Determinants of Ecological Footprint: A Quantile Regression Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How does industrialization contribute to the increase in the global ecological footprint?
- What is the impact of renewable energy consumption on the global ecological footprint?
- How does urbanization affect the global ecological footprint?
- What is the relationship between foreign direct investment, GDP per capita, and the global ecological footprint?
2. Determinants of Ecological Footprint
3. Literature Review
4. Materials and Method
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
7.1. Conclusions
7.2. Policy Recommendations
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Countries
| Country | Country | Country | Country |
| Antigua and Barbuda | Egypt | Lithuania | Senegal |
| Argentina | El Salvador | Madagascar | Seychelles |
| Armenia | Estonia | Malawi | Sierra Leone |
| Australia | Eswatini | Malaysia | Singapore |
| Austria | Ethiopia | Maldives | Slovakia |
| Bahamas | Fiji | Mali | Slovenia |
| Bangladesh | Finland | Mauritania | South Africa |
| Barbados | France | Mauritius | Spain |
| Belarus | Gabon | Mexico | Sri Lanka |
| Belgium | Germany | Moldova | St. Kitts and Nevis |
| Benin | Greece | Mongolia | St. Lucia |
| Bolivia | Grenada | Morocco | Sweden |
| Botswana | Guatemala | Mozambique | Switzerland |
| Brazil | Guinea | Namibia | Tajikistan |
| Brunei Darussalam | Guyana | Nepal | Tanzania, United Republic of |
| Bulgaria | Haiti | Netherlands | Thailand |
| Burkina Faso | Honduras | New Zealand | Togo |
| Burundi | Hungary | Nicaragua | Tonga |
| Cabo Verde | Iceland | Niger | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Cambodia | India | Nigeria | Turkiye |
| Cameroon | Indonesia | North Macedonia | Uganda |
| Canada | Iran, Islamic Republic of | Norway | Ukraine |
| Chile | Ireland | Pakistan | United Kingdom |
| China | Israel | Panama | United States of America |
| Colombia | Italy | Paraguay | Uruguay |
| Comoros | Jamaica | Peru | Uzbekistan |
| Costa Rica | Jordan | Philippines | Viet Nam |
| Croatia | Kazakhstan | Poland | Zambia |
| Cyprus | Kenya | Portugal | Zimbabwe |
| Czech Republic | Kiribati | Romania | |
| Denmark | Korea, Republic of | Russian Federation | |
| Dominica | Kyrgyzstan | Rwanda | |
| Dominican Republic | Latvia | Samoa | |
| Ecuador | Lebanon | Saudi Arabia |
Appendix B


References
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A.; Ormeño-Candelario, V.; Sanchez-Loor, D.A. Global ecological footprint and spatial dependence between countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, F.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. A safe operating space for humanity. Nature 2009, 461, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, G.; Szigeti, C. The historical ecological footprint: From over-population to over-consumption. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Hanscom, L.; Murthy, A.; Galli, A.; Evans, M.; Neill, E.; Mancini, M.S.; Martindill, J.; Medouar, F.-Z.; Huang, S.; et al. Ecological Footprint Accounting for Countries: Updates and Results of the National Footprint Accounts, 2012–2018. Resources 2018, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, C.; Yi, Y.; Bu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Shu, A. An Improved Ecological Footprint Method for Water Resources Utilization Assessment in the Cities. Water 2020, 12, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y. Human appropriation of natural capital: A comparison of ecological footprint and water footprint analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, W.E. Ecological footprints and appropriated carrying capacity: What urban economics leaves out. Environ. Urban. 1992, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisi, S.; Alizadeh, H.; Lotfi, W.; Mohammadi, S. Developing the Ecological Footprint Assessment for a University Campus, the Component-Based Method. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo-Iacono-Ferreira, V.G.; Torregrosa-López, J.I.; Capuz-Rizo, S.F. Use of Life Cycle Assessment methodology in the analysis of Ecological Footprint Assessment results to evaluate the environmental performance of universities. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daferera, M.; Abaskharoun, M.; Theodoratou, E. The Ecological Footprint Nowadays. Open Sch. J. Open Sci. 2019, 2, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.; McLoone, A.; O’Regan, B.; Moles, R.; Curry, R. The application of the ecological footprint in two Irish urban areas: Limerick and Belfast. Ir. Geogr. 2006, 39, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Usman, M.; Jahanger, A. Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rehman, M.A.; Fahad, S. The dynamic influence of renewable energy, trade openness, and industrialization on the sustainable environment in G-7 economies. Renew. Energy 2022, 198, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Felgueiras, C.; Smitkova, M.; Caetano, N. Analysis of Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption and Environmental Impacts in European Countries. Energies 2019, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufutau Opeyemi, B. Path to sustainable energy consumption: The possibility of substituting renewable energy for non-renewable energy. Energy 2021, 228, 120519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Moslehpour, M.; Tran, T.K.; Trung, L.M.; Ou, J.P.; Tien, N.H. Impact of non-renewable energy and natural resources on economic recovery: Empirical evidence from selected developing economies. Resour. Policy 2023, 80, 103221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shut’ko, L.; Samorodova, L.; Ivanov, A. Ecological footprint and decoupling in the sustainable development of a region. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 174, 04058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yu, Z.-G.; Klemeš, J.J.; Bokhari, A. A state-of-the-art review of greenhouse gas emissions from Indian hydropower reservoirs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, A.; Syed Ismail, S.N.; Awang, S.; Praveena, S.M.; Zainal Abidin, E. Land use change in highland area and its impact on river water quality: A review of case studies in Malaysia. Ecol. Process. 2018, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, B.A.; Onifade, S.T.; Erdoğan, S.; Ali, E.B. Colligating ecological footprint and economic globalization after COP21: Insights from agricultural value-added and natural resources rents in the E7 economies. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2023, 30, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Wang, S.; Adebayo, T.S.; Saleh Al-Faryan, M.A. The potency of natural resources on ecological sustainability in PIIGS economies. Resour. Policy 2022, 79, 102941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, F.F.d.; Kamino, L.H.Y.; Junior, R.T.; Campos, I.C.d.; Carmo, F.F.d.; Silvino, G.; Castro, K.J.d.S.X.d.; Mauro, M.L.; Rodrigues, N.U.A.; Miranda, M.P.d.S.; et al. Fundão tailings dam failures: The environment tragedy of the largest technological disaster of Brazilian mining in global context. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 15, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckeneder, S.; Giljum, S.; Schaffartzik, A.; Maus, V.; Tost, M. Surge in global metal mining threatens vulnerable ecosystems. Glob. Environ. Change 2021, 69, 102303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlanyo, A.S.; Jiangfeng, L. Evaluating the environmental and economic impact of mining for post-mined land restoration and land-use: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevskaya, M.A.; Seleznev, S.G.; Masloboev, V.A.; Klyuchnikova, E.M.; Makarov, D.V. Environmental and Business Challenges Presented by Mining and Mineral Processing Waste in the Russian Federation. Minerals 2019, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimbaev, T.; Mazhitova, Z.; Beksultanova, C.; TentigulKyzy, N. Activities of mining and metallurgical industry enterprises of the Republic of Kazakhstan: Environmental problems and possible solutions. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 175, 14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-y.; Ye, X.-y.; Qi, Z.-f.; Zhang, H. Impacts of land use/land cover change and socioeconomic development on regional ecosystem services: The case of fast-growing Hangzhou metropolitan area, China. Cities 2013, 31, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Han, L.; Hong, H.; Zhou, T. Research on the Enhancement Effects of Using Ecological Principles in Managing the Lifecycle of Industrial Land. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, M. Decomposition and Decoupling Analysis of Industrial Solid Waste in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. E3s Web of Conf. 2021, 275, 02054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, D. Mining productivity and the fourth industrial revolution. Miner. Econ. 2020, 33, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P. Mining industry and sustainable development: Time for change. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budihardjo, S.; Hadi, S.P.; Sutikno, S.; Purwanto, P. The Ecological Footprint Analysis for Assessing Carrying Capacity of Industrial Zone in Semarang. J. Hum. Resour. Sustain. Stud. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Mursheed, N.; Islam, M.M.; Bhuyan, M.I.; Islam, M.S.; Mithu, T.N. Heavy metal toxicity in agricultural soil due to rapid industrialization in Bangladesh: A review. Int. J. Adv. Geosci. 2018, 6, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Alkhateeb, T.T.Y.; Furqan, M. Industrialization, urbanization and CO2 emissions in Saudi Arabia: Asymmetry analysis. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y. Industrial agglomeration and environmental pollution: Evidence from China under New Urbanization. Energy Environ. 2018, 30, 1010–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, H.; Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Environmental Regulation for Transfer of Pollution-Intensive Industries: Evidence from Chinese Provinces. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 604005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.R.; Frickel, S. The Historical Nature of Cities:A Study of Urbanization and Hazardous Waste Accumulation. Am. Sociol. Rev. 2013, 78, 521–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berkel, R.; Willems, E.; Lafleur, M. The Relationship between Cleaner Production and Industrial Ecology. J. Ind. Ecol. 1997, 1, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, A. Influence of Agricultural Chains on the Carbon Footprint in the Context of European Green Pact and Crises. Agriculture 2022, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, V.C.; Stavropoulos, P.; Chryssolouris, G. A critical review on the environmental impact of manufacturing: A holistic perspective. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 118, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadarso, M.Á.; Gómez, N.; López, L.A.; Tobarra, M.Á. Calculating tourism’s carbon footprint: Measuring the impact of investments. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 111, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Dong, K. How digital industries affect China’s carbon emissions? Analysis of the direct and indirect structural effects. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, N.C.; Kucukvar, M. Carbon footprint of construction industry: A global review and supply chain analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 124, 109783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, M.; Luan, Y.; Cui, W.; Lin, X. Spatial Evolutionary Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Urban Industrial Carbon Emission in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, Y. Estimating Smart Grid’s Carbon Emission Reduction Potential in China’s Manufacturing Industry Based on Decomposition Analysis. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 681244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong, J.; Namwamba, J.B.; Twumasi, Y.A.; Ning, Z.H.; Asare-Ansah, A.B.; Akinrinwoye, C.; Antwi, R.; Osimbo, B.M.; Loh, P.; Frimpong, D.B.; et al. Urbanization and urban forest loss: A spatial analysis of five metropolitan districts in Ghana. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Useni Sikuzani, Y.; Sambiéni Kouagou, R.; Maréchal, J.; Ilunga wa Ilunga, E.; Malaisse, F.; Bogaert, J.; Munyemba Kankumbi, F. Changes in the Spatial Pattern and Ecological Functionalities of Green Spaces in Lubumbashi (the Democratic Republic of Congo) in Relation With the Degree of Urbanization. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2018, 11, 1940082918771325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Yin, H.; Kong, F.; Fan, F. Developing green space ecological networks in Shijiazhuang city, China. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rastandeh, A.; Jarchow, M. Urbanization and biodiversity loss in the post-COVID-19 era: Complex challenges and possible solutions. Cities Health 2021, 5, S37–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeczko, E.; Dąbrowski, R.; Budnicka-Kosior, J.; Woźnicka, M. Influence of Urbanization Processes on the Dynamics and Scale of Spatial Transformations in the Mazowiecki Landscape Park. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, K.; Lal, R. Managing soil carbon stocks to enhance the resilience of urban ecosystems. Carbon Manag. 2015, 6, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Odorico, P.; Davis, K.F.; Rosa, L.; Carr, J.A.; Chiarelli, D.; Dell’Angelo, J.; Gephart, J.; MacDonald, G.K.; Seekell, D.A.; Suweis, S.; et al. The Global Food-Energy-Water Nexus. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 456–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinga, S.A.; Paudel, D.; Mouzakitis, S.A.; Athanasiadis, I.N. Big data in agriculture: Between opportunity and solution. Agric. Syst. 2022, 195, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehringer, J.G.; Wambugu, G.; Kiteme, B.; Eckert, S. How do large-scale agricultural investments affect land use and the environment on the western slopes of Mount Kenya? Empirical evidence based on small-scale farmers’ perceptions and remote sensing. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Verstaen, J.; Rayner, P.-E.; Clawson, G.; Blanchard, J.L.; Cottrell, R.S.; Froehlich, H.E.; Gephart, J.A.; Jacobsen, N.S.; et al. The environmental footprint of global food production. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avtar, R.; Tripathi, S.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Kumar, P. Population–Urbanization–Energy Nexus: A Review. Resources 2019, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Radulescu, M.; Cismaș, L.M.; Cismaș, C.-M.; Chandio, A.A.; Simoni, S. Renewable Energy, Urbanization, Fossil Fuel Consumption, and Economic Growth Dilemma in Romania: Examining the Short- and Long-Term Impact. Energies 2022, 15, 7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, J.K.; Roberts, J.T.; Peters, G.P.; Baiocchi, G. Pathways of human development and carbon emissions embodied in trade. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdunnur, A. Nexus of Fisheries and Agriculture Production and Urbanization on Ecological Footprint: New Evidence from Indonesian Economy. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2020, 10, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quito, B.; del Río-Rama, M.d.l.C.; Álvarez-García, J.; Durán-Sánchez, A. Impacts of industrialization, renewable energy and urbanization on the global ecological footprint: A quantile regression approach. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.; Sobhani, P.; Sayahnia, R. Assessment of the ecological footprint associated with consumption resources and urbanization development in Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhuo, L.; Li, Z.; Ji, X.; Wu, P. Effects of multidimensional urbanisation on water footprint self-sufficiency of staple crops in China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergül, Ö.C.; Göker, P. Evaluating Eco-Cities with A Sustainable Perspective In Human-Nature Interaction. Avrupa Bilim Ve Teknol. Derg. 2021, 21, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Yaqoob, T. The potency of eco-innovation, natural resource and financial development on ecological footprint: A quantile-ARDL-based evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50675–50685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Zafar, M.W.; Ali, S.; Danish. Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: An empirical analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Lin, X. The eco-environmental guarantee for China’s urbanization process. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish; Wang, Z. Investigation of the ecological footprint’s driving factors: What we learn from the experience of emerging economies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 49, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Ji, X.; Ulgiati, S. Is urbanization eco-friendly? An energy and land use cross-country analysis. Energy Policy 2017, 100, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghutla, C.; Padmagirisan, P.; Sakthivel, P.; Chittedi, K.R.; Mishra, S. The effect of renewable energy consumption on ecological footprint in N-11 countries: Evidence from Panel Quantile Regression Approach. Renew. Energy 2022, 197, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, Y.; Burbano, M.; Roush, J.; Kang, H.; Sridhar, V.; Hyndman, D.W. A Review of the Integrated Effects of Changing Climate, Land Use, and Dams on Mekong River Hydrology. Water 2018, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, G.T.; Ma’Arof, M.I.N.; Sharma, R. Trends in an increased dependence towards hydropower energy utilization—A short review. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 1631541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renöfält, B.M.; Jansson, R.; Nilsson, C. Effects of hydropower generation and opportunities for environmental flow management in Swedish riverine ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, K.; Omri, A. The impact of renewable energy on carbon emissions and economic growth in 15 major renewable energy-consuming countries. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Sun, R.; Mei, H.; Yue, S.; Yuliang, L. Does renewable energy consumption reduce energy ecological footprint: Evidence from China. Environ. Res. Ecol. 2023, 2, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, O.; Iorember, P.T.; Jelilov, G.; Isik, A.; Ike, G.N.; Sarkodie, S.A. Towards mitigating ecological degradation in G-7 countries: Accounting for economic effect dynamics, renewable energy consumption, and innovation. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, W.P.; Khalid, B.; Urbański, M.; Kot, M. Factors Influencing Consumer’s Adoption of Renewable Energy. Energies 2021, 14, 5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, A.A.; Mosly, I. Factors Affecting Public Willingness to Adopt Renewable Energy Technologies: An Exploratory Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomianek, I. Differentiation of the Level of Socio-Economic Development of Rural and Semi-Urban Municipalities of the Wielkopolskie Voivodeship in 2004–2020. Acta Sci. Polonorum. Oeconomia 2022, 21, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wynsberghe, A. Sustainable AI: AI for sustainability and the sustainability of AI. AI Ethics 2021, 1, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Environment and Development. Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, J. Sustainable development: Meaning, history, principles, pillars, and implications for human action: Literature review. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2019, 5, 1653531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggerio, C.A. Sustainability and sustainable development: A review of principles and definitions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płonka, A.; Dacko, M.; Satoła, Ł.; Dacko, A. The Idea of Sustainable Development and the Possibilities of Its Interpretation and Implementation. Energies 2022, 15, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-mulali, U.; Weng-Wai, C.; Sheau-Ting, L.; Mohammed, A.H. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayob, M.R.A.-M.B.; Rohni, A.M. Mathematical Approach for Predicting the Gross Domestic Product of Malaysia. Malays. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. (Mjssh) 2020, 5, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincheira, R.; Zuniga, F. Environmental Kuznets curve bibliographic map: A systematic literature review. Account. Financ. 2021, 61, 1931–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Rodríguez, J.C. The Ecological Footprint and Kuznets Environmental Curve in the USMCA Countries: A Method of Moments Quantile Regression Analysis. Energies 2020, 13, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouri, M.E.H.; Ben Youssef, A.; M’Henni, H.; Rault, C. Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energy Policy 2012, 45, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, A. CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth nexus in MENA countries: Evidence from simultaneous equations models. Energy Econ. 2013, 40, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, C.; Wang, A. Environmental Governance, Public Health Expenditure, and Economic Growth: Analysis in an OLG Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Deng, W.J.; Cheng, H.; Gao, Q.; Deng, Z.W.; Deng, H.C. The Impact of Local Economic Growth Target Setting on the Quality of Public Occupational Health: Evidence From Provincial and City Government Work Reports in China. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 769672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, H. An Empirical Study on Economic Growth and Carbon Emissions of G20 Group; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 318–321. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.S.; Kabir, N. Economic growth and environmental sustainability: Empirical evidence from East and South-East Asia. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2013, 5. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2199374 (accessed on 11 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Selishcheva, T.; Dyatlov, S.; Sopina, N.; Ilyina, O.; Trunin, V. Comprehensive analysis of sustainable development of the countries of the Eurasian Economic Union. SHS Web Conf. 2021, 129, 09018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, S. The Environmental Kuznets Curve: A Survey of the Literature. 1999. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.200556 (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Selden, T.M.; Song, D. Environmental Quality and Development: Is There a Kuznets Curve for Air Pollution Emissions? J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1994, 27, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango Miranda, R.; Hausler, R.; Romero Lopez, R.; Glaus, M.; Pasillas-Diaz, J.R. Testing the Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis in North America’s Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) Countries. Energies 2020, 13, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, R.; Yang, J.; Bai, B.; Jiang, T. Non-linear effects of industrial structure on urban haze pollution: A test and extension of the environmental Kuznets curve. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1033563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, D.; Yamamoto, M.; Yoshida, Y. The decoupling of affluence and waste discharge under spatial correlation: Do richer communities discharge more waste? Environ. Dev. Econ. 2015, 20, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozgor, G.; Can, M. Export product diversification and the environmental Kuznets curve: Evidence from Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21594–21603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlongwane, N.W.; Daw, O.D. Testing Environmental Kuznets Curve Hold in South Africa: An Econometric Approach. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2022, 12, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ella, P.N.; Mabiala, J.F.; Ikinda, L.B.O. Testing the Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis in CEMAC Countries. Asian J. Empir. Res. 2022, 12, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytch, N. The impact of foreign direct investment on the ecological footprints of nations. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2020, 8, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, A.K. Does Foreign Investment Harm the Air We Breathe and the Water We Drink? A Cross-National Study of Carbon Dioxide Emissions and Organic Water Pollution in Less-Developed Countries, 1975 to 2000. Organ. Environ. 