Another Example of Conditioned Taste Aversion: Case of Snails
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
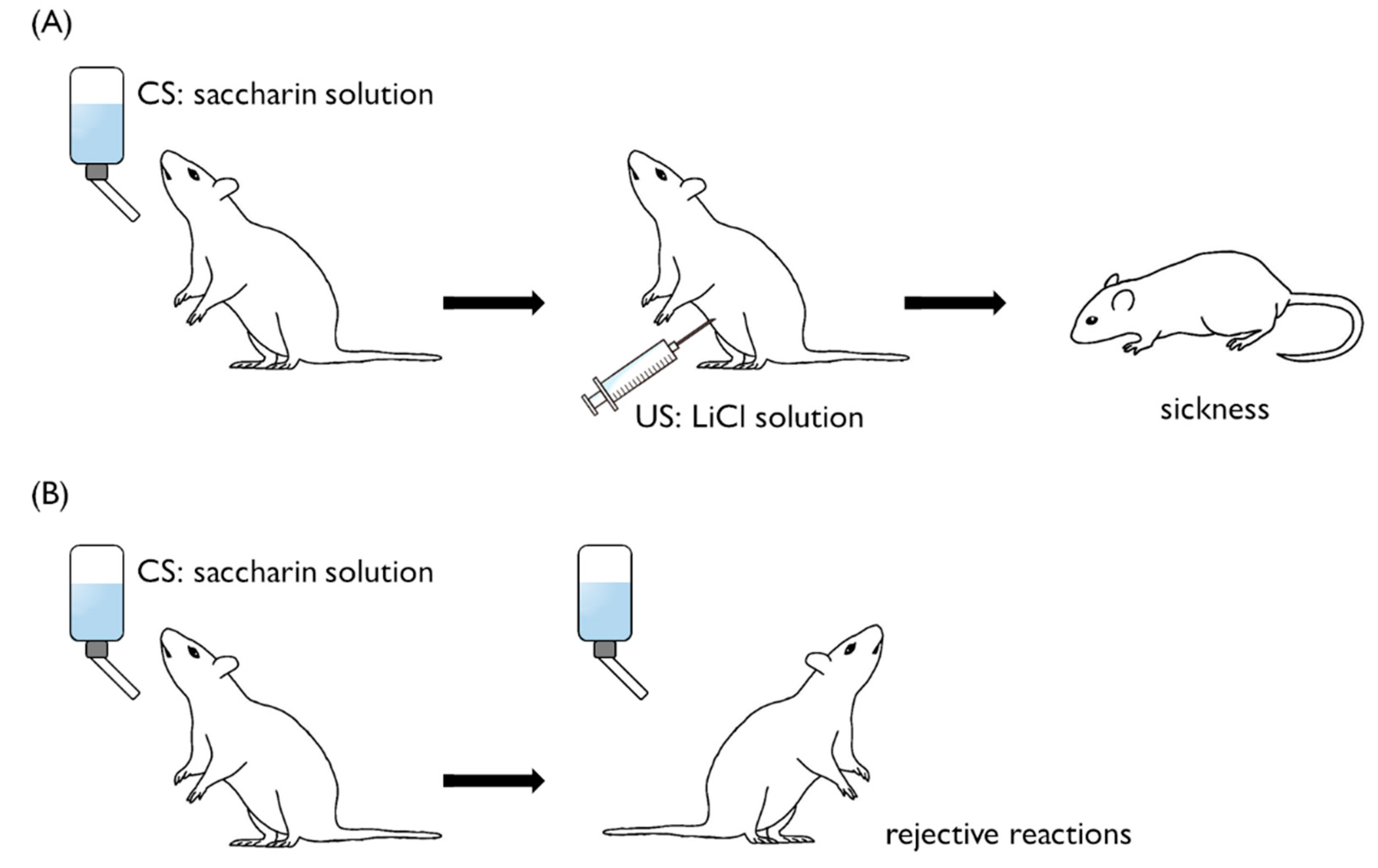
2. Conditioned Taste Aversion in Mammals
2.1. Selective Associability and Latent Inhibition
2.2. Long-Delay Learning
2.3. Single-Trial Learning
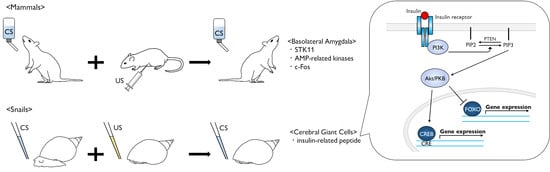
3. Molecular Events in Mammalian CTA
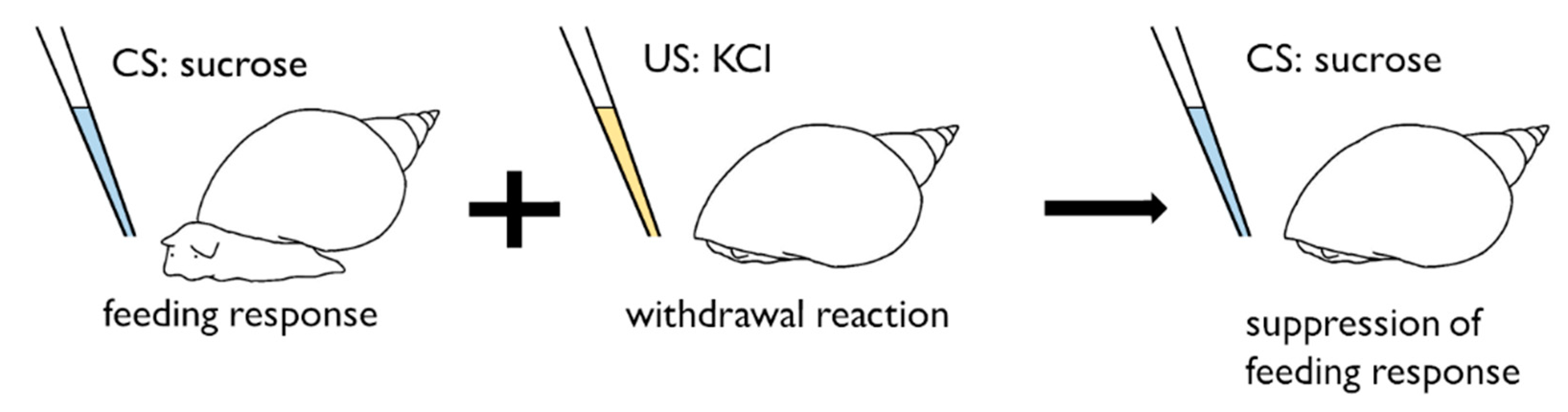
4. Conditioned Taste Aversion in Snails
5. ‘Necessity Knows No Law’ Manner of Snail CTA
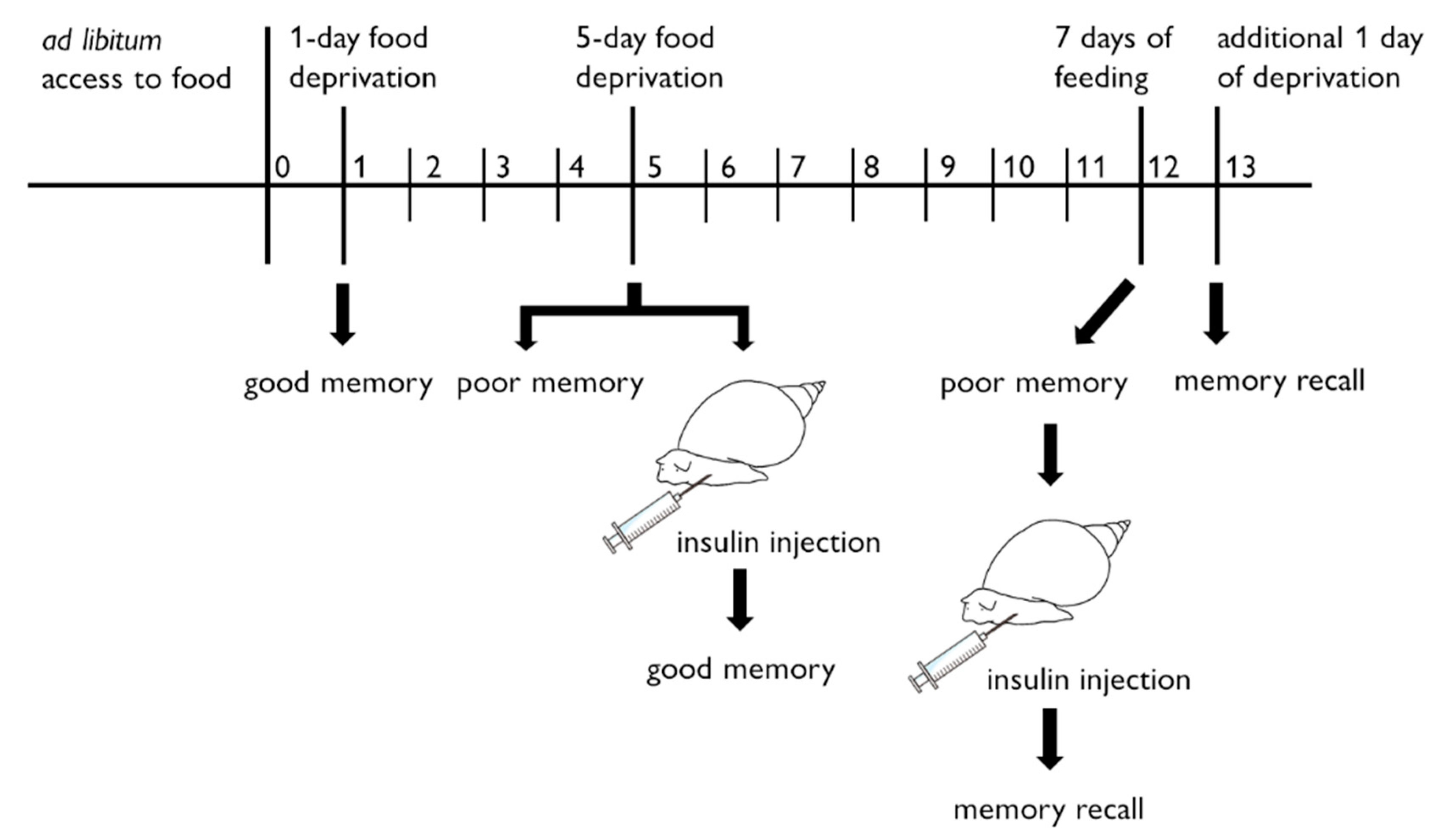
6. Role of Insulin-Related Peptide in Learning and Memory Formation for Snail CTA
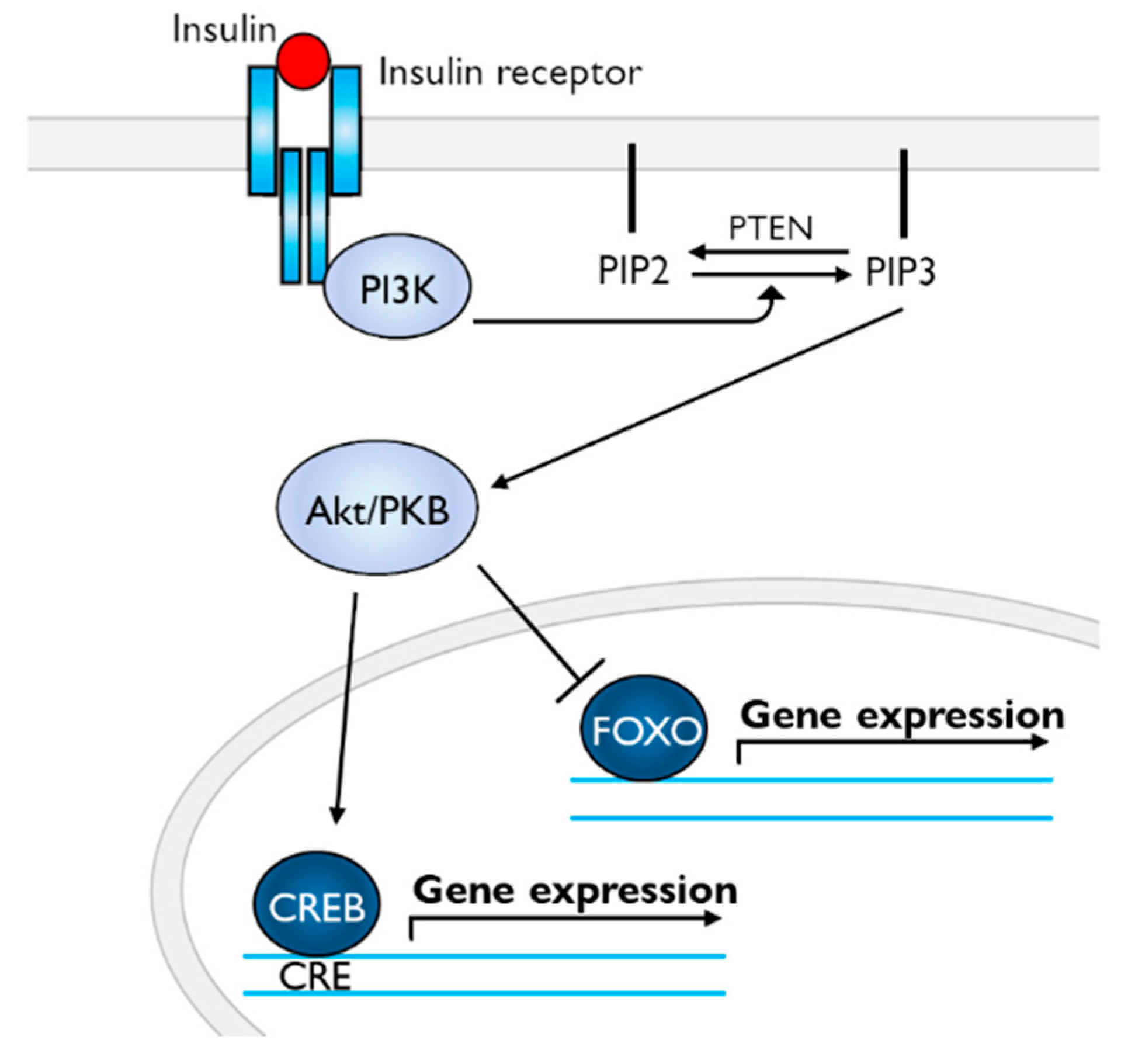
7. Perspectives in Molecular Events after Insulin Reception
8. Role of Insulin in Mammalian Brain
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schafe, G.E.; Bernstein, I.L. Taste aversion learning. In Why We Eat What We Eat: The Psychology of Eating; Capaldi, E.D., Ed.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.; Schachtman, T.R. Conditioned Taste Aversion: Behavioral and Neural Processes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, K.C. Conditioned taste aversions. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudai, Y. The Neurobiology of Memory; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, K.B.; Riley, A.L. The Origins of Conditioned Taste Aversion Learning: A Historical Analysis. In Conditioned Taste Aversion, Behavioral and Neural Processes; Reilly, S., Schachtman, T.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 8–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bures, J.; Bermudez-Rattoni, F.; Yamamoto, T. Conditioned Taste Aversion: Memory of a Special Kind; Oxford Psychology Series No. 31; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S. Effect of pretrial running on running-based taste aversion learning in rats. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Learn. Cogn. 2020, 46, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karniol, I.G.; Dalton, J.; Lader, M.H. Acute and chronic effects of lithium chloride on physiological and psychological measures in normals. Psychopharmacology 1978, 57, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meachum, C.L.; Bernstein, I.L. Conditioned responses to a taste conditioned stimulus paired with lithium chloride administration. Behav. Neurosci. 1990, 104, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, D.; Brown, R.; King, M.; Husband, A. Modulation of body temperature through taste aversion conditioning. Physiol. Behav. 1991, 49, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Kimeldorf, D.J.; Koelling, R.A. Conditioned aversion to saccharin resulting from exposure to gamma radiation. Science 1955, 122, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Lasiter, P.S.; Bermudez-Rattoni, F.; Deems, D.A. A General Theory of Aversion Learning. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1985, 443, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Koelling, R.A. Relation of cue to consequence in avoidance learning. Psychon. Sci. 1966, 4, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, R.A. Selective Associations: A Methodological Critique. Psychol. Rec. 1992, 42, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garb, J.L.; Stunkard, A.J. Taste aversions in man. Am. J. Psychiatry 1974, 131, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, A.C.; Smith, J.C.; Hollander, G.R. A comparison of dependent measures used to quantify radiation-induced taste aversion. Physiol. Behav. 1981, 27, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, A.C.; Smith, J.C.; Hollander, G.R. The effect of postconditioning CS experience on recovery from radiation-induced taste aversion. Physiol. Behav. 1983, 30, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revusky, S.H.; Bedarf, E.W. Association of Illness with Prior Ingestion of Novel Foods. Science 1967, 155, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalat, J.W.; Rozin, P. “Learned safety” as a mechanism in long-delay taste-aversion learning in rats. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1973, 83, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Ervin, F.R.; Koelling, R.A. Learning with prolonged delay of reinforcement. Psychon. Sci. 1966, 5, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etscorn, F.; Stephens, R. Establishment of conditioned taste aversions with a 24-h CS-US interval. Physiol. Psychol. 1973, 1, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafe, G.E.; Sollars, S.I.; Bernstein, I.L. The CS–US interval and taste aversion learning: A brief look. Behav. Neurosci. 1995, 109, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.; Hankins, W.G.; Rusiniak, K.W. Behavioral Regulation of the Milieu Interne in Man and Rat. Science 1974, 185, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swank, M.W.; Bernstein, I.L. c-Fos induction in response to a conditioned stimulus after single trial taste aversion learning. Brain Res. 1994, 636, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtman, T.R.; Ramsey, A.; Pineño, O. Postconditioning event manipulations on processing of the target conditioned stimulus in conditioned taste aversion. In Conditioned Taste Aversion, Behavioral and Neural Processes; Reilly, S., Schachtman, T.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 134–158. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, D.M.; Burgess, K.V.; Honey, R.C. Avoidance but not aversion following sensory preconditioning with flavors: A challenge to stimulus substitution. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process 2012, 38, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, D.; Liu, C.; Yang, T.; Shima, Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Wachutka, J.; Marrero, Y.; Ali Marandi Ghoddousi, R.; da Veiga Beltrame, E.; Richter, T.A.; et al. Deletion of Stk11 and Fos in mouse BLA projection neurons alters intrinsic excitability and impairs formation of long-term aversive memory. eLife 2020, 9, e61036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki-Harrington, L.; Belelovsky, K.; Doron, G.; Rosenblum, K. Molecular mechanisms of taste learning in the insular cortex and amygdala. In Conditioned Taste Aversion, Behavioral and Neural Processes; Reilly, S., Schachtman, T.