Risk Factors for Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality after Small Bowel Surgery in Patients with Cirrhotic Liver Disease—A Retrospective Analysis of 76 Cases in a Tertiary Center
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Surgery
2.3. Morbidity and Mortality
- -
- bleeding requiring transfusion of 2 or more units of red blood cells
- -
- wound complications requiring vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) therapy or other surgical intervention
- -
- anastomotic leakage and peritonitis
- -
- redo procedures related to the initial small bowel surgery
- -
- hydropic decompensation with drainage for more than ten days
- -
- respiratory complications such as pneumonia requiring thoracentesis or mechanical ventilation
- -
- hepatorenal syndrome or renal complications that necessitated renal replacement therapy (RRT)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient’s Characteristics and Surgical Therapy
3.2. Postoperative Complications
3.2.1. General Postoperative Complications
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of General Postoperative Complications
3.2.2. Bleeding Complications
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.3. Respiratory Complications
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.4. Wound Healing Disorders
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.5. Hydropic Decompensation
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.6. Redo Procedures
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.7. Renal Replacement
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.8. Anastomotic Leakage
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
3.2.9. Hospital Mortality and 30-day Mortality
Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, R.J.; Ahmed, A. Obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Disparate associations among Asian populations. World J. Hepatol. 2014, 6, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, K.E.; Kaplan, L.M. Obesity and liver disease: The epidemic of the twenty-first century. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, M.; Lonardo, A.; Mussi, C.; Baldelli, E.; Pellegrini, E.; Ballestri, S.; Romagnoli, D.; Loria, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and aging: Epidemiology to management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14185–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, L.S. Surgery in the Patient with Liver Disease. Trans. Am. Clin. Clim. Assoc. 2010, 121, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millwala, F.; Nguyen, G.C.; Thuluvath, P.J. Outcomes of patients with cirrhosis undergoing non-hepatic surgery: Risk assessment and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 4056–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeff, H.; Mariaskin, D.; Spangenberg, H.-C.; Hopt, U.T.; Makowiec, F. Perioperative mortality after non-hepatic general surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis: An analysis of 138 operations in the 2000s using Child and MELD scores. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2010, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.M.; Chang, J.; Gu, W.; Manekeller, S.; Jansen, C.; Lingohr, P.; Praktiknjo, M.; Kalf, J.C.; Schulz, M.; Spengler, U.; et al. The Development and Outcome of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure after Surgical Interventions. Liver Transplant. 