2007, 20, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Foreign Direct Investment, Pollution, and the Environmental Quality: A Model with Empirical Evidence from the Chinese Regions. Int. Trade J. 2015, 29, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.W.; Zaidi, S.A.H.; Khan, N.R.; Mirza, F.M.; Hou, F.; Kirmani, S.A.A. The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: The case of the United States. Resour. Policy 2019, 63, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markusen, J.R.; Venables, A.J. Multinational Firms and The New Trade Theory; Working Paper No. 5036; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Testing the Pollution Haven Effect: Does the Type of FDI Matter? Environ. Resour. Econ. 2015, 60, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W. The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, M.; Bölük, G. Do foreign direct investment and renewable energy consumption affect the CO2 emissions? New evidence from a panel ARDL approach to Kyoto Annex countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21669–21681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivyiro, P.; Arminen, H. Carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and foreign direct investment: Causality analysis for Sub-Saharan Africa. Energy 2014, 74, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, P.; Taylor, G. Globalization and the Environment: Determinants of Firm Self-Regulation in China. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2001, 32, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X. The Spatial Correlation between Foreign Direct Investment and Air Quality in China and the Potential Channel. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, A.; Yakubu, I.N. Exploring Industrialization and Environmental Sustainability Dynamics in Ghana: A Fully Modified Least Squares Approach. Technol. Sustain. 2022, 2, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Okumus, I. Does Pollution Haven Hypothesis Hold in Newly Industrialized Countries? Evidence From Ecological Footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23689–23695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, T. Carbon Footprint of Logistics and Transportation: A Systematic Literature Review. Kent Akad. 2022, 2, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouachi, M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Environmental strategies for achieving a new foreign direct investment golden decade in Algeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37660–37675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, P.; Álvarez-García, J.; Álvarez, V.P.; Irfan, M. Analysing the Influence of Foreign Direct Investment and Urbanization on the Development of Private Financial System and Its Ecological Footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 9624–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, T.; Meo, M.S.; Bekun, F.V.; Ibrahim, T.O. The Impact of Energy Consumption to Environmental Sustainability: An Extension of Foreign Direct Investment Induce Pollution in Vietnam. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2021, 15, 1144–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alola, A.A.; Adebayo, T.S.; Onifade, S.T. Examining the dynamics of ecological footprint in China with spectral Granger causality and quantile-on-quantile approaches. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2022, 29, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Baris-Tuzemen, O.; Uzuner, G.; Ozturk, I.; Sinha, A. Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: Evidence from Quantile ARDL approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 57, 102138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, Ö.K.; Topal, S.; Çamkaya, S. The Impact of Economic Growth, Renewable Energy, Non-Renewable Energy and Trade Openness on the Ecological Footprint and Forecasting in Turkiye: An Case of the ARDL and NMGM Forecasting Model. Alphanumeric J. 2022, 10, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anser, M.K.; Syed, Q.R.; Lean, H.H.; Alola, A.A.; Ahmad, M. Do Economic Policy Uncertainty and Geopolitical Risk Lead to Environmental Degradation? Evidence from Emerging Economies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Al-Mulali, U.; Saboori, B. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahiem, D.M.; Hanafy, S.A. Dynamic Linkages Amongst Ecological Footprints, Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption and Globalization: An Empirical Analysis. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 1549–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, M.; Sethi, N. The dynamic impact of urbanization, structural transformation, and technological innovation on ecological footprint and PM2.5: Evidence from newly industrialized countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 4244–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish; Ulucak, R.; Khan, S.U.