Abstract
Given that risk-taking is an essential channel for companies to obtain high returns and realize value enhancement, the goal of this study is to holistically explore the determinants of corporate risk-taking using various machine learning algorithms. Based on the data from Chinese listed companies between 2010 and 2019, we document that the adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) model makes better predictions of corporate risk-taking. We further visualize the importance and influence of the firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and chief executive officer (CEO) characteristics and discover that in the AdaBoost model, the firm basic characteristics, and performance factors, such as the firm’s fixed asset investments, size, and return on equity, are important in predicting corporate risk-taking, while CEO characteristics are less important. Finally, the role of variables in corporate risk-taking varies among large and small enterprises. Overall, our findings deepen the comprehension of what drives corporate risk-taking and provide a potential way for real-world firms seeking to adjust their risk-taking level.
1. Introduction
Corporate risk-taking—a byproduct of a firm’s profit-seeking business operations—is an essential part of investment decisions [1,2]. The literature has provided some insights into the influence factors of corporate risk-taking from the aspects of corporate governance [3,4], ownership structure [5,6], CEO gender [7,8], and CEO overconfidence [9,10]. However, there is still no consensus on the determinants of corporate risk-taking. This study aims to comprehensively explore the key forces behind corporate risk-taking behavior, guiding enterprises to make better decisions on investment projects with high risk and high return.
Higher risk-taking implies that firms tend to invest in projects with higher risk but positive expected net present values [11], which is beneficial to obtaining higher returns and achieving value enhancement [12]. However, high-risk investment projects often come with great uncertainty, especially in the context of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, which has increased economic instability. Under such complex and changeable circumstances, how firms choose an appropriate risk-taking level based on their business situation is an important question not only for Chinese companies but also for companies in other transitional economies. If enterprises can identify the drivers of risk-taking, it can help them adjust risk-taking, achieving profit acquisition and value creation. Therefore, it is critical to examine the determinants of corporate risk-taking.
Some studies suggest that corporate ownership concentration increases the risk it takes [13]. While Lee et al. [14] found a U-shaped relationship between them. Adams and Funk [15] discovered that there are positive effects of board gender diversity on corporate risk-taking, contrary to the traditional idea that women are more risk-averse [16]. Other studies have examined the influence of firm size [17] and CEO rights [18] on corporate risk-taking. Nevertheless, these studies mostly consider several influencing factors and the conclusions are inconsistent. We cannot determine which factors are the decisive factors of corporate risk-taking based on the findings of previous studies. Moreover, when many factors are considered simultaneously, which factors are most important and whether and how various factors affect corporate risk-taking remain to be further discussed. This paper intends to make up for this research gap.
The goal of this study is to construct a comprehensive corporate risk-taking analytical framework that scrutinizes numerous cross-sectional factors and documents their effect and importance to help firms know the drivers of risk-taking and perform risk management. We mainly discuss the determinants of risk-taking from the perspectives of firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics. On the one hand, corporate risk-taking requires continuous resource input, which means that it is affected by firm basic characteristics and performance factors, such as firm size, fixed asset investment, income, and return on assets. On the other hand, corporate risk-taking behavior is accompanied by high uncertainty. As the essential decision-maker of a company, the CEO’s personal and cognitive characteristics, will affect corporate risky investment decisions. In addition, we employ a more flexible model to explain their linkages. Machine learning (ML), as a practical new tool for creating theories from data, has captured the interest of academics [19]. ML methods can handle high-dimensional data and do not impose a specified structure on the potential relationships between variables and predicted outcomes, revealing complex patterns between them [20,21]. This flexibility allows us to address complex prediction problems and provides a more accurate analysis of corporate risk-taking.
Based on the above discussion, we construct a sample of Chinese listed companies during the period from 2010 to 2019 and use ML methods to attempt to answer the following research questions (RQs):
RQ1.
Which ML method performs better in predicting corporate risk-taking?
RQ2.
Which factors of firm basic characteristics, performance, and CEO characteristics are more important in predicting corporate risk-taking and their effect?
RQ3.
Do the contribution and effect of influence factors differ by firm type?
The findings and contributions of our study are as follows. First, we contribute to the literature on corporate risk-taking. Previous studies have investigated the effect of certain firm or CEO characteristics on corporate risk-taking separately [22,23], making it not intuitive to judge the decisive factors of corporate risk-taking based on previous results. Our research supplements them by incorporating various firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics into a unified analytical framework and identifying the determinants of corporate risk-taking. The results indicate that the most important factors in predicting corporate risk-taking are the firm’s fixed asset investments, size, and return on equity based on the AdaBoost model, which performs best in predicting corporate risk-taking. Second, we add to the current literature by expanding on the application of ML algorithms [20,24]. The inconsistent results regarding corporate risk-taking in the existing literature may be due to their failure to accurately identify the driving factors of risk-taking [13,14]. In recent years, ML methods have proven to be exceptionally good at making predictions using complex and large-scale datasets [25], which can help us effectively predict corporate risk-taking and explore the key forces behind it. In this paper, we find that firm basic characteristics and performance factors are more useful in predicting risk-taking, while CEO characteristics play a lesser role. Finally, our study provides suggestions for China and other transitional economies to adjust corporate risk-taking. It is of great significance for promoting the stability and sustainable development of the real economy. We also provide insight into managers and investors into the fact that firm basic characteristics and performance deserve more attention than CEO characteristics in risk management and investment decisions. For example, to take on more risky investments and improve enterprise value, managers should increase fixed asset investments. Additionally, the different roles of risk-taking determinants in small and large enterprises remind managers to formulate accurate management measures according to firm types.
2. Literature Review
Risk-taking, as an important way to improve corporate performance and future development, has triggered a series of studies that explore its influence factors [8,22,26]. In this paper, we mainly review the existing literature from the perspective of the firm and CEO characteristics.
Regarding firm characteristics, several researchers highlight the impact of firm ownership and find that firms with state ownership have the protection of the government and they are more likely to take on risky investment projects [27]. However, Boubakri et al. [5] used the data of 381 newly privatized companies and found that state ownership was negatively correlated with firm risk-taking as government policies that seek to maximize social stability could lead firms to pursue less risky investment projects. Moreover, based on a sample of American financial institutions between 2002 and 2012, Bhagat et al. [17] found that firm size was positively related to risk-taking before and during the crisis period, but negatively after. Faccio et al. [28] found that small and young companies were more willing to take risks. Shahzad et al. [23] examined the different life cycle stages of risk-taking and found that enterprises in the growth and maturity stages had higher risk-taking levels, while those in the entry and recession stages had lower levels. In addition, higher leverage comes with an increased likelihood of financial distress, reducing the risk-taking capacity of firms and managers [29]. Moreover, firm performance also has important influences on risk-taking. Traditional investment theories believe that high profitability generally corresponds to high risks. While some researches reveal a link between firm profitability and risk-taking that is negative [30,31], firms with low profitability may tend to choose more risky investment projects to improve their financial situation. Do et al. [32] argued that companies with poor interim performance took more risks than companies with better interim performance.
