Current Trends in Proteomic Advances for Food Allergen Analysis
Abstract
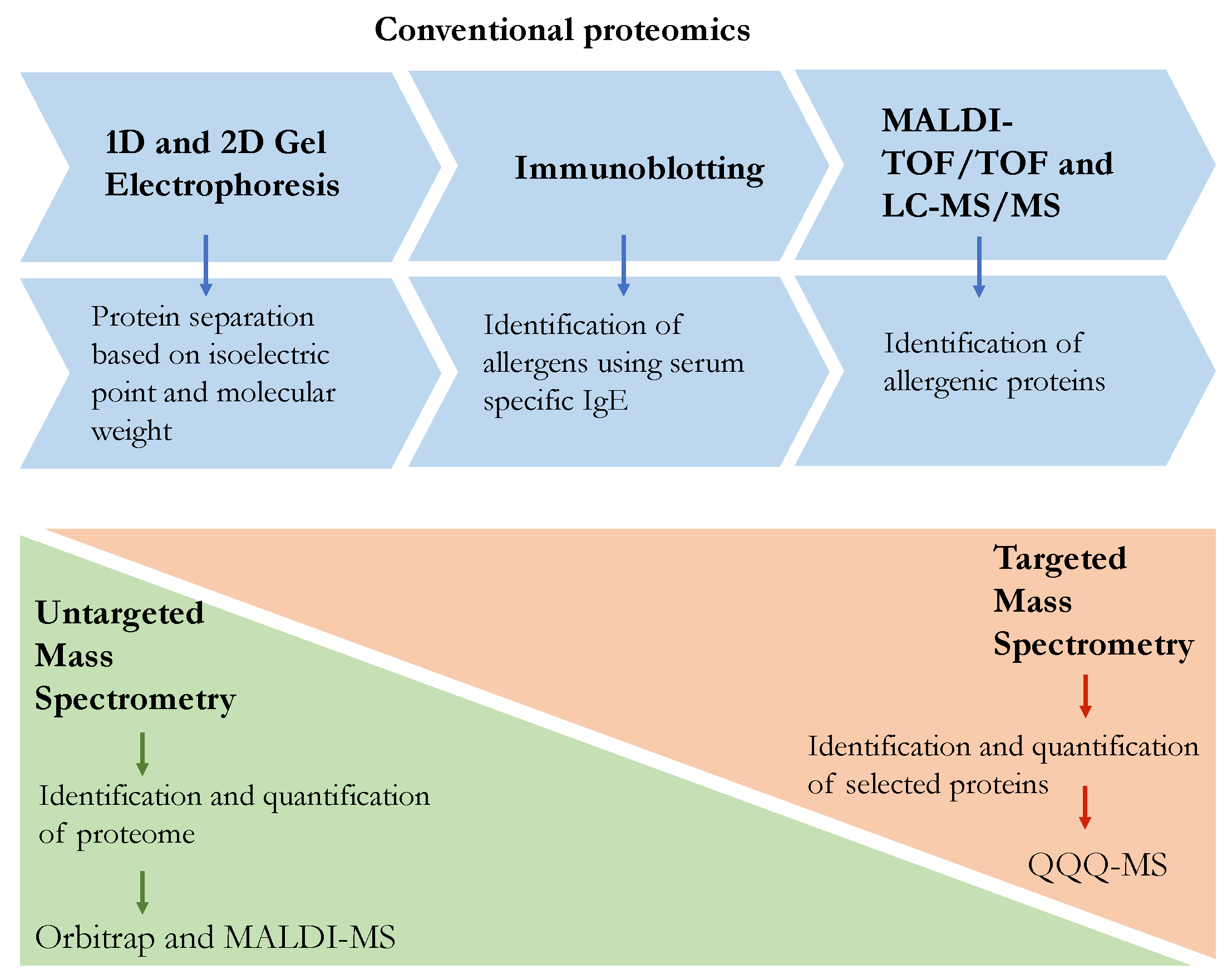
:1. Introduction
2. Food Allergens in Vegetable and Animal Products
2.1. Plant-Based Food Allergens
2.2. Animal-Based Food Allergens
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S116–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.S.; Springston, E.E.; Warrier, M.R.; Smith, B.; Kumar, R.; Pongracic, J.; Holl, J.L. The prevalence, severity, and distribution of childhood food allergy in the United States. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.; Holdford, D.; Bilaver, L.; Dyer, A.; Holl, J.L.; Meltzer, D. The economic impact of childhood food allergy in the United States. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koplin, J.J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Ponsonby, A.L.; Tang, M.L.K.; Lowe, A.J.; Gurrin, L.C.; Osborne, N.J.; Martin, P.E.; Robinson, M.N.; Wake, M.; et al. Environmental and demographic risk factors for egg allergy in a population-based study of infants. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 67, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.S.Y.; Wong, G.W.K.; Tang, M.L.K. Food allergy in the developing world. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branum, A.M.; Lukacs, S.L. Food allergy among U.S. children: Trends in prevalence and hospitalizations. NCHS Data Brief 2008, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Verrill, L.; Bruns, R.; Luccioli, S. Prevalence of self-reported food allergy in U.S. adults: 2001, 2006, and 2010. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2015, 36, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nwaru, B.I.; Hickstein, L.; Panesar, S.S.; Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.E.J.; Halken, S.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Poulsen, L.K.; et al. The epidemiology of food allergy in Europe: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 69, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opinion, S. Scientific Opinion on the evaluation of allergenic foods and food ingredients for labelling purposes. EFSA J. 2014, 12, e3894. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Wang, Z.; Ji, C.; Leung, P.S.C.; Woo, E.; Chang, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, B.; Wei, J.; Sun, J. Regional Differences in Food Allergies. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 57, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.L.K.; Mullins, R.J. Food allergy: Is prevalence increasing? Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Administration Qualified Health Claims, Letter of Enforcement Discretion—Nuts and Coronary Heart Disease (Docket No 02P-0505), Ingredients, Packaging & Labeling. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/qualified-health-claims-letters-enforcement-discretion (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Regulation (EU) no 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2011/1169/2018-01-01 (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Mazzucchelli, G.; Holzhauser, T.; Cirkovic Velickovic, T.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Molina, E.; Roncada, P.; Rodrigues, P.; Verhoeckx, K.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K. Current (Food) Allergenic Risk Assessment: Is It Fit for Novel Foods? Status Quo and Identification of Gaps. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1700278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Gallardo, J.M. Advanced proteomics and systems biology applied to study food allergy. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 22, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhondalay, G.K.; Rael, E.; Acharya, S.; Zhang, W.; Sampath, V.; Galli, S.J.; Tibshirani, R.; Boyd, S.D.; Maecker, H.; Nadeau, K.C.; et al. Food allergy and omics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volpicella, M.; Leoni, C.; Dileo, M.C.G.; Ceci, L.R. Progress in the Analysis of Food Allergens through Molecular Biology Approaches. Cells 2019, 8, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagaoua, M.; Hughes, J.; Terlouw, E.M.C.; Warner, R.D.; Purslow, P.P.