2.1. Digital Technology Application in Talent Management
Talent management is a typical practical application that precedes theoretical research, and not all employees possess skills that are of equal strategic importance to the organization [
16]. It has received groundbreaking empirical research in academia [
1]. Although the application of digital technology in human resource management still requires significant data support for improved efficiency, it has become increasingly prevalent in various aspects of organizational management, including talent selection [
17], training and development, assessment and supervision, rewards and incentives, talent evaluation, employee relations, and other areas of human resource management [
18,
19]. Research has shown that the introduction of artificial intelligence technology into human resource management functions can effectively change and manage organizations through their workforce, which is beneficial for improving internal and external performance as well as the work attitude of employees. Consequently, it positively impacts overall organizational performance [
20,
21]. IBM has launched Watson Recruitment, an innovative application powered by artificial intelligence (AI), aimed at revolutionizing the candidate selection process for organizations. By employing digital technology, organizations can enhance their employer brand, expand the pool of potential candidates, and ultimately improve the overall selection process. However, despite its numerous benefits, the adoption of AI technology in recruitment is hindered by concerns regarding security, privacy, and the so-called “black box problem [
21].” Although there are ethical considerations surrounding its use at an individual level or with regard to employee emotions; at an organizational level digital technology is becoming increasingly prevalent.
In line with the theory that posits the influence of the environment on organizational structure, three key factors shape the design of organizational structures: overall ecology, system dynamics, and resource dependence. Specifically, the competitive environment, technical and task requirements and the size of the organization are key drivers that shape the organizational structure. In the context of human resource management, the introduction of digital technology necessitates adjustments to the organizational structure. This adaptation prompts changes in the management system, impacts the utilization of external resources, and ultimately affects talent effectiveness and organizational performance. It becomes evident that digital transformation is not merely a targeted adjustment but rather a Darwinian evolution process for organizations. When an organization fails to adapt its overall capabilities to meet competitive environmental demands adequately, it risks being replaced by more resilient entities. China’s “Digital China Development Report” from 2022 reveals that as global digital technology continues to develop rapidly, China’s digital economy scale amounts to 45.5 trillion yuan (39.8% of GDP). In light of this trend, numerous human resource management practices have emerged due to advancements in digital technology usage within organizations’ operations. Therefore, undertaking a digital transformation in talent management becomes an inevitable choice for evolutionary development based on Darwinian principles. Hence, this study presents several assumptions:
H1a: Digital technology application in human resource management has a positive influence on organizational performance.
Digital technology allows for the seamless integration of real-time data into talent management, connecting an organization’s human resource management system with external market dynamics, internal production information, and other management systems. This resolves issues related to delayed, inaccurate, or incomplete data analysis in traditional talent management approaches. Additionally, it addresses the limitations of talent management in terms of forecasting and its impact on team management [
22,
23]. The Uber platform utilizes real-time analysis of a driver’s braking and acceleration data to assess their driving behavior and provide timely reminders for necessary rest breaks. Previous studies suggest that ITM places significant emphasis on the strategic role of human resources in organizational development. It encompasses various aspects of talent management, including attraction, identification, development, retention, and deployment through systematic projects. ITM advocates for the interactive integration of people and technology to ensure equal development rights for every employee, and this approach promotes a people-oriented mindset that fosters harmonious development between organizations and employees [
24]. Additionally, it highlights using digital technology to enhance individual work efficiency and team performance [
25]. Research has shown that traditional talent management relies on static information stored within human resources information systems. In contrast, digital age talent analysis can span across entire business processes by accurately capturing dynamic data on talent characteristics. This allows for the efficient identification of proprietary talents within an organization—high-potential individuals who contribute directly or have a significant future impact on organizational performance [
26]. By investing more resources into these talents’ growth and commitment to the organization, overall performance can be improved.
H1b: Digital technology application in human resource management has a positive influence on ITM.
H1c: Digital technology application in human resource management has a positive influence on ETM.
2.2. ITM and ETM
This paper examines the impact of digital technology on talent management, contributing to the existing empirical research in this field. Talent management encompasses two main areas: ITM and ETM. ITM focuses on analyzing human capital at the organizational level, aiming to improve individual efficiency and overall organizational performance. On the other hand, ETM concentrates on managing high-performance and high-potential employees within an organization [
27]. These individuals are considered exclusive talents due to their relative value to the organization, leading to focused investment in their development. Digital talent management enables the establishment of a dynamic team operation model [
22]. By leveraging comprehensive talent data prediction and analysis through digital technology, organizations can effectively identify and attract top talents as well as provide targeted training for new employees [
28,
29]. This approach improves decision-making by analyzing risk and sensitivity data. It efficiently meets business needs while seamlessly integrating human resources with front-end operations, transforming HR into effective business partners [
30,
31]. This study argues that both ITM and ETM have the potential to serve as valuable business partners. Therefore, this study puts forward the following assumptions:
H2a: ITM has a positive influence on organizational performance.
H2b: ETM has a positive influence on organizational performance.
After implementing digital technology and artificial intelligence equipment, organizations can transform the work environment for employees. This transformation provides effective technical support to enhance work efficiency and encourages employees to actively explore and adapt to changes in their roles. Inclusive talent management in organizations, where team members are treated fairly and their strengths are fully utilized, can significantly impact team performance [
32]. The Annual Observation Report on Human Resource Management in China in 2022 issued by Beisen highlights that enterprises currently face a significant challenge of talent shortage, leading to intensified competition among them. Instead of relying solely on high salaries to attract external talents from the market, it is more practical for organizations to identify, develop, and retain exclusive talents within their existing teams using digital technology and talent inventory [
33]. These efforts should primarily focus on key positions and proprietary talents within the organization. By leveraging big data and artificial intelligence technology, organizations can effectively label and externalize the work behavior of proprietary talents based on network node characteristics, connections, and content. This enables the efficient identification of talented individuals [
34] who exhibit positive emotional responses toward their work while demonstrating higher dedication to the organization. They often find ways to complete tasks faster with lower costs while making contributions beyond their assigned roles. Both ETM—which enhances organizational competitive advantage through employee potential—and ITM should be implemented according to the organization’s development stage [
35]. Hence, this study puts forward the following assumptions:
H3a: ITM plays an intermediary role between digital technology application and organizational performance.
