Loss of Class III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Vps34 Results in Cone Degeneration
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of Cone Photoreceptor Cells by Density Step-Gradient Centrifugation
2.4. Determination of PI(3)P Levels in Cone-Dominant Nrl−/− and Ground Squirrel Retina
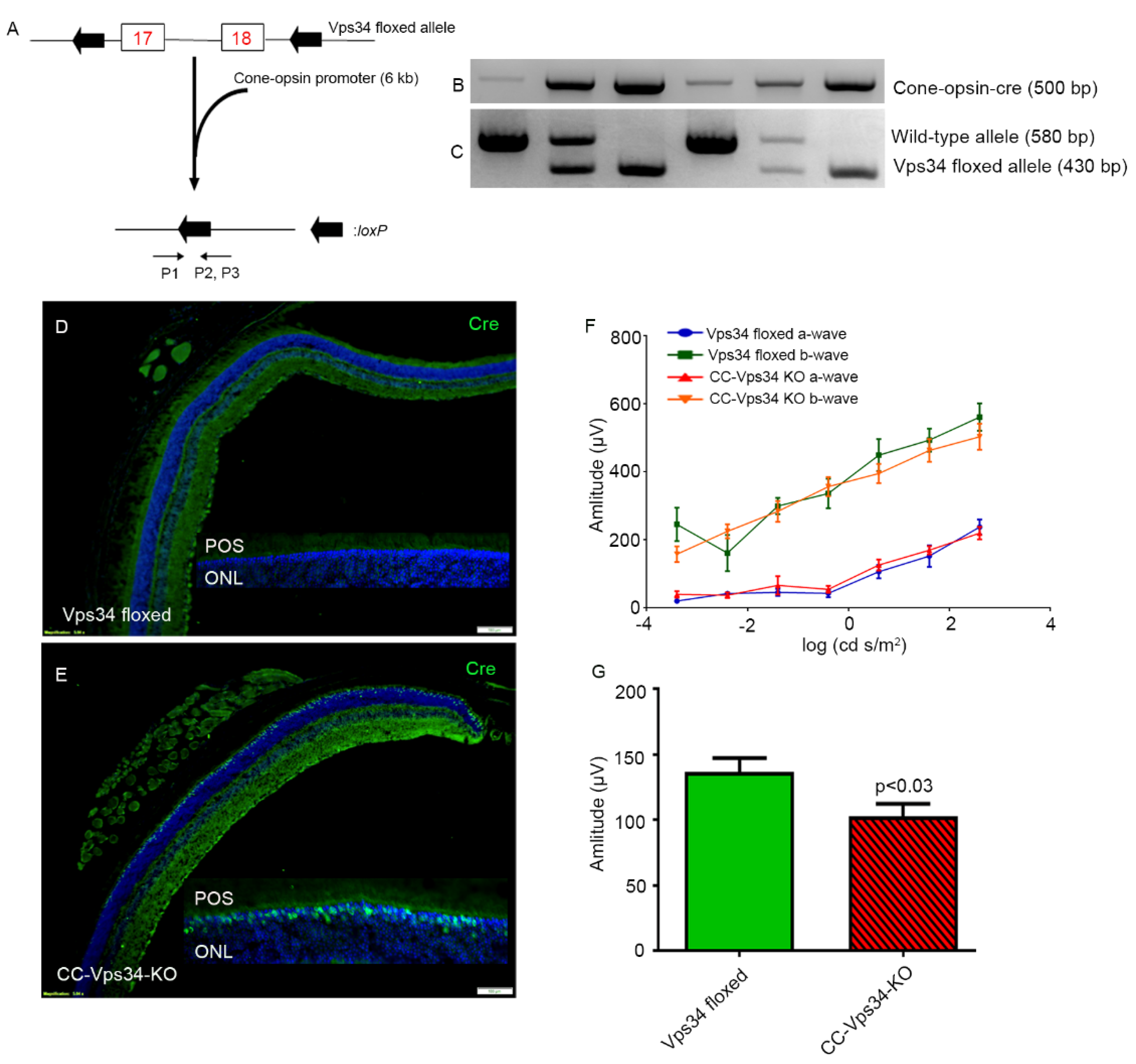
2.5. Generation of Cone-Vps34 Knockout Mice
2.6. Immunohistochemistry and Immunoblot Analyses of Retinas and Cone Photoreceptor Membranes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Other methods
3. Results
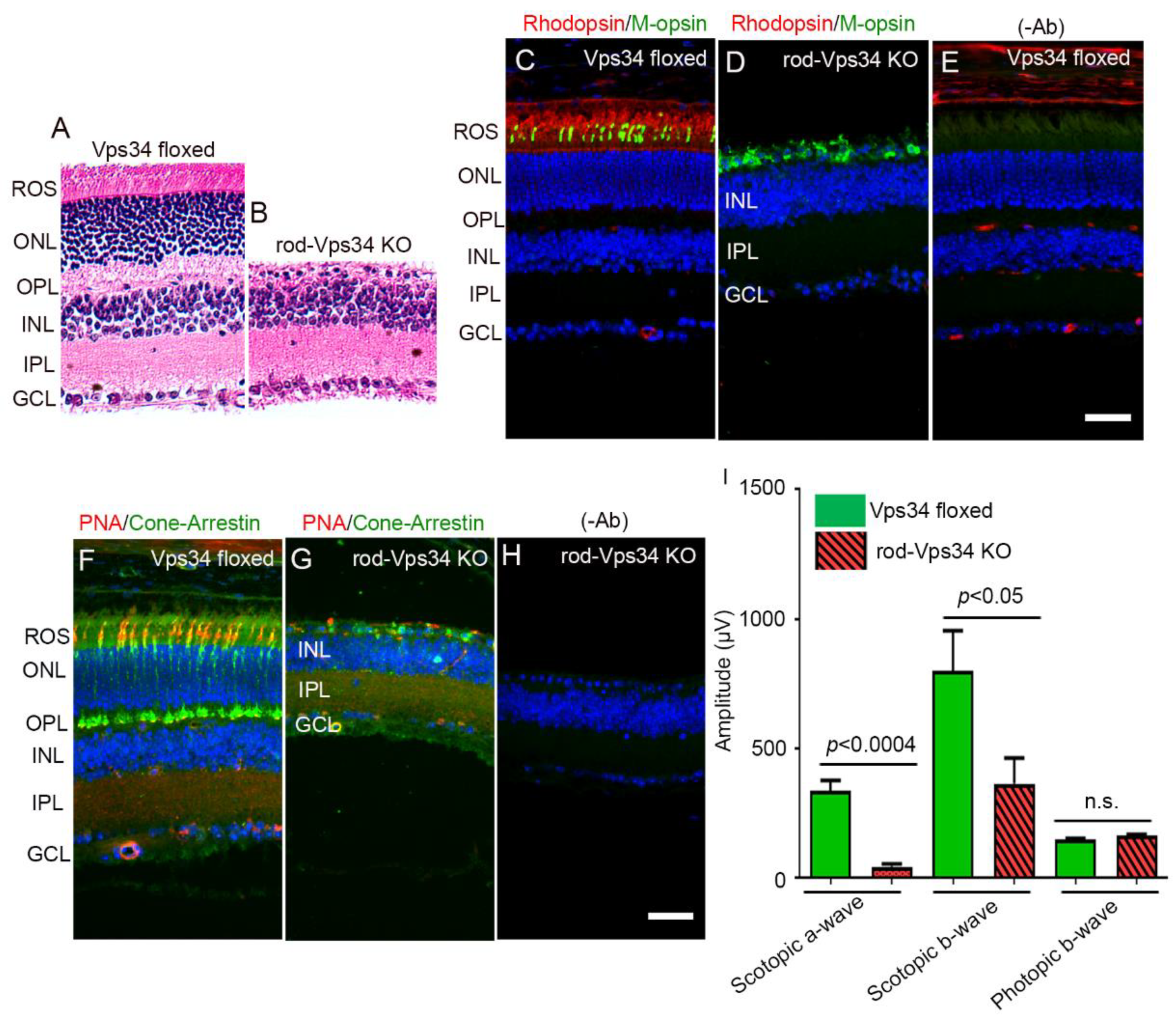
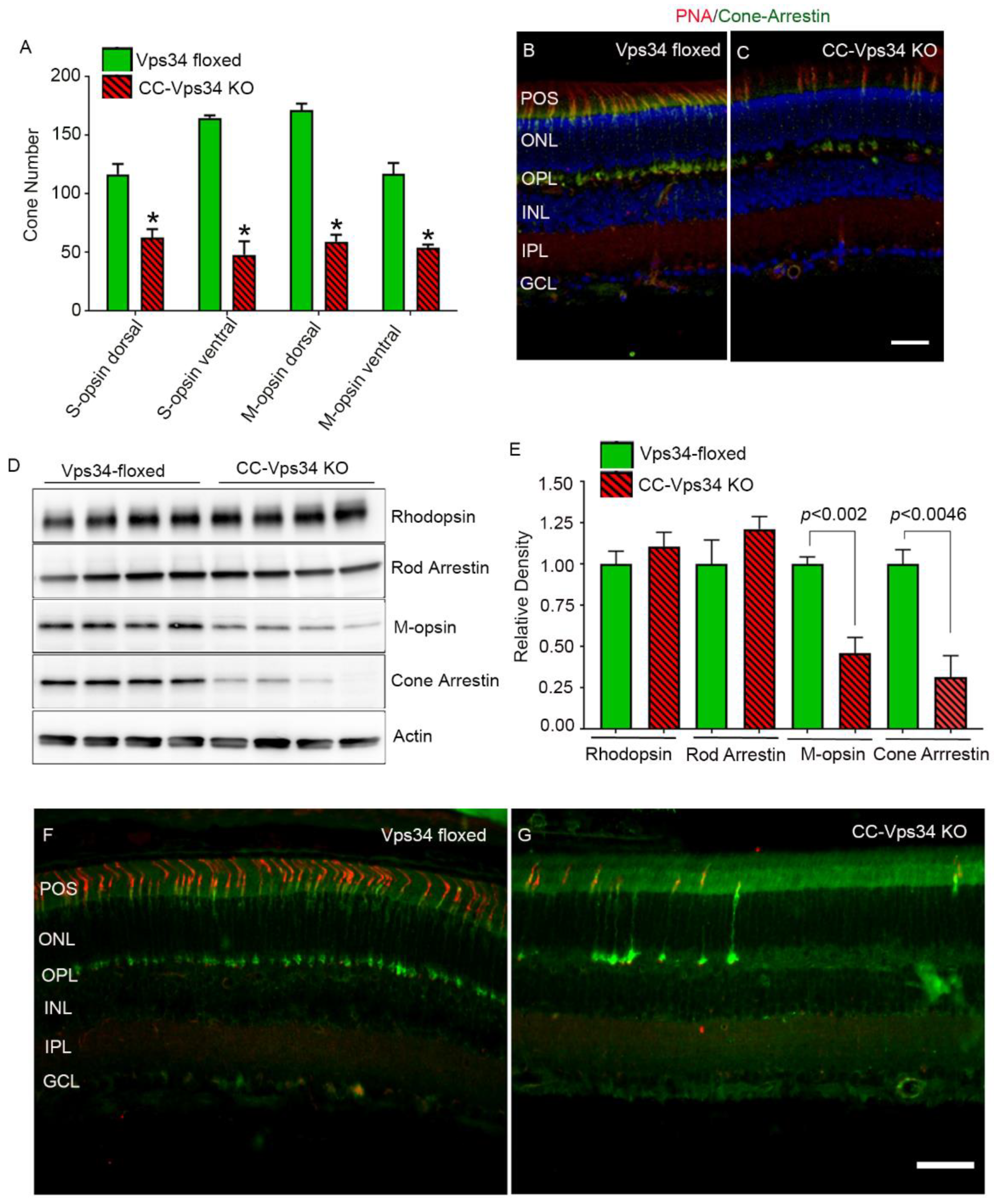
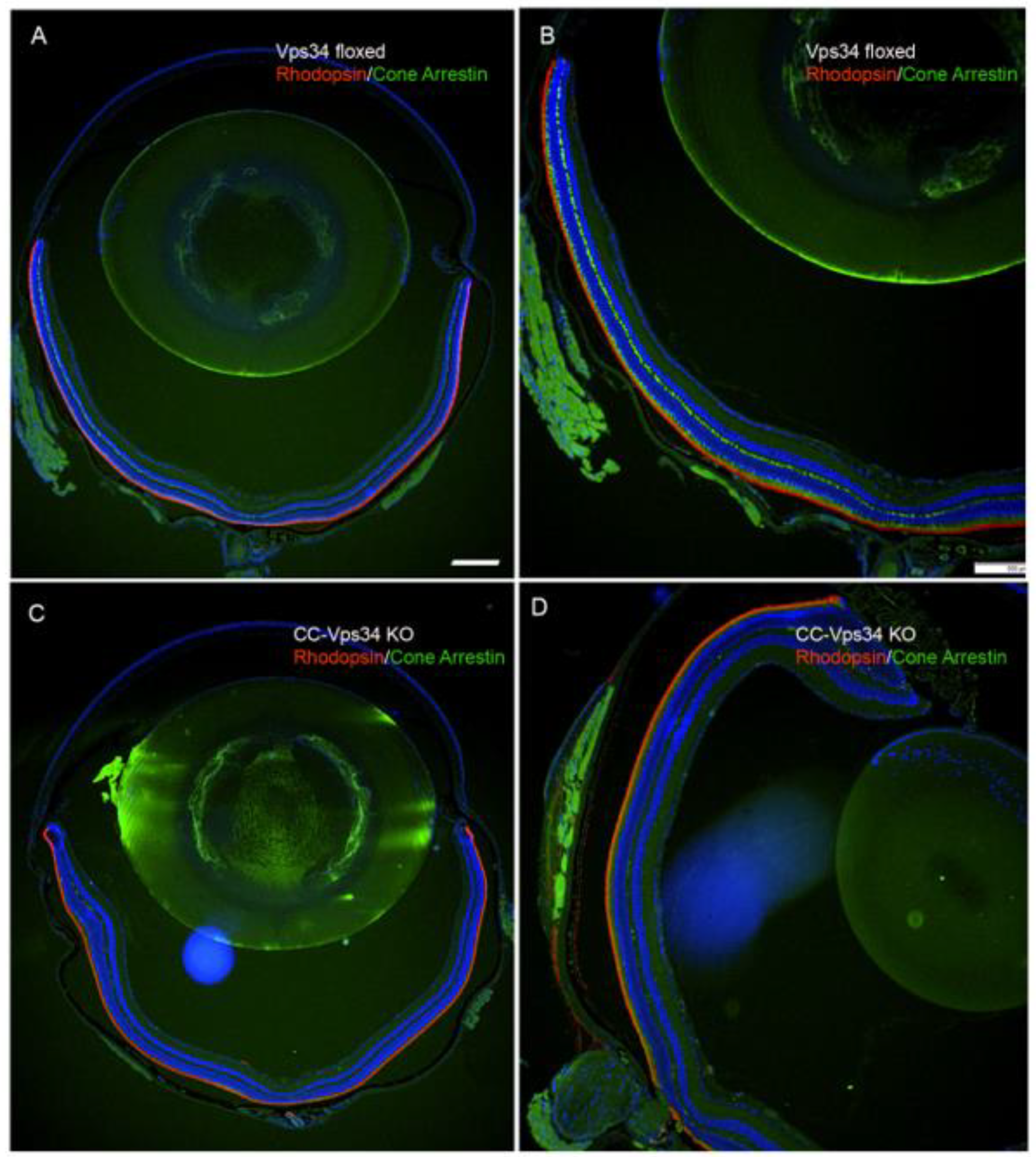
3.1. Effect of Loss of Vps34 in Rods on Cone Structure and Function
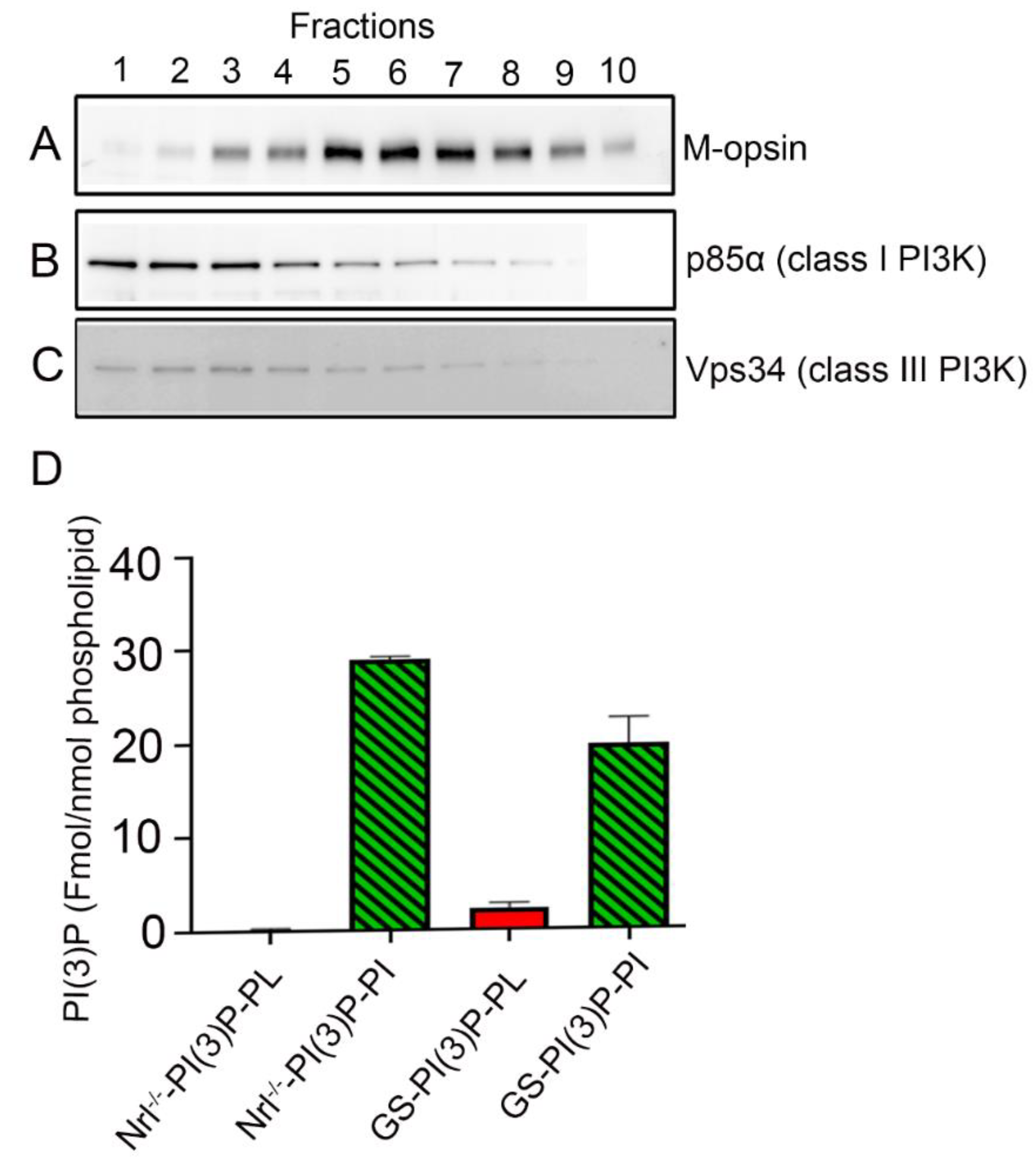
3.2. Expression of Vps34 in the Cone-Dominant Retina
3.3. PI(3)P Levels in the Cone-Dominant Retina
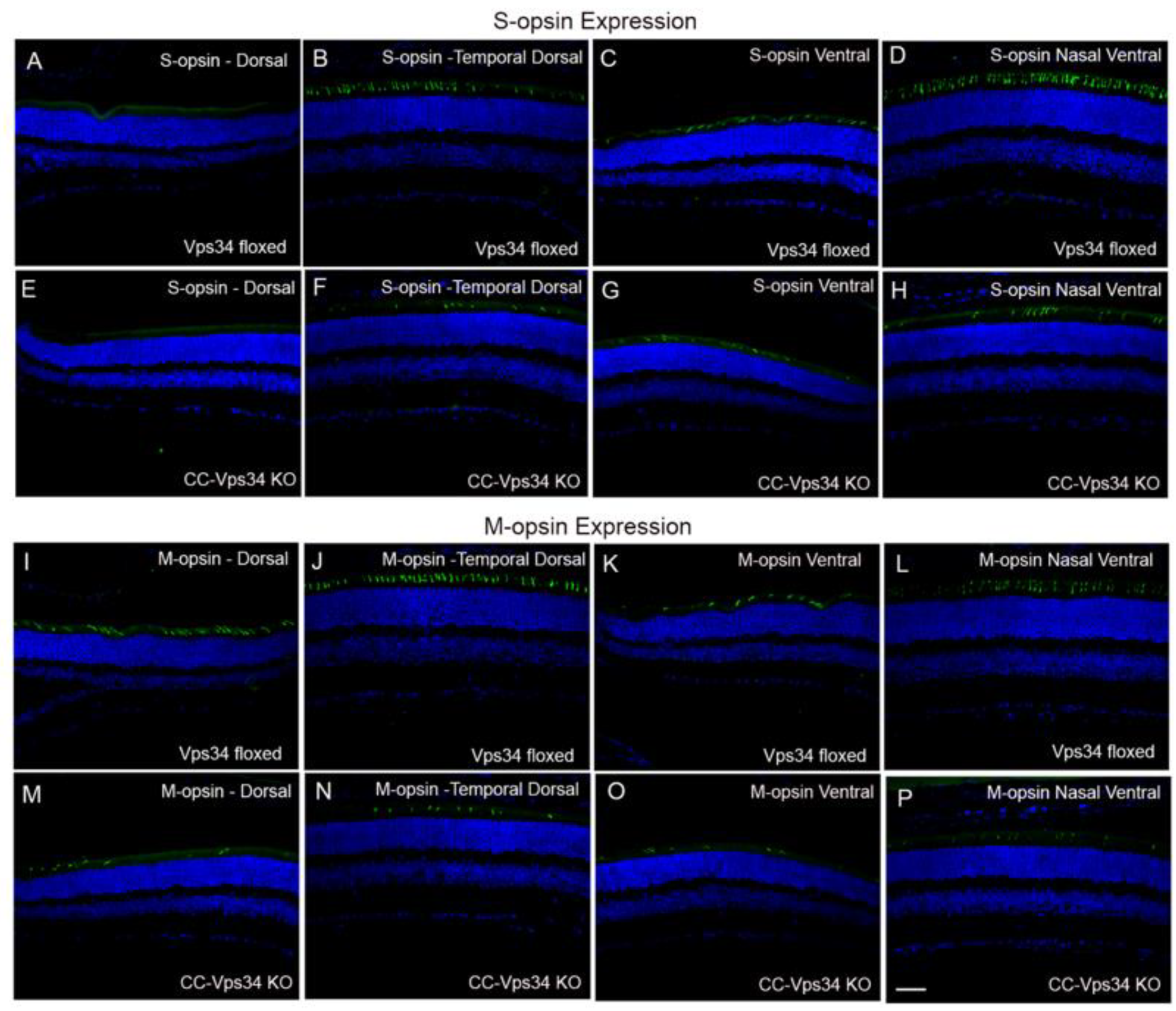
3.4. The Functional Role of Vps34 in Cones
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, T.F. Phosphoinositide lipids as signaling molecules: Common themes for signal transduction, cytoskeletal regulation, and membrane trafficking. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 231–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, T. Phosphoinositides: Tiny lipids with giant impact on cell regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1019–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, K.O.; Tan, K.W.; Stenmark, H. Phosphoinositides in Control of Membrane Dynamics. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 32, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensel, T.G. Phosphoinositides in Retinal Function and Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, R.V.S. Signaling roles of phosphoinositides in the retina. J. Lipid Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Meyers, R.E.; Cantley, L.C. Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, T.E.; Stenmark, H. Analyzing phosphoinositides and their interacting proteins. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Craene, J.O.; Bertazzi, D.L.; Bär, S.; Friant, S. Phosphoinositides, Major Actors in Membrane Trafficking and Lipid Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenmark, H.; Aasland, R.; Driscoll, P.C. The phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-binding FYVE finger. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, R.V.; Ranjo-Bishop, M.; Wang, Y.; Rajala, A.; Anderson, R.E. The p110alpha isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase is essential for cone photoreceptor survival. Biochimie 2015, 112, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovic, I.; Anderson, R.E.; Le, Y.Z.; Fliesler, S.J.; Sherry, D.M.; Rajala, R.V. Deletion of the p85alpha regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in cone photoreceptor cells results in cone photoreceptor degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3775–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Agosto, M.A.; Anastassov, I.A.; Tse, D.Y.; Wu, S.M.; Wensel, T.G. Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate is light-regulated and essential for survival in retinal rods. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Nichols, R.M.; Kailasam, L.; Wensel, T.G.; Agosto, M.A. Critical Role for Phosphatidylinositol-3 Kinase Vps34/PIK3C3 in ON-Bipolar Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 2861–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Hasegawa, H.; Amin, P.; Han, B.X.; Kaneko, S.; He, Y.; Wang, F. Deletion of PIK3C3/Vps34 in sensory neurons causes rapid neurodegeneration by disrupting the endosomal but not the autophagic pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9424–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, D.; Sauve, Y.; McCandless, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, C.K. Rhodopsin-iCre transgenic mouse line for Cre-mediated rod-specific gene targeting. Genesis 2005, 41, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avasthi, P.; Watt, C.B.; Williams, D.S.; Le, Y.Z.; Li, S.; Chen, C.K.; Marc, R.E.; Frederick, J.M.; Baehr, W. Trafficking of membrane proteins to cone but not rod outer segments is dependent on heterotrimeric kinesin-II. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14287–14298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajala, R.V.; Rajala, A.; Kooker, C.; Wang, Y.; Anderson, R.E. The Warburg Effect Mediator Pyruvate Kinase M2 Expression and Regulation in the Retina. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajala, A.; McCauley, A.; Brush, R.S.; Nguyen, K.; Rajala, R.V.S. Phosphoinositide Lipids in Ocular Tissues. Biology 2020, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouser, G.; Siakotos, A.N.; Fleischer, S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids 1966, 1, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortner, W.A. An evaluation of micromethods for phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1945, 159, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rajala, A.; Dighe, R.; Agbaga, M.P.; Anderson, R.E.; Rajala, R.V. Insulin Receptor Signaling in Cones. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19503–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, A.J.; Kondo, M.; Swain, P.K.; Takada, Y.; Bush, R.A.; Saunders, T.L.; Sieving, P.A.; Swaroop, A. Nrl is required for rod photoreceptor development. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Brown, B.; Li, A.; Mears, A.J.; Swaroop, A.; Craft, C.M. GRK1-dependent phosphorylation of S and M opsins and their binding to cone arrestin during cone phototransduction in the mouse retina. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6152–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonov, S.S.; Daniele, L.L.; Zhu, X.; Craft, C.M.; Swaroop, A.; Pugh, E.N., Jr. Photoreceptors of Nrl-/-mice coexpress functional S- and M-cone opsins having distinct inactivation mechanisms. J. Gen. Physiol. 2005, 125, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, L.L.; Lillo, C.; Lyubarsky, A.L.; Nikonov, S.S.; Philp, N.; Mears, A.J.; Swaroop, A.; Williams, D.S.; Pugh, E.N., Jr. Cone-like morphological, molecular, and electrophysiological features of the photoreceptors of the Nrl knockout mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2156–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriman, D.K.; Sajdak, B.S.; Li, W.; Jones, B.W. Seasonal and post-trauma remodeling in cone-dominant ground squirrel retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 150, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.T.; Du, W.; Zhu, P.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Sun, J.; Gerstner, C.D.; Baehr, W.; Boye, S.L.; et al. Gene-based Therapy in a Mouse Model of Blue Cone Monochromacy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, A.; Wang, Y.; Soni, K.; Rajala, R.V.S. Pyruvate kinase M2 isoform deletion in cone photoreceptors results in age-related cone degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, F.M.; Traer, C.J.; Abraham, S.M.; Fry, M.J. The phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase family. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3037–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, J.M. The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: Novel roles for Vps34. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.X.; Russell, R.C.; Guan, K.L. Regulation of PIK3C3/VPS34 complexes by MTOR in nutrient stress-induced autophagy. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.S. Vps34 and PLD1 take center stage in nutrient signaling: Their dual roles in regulating autophagy. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2015, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, N.; Dou, Z.; Chen, J.S.; Catanzaro, J.; Jiang, Y.P.; Ballou, L.M.; Selinger, E.; Ouyang, X.; Lin, R.Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. Class III PI3K Vps34 plays an essential role in autophagy and in heart and liver function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reifler, A.; Li, X.; Archambeau, A.J.; McDade, J.R.; Sabha, N.; Michele, D.E.; Dowling, J.J. Conditional knockout of pik3c3 causes a murine muscular dystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieco, G.; Janssens, V.; Gaide Chevronnay, H.P.; N’Kuli, F.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Wang, T.; Shan, J.; Vainio, S.; Bilanges, B.; Jouret, F.; et al. Vps34/PI3KC3 deletion in kidney proximal tubules impairs apical trafficking and blocks autophagic flux, causing a Fanconi-like syndrome and renal insufficiency. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicinanza, M.; Korolchuk, V.I.; Ashkenazi, A.; Puri, C.; Menzies, F.M.; Clarke, J.H.; Rubinsztein, D.C. PI(5)P regulates autophagosome biogenesis. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.; Curcio, C.; Hicks, D.; Price, D.; Wong, F. Cell death in age-related macular degeneration. Mol. Vis. 1999, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stone, E.M.; Braun, T.A.; Russell, S.R.; Kuehn, M.H.; Lotery, A.J.; Moore, P.A.; Eastman, C.G.; Casavant, T.L.; Sheffield, V.C. Missense