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Picard, B. Proteomic biomarkers of beef colour. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Bernal, J.; Franco, D.; Zapata, C. Evaluating two-dimensional electrophoresis profiles of the protein phaseolin as markers of genetic differentiation and seed protein quality in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7200–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Pérez-Santaescolástica, C.; Franco, D.; Carballo, J.; Garcia-Perez, J.V.; Benedito, J.; Zapata, C.; Lorenzo, J.M. Proteomic footprint of ultrasound intensification on sliced dry-cured ham subjected to mild thermal conditions. J. Proteom. 2019, 193, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korte, R.; Brockmeyer, J. Novel mass spectrometry approaches in food proteomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 96, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaci, L.; De Angelis, E.; Montemurro, N.; Pilolli, R. Comprehensive overview and recent advances in proteomics MS based methods for food allergens analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishina, G.; Bardina, L.; Grish, A. 2D-Electrophoresis and inmunoblotting in food allergy. In Food Allergens: Methods and Protocols; Jing, L., Alcocer, M., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2017; Volume 1592, pp. 1–299. ISBN 978-1-4939-6923-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vidova, V.; Spacil, Z. A review on mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics: Targeted and data independent acquisition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 964, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, V.; Tilocca, B.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Vernocchi, P.; Levi Mortera, S.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P.; Putignani, L. Perusal of food allergens analysis by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, e103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croote, D.; Quake, S.R. Food allergen detection by mass spectrometry: The role of systems biology. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bräcker, J.; Brockmeyer, J. Characterization and Detection of Food Allergens Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Current Status and Future Perspective. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8935–8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pali-Schöll, I.; Verhoeckx, K.; Mafra, I.; Bavaro, S.L.; Clare Mills, E.N.; Monaci, L. Allergenic and novel food proteins: State of the art and challenges in the allergenicity assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, N.; Rao, R.S.P.; Gruppuso, P.A.; Ramratnam, B.; Salomon, A.R. Targeted proteomics: Current status and future perspectives for quantification of food allergens. J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadam, K.; Karbhal, R.; Jayaraman, V.K.; Sawant, S.; Kulkarni-Kale, U. AllerBase: A comprehensive allergen knowledgebase. Database (Oxford) 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Fu, L. Food allergomics based on high-throughput and bioinformatics technologies. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, e108942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, R.; Teshima, R. Proteomic Approaches for Allergen Analysis in Crop Plants; Elsevier Inc.: London Wall, London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780128040577. [Google Scholar]
