Biomass and Astaxanthin Productivities of Haematococcus pluvialis in an Angled Twin-Layer Porous Substrate Photobioreactor: Effect of Inoculum Density and Storage Time
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
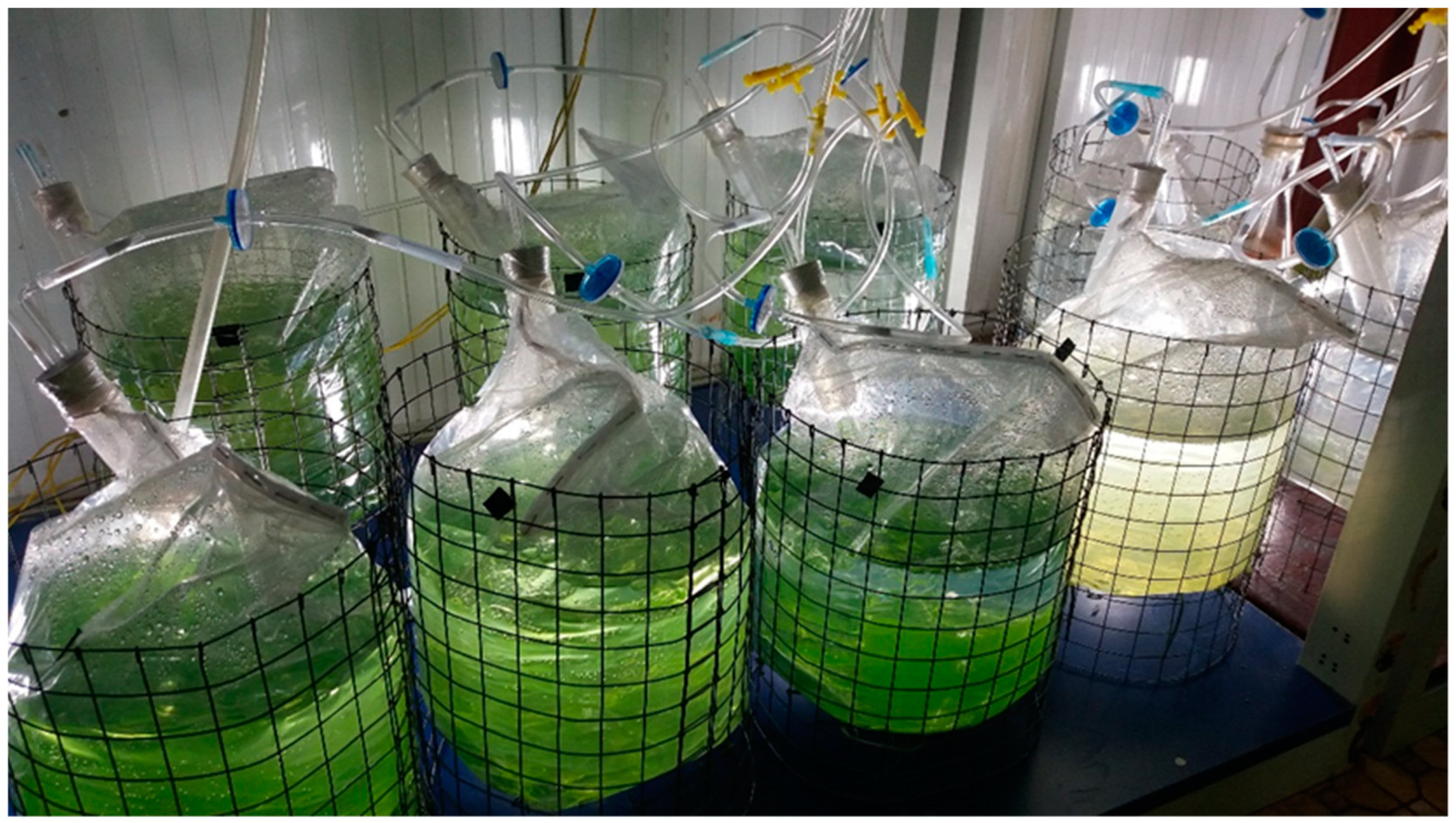
2.1. Algal Strain and Culture Maintenance
2.2. Experimental Designs
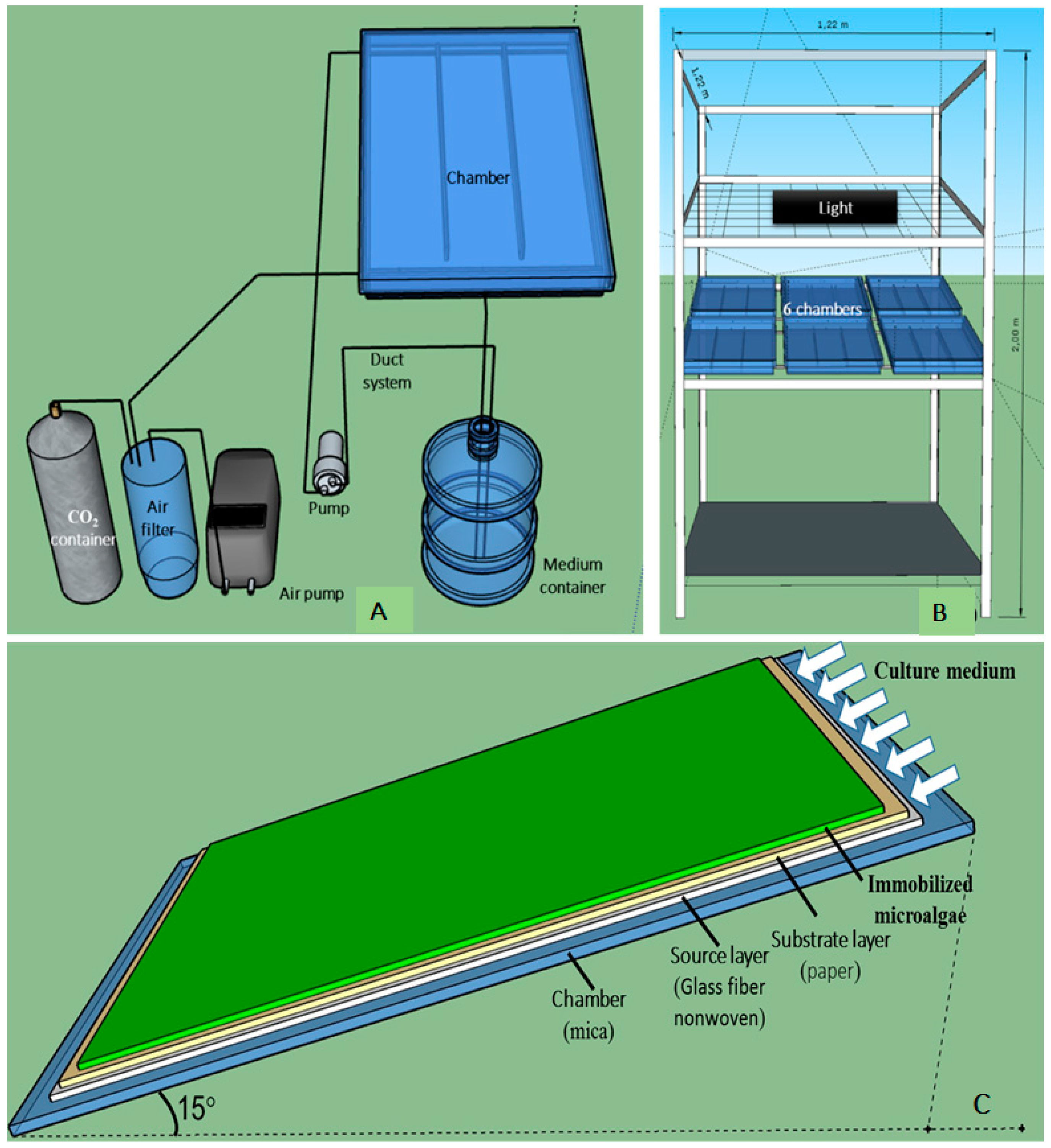
2.2.1. Experiments with the Small-Scale TL-PSBR
2.2.2. Experiment with the Large Scale TL-PSBR
2.3. Preparation of H. pluvialis Biomass for Experiments on Angled TL-PSBRs
2.4. Algae Immobilization on Angled TL-PSBRs
2.5. Culture Conditions after Algal Immobilization
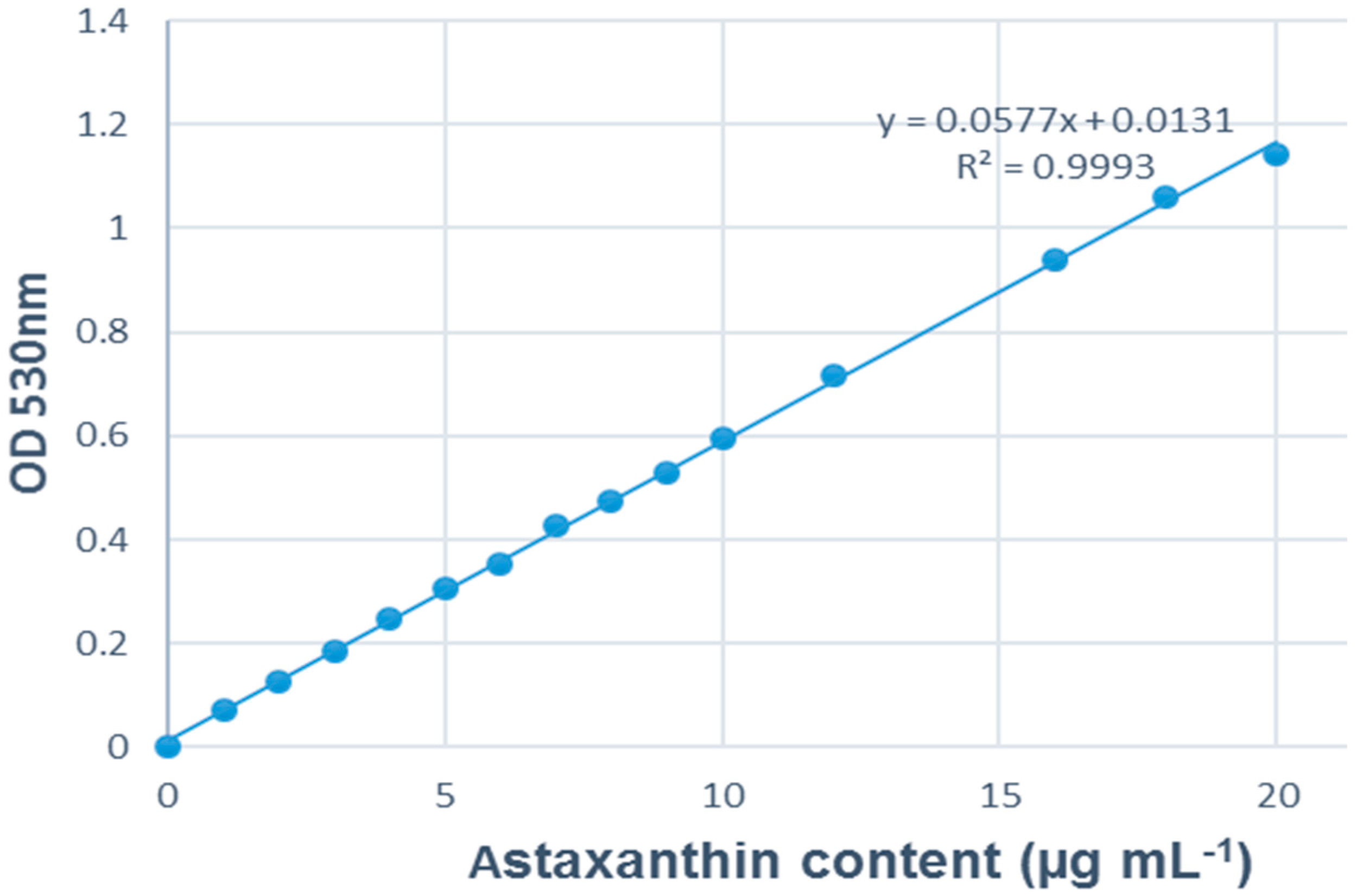
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dry Biomass Growth and Astaxanthin Accumulation of Immobilized H. pluvialis Cultivated in an Angled TL-Photobioreactor at Different Initial Biomass Density
3.2. Influence of Algal Storage Time after Centrifugation of a Suspension Culture on Biomass Growth and Astaxanthin Accumulation in a TL-PSBR
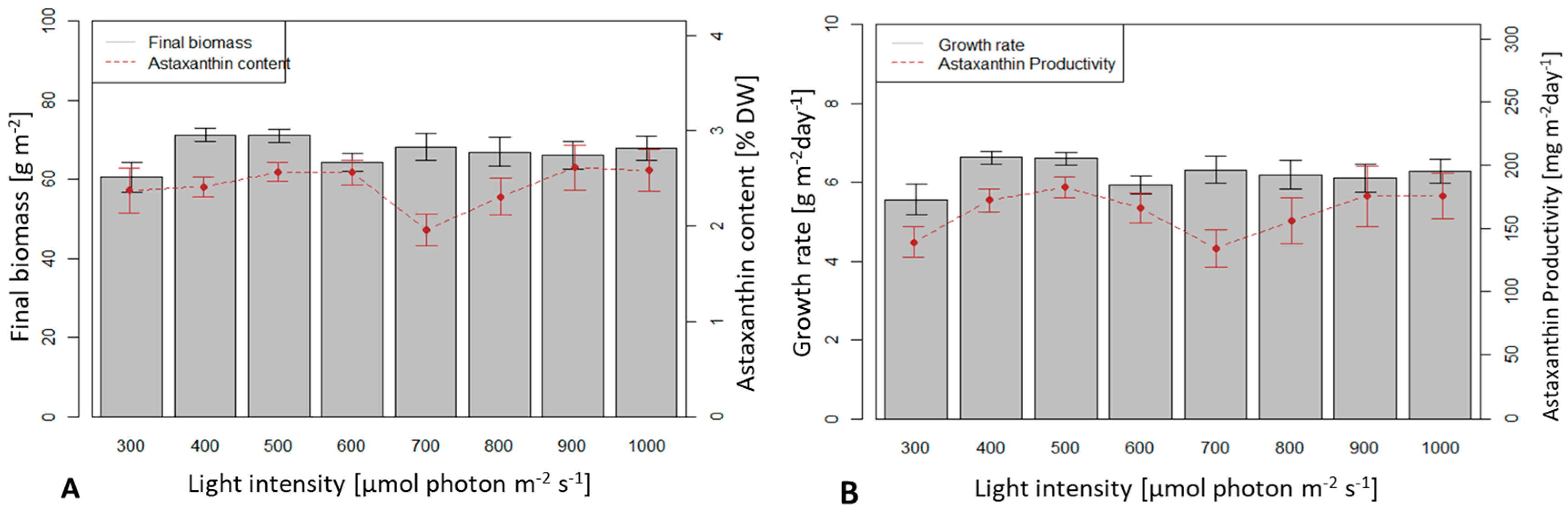
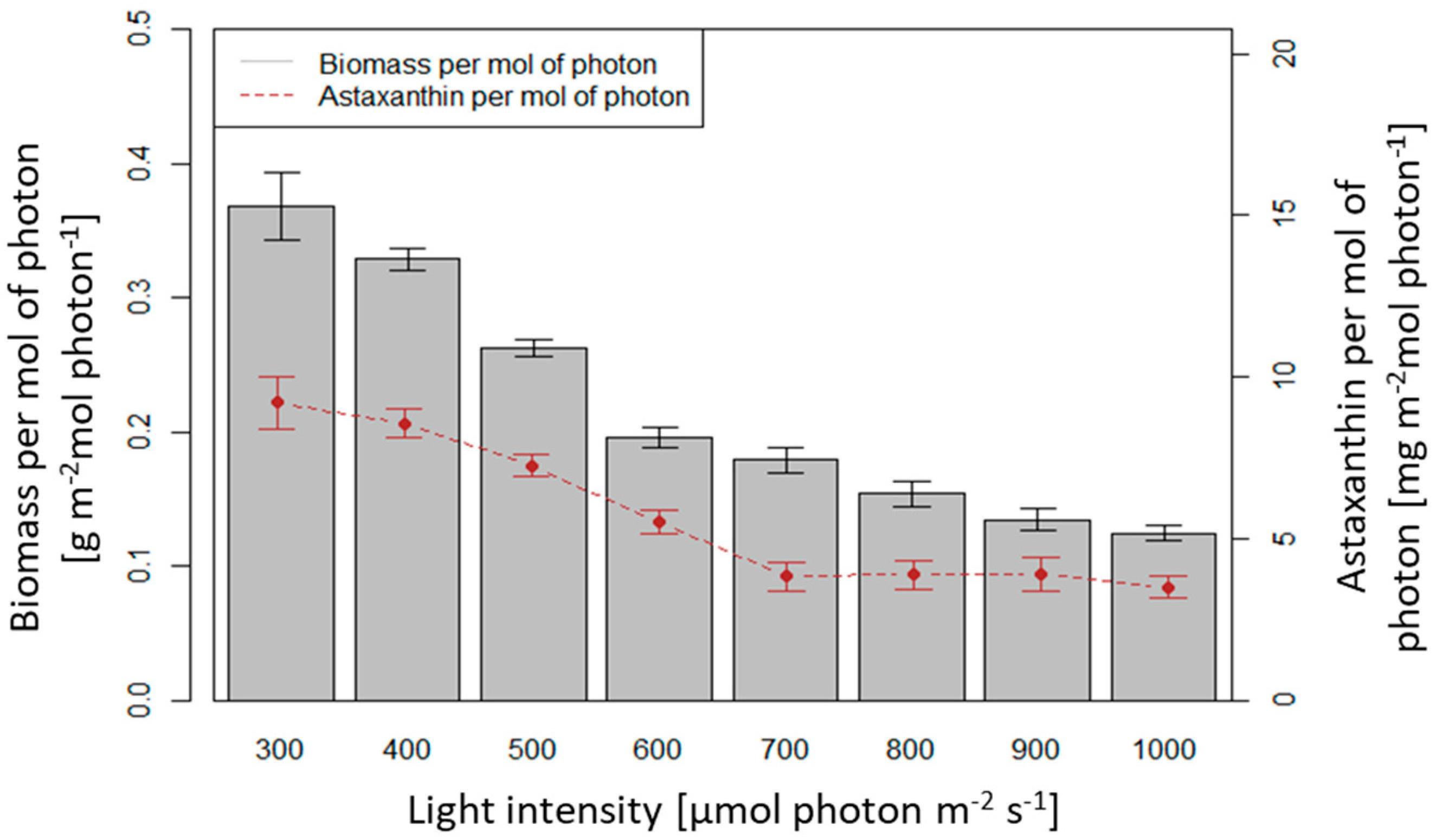
3.3. Influence of Light Intensity on Biomass Growth and Astaxanthin Accumulation of H. pluvialis in an Angled TL-PSBR
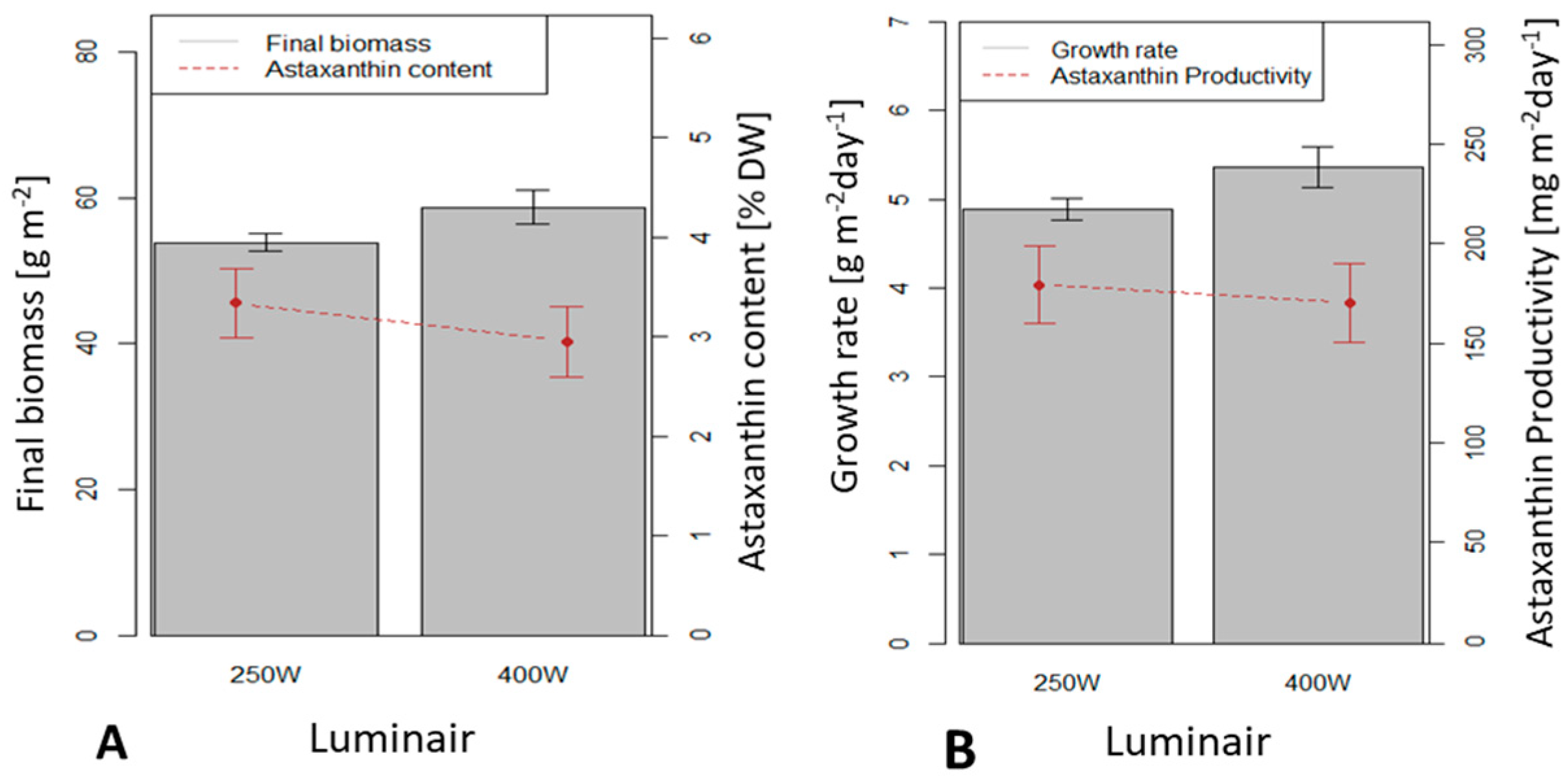
3.4. Influence of the Light Source on H. pluvialis Immobilized Cultivation in a 0.5 m2 x 4 (Large Scale) Twin-Layer Photobioreactor