More recently, a growing body of work has identified the CEO’s role in corporate risk-taking as the key decision-maker for the company whose personality characteristics and cognitive patterns will shape the firm’s strategic decisions. Some studies look at the influence of CEOs’ age on risk-taking and come to conflicting conclusions. On the one hand, scholars discover that older CEOs have more management experience and accumulated rich social network resources in their careers, which can help CEOs to obtain important resources and market information, enhancing corporate risk-taking [33,34]. Nevertheless, there are also studies showing that individuals’ risk aversion rises with age; compared to young CEOs, senior CEOs seem to be more risk-averse and likely to make less risky investment decisions [35,36]. Regarding CEOs’ gender, scholars generally assume that female CEOs would be more risk-averse than male CEOs [16]. However, it has been shown that women are not always risk-averse [37,38]. For instance, Safiullah et al. [39] discovered that Spanish companies with more female directors had higher risk-taking after the implementation of the “Gender Equality Act”. Ingersoll et al. [22] used a sample of S&P 500 companies from 2009 to 2019 and found that companies with more female executives take more financial risks than those with male executives. In addition, the level of corporate risk-taking is also related to the personality characteristics of CEOs. Narcissistic CEOs with a proclivity for hubris are more willing to take risks [40]. Moreover, CEOs’ power [41], reputation [26], educational experience [7,35], professional experience [42], and social network [43,44] have also been found to affect corporate risk-taking.
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data
We gathered a sample of Chinese listed firms from 2010 to 2019 to investigate the impact of firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics on risk-taking. We obtained all of our data from the China Stock Market and Accounting Research (CSMAR) database. The following observations were removed: (1) Financial companies, as the financial industry does not belong to the real economy and the structure of its financial statements differs from that of non-financial companies; (2) Designated as special treatment (i.e., ST and *ST) firms; (3) Missing data for the main variables. Finally, our sample, which consists of 15,774 firm-year observations for 2329 companies, was finally obtained. To ensure that extreme values do not influence our results, we winsorized all continuous variables at the 1% and 99% levels.
3.2. Variable Definitions
Risk-taking. Following the study of Jiang and Chen [45], we define corporate risk-taking (Risk_taking) as the three-year standard deviation of adjusted return on assets (AdjROA), which is the percentage of earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) to total assets (Asset) adjusted for the firm’s industry and yearly averages. For example, the rolling standard deviation of AdjROA from t to t + 2 is used to measure the value of Risk-taking at time t. The calculations are as follows:
where i, j, and t denote the firm, industry, and year, respectively. N stands for the number of firms in industry j in year t. In Formula (2), T denotes the window period used in this paper, where T = 3, meaning that we use the three-year window and rolling standard deviation of AdjROA to measure Risk_taking.
We construct a series of variables based on prior studies [5,8,16,39,45], which influence corporate risk-taking from three aspects: firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics. The detailed definitions of the variables used in this study are shown in Appendix A.
Firm basic characteristics. In this paper, firm basic characteristics refer to the fundamental information variables of a firm, including firm age (Firm_age), initial public offering age (IPO_age), size (Size), ownership (SOE), fixed asset investments (Fixed_assets), sales growth (Sale_growth), debt-to-equity ratio (DER), and leverage (Leverage). Specifically, Firm_age refers to the years between the founding date and the observations [16], while IPO_age refers to the years after a firm’s IPO date [46]. Size is calculated by the natural logarithm of total assets [39]. The value of the dummy variable SOE is 1 if the government is the actual controller of the company, and 0 if otherwise [45]. Fixed_assets is the proportion of fixed assets to total assets [47]. Sale_growth refers to the annual growth of sales from time t − 1 to t [45]. The definitions of DER and Leverage are the percentage of total debt to total equity and total debt to total assets, respectively [30,46].
Firm performance. To measure firm performance, we include firm return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), net profit margin (Net_margin), Tobin’s Q value (Tobinq), market-to-book ratio (MTB), and sales (Sales). Specifically, ROA and ROE are the proportions of net income to total assets and total equity, respectively [16,25], Net_margin is measured as net profit divided by total revenue [25], Tobinq is determined by the ratio of the market value to book value of total assets [32], MTB is a firm’s equity market value to its book value [23], and Sales is the natural logarithm of total sales [46].
CEO characteristics. We consider 15 CEO characteristics that may influence corporate risk-taking, which are CEO gender (CEO_gender), age (CEO_age), duality (CEO_duality), education (CEO_education), tenure (CEO_tenure), board experience (CEO_boardexperience), role as an outside directorate (CEO_outsidedirectorates), production experience (CEO_production), R&D experience (CEO_RD), design experience (CEO_design), human resource experience (CEO_HRM), administration experience (CEO_administration), finance experience (CEO_finance), accounting experience (CEO_accounting), and legal experience (CEO_legal). Specifically, CEO_gender is a dummy variable that has a value of 1 for female CEOs and 0 for male CEOs [16]; CEO_age is measured by the age of the CEO [16]. CEO_duality is assessed by a binary variable that is 1 if the CEO simultaneously works as the chairman and 0 is otherwise [48]. CEO_education is defined by whether the CEO has a postgraduate degree. If the CEO has a postgraduate degree, the value is 1; otherwise, it is 0 [35]. The natural logarithm of the CEO’s tenure is used to define CEO_tenure [48]. A dummy variable named CEO_boardexperience equals 1 if the CEO also serves as a director and 0 if otherwise [35]. The variable CEO_outsidedirectorates is the total number of outside directorates a CEO holds or has held on other firms’ boards [49]. Moreover, we have defined a series of dummy variables based on the CEOs’ professional experience: CEO_production, CEO_RD, CEO_design, CEO_HRM, CEO_administration, CEO_finance, CEO_accounting, and CEO_legal. For example, CEO_finance takes the value of 1 if the CEO has a career experience in finance and 0 if otherwise [35]. Finally, the descriptive statistics of variables used in this study are shown in Appendix B.
3.3. Methodology
We use ML methods to predict corporate risk-taking. Given that there is no agreement regarding the best performing algorithm for predicting risk-taking, 11 ML methods are employed in this study. In terms of linear models, we include linear regression (LinearRegression), ridge regression (Ridge), the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso), elastic net (ElasticNet), and Bayesian ridge regression (BayesianRidge). Moreover, we consider ensemble models, all of which are important ML algorithms, including extremely randomized trees (ExtraTree), random forest (RandomForest), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), adaptive boosting (AdaBoost), gradient boosted regression trees (GradientBoost), and light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM).
We randomly divide our data into two subsets (i.e., training and test datasets) following an 80%/20% split, which is a commonly used split criterion in previous studies [20]. The training dataset is used to optimize the hyperparameters of each prediction model and identify the optimum combinations of variables to predict risk-taking. The test dataset is used to compare the performance of each prediction to the observed out-of-sample data.
