A Novel D–SCRI–EDAS Method and Its Application to the Evaluation of an Online Live Course Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Dempster–Shafer Theory
2.2. D Number Theory
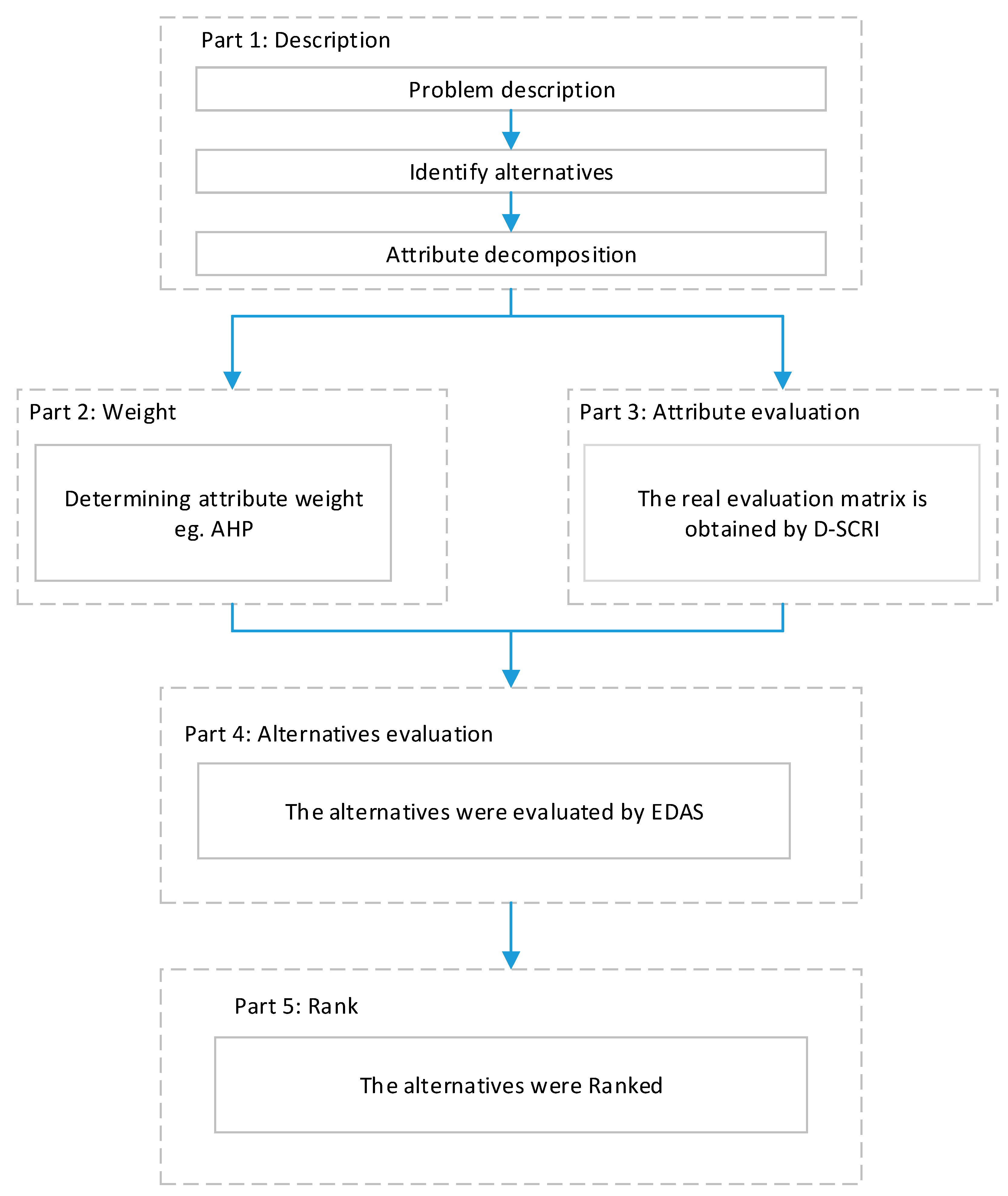
3. Proposed Method
3.1. D Numbers Stepwise Comparison and Replacement Integration (SCRI) Method
3.2. D–SCRI–EDAS Method
4. The Numerical Example and Comparative Analysis
4.1. A Numerical Example
4.2. Comparative Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, J.L. The control problem of gray systems. Syst. Control. Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, A.P. Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann. Math. Stat. 1967, 38, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, G. A Mathematical Theory of Evidence; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Yager, R.R. Generalized dempster–shafer structures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassov, K. Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1986, 20, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.R.; Reformat, M.; To, N.D. Drawing on the ipad to input fuzzy sets with an application to linguistic data science. Inf. Sci. 2019, 479, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough sets. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1982, 11, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Su, Q.; Li, J. The group decision-making rules based on rough sets on large scale engineering emergency. Syst. Eng. Procedia 2012, 4, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, M. Improving group decision support systems using rough set. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 69, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y. D numbers: Theory and applications. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2012, 9, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Yi, X.; Zhao, J. The improved combination rule of D numbers and its application in radiation source identification. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 6025680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F. A novel multi-criteria decision making method for assessing health-care waste treatment technologies based on D numbers. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 71, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiti, H.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Herrera-Viedma, E.E. A novel linguistic approach for multi-granular information fusion and decision-making using risk-based linguistic D numbers. Inf. Sci. 2020, 530, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.M.; Deng, Y. A new MADA methodology based on D numbers. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 2458–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y. A novel distance function of D numbers and its application in product engineering. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 47, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.; Fei, L. On entropy function and reliability indicator for d numbers. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 3248–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.K.; Liu, X.M.; Wei, D.J. A modified D numbers’ integration for multiple attributes decision making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhao, C. A Novel Integration Method for D Numbers Based on Horizontal Comparison. Axioms 2021, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Mahadevan, S. Supplier selection using AHP methodology extended by D numbers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Chen, X. A D-VIKOR Method for Medicine Provider Selection. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences & Optimization, Beijing, China, 4–6 July 2014; pp. 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, F.; Chen, L.; Deng, Y. A Modified TOPSIS Method Based on D Numbers and Its Applications in Human Resources Selection. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 6145196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Deng, X.; Deng, Y.; Mahadevan, S. Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis based on D numbers and AHP. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2017, 313, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, F.; Wang, L. Evaluation of university scientific research ability based on the output of sci-tech papers: A D-AHP approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, T.; Zheng, H.; Yin, L.; Deng, Y. Failure mode and effects analysis based on D numbers and topsis. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2018, 34, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X. A Multicriteria Decision-Making Approach with Linguistic D Numbers Based on the Choquet Integral. Cogn. Comput. 2019, 11, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. An Extended VIKOR Method for Multiple Attribute Decision Making with Linguistic D Numbers Based on Fuzzy Entropy. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2020, 19, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Mi, X.; Liu, L.; Kang, B. A New Soft Likelihood Function Based on D Numbers in Handling Uncertain Information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 22, 2333–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi Mousavi-Nasab, S.; Sotoudeh-Anvari, A. An extension of best-worst method with D numbers: Application in evaluation of renewable energy resourcesSustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 40, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H. A New Evaluation Methodology for Quality Goals Extended by D Number Theory and FAHP. Information 2020, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, X. A novel approach to multi-criteria group decision-making problems based on linguistic D numbers. Comp. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Tian, Y.; Kang, B. A hybrid multi-criteria decision making approach for assessing health-care waste management technologies based on soft likelihood function and D-numbers. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 6708–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Liao, H. A multi-criteria decision making method based on DNMA and CRITIC with linguistic D numbers for blockchain platform evaluation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 101, 104200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Puška, A.; Stević, Ž.; Cirovic, G. A new intelligent MCDM model for HCW management: The integrated BWM-MABAC model based on D numbers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 175, 114862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H. A SWOT method to evaluate safety risks in life cycle of wind turbine extended by D number theory. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 4439–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Tian, Y.; Kang, B. MADA Problem: A New Scheme Based on D Numbers and Aggregation Functions. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 11231–11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Fang, W.; Wu, M. Selection of Battery Suppliers for New Energy Vehicles by an Integrated Model Based on D Numbers. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 3293–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Olfat, L.; Turskis, Z. Multi-criteria inventory classification using a new method of Evaluation Based on Distance from Average Solution (EDAS). Informatica 2015, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Amiri, M.; Turskis, Z. Extended EDAS method for fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making: An application to supplier selection. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2016, 11, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Amiri, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Antucheviciene, J. Stochastic EDAS method for multi-criteria decision-making with normally distributed data. J. Intell. Fuzzy. Syst. 2017, 33, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorabaee, M.K.; Amiri, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Antucheviciene, J. A new multi-criteria model based on interval type-2 fuzzy sets and EDAS method for supplier evaluation and order allocation with environmental considerations. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 112, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanujkic, D.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Ghorabaee, M.K.; Turskis, Z. An Extension of the EDAS Method Based on the Use of Interval Grey Numbers. Stud. Inform. Control. 2017, 26, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecer, F. Third-party logistics (3PLs) provider selection via Fuzzy AHP and EDAS integrated model. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 24, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaşan, A.; Kahraman, C. A novel interval-valued neutrosophic EDAS method: Prioritization of the United Nations national sustainable development goals. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 4891–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Stević, Ž.; Turskis, Z.; Tomašević, M. A Novel Extended EDAS in Minkowski Space (EDAS-M) Method for Evaluating Autonomous Vehicles. Stud. Inform. Control. 