Effects of Fiddler Crab Burrows on Sediment Properties in the Mangrove Mudflats of Sungai Sepang, Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Field Sampling
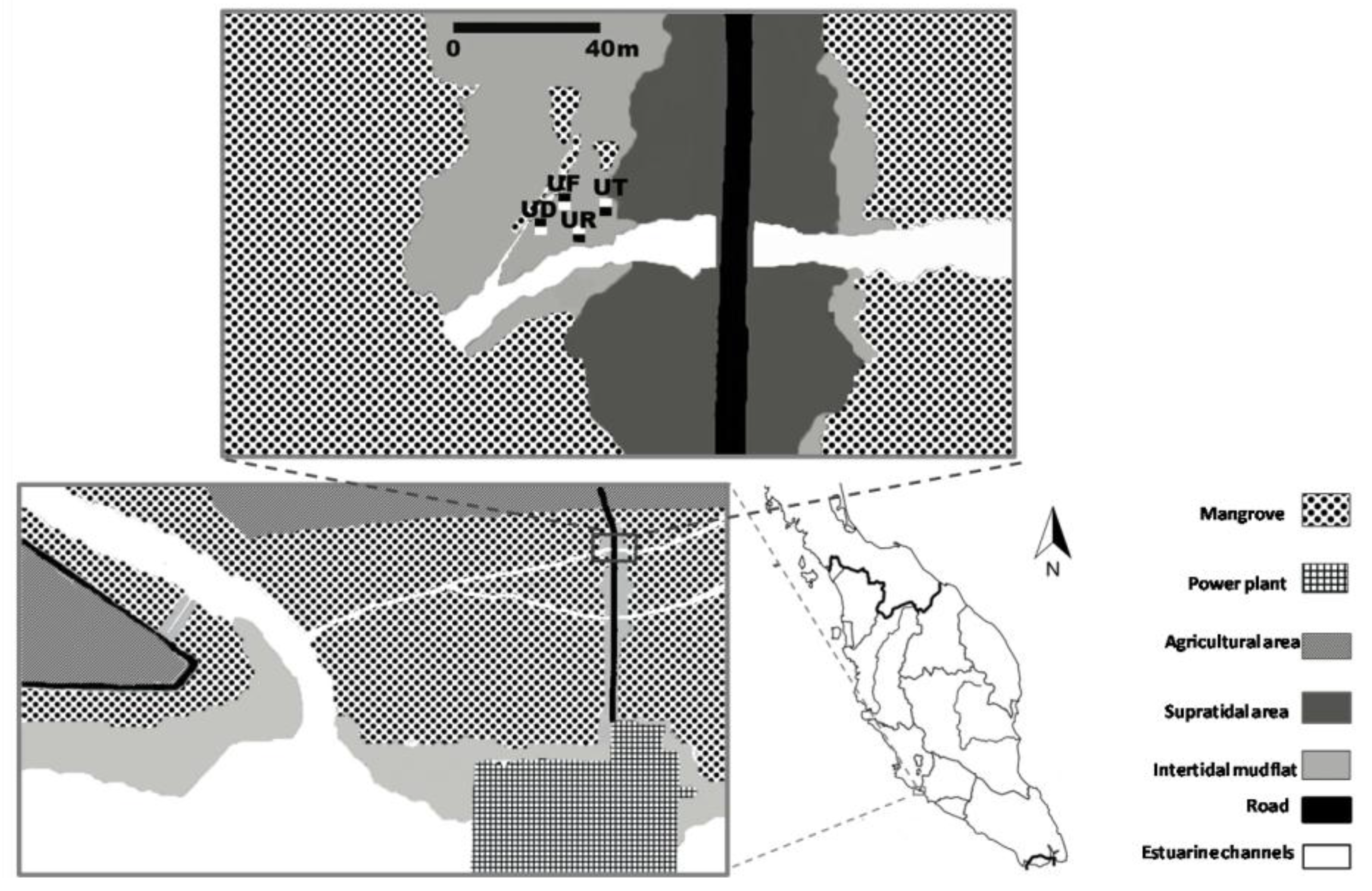
2.2. Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