3.4. Model Predictive Performance
We assess each model’s predictive performance of corporate risk-taking by its out-of-sample predictive R2. The out-of-sample predictive R2 is calculated as follows:
where is the out-of-sample predictive R2, Τ represents a series of predictor variables, is firm i’s real risk-taking in period t, and is firm i’s predicted risk-taking using a specific model on the test datasets.
3.5. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) Method
To determine how the variables affect corporate risk-taking, whether positively, negatively, or via other more complex correlations. We use the SHAP method, which uses SHAP values to assess the contribution and influence of each variable to corporate risk-taking, thus improving the ML model’s interpretability [20,50]. According to Lundberg and Lee [50], SHAP values are calculated as follows:
where i is an input feature, N is the set of all input features excluding i, and M is their total number. S is a subset of N, whose number of input features is |S|. is the predicted value using the set of feature S on data instance x. represents the predicted value using the set of feature S plus feature i.
4. Results
4.1. Model Predictive Performance Comparison
We start by examining the prediction performance of ML models in the total sample, then divide the total sample into large and small enterprises subsamples, with the top 30% in the firm size category being considered as large enterprises and all others as small enterprises [24], to further verify the prediction performance. Table 1 are the results of the model’s predictive performance.

Table 1.
Out-of-sample predictive R2 in percentage.
Total sample. As demonstrated in Table 1, in the linear models, we can find that the LinearRegression model, which is the simplest model, has an out-of-sample predictive R2 of 6.58%, indicating that even the basic model has some degree of predictive validity. The out-of-sample predictive R2 for Ridge, Lasso, ElasticNet, and BayesianRidge do not change substantially when compared to the LinearRegression model. In addition, the prediction performances of the ensemble models are generally better than the linear models. For example, the out-of-sample predictive R2 of the AdaBoost model is 13.77%, which outperforms all the linear models we used. We have also discovered that the RandomForest model performs well in predicting risk-taking.
Small and large enterprises. Next, we focus on the model predictive performance for small enterprises (i.e., the bottom 30% of firms by total assets) and large enterprises (i.e., the top 70% of firms by total assets). Table 1 demonstrates that in the small enterprise subsample, the AdaBoost model has the best predictive performance with an out-of-sample predictive R2 of 17.70%. While in the large enterprise subsample, LightGBM is the better predictive model and the AdaBoost model also has a good performance.
Although we have used out-of-sample R2 to select predictive models of corporate risk-taking, some problems remain as some models have very close out-of-sample R2, and the predictive models show inconsistent performance across subsamples. Specifically, in the total sample, the RandomForest model has the best predictive performance. In the small enterprise subsample, the best predictive model is the AdaBoost model, while it is the LightGBM model in the large enterprise subsample. Thus, we cannot identify the optimal predictive model of corporate risk-taking. To address this problem, we use the conditional superiority predictive ability (CSPA) test proposed by Li et al. [51] for alternative model selection.
The CSPA test assumes that the conditional expected loss in the baseline model is not greater than that of the competing model, and thus, compares the predictive performance of the two models. The results are shown in Table 2. The CSPA test results show that the AdaBoost model is the best predictive model as it has the lowest rejection frequency when conditioned on industry average risk-taking. The RandomForest and LightGBM models perform well, but when compared to the AdaBoost model, all of them are rejected; thus, we believe that that the AdaBoost model outperforms them in predicting corporate risk-taking.

Table 2.
Unconditional superior predicative ability for risk-taking.
The AdaBoost algorithm is one of the most popular and extensively researched algorithms developed by Freund and Schapire [52]. It is the first practical boosting algorithm, and its main idea is that if samples are correctly classified, the weight assigned to them in the next round will be lowered. On the contrary, samples that are misclassified will obtain higher weights [21]. In addition, the AdaBoost model does not need to filter features and can avoid overfitting problems. It also has high prediction accuracy and performs optimal learning (theoretically) even in noisy environments [53].
4.2. Which Variables Matter?
After determining that the AdaBoost model has the best prediction performance, we next explore the importance of variables that cover firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics in the total sample. To gauge the importance of each variable and compare it with other variables, we use the total average reduction in predictive R2 when the value of a certain variable is set to zero within every training dataset [24]. Observing Table 3, we notice that using firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics at the same time can have a better out-of-sample R2. This demonstrates that adding these variables to the corporate risk-taking prediction model helps improve its predictive performance.

Table 3.
Out-of-sample predictive R2 in percentage.
Firm basic characteristics. Table 4 reports the importance of variables. We find that in the AdaBoost model, the most important variable is Fixed_assets. Firm fixed asset investments reflect the abundance of a firm’s internal resources and the potential for development. Additionally, firms with higher levels of fixed assets have more ability to obtain financing to support the firm’s risker activities. Moreover, Size, Sales_growth, and Firm_age are also important in predicting corporate risk-taking, while IPO_age, Leverage, DER, and SOE are less important. The results of the variables’ importance in other ML methods are shown in Appendix C.

Table 4.
Relative importance of variables in the AdaBoost model.
In addition, we use box plots for robustness tests. Figure 1 shows the box plots that aggregate the importance of each firm basic characteristic variable across all ML models. Box plots are not affected by outliers and provide an accurate and stable depiction of the discrete distribution of data. We also discover that Fixed_assets is the most influential firm basic characteristic variable for predicting corporate risk-taking.
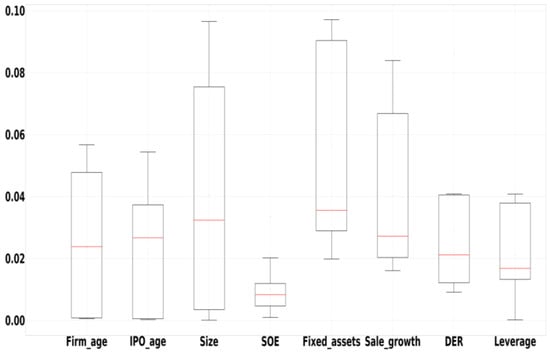
Figure 1.
Variable importance for firm basic characteristics. Notes: this figure displays a box plot of the importance of each firm basic characteristic variable, including Firm_age, IPO_age, Size, SOE, Fixed_assets, Sale_growth, DER, and Leverage, aggregated across all machine learning models.
Firm performance. We consider firm performance variables—ROA, ROE, Net_margin, Tobinq, MTB, and Sales—that may affect corporate risk-taking. Table 4 shows the importance of our firm performance variables in the total sample. In the AdaBoost model, the most important firm performance variable is Net_margin, which reflects a firm’s profitability. We also find that ROA and ROE are also important predictor variables and their importance is less different from that of Net_margin.
Figure 2
demonstrates box plots that aggregate the importance of each firm performance
variable across all models. The results show that ROA, ROE, and Net_margin
are the top three most influential firm performance variables. Although this
result is slightly different from that in the AdaBoost model, it still
demonstrates the importance of Net_margin for predicting corporate
risk-taking.
