Incretin Hormones and Type 2 Diabetes—Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. GLP-1
2.1. Secretion and Metabolism of Endogenous GLP-1
2.2. The GLP-1 Receptor
3. GIP
3.1. Secretion and Metabolism of Endogenous GIP
3.2. The GIP Receptor
4. The Role of GLP-1 and GIP in Health and under T2DM Conditions
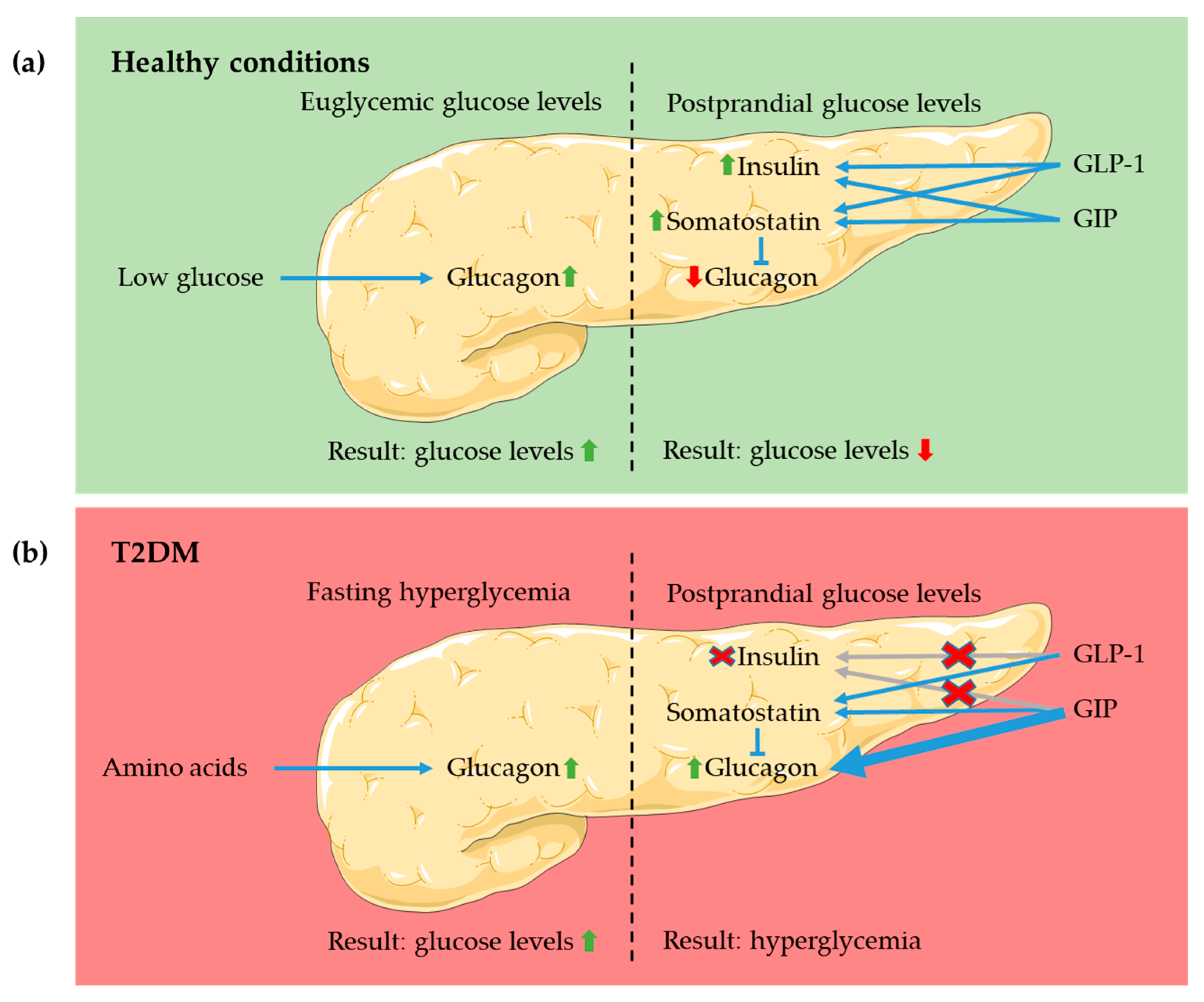
4.1. Pancreas
4.2. CNS
4.3. Adipose Tissue
4.4. Bone
5. Therapies for T2DM
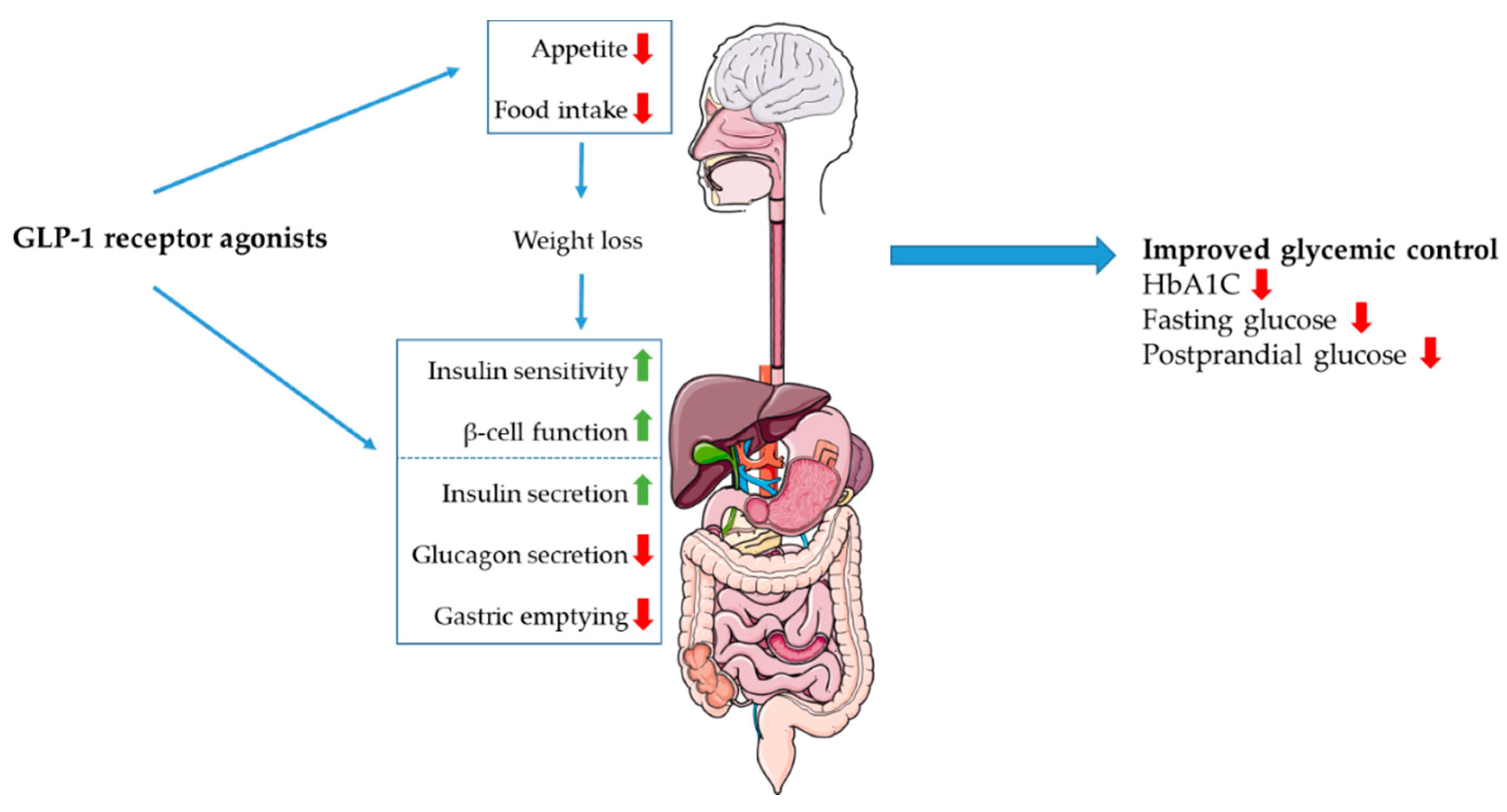
5.1. Incretin Receptor Agonists
5.2. DPP-4 Inhibitors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nauck, M.A.; Homberger, E.; Siegel, E.G.; Allen, R.C.; Eaton, R.P.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Incretin Effects of Increasing Glucose Loads in Man Calculated from Venous Insulin and C-Peptide Responses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 63, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.; Stöckmann, F.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Reduced incretin effect in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia 1986, 29, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Helsted, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Jensen, M.H.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Veedfald, S.; Stensen, S.; Lanng, A.R.; Bergmann, N.C.; et al. Separate and Combined Glucometabolic Effects of Endogenous Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide and Glucagon-like Peptide 1 in Healthy Individuals. Diabetes 2019, 68, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. GIP and GLP-1: Stepsiblings Rather Than Monozygotic Twins Within the Incretin Family. Diabetes 2019, 68, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Preserved incretin activity of glucagon-like peptide 1 [7-36 amide] but not of synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with type- 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Kleine, N.; Ørskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Willms, B.; Creutzfeldt, W. Normalization of fasting hyperglycaemia by exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36 amide) in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, M.; Madsbad, S.; Madsen, J.L.; Holst, J.J. Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: A parallel-group study. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2002, 359, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Ørskov, C.; Vagn Nielsen, O.; Schwartz, T.W. Truncated glucagon-like peptide I, an insulin-releasing hormone from the distal gut. FEBS Lett. 1987, 211, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissele, R.; GÖKe, R.; Willemer, S.; Harthus, H.P.; Vermeer, H.; Arnold, R.; GÖKe, B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 cells in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas of rat, pig and man. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 22, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solcia, E.; Capella, C.; Buffa, R.; Fiocca, R.; Frigerio, B.; Usellini, L. Identification, ultrastructure and classification of gut endocrine cells and related growths. Investig. Cell Pathol. 1980, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, C.F.; Vrang, N.; Torp Sangild, P.; Jelsing, J. Novel insight into the distribution of L-cells in the rat intestinal tract. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2013, 5, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Brubaker, P.L.; Drucker, D.J. Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of proglucagon gene expression. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ørskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Knuhtsen, S.; Baldissera, F.G.A.; Poulsen, S.S.; Nielsen, O.V. Glucagon-like peptides GLP-1 and GLP-2, predicted products of the glucagon gene, are secreted separately from pig small intestine but not pancreas. Endocrinology 1986, 119, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanvantari, S.; Seidah, N.G.; Brubaker, P.L. Role of prohormone convertases in the tissue-specific processing of proglucagon. Mol. Endocrinol. 1996, 10, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloth, B.; Holst, J.J.; Flint, A.; Gregersen, N.T.; Astrup, A. Effects of PYY1-36 and PYY3-36 on appetite, energy intake, energy expenditure, glucose and fat metabolism in obese and lean subjects. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1062–E1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.M.; Tatemoto, K.; Terenius, L.; Hellström, P.M.; Mutt, V.; Hökfelt, T.; Hamberger, B. Localization of peptide YY (PYY) in gastrointestinal endocrine cells and effects on intestinal blood flow and motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 4471–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinert, R.E.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Asarian, L.; Horowitz, M.; Beglinger, C.; Geary, N. Ghrelin, CCK, GLP-1, and PYY(3-36): Secretory Controls and Physiological Roles in Eating and Glycemia in Health, Obesity, and After RYGB. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 411–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, G.; Alumets, J.; Håkanson, R.; Sundler, F. Co-existence of glicentin and peptide YY in colorectal L-cells in cat and man. An electron microscopic study. Regul. Pept. 1986, 13, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.E.; Brubaker, P.L. Glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion by the L-cell: The view from within. Diabetes 2006, 55, S70–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.E.; Adriaenssens, A.; Rogers, G.; Richards, P.; Koepsell, H.