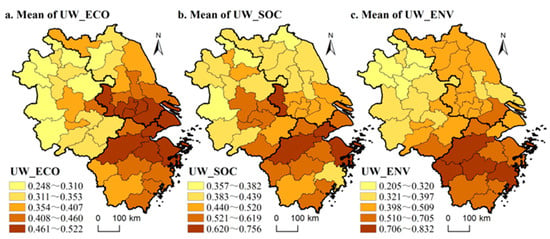
Figure 4.
Spatial evolution patterns of the sub-dimensions of urban welfare. (a), (b), (c) respectively represent the spatial patterns of the annual average of economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare.
4.2. The Impact and Spatial Spillover Effects of TD on UW
4.2.1. The Global Spatial Correlation between TD and UW
By calculating the univariate Moran’s I values for TD and UW, as well as the sub-dimensions of UW, across 41 urban units in the YRD region from 2000 to 2021, this research aims to reveal the clustering characteristics of the spatial distribution within the tourism and welfare systems themselves. Subsequently, using the multivariate local indicators of spatial autocorrelation (LISA) module in the Geoda 1.14, bivariate Moran’s I values were computed for TD and UW, including UW’s sub-dimensions, to further explore the spatial correlation features between the two systems (Table 3).

Table 3.
Univariate and bivariate Moran′s I values of tourism development and urban welfare.
The overall TD and UW in the YRD region exhibited significant spatial clustering characteristics, with the degree of spatial dependence gradually increasing. Throughout the study period, except for 2001 and 2021, the univariate Moran’s I values for TD were positive and passed a significance test of at least 0.1, indicating that cities with higher levels of TD tended to be spatially adjacent, as did cities with lower levels of development. This finding validated the existence of the spillover effect Ⅰ in the theoretical mechanism. The lack of significance in Moran’s I in 2021 may have been attributed to the disruption of the tourism development pattern caused by the epidemic. Since the beginning of the new century, Moran’s I for UW was also positive, showing a fluctuating upward trend and consistently significant at the 0.01 level, indicating an increasingly strengthened spatial autocorrelation of UW. The spatial dependency characteristics of sub-dimensions of UW were broadly similar to UW, with all sub-dimensions showing significantly positive Moran’s I values. Specifically, the spatial clustering degree of economic and environmental welfare was stronger than that of social welfare.
A strong spatial correlation was observed between TD and UW, with the bivariate Moran’s I fluctuating between 0.245 and 0.498. This suggested that cities with high levels of UW tended to be adjacent to cities with high levels of TD and vice versa. While the bivariate Moran’s I values for TD in relation to economic, social, and environmental welfare did not exhibit a clear trend in variation, they consistently showed significant positive correlations at the 1% level, indicating a positive spatial relationship between TD and the sub-dimensions of UW. The findings above revealed the existence of a strong spatial correlation and coupling between the tourism system and the welfare system. In the quantitative analysis of the welfare effects of TD, it was crucial not to overlook this prevalent spatial correlation effect.
4.2.2. Estimate Model Identification
Prior to model identification, tests were conducted on the stationarity and causality of time series data for TD and UW. The findings revealed that both variables were first-order integrated, and TD served as a Granger cause for UW, successfully passing the 1% significance level test (test results were not disclosed due to article length constraints). This study constructed spatial panel econometric models for the impact of TD on UW based on the knn4 and knn5 weight matrices, respectively. Through a comprehensive series of evaluations, the optimal type of spatial panel econometric model was identified, with the findings detailed in Table 4. Firstly, based on the LM test, it was found that the model for the impact of TD on UW exhibited both spatial error terms and spatial lag terms. Secondly, through LR tests and Wald tests, it was discovered that the SPDM could not be reduced to SPEM or SPLM, making SPDM the optimal model. Lastly, the outcomes of the Hausman test indicated that choosing a fixed effects model was more appropriate. Furthermore, due to the temporal continuity in the spatial distribution of TD and UW and following the approach of existing studies [28,69], this paper selected the spatially fixed SPDM for estimation, disregarding control for unobserved time effects.