-D. Determinants of the ecological footprint: Role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.; Khan, D.; Gupta, R.; Popp, J.; Oláh, J. Assessing the asymmetric impact of physical infrastructure and trade openness on ecological footprint: An empirical evidence from Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirikkaleli, D.; Adebayo, T.S.; Khan, Z.; Ali, S. Does globalization matter for ecological footprint in Turkey? Evidence from dual adjustment approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14009–14017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G. Regression Quantiles. Econometrica 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lin, B. Factors affecting CO2 emissions in China’s agriculture sector: Evidence from geographically weighted regression model. Energy Policy 2017, 104, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, P.M.D.C.; Silva, J.M.C.S. Quantile Regression with Clustered Data. J. Econom. Methods 2016, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D. Quantile Treatment Effects in the Presence of Covariates. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2020, 102, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmert, G.A.J.; Schons, L.M.; Wieseke, J.; Schimmelpfennig, H. Log-likelihood-based Pseudo-R2 in Logistic Regression:Deriving Sample-sensitive Benchmarks. Sociol. Methods Res. 2018, 47, 507–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arogundade, S.; Mduduzi, B.; Hassan, A.S. Spatial impact of foreign direct investment on ecological footprint in Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 51589–51608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.F.; Shanto, P.A.; Ahmed, A.; Rumana, R.H. Does foreign direct investments impair the ecological footprint? New evidence from the panel quantile regression. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14372–14385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Y. The environmental consequences of domestic and foreign investment: Evidence from China. Energy Policy 2017, 108, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Doytch, N.; Uctum, M. Foreign direct investment and the environment: Disentangling the impact of greenfield investment and merger and acquisition sales. Sustain. Account. Manag. Policy J. 2021, 12, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W. Lagged effect of exports, industrialization and urbanization on carbon footprint in Southeast Asia. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2019, 26, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: Can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Energy Policy 2022, 162, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalkı, İ. Industrialization Impact on Climate Change: An Examination of NICs. In Handbook of Research on Sustainable Consumption and Production for Greener Economies; Goel, R., Baral, S.K., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Destek, M.A. Deindustrialization, reindustrialization and environmental degradation: Evidence from ecological footprint of Turkey. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J. Measurement and analysis of ecological pressure due to industrial development in the Yangtze River economic belt from 2010 to 2018. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 353, 131614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, E.E.O.; Aluko, O.A. Heterogeneous effects of industrialization on the environment: Evidence from panel quantile regression. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2021, 59, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Sakrafi, H.; Gheraia, Z.; Abdelli, H. Does renewable energy consumption affect ecological footprints in Saudi Arabia? A bootstrap causality test. Renew. Energy 2022, 189, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Razzaq, A.; Adebayo, T.S.; Awosusi, A.A. Do renewable energy consumption and financial globalisation contribute to ecological sustainability in newly industrialized countries? Renew. Energy 2022, 187, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Jiang, P.; Murshed, M.; Shehzad, K.; Akram, R.; Cui, L.; Khan, Z. Modelling the dynamic linkages between eco-innovation, urbanization, economic growth and ecological footprints for G7 countries: Does financial globalization matter? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, U.; Sabir, S.; Anjum, S. Urbanization, informal economy, and ecological footprint quality in South Asia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67011–67021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, J.T.; Adeiza, A.; Ismail, N.A.; Marina, A. Investigating the link between economic growth, financial development, urbanization, natural resources, human capital, trade openness and ecological footprint: Evidence from Nigeria. J. Bioeconomics 2022, 24, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Abbasi, K.R.; Salem, S.; Almulhim, A.I.; Alvarado, R. Do natural resources, economic growth, human capital, and urbanization affect the ecological footprint? A modified dynamic ARDL and KRLS approach. Resour. Policy 2022, 78, 102782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, T. Any sustainable decoupling in the Finnish economy? A comparison of the pathways and sensitivities of GDP and ecological footprint 2002–2005. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 16, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
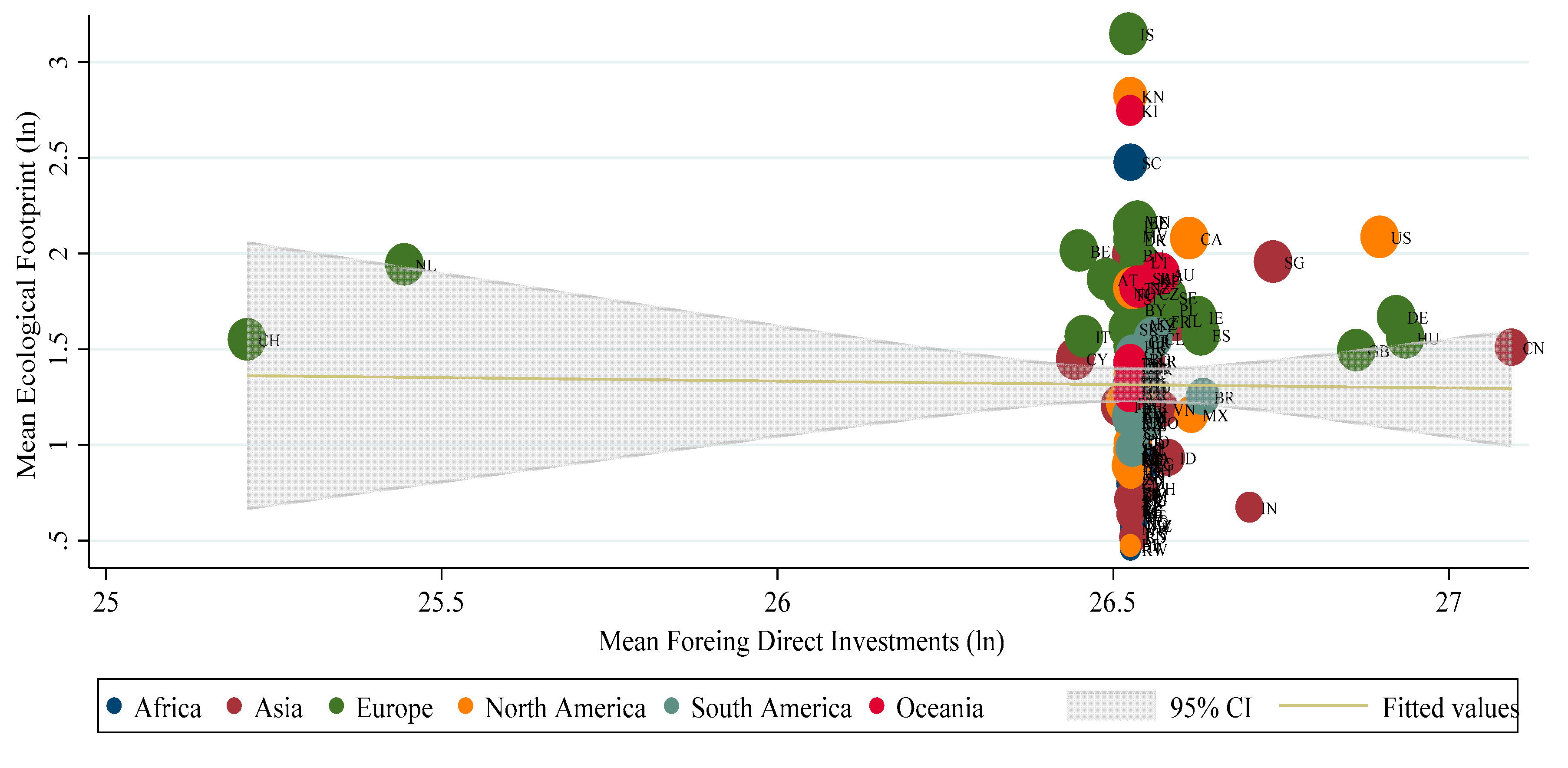

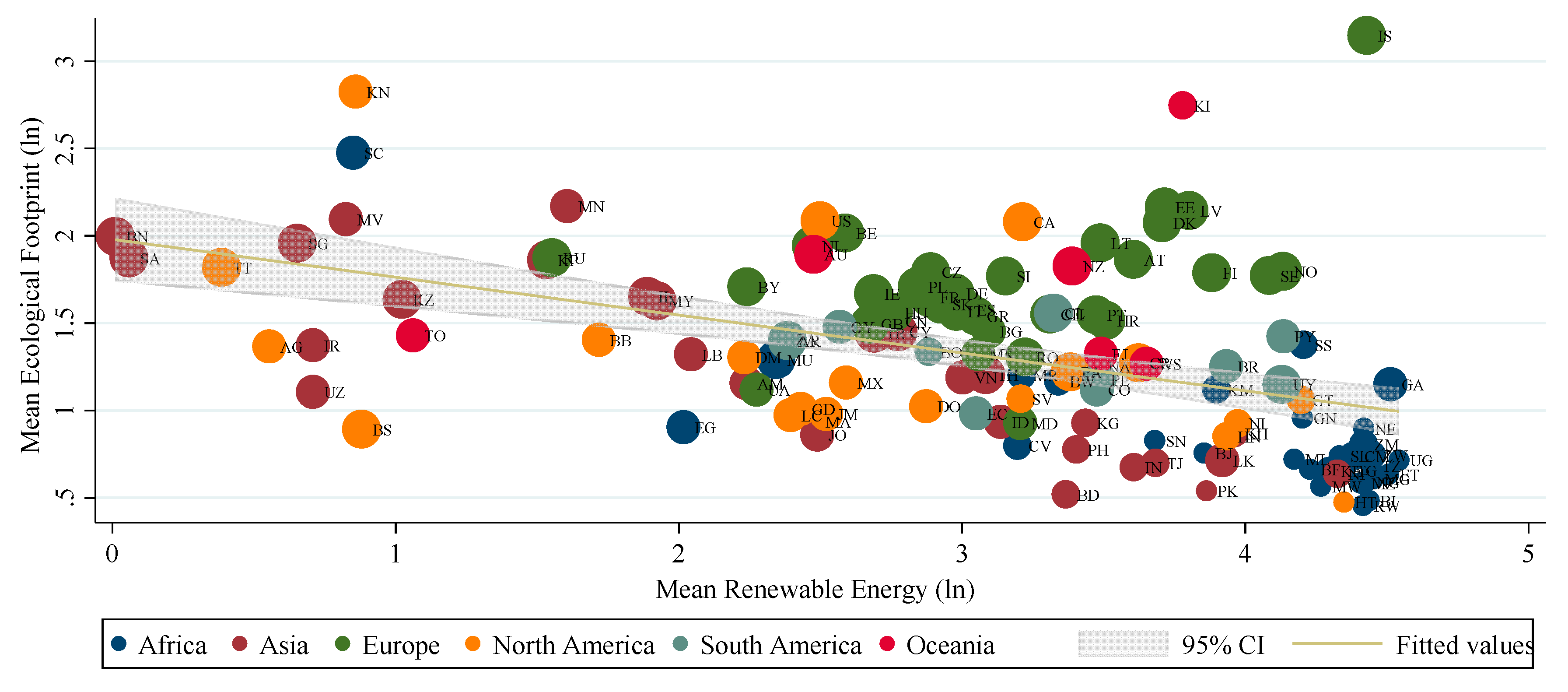


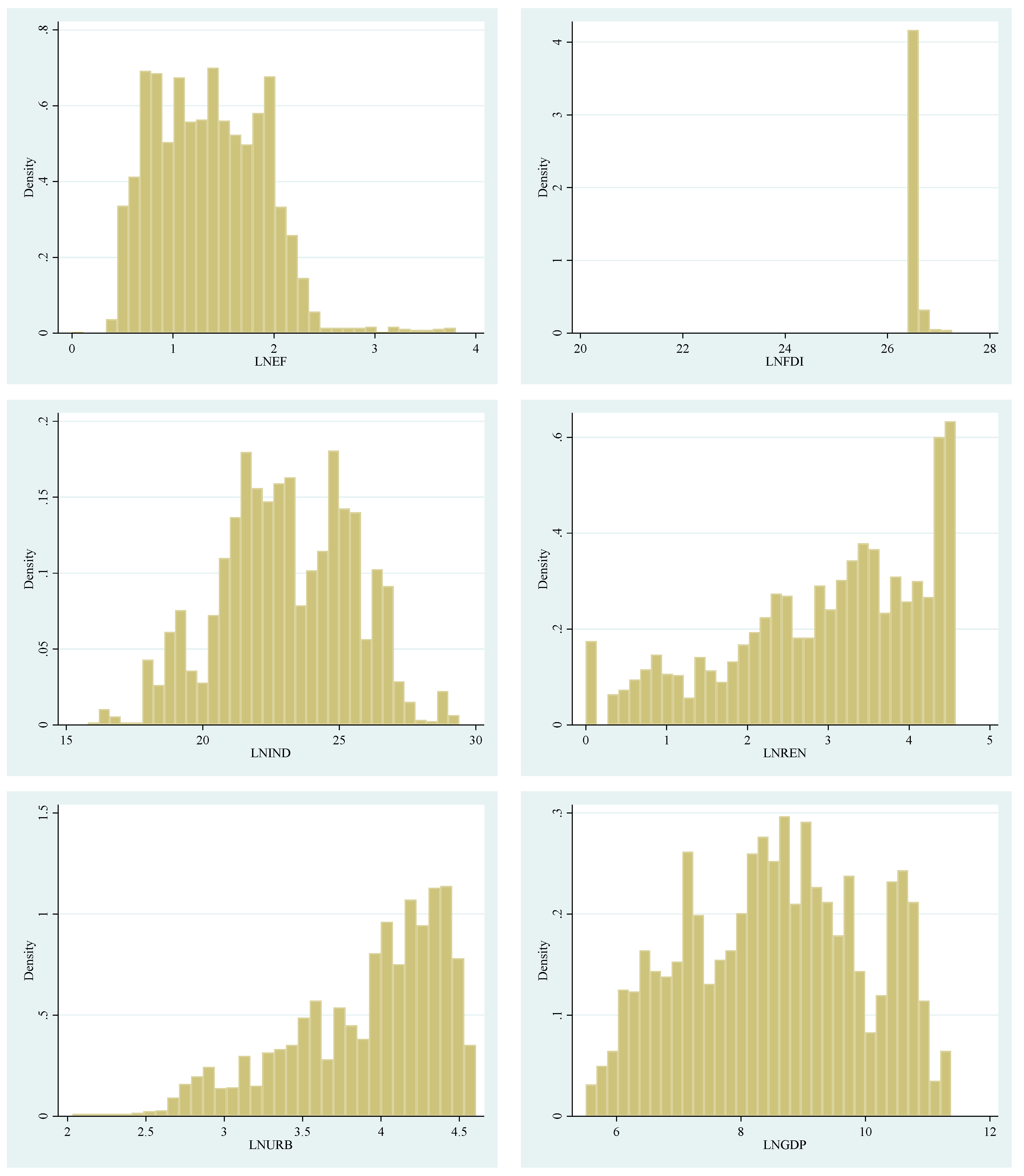