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Predominant role of active versus facilitative glucose transport for glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Mechanisms underlying glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roder, P.V.; Geillinger, K.E.; Zietek, T.S.; Thorens, B.; Koepsell, H.; Daniel, H. The Role of SGLT1 and GLUT2 in Intestinal Glucose Transport and Sensing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psichas, A.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Gut chemosensing mechanisms. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, F.M.; Williams, L.; Simpson, A.K.; Reimann, F. A novel glucose-sensing mechanism contributing to glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from the GLUTag cell line. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakogiannaki, E.; Pais, R.; Tolhurst, G.; Parker, H.E.; Horscroft, J.; Rauscher, B.; Zietek, T.; Daniel, H.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Oligopeptides stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in mice through proton-coupled uptake and the calcium-sensing receptor. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modvig, I.M.; Kuhre, R.E.; Holst, J.J. Peptone-mediated glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion depends on intestinal absorption and activation of basolaterally located Calcium-Sensing Receptors. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conigrave, A.D.; Ward, D.T. Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR): Pharmacological properties and signaling pathways. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, O.J.; Schindler, M.; Patel, S. The regulation of K- and L-cell activity by GLUT2 and the calcium-sensing receptor CasR in rat small intestine. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2917–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolhurst, G.; Zheng, Y.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Glutamine triggers and potentiates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion by raising cytosolic Ca2+ and cAMP. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundström, L.; Myhre, S.; Sundqvist, M.; Ahnmark, A.; McCoull, W.; Raubo, P.; Groombridge, S.D.; Polla, M.; Nyström, A.C.; Kristensson, L.; et al. The acute glucose lowering effect of specific GPR120 activation in mice is mainly driven by glucagon-like peptide 1. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edfalk, S.; Steneberg, P.; Edlund, H. Gpr40 is expressed in enteroendocrine cells and mediates free fatty acid stimulation of incretin secretion. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psichas, A.; Larraufie, P.F.; Goldspink, D.A.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Chylomicrons stimulate incretin secretion in mouse and human cells. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.B.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Knop, F.K.; Wellner, N.; Diep, T.A.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Andersen, U.B.; Holst, J.J.; Hansen, H.S. 2-Oleoyl glycerol is a GPR119 agonist and signals GLP-1 release in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1409–E1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhre, R.E.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Larsen, O.; Jepsen, S.L.; Balk-Møller, E.; Andersen, D.B.; Deacon, C.F.; Schoonjans, K.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; et al. Bile acids are important direct and indirect regulators of the secretion of appetite- and metabolism-regulating hormones from the gut and pancreas. Mol. Metab. 2018, 11, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, C.B.; Trammell, S.A.J.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Schoonjans, K.; Albrechtsen, R.; Gillum, M.P.; Kuhre, R.E.; Holst, J.J. Bile acids drive colonic secretion of glucagon-like-peptide 1 and peptide-YY in rodents. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G574–G584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Christensen, M.B.; Hartmann, B.; Lanng, A.R.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Dela, F.; Vilsbøll, T.; Holst, J.J.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; et al. GIP(3-30)NH2 is an efficacious GIP receptor antagonist in humans: A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Diabetologia 2017, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberge, J.N.; Brubaker, P.L. Regulation of intestinal proglucagon-derived peptide secretion by glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide in a novel enteroendocrine loop. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, S.L.; Grunddal, K.V.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Jensen, E.P.; Ørskov, C.; Poulsen, S.S.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Pedersen, J.; et al. Paracrine crosstalk between intestinal L- And D-cells controls secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E1081–E1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veedfald, S.; Plamboeck, A.; Deacon, C.F.; Hartmann, B.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T.; Holst, J.J. Cephalic phase secretion of insulin and other enteropancreatic hormones in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G43–G51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.; Lampert, S.; Mineo, H.; Holst, J.J. Neural regulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in pigs. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E939–E947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Deacon, C.F. Physiology of the Incretin Hormones, GIP and GLP -1—Regulation of Release and Posttranslational Modifications. Compr. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1339–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orskov, C.; Bersani, M.; Johnsen, A.H.; Hojrup, P.; Holst, J.J. Complete sequences of glucagon-like peptide-1 from human and pig small intestine. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12826–12829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.; Deacon, C.F.; Ørskov, C.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)amide is transformed to glucagon-like peptide-1-(9-36)amide by dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the capillaries supplying the L cells of the porcine intestine. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 5356–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, C.F.; Plamboeck, A.; Møller, S.; Holst, J.J. GLP-1-(9-36) amide reduces blood glucose in anesthetized pigs by a mechanism that does not involve insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E873–E879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plamboeck, A.; Holst, J.J.; Carr, R.D.; Deacon, C.F. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 and dipeptidyl peptidase IV are both mediators of the degradation of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the anaesthetised pig. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjøllund, K.R.; Deacon, C.F.; Holst, J.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition increases portal concentrations of intact glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) to a greater extent than peripheral concentrations in anaesthetised pigs. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2206–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, A.; Simonsen, L.; Asmar, M.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J.; Frandsen, E.; Moro, C.; Jonassen, T.; Bülow, J. Renal extraction and acute effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on central and renal hemodynamics in healthy men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E641–E649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.K.; Richards, J.E.; Cook, D.R.; Brierley, D.I.; Williams, D.L.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Trapp, S. Preproglucagon Neurons in the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract Are the Main Source of Brain GLP-1, Mediate Stress-Induced Hypophagia, and Limit Unusually Large Intakes of Food. Diabetes 2019, 68, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrang, N.; Phifer, C.B.; Corkern, M.M.; Berthoud, H.R. Gastric distension induces c-Fos in medullary GLP-1/2-containing neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 285, R470–R478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisadome, K.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Trapp, S. Leptin directly depolarizes preproglucagon neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius: Electrical properties of glucagon-like Peptide 1 neurons. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, S.R.J. Mechanisms of peptide and nonpeptide ligand binding to Class B G-protein-coupled receptors. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J.S.; Tanizawa, Y.; Wheeler, M.B.; Leng, X.H.; Ligon, B.B.; Rabin, D.U.; Yoo-Warren, H.; Permutt, M.A.; Boyd, A.E., 3rd. Cloning and functional expression of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 1907–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, L.L.; Drucker, D.J. Biology of Incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2131–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.L.; Baskin, D.G.; Schwartz, M.W. Evidence that intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 plays a physiological role in satiety. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yang, L.; Hang, K.; Laursen, M.; Wu, L.; Han, G.W.; Ren, Q.; Roed, N.K.; Lin, G.; Hanson, M.A.; et al. Full-length human GLP-1 receptor structure without orthosteric ligands. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootten, D.; Reynolds, C.A.; Smith, K.J.; Mobarec, J.C.; Koole, C.; Savage, E.E.; Pabreja, K.; Simms, J.; Sridhar, R.; Furness, S.G.B.; et al. The Extracellular Surface of the GLP-1 Receptor Is a Molecular Trigger for Biased Agonism. Cell 2016, 165, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D′Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Dryburgh, J.R.; Ross, S.A.; Dupré, J. Identification and actions of gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1975, 31, 487–532. [Google Scholar]
- Sjölund, K.; Sandén, G.; Håkanson, R.; Sundler, F. Endocrine Cells in Human Intestine: An Immunocytochemical Study. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorsal, T.; Rhee, N.A.; Pedersen, J.; Wahlgren, C.D.; Mortensen, B.; Jepsen, S.L.; Jelsing, J.; Dalbøge, L.S.; Vilmann, P.; Hassan, H.; et al. Enteroendocrine K and L cells in healthy and type 2 diabetic individuals. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugleholdt, R.; Poulsen, M.L.H.; Holst, P.J.; Irminger, J.C.; Orskov, C.; Pedersen, J.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Zhu, X.; Steiner, D.F.; Holst, J.J. Prohormone convertase 1/3 is essential for processing of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11050–11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Asadi, A.; Yang, G.K.; Kwok, Y.N.; Kieffer, T.J. Differential processing of pro-glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in gut. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G608–G614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Wideman, R.D.; Asadi, A.; Yang, G.K.; Baker, R.; Webber, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R.; Ao, Z.; Warnock, G.L.; et al. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Is Expressed in Pancreatic Islet α-Cells and Promotes Insulin Secretion. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1966–1975.e1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okawa, M.; Fujii, K.; Ohbuchi, K.; Okumoto, M.; Aragane, K.; Sato, H.; Tamai, Y.; Seo, T.; Itoh, Y.; Yoshimoto, R. Role of MGAT2 and DGAT1 in the release of gut peptides after triglyceride ingestion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekberg, J.H.; Hauge, M.; Kristensen, L.V.; Madsen, A.N.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Husted, A.S.; Sichlau, R.; Egerod, K.L.; Timshel, P.; Kowalski, T.J.; et al. GPR119, a major enteroendocrine sensor of dietary triglyceride metabolites coacting in synergy with FFA1 (GPR40). Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4561–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankoda, A.; Harada, N.; Kato, T.; Ikeguchi, E.; Iwasaki, K.; Yamane, S.; Murata, Y.; Hirasawa, A.; Inagaki, N. Free fatty acid receptors, G protein-coupled receptor 120 and G protein-coupled receptor 40, are essential for oil-induced gastric inhibitory polypeptide secretion. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xian, Y.; Wang, C.; Ding, L.; Meng, X.; Zhu, W.; Hang, S. Calcium-sensing receptor-mediated L-tryptophan-induced secretion of cholecystokinin and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide in swine duodenum. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 19, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, G.R.; Pokol-Daniel, S. Neural modulation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) and insulin secretion in conscious dogs. Pancreas 1994, 9, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoud, H.R.; Trimble, E.R.; Moody, A.J. Lack of Gastric Inhibitory Polypepetide (GIP) response to vagal stimulation in the rat. Peptides 1982, 3, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, R.A.; Dryburgh, J.R.; Brown, J.C. The effect of somatostatin on release and insulinotropic action of gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1975, 53, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.; Hücking, K.; Holst, J.J. Degradation of endogenous and exogenous gastric inhibitory polypeptide in healthy and in type 2 diabetic subjects as revealed using a new assay for the intact peptide. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boer, G.A.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J. Pharmacokinetics of exogenous GIP(1-42) in C57Bl/6 mice; extremely rapid degradation but marked variation between available assays. Peptides 2020, 170457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlein, R.; Gallwitz, B.; Schmidt, W.E. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36)amide, peptide histidine methionine and is responsible for their degradation in human serum. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 214, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabe, M.B.N.; van der Velden, W.J.C.; Smit, F.X.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Molecular interactions of full-length and truncated GIP peptides with the GIP receptor–A comprehensive review. Peptides 2020, 125, 170224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupe-Sodmann, K.; McGregor, G.P.; Bridenbaugh, R.; Goke, R.; Goke, B.; Thole, H.; Zimmermann, B.; Voigt, K. Characterisation of the processing by human neutral endopeptidase 24.11 of GLP-1(7-36) amide and comparison of substrate specificity of the enzyme for other glucagon-like peptides. Regul. Pept. 1995, 58, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usdin, T.B.; Mezey, E.; Button, D.C.; Brownstein, M.J.; Bonner, T.I. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor, a member of the secretin- vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor family, is widely distributed in peripheral organs and the brain. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 2861–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollag, R.J.; Zhong, Q.; Phillips, P.; Min, L.; Zhong, L.; Cameron, R.; Mulloy, A.L.; Rasmussen, H.; Qin, F.; Ding, K.H.; et al. Osteoblast-derived cells express functional glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide receptors. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Biggs, E.K.; Darwish, T.; Tadross, J.; Sukthankar, T.; Girish, M.; Polex-Wolf, J.; Lam, B.Y.; Zvetkova, I.; Pan, W.; et al. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor-Expressing Cells in the Hypothalamus Regulate Food Intake. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 987–996.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabe, M.B.N.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Pedersen, M.F.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Inoue, A.; Bräuner-Osborne, H.; Hartmann, B.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Human GIP(3-30)NH(2) inhibits G protein-dependent as well as G protein-independent signaling and is selective for the GIP receptor with high-affinity binding to primate but not rodent GIP receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Patel, R.T.; Bruno, J.; Panhwar, M.S.; Wen, J.; McGraw, T.E. A Naturally occurring GIP receptor variant undergoes enhanced agonist-induced desensitization, which impairs GIP control of adipose insulin sensitivity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 3618–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Gherardi, M.-J.; Froese, A.; Zanoun, M.; Gigoux, V.; Clerc, P.; Gaits-Iacovoni, F.; Steyaert, J.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Fourmy, D. Internalized Receptor for Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Peptide stimulates adenylyl cyclase on early endosomes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 120, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Hansen, L.S.; Svendsen, B.; Christensen, M.; Knop, F.K.