Characterisation and Mutagenesis Study of An Alternative Sigma Factor Gene (hrpL) from Erwinia mallotivora Reveal Its Central Role in Papaya Dieback Disease
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retrieval of EmhrpL Gene Sequence
2.2. Sequence Analysis, Gene Characterisation, and Phylogenetic Inferring of EmhrpL Gene
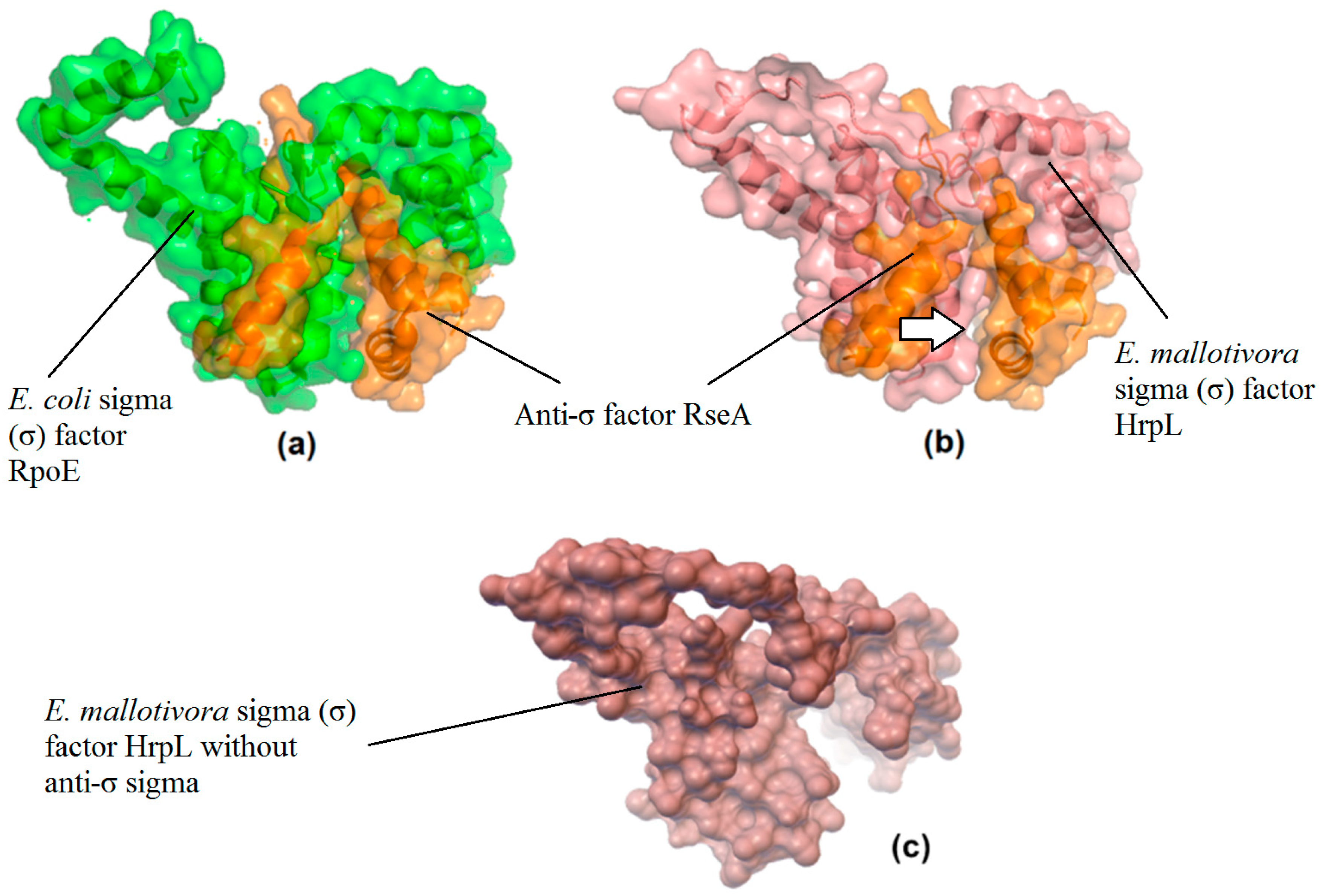
2.3. Molecular Docking Analysis of EmHrpL with an Anti-σ Factor
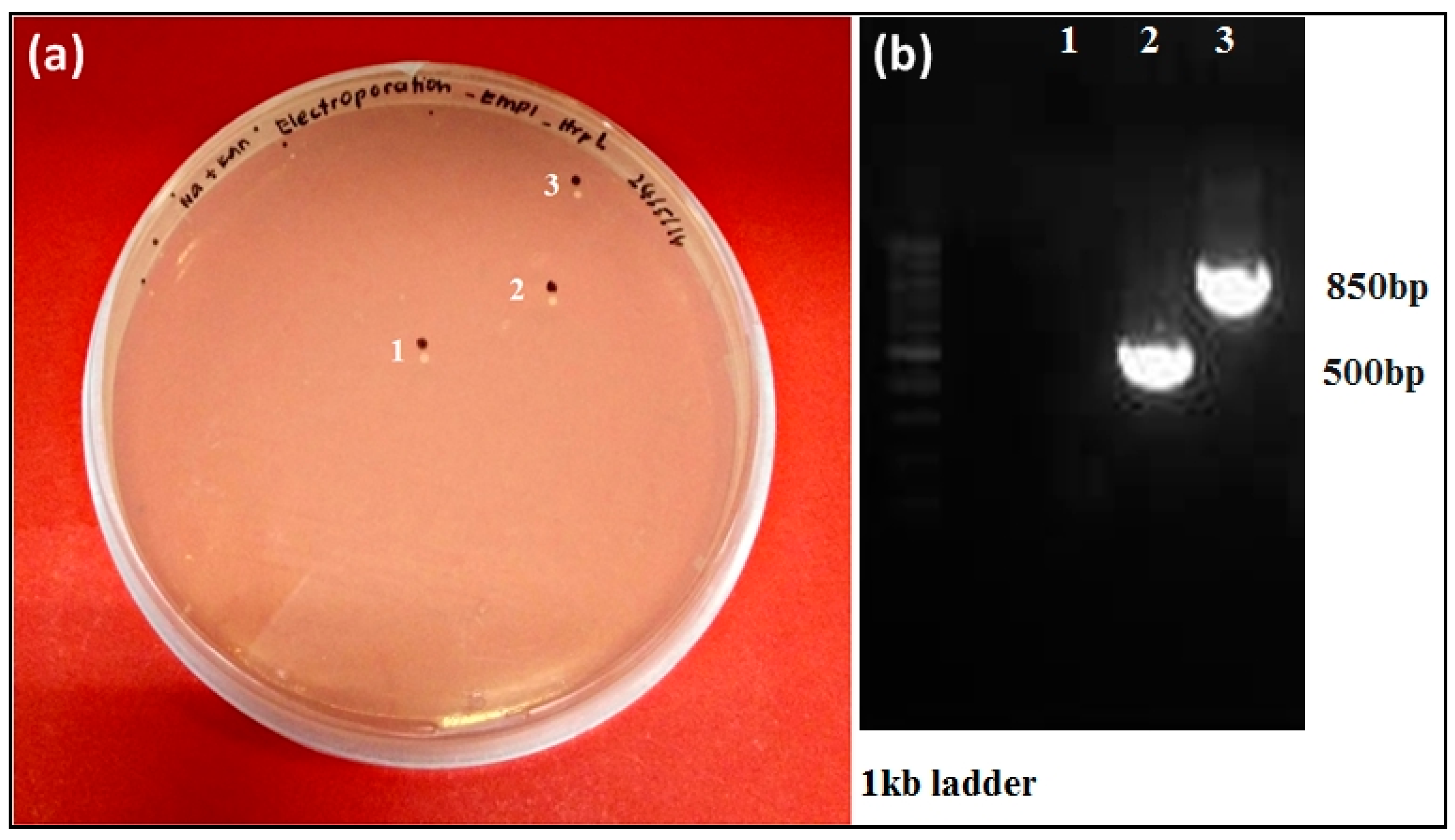
2.4. Competent Cell Preparation, Construct Development, and Mutagenesis and Mutant Selection
2.5. Pathogenesis Assay of the Mutant Strain
3. Results
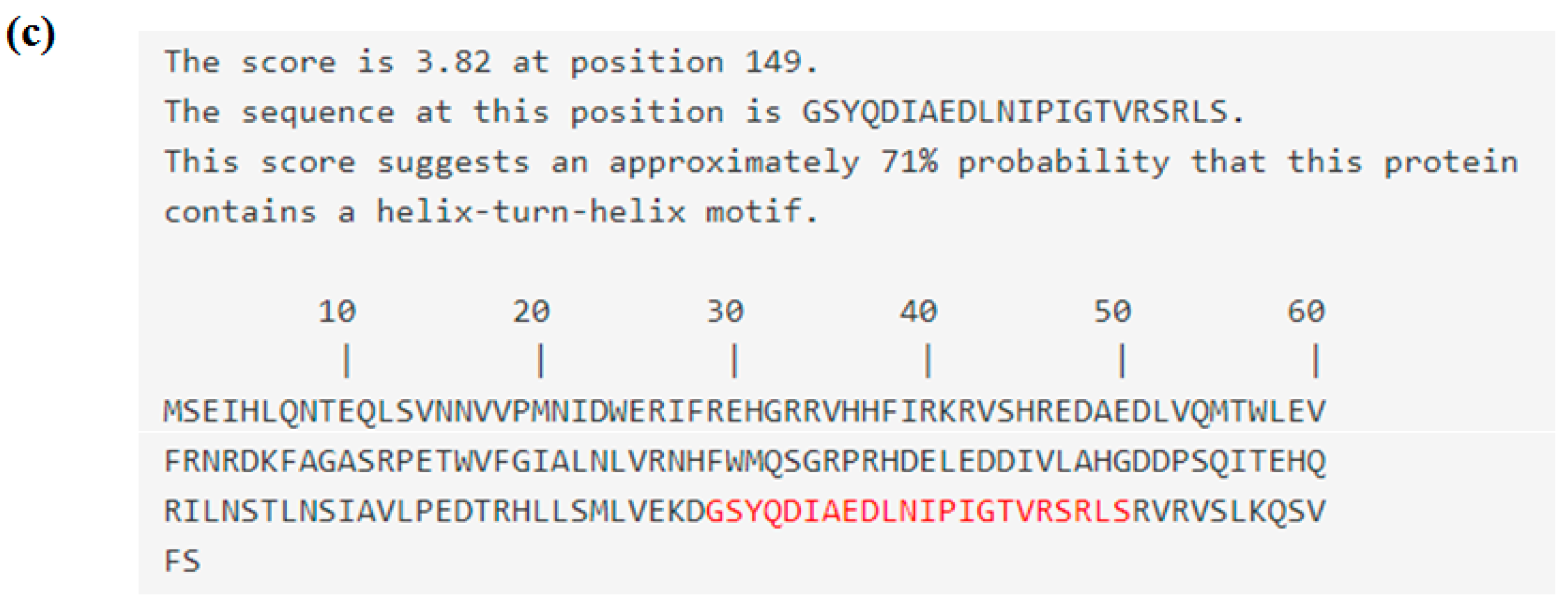
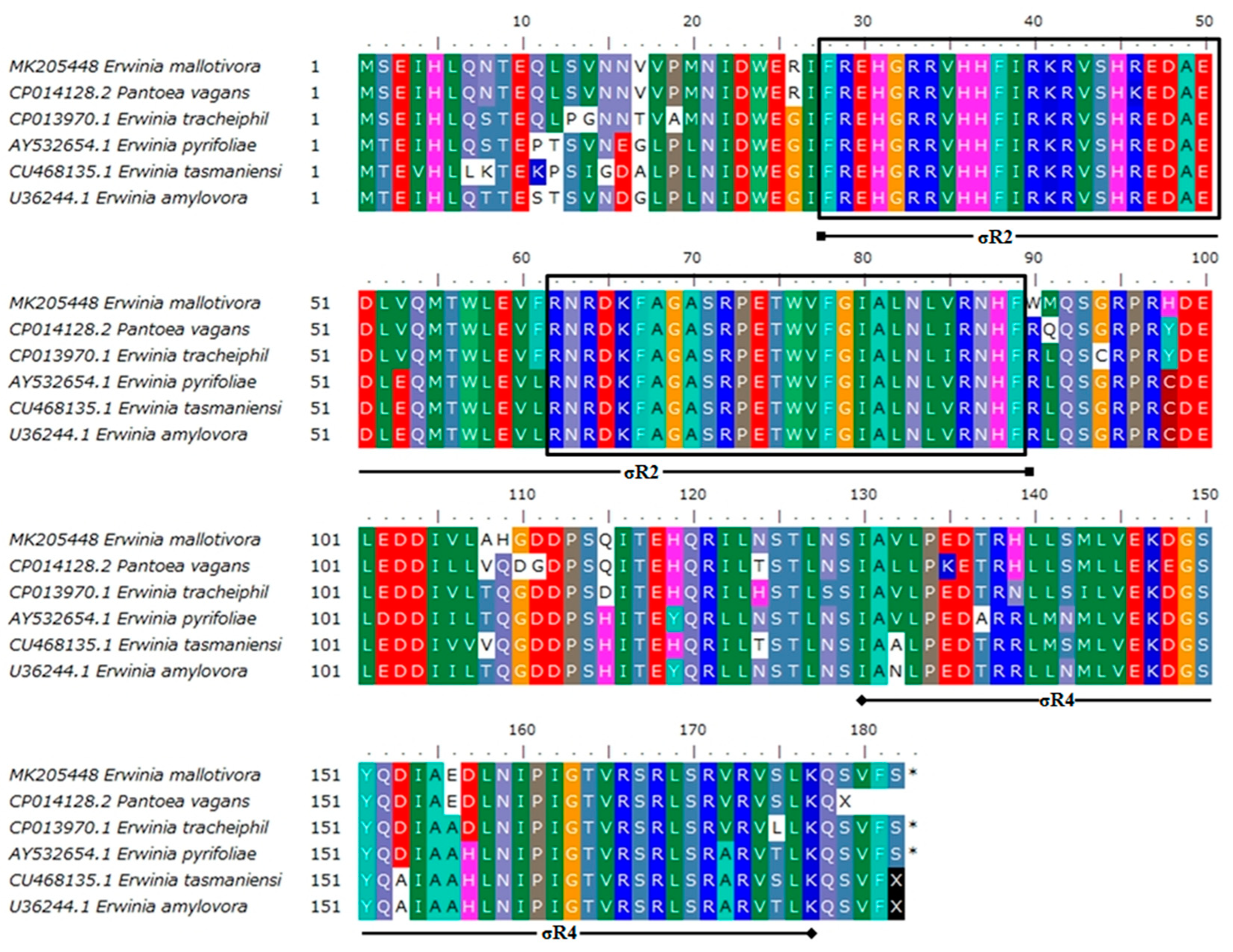
3.1. Sequence Characterisation of EmhrpL Gene and Its Product, HrpL
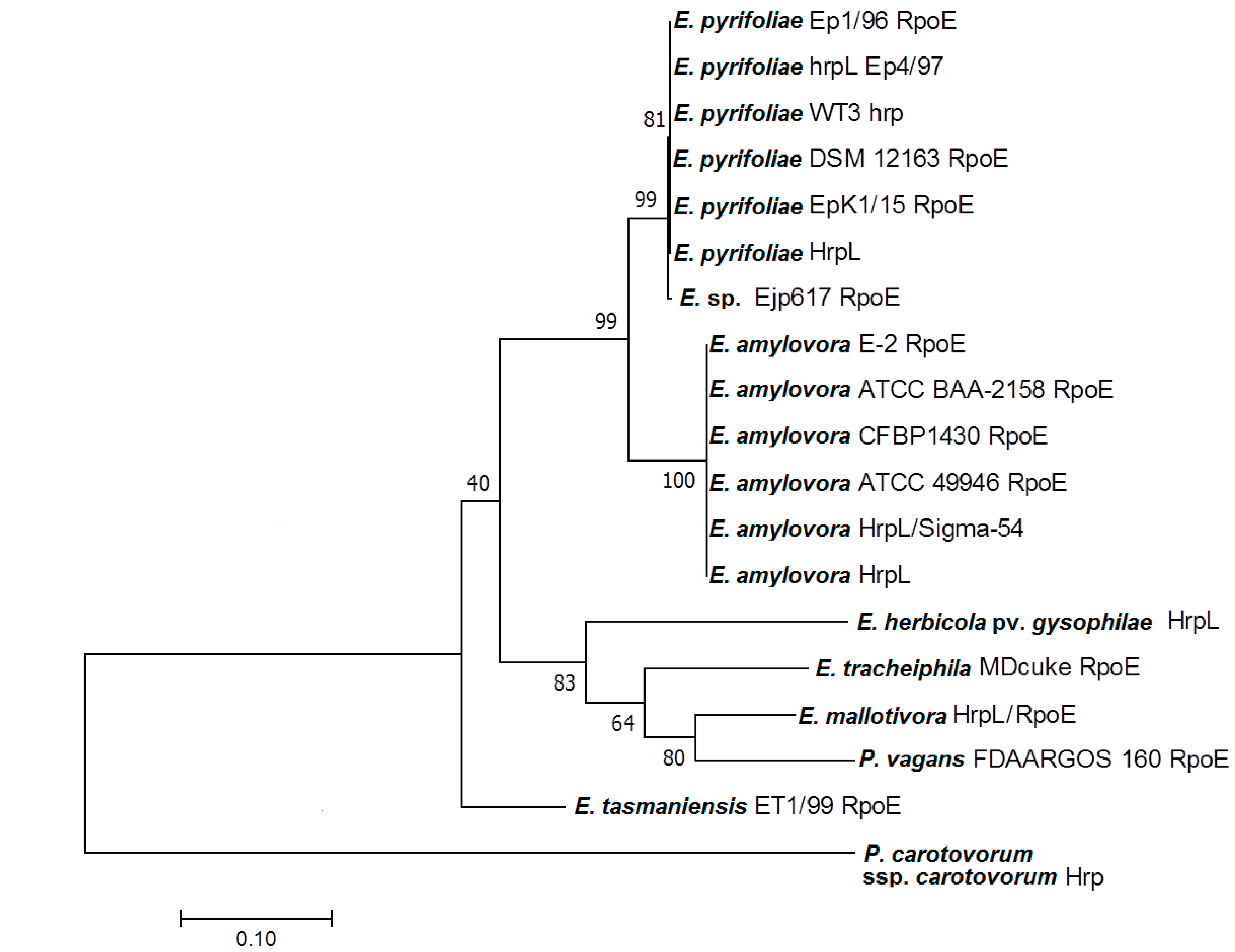
3.2. Homology of EmHrpL
3.3. Prediction of a Potential Inhibitor and Its Binding Affinity (Kd) with EmHrpL through PPI In Silico Analysis
3.4. Targeted hrpL Disruption in E. mallotivora by Using a Group II Intron (TargeTron®) System
3.5. Mutagenesis Study Revealed Involvement of hrpL in the Pathogenicity of E. mallotivora
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walterson, A.M.; Stavrinides, J. Pantoea: Insights into a highly versatile and diverse genus within the Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, W.J.; Darst, S.A. The structural basis for promoter –35 element recognition by the group IV σ factors. PLOS Biol. 2006, 4, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redford, P.; Welch, R.A. Role of sigma E-regulated genes in Escherichia coli uropathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4030–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmierczak, M.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Boor, K.J. Alternative sigma factors and their roles in bacterial virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Till, R.; Hobley, L.; Sockett, R.E. Mutagenesis of RpoE-like sigma factor genes in Bdellovibrio reveals differential control of groEL and two groES genes. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmann, J.D. The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2002, 46, 47–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, D.; Bonas, U. Who comes first? How plant pathogenic bacteria orchestrate type III secretion. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhar, A.; Sansonetti, P.J. Type III secretion system. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R784–R791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.A.; Muzzin, O.; Chlenov, M.; Sun, J.L.; Olson, C.A.; Weinman, O.; Trester-Zedlitz, M.L.; Darst, S.A. Structure of the bacterial RNA polymerase promoter specificity σ subunit. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.; Oh, C. Harpins, multifunctional proteins secreted by gram-negative plant-pathogenic bacteria. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrough, T.G.; Miller, S.I. Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium type III secretion components to needle complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11008–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.Y.; Schoedel, C.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Collmer, A. Extracellular secretion of pectate lyase by the Erwinia chrysanthemi out pathway is dependent upon sec-mediated export across the inner membrane. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 4310–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.M.; Beer, S.V. HrpL activates Erwinia amylovora hrp gene transcription and is a member of the ECF subfamily of sigma factors. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissan, G.; Manulis, S.; Weinthal, D.M.; Sessa, G.; Barash, I. Analysis of promoters recognized by HrpL, an alternative sigma-factor protein from Pantoea agglomerans pv. gypsophilae. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Yang, S.; Charkowski, A.O.; Yap, M.N.; Steeber, D.A.; Keen, N.T.; Yang, C.H. Population behavior analysis of dspE and pelD regulation in Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, L.; Li, Y.; Robert, C.; Pritchard, L.; Liu, H.; Hovey, R.; Wang, Q.; et al. Genome-wide identification of HrpL-regulated genes in the necrotrophic phytopathogen Dickeya dadantii 3937. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat-Amin, N.; Bunawan, H.; Ahmad-Redzuan, R.; Jaganath, I.B. Erwinia mallotivora sp., a new pathogen of papaya (Carica papaya) in Peninsular Malaysia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 12, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Redzuan, R.; Abu-Bakar, N.; Rozano, L.; Badrun, R.; Mat-Amin, N.; Mohd-Raih, M.F. Draft genome sequence of Erwinia mallotivora BT-MARDI, causative agent of papaya dieback disease. Genome Announc. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Bakar, N.; Badrun, R.; Rozano, L.; Ahmad, L.; Ahmad-Redzuan, R.; Mohd-Raih, M.F.; Tamizi, A.A. Identification and validation of putative Erwinia mallotivora effectors proteins via quantitative proteomics and real time analysis. J. Agric. Food. Technol. 2017, 7, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Juri, N.M.; Samsuddin, A.F.; Abdul-Murad, A.M.; Tamizi, A.A.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Abu-Bakar., N. Discovery of pathogenesis related and effector genes of Erwinia mallotivora in Carica papaya (Eksotika I) seedlings via transcriptomic analysis. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2020, 23, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juri, N.M.; Samsuddin, A.F.; Abdul-Murad, A.M.; Tamizi, A.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Abu-Bakar., N. In silico analysis and functional characterization of FHUB, a component of Erwinia mallotivora ferric hydroxamate uptake system. J. Teknol. 2020, 82, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.R.; Paulson, J.N.; Arnold, B.J.; Scully, E.D.; Zhaxybayeva, O.; Pierce, N.E.; Rocha, J.