- Shahali, Y.; Dadar, M. Plant food allergy: Influence of chemicals on plant allergens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Allergenicity of Foods Derived from Biotechnology. Biotechnology 2001, 26, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Selb, R.; Wal, J.M.; Moreno, F.J.; Lovik, M.; Mills, C.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Fernandez, A. Assessment of endogenous allergenicity of genetically modified plants exemplified by soybean—Where do we stand? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 101, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rödiger, A.; Baginsky, S. Tailored use of targeted proteomics in plant-specific applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Downs, M.L.; Johnson, P. Target selection strategies for LC-MS/MS food allergen methods. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromilow, S.; Gethings, L.A.; Buckley, M.; Bromley, M.; Shewry, P.R.; Langridge, J.I.; Clare Mills, E.N. A curated gluten protein sequence database to support development of proteomics methods for determination of gluten in gluten-free foods. J. Proteom. 2017, 163, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenbach, S.B.; Chang, H.C.; Simon-Buss, A.; Jang, Y.R.; Denery-Papini, S.; Pineau, F.; Gu, Y.Q.; Huo, N.; Lim, S.H.; Kang, C.S.; et al. Towards reducing the immunogenic potential of wheat flour: Omega gliadins encoded by the D genome of hexaploid wheat may also harbor epitopes for the serious food allergy WDEIA. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexhaller, B.; Colgrave, M.L.; Scherf, K.A. Characterization and Relative Quantitation of Wheat, Rye, and Barley Gluten Protein Types by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaheen, N.; Halima, O.; Akhter, K.T.; Nuzhat, N.; Rao, R.S.P.; Wilson, R.S.; Ahsan, N. Proteomic characterization of low molecular weight allergens and putative allergen proteins in lentil (Lens culinaris) cultivars of Bangladesh. Food Chem. 2019, 297, e124936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, S.; Stevenson, S.E.; Brownie, C.; Herouet-Guicheney, C.; Herman, R.A.; Ladics, G.S.; Privalle, L.; Ward, J.M.; Doerrer, N.; Thelen, J.J. Variation in seed allergen content from three varieties of soybean cultivated in nine different locations in iowa, illinois, and indiana. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhu, K.; Zhou, H.; Guo, X. High hydrostatic pressure reducing allergenicity of soy protein isolate for infant formula evaluated by ELISA and proteomics via Chinese soy-allergic children’s sera. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I.; Cabo, S.; Silva, A.P.; Gonçalves, B.; Hillion, M.; Hébraud, M.; Igrejas, G. Natural variation of hazelnut allergenicity: Is there any potential for selecting hypoallergenic varieties? Nutrients 2020, 12, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, H.; Kalveram, K.J.; Forck, G.; Sterry, W. Kiwi fruit allergy: A new birch pollen-associated food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, E.E.G.; Heathcote, K.; Teran, L.M.; Righetti, P.G.; Boschetti, E.; D’Amato, A. Novel low-abundance allergens from mango via combinatorial peptide libraries treatment: A proteomics study. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, J.; Nešić, A.; Kull, S.; Schocker, F.; Jappe, U.; Gavrović-Jankulović, M. Employment of proteomic and immunological based methods for the identification of catalase as novel allergen from banana. J. Proteom. 2018, 175, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.E.; Sayers, R.L.; Gethings, L.A.; Balasundaram, A.; Marsh, J.T.; Langridge, J.I.; Mills, E.N.C. Quantitative Proteomic Profiling of Peanut Allergens in Food Ingredients Used for Oral Food Challenges. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5689–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prodic, I.; Stanic-Vucinic, D.; Apostolovic, D.; Mihailovic, J.; Radibratovic, M.; Radosavljevic, J.; Burazer, L.; Milcic, M.; Smiljanic, K.; van Hage, M.; et al. Influence of peanut matrix on stability of allergens in gastric-simulated digesta: 2S albumins are main contributors to the IgE reactivity of short digestion-resistant peptides. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shih, Y.C.; Hsiao, J.T.; Sheu, F. Feasibility of utilizing stable-isotope dimethyl labeling in liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry-based determination for food allergens—Case of kiwifruit. Molecules 2019, 24, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uasuf, C.G.; De Angelis, E.; Guagnano, R.; Pilolli, R.; D’anna, C.; Villalta, D.; Brusca, I.; Monaci, L. Emerging allergens in goji berry superfruit: The identification of new ige binding proteins towards allergic patients’ sera. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E. Red meat allergy in children and adults. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 19, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolovic, D.; Tran, T.A.T.; Hamsten, C.; Starkhammar, M.; Cirkovic Velickovic, T.; Van Hage, M. Immunoproteomics of processed beef proteins reveal novel galactose-α-1,3-galactose-containing allergens. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 69, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogawa, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Satoh, M.; Kodera, Y.; Nomura, F.; Tanaka, T.; Sato, H.; Yamaide, F.; Nakano, T.; et al. Search for a Novel Allergen in Hen’s Egg Allergy Using an IgE Immunoblotting Assay. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Kalic, T.; McLean, T.R.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Seafood allergy: A comprehensive review of fish and shellfish allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Magalhães, C.R.; Schrama, D.; Fonseca, F.; Kuehn, A.; Morisset, M.; Ferreira, S.R.; Gonçalves, A.; Rodrigues, P.M. Effect of EDTA enriched diets on farmed fish allergenicity and muscle quality; a proteomics approach. Food Chem. 2020, 305, e125508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrama, D.; Cerqueira, M.; Raposo, C.S.; Rosa Da Costa, A.M.; Wulff, T.; Gonçalves, A.; Camacho, C.; Colen, R.; Fonseca, F.; Rodrigues, P.M. Dietary creatine supplementation in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata): Comparative proteomics analysis on fish allergens, muscle quality, and liver. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, e1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrera, M.; González-Fernández, Á.; Magadán, S.; Mateos, J.; Pedrós, L.; Medina, I.; Gallardo, J.M. Molecular characterization of B-cell epitopes for the major fish allergen, parvalbumin, by shotgun proteomics, protein-based bioinformatics and IgE-reactive approaches. J. Proteom. 2019, 200, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, R.; Kamath, S.D.; Johnston, E.; Zenger, K.R.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Lopata, A.L. Rapid and comprehensive discovery of unreported shellfish allergens using large-scale transcriptomic and proteomic resources. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Auria, E.; Mameli, C.; Piras, C.; Cococcioni, L.; Urbani, A.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Roncada, P. Precision medicine in cow’s milk allergy: Proteomics perspectives from allergens to patients. J. Proteom. 2018, 188, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Liu, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Ding, X.; Qin, W.; Yang, Y. A rapid immobilized trypsin digestion combined with liquid chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry for the detection of milk allergens in baked food. Food Control 2019, 102, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzone, G.; Arena, S.; Salzano, A.M.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Sassi, M.; Scaloni, A. Proteomic Characterization of Nonenzymatic Modifications Induced in Bovine Milk Following Thermal Treatments; Elsevier Inc.: London Wall, London, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780128040577. [Google Scholar]