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 341–363. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.-I.; Ferreira, G.; Ramírez-Lugo, L.; Bermudez-Rattoni, F. Glutamatergic activity in the amygdala signals visceral input during taste memory formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11417–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.; Miranda, M.-I.; De La Cruz, V.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, C.; Bermúdez-Rattoni, F. Basolateral amygdala glutamatergic activation enhances taste aversion through NMDA receptor activation in the insular cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 2596–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, B.; Tapia, R. Biochemical modulation of NMDA receptors: Role in conditioned taste aversion. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, S.L.; De La Cruz, V.; Bermudez-Rattoni, F.; Coutureau, E.; Ferreira, G. Differential role of insular cortex muscarinic and NMDA receptors in one-trial appetitive taste learning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 116, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitan, D.; Gal-Ben-Ari, S.; Heise, C.; Rosenberg, T.; Elkobi, A.; Inberg, S.; Sala, C.; Rosenblum, K. The differential role of cortical protein synthesis in taste memory formation and persistence. NPJ Sci. Learn. 2016, 1, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamprecht, R.; Dudai, Y. Differential modulation of brain immediate early genes by intraperitoneal LiCl. Neuroreport 1995, 7, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannakas, A.; Rosenblum, K. The Insula and Taste Learning. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, M.S.; Bruno, S.; Fontanini, A.; Maffei, A. LTD at amygdalocortical synapses as a novel mechanism for hedonic learning. eLife 2020, 9, 55175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, M.L.; Figueroa-Guzmán, Y.; Gómez-Palacio-Schjetnan, A. In vivo insular cortex LTP induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Brain Res. 2003, 991, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, D.V.; Escobar, M.L. A role for MAPK and PI-3K signaling pathways in brain-derived neurotrophic factor modification of conditioned taste aversion retention. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 217, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alapin, J.M.; Dines, M.; Lamprecht, R. EphB2 receptor forward signaling is needed for normal long-term memory formation in aged mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 86, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, X.