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Holton, K.; Kolter, R. An introduced crop plant is driving diversification of the virulent bacterial pathogen Erwinia tracheiphila. mBio 2018, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, C.L.; Venter, S.N.; Cleenwerck, I.; Engelbeen, K.; Vancanneyt, M.; Swings, J.; Coutinho, T.A. Pantoea vagans sp. nov., Pantoea eucalypti sp. nov., Pantoea deleyi sp. nov. and Pantoea anthophila sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ades, S.E.; Grigorova, I.L.; Gross, C.A. Regulation of the alternative sigma factor sigma (E) during initiation, adaptation, and shutoff of the extracytoplasmic heat shock response in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Las Peñas, A.; Connolly, L.; Gross, C.A. The sigmaE-mediated response to extracytoplasmic stress in Escherichia coli is transduced by RseA and RseB, two negative regulators of sigmaE. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, E.A.; Tupy, J.L.; Gruber, T.M.; Wang, S.; Sharp, M.M.; Gross, C.A.; Darst, S.A. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli sigmaE with the cytoplasmic domain of its anti-sigma RseA. Mol. Cell. 2003, 11, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Collinet, B.; Lau, G.; Raina, S.; Missiakas, D. Interaction of the conserved region 4.2 of ςE with the RseA anti-sigma factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27282–27287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janin, J.; Bahadur, R.P.; Chakrabarti, P. Protein-protein interaction and quaternary structure. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erijman, A.; Rosenthal, E.; Shifman, J.M. How structure defines affinity in protein-protein interactions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, L.M.; Vencato, M.; Jordan, K.L.; Schneider, S.E.; Schneider, D.J.; Collmer, A. Multiple approaches to a complete inventory of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 type III secretion system effector proteins. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, J.M. Regulation of the type III secretion system in phytopathogenic bacteria. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2006, 19, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagne, S.; Allain, F.H.T.; Vorholt, J.A. Extra Cytoplasmic Function sigma factors, recent structural insights into promoter recognition and regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 30, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, T. Signaling diversity and evolution of extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missiakas, D.; Raina, S. The extracytoplasmic function sigma factors: Role and regulation. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.M.; Levchenko, I.; Sauer, R.T.; Baker, T.A. Modulating substrate choice: The SspB adaptor delivers a regulator of the extracytoplasmic-stress response to the AAA+ protease ClpXP for degradation. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonetto, M.; Gribskov, M.; Gross, C.A. The sigma 70 family: Sequence conservation and evolutionary relationships. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3843–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paget, M.S.B.; Helmann, J.D. The σ70 family of sigma factors. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Shimamoto, N. Regions of the Escherichia coli primary sigma factor σ 70 that are involved in interaction with RNA polymerase core enzyme. Genes Cells 1997, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Severinova, E.; Darst, S.A. Crystal structure of a sigma 70 subunit fragment from Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Cell 1996, 87, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.; Waite, C.; James, E.; Synn, N.; Simpson, T.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Buck, M. Functional characterization of key residues in regulatory proteins HrpG and HrpV of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. Regulation of Erwinia carotovora hrpLEcc (sigma-LEcc), which encodes an extracytoplasmic function subfamily of sigma factor required for expression of the HRP regulon. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldrin, F.; Cioetto Mazzabò, L.; Anoosheh, S.; Palù, G.; Gaudreau, L.; Manganelli, R.; Provvedi, R. Assessing the role of Rv1222 (RseA) as an anti-sigma factor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis extracytoplasmic sigma factor SigE. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.M.; Fisher, D.J. Site-specific, insertional inactivation of incA in Chlamydia trachomatis using a group II intron. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e83989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, M.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Ko, C.; Converse, P.J.; Bishai, W.R. Deletion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sigma factor E results in delayed time to death with bacterial persistence in the lungs of aerosol-infected mice. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 7170–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supian, S.; Saidi, N.B.; Wee, C.; Abdullah, M.P. Antioxidant-mediated response of a susceptible papaya cultivar to a compatible strain of Erwinia mallotivora. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 98, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Description | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E Value | Identity | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantoe vagans FDAARGOS 160 | 598 | 598 | 97% | 8 × 10−167 | 85% | CP014128.2 |
| Erwinia tracheiphila MDcuke | 576 | 576 | 100% | 3 × 10−160 | 83% | CP013970.1 |
| Erwinia sp. Ejp617, | 519 | 519 | 99% | 6 × 10−143 | 81% | CP002124.1 |
| E. pyrifoliae EpK1/15 | 510 | 510 | 99% | 3 × 10−140 | 81% | CP023567.1 |
| E. pyrifoliae DSM 12163 | 510 | 510 | 99% | 3 × 10−140 | 81% | FN392235.1 |
| E. pyrifoliae WT3 | 510 | 510 | 99% | 3 × 10−140 | 81% | DQ180962.2 |
| E. pyrifoliae Ep1/96 | 510 | 510 | 99% | 3 × 10−140 | 81% | FP236842.1 |
| E. pyrifoliae | 510 | 510 | 99% | 3 × 10−140 | 81% | AY532654.1 |
| E. pyrifoliae Ep4/97 | 510 | 510 | 99% | 3 × 10−140 | 81% | AJ438881.1 |
| E. tasmaniensis ET1/99 | 488 | 488 | 99% | 1 × 10−133 | 80% | CU468135.1 |
| E. amylovora E-2 | 465 | 465 | 99% | 1 × 10−126 | 79% | CP024970.1 |
| E. amylovora ATCC BAA-2158 | 465 | 465 | 99% | 1 × 10−126 | 79% | FR719186.1 |
| E. amylovora CFBP1430 | 465 | 465 | 99% | 1 × 10−126 | 79% | FN434113.1 |