Table 4.
Test results of spatial panel econometric models.
4.2.3. Point Estimate Results
Based on the model identification results, the spatially fixed effects SPDM was selected for parameter estimation. A comparative study was conducted with two non-spatial econometric models, Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) and Individual Fixed Effects (FE). The comparison results are presented in Table 5. (1) When examining the impact of tourism development on local urban welfare, both non-spatial econometric models and spatial panel Durbin models with two different weight matrices consistently showed a positive coefficient for TD. Furthermore, this coefficient passed significance tests of at least 0.1, suggesting an initial positive influence of tourism development on local urban welfare. When comparing the coefficients of TD in non-spatial econometric models, such as OLS (0.661) and FE (0.533), with those derived from the spatial panel Durbin model under knn4 (0.086) and knn5 (0.080) weights matrices, it became clear that disregarding spatial effects resulted in an overestimation of tourism development’s contribution to urban welfare. This insight resonated with the research conducted by Tang et al. [30]. (2) From the perspective of spatial spillover, the estimated values of W×TD under the two weight matrices were 0.242 and 0.210, both passing the significance test at the 0.01 level. This suggested that tourism development had a strong promoting effect on the welfare improvement of neighboring cities. Additionally, the ρ values under the knn4 and knn5 weight matrices were significantly positive at the 0.01 level, further confirming the spatial spillover effect of urban welfare on itself.

Table 5.
Regression results of urban welfare based on non-spatial econometric models and SPDM.
4.2.4. Partial Differential Estimation Results
Due to the potential bias in the regression coefficients of point estimates [69], a partial differential method was adopted to decompose the spatial effects, with the results presented in Table 6. (1) Under two distinct weight matrices, the direct effects (0.127, 0.118) and indirect effects (0.532, 0.546) of TD were both significantly positive, confirming that tourism development had played a promotive role in enhancing the welfare of both local and neighboring cities, in accordance with the point estimate results. This discovery suggested that both Hypothesis 1 and Hypothesis 2 were substantiated. (2) Regardless of how the spatial weight matrix was set, the indirect effects of TD were significantly greater than its direct effects, indicating that the enhancement of regional urban welfare by tourism development was primarily manifested through spatial spillover effects. On the one hand, the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, with its convenient transportation, close connections, and frequent exchanges, had formed an integrated development pattern of “you are in me, and I am in you”. The spillover effects generated by the tourism development of many neighboring cities intertwined and accumulated layer by layer, forming a more complex and powerful influence than local tourism development alone. On the other hand, the negative impacts on welfare caused by tourism development were mainly borne by the cities where the destinations were located, thereby weakening the direct effects. (3) In terms of controlling variables, ED and ER had a significantly positive direct impact and spatial spillover effects on urban welfare, highlighting the importance of a strong material economic foundation and effective environmental governance in promoting overall well-being. The direct effects of GI and IC were notably positive, while the indirect effects were not significant, indicating that proactive government macro-control and advanced science and technology were crucial for enhancing local residents’ happiness. Conversely, PA and FDI had an overall negative impact on urban welfare, suggesting the presence of the “urban disease” and “pollution haven” phenomena in the Yangtze River Delta region.

Table 6.
Spatial effect decomposition results.
4.2.5. Decomposition Analysis of Influence Pathways
Urban welfare is jointly composed of economic, social, and environmental dimensions. The impact of tourism development on urban welfare, as well as the spatial spillover effects, needed to be realized through the transmission of the three-dimensional welfare. Therefore, this paper further discussed the impact of tourism development on economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare, aiming to clarify the pathways of the welfare effects of tourism development (Table 7). Considering that the estimated results under the knn4 and knn5 weight matrices were generally close, the following analysis focused solely on the effect values under the knn4 matrix.

Table 7.
Regression and spatial effect decomposition results of the sub-dimensions of urban welfare.