- Brick, T.; Ege, M.; Boeren, S.; Böck, A.; Von Mutius, E.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Effect of processing intensity on immunologically active bovine milk serum proteins. Nutrients 2017, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bavaro, S.L.; De Angelis, E.; Barni, S.; Pilolli, R.; Mori, F.; Novembre, E.M.; Monaci, L. Modulation of milk allergenicity by baking milk in foods: A proteomic investigation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbring, S.; Xiong, L.; Diks, M.A.P.; Baars, T.; Garssen, J.; Hettinga, K.; van Esch, B.C.A.M. Loss of allergy-protective capacity of raw cow’s milk after heat treatment coincides with loss of immunologically active whey proteins. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4982–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, B.; Yang, C.T.; Downs, M.L. A Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mass Spectrometry Method for Detection of Both Casein and Whey Milk Allergens from a Baked Food Matrix. J. Proteome Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gier, S.; Verhoeckx, K. Insect (food) allergy and allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leni, G.; Tedeschi, T.; Faccini, A.; Pratesi, F.; Folli, C.; Puxeddu, I.; Migliorini, P.; Gianotten, N.; Jacobs, J.; Depraetere, S.; et al. Shotgun proteomics, in-silico evaluation and immunoblotting assays for allergenicity assessment of lesser mealworm, black soldier fly and their protein hydrolysates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francis, F.; Doyen, V.; Debaugnies, F.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Caparros, R.; Alabi, T.; Blecker, C.; Haubruge, E.; Corazza, F. Limited cross reactivity among arginine kinase allergens from mealworm and cricket edible insects. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martos, G.; López-Fandiño, R.; Molina, E. Immunoreactivity of hen egg allergens: Influence on in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of the presence of other egg white proteins and of egg yolk. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Nugraha, R.; Cao, T.T.; Koeberl, M.; Kamath, S.D.; Williamson, N.A.; O’Callaghan, S.; Nie, S.; Mehr, S.S.; et al. Variability of allergens in commercial fish extracts for skin prick testing. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 74, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalic, T.; Kamath, S.D.; Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Humeniuk, P.; Williamson, N.A.; Hira, D.; Rolland, J.M.; et al. Collagen—An important fish allergen for improved diagnosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Wu, C.C.; Tyan, Y.C.; Yu, W.T.; Huang, E.S.; Yu, H.S. Identification of pyruvate kinase as a novel allergen in whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) by specific-IgE present in patients with shrimp allergy. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.B.; Kamath, S.D.; Iyer, S.P.; Pratap, K.; Karnaneedi, S.; Taki, A.C.; Nugraha, R.; Schaeffer, P.M.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; et al. Defining specific allergens for improved component-resolved diagnosis of shrimp allergy in adults. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikovsky, M.; Fernand, F.; Sack, M.; Frey, W.; Müller, G.; Golberg, A. In silico food allergenic risk evaluation of proteins extracted from macroalgae Ulva sp. with pulsed electric fields. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Food | Allergen | Allergenic Protein | Proteomic Technology | Aim | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereals containing gluten | |||||
| Wheat Rye Barley | - | Gliadins (wheat) | MRM by LC-MS/MS | I, Q | [40] |
| Secalins (Rye) | |||||
| Hordeins (Barley) | |||||
| Wheat | - | Omega-5 gliadin | 2-DE immunoblotting | I | [39] |
| Gamma gliadins | |||||
| Legumes and soy | |||||
| Lentil | Len c 1 Len c 2 | Vincillin Legumin Lectin Lipid transfer proteins | MRM by LC–MS/MS | I, Q | [41] |
| Soy | Glycinin G1 Glycinin G2 Glycinin G3 Glycinin G4 | Glycinin | SMR by LC-MS/MS | I, Q | [42] |
| Gly m Bd 28k | Vincilin | ||||
| Gly m Bd 30k | Cysteine protease | ||||
| Β-Conglycinin α subunit | Vincilin | ||||
| Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor 1 Kunitz Trypsin Inhibitor 3 | - | ||||
| Fruits | |||||