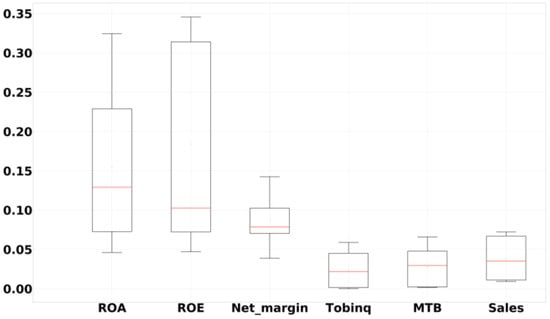
Figure 2.
Variable importance for firm performance. Notes: this figure displays a box plot of the importance of each firm performance variable, including ROA, ROE, Net_margin, Tobinq, MTB, and Sales, aggregated across all machine learning models.
CEO characteristics. Table 4 displays the importance of the CEO’s personal characteristics, educational experience, and professional experience variables on corporate risk-taking based on out-of-sample predictive R2. In the AdaBoost model, we find that not all CEO characteristics are equally important in predicting corporate risk-taking. The most important variable is CEO_age, followed by CEO_tenure and CEO_outsidedirectorates, while CEO_accounting, CEO_boardexperience, and CEO_legal have less influence.
Figure 3 demonstrates the aggregate importance of each CEO characteristics variable in all models and displays that CEO_age is also an important variable in predicting corporate risk-taking.
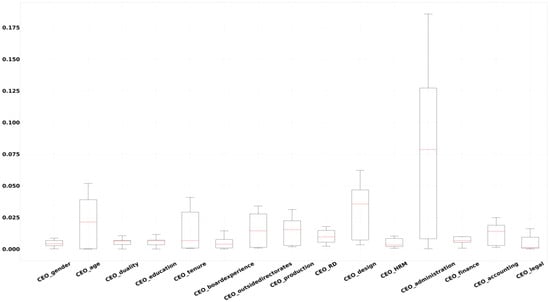
Figure 3.
Variable importance for CEO characteristics. Notes: this figure displays a box plot of the importance of each CEO characteristics variable aggregated across all machine learning models.
4.3. The Variable Effects on Corporate Risk-taking
We use the SHAP approach to visualize the overall contribution and effects (positive or negative) of the firm basic characteristics, performance, and CEO characteristics on corporate risk-taking using the AdaBoost model in the total sample and subsamples (i.e., small and large enterprises). Table 5 summarizes the top ten variables, which enables us to pinpoint the motivating factors behind corporate risk-taking in the total sample and subsamples (small and large enterprises) by computing the variable’s SHAP value. The detailed overall importance and effect of all variables on risk-raking are shown in Figure 4. The horizontal axis represents the SHAP value of variables. The larger the SHAP value, the more important this variable is for predicting corporate risk-taking. The vertical axis represents each variable, and they are ordered from highest to lowest based on their importance.

Table 5.
Top ten important variables of corporate risk-taking.
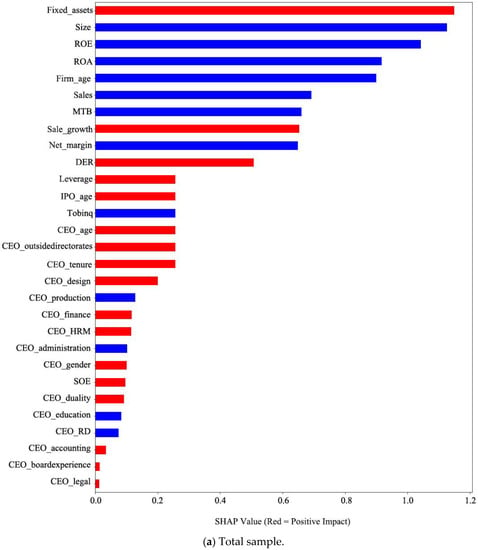
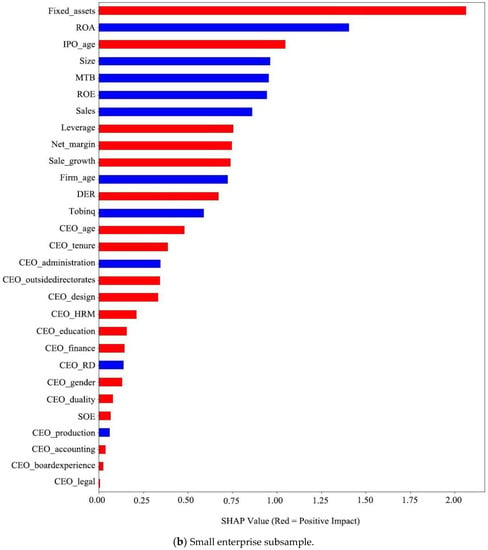
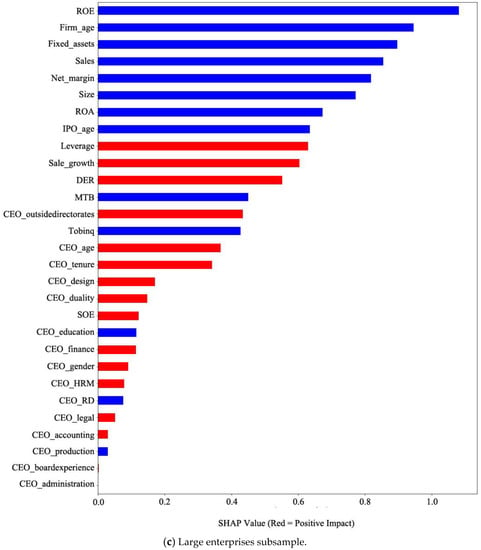
Figure 4.
Summary of SHAP values of variables. Notes: this figure presents the SHAP values of variables using the AdaBoost model. Predictors are ranked from highest to lowest according to their importance. Variables in red (blue) indicate that they have a positive (negative) effect on corporate risk-taking.
4.3.1. Total Sample
In Table 5, we find that in the total sample, Fixed_assets, Size, ROE, ROA, and Firm_age are the top five most important variables in predicting corporate risk-taking, while CEO_education, CEO_RD, CEO_accounting, CEO_boardexperience, and CEO_legal have less importance. By investigating the categories these variables belong to, we can find that although CEOs are the key decision-makers of firms whose characteristics, risk preferences, and cognitive patterns can influence a firm’s investment decisions and behavior of taking risks [8,39], the importance of CEO characteristics in predicting corporate risk-taking is less than the firm basic characteristics and performance, meaning that the firm characteristics are the main drivers behind corporate risk-taking behavior. Next, we specifically analyze the effect of variables in each category.