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Species-specific action of (Pro3)GIP -A full agonist at human GIP receptors, but a partial agonist and competitive antagonist at rat and mouse GIP receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Brown, J.C.; Ma, P.; Pederson, R.A.; McIntosh, C.H. Effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-I-(7-36) on insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 268, E645–E651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widenmaier, S.B.; Ao, Z.; Kim, S.J.; Warnock, G.; McIntosh, C.H.S. Suppression of p38 MAPK and JNK via Akt-mediated inhibition of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 constitutes a core component of the β-cell pro-survival effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30372–30382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farilla, L.; Hongxiang, H.; Bertolotto, C.; Kang, E.; Bulotta, A.; Mario, U.D.I.; Perfetti, R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 promotes islet cell growth and inhibits apoptosis in Zucker diabetic rats. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 4397–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seino, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Yabe, D. GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, J.J.; Gallwitz, B.; Siepmann, N.; Holst, J.J.; Deacon, C.F.; Schmidt, W.E.; Nauck, M.A. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) dose-dependently stimulates glucagon secretion in healthy human subjects at euglycaemia. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Heer, J.; Rasmussen, C.; Coy, D.H.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1, but not glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, inhibits glucagon secretion via somatostatin (receptor subtype 2) in the perfused rat pancreas. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El, K.; Campbell, J.E. The role of GIP in α-cells and glucagon secretion. Peptides 2020, 125, 170213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, T.J.; Pilichiewicz, A.N.; Russo, A.; Phillips, L.; Jones, K.L.; Nauck, M.A.; Wishart, J.; Horowitz, M.; Feinle-Bisset, C. Effects of intravenous glucagon-like peptide-1 on gastric emptying and intragastric distribution in healthy subjects: Relationships with postprandial glycemic and insulinemic responses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilsbøll, T.; Krarup, T.; Sonne, J.; Madsbad, S.; Vølund, A.; Juul, A.G.; Holst, J.J. Incretin secretion in relation to meal size and body weight in healthy subjects and people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Højberg, P.V.; Vilsbøll, T.; Rabøl, R.; Knop, F.K.; Bache, M.; Krarup, T.; Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S. Four weeks of near-normalisation of blood glucose improves the insulin response to glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 52, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilsbøll, T.; Krarup, T.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J. Defective amplification of the late phase insulin response to glucose by gip in obese type ii diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.B.; Calanna, S.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide: Blood Glucose Stabilizing Effects in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E418–E426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, A.; Satake, H.; Nakabayashi, H.; Nishizawa, M.; Furuya, K.; Nakano, S.; Kigoshi, T.; Nakayama, K.; Uchida, K. Receptor gene expression of glucagon-like peptide-1, but not glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, in rat nodose ganglion cells. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2004, 110, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Pedersen, J.; Knop, F.K. Glucagon and Amino Acids Are Linked in a Mutual Feedback Cycle: The Liver–α-Cell Axis. Diabetes 2017, 66, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzwiller, J.P.; Drewe, J.; Göke, B.; Schmidt, H.; Rohrer, B.; Lareida, J.; Beglinger, C. Glucagon-like peptide-1 promotes satiety and reduces food intake in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, R1541–R1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, M.D.; O′Shea, D.; Gunn, I.; Beak, S.A.; Edwards, C.M.; Meeran, K.; Choi, S.J.; Taylor, G.M.; Heath, M.M.; Lambert, P.D.; et al. A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 1996, 379, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shughrue, P.J.; Lane, M.V.; Merchenthaler, I. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1-R) mRNA in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5159–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, L.E.; Mietlicki-Baase, E.G.; Zimmer, D.J.; McGrath, L.E.; Olivos, D.R.; Hayes, M.R. Hindbrain GLP-1 receptor-mediated suppression of food intake requires a PI3K-dependent decrease in phosphorylation of membrane-bound Akt. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E751–E759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahl, T.P.; Tauchi, M.; Durler, T.S.; Elfers, E.E.; Fernandes, T.M.; Bitner, R.D.; Ellis, K.S.; Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J.; Herman, J.P.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors expressed on nerve terminals in the portal vein mediate the effects of endogenous GLP-1 on glucose tolerance in rats. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4965–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J. Incretin hormones and the satiation signal. Int. J. Obes. (2005) 2013, 37, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, C.R.; Monteiro, M.; Small, C.J.; Sajedi, A.; Smith, K.L.; Parkinson, J.R.