The local welfare effects of tourism development in the YRD region showed a characteristic of “single-core support” in economic welfare, with the impact intensity of tourism development on economic welfare far exceeding that on social welfare and environmental welfare. Hypothesis 1a was adequately validated, but Hypotheses 1b and 1c were not supported in this study. Specifically, the direct effect of TD on UW_ECO was 0.152, passing a 1% significance test, suggesting a strong promoting effect of tourism development on local economic welfare. This could be attributed to two factors: Firstly, the enormous tourism revenue generated in the YRD region each year, under the multiplier effect and multiple rounds of circulation, brought indirect profits to related businesses, ultimately leading to increased income for destination residents. Secondly, the booming tourism reception industry and rising income levels made traveling gradually become a part of daily life for residents, objectively promoting a shift in consumption patterns from “necessities-oriented” to “leisure-oriented”, thereby reducing the Engel coefficient and enhancing economic welfare. The direct effects of TD on UW_SOC and UW_ENV are positive but not statistically significant, indicating that the development of tourism had a positive impact on local social welfare and environmental welfare but was not significant. The reasons may be as follows: Firstly, under the influence of “GDP-centrism”, the government paid more attention to the economic benefits of tourism development while relatively neglecting the social and environmental benefits. Secondly, phenomena like the disorderly development of tourist attractions, the rapid expansion of the tourism market, and imperfect tourism management systems led to occurrences of “over-tourism” in the research area, resulting in a series of negative impacts such as infrastructure congestion, conflicts between hosts and guests, social disorder, and ecological damage. These negative impacts were mainly borne by the cities where the destinations are located, thus preventing the release of the direct effects of tourism development on social and environmental welfare.
The indirect effects of TD on UW_ECO, UW_SOC, and UW_ENV were, respectively, 0.648, 0.198, and 0.415, each surpassing at least the 5% significance level test. This revealed the “three-wheel drive” feature of tourism development’s spatial spillover effect on the welfare of neighboring areas. Such a discovery not only resonated with the earlier assertion that the spillover effect of TD on UW exceeded its direct effect but also further corroborated the existence of spillover effects Ⅱ, Ⅲ, and Ⅳ as well as the validity of hypotheses 2a, 2b, and 2c. The favorable characteristics of spatial externalities mentioned above might be attributed to (1) the YRD region possessing a systematic and well-established tourism industry chain, with cities collaborating and complementing each other through the “tourism+” model. In this context, the development of tourism in one area could lead to the collective growth of neighboring upstream and downstream supporting industries, thereby promoting the spatial spillover of TD on the economic welfare of neighboring areas. (2) In the wave of integrated development of culture and tourism, the YRD region leveraged brands such as “Wu Culture”, “Grand Canal Culture”, and “Yangtze River Culture” to create a series of cross-regional cultural tourism belts, promoting the collective enhancement of nearby cities’ cultural soft power. Furthermore, the comprehensive transportation infrastructure in the tourism development pilot areas was also available for use by residents in neighboring areas, all of which contributed to the spatial spillover of TD on neighboring social welfare. (3) As the development concept of “all-for-one tourism” deepened and the integration strategy of the YRD region progressed, cities increasingly overcame traditional zoning constraints and administrative hurdles. They actively implemented a joint prevention and control mechanism for the environment, promoting the overall improvement of regional environmental welfare while turning the beautiful vision of “scenery everywhere” into reality. Moreover, the ρ values under the three models were 0.722, 0.297, and 0.422, respectively, all of which were significant at the 0.01 level. This indicated that economic, social, and environmental welfare themselves possessed significant spatial spillover characteristics, confirming the spillover effects Ⅴ, Ⅵ, Ⅶ.
4.2.6. Robustness Test
This article tested the robustness of the research conclusions by altering the spatial econometric model and replacing the spatial weight matrix.
Firstly, this study applied alternative spatial econometric models. Referencing the study by Tang et al. [30], this paper used the spatial panel lag model and spatial panel error model to verify the impact of tourism development on urban welfare. As shown in Table 8, the coefficients of TD in both alternative models were significantly positive at a level of at least 0.05, consistent with the findings previously presented in this paper, which demonstrated the robustness of the research conclusions.