Figure 4 also reflects how each variable affects corporate risk-taking. Variables in red (blue) indicate that they have a positive (negative) effect on corporate risk-taking. In the firm basic characteristics, Fixed_assets is the most important variable; its red color means that Fixed_assets is positive with corporate risk-taking. Firms need fixed asset investments to support their performance and investment decision, which has an important positive impact on corporate risk-taking. The color of the “Size” bar is blue, indicating that Size has a negative effect on corporate risk-taking; these results coincide with earlier studies that demonstrate that large enterprises are less risk-taking, while smaller enterprises are more aggressive and tend to make riskier investments [30,47]. Firm_age is negatively associated with corporate risk-taking; that is, younger firms are more risk-seeking, which is similar to the findings of Faccio et al. [28]. Contrarily, IPO_age is positive; the reason may be that IPOs can provide companies with funds to undertake new project [54]. Other firm basic characteristics variables used in this paper all have positive effects on corporate risk-taking. In particular, firms with state ownership tend to take risks more, which is consistent with the results of the studies of Dong et al. [27] and Zhu and Yang [6], providing an explanation for the conflicting findings in the literature. However, it should be noted that SOE is not important in predicting corporate risk-taking.
In the firm performance category, the color of all the bars is blue, including Net_margin, ROA, ROE, Sales, MTB, and Tobinq, which means that these variables all have negative effects on corporate risk-taking. These results imply that the better the firm performance, the lower the risk-taking, agreeing with the results of Khaw et al. [30] and Do et al. [32].
With regard to the CEO characteristics, almost all variables have positive effects on corporate risk-taking except CEO_administration, CEO_education, CEO_RD, and CEO_production, which have negative effects. For example, the impact of CEO_age on corporate risk-taking is positive; that is, older CEOs tend to have more experience and capabilities, which can help them to obtain resources and market information, enhancing corporate risk-taking [33], while younger CEOs may prefer conservative investment strategies to avoid losses caused by decision-making mistakes [31]. In terms of CEO_outsidedirectorates, if a CEO also serves as the outside directorate in other firms, the increased CEO power and social networks encourage an optimistic risk attitude in them and greater discretion on corporate investment decisions, improving the firm’s risk behavior [41,43]. For CEO_tenure, Wang and Poutziouris [55] explored the link between the tenure of CEOs and corporate risk-taking. They believe that with the increase in tenure, managers become more familiar with the situation of the industry and increase their risk behavior. CEO_gender, a CEO characteristics variable that has been paid more attention to in previous studies, has a positive impact on corporate risk-taking, thus supporting that female CEOs are not always risk-averse [22,39].
4.3.2. Large and Small Enterprises
In the large enterprise subsample, ROE, Firm_age, Fixed_assets, Sales, and Net_margin are important predictive variables, while Fixed_assets, ROA, IPO_age, Size, and MTB are important predictive variables in the small enterprise subsample. Moreover, Table 5 demonstrates that Fixed_assets is an important variable for both small and large enterprises. Firm_age is a critical variable in large enterprises, while less important in small enterprises. Additionally, MTB is vital in predicting risk-taking for small enterprises but less so for large enterprises. In addition, the predictive performance of CEO characteristics on risk-taking is relatively weak among large and small enterprises weak compared to other variables.
Then, we compare the differences in the variable’s impact on risk-taking for large and small enterprises. Fixed_assets and IPO_age have positive effects on small enterprises, while they have negative effects on large enterprises. In other words, increasing the firm’s fixed asset investments and promoting listing firms as soon as possible are helpful in enhancing the level of risk-taking, but these mainly affect small enterprises. If the same measures are taken for large enterprises, their risk-taking level will be reduced. Furthermore, Net_margin has a negative effect on risk-taking for large enterprises and a positive influence on small enterprises. One possible reason for this result is that smaller and lower net profit firms are more likely to enhance firm performance through high risk-taking.
4.3.3. Robustness Tests
To guarantee the correctness of our findings, we used the bootstrap method, which randomly selects several samples from the total dataset and forms a new training dataset, to further test the overall importance and effect of variables on corporate risk-taking. The results are shown in Table 6. In the total sample, we can find that Fixed_assets, Size, and ROE are also important variables in predicting corporate risk-taking. Additionally, the importance of CEO characteristics in predicting corporate risk-taking is less than the firm basic characteristics and performance. From the effects of variables, in the total sample, we can also discover that Fixed_assets have a positive effect and Size and ROE have a negative effect on corporate risk-taking. In small and large enterprises, Fixed_assets is also a vital predictive variable, and has positive effects on the risk-taking of small enterprises, while it has a negative effect on large enterprises. Overall, our main results are robust.

Table 6.
The SHAP values of the top ten important variables of corporate risk-taking.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This study uses ML methods to explore the determinants of corporate risk-taking from firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics using Chinese listed companies during the period from 2010 to 2019. Our results show that, first, the AdaBoost model performs better at predicting corporate risk-taking than the other ML algorithms, and considering firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics at the same time is helpful in improve ML models’ predictive performance. Second, using the SHAP method, we have found that in the total sample, the most important predictors for risk-taking are the firm’s fixed asset investments, size, and ROE, implying these variables have better predictive power for corporate risk-taking. From the perspective of the impact of these variables on corporate risk-taking, we have discovered that the firm’s fixed asset investments positively affect corporate risk-taking, while the firm’s size and ROE have a negative effect. Moreover, CEO characteristics, such as CEO accounting experience, board experience, and legal experience, play a lesser role in predicting firm risk-taking. Finally, the variables’ contribution and effect on corporate risk-taking are heterogeneous in large and small firms based on their SHAP values. The firm’s fixed asset investments are important in predicting risk-taking for both small and large enterprises. However, the firm’s age is only important for large enterprises’ risk-taking, while the firm’s market-to-book ratio is only vital for small enterprises’ risk-taking. For the variable’s impact, our results demonstrate that the firm’s fixed asset investments, net profit, and IPO age have positive effects on risk-taking for small enterprises, but negative on large enterprises. This study provides significant theoretical and practical implications for understanding corporate risk-taking.
5.1. Theoretical Implications
Our research contributes to the growing literature on corporate risk-taking [8,22,23,29]. The conclusions of the literature are inconsistent. Specifically, corporate risk-taking is affected by many factors, but it remains unknown how important each factor is, and whether and how various factors affect corporate risk-taking when many factors are considered simultaneously. This study contributes to filling this gap by exploring the drivers behind corporate risk-taking from the perspectives of firm basic characteristics, performance, and CEO characteristics, and analyzing their complex relationship with corporate risk-taking. Specifically, we find that CEO characteristics are relatively less important for predicting corporate risk-taking when compared to firm basic characteristics and performance, which provide novel insights into the determinants of corporate risk-taking.
Second, this paper complements the literature on applying ML methods to risk prediction [24,25]. ML algorithms, as a new technique, perform well in classification and prediction, especially with big data. Using ML methods to predict corporate risk-taking and the SHAP approach to interpret the ML model, our research analyzes the contribution and impact of various predictors on corporate risk-taking, providing essential and novel insights into the drivers of corporate risk-taking. Overall, the findings show that the firm’s fixed asset investments, size, and ROE have better predictive power for corporate risk-taking, whereas CEO accounting experience, board experience, and legal experience play lesser roles.