2019, 26, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Olmo, J.A.; Flor-Lorente, B.; Flor-Civera, B.; Rodriguez, F.; Serra, M.A.; Escudero, A.; Lledó, S.; Rodrigo, J.M. Risk factors for nonhepatic surgery in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Surg. 2003, 27, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Ballus, J.; Esteve, F.; Betancur-Zambrano, N.L.; Corral-Velez, V.; Mañez, R.; Betbese, A.J.; A Roncal, J.; Javierre, C. Outcomes of abdominal surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziser, A.; Plevak, D.J.; Wiesner, R.H.; Rakela, J.; Offord, K.P.; Brown, D.L. Morbidity and mortality in cirrhotic patients undergoing anesthesia and surgery. Anesthesiol. 1999, 90, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Watson, W.; Shayani, V.; Pickleman, J. Abdominal operations in patients with cirrhosis: Still a major surgical challenge. Surgery 1997, 122, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhangui, P.; Laurent, A.; Amathieu, R.; Azoulay, D. Assessment of risk for non-hepatic surgery in cirrhotic patients. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, J.P.; Aranha, G.V.; Wilkinson, W.A.; Stanley, M.; Greenlee, H.B. Umbilical herniorrhaphy in cirrhotic patients. Arch. Surg. 1984, 119, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranha, G.V.; Sontag, S.J.; Greenlee, H.B. Cholecystectomy in cirrhotic patients: A formidable operation. Am. J. Surg. 1982, 143, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.C.; Correia, A.J.; Thuluvath, P.J. The impact of cirrhosis and portal hypertension on mortality following colorectal surgery: A nationwide, population-based study. Dis. Colon Rectum 2009, 52, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, A.; Barnes, D.S.; Zein, N.N.; Levinthal, G.N.; Connor, J.T.; Carey, W.W. Predicting outcome after cardiac surgery in patients with cirrhosis: A comparison of Child-Pugh and MELD scores. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 2, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.-A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Hanley, J.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northup, P.G.; Wanamaker, R.C.; Lee, V.D.; Adams, R.B.; Berg, C.L. Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) predicts nontransplant surgical mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Befeler, A.S.; Palmer, D.E.; Hoffman, M.; Longo, W.; Solomon, H.; Di Bisceglie, A.M. The safety of intra-abdominal surgery in patients with cirrhosis: Model for end-stage liver disease score is superior to Child-Turcotte-Pugh classification in predicting outcome. Arch. Surg. 2005, 140, 650–654, discussion 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, S.H.; Nagorney, D.M.; Stevens, S.R.; Offord, K.P.; Therneau, T.M.; Plevak, D.J.; Talwalkar, J.A.; Kim, W.R.; Kamath, P.S. Risk factors for mortality after surgery in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.C.; Ryoo, S.-B.; Park, J.W.; Yi, J.W.; Oh, H.-K.; Choe, E.K.; Ha, H.-K.; Park, B.K.; Moon, S.H.; Jeong, S.-Y.; et al. Oncologic and surgical outcomes in colorectal cancer patients with liver cirrhosis: A propensity-matched study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacatus, M.; Costin, L.; Bodean, V.; Manuc, M.; Vasilescu, C. The Outcome of Colorectal Surgery in Cirrhotic Patients: A Case Match Report. Chirurgia 2018, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaferi, A.A.; Mathur, A.K.; Sonnenday, C.J.; Dimick, J.B. Adverse outcomes in patients with chronic liver disease undergoing colorectal surgery. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, K.; Mucci, S.; Quentin, V.; Azoulay, R.; Arnaud, J.P.; Hamy, A. Colorectal surgery in cirrhotic patients: Assessment of operative morbidity and mortality. Dis. Colon Rectum 2008, 51, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yu, C.S.; Kim, C.W.; Yoon, Y.S.; Oh, S.G.; Lim, S.-B. Factors affecting the postoperative morbidity and survival of patients with liver cirrhosis following colorectal cancer surgery. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2016, 32, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z.; Ying, X.; Xu, M. Safety of laparoscopic resection for colorectal cancer in patients with liver cirrhosis: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 55, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Park, C.H.; Kim, W.; Jin, H.M.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, J.H. Safety of laparoscopic radical gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients with liver cirrhosis. Surg. Endosc. 2017, 31, 3898–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, M.; Pache, B.; Solà, J.; Blanc, C.; Hahnloser, D.; Demartines, N.; Grass, F. Thresholds for optimal fluid administration and weight gain after laparoscopic colorectal surgery. BJS Open 2019, 3, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurt, J.; Hübner, M.; Pache, B.; Hahnloser, D.; Demartines, N.; Grass, F. Respiratory Complications after Colorectal Surgery: Avoidable or Fate? World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 2708–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solbach, P.; Zu Siederdissen, C.H.; Taubert, R.; Ziegert, S.; Port, K.; Schneider, A.; Hueper, K.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Jaeckel, E. Home-based drainage of refractory ascites by a permanent-tunneled peritoneal catheter can safely replace large-volume paracentesis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, A.N.; Kimer, N.; Hobolth, L.; Gluud, L.L. Prognosis of patients with ascites after PleurX insertion: An observational study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramonell, K.M.; Fang, S.; Perez, S.D.; Srinivasan, J.K.; Sullivan, P.S.; Galloway, J.R.; Staley, C.A.; Lin, E.; Sharma, J.; Sweeney, J.F.; et al. Development and Validation of a Risk Calculator for Renal Complications after Colorectal Surgery Using the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Participant Use Files. Am. Surg. 2016, 82, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praktiknjo, M.; Clees, C.; Pigliacelli, A.; Fischer, S.; Jansen, C.; Lehmann, J.; Pohlmann, A.; Lattanzi, B.; Krabbe, V.K.; Strassburg, C.P.; et al. Sarcopenia Is Associated With Development of Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis Receiving Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praktiknjo, M.; Book, M.; A Luetkens, J.; Pohlmann, A.; Meyer, C.; Thomas, D.; Jansen, C.; Feist, A.; Chang, J.; Grimm, J.; et al. Fat-free muscle mass in magnetic resonance imaging predicts acute-on-chronic liver failure and survival in decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosquera, C.; Koutlas, N.J.; Edwards, K.C.; Strickland, A.; Vohra, N.A.; Zervos, E.E.; Fitzgerald, T.L. Impact of malnutrition on gastrointestinal surgical patients. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 205, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.W.; Wu, A.H.; Lee, M.W.; Lau, S.-Y.; Lam, P.-S.; Lau, W.-S.; Kwok, S.S.; Kwan, R.Y.; Lam, C.-F.; Tam, C.-K.; et al. Malnutrition risk predicts surgical outcomes in patients undergoing gastrointestinal operations: Results of a prospective study. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Culebras, J.M.; Aller, R.; Eiros-Bouza, J.M. Surgical infection and malnutrition. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackl, C.; Schlitt, H.J.; Renner, P.; A Lang, S. Liver surgery in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2725–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, C.; López-Balaguer, J.M.; Aracil, C.; Kolle, L.; González, B.; Miñana, J.; Soriano, G.; Guarner, C.; Balanzó, J. Maintenance of hemodynamic response to treatment for portal hypertension and influence on complications of cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirocchi, R.; Campanile, F.C.; Di Saverio, S.; Popivanov, G.; Carlini, L.; Pironi, D.; Tabola, R.; Vettoretto, N. Laparoscopic versus open colectomy for obstructing right colon cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Visc. Surg. 2017, 154, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.-P.; Qiu, H.; Liao, S.-J.; Ai, J.-H.; Shi, J. Mini-invasive vs open resection of colorectal cancer and liver metastases: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2819–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
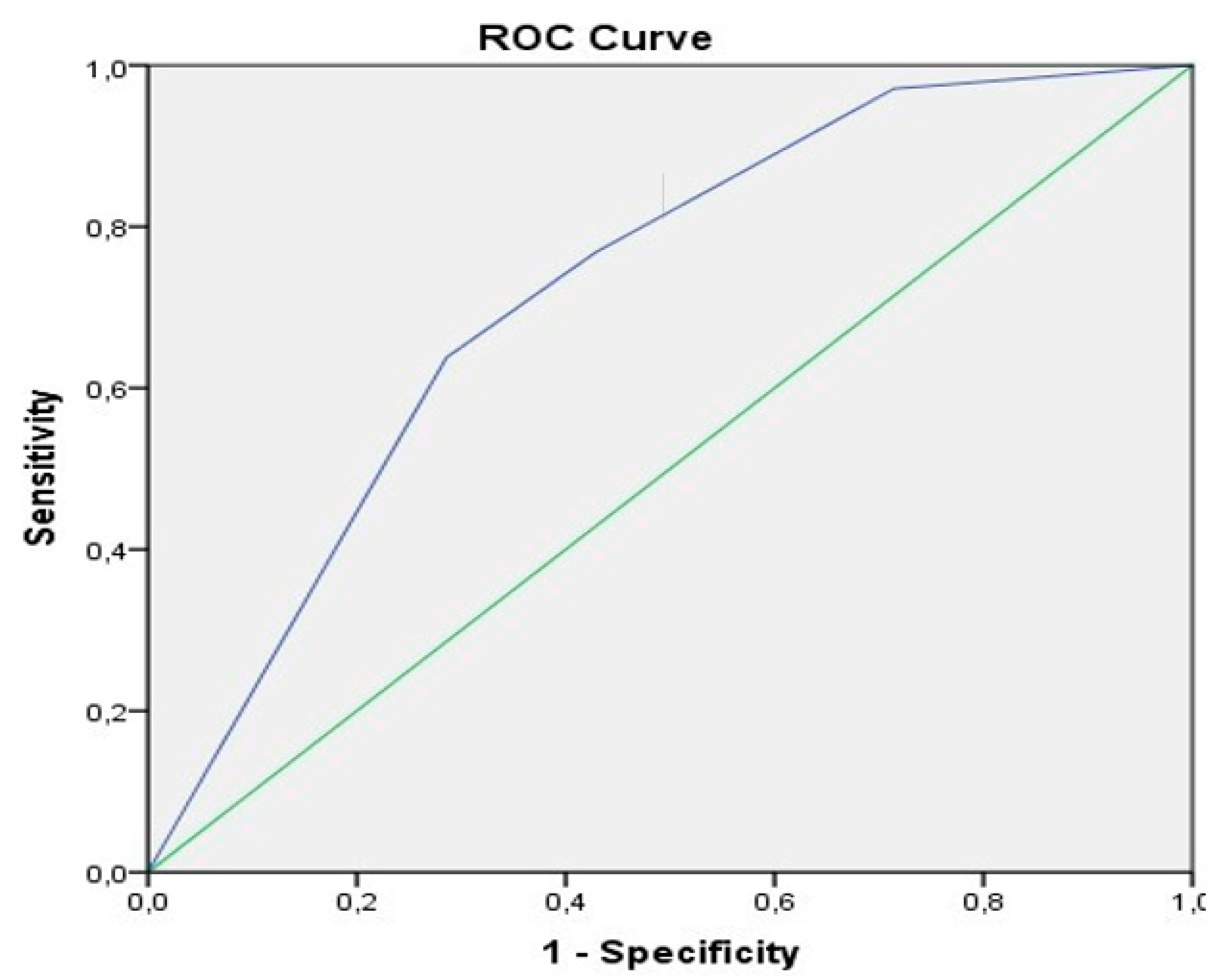


| Factors | Total (n = 76)/Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male | 61 (80.3%) |
| Female | 15 (19.7%) |
| Age (years) | 61.5 (15) |
| Age group | |
| <40 years | 1 (1.3%) |
| 41–74 years | 66 (86.8%) |
| >74 years | 9 (11.8%) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 (0.79) |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.65 (0.81) |
| PT (INR) | 1.1 (0.2) |
| Thrombocytes (G/L) | 185 (129) |
| Leucocytes (G/L) | 7.03 (4.94) |
| MELD score | 10 (7) |
| CTP classification | |
| A | 40 (52.6%) |
| B | 30 (39.5%) |
| C | 6 (7.9%) |
| ASA classification | |
| II | 5 (6.6%) |
| III | 68 (89.5%) |
| IV | 3 (3.9%) |
| Etiology of liver cirrhosis | |
| Alcoholic | 27 (35.5%) |
| HBV and/or HCV | 9 (11.8%) |
| Cryptogenic | 36 (47.4%) |
| PBC or PSC | 4 (5.2%) |
| Splenomegaly | 21 (27.6%) |
| Portal hypertension | 27 (35.5%) |
| Varices | 27 (35.5%) |
| Ascites | |
| No/mild | 42 (55.3%) |
| Moderate | 23 (30.3%) |
| Severe/refractory | 11 (14.5%) |
| Encephalopathy | |
| No | 70 (92.1%) |
| Grade 1/2 | 5 (6.6%) |
| Grade 3/4 | 1 (1.3%) |
| Presence of HCC | 4 (5.3%) |
| Pre-existing metabolic condition/diabetes | 28 (36.8%) |
| Pre-existing cardiac condition | 50 (65.8%) |
| Pre-existing renal condition | 27 (35.5%) |
| Pre-existing neurological condition | 20 (26.3%) |
| Pre-existing respiratory condition | 14 (18.4%) |
| Surgery location | |
| Duodenum | 14 (18.4%) |
| Jejunum | 39 (51.3%) |
| Ileum | 37 (48.7%) |
| Incision-suture time (min) | 209.50 (153) |
| Elective vs. emergency surgery | 56 (73.7%) vs. 20 (26.3%) |
| Anastomosis vs. ostomy | 59 (77.6%) vs. 17 (22.4%) |
| Postoperative hospital days | 23 (26) |
| Postoperative hospital days at ICU | 2.5 (7) |
| Complication | Total (n = 76) |
|---|---|