Table 8.
Results of the robustness test.
Secondly, this study switched the spatial weight matrices. Following standard research practices, this study further employed a geographic distance weight matrix and an economic–geographic distance nested matrix to test the welfare effects of tourism development (Table 8). After replacing the spatial weight matrices, the coefficients for TD and W×TD remained significantly positive, with the coefficient for W×TD being relatively larger, reaffirming the previous conclusion that the “spillover effects are greater than the direct effects”.
5. Conclusions
Based on data from 41 cities in the YRD region from 2000 to 2021, this study utilized principal component analysis to assess the levels of TD and UW. Additionally, employing the spatial panel Durbin model, it investigated the impact and spatial spillover effects of TD on UW. Through a three-dimensional decomposition of UW, it further elucidated the pathways of influence. The primary findings were as follows:
Firstly, this article unveiled the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of TD and UW in the YRD region. From the perspective of temporal progression, the level of TD steadily increased at an average annual growth rate of 8.99% between 2000 and 2019. However, in 2020 and 2021, the devastating impact of the COVID-19 pandemic brought about a downturn in the tourism industry, which resulted in a significant decline in the TD level. Throughout the period from 2000 to 2021, the UW level across the region exhibited fluctuating upward trends, with an average annual growth rate of 4.92%. In the sub-dimensions of UW, economic welfare and social welfare experienced rapid growth, while environmental welfare progressed at a slower pace. In terms of spatial patterns, both TD and UW in the study area displayed a dual-core distribution feature with a ‘higher in the south, lower in the north’ trend. The high-value areas of TD were concentrated along the Yangtze River and in southern Anhui province, while the high-value areas of UW clustered around the mouth of the Yangtze River and in northern Zhejiang province. Moreover, there was also a noticeable spatial mismatch between economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare. From a spatial correlation perspective, the bivariate global Moran’s indices for TD and UW were both significantly positive at the 1% level during the study period, highlighting a strong spatial association between the tourism system and the welfare system.
Secondly, this study empirically examined the direct impact and spatial spillover effect of TD on UW. According to the results of the spatial panel Durbin model, TD played a significant role in boosting local and neighboring UW. Under the knn4 and knn5 spatial weight matrices, a 1% increase in TD, respectively, led to a 0.127% and 0.118% improvement in local UW while indirectly fostering a 0.532% and 0.546% growth in neighboring UW. Hypothesis 1 and Hypothesis 2 were substantiated. This result indicated that tourism development was indeed a significant factor driving the growth of regional urban welfare. In conjunction with the robustness test, it was found that when considering geographic proximity, geographic distance, and combined distance, the indirect effect of TD on neighboring UW exceeded the direct effect on local UW. Spatial spillover emerged as the primary form through which TD enhanced regional UW.
Thirdly, this paper further explored the impact pathway of TD on UW. The results of path analysis based on the knn4 spatial weight matrix showed that the direct effect of TD on economic welfare was significantly positive at the 1% level (0.152), but the direct effects on social welfare (0.045) and environmental welfare (0.069) did not pass the significance test. Hypothesis 1a was fully confirmed, but Hypotheses 1b and 1c were not supported. This finding suggested that the local welfare effects of TD were primarily sustained by the “single-core support” of economic welfare. From a neighboring perspective, the indirect effects of TD on economic welfare (0.648), social welfare (0.198), and environmental welfare (0.415) were all fully unleashed. Hypotheses 2a, 2b, and 2c were verified. The spatial spillover effects of TD on UW exhibited a “three-wheel drive” characteristic. Additionally, the path analysis results under knn5 spatial weight were consistent with the above findings, indicating the robustness of the research conclusions.
6. Discussion
6.1. Theoretical Implications
This article potentially contributed in the following ways: (1) It integrated the evaluation indicators of TD and UW into the same research framework, providing evidence for the “happiness industry” attributes of tourism at the macro level. (2) From a spatial spillover perspective, it constructed a theoretical framework for the welfare effects of TD, expanding the research scope of welfare economics and tourism geography. (3) Based on a three-dimensional decomposition of UW, it revealed the paths and mechanisms through which TD promoted UW.