2019, 28, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, D.; He, Z.; Adjei, N.O.; Asante, B. Exploring the barriers to renewable energy adoption utilising MULTIMOORA-EDAS method. Energy Policy 2020, 142, 111479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Wei, C.; Guo, Y. EDAS method for probabilistic linguistic multiple attribute group decision making and their application to green supplier selection. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 9045–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Peng, L.; Jing, B.; Wu, C.; Yang, J.; Cong, G. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on User Experience with Online Education Platforms in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Song, F.H.; Xie, X.; Yu, D. Research on evaluation system of user experience with online live course platform. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23863–23875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deng, Y. TDBF: Two Dimension Belief Function. Intl. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 34, 1968–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Xian, S.; Lu, S. Z probabilistic linguistic term sets and its application in multi-attribute group decision making. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Making 2021, 20, 529–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Combined with Other MADM Method | Applications | Lierature Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | D-AHP | Supplier Selection | [20] |
| D-VIKOR | Medicine Provider Selection | [21] | |
| 2016 | D-TOPSIS | Human Resources Selection | [22] |
| 2017 | D-AHP | Human Reliability Analysis | [23] |
| University Scientific Research Ability | [24] | ||
| 2018 | D-TOPSIS | Failure Mode and Effects Analysis | [25] |
| 2019 | D-TODIM-Choquet Integral | Performance of Motor Engine | [26] |
| 2020 | D-VIKOR-Fuzzy Entropy | Medicine Provider Selection | [27] |
| D-Soft Likelihood Function | Performance of Automobiles | [28] | |
| D-BWM-COPRAS-WASPAS | Evaluation of Renewable Energy Resources | [29] | |
| D-FAHP | Promoting Quality Goals | [30] | |
| D-TOPSIS-BM Operator | Supplier Selection | [31] | |
| 2021 | D-Soft Likelihood Function | Healthcare Waste Management | [32] |
| D-DNMA-CRITIC | Blockchain Platform Evaluation | [33] | |
| D-MABAC-BWM | Healthcare Waste Management | [34] | |
| D-SWOT | Safety risk | [35] | |
| D-POWA Aggregation-Soft Likelihood Function | Car Performance Assessment | [36] | |
| 2022 | D-BWM-EDAS | Battery Suppliers for New Energy Vehicles | [37] |
| Basic Attribute | Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.5), (7, 0.3)} | {(8, 0.5), (7,0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1)} | {(7, 0.5), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2), (4,0.1)} |
| Y2 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.5), (6, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.1), (5, 0.1)} |
| Y3 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.4), (5, 0.1)} |