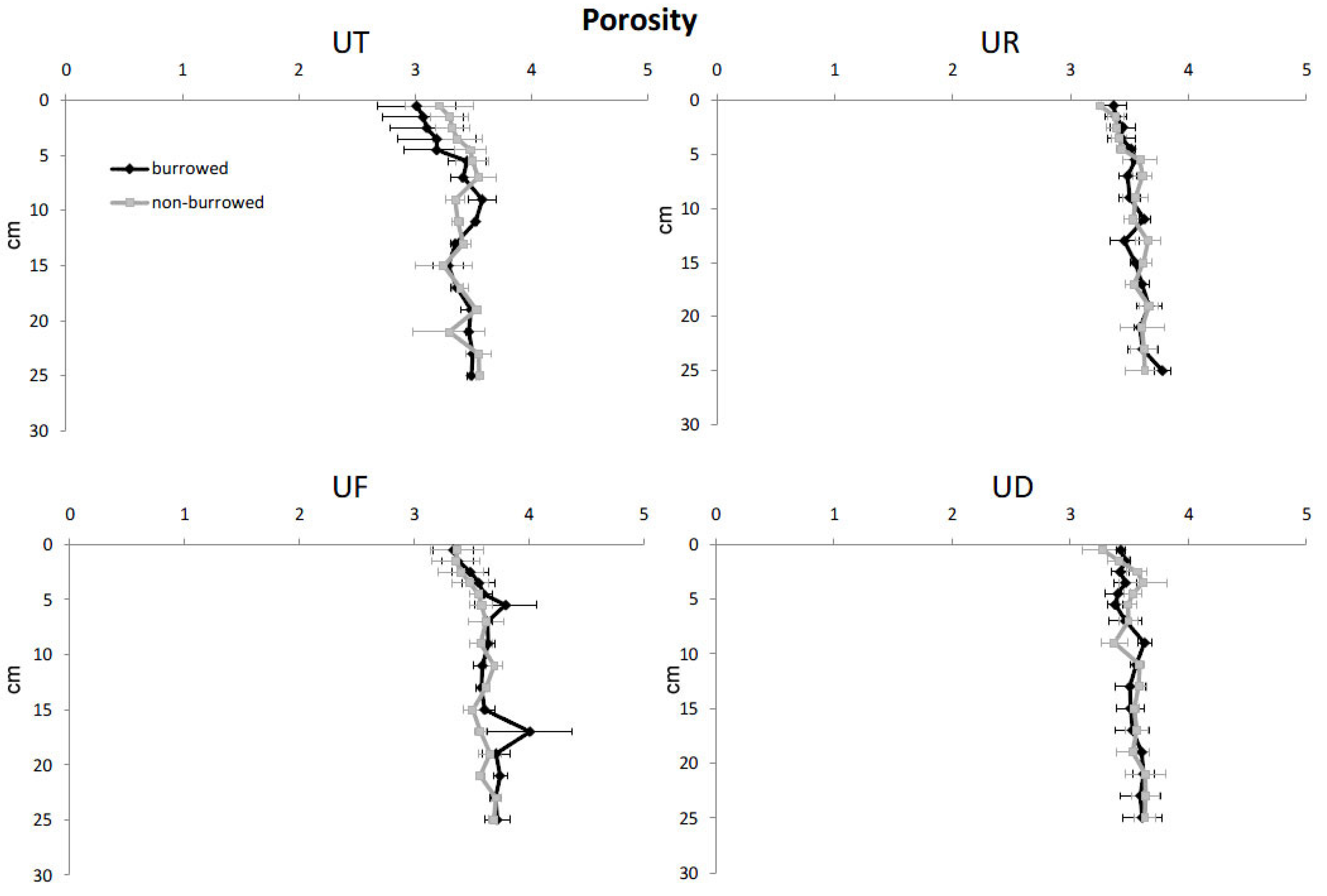
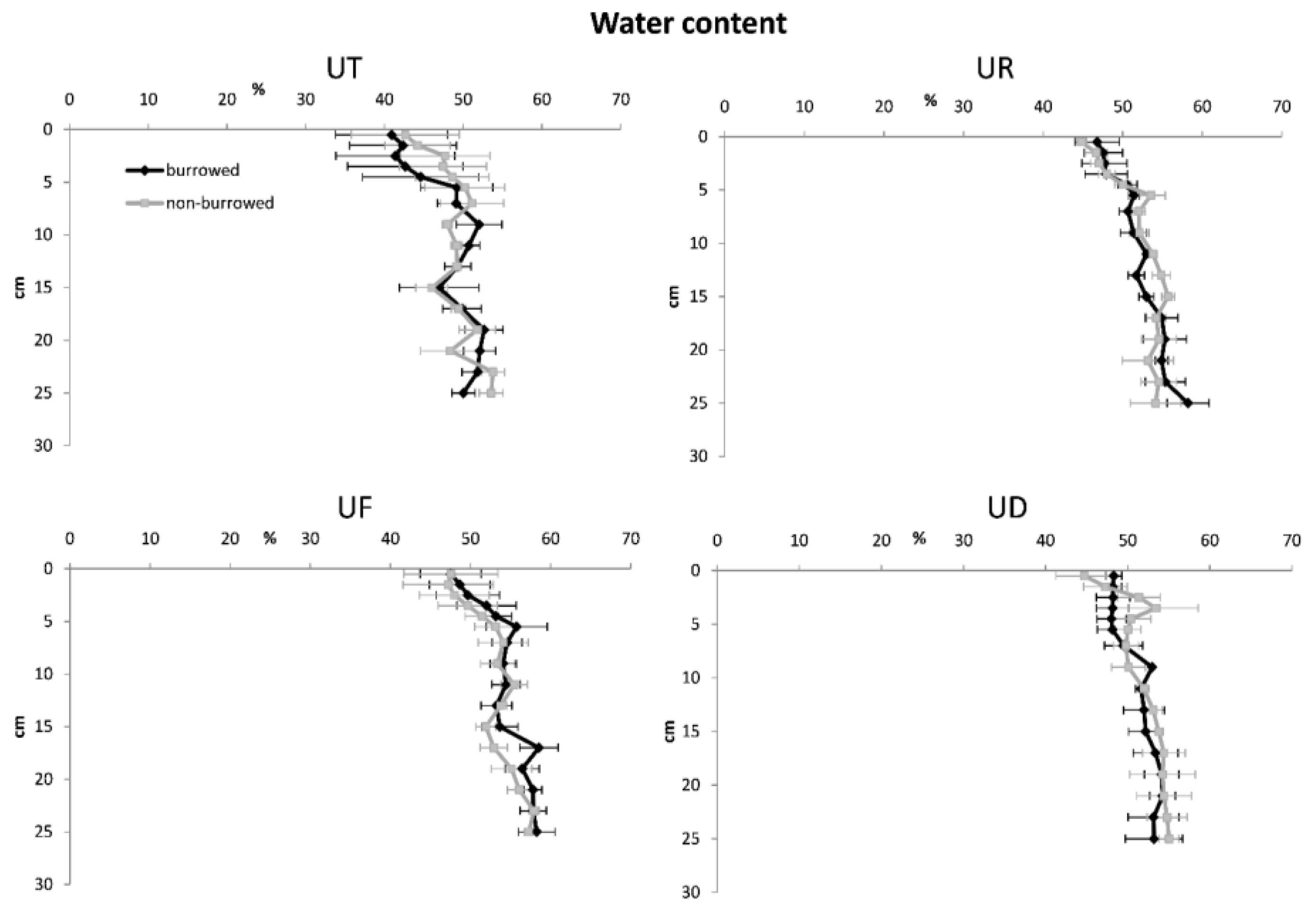
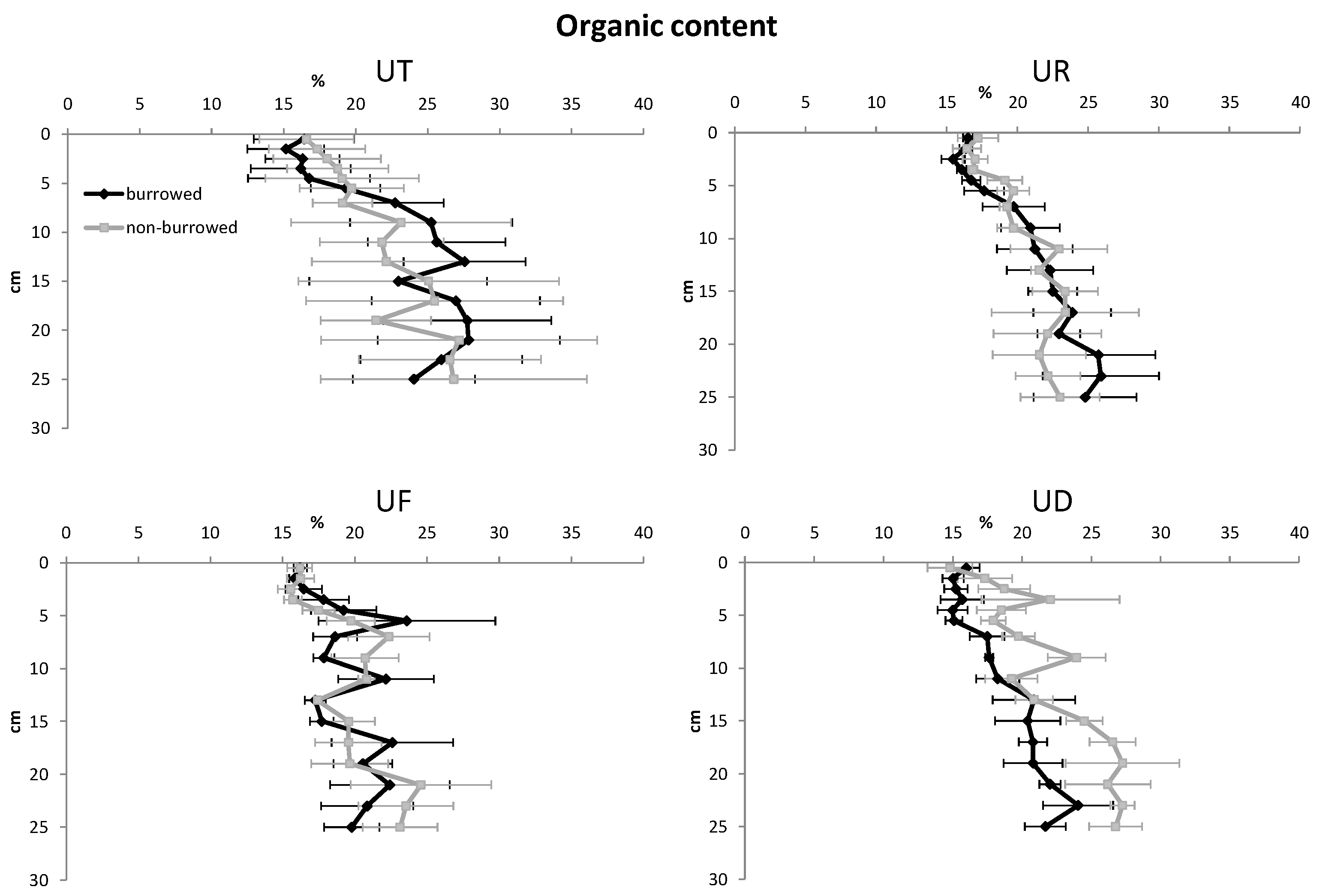