6.2. Policy Implications
On the one hand, it is crucial for cities in the YRD region to continue strengthening tourism development’s role in promoting local welfare, recognizing it as a pivotal factor in building “happy cities”. Local governments are urged to move away from the outdated “GDP-centrism” concept and understand that tourism is not just an economic industry but also a comprehensive “happiness industry” intricately linked to social employment, cultural promotion, infrastructure development, environmental protection, and many other aspects. Given that the positive direct effects of TD on social and environmental welfare are not significant, the following targeted recommendations are put forward: (1) The relevant authorities should expedite the high-quality integration of culture and tourism industries, considering tourism as a medium and platform for showcasing the cultural personality of the cities. Meanwhile, efforts should be made to optimize the distribution of tourism facilities, improve tourism capacity, and minimize the inconvenience to local residents’ social lives caused by infrastructure congestion during peak tourism seasons. (2) The governments at all levels in the YRD region should firmly implement the “ecological priority” principle for tourism development. They should always bear in mind the important assertion that “green mountains and clear waters are as valuable as mountains of gold and silver”, which sets strict requirements for resource consumption and environmental pollution brought by the tourism industry. Furthermore, it is essential to actively promote various nature-friendly tourism formats such as eco-tourism, green hiking, and forest health tourism. Simultaneously, accelerating the construction of parks, green spaces, and garden cities is crucial to effectively ensure environmental welfare. Moreover, with the gradual rise of smart tourism, new technologies like VR virtual simulation, new energy RVs, and waterless eco-friendly toilets should be fully utilized to drive the green transformation of the tourism industry.
On the other hand, it is crucial to fully recognize the spatial externalities of the tourism industry and to thoroughly construct a spatial spillover mechanism of TD on neighboring UW. (1) During the initial stages of tourism planning, the YRD region should be guided by the concept of “all-for-one tourism” to comprehensively optimize the layout of tourism development. To avoid homogeneous competition among cities with similar conditions and geographical proximity, each region should tailor its development strategies to its local conditions. In leading tourist cities such as Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Huangshan, each region should rely on its own resource endowment and location advantages to create regional tourism growth poles, thereby facilitating the gradual development of neighboring cities’ tourism industry through a spatial evolution approach known as “point-axis-area”. For the cities in northern Anhui and northern Jiangsu regions with relatively lagging TD, they should focus on accelerating industrial structural transformation and enhancing the position of the tourism industry. At the same time, it is crucial to strengthen cooperation with leading tourist cities to create a conducive external environment for their own development. (2) In the YRD region, cities can foster a regional tourism community by sharing customer markets, constructing public supporting facilities, engaging in joint marketing promotions, and collectively designing tourism routes. This collaborative approach will pave the way for the creation of regional tourism brands such as “Charming Jiangsu”, “Picturesque Zhejiang”, and “Beautiful Anhui, Welcoming the World”, thereby advancing synergistic and high-quality development of the regional tourism industry.
6.3. Limitations and Future Research
As an initial exploration into the impact of TD on UW, this paper still has some limitations that need to be acknowledged. In the future, research in this field can be further deepened in the following aspects:
Firstly, the evaluation of UW levels needs to be more comprehensive. Due to constraints in data acquisition, this paper primarily relies on objective statistical data to measure UW levels. Urban welfare is a holistic concept that encompasses economic, social, and environmental dimensions, integrating subjective happiness experiences with objective utility acquisition [9]. In the future, subjective welfare data from residents can be further collected through methods such as questionnaire surveys and field investigations. A combined system of subjective and objective indicators can more scientifically and accurately assess UW levels.