| Y4 | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.4)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.6)} | {(7, 0.2), (6, 0.4), (5, 0.2), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y5 | {(9, 0.6), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.1), (5, 0.4)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} |
| Y6 | {(7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1), (4, 0.2)} | {(7, 0.2), (5, 0.4), (4, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (5, 0.1)} |
| Y7 | {(8, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.4)} | {(9, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.4)} | {(7, 0.4), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} |
| Y8 | {(9, 0.4), (8, 0.4), (6, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.3), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.1), (5, 0.2), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y9 | {(9, 0.1), (8, 0.4), (6, 0.3)} | {(8, 0.1), (7, 0.6), (6, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.3), (4, 0.2)} |
| Y10 | {(9, 0.3), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.4)} | {(8, 0.5), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.6)} |
| Y11 | {(6, 0.6), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2),(4, 0.1), (3, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.4), (6, 0.2), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y12 | {(8, 0.3), (7, 0.4), (5, 0.1)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.2), (6, 0.3), (5, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.3), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1)} |
| Y13 | {(9, 0.4), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (7, 0.4), (6, 0.2)} |
| Y14 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.4), (6, 0.3)} | {(7, 0.4), (6, 0.4), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y15 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.4), (7, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.6)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.4)} |
| Y16 | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.1), (6, 0.4)} | {(8, 0.3), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.4)} | {(7, 0.5), (6, 0.1), (5, 0.3)} |
| Basic Attribute | Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.5), (7, 0.3)} | {(8, 0.5), (7,0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1)} | {(7, 0.5), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2), (4,0.1)} |
| Y2 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.5), (6, 0.2), (58/7, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.3), (5, 0.2), (47/7, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2), (48/7, 0.1)} |
| Y3 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.2), (55/7,0.1)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.2), (53/7, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.4), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1), (49/7, 0.1)} |
| Y4 | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.5), (4, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.6)} | {(7, 0.2), (6, 0.5), (5, 0.2), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y5 | {(9, 0.6), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (6, 0.1), (5, 0.4)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.3), (5, 0.3)} |