H3b: ETM plays an intermediary role between digital technology application and organizational performance.
2.3. The Regulatory Role of NET
According to the resource-based theory, differences in organizational performance are attributed to variations in resource investment and efficiency levels. The uniqueness and scarcity of exclusive talents play a crucial role in achieving high performance and competitive advantage. Technology application across different organizational levels, as well as the varying contributions of talents, justifies uneven investment [
14]. Albert Hirschman’s unbalanced development theory suggests that investing more resources in proprietary talents promotes inclusive talent development through the diffusion effect. Williamson’s inverted “U” theory further explains how different talent management approaches impact organizational performance. During the early stages of organizational development, growth disparities among talents are necessary for performance improvement. As organizations mature, talent level differences gradually diminish, allowing for inclusive talent management practices. In practice, having employees with high creative potential is the key to improving an organization’s innovation performance, and talent retention is proven to provide the best value to customers [
36], Google’s talent analysis team maximizes retention of proprietary talents through salary policies but does not extend similar material and spiritual incentives to ordinary employees [
37]. The following assumptions are put forward:
H4a: NET has a positive influence on organizational performance.
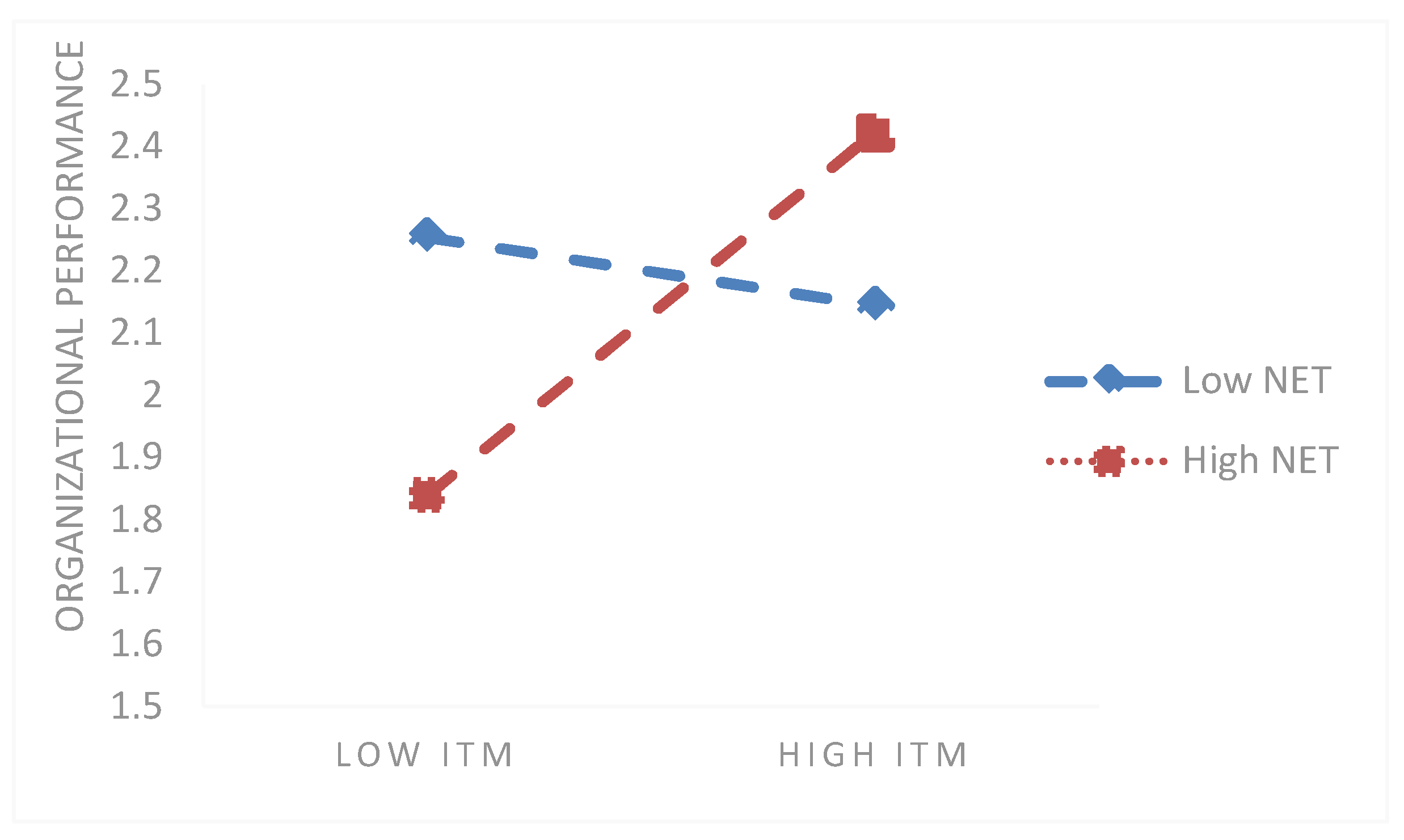
H4b: NET has a positive influence on the relationship between ITM and organizational performance.
In summary, the research model of this study is shown in
Figure 1.