Secondly, the impact pathways of TD on UW require a more refined analysis. This study has already preliminarily explored the impact of TD on economic welfare, social welfare, and environmental welfare subsystems. However, taking tourism development as a research entry point might be too macroscopic. Future research could focus on specific dimensions such as tourism economic benefits, tourism industry status, and tourism reception capacity. Examining how various attributes within the tourism industry affect UW differently will help clarify the pathways through which TD affects UW.
Thirdly, the nonlinear impact of TD on UW needs to be examined. While the spatial panel Durbin model employed in this study accounts for geographical factors comprehensively, it still relies on a linear perspective for empirical research. TD and UW are both vast social systems. The interaction between these two systems is complex and continuously evolving. Factors like the stage of tourism development and the heterogeneity of tourist destinations may lead to the emergence of nonlinear relationships between these two major systems [70]. In the future, methods such as the panel threshold model, random forest model, and panel smooth transition model can be utilized to investigate the nonlinear impacts of TD on UW, thereby deepening our understanding of this issue.
Finally, it is worth delving deeper into the scale differences regarding the welfare effects of TD. This study selected 41 cities in the YRD region as the sample. In the future, the research could be expanded to the provincial level nationwide or refined to the county level within specific regions to investigate whether the research results are mutually supportive under different spatial scales. Furthermore, it is worthwhile to consider employing methods such as bivariate LISA clustering and geographically weighted regression for exploring spatial heterogeneity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.; methodology, G.C.; software, G.C.; validation, M.H., Z.L. and L.K.; formal analysis, G.C.; investigation, M.H.; resources, Z.L.; data curation, M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.C.; writing—review and editing, Z.L.; visualization, L.K.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, M.H.; funding acquisition, M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [the National Natural Science Foundation of China] grant number [42301189], [the Jiangsu Province universities and colleges students’ innovation and entrepreneurship training plan project] grant number [42301189], and [the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province] project name [“The Effects and Mechanisms of the Tourism Industry on Enhancing Urban Welfare”].
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, X.S. Critical Study of Western Welfare Economics; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.K.; Diekmann, A. Tourism and wellbeing. Ann. Tour. Res. 2017, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; He, Z.L.; Guo, Y.Z.; Guo, A.X. Does Tourism Poverty Alleviation Have Spatial Spillover Effect? Bus. Manag. J. 2020, 42, 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, A.; Fatima, T.; Murshed, M. Asymmetric effects of tourism development and green innovation on economic growth and carbon emissions in Top 10 GDP Countries. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 66, 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.X.; Li, F.; Wang, X.J. “Tourism China”: Forty Years of Tourism Development and Contemporary Social Changes. Soc. Sci. China 2023, 11, 84–104+206. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, L. Tourism development and sustainable well-being: A Beyond GDP perspective. J. Sustain. Tour. 2023, 31, 2399–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Zhao, J. Impact of tourism industry agglomeration on livelihood and welfare: A case study of Western Hunan. Prog. Geogr. 2023, 42, 1486–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.J.; Li, Z.J.; Ding, Z.S.; Zhou, N.X.; Qin, D.L.; Zhang, C. Urban ecological well-being intensity and driving mode based on three-dimensional well-being: Taking the Yangtze Delta as an example. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.J.; Li, Z.J.; Hou, B. The Effect and Formation Mechanism of “Well-being Threshold” in Cities of Yangtze River Delta. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, D.; Abdullah, J. A study of the impact of the expectation of a holiday on an individual’s sense of well-being. J. Vacat. Mark. 2002, 8, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbins, R.A. Right leisure: Serious, casual, or project-based? Neurorehabilitation 2008, 23, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajić, T.; Minasyan, L.A.; Petrović, M.D.; Bakhtin, V.A.; Kaneeva, A.V.; Wiegel, N.L. Travelers’(in) Resilience to Environmental Risks Emphasized in the Media and Their Redirecting to Medical Destinations: Enhancing Sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sie, L.; Pegg, S.; Phelan, K.V. Senior tourists’ self-determined motivations, tour preferences, memorable experiences and subjective well-being: An integrative hierarchical model. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 47, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, X. Online expression as Well-be (com) ing: A study of travel blogs on Nepal by Chinese female tourists. Tour. Manag. 