| Statistics | LNEF | LNFDI | LNIND | LNREN | LNURB | LNGDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 3.61 | 11,300,000,000 | 111,000,000,000 | 32.88 | 55.56 | 12,656.29 |
| Median | 2.83 | 814,000,000 | 9,520,000,000 | 24.015 | 56.84 | 5544.124 |
| Max | 43.67 | 734,000,000,000 | 5,770,000,000,000 | 96.04 | 100.00 | 87,123.66 |
| Min. | 0.00 | −330,000,000,000 | 7,184,645 | 0.00 | 7.62 | 246.39 |
| Std. Dev. | 3.50 | 41,300,000,000 | 414,000,000,000 | 29.22 | 22.64 | 16,413.30 |
| S | 0.556 | −23.654 | −0.135 | −0.648 | −0.900 | −0.068 |
| K | 3.608 | 1050.411 | 2.572 | 2.520 | 3.115 | 2.076 |
| Normality (χ2(02)) | 141.47 *** | 190.53 *** | 42.04 *** | 193.82 *** | 258.08 *** | 384.63 *** |
| [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | |
| Obs. | 3144 | 3144 | 3144 | 3144 | 3144 | 3144 |
| LNEF | LNFDI | LNIND | LNREN | LNURB | LNGDP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LNEF | 1.000 | |||||
| - | ||||||
| LNFDI | 0.144 *** | 1.000 | ||||
| [0.000] | - | |||||
| LNIND | 0.280 *** | 0.262 *** | 1.000 | |||
| [0.000] | [0.000] | - | ||||
| LNREN | −0.530 *** | −0.103 *** | −0.199 *** | 1.000 | ||
| [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | - | |||
| LNURB | 0.623 *** | 0.128 *** | 0.530 *** | −0.445 *** | 1.000 | |
| [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | - | ||
| LNGDP | 0.831 *** | 0.171 *** | 0.478 *** | −0.549 *** | 0.725 *** | 1.000 |
| [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | [0.000] | - |
| Variable | Quantiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |
| LNFDI | 0.122 | 0.359 | 0.331 | 0.290 | 0.238 |
| 0.036 | 0.096 | 0.077 | 0.072 | 0.095 | |
| 3.34 *** [0.001] | 3.74 *** [0.000] | 4.29 *** [0.000] | 4.06 *** [0.000] | 2.5 *** [0.012] | |
| LNIND | −0.039 | −0.007 | −0.016 | −0.020 | −0.023 |
| 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | |
| −15.16 *** [0.000] | −1.95 *** [0.051] | −5.7 *** [0.000] | −6.89 *** [0.000] | −6.8 *** [0.000] | |
| LNREN | −0.037 | −0.043 | −0.030 | −0.039 | −0.047 |
| 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.005 | |
| −7.21 *** [0.000] | −4.67 *** [0.000] | −4.82 *** [0.000] | −7.38 *** [0.000] | −8.72 *** [0.000] | |
| LNURB | 0.113 | 0.033 | 0.041 | 0.068 | 0.068 |
| 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.017 | |
| 7.12 *** [0.000] | 2.03 *** [0.042] | 2.97 *** [0.000] | 4.50 *** [0.000] | 4.03 *** [0.000] | |
| LNGDP | 0.301 | 0.273 | 0.285 | 0.283 | 0.286 |
| 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.006 | |
| 52.34 *** [0.000] | 34.11 *** [0.000] | 46.08 *** [0.000] | 45.02 *** [0.000] | 45.82 *** [0.000] | |
| Constant | −3.877 | −10.640 | −9.782 | −8.600 | −7.106 |
| 0.957 | 2.492 | 2.018 | 1.873 | 2.493 | |
| −4.05 *** [0.000] | −4.27 *** [0.000] | −4.85 *** [0.000] | −4.59 *** [0.000] | −2.85 *** [0.004] | |
| R2 | 0.719 | 0.473 | 0.534 | 0.559 | 0.567 |
| Variable | Quantiles | ||||
| 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | |
| LNFDI v | 0.237 | 0.250 | 0.296 | 0.351 | 0.368 |
| 0.101 | 0.102 | 0.102 | 0.112 | 0.104 | |
| 2.34 *** [0.000] | 2.45 *** [0.014] | 2.91 *** [0.004] | 3.13 *** [0.000] | 3.53 *** [0.000] | |
| LNIND | −0.027 | −0.035 | −0.050 | −0.069 | −0.088 |
| 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.006 | |
| −7.11 *** [0.000] | −8.06 *** [0.000] | −8.84 *** [0.000] | −12.55 *** [0.000] | −15.71 *** [0.000] | |
| LNREN | −0.055 | −0.059 | −0.067 | −0.088 | −0.114 |
| 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.011 | |
| −10.57 *** [0.000] | −10.04 *** [0.000] | −9.37 *** [0.000] | −10.58 *** [0.000] | −10.00 *** [0.000] | |
| LNURB | 0.080 | 0.103 | 0.092 | 0.057 | 0.073 |
| 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.024 | 0.023 | 0.032 | |
| 4.28 *** [0.000] | 4.94 *** [0.000] | 3.76 *** [0.000] | 2.49 ** [0.013] | 2.31 ** [0.021] | |
| LNGDP | 0.284 | 0.288 | 0.301 | 0.321 | 0.332 |
| 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.010 | |
| 46.73 *** [0.000] | 42.14 *** [0.000] | 36.56 *** [0.000] | 39.82 *** [0.000] | 34.39 *** [0.000] | |
| Constant | −6.906 | −7.119 | −7.986 | −8.890 | −8.865 |
| 2.642 | 2.652 | 2.625 | 2.906 | 2.698 | |
| −2.61 *** [0.009] | −2.68 *** [0.007] | −3.04 *** [0.002] | −3.06 *** [0.002] | −3.29 *** [0.001] | |
| R2 | 0.566 | 0.557 | 0.539 | 0.504 | 0.453 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akyol Özcan, K. Determinants of Ecological Footprint: A Quantile Regression Approach. Systems 2024, 12, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12020059
Akyol Özcan K. Determinants of Ecological Footprint: A Quantile Regression Approach. Systems. 2024; 12(2):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12020059
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkyol Özcan, Kübra. 2024. "Determinants of Ecological Footprint: A Quantile Regression Approach" Systems 12, no. 2: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12020059
APA StyleAkyol Özcan, K. (2024). Determinants of Ecological Footprint: A Quantile Regression Approach. Systems, 12(2), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12020059