Finally, this paper further explores the differences in the importance and influence of various factors on corporate risk-taking among large and small enterprises, improving the analysis of risk-taking from the perspective of firm size. We find that firm size negatively affects risk-taking, supporting the view that large enterprises are less risk-taking, while smaller enterprises are more aggressive and tend to make riskier investments [30,47]. Moreover, the determinants of corporate risk-taking vary by firm size. Firm fixed asset investments are important in predicting risk-taking for both small and large enterprises. However, firm age is only critical for the risk-taking of large enterprises, whereas firm market-to-book ratio is only critical for small enterprises.
5.2. Practical Implications
This research has significant practical implications in helping China and other transitional economies increase their corporate risk-taking and promoting stability and the sustainable development of the real economy. As scholars have emphasized, taking risks can promote a firm’s capital accumulation and improve its market competitiveness [11,12]. However, high-risk investment projects come with a great level of uncertainty; the failure of investment could cause heavy losses for firms or even bankruptcy [56]. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the driving factors of corporate risk-taking and help companies, especially those in transitional economies, choose a reasonable risk-taking level in complex and changeable environments. This study emphasizes that firm basic characteristics and profitability are critical in predicting risk-taking, while CEO characteristics have less of an impact. These findings can help managers realize that they should pay more attention to the effect of firm characteristics, such as the firm’s fixed asset investment, size, and ROE on risk-taking, rather than the effects of CEO characteristics.
Moreover, our findings can provide valuable information for risk management in different companies. We find that there are differences in the contributions and effects of various factors on corporate risk-taking for large and small enterprises. Managers should choose the appropriate level of risk-taking according to their scale. For example, we emphasize that increasing firm fixed asset investments, net profit, and promoting firms to go public can help improve the risk-taking ability of small enterprises, but negatively impact large enterprises.
5.3. Limitations and Recommendations
Although this study reveals important findings, it has several limitations. The sample used in this paper is China’s listed firms; the results are applicable in that region and may not be generalized. Future research can consider including diverse data from other economies to solve this problem. Furthermore, corporate risk-taking may be industry-specific. We have analyzed the overall risk-taking of Chinese listed firms and do not distinguish the heterogeneity of risk-taking in different industries. Future research can consider using ML methods to predict corporate risk-taking in specific industries. Finally, there may be additional omitted variables that are associated with both the predictors and outcome variables. Future research can consider more factors in the framework of corporate risk-taking based on this paper.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and F.L.; methodology, C.L., Y.C., S.H. and F.L.; software, Y.C.; formal analysis, Y.C. and F.L.; resources, F.L.; data curation, C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L., S.H. and F.L.; writing—review and editing, C.L., X.C. and F.L.; supervision, X.C. and F.L.; project administration, F.L.; funding acquisition, F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Humanities and Social Sciences Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (Grant No.21YJC630076).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge insightful suggestions from the Editors and the anonymous reviewers, which substantively improved this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Variable definition.
Table A1.
Variable definition.
| Variable | Definition |
|---|---|
| Risk_taking | The three-year standard deviation of adjusted return on assets (AdjROA), which is the ratio of earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) to total assets (Asset) adjusted for the firm’s industry and yearly averages. |
| Firm basic characteristics | |
| Firm_age | The number of years between founding and the year of observation. |
| IPO_age | The number of years since the IPO date. |
| Size | The natural logarithm of total assets. |
| SOE | Takes the value of 1 if the firm’s actual controller belongs to government and 0 if otherwise. |
| Fixed_assets | Fixed assets are divided by total assets. |
| Sale_growth | The annual growth of sales from t−1 to t. |
| DER | The ratio of total debt to total equity. |
| Leverage | The percentage of total debt to total assets. |
| Firm performance | |
| ROA | Net income/Total assets. |
| ROE | Net income/Total equity. |
| Net_margin | Net profit/Total revenue. |
| Tobinq | The percentage of the market value to the book value of total assets. |
| MTB | The ratio of the market value to the book value of equity. |
| Sales | The natural logarithm of total sales. |
| CEO characteristics | |
| CEO_gender | 1 for female CEOs and 0 for male CEOs. |
| CEO_age | Age of the CEO. |
| CEO_duality | 1 if the CEO also serves as chairman and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_education | If the CEO holds a postgraduate degree, CEO_education = 1, and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_tenure | The natural logarithm of CEO tenure. |
| CEO_boardexperience | It is 1 if the CEO is also a director and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_outsidedirectorates | The total number of outside directorates a CEO holds or has held on other firm boards. |
| CEO_production | 1 if the CEO has production career experience and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_RD | 1 if the CEO has R&D career experience and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_design | 1 if the CEO has design career experience and 0 if otherwise |
| CEO_HRM | CEO_HRM = 1 for CEOs who have career experience in the human resource management area and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_administration | CEO_administration = 1 for CEOs who have administration career experience and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_finance | 1 if the CEO has finance career experience and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_accounting | CEO_accounting = 1 if the CEO has accounting career experience and 0 if otherwise. |
| CEO_legal | 1 if the CEO has career experience in the legal area and 0 if otherwise. |
Appendix B

Table A2.
Descriptive statistics.
Table A2.
Descriptive statistics.
| Variable | Number | Mean | S.D. | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk_taking | 15,774 | 4.8582 | 10.0107 | 2.1180 |
| Firm_age | 15,774 | 17.3617 | 5.5258 | 17 |
| IPO_age | 15,774 | 8.9710 | 6.8454 | 7 |
| Size | 15,774 | 12.7666 | 1.2053 | 12.6045 |
| SOE | 15,774 | 0.0884 | 0.2839 | 0 |
| Fixed_assets | 15,774 | 0.2089 | 0.1552 | 0.1775 |
| Sale_growth | 15,774 | 0.1988 | 0.4106 | 0.1262 |
| DER | 15,774 | 1.0105 | 1.1126 | 0.6493 |
| Leverage | 15,774 | 0.4036 | 0.2082 | 0.3937 |
| ROA | 15,774 | 0.0403 | 0.0568 | 0.0395 |
| ROE | 15,774 | 0.0609 | 0.1196 | 0.0684 |
| Net_margin | 15,774 | 0.0803 | 0.1494 | 0.0759 |
| Tobinq | 15,774 | 2.0838 | 1.2827 | 1.6595 |
| MTB | 15,774 | 3.7561 | 3.0469 | 2.8444 |
| Sales | 15,774 | 12.0757 | 1.3690 | 11.9620 |
| CEO_gender | 15,774 | 0.0688 | 0.2532 | 0 |
| CEO_age | 15,774 | 49.3281 | 6.4256 | 49 |
| CEO_duality | 15,774 | 0.2973 | 0.4571 | 0 |
| CEO_education | 15,774 | 0.4562 | 0.4981 | 0 |
| CEO_tenure | 15,774 | 3.7679 | 3.3586 | 3 |
| CEO_boardexperience | 15,774 | 1.0153 | 0.1745 | 1 |
| CEO_outsidedirectorates | 15,774 | 1.9769 | 3.3095 | 1 |
| CEO_production | 15,774 | 0.1310 | 0.3374 | 0 |
| CEO_RD | 15,774 | 0.2704 | 0.4442 | 0 |
| CEO_design | 15,774 | 0.0330 | 0.1787 | 0 |
| CEO_HRM | 15,774 | 0.0209 | 0.1429 | 0 |
| CEO_administration | 15,774 | 0.9970 | 0.0551 | 1 |
| CEO_finance | 15,774 | 0.1144 | 0.3183 | 0 |
| CEO_accounting | 15,774 | 0.0959 | 0.2945 | 0 |
| CEO_legal | 15,774 | 0.0079 | 0.0887 | 0 |
Notes: This table shows the descriptive statistics of variables.