2021, 83, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ou, C.; Zhang, M.; Cao, X. Adult children traveling with parents: Exploring travel conflict and parents’ subjective well-being. Tour. Rev. 2023, 78, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhangt, W.; Wum, Y. The Constitution of Tourism Well-being Based on a Grounded Theory Analysis of Internet Travel Blogs. Tour. Trib. 2014, 29, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Moyle, B.D.; Vada, S.; Filep, S.; Dupre, K.; Liu, B. Re-thinking tourist wellbeing: An integrative model of affiliation with nature and social connections. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2024, 26, e2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla-González, J.A. Does the tourism development of a destination determine its socioeconomic development? An analysis through structural equation modeling in medium-sized cities of Andalusia, Spain. Land 2021, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max, F.; Hus, L. Coordinated development and evolution of natural resource-driven tourism urbanization and residents’ happiness: Take Zhangjiajie as an example. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 442–459. [Google Scholar]
- Kadiyali, V.; Kosová, R. Inter-industry employment spillovers from tourism inflows. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2013, 43, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Liu, H.M.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R. The influence and spatial spillover effects of tourism economy on urban green development in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2504–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z. Exploring the Rural Revitalization Effect under the Interaction of Agro-Tourism Integration and Tourism-Driven Poverty Reduction: Empirical Evidence for China. Land 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Q.H.; Wang, H. Study on the spatial effect and mechanism of rural tourism development promoting rural sustainable livelihood. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 490–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Q.; Li, Q.Y.; Liu, J.S. Coordination Relationship Between Tourism Development and Regional Development with Improvement of People’s Livelihood in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.F.; Zhang, X.T. A Research on the Dynamic Response and Coordination Effect of Provincial Tourism Development and the Residents’ Well-being in China. Tour. Sci. 2023, 37, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Fang, C.; Wu, X.M. Tourism Development, Spatial Spillover and Economic Growth: An Empirical Evidence from China. Tour. Trib. 2014, 29, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Zhong, Z. Optimum spatial scale of regional tourism cooperation based on spillover effects in tourism flows. Tour. Econ. 2023, 29, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M. Spatial Panel Econometric Analysis of Tourism Economic Growth and Its Spillover Effects. Tour. Trib. 2014, 29, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Hong, T.; Zhang, H. Tourism spatial spillover effects and urban economic growth. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Cai, C.Y.; Liu, Y.J. Impact of tourism development on the construction of urban ecological civilization and its spatial spillover effect: An empirical study on 284 prefecture level and above cities in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 2800–2817. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Tsai, H. Spatial spillover and determinants of tourism efficiency: A low carbon emission perspective. Tour. Econ. 2024, 30, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Sarwar, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, N. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving effects of the ecological intensity of urban well-being in the Yangtze River Delta. Energy Environ. 2022, 33, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hux, W. Research on the connotation and index system of urban welfare in a broad sense. Dongyue Trib. 2011, 32, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.T.; Saboori, B.; Ranjbar, O.; Can, M. Global perspective on tourism-economic growth Nexus: The role of tourism market diversification. Tour. Plan. Dev. 2023, 20, 919–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsous, G.; Corderi, D.; Velasco, M.; Colombo, A. Tax incentives and job creation in the tourism sector of Brazil’s SUDENE area. World Dev. 2017, 96, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Tourism, transport infrastructure and income inequality: A panel data analysis of China. Curr. Issues Tour. 2022, 25, 1607–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurriyati, R. An analysis of place branding to enhance the image of Bandung city and its implications toward the decisions to visit tourism destination. Sosiohumanika 2015, 8, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, A.; Hu, M. Spatio-temporal coordination analysis of urban welfare and tourism development in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Systems 2022, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, A. Tourism and the green economy: A place for an environmental ethic? Tour. Recreat. Res. 2013, 38, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tong, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, B. The carbon emission reduction effect of tourism economy and its formation mechanism: An empirical study of China’s 92 tourism-dependent cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voumik, L.C.; Islam, M.A.; Nafi, S.M. Does tourism have an impact on carbon emissions in Asia? An application of fresh panel methodology. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 9481–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Hou, B. The Influencing Effect of Tourism Economy on Green Development Efficiencyin the Yangtze River Delta. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wong, K.K.F. A spatial econometric approach to model spillover effects in tourism flows. J. Travel Res. 2012, 51, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.H. A Study on Catching up Mode and Path of Late-Development Tourism Destination; Tianjin University of Finance and Economics: Tianjin, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.L.; Wang, Y.J. The Spatial Spillover Effect of Tourism Industry Agglomeration on Economic Growth: Empirical Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Region. Shanghai Econ. 2018, 04, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, J.N. Inter-Provincial Comparison and Promotion Path of Cultural Industry Development in the Cultural Belt of the Grand Canal. Res. Financ. Econ. Issues 2020, 07, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.W.; Sun, J.; Lei, T.; Lu, G.J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.X. Coupling mechanism and spatiotemporal differentiation between grain production efficiency and tourism development in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 2651–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.A. A Research Protocol to Evaluate the Effectiveness of Public-Private Partnerships as a Means to Improve Health and Welfare Systems Worldwide. Am. J. Public Health 2007, 97, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, J.; Daly, H. For the Common Good, Redirecting the Economy toward Community, the Environment and a Sustainable Future; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H. A multivariate analysis of the distribution of individual’s welfare in China: What is the role of health? J. Health Econ. 2009, 28, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneau, E.; Qannari, E.M.; Bertrand, D. A new method of regression on latent variables. Appl. Spectr. Data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2002, 63, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Aldstadt, J. Constructing the spatial weights matrix using a local statistic. Geogr. Anal. 2004, 36, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Spatial weights matrix selection and model averaging for spatial autoregressive models. J. Econom. 2018, 203, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, J. Research on the Specification Methods of Spatial Weight Matrix. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2017, 01, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, Q.; Duan, Y.; Liu, W. Spatial Correlation between Water Resources and Rural Settlements in the Yanhe Watershed Based on Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Methods. Land 2023, 12, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armiento, M. The sustainable welfare index: Towards a threshold effect for Italy. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 152, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Sarwar, S.; Li, Z. Spatio-temporal differentiation mode and threshold effect of yangtze river delta urban ecological well-being performance based on network DEA. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Deng, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Population agglomeration in Chinese cities: Is it benefit or damage for the quality of economic development? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 10106–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Buysse, J.; Begum, I.A.; Wailes, E.; Van Huylenbroeck, G. The welfare impact of policy interventions in the foodgrainmarkets in Bangladesh. J. Econ. Policy Reform 2011, 14, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, B.N. Economic impact of government interventions during the COVID-19 pandemic: International evidence from financial markets. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2020, 27, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G. Welfare, innovation capacity, and economic performance: Evidence from American federalism. Public Policy Adm. 2019, 34, 349–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Pan, A. Do Export and FDI Aggravate Environmental Pollution in Resources-based Cities?—An Empirical Analysis Based on Panel Data of 285 Prefecture Cities in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zelity, B. The welfare effects of FDI: A quantitative analysis. J. Comp. Econ. 2022, 50, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atitianti, P.A.; Dai, Q. Does Chinese foreign direct investment improve the welfare of Africans? J. Afr. Bus. 2022, 23, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tian, P. How does heterogeneous environmental regulation affect net carbon emissions: Spatial and threshold analysis for China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchen, A.; Montargot, N. Non-spatial and spatial econometric analysis of tourism demand in a panel of countries around the world. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2022, 17, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Huang, Z.F.; Huang, R. The spatial effects of haze on tourism flows of Chinese cities: Empirical research based on the spatial panel econometric model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 814–830. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.A.; Qureshi, M.A.; Ahmed, M.; Qaiser, S.; Ali, R.; Ahmed, F. Non-linear relationship between tourism, economic growth, urbanization, and environmental degradation: Evidence from smooth transition models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1426–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).