| E. amylovora ATCC 49946 | 465 | 465 | 99% | 1 × 10−126 | 79% | FN666575.1 |
| E. amylovora | 465 | 465 | 99% | 1 × 10−126 | 79% | AF083877.1 |
| E. amylovora | 465 | 465 | 99% | 1 × 10−126 | 79% | U36244.1 |
| E. herbicola pv. gypsophilae | 445 | 445 | 100% | 1 × 10−120 | 78% | AF272053.1 |
| Pseudomonas carotovorum ssp. carotovorum | 109 | 109 | 73% | 1 × 10−19 | 67% | EU420066.1 |
| Seq ID: MK205448.1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Erwinia mallotivora strain BT-MARDI RNA Polymerase Sigma Factor RpoE/hrpL | ||
| Analysis Report | ||
| Analytical Modules | Prediction | Details |
| CMSVM | Unknown | - |
| CytoSVM | Cytoplasmic | - |
| SCL-BLAST | Cytoplasmic | Matched 16130498: RNA polymerase, sigma 24 (sigma E) factor [Escherichia coli K12] |
| SCL-BLAST | Unknown | - |
| Signal | Unknown | - |
| Localisation | Scores | |
| Cytoplasmic | 9.97 | |
| Cytoplasmic Membrane | 0.01 | |
| Periplasmic | 0.01 | |
| Outer membrane | 0.00 | |
| Extracellular | 0.00 | |
| Final Prediction | ||
| Cytoplasmic | 9.97 | |
| Template | Alignment Coverage | Confidence | % Identity | Template Formation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c1or7A_ | 8–181 (95%) | 100 | 23 | PDB header: transcription Chain: A: PDB Molecule: RNA polymerase sigmaE factor; PDB Title: crystal structure of Escherichia coli sigmaE with the cytoplasmic domain of its anti-sigma RseA |
| c4cxfA_ | 7–182 (96%) | 100 | 20 | PDB header: transcription Chain: A: PDB Molecule: RNA polymerase sigma factor CnrH; PDB Title: structure of CnrH in complex with the cytosolic domain of CnrY |
| c5wurB_ | 7–181 (95%) | 100 | 23 | PDB header: metal-binding protein Chain: B: PDB Molecule: ECF RNA polymerase sigma factor SigW; PDB Title: crystal structure of SigW in complex with its anti-sigma RsiW, an oxidised form |
| c2q1zA_ | 5–180 (96%) | 100 | 18 | PDB header: transcription Chain: A: PDB Molecule: RpoE, ECF SigE; PDB Title: crystal structure of Rhodobacter sphaeroides SigE in complex with the anti-sigma ChrR |