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. The inhibitory effects of peripheral administration of peptide YY(3-36) and glucagon-like peptide-1 on food intake are attenuated by ablation of the vagal-brainstem-hypothalamic pathway. Brain Res. 2005, 1044, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plamboeck, A.; Veedfald, S.; Deacon, C.F.; Hartmann, B.; Wettergren, A.; Svendsen, L.B.; Meisner, S.; Hovendal, C.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K.; et al. The effect of exogenous GLP-1 on food intake is lost in male truncally vagotomized subjects with pyloroplasty. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G1117–G1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeran, K.; O′Shea, D.; Edwards, C.M.B.; Turton, M.D.; Heath, M.M.; Gunn, I.; Abusnana, S.; Rossi, M.; Small, C.J.; Goldstone, A.P.; et al. Repeated intracerebroventricular administration of glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide or exendin-(9-39) alters body weight in the rat. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, D.A.; Bagnol, D.; Woods, S.C.; D′Alessio, D.A.; Seeley, R.J. Arcuate glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors regulate glucose homeostasis but not food intake. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Kulve, J.S.; Veltman, D.J.; Van Bloemendaal, L.; Groot, P.F.C.; Ruhé, H.G.; Barkhof, F.; Diamant, M.; Ijzerman, R.G. Endogenous GLP1 and GLP1 analogue alter CNS responses to palatable food consumption. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 229, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roux, C.W.; Welbourn, R.; Werling, M.; Osborne, A.; Kokkinos, A.; Laurenius, A.; Lönroth, H.; Fändriks, L.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; et al. Gut hormones as mediators of appetite and weight loss after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. The glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide signaling axis in the central nervous system. Peptides 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Sloop, K.W.; Loghin, C.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Urva, S.; Bokvist, K.B.; Cui, X.; Briere, D.A.; Cabrera, O.; Roell, W.C.; et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørregaard, P.K.; Deryabina, M.A.; Tofteng Shelton, P.; Fog, J.U.; Daugaard, J.R.; Eriksson, P.-O.; Larsen, L.F.; Jessen, L. A novel GIP analogue, ZP4165, enhances glucagon-like peptide-1-induced body weight loss and improves glycaemic control in rodents. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killion, E.A.; Wang, J.; Yie, J.; Shi, S.D.H.; Bates, D.; Min, X.; Komorowski, R.; Hager, T.; Deng, L.; Atangan, L.; et al. Anti-obesity effects of GIPR antagonists alone and in combination with GLP-1R agonists in preclinical models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, E.A.; Chen, M.; Falsey, J.R.; Sivits, G.; Hager, T.; Atangan, L.; Helmering, J.; Lee, J.; Li, H.; Wu, B.; et al. Chronic glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) agonism desensitizes adipocyte GIPR activity mimicking functional GIPR antagonism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, V. GIP -The Obesity Hormone. In Current Approaches: Obesity; James, W.P.T., Parker, S.W., Eds.; Duphar Laboratories Limited: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ban, N.; Ihara, Y.; Tsukiyama, K.; Zhou, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Oku, A.; Tsuda, K.; Toyokuni, S.; et al. Inhibition of gastric inhibitory polypeptide signaling prevents obesity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, E.A.; Lu, S.C.; Fort, M.; Yamada, Y.; Véniant, M.M.; Lloyd, D.J. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor Therapies for the Treatment of Obesity, Do Agonists = Antagonists? Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, R.G.C.; Boylan, M.O.; Kieffer, T.J.; Wolfe, M.M. Functional GIP receptors are present on adipocytes. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4004–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Nian, C.; McIntosh, C.H.S. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in adipocytes: A role for a protein kinase B, LKB1, and AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8557–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, M.; Simonsen, L.; Madsbad, S.; Stallknecht, B.; Holst, J.J.; Bülow, J. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide may enhance fatty acid re-esterification in subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue in lean humans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, M.; Asmar, A.; Simonsen, L.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Dela, F.; Holst, J.J.; Bülow, J. The gluco-and liporegulatory and vasodilatory effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are abolished by an antagonist of the human GIP receptor. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thondam, S.K.; Daousi, C.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Holst, J.J.; Ameen, G.I.; Yang, C.; Whitmore, C.; Mora, S.; Cuthbertson, D.J. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide promotes lipid deposition in subcutaneous adipocytes in obese type 2 diabetes patients: A maladaptive response. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 312, E224–E233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.; Zhang, X.; Barrett, E.J.; Liu, Z. Glucagon-like peptide 1 recruits muscle microvasculature and improves insulin′s metabolic action in the presence of insulin resistance. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2788–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challa, T.D.; Beaton, N.; Arnold, M.; Rudofsky, G.; Langhans, W.; Wolfrum, C. Regulation of adipocyte formation by GLP-1/GLP-1R signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6421–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hygum, K.; Starup-Linde, J.; Harsløf, T.; Vestergaard, P.; Langdahl, B.L. Diabetes mellitus, a state of low bone turnover-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, R137–R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensen, S.