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Initial Biomass Density
4.2. Influence of Algal Storage Time
4.3. Influence of Light Conditions and CO2 Supplement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, A.R.; Sindhuja, H.N.; Dharmesh, S.M.; Sankar, K.U.; Sarada, R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Effective inhibition of skin cancer, tyrosinase, and antioxidative properties by astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3842–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, G.J.; Hazen, S.L.; Lockwood, S.F. Seven day oral supplementation with Cardax (disodium disuccinate astaxanthin) provides significant cardioprotection and reduces oxidative stress in rats. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2006, 283, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambati, R.R.; Phang, S.M.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R.G. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications—A review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.Y.; Jin, J.; Lu, G.; Kang, X.L. Astaxanthin attenuates the apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in db/db mice by inhibition of oxidative stress. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.D.; An, J.Y.; Park, T.H.; Sim, S.J. Astaxanthin biosynthesis from simultaneous N and P uptake by the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis in primary-treated wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.T.; Cysewski, G.R. Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Attached cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis for astaxanthin production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaizola, M.; Huntley, M. Recent advances in commercial production of astaxanthin from microalgae. In Biomaterials and Bioprocessing; Fingerman, M., Nagabhushanam, R., Eds.; Science Publishers: Grafton County, NH, USA, 2003; Volume 9, pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Aflalo, C.; Meshulam, Y.; Zarka, A.; Boussiba, S. On the relative efficiency of two- vs. one-stage production of astaxanthin by the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 98, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, I.S.; Joo, H.N.; Lee, C.G. A novel double-layered photobioreactor for simultaneous Haematococcus pluvialis cell growth and astaxanthin accumulation. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 125, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acién, F.G.; Molina, E.; Reis, A.; Torzillo, G.; Zittelli, G.C.; Sepúlveda, C.; Masojídek, J. 1—Photobioreactors for the production of microalgae. In Microalgae-Based Biofuels and Bioproducts; Gonzalez-Fernandez, C., Muñoz, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L.; Owende, P. Biofuels from microalgae—A review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe, O.; Piero, S.; Antonio, M. Advances