| Complications Dindo-Clavien ≥ II | 69 (90.8%) |
| Severe complications Dindo-Clavien ≥ IIIB | 41 (53.9%) |
| Bleeding requiring transfusion | 31 (40.8%) |
| Respiratory complication (pneumonia, thoracentesis, mechanical ventilation) | 29 (38.2%) |
| Wound healing disorder | 25 (32.9%) |
| Hydropic decompensation | 23 (30.3%) |
| Redo procedures | 21 (27.6%) |
| Renal complication (renal replacement therapy) | 11 (14.5%) |
| Anastomotic leakage | 9 (11.8%) |
| Hospital Mortality | 9 (11.8%) |
| 30-day mortality | 3 (3.9%) |
| Sex | Age | CTP | MELD | Operation | Complications | Cause of Death | Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 69 | A | 10 | Jejunal and ileal anastomosis | Bleeding, Resp, Renal, AnaLeak, Redo (2) | Sepsis (peritonitis) | 5 |
| F | 72 | B | 15 | Jejunal anastomosis | Bleeding, Resp, Renal, WHD, HRS, HyDecomp, Redo (1) | Liver failure (limited therapy) | 148 |
| M | 60 | A | 12 | Ileal anastomosis | Peritonitis, Redo (3) | Sepsis (peritonitis) | 3 |
| M | 67 | B | 20 | Ileal anastomosis | Resp, Renal, HRS, HyDecomp | Sepsis (pneumonia, limited therapy) | 36 |
| M | 54 | C | 18 | Jejunal anastomosis | Resp, Renal, HRS, | Sepsis (pneumonia) | 31 |
| F | 72 | C | 16 | Jejunal anastomosis | Bleeding, Resp, Peritonitis | Sepsis (peritonitis) | 2 |
| M | 60 | B | 25 | Ileal stoma | Resp, Renal, WHD, HyDecomp, Peritonitis, Redo (1) | Hemorrhagic shock | 40 |
| M | 69 | A | 13 | Ileal stoma | Bleeding, Resp, Renal, WHD, Redo (10) | Sepsis (peritonitis) | 39 |
| M | 44 | C | 22 | Duodenal anastomosis | Bleeding, Resp, Renal, HyDecomp, Peritonitis | Sepsis (peritonitis) | 51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wetterkamp, M.; van Beekum, C.J.; Willis, M.A.; Glowka, T.R.; Manekeller, S.; Fimmers, R.; Praktiknjo, M.; Chang, J.; Kalff, J.C.; Vilz, T.O. Risk Factors for Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality after Small Bowel Surgery in Patients with Cirrhotic Liver Disease—A Retrospective Analysis of 76 Cases in a Tertiary Center. Biology 2020, 9, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110349
Wetterkamp M, van Beekum CJ, Willis MA, Glowka TR, Manekeller S, Fimmers R, Praktiknjo M, Chang J, Kalff JC, Vilz TO. Risk Factors for Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality after Small Bowel Surgery in Patients with Cirrhotic Liver Disease—A Retrospective Analysis of 76 Cases in a Tertiary Center. Biology. 2020; 9(11):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110349
Chicago/Turabian StyleWetterkamp, Maximilian, Cornelius J. van Beekum, Maria A. Willis, Tim R. Glowka, Steffen Manekeller, Rolf Fimmers, Michael Praktiknjo, Johannes Chang, Joerg C. Kalff, and Tim O. Vilz. 2020. "Risk Factors for Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality after Small Bowel Surgery in Patients with Cirrhotic Liver Disease—A Retrospective Analysis of 76 Cases in a Tertiary Center" Biology 9, no. 11: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110349
APA StyleWetterkamp, M., van Beekum, C. J., Willis, M. A., Glowka, T. R., Manekeller, S., Fimmers, R., Praktiknjo, M., Chang, J., Kalff, J. C., & Vilz, T. O. (2020). Risk Factors for Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality after Small Bowel Surgery in Patients with Cirrhotic Liver Disease—A Retrospective Analysis of 76 Cases in a Tertiary Center. Biology, 9(11), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9110349