| Y6 | {(7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1), (4, 0.3), (39/7, 0.2)} | {(7, 0.2), (5, 0.4), (4, 0.2), (38/7, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.3), (5, 0.1), (55/7, 0.2)} |
| Y7 | {(8, 0.2), (6, 0.4), (5, 0.4)} | {(9, 0.2), (7, 0.4), (6, 0.4)} | {(7, 0.4), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2), (50/8, 0.2)} |
| Y8 | {(9, 0.4), (8, 0.4), (6, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.3), (6, 0.3), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.1), (6, 0.1), (5, 0.3), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y9 | {(9, 0.1), (8, 0.4), (6, 0.3), (4, 0.1), (59/8, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.1), (7, 0.7), (6, 0.1), (4, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.3), (4, 0.2), (57/8, 0.1)} |
| Y10 | {(9, 0.3), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.4), (59/8, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.5), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (60/8, 0.1)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.6), (6, 0.1), (66/8, 0.1)} |
| Y11 | {(6, 0.6), (5, 0.2), (41/7, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2),(4, 0.1), (3, 0.1), (46/7, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.4), (6, 0.2), (4, 0.1), (3, 0.1), (48/7, 0.2)} |
| Y12 | {(8, 0.3), (7, 0.4), (5, 0.1), (57/8, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.2), (6, 0.3), (5, 0.1), (57/8, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.3), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.1), (55/8, 0.2)} |
| Y13 | {(9, 0.4), (8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(9, 0.2), (7, 0.4), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} |
| Y14 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.4), (6, 0.3), (5, 0.1)} | {(7, 0.4), (6, 0.4), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.3), (4, 0.1)} |
| Y15 | {(9, 0.2), (8, 0.4), (7, 0.2), (5, 0.2)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.6)} | {(8, 0.2), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.2), (5, 0.4)} |
| Y16 | {(8, 0.4), (7, 0.1), (6, 0.4), (63/9, 0.1)} | {(8, 0.3), (7, 0.2), (6, 0.4), (62/9, 0.1)} | {(7, 0.5), (6, 0.1), (5, 0.3), (56/9, 0.1)} |
| Basic Attribute | Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 7.9000 | 7.1000 | 6.1000 |
| Y2 | 7.8286 | 6.4714 | 6.5857 |
| Y3 | 7.4857 | 7.2571 | 6.8000 |
| Y4 | 6.4000 | 6.6000 | 5.8000 |
| Y5 | 8.4000 | 6.3000 | 6.8000 |
| Y6 | 5.4143 | 5.2857 | 7.5714 |
| Y7 | 6.0000 | 7.0000 | 6.2500 |
| Y8 | 8.0000 | 7.0000 | 6.4000 |
| Y9 | 7.0375 | 6.7000 | 6.8125 |
| Y10 | 7.2375 | 7.3500 | 8.0250 |
| Y11 | 5.7714 | 6.2143 | 6.4714 |
| Y12 | 7.1250 | 7.1250 | 6.8750 |
| Y13 | 7.6000 | 6.8000 | 6.8000 |
| Y14 | 7.3000 | 6.2000 | 6.1000 |
| Y15 | 7.4000 | 6.6000 | 6.2000 |
| Y16 | 7.0000 | 6.8889 | 6.2222 |
| Basic Attribute | Average Integration Value | Basic Attribute | Average Integration Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 7.0333 | Y9 | 6.8500 |