in photobioreactors for intensive microalgal production: Configurations, operating strategies and applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.; Jarboe, D.; Wen, Z. Biofilm-based algal cultivation systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, T.; Çebi, Z.; Podola, B.; Melkonian, M. Growing microalgae as aquaculture feeds on twin-layers: A novel solid-state photobioreactor. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podola, B.; Li, T.; Melkonian, M. Porous substrate bioreactors: A paradigm shift in microalgal biotechnology? Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowack, E.C.M.; Podola, B.; Melkonian, M. The 96-well twin-tayer system: A novel approach in the cultivation of microalgae. Protist 2005, 156, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiperstok, A.C. Optimizing immobilized cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis for astaxanthin production. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität zu Köln., Cologne, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, M.; Hou, D.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Huang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, W.; Pan, R.; Wang, J.; Li, S. The effective photoinduction of Haematococcus pluvialis for accumulating astaxanthin with attached cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Zhang, J.; Hou, D.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, J. The effect of temperature on cell growth and astaxanthin accumulation of Haematococcus pluvialis during a light-dark cyclic cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, T. The water footprint of biofilm cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis is greatly decreased by using sealed narrow chambers combined with slow aeration rate. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Podola, B.; Melkonian, M. Removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater using microalgae immobilized on twin layers: An experimental study. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiperstok, A.C.; Sebestyén, P.; Podola, B.; Melkonian, M. Biofilm cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis enables a highly productive one-phase process for astaxanthin production using high light intensities. Algal Res. 2017, 21, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.D.; Do, T.T.; Le, T.L.; Tran-Nguyen, M.L.; Pham, C.H.; Melkonian, M. Cultivation of Haematococcus pluvialis for astaxanthin production on angled bench-scale and large-scale biofilm-based photobioreactors. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2019, 61, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, F.; Geng, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, M. Accurate quantification of astaxanthin from Haematococcus crude extract spectrophotometrically. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Sommerfeld, M.; Lu, Y.; Han, D. Cellular capacities for high-light acclimation and changing lipid profiles across life cycle stages of the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Torzillo, G.; Goksan, T.; Faraloni, C.; Kopecky, J.; Masojídek, J. Interplay between photochemical activities and pigment composition in an outdoor culture of Haematococcus pluvialis during the shift from the green to red stage. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Geng, Y.H.; Li, Z.K.; Hu, H.J.; Li, Y.G. Production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus in open pond by two-stage growth one-step process. Aquaculture 2009, 295, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klochkova, T.; Seok Kwak, M.; Han, J.W.; Motomura, T.; Nagasato, C.; Kim, G.H. Cold-tolerant strain of Haematococcus pluvialis (Haematococcaceae, Chlorophyta) from Blomstrandhalvøya (Svalbard). Algae 2013, 28, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cai, M.; Lin, M.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Ke, H.; Zheng, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; et al. Differences between Motile and Nonmotile Cells of Haematococcus pluvialis in the Production of Astaxanthin at Different Light Intensities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Strous, M.; Melkonian, M. Biofilm-based photobioreactors: Their design and improving productivity through efficient supply of dissolved inorganic carbon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Do, T.-T.; Ong, B.-N.; Nguyen Tran, M.-L.; Nguyen, D.; Melkonian, M.; Tran, H.-D. Biomass and Astaxanthin Productivities of Haematococcus pluvialis in an Angled Twin-Layer Porous Substrate Photobioreactor: Effect of Inoculum Density and Storage Time. Biology 2019, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8030068
Do T-T, Ong B-N, Nguyen Tran M-L, Nguyen D, Melkonian M, Tran H-D. Biomass and Astaxanthin Productivities of Haematococcus pluvialis in an Angled Twin-Layer Porous Substrate Photobioreactor: Effect of Inoculum Density and Storage Time. Biology. 2019; 8(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleDo, Thanh-Tri, Binh-Nguyen Ong, Minh-Ly Nguyen Tran, Doan Nguyen, Michael Melkonian, and Hoang-Dung Tran. 2019. "Biomass and Astaxanthin Productivities of Haematococcus pluvialis in an Angled Twin-Layer Porous Substrate Photobioreactor: Effect of Inoculum Density and Storage Time" Biology 8, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8030068
APA StyleDo, T.-T., Ong, B.-N., Nguyen Tran, M.-L., Nguyen, D., Melkonian, M., & Tran, H.-D. (2019). Biomass and Astaxanthin Productivities of Haematococcus pluvialis in an Angled Twin-Layer Porous Substrate Photobioreactor: Effect of Inoculum Density and Storage Time. Biology, 8(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology8030068