variations in the fibulin 5 gene and age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Dong, A.; Petters, R.M.; Peng, Y.W.; Wong, F.; Campochiaro, P.A. Oxidative damage is a potential cause of cone cell death in retinitis pigmentosa. J. Cell Physiol. 2005, 203, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.C.; Poulsen, G.L.; Ver Hoeve, J.N.; Nork, T.M. Selective loss of S-cones in diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nork, T.M. Acquired color vision loss and a possible mechanism of ganglion cell death in glaucoma. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2000, 98, 331–363. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, J.S.; Georgiou, M.; Kalitzeos, A.; Moore, A.T.; Michaelides, M. Progressive cone and cone-rod dystrophies: Clinical features, molecular genetics and prospects for therapy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimbeni, A.C.; Codogno, P.; Morel, E. Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate in the regulation of autophagy membrane dynamics. Febs J. 2017, 284, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Vinberg, F.; Schottler, F.; Doggett, T.A.; Kefalov, V.J.; Ferguson, T.A. Autophagy supports color vision. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoz, R.; Rojas, B.; Ramírez, A.I.; Salazar, J.J.; Gallego, B.I.; Triviño, A.; Ramírez, J.M. Retinal Macroglial Responses in Health and Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2954721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter-Dawson, L.D.; LaVail, M.M. Rods and cones in the mouse retina. II. Autoradiographic analysis of cell generation using tritiated thymidine. J. Comp. Neurol. 1979, 188, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter-Dawson, L.D.; LaVail, M.M. Rods and cones in the mouse retina. I. Structural analysis using light and electron microscopy. J. Comp. Neurol. 1979, 188, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajala, A.; He, F.; Anderson, R.E.; Wensel, T.G.; Rajala, R.V.S. Loss of Class III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Vps34 Results in Cone Degeneration. Biology 2020, 9, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110384
Rajala A, He F, Anderson RE, Wensel TG, Rajala RVS. Loss of Class III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Vps34 Results in Cone Degeneration. Biology. 2020; 9(11):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110384
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajala, Ammaji, Feng He, Robert E. Anderson, Theodore G. Wensel, and Raju V. S. Rajala. 2020. "Loss of Class III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Vps34 Results in Cone Degeneration" Biology 9, no. 11: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110384
APA StyleRajala, A., He, F., Anderson, R. E., Wensel, T. G., & Rajala, R. V. S. (2020). Loss of Class III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Vps34 Results in Cone Degeneration. Biology, 9(11), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110384