| Y2 | 6.9619 | Y10 | 7.5375 |
| Y3 | 7.1809 | Y11 | 6.1524 |
| Y4 | 6.2667 | Y12 | 7.0417 |
| Y5 | 7.1667 | Y13 | 7.0667 |
| Y6 | 6.0905 | Y14 | 6.5333 |
| Y7 | 6.4167 | Y15 | 6.7333 |
| Y8 | 7.1333 | Y16 | 6.7037 |
| Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WSP | WSP1 = 0.0741 | WSP2 = 0.0122 | WSP3 = 0.0145 |
| WSN | WSN1 = 0.0102 | WSN2 = 0.0297 | WSN3 = 0.0609 |
| Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NWSP | NWSP1 = 1 | NWSP2 = 0.1646 | NWSP3 = 0.1957 |
| NWSN | NWSN1 = 0.8325 | NWSN2 = 0.5123 | NWSN3 = 0 |
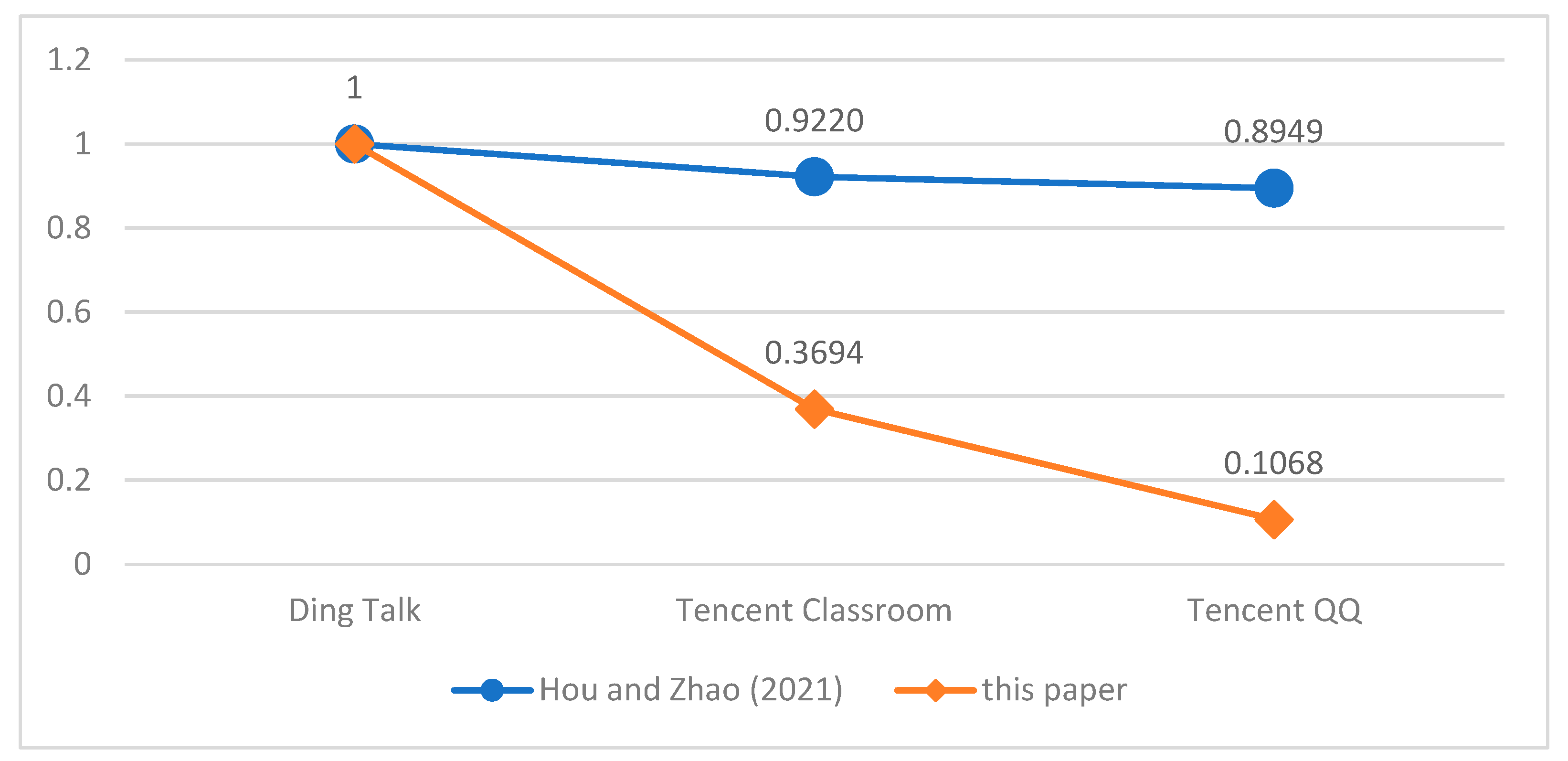
| Score Type | Method | Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation scores | Hou and Zhao [19] | 7.2508 | 6.6856 | 6.4891 |
| D-EDAS (this paper) | 0.9163 | 0.3385 | 0.0979 | |
| Normalized scores | Hou and Zhao [19] | 1 | 0.9220 | 0.8949 |
| D-EDAS (this paper) | 1 | 0.3694 | 0.1068 |
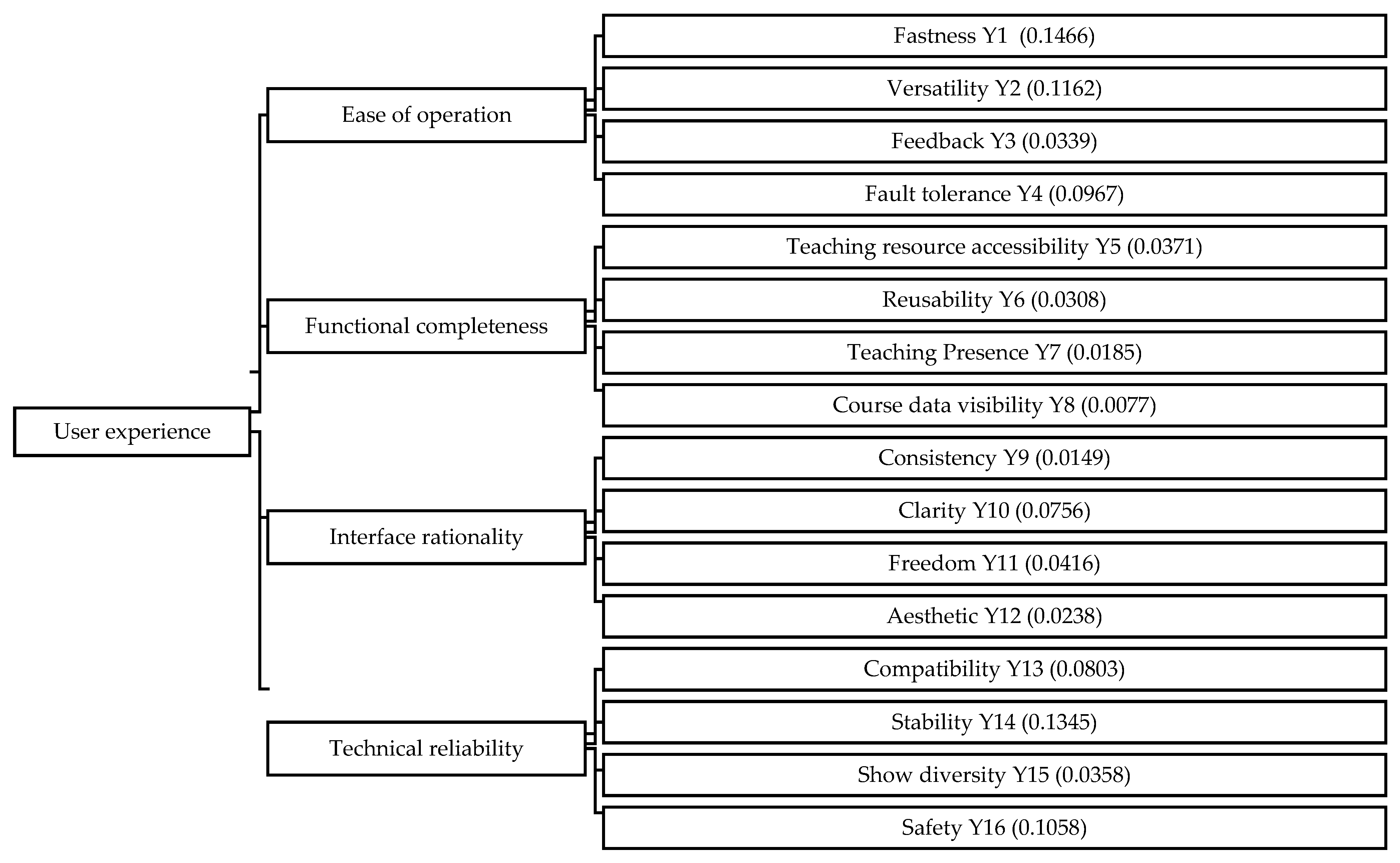
| Basic Attribute | The Weight of the First Random Change | The Weight of the Second Random Change |
|---|---|---|
| Y1 | 0.1027 | 0.0787 |
| Y2 | 0.1511 | 0.0319 |
| Y3 | 0.0719 | 0.0526 |
| Y4 | 0.0222 | 0.0985 |
| Y5 | 0.0227 | 0.0679 |
| Y6 | 0.0289 | 0.0625 |
| Y7 | 0.0017 | 0.0901 |
| Y8 | 0.1213 | 0.0767 |
| Y9 | 0.0797 | 0.0891 |
| Y10 | 0.0823 | 0.0432 |
| Y11 | 0.0476 | 0.0117 |
| Y12 | 0.0285 | 0.0356 |
| Y13 | 0.1237 | 0.0732 |
| Y14 | 0.0317 | 0.0657 |
| Y15 | 0.0571 | 0.0892 |
| Y16 | 0.0269 | 0.0334 |
| Evaluation Method | Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| D-SCRI/1 | 1.0000 | 0.9125 | 0.8981 |
| D-SCRI-EDAS/1 | 1.0000 | 0.2763 | 0.1064 |
| D-SCRI/2 | 1.0000 | 0.9354 | 0.9150 |
| D-SCRI-EDAS/2 | 1.0000 | 0.3905 | 0.1655 |
| The Ranking Index | Ding Talk | Tencent Classroom | Tencent QQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.1819 | 0.5619 | 0.8236 |
| R | 0.0756 | 0.1233 | 0.1466 |
| Q | 0 | 0.6298 | 1 |
| The Ranking Index | The Ascending Ranks |
|---|---|
| S | Ding Talk ≫ Tencent Classroom ≫ Tencent QQ |
| R | Ding Talk ≫ Tencent Classroom ≫ Tencent QQ |
| Q | Ding Talk ≫ Tencent Classroom ≫ Tencent QQ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, H.; Zhao, C. A Novel D–SCRI–EDAS Method and Its Application to the Evaluation of an Online Live Course Platform. Systems 2022, 10, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050157
Hou H, Zhao C. A Novel D–SCRI–EDAS Method and Its Application to the Evaluation of an Online Live Course Platform. Systems. 2022; 10(5):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050157
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Haiyang, and Chunyu Zhao. 2022. "A Novel D–SCRI–EDAS Method and Its Application to the Evaluation of an Online Live Course Platform" Systems 10, no. 5: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050157
APA StyleHou, H., & Zhao, C. (2022). A Novel D–SCRI–EDAS Method and Its Application to the Evaluation of an Online Live Course Platform. Systems, 10(5), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10050157