Appendix C

Table A3.
Relative importance of variables based on predictive R2.
Table A3.
Relative importance of variables based on predictive R2.
| Panel A: Relative importance of firm basic characteristics variables. | ||||||||||
| Variables | Linear Regression | Ridge | Lasso | Elastic Net | Bayesian Ridge | Extra Tree | Random Forest | XGBoost | Gradient Boost | LightGBM |
| Firm_age | 0.073 | 0.063 | 0.050 | 0.079 | 0.133 | 5.184 | 5.221 | 2.373 | 2.650 | 4.350 |
| IPO_age | 0.058 | 0.032 | 0.018 | 0.033 | 0.102 | 3.737 | 3.708 | 2.659 | 3.451 | 5.433 |
| Size | 0.482 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.230 | 0.452 | 7.186 | 7.253 | 3.227 | 9.641 | 7.815 |
| SOE | 1.090 | 0.958 | 0.821 | 1.279 | 2.009 | 0.476 | 0.447 | 3.344 | 0.088 | 0.177 |
| Fixed_assets | 1.975 | 2.677 | 2.523 | 3.491 | 3.087 | 9.005 | 9.051 | 3.542 | 8.073 | 9.705 |
| Sale_growth | 1.596 | 1.793 | 1.776 | 2.248 | 2.708 | 7.164 | 7.140 | 2.891 | 2.375 | 8.386 |
| DER | 0.899 | 1.034 | 1.064 | 1.351 | 1.865 | 4.078 | 4.020 | 3.107 | 2.108 | 8.602 |
| Leverage | 0.010 | 1.722 | 1.671 | 1.506 | 3.562 | 3.995 | 4.017 | 1.150 | 1.484 | 0.020 |
| Panel B: Relative importance of firm performance variables. | ||||||||||
| Variables | Linear Regression | Ridge | Lasso | Elastic Net | Bayesian Ridge | Extra Tree | Random Forest | XGBoost | Gradient Boost | LightGBM |
| ROA | 32.362 | 22.170 | 23.623 | 7.987 | 4.603 | 13.111 | 12.901 | 7.360 | 32.451 | 7.028 |
| ROE | 28.472 | 31.525 | 32.897 | 34.568 | 31.252 | 7.457 | 7.590 | 4.704 | 10.265 | 6.535 |
| Net_margin | 10.534 | 9.984 | 9.518 | 11.284 | 14.244 | 6.963 | 7.117 | 3.864 | 7.856 | 6.791 |
| Tobinq | 0.202 | 0.088 | 0.000 | 0.066 | 0.401 | 4.542 | 4.476 | 2.618 | 2.165 | 5.532 |
| MTB | 0.205 | 0.188 | 0.150 | 0.264 | 0.457 | 4.801 | 4.777 | 2.956 | 3.601 | 6.240 |
| Sales | 1.202 | 0.978 | 0.926 | 1.009 | 1.700 | 6.684 | 6.691 | 3.501 | 5.100 | 7.224 |
| Panel C: Relative importance of CEO characteristics variables. | ||||||||||
| Variables | Linear Regression | Ridge | Lasso | Elastic Net | Bayesian Ridge | Extra Tree | Random Forest | XGBoost | Gradient Boost | LightGBM |
| CEO_gender | 0.860 | 0.330 | 0.209 | 0.427 | 1.498 | 0.488 | 0.502 | 3.415 | 0.019 | 0.079 |
| CEO_age | 0.023 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.042 | 3.905 | 3.896 | 2.761 | 2.129 | 5.177 |
| CEO_duality | 0.380 | 0.334 | 0.218 | 0.383 | 0.651 | 0.665 | 0.657 | 2.822 | 0.000 | 1.043 |
| CEO_education | 0.361 | 0.310 | 0.251 | 0.402 | 0.672 | 0.659 | 0.654 | 2.036 | 0.000 | 1.142 |
| CEO_tenure | 0.076 | 0.062 | 0.052 | 0.085 | 0.142 | 2.898 | 2.927 | 1.860 | 0.660 | 4.075 |
| CEO_boardexperience | 0.781 | 0.580 | 0.380 | 0.722 | 1.446 | 0.119 | 0.109 | 1.309 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CEO_outsidedirectorates | 0.080 | 0.120 | 0.107 | 0.151 | 0.150 | 2.766 | 2.788 | 3.395 | 1.443 | 2.972 |
| CEO_production | 1.760 | 2.268 | 2.215 | 2.948 | 3.126 | 0.202 | 0.208 | 1.520 | 0.461 | 0.177 |
| CEO_RD | 0.959 | 1.287 | 1.237 | 1.640 | 1.682 | 0.511 | 0.499 | 1.775 | 0.214 | 0.551 |
| CEO_design | 3.556 | 4.276 | 4.178 | 5.538 | 6.220 | 0.641 | 0.644 | 5.058 | 0.831 | 0.335 |
| CEO_HRM | 0.162 | 0.266 | 0.052 | 0.307 | 0.230 | 1.025 | 0.980 | 8.073 | 0.498 | 0.079 |
| CEO_administration | 7.851 | 14.198 | 13.823 | 18.569 | 10.651 | 0.754 | 0.754 | 11.615 | 2.151 | 0.020 |
| CEO_finance | 0.979 | 0.743 | 0.656 | 0.970 | 1.722 | 0.530 | 0.525 | 2.701 | 0.075 | 0.335 |
| CEO_accounting | 1.404 | 1.715 | 1.581 | 2.181 | 2.493 | 0.315 | 0.310 | 2.033 | 0.135 | 0.177 |
| CEO_legal | 1.607 | 0.268 | 0.000 | 0.268 | 2.703 | 0.140 | 0.138 | 2.332 | 0.076 | 0.000 |
Notes: This table reports the R2-based variable importance of firm basic characteristics, firm performance, and CEO characteristics variables in other ML models used in our study except for the AdaBoost model. For a given model, the sum of the feature importance of all predictors is normalized to 1. All values are in percentages.