| Culture/Suspension | Averaged Scoring of Infection (Disease Severity) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day3 | Day6 | Day9 | Day12 | Day16 | Day20 | Day30 | |
| Wild type E. mallotivora | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Knockout mutant, ΔEmhrpL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1× phosphate-buffered saline (negative control) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Strain of Erwinia mallotivora | Disease progression Day 3 (D3) until Day 30 (D30) post inoculation with respective E. mallotivora strain | ||||||
| Wild Type (Control) |  | ||||||
| Knockout Mutant (ΔEmhrpL) |  | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamizi, A.-A.; Abu-Bakar, N.; Samsuddin, A.-F.; Rozano, L.; Ahmad-Redzuan, R.; Abdul-Murad, A.-M. Characterisation and Mutagenesis Study of An Alternative Sigma Factor Gene (hrpL) from Erwinia mallotivora Reveal Its Central Role in Papaya Dieback Disease. Biology 2020, 9, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100323
Tamizi A-A, Abu-Bakar N, Samsuddin A-F, Rozano L, Ahmad-Redzuan R, Abdul-Murad A-M. Characterisation and Mutagenesis Study of An Alternative Sigma Factor Gene (hrpL) from Erwinia mallotivora Reveal Its Central Role in Papaya Dieback Disease. Biology. 2020; 9(10):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100323
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamizi, Amin-Asyraf, Norliza Abu-Bakar, Aimera-Farhana Samsuddin, Lina Rozano, Rohaiza Ahmad-Redzuan, and Abdul-Munir Abdul-Murad. 2020. "Characterisation and Mutagenesis Study of An Alternative Sigma Factor Gene (hrpL) from Erwinia mallotivora Reveal Its Central Role in Papaya Dieback Disease" Biology 9, no. 10: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100323
APA StyleTamizi, A.-A., Abu-Bakar, N., Samsuddin, A.-F., Rozano, L., Ahmad-Redzuan, R., & Abdul-Murad, A.-M. (2020). Characterisation and Mutagenesis Study of An Alternative Sigma Factor Gene (hrpL) from Erwinia mallotivora Reveal Its Central Role in Papaya Dieback Disease. Biology, 9(10), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100323