-P.; Parkinson, D.B. Classic axon guidance molecules control correct nerve bridge tissue formation and precise axon regeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.D.; Fraley, S.M. Extinction of a conditioned taste aversion in young, mid-aged, and aged C57/BL6 mice. Behav. Neural Biol. 1981, 32, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Yamanaka, M.; Fujito, Y.; Ito, E. Differential Neuroethological Effects of Aversive and Appetitive Reinforcing Stimuli on Associative Learning in Lymnaea stagnalis. Zool. Sci. 1996, 13, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Kojima, S.; Sadamoto, H.; Hatakeyama, D. Associative Learning in the Pond Snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. Zool. Sci. 1999, 16, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Kojima, S.; Lukowiak, K.; Sakakibara, M. From likes to dislikes: Conditioned taste aversion in the great pond snail (Lymnaea stagnalis). Can. J. Zool. 2013, 91, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Yamagishi, M.; Takigami, S.; Sakakibara, M.; Fujito, Y.; Lukowiak, K. The Yerkes-Dodson law and appropriate stimuli for conditioned taste aversion in Lymnaea. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totani, Y.; Kotani, S.; Odai, K.; Ito, E.; Sakakibara, M. Real-Time Analysis of Animal Feeding Behavior With a Low-Calculation-Power CPU. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, J.; Totani, Y.; Kojima, S.; Sakakibara, M.; Ito, E. Features of behavioral changes underlying conditioned taste aversion in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2020, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavson, C.R.; Gustavson, J.C. Predation Control Using Conditioned Food Aversion Methodology: Theory, Practice, and Implications. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1985, 443, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Despouy, E.; Sandoz, J.-C.; Su, S.; de Brito Sanchez, M.G.; Giurfa, M. Degradation of an appetitive olfactory memory via devaluation of sugar reward is mediated by 5-HT signaling in the honey bee. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2020, 173, 107278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Nanakamura, H.; Nagayama, S.; Fujito, Y.; Ito, E. Enhancement of an inhibitory input to the feeding central pattern generator in Lymnaea stagnalis during conditioned taste-aversion learning. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 230, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, E.; Matsunaga, M.; Okada, R.; Yamagishi, M.; Okuta, A.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Increase in cyclic AMP concentration in a cerebral giant interneuron mimics part of a memory trace for conditioned taste aversion of the pond snail. Biophysics 2013, 9, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sunada, H.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Cerebral Giant Cells are Necessary for the Formation and Recall of Memory of Conditioned Taste Aversion in Lymnaea. Zool. Sci. 2017, 34, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugai, R.; Azami, S.; Shiga, H.; Watanabe, T.; Sadamoto, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Hatakeyama, D.; Fujito, Y.