Sialidase Activity in Human Blood Serum Has a Distinct Seasonal Pattern: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Serum Collection
2.2. Sialic Acid Labeling with Fetuin
2.3. Preparation of Agarose Gel Covalently Linked to Fetuin Labeled with Sialic Acid Tritium
2.4. Acidic Hydrolysis for Obtaining of Desialylated Fetuin
2.5. Measurement of Sialidase Activity with Labeled with Sialic Acid Tritium Fetuin, Covalently Linked to Agarose Gel, as a Substrate
2.6. Molecular Genetics Experiments
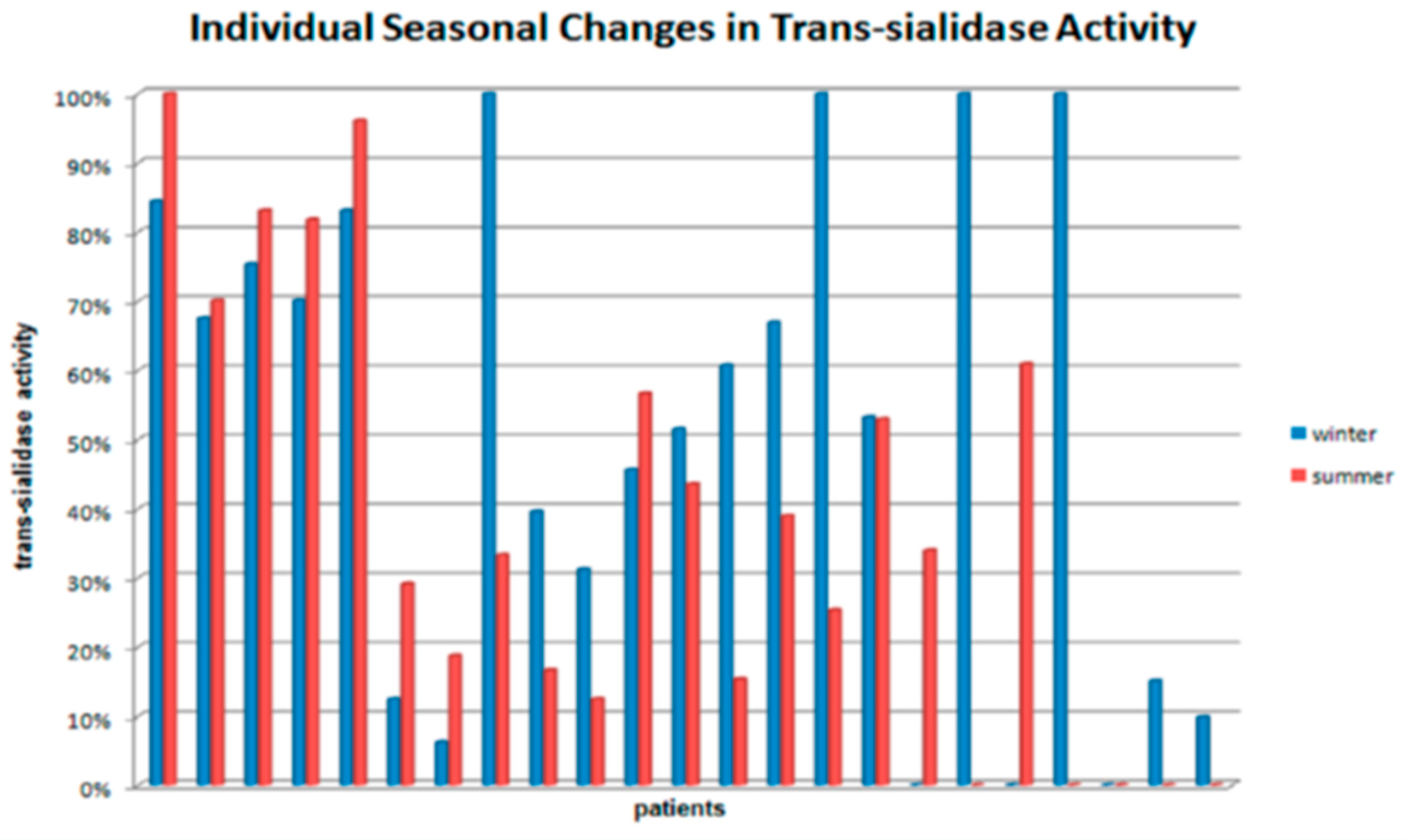
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, E.J.; Gyulay, G.; Lhoták, Š.; Szewczyk, M.M.; Chong, T.; Fuller, M.T.; Dadoo, O.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Austin, R.C.; Trigatti, B.L.; et al. Sialidase down-regulation reduces non-HDL cholesterol, inhibits leukocyte transmigration, and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14689–14706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fougerat, A.; Pan, X.; Smutova, V.; Heveker, N.; Cairo, C.W.; Issad, T.; Larrivée, B.; Medin, J.A.; Pshezhetsky, A.V. Neuraminidase 1 activates insulin receptor and reverses insulin resistance in obese mice. Mol. Metab. 2018, 12, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forcella, M.; Mozzi, A.; Stefanini, F.M.; Riva, A.; Epistolio, S.; Molinari, F.; Merlo, E.; Monti, E.; Fusi, P.; Frattini, M. Deregulation of sialidases in human normal and tumor tissues. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 21, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orekhov, A.N.; Ivanova, E.A. Introduction of the special issue “Atherosclerosis and Related Diseases”. Vessel Plus 2017, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harangi, M.; Szentpéteri, A.; Nádró, B.; Lőrincz, H.; Seres, I.; Páll, D.; Paragh, G. HDL subfraction distribution and HDL function in untreated dyslipidemic patients. Vessel Plus 2017, 1, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipov, V.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Karagodin, V.P.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Chemical composition of circulating native and desialylated low density lipoprotein: What is the difference? Vessel Plus 2017, 1, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V.; Sobenin, I.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Chistiakov, D.A. Modified low density lipoprotein and lipoprotein-containing circulating immune complexes as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of atherosclerosis and type 1 diabetes macrovascular disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12807–12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tertov, V.V.; Kaplun, V.V.; Sobenin, I.A.; Boytsova, E.Y.; Bovin, N.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Human plasma trans-sialidase causes atherogenic modification of low density lipoprotein. Atherosclerosis 2001, 159, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinyov, V.V.; Sazonova, M.A.; Ryzhkova, A.I.; Galitsyna, E.V.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Postnov, A.Y.; Orekhov, A.N.; Grechko, A.V.; Sobenin, I.A. Potential use of buccal epithelium for genetic diagnosis of atherosclerosis using mtDNA mutations. Vessel Plus 2017, 1, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Silvestri, I.; Testa, F.; Zappasodi, R.; Cairo, C.W.; Zhang, Y.; Lupo, B.; Galli, R.; Di Nicola, M.; Venerando, B.; Tringali, C. Sialidase NEU4 is involved in glioblastoma stem cell survival. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Haxho, F.; Neufeld, R.J.; Szewczuk, M.R. Neuraminidase-1: A novel therapeutic target in multistage tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40860–40881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samraj, A.N.; Läubli, H.; Varki, N.; Varki, A. Involvement of a non-human sialic acid in human cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.R.; Gahl, W.A. Lysosomal storage diseases. Transl. Sci. Rare Dis. 2017, 2, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wuhrer, M.; Holst, S. Serum sialylation changes in cancer. Glycoconj. J. 2018, 35, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, A. Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, A.J.; Baranovich, T.; Govorkova, E.A. Neuraminidase inhibitors for influenza B virus infection: Efficacy and resistance. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurebayashi, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Otsubo, T.; Ikeda, K.; Takahashi, S.; Takano, M.; Agarikuchi, T.; Sato, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Minami, A.; et al. Imaging of influenza virus sialidase activity in living cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, E.; Bonten, E.; D’Azzo, A.; Bresciani, R.; Venerando, B.; Borsani, G.; Schauer, R.; Tettamanti, G. Sialidases in vertebrates. A family of enzymes tailored for several cell functions. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2010, 64, 404–479. [Google Scholar]
- Quach, M.E.; Chen, W.; Li, R. Mechanisms of platelet clearance and translation to improve platelet storage. Blood 2018, 131, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| NEU1 | f-CGCTACGGAAGTGGGGTCAG r-AGTCCTGAAGGCAGAATACC |
| NEU2 | f-ACCAGGTTCAGTGGCAAGCTC r-GTGAAGTTTCCGGTAGGCGT |
| NEU3 | f-CAGTGCAGAGGTCATGGAAGAA r-AAGTCCCTCACCTCACTCCA |
| NEU4 | f-CCTTCACGGACAGTGCTCTT r-AATGTGGCCCAGTCCTGC |
| Viral RT primer | AGCAAAAGCAGG |
| Viral sialidase | f-TATTGGTCTCAGGGAGCAAAAGCAGGAGT r-ATATGGTCTCGTATTAGTAGAAACAAGGAGTTTTTT |
| Type of Genetic Target | Expression of Endogenous and Viral Sialidases | Р (ANOVA) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total n = 23 | Low Sialidase Activity n = 11 | Moderate Sialidase n = 5 | High Sialidase Activity n = 7 | ||
| NEU1 | 0.3 (1.0) | 0.3 (0.7) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.6 (1.5) | 0.45 |
| NEU2 | 6.3 (12.6) | 5.4 (10.9) | 1.1 (1.4) | 10.9 (17.3) | 0.21 |
| NEU3 | 0.7 (2.6) | 1.2 (3.8) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.6) | 0.50 |
| NEU4 | 0.3 (0.6) | 0.3 (0.6) | 0.2 (0.3) | 0.4 (0.9) | 0.80 |
| Exogenous NEU | 0.5 (1.0) | 0.4 (0.8) | 0.8 (1.3) | 0.4 (0.9) | 0.59 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glanz, V.Y.; Kashirskikh, D.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Yet, S.-F.; Sobenin, I.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Sialidase Activity in Human Blood Serum Has a Distinct Seasonal Pattern: A Pilot Study. Biology 2020, 9, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080184
Glanz VY, Kashirskikh DA, Grechko AV, Yet S-F, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN. Sialidase Activity in Human Blood Serum Has a Distinct Seasonal Pattern: A Pilot Study. Biology. 2020; 9(8):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080184
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlanz, Victor Y., Dmitry A. Kashirskikh, Andrey V. Grechko, Shaw-Fang Yet, Igor A. Sobenin, and Alexander N. Orekhov. 2020. "Sialidase Activity in Human Blood Serum Has a Distinct Seasonal Pattern: A Pilot Study" Biology 9, no. 8: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080184
APA StyleGlanz, V. Y., Kashirskikh, D. A., Grechko, A. V., Yet, S.-F., Sobenin, I. A., & Orekhov, A. N. (2020). Sialidase Activity in Human Blood Serum Has a Distinct Seasonal Pattern: A Pilot Study. Biology, 9(8), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080184