References
- Cucculelli, M.; Ermini, B. New product introduction and product tenure: What effects on firm growth? Res. Policy 2012, 41, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, A. Managerial risk-taking behavior and equity-based compensation. J. Financ. Econ. 2009, 92, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraporn, P.; Chatjuthamard, P.; Tong, S.; Kim, Y.S. Does corporate governance influence corporate risk-taking? Evidence from the Institutional Shareholders Services (ISS). Financ. Res. Lett. 2015, 13, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, O.; Williams, R. Tournament incentives, firm risk, and corporate policies. J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 103, 350–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, N.; Cosset, J.C.; Saffar, W. The role of state and foreign owners in corporate risk-taking: Evidence from privatization. J. Financ. Econ. 2013, 108, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, J. State ownership, cross-border acquisition, and risk-taking: Evidence from China’s banking industry. J. Bank Financ. 2016, 71, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Okafor, C.; Ujah, N.; Zhang, L. Executives’ gender-diversity, education, and firm’s bankruptcy risk: Evidence from China. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2021, 30, 100500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccio, M.; Marchica, M.T.; Mura, R. CEO gender, corporate risk-taking, and the efficiency of capital allocation. J. Corp. Financ. 2016, 39, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.H.; Huang, C.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Yen, J.F. CEO overconfidence and financial crisis: Evidence from bank lending and leverage. J. Financ. Econ. 2016, 120, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Ha, Y.J.; Wei, Y.; Sarala, R.M. CEO Narcissism and Global Performance Variance in Multinational Enterprises: The Roles of Foreign Direct Investment Risk-Taking and Business Group Affiliation. BRIT J. Manag. 2023, 34, 512–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, V.V.; Amihud, Y.; Litov, L. Creditor rights and corporate risk-taking. J. Financ. Econ. 2011, 102, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.; Litov, L.; Yeung, B. Corporate governance and risk-taking. J. Financ. 2008, 63, 1679–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltratti, A.; Stulz, R.M. The credit crisis around the globe: Why did some banks perform better? J. Financ. Econ. 2012, 105, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Chae, J.; Lee, Y.K. Family ownership and risk taking. Financ. Res. Lett. 2018, 25, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.B.; Funk, P. Beyond the glass ceiling: Does gender matter? Manag. Sci. 2012, 58, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, N.B. Cash is queen: Female CEOs’ propensity to hoard cash. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2021, 29, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.; Bolton, B.; Lu, J. Size, leverage, and risk-taking of financial institutions. J. Bank Financ. 2015, 59, 520–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Boateng, A.; Ly, K.C.; Jiang, Y. Are bonds blind? Board-CEO social networks and firm risk. J. Corp. Financ. 2021, 68, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, Y.R.; He, V.F.; Puranam, P.; von Krogh, G. Algorithm supported induction for building theory: How can we use prediction models to theorize? Organ Sci. 2021, 32, 856–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, I.; Stern, L.H.; Tan, C.; Weisbach, M.S. Selecting directors using machine learning. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2021, 34, 3226–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; He, C.; Hsu, S.C.; Sarkis, J.; Chen, J.H. Corporate environmental performance prediction in China: An empirical study of energy service companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, A.R.; Cook, A.; Glass, C. A free solo in heels: Corporate risk taking among women executives and directors. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 157, 113651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, F.; Lu, J.; Fareed, Z. Does firm life cycle impact corporate risk taking and performance? J. Multinatl. Financ. Manag. 2019, 51, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leippold, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W. Machine learning in the Chinese stock market. J. Financ. Econ. 2022, 145, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Sohn, S.Y. Support vector machines for default prediction of SMEs based on technology credit. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 201, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, S. CEO Reputation and Corporate Risk-Taking: Managerial Competence or Managerial Defence? Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Meng, C.; Firth, M.; Hou, W. Ownership structure and risk-taking: Comparative evidence from private and state-controlled banks in China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2014, 36, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccio, M.; Marchica, M.T.; Mura, R. Large shareholder diversification and corporate risk-taking. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2011, 24, 3601–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Patro, S.; Pereira, R. Option incentives, leverage, and risk-taking. J. Corp. Financ. 2017, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, K.L.H.; Liao, J.; Tripe, D.; Wongchoti, U. Gender diversity, state control, and corporate risk-taking: Evidence from China. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2016, 39, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.F.; Fang, S.C. Risk–return paradox? The moderating effects of risk-taking capabilities. Manag. Decis. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Do, T.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, L. Rocking the boat: How relative performance evaluation affects corporate risk taking. J. Account. Econ. 2022, 73, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, T.A.; Matsa, D.A. Playing it safe? Managerial preferences, risk, and agency conflicts. J. Financ. Econ. 2016, 122, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabert, S. Do younger CEOs really increase firm risk? Evidence from sudden CEO deaths. J. Corp. Financ. 2023, 79, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, H.; Mallin, C. The influence of CEO demographic characteristics on corporate risk-taking: Evidence from Chinese IPOs. Eur. J. Financ. 2018, 24, 1528–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfling, M.A. CEO age and the riskiness of corporate policies. J. Corp. Financ. 2014, 25, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, T.; Iskandar-Datta, M. Are female top executives more risk-averse or more ethical? Evidence from corporate cash holdings policy. J. Empir. Financ. 2020, 55, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, V.; Gonzalez, A.; Hagendorff, J. Women on board: Does boardroom gender diversity affect firm risk? J. Corp. Financ. 2016, 36, 26–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiullah, M.; Akhter, T.; Saona, P.; Azad, M.A.K. Gender diversity on corporate boards, firm performance, and risk-taking: New evidence from Spain. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2022, 35, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, Y.I. CEO hubris and firm risk taking in China: The moderating role of managerial discretion. Acad. Manag. J. 2010, 53, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunbaş, Y.; Thornton, J.; Uymaz, Y. The effect of CEO power on bank risk: Do boards and institutional investors matter? Financ. Res. Lett. 2020, 33, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Anderson, H.; Chi, J. Managerial foreign experience and corporate risk-taking: Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2023, 86, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dbouk, W.; Fang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. Do social networks encourage risk-taking? Evidence from bank CEOs. J. Financ. Stab. 2020, 46, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, S.P.; Javakhadze, D.; Rajkovic, T. CEO social capital, risk-taking and corporate policies. J. Corp. Financ. 2017, 47, 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, Y. How does labor protection influence corporate risk-taking? Evidence from China. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2021, 68, 101572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.X. Credit rating prediction through supply chains: A machine learning approach. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P. Corporate governance and risk-taking: Evidence from Japanese firms. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2011, 19, 278–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, H. Does social capital influence corporate risk-taking? J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 2020, 26, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellyn, K.B.; Muller-Kahle, M.I. CEO power and risk taking: Evidence from the subprime lending industry. Corp. Gov. 2012, 20, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 4765–4774. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liao, Z.; Quaedvlieg, R. Conditional superior predictive ability. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2022, 89, 843–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapire, R.E. Explaining AdaBoost. In Empirical Inference; Schölkopf, B., Luo, Z., Vovk, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.J. Venture capital financing, strategic alliances, and the initial public offerings of Internet startups. J. Bus. Ventur. 2004, 19, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Poutziouris, P. Entrepreneurial risk taking: Empirical evidence from UK family firms. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2010, 16, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijns, B.; Hubers, F.; Kim, D.; Roh, T.Y.; Xu, Y. National culture and corporate risk-taking around the world. Glob. Financ. J. 2022, 52, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).