| Mango | Man i 1 | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 2-DE immunoblotting followed by nano LC-MS/MS | I | [46] |
| Man i 2 | |||||
| Mus a 1 | Profilin | ||||
| Mus a 2 | Class 1 chitinase | ||||
| Mus a 5 | Beta-1-3-glucanase | ||||
| - | Pectinesterase | ||||
| - | Superoxide dismutase | ||||
| Kiwifruit | Act d 1 | Actinidin | MRM by LC-MS | I, Q | [50] |
| Act d 5 | Kiwellin | ||||
| Act d 11 | Ripening-related protein family | ||||
| Goji Berry Superfruit | - | Vincilin | 1D immunoblotting followed by LC-MS/MS | I | [51] |
| Legumin | |||||
| 11S globulin | |||||
| Banana | Mus a 7 | Catalase | 2-DE immunoblotting and LC-MS/MS | I | [47] |
| Peanuts | |||||
| Peanut | Ara h 1 Ara h 3 | Cupin | LC-MS | I, Q | [48] |
| Ara h 5 | Profilin | ||||
| Ara h 2 Ara h 6 Ara h 7 Ara h 9 | Prolamin | ||||
| Ara h 10 Ara h 11 | Oleosin | ||||
| Peanut | Ara h 1 Ara h 3 | Cupin | 1D and 2-DE immunoblotting and nLC-MS/MS | [49] | |
| Ara h 2 Ara h 6. | Prolamin | ||||
| Food | Allergen | Allergenic Protein | Proteomic Technology | Aim | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eggs | |||||
| Hen egg | Gal d 1 | Ovomucoid | 1D and 2-DE immunoblotting and MALDI-TOF/TOF | I | [70] |
| Gal d 2 | Ovalbumin | ||||
| Gal d 3 | Ovotransferrin | ||||
| Gal d 4 | Lysozyme | ||||
| Fish and shellfish | |||||
| Ray’s bream White seabream Cod Pink cusk-eel Four-spot megrim Angler Deep-cape hake Common seabream Salmon Club mackerel Common sole Gilthead seabream Yellowfin tuna Horse mackerel Swordfis | - | β-parvalbumin | Shotgun proteomics | I | [58] |
| Gilthead seabream | - | β-parvalbumin | 1D and 2-DE immunoblotting and MALDI-TOF/TOF | I | [56] |
| Cod Flounder Hake Herring Mackerel Bass Tuna Trout Salmon | - | Parvalbumin Tropomyosin Aldolase β-enolase Collagen | 1D and 2-DE immunoblotting and LC-MS/MS | I | [71] |
| Gilthead Seabream | - | Parvalbumin | 2-DE immunoblotting and MALDI-TOF/TOF | I | [57] |
| Barramundi Salmon, Tuna | - | Collagen chains | LC-MS/MS | I | [72] |
| Whiteleg shrimp | - | Arginine kinase Myosin light chain Pyruvate kinase Tropomyosin | 1D and RP-nano-UPLC- ESI-MS/MS | I | [73] |
| Shrimp allergy | - | Tropomyosin | 1D immunoblotting and LC-MS/MS | [74] | |
| Milk | |||||
| Cow’s milk and muffins | Bos d 5 | β-lactoglobulin | SDS-PAGEUPLC coupled with HR-MS/MS | I | [64] |
| Bos d 4 | α-lactalbumin | ||||
| Bos d 6 | Serum albumin | ||||
| Bos d 7 | Inmunoglobulins | ||||
| Bos d 9 | αS1-casein | ||||
| Bos d 10 | αS2-casein | ||||
| Bos d 11 | β-casein | ||||
| Bos d 12 | κ-casein | ||||
| Baked food | Bos d 9 | αs1-casein | UPLC-MS/MS | I | [61] |
| Bos d 10 | αs2-casein | ||||
| Bos d 11 | β-casein | ||||
| Bos d 12 | κ-casein | ||||
| Cow’s milk | - | Whey proteins | 1D and LC-MS/MS | I | [65] |
| Alternative foods | |||||
| Lesser mealworm Black soldier fly | - | Actin Tropomyosin Myosin | 1D immunoblotting and LQT-orbitrap | I | [68] |
| Mealworms Crickets | - | Arginine kinase | MALDI | I | [69] |
| Macroalgae Ulva sp. | - | Superoxide dismutase Troponin C Aldolase A Thioredoxin h | LC-MS/MS | I | [75] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Pedrouso, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gagaoua, M.; Franco, D. Current Trends in Proteomic Advances for Food Allergen Analysis. Biology 2020, 9, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9090247
López-Pedrouso M, Lorenzo JM, Gagaoua M, Franco D. Current Trends in Proteomic Advances for Food Allergen Analysis. Biology. 2020; 9(9):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9090247
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Pedrouso, María, José M. Lorenzo, Mohammed Gagaoua, and Daniel Franco. 2020. "Current Trends in Proteomic Advances for Food Allergen Analysis" Biology 9, no. 9: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9090247
APA StyleLópez-Pedrouso, M., Lorenzo, J. M., Gagaoua, M., & Franco, D. (2020). Current Trends in Proteomic Advances for Food Allergen Analysis. Biology, 9(9), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9090247