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. One-trial conditioned taste aversion in Lymnaea: Good and poor performers in long-term memory acquisition. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerkes, R.M.; Dodson, J.D. The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation. J. Comp. Neurol. Psychol. 1908, 18, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Yamagishi, M.; Hatakeyama, D.; Watanabe, T.; Fujito, Y.; Dyakonova, V.; Lukowiak, K. Memory block: A consequence of conflict resolution. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, E.; Totani, Y.; Oike, A. Necessity knows no law in a snail. Eur. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulka, P.; Klein, S. Resistance to Extinction of a Taste Aversion: Effects of Level of Training and Procedures Used in Acquisition and Extinction. Am. J. Psychol. 1980, 93, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, S.; Wagatsuma, A.; Sadamoto, H.; Hatakeyama, D.; Usami, T.; Fujie, M.; Koyanagi, R.; Azumi, K.; Fujito, Y.; Lukowiak, K.; et al. Altered gene activity correlated with long-term memory formation of conditioned taste aversion in Lymnaea. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, J.; Okada, R.; Sadamoto, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Mita, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yamagishi, M.; Hatakeyama, D.; Otsuka, E.; Okuta, A.; et al. Involvement of Insulin-Like Peptide in Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity and Long-Term Memory of the Pond Snail Lymnaea stagnalis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, J.; Okada, R.; Fujito, Y.; Sakakibara, M.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Paired pulse ratio analysis of insulin-induced synaptic plasticity in the snail brain. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, D.; Okuta, A.; Otsuka, E.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Consolidation of long-term memory by insulin in Lymnaea is not brought about by changing the number of insulin receptors. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2013, 6, e23955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, K.; Okuta, A.; Okada, R.; Hatakeyama, D.; Otsuka, E.; Yamagishi, M.; Morikawa, M.; Naganuma, Y.; Fujito, Y.; Dyakonova, V.; et al. What are the elements of motivation for acquisition of conditioned taste aversion? Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 107, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, K.; Yamagishi, M.; Fujito, Y.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. An increase in insulin is important for the acquisition conditioned taste aversion in Lymnaea. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2014, 116, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Sunada, H.; Mita, K.; Sakakibara, M.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Function of insulin in snail brain in associative learning. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2015, 201, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aonuma, H.; Totani, Y.; Kaneda, M.; Nakamura, R.; Watanabe, T.; Hatakeyama, D.; Dyakonova, V.E.