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Helsted, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Christensen, M.B.; Knop, F.K. GIP and the gut-bone axis–Physiological, pathophysiological and potential therapeutic implications. Peptides 2020, 125, 170197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torekov, S.S.; Harsløf, T.; Rejnmark, L.; Eiken, P.; Jensen, J.B.; Herman, A.P.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Holst, J.J.; Langdahl, B.L. A functional amino acid substitution in the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) gene is associated with lower bone mineral density and increased fracture risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E729–E773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, N.C.; Lund, A.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Jessen, L.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Christensen, M.B.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Separate and Combined Effects of GIP and GLP-1 Infusions on Bone Metabolism in Overweight Men Without Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krarup, T.; Saurbrey, N.; Moody, A.J.; Kühl, C.; Madsbad, S. Effect of porcine gastric inhibitory polypeptide on β-cell function in type I and type II diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 1987, 36, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, N.; O′Harte, F.P.M.; Gault, V.A.; Green, B.D.; Greer, B.; Harriott, P.; Bailey, C.J.; Flatt, P.R. GIP(Lys16PAL) and GIP(Lys37PAL): Novel Long-Acting Acylated Analogues of Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide with Improved Antidiabetic Potential. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinke, S.A.; Gelling, R.W.; Pederson, R.A.; Manhart, S.; Nian, C.; Demuth, H.-U.; McIntosh, C.H.S. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV-Resistant [d-Ala2]Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) Improves Glucose Tolerance in Normal and Obese Diabetic Rats. Diabetes 2002, 51, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, V.A.; Kerr, B.D.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. C-terminal mini-PEGylation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide exhibits metabolic stability and improved glucose homeostasis in dietary-induced diabetes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F.; Pridal, L.; Klarskov, L.; Olesen, M.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 undergoes differential tissue-specific metabolism in the anesthetized pig. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 271, E458–E464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göke, R.; Fehmann, H.C.; Linn, T.; Schmidt, H.; Krause, M.; Eng, J.; Göke, B. Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-(9-39)-amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide 1-(7-36)-amide receptor of insulin-secreting beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 19650–19655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B.; Porret, A.; Bühler, L.; Deng, S.P.; Morel, P.; Widmann, C. Cloning and functional expression of the human islet GLP-1 receptor. Demonstration that exendin-4 is an agonist and exendin-(9-39) an antagonist of the receptor. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.M.B.; Stanley, S.A.; Davis, R.; Brynes, A.E.; Frost, G.S.; Seal, L.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Exendin-4 reduces fasting and postprandial glucose and decreases energy intake in healthy volunteers. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E155–E161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolterman, O.G.; Kim, D.D.; Shen, L.; Ruggles, J.A.; Nielsen, L.L.; Fineman, M.S.; Baron, A.D. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of exenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2005, 62, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A. Exenatide (Byetta) as a novel treatment option for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Proc (Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent.) 2006, 19, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilsboll, T. Liraglutide: A new treatment for type 2 diabetes. Drugs Today (Barc.) 2009, 45, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Nielsen, P.F.; Huusfeldt, P.O.; Johansen, N.L.; Madsen, K.; Pedersen, F.Z.; Thøgersen, H.; Wilken, M.; Agersø, H. Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. Incretin therapy for diabetes mellitus type 2. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2020, 27, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Petrie, J.R.; Sesti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Courrèges, J.P.; Lindegaard, M.L.; Jensen, C.B.; Atkin, S.L. A Phase 2, Randomized, Dose-Finding Study of the Novel Once-Weekly Human GLP-1 Analog, Semaglutide, Compared With Placebo and Open-Label Liraglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratley, R.E.; Aroda, V.R.; Lingvay, I.; Lüdemann, J.; Andreassen, C.; Navarria, A.; Viljoen, A. Semaglutide versus dulaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): A randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; D′Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanami, D.; Takashi, Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Clinical Outcomes to Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górriz, J.L.; Soler, M.J.; Navarro-González, J.F.; García-Carro, C.; Puchades, M.J.; D′Marco, L.; Martínez Castelao, A.; Fernández-Fernández, B.; Ortiz, A.; Górriz-Zambrano, C.; et al. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Call of Attention to Nephrologists. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular mechanisms by which GLP-1 RA and DPP-4i induce insulin sensitivity. Life Sci. 2019, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinnouchi, H.; Sugiyama, S.; Yoshida, A.; Hieshima, K.; Kurinami, N.; Suzuki, T.; Miyamoto, F.; Kajiwara, K.; Matsui, K.; Jinnouchi, T. Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, increased insulin sensitivity assessed by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp examination in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 706416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Del Prato, S.; Ludvik, B.; Milicevic, Z.; de la Peña, A.; Shurzinske, L.; Karanikas, C.A.; Pechtner, V. Differential effects of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide and metformin on pancreatic β-cell and insulin sensitivity during a standardized test meal in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.A.; Capehorn, M.S.; Garg, S.K.; Jódar Gimeno, E.; Hansen, O.H.; Holst, A.G.; Nayak, G.; Seufert, J. Reductions in Insulin Resistance are Mediated Primarily via Weight Loss in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes on Semaglutide. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4078–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Sattar, N. Understanding the mechanisms of reversal of type 2 diabetes. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Bartels, E.; Orskov, C.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Additive insulinotropic effects of exogenous synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36) amide infused at near-physiological insulinotropic hormone and glucose concentrations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J. GIP analogues and the treatment of obesity-diabetes. Peptides 2020, 125, 170202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Nauck, M.A.; Van, J.; Kutner, M.E.; Cui, X.; Benson, C.; Urva, S.; Gimeno, R.E.; Milicevic, Z.; Robins, D.; et al. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 2180–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.; Miossec, P.; Larsen, B.D.; Werner, U.; Knop, F.K. The design and discovery of lixisenatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 1223–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, A.N.; Juris, J.M. MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Are all GLP-1 agonists equal in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R211–R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, S. A review of GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A focus on the mechanism of action of once-weekly agents. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Yang, B.; Ottaway, N.; Smiley, D.L.; Ma, T.; Clemmensen, C.; Chabenne, J.; Zhang, L.; Habegger, K.M.; Fischer, K.; et al. A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, V.A.; Bhat, V.K.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. A novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)/glucagon hybrid peptide with triple-acting agonist activity at glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors and therapeutic potential in high fat-fed mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35581–35591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Ma, T.; Ottaway, N.; Müller, T.D.; Habegger, K.M.; Heppner, K.M.; Kirchner, H.; Holland, J.; Hembree, J.; Raver, C.; et al. Unimolecular dual incretins maximize metabolic benefits in rodents, monkeys, and humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, C.F.; Danielsen, P.; Klarskov, L.; Olesen, M.; Holst, J.J. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibition Reduces the Degradation and Clearance of GIP and Potentiates Its Insulinotropic and Antihyperglycemic Effects in Anesthetized Pigs. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D Deacon, C.F. A review of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Hot topics from randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Structure | FDA Approved | Dosage Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exenatide | Synthetic exendin-4, amino acid substitution at position 2 | 2005 | Twice daily |
| Lixisenatide | Based on exendin-4, amino acid substitution at position 2. Deletion of proline36 and C-terminally addition of a poly-lysine tail | 2016 | Once daily |
| Liraglutide | Acylated mammalian GLP-1 | 2010 | Once daily |
| Dulaglutide | Two stable GLP-1 moieties linked to an immunoglobulin fragment | 2014 | Once-weekly |
| Semaglutide | Acylated mammalian GLP-1, amino acid substitution at position 2. | Subcutaneous injection: 2017 Oral administration: 2019 | Subcutaneous injection: once weekly Oral administration: once daily |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boer, G.A.; Holst, J.J. Incretin Hormones and Type 2 Diabetes—Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Approaches. Biology 2020, 9, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120473
Boer GA, Holst JJ. Incretin Hormones and Type 2 Diabetes—Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Approaches. Biology. 2020; 9(12):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120473
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoer, Geke Aline, and Jens Juul Holst. 2020. "Incretin Hormones and Type 2 Diabetes—Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Approaches" Biology 9, no. 12: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120473
APA StyleBoer, G. A., & Holst, J. J. (2020). Incretin Hormones and Type 2 Diabetes—Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Approaches. Biology, 9(12), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120473