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Effects of 5-HT and insulin on learning and memory formation in food-deprived snails. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2018, 148, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totani, Y.; Aonuma, H.; Oike, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hatakeyama, D.; Sakakibara, M.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Monoamines, Insulin and the Roles They Play in Associative Learning in Pond Snails. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totani, Y.; Nakai, J.; Dyakonova, V.; Lukowiak, K.; Sakakibara, M.; Ito, E. Induction of LTM following an Insulin Injection. eNeuro 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrett, R.J.; Keen, H. Diurnal Variation of Oral Glucose Tolerance: A Possible Pointer to the Evolution of Diabetes Mellitus. BMJ 1969, 2, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauter, E.; Polonsky, K.S.; Scheen, A.J. Roles of Circadian Rhythmicity and Sleep in Human Glucose Regulation. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 716–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P. An Evolutionary Perspective on Why Food Overconsumption Impairs Cognition. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagatsuma, A.; Sugai, R.; Chono, K.; Azami, S.; Hatakeyama, D.; Sadamoto, H.; Ito, E. The early snail acquires the learning. Comparison of scores for conditioned taste aversion between morning and afternoon. Acta Biol. Hung. 2004, 55, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Webb, A.E. Neuronal functions of FOXO/DAF-16. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 4, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nässel, D.R.; Zandawala, M. Recent advances in neuropeptide signaling in Drosophila, from genes to physiology and behavior. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 179, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Saitoe, M. Hunger and memory; CRTC coordinates long-term memory with the physiological state, hunger. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2013, 6, e25152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altarejos, J.Y.; Montminy, M. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: Sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totani, Y.; Nakai, J.; Ito, E. Impact of insulin on memory recall. J. Data Min. Genom. Proteom. 2020, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totani, Y.; Nakai, J.; Hatakeyama, D.; Ito, E. Memory-enhancing effects of short-term fasting. Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin Receptor Isoforms and Insulin Receptor/Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Hybrids in Physiology and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Montminy, M. CREB Is a Regulatory Target for the Protein Kinase Akt/PKB. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32377–32379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Ding, J.; Du, K. Differential activation of CREB by Akt1 and Akt2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 54, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Torres-Alemán, I. The many faces of insulin-like peptide signalling in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.J.; Serfozo, Z.; Papp, A.; Kemenes, I.; O’Shea, M.; Yin, J.C.P.; Benjamin, P.R.; Kemenes, G. Cyclic AMP response element-binding (CREB)-like proteins in a molluscan brain: Cellular localization and learning-induced phosphorylation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadamoto, H.; Sato, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Murakami, J.; Aonuma, H.; Ando, H.; Fujito, Y.; Hamano, K.; Awaji, M.; Lukowiak, K.; et al. CREB in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis: Cloning, gene expression, and function in identifiable neurons of the central nervous system. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 58, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagatsuma, A.; Azami, S.; Sakura, M.; Hatakeyama, D.; Aonuma, H.; Ito, E. De Novo synthesis of CREB in a presynaptic neuron is required for synaptic enhancement involved in memory consolidation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadamoto, H.; Kitahashi, T.; Fujito, Y.; Ito, E. Learning-dependent gene expression of CREB1 isoforms in the molluscan brain. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadamoto, H.; Saito, K.; Muto, H.; Kinjo, M.; Ito, E. Direct Observation of Dimerization between Different CREB1 Isoforms in a Living Cell. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagatsuma, A.; Sadamoto, H.; Kitahashi, T.; Lukowiak, K.; Urano, A.; Ito, E. Determination of the exact copy numbers of particular mRNAs in a single cell by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horwood, J.M.; Dufour, F.; Laroche, S.; Davis, S. Signalling mechanisms mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt cascade in synaptic plasticity and memory in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 3375–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, N. Interplay between FOXO, TOR, and Akt. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, T.; Iino, Y.; Tomioka, M. DAF-16/FOXO promotes taste avoidance learning independently of axonal insulin-like signaling. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitakis, Z.; Tatavarthy, M.; Bennett, D.A. The Relation of Diabetes to Memory Function. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, R.A.L.; Harmer, A.R.; Freitas, D.A.; Mendonça, V.A.; Lacerda, A.C.R.; Leite, H.R. An update on potential links between type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6347–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Jiménez, M.; Zaarkti, A.; García-Arnés, J.A.; García-Casares, N. Antidiabetic Drugs in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellar, D.; Craft, S. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowles, J.E.; Keane, K.N.; Gomes Heck, T.; Cruzat, V.; Verdile, G.; Newsholme, P. Are Heat Shock Proteins an Important Link between Type 2 Diabetes and Alzheimer Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.H.; Sun, L.H.; Yang, W.; Li, B.J.; Cui, R. Potential role of insulin on the pathogenesis of depression. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.H.; Fatima, M.; Mondal, A.C. Role of Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis, Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis and Insulin Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropsychobiology 2019, 77, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, A. Is the HPA Axis as Target for Depression Outdated, or Is There a New Hope? Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Yamada, T.; Mitani, H.; Yamada, S.; Pu, S.; Yamanashi, T.; Matsumura, H.; Nakagome, K.; Kaneko, K. Relationship between hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis dysregulation and insulin resistance in elderly patients with depression. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 226, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunada, H.; Totani, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Sakakibara, M.; Lukowiak, K.; Ito, E. Two Strains of Lymnaea stagnalis and the Progeny from Their Mating Display Differential Memory-Forming Ability on Associative Learning Tasks. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marosi, K.; Moehl, K.; Navas-Enamorado, I.; Mitchell, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Lehrmann, E.; Aon, M.A.; Cortassa, S.; Becker, K.G.; Mattson, M.P. Metabolic and molecular framework for the enhancement of endurance by intermittent food deprivation. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3844–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockman, M.-C.; Thomas, D.D.; Burke, J.; Apovian, C.M. Intermittent Fasting: Is the Wait Worth the Weight? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Dey, A.; Yu, X.; Stranahan, A.M. Dietary obesity reversibly induces synaptic stripping by microglia and impairs hippocampal plasticity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 51, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Longo, V.D.; Harvie, M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakai, J.; Totani, Y.; Hatakeyama, D.; Dyakonova, V.E.; Ito, E. Another Example of Conditioned Taste Aversion: Case of Snails. Biology 2020, 9, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120422
Nakai J, Totani Y, Hatakeyama D, Dyakonova VE, Ito E. Another Example of Conditioned Taste Aversion: Case of Snails. Biology. 2020; 9(12):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120422
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakai, Junko, Yuki Totani, Dai Hatakeyama, Varvara E. Dyakonova, and Etsuro Ito. 2020. "Another Example of Conditioned Taste Aversion: Case of Snails" Biology 9, no. 12: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120422
APA StyleNakai, J., Totani, Y., Hatakeyama, D., Dyakonova, V. E., & Ito, E. (2020). Another Example of Conditioned Taste Aversion: Case of Snails. Biology, 9(12), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9120422