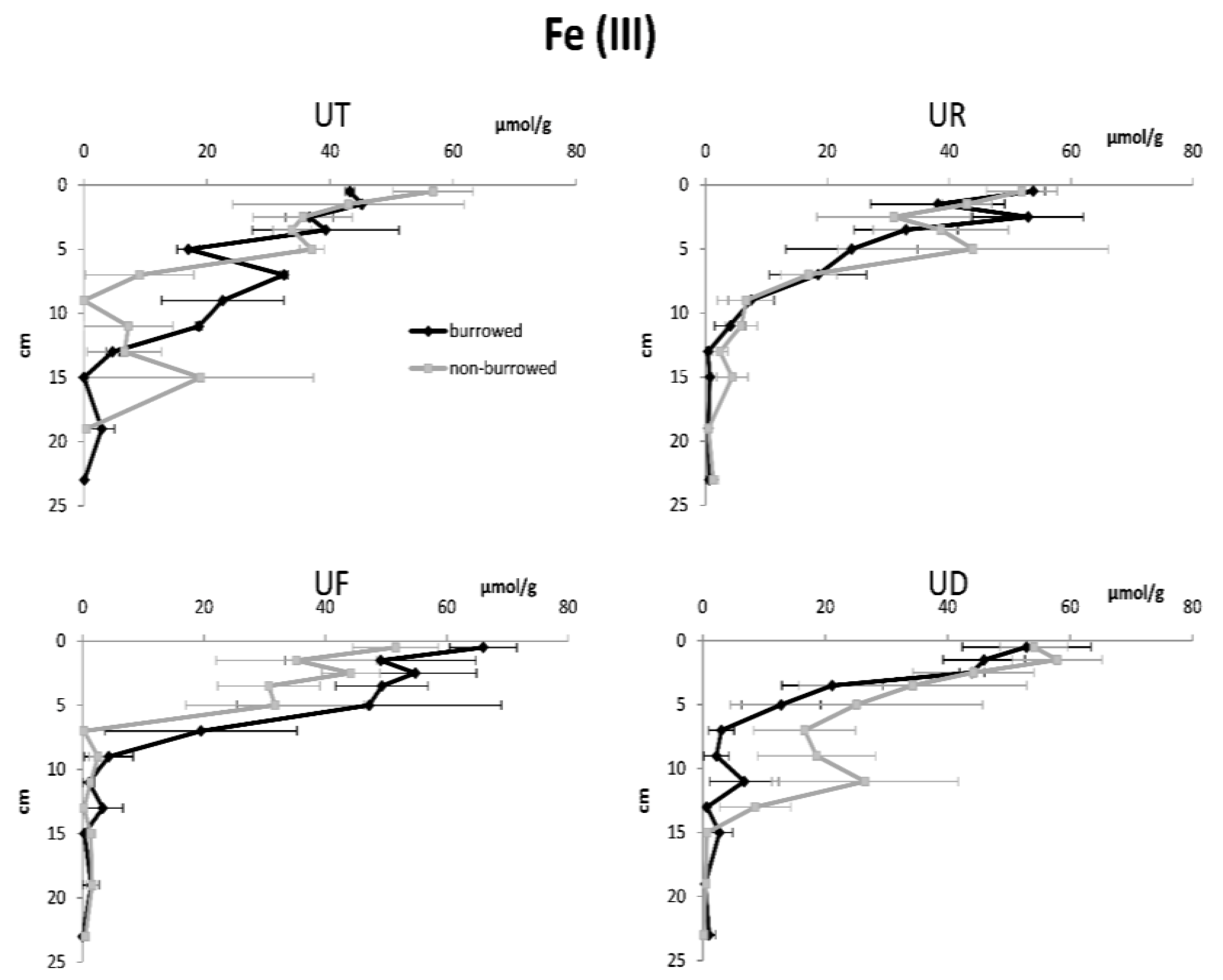
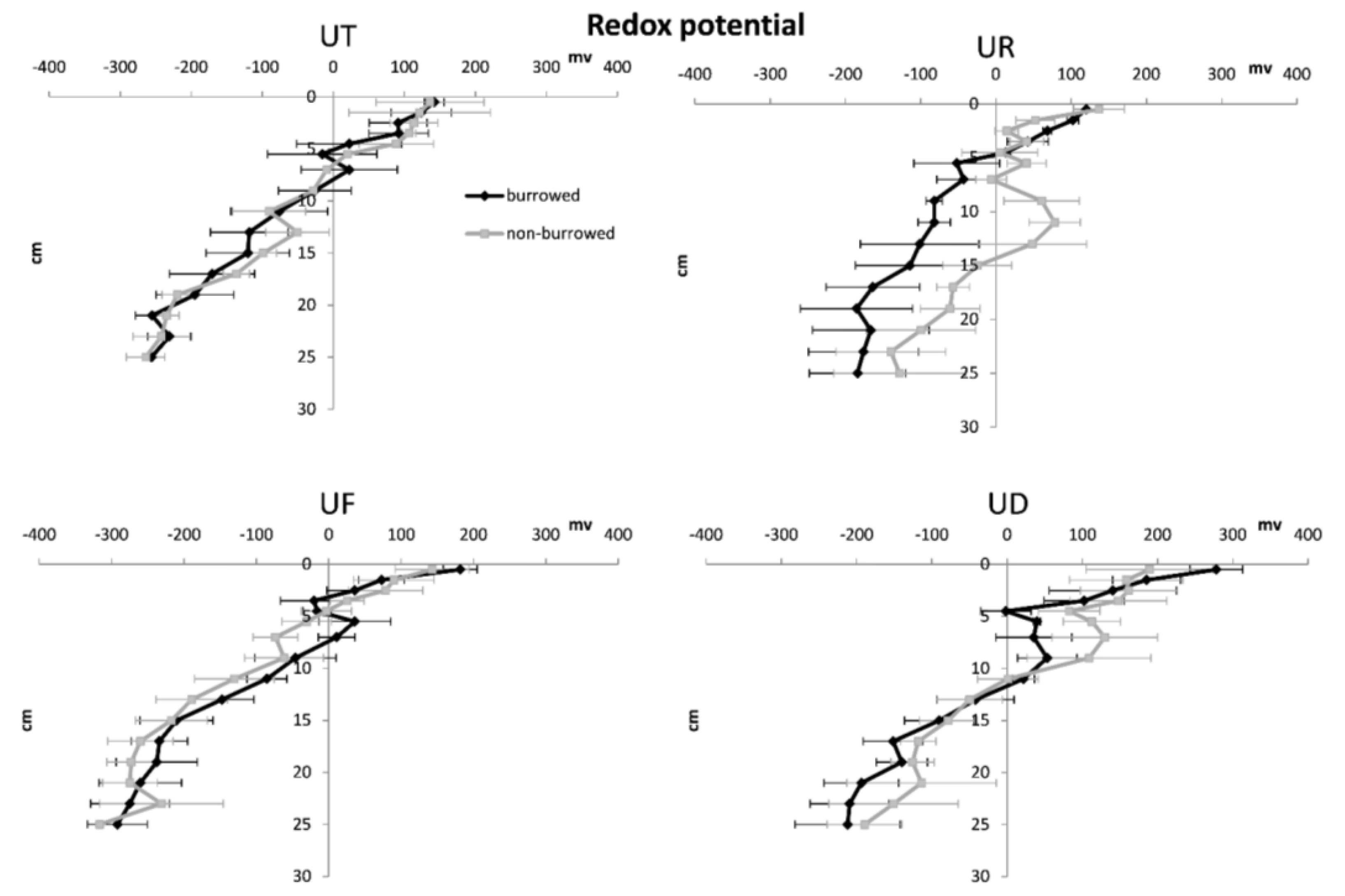
3. Results
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares (SS) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redox potential | |||||
| Depth | 15 | 5,258,508 | 350,567 | 49.56 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 492,236 | 164,079 | 23.20 | <0.001 |
| Burrow | 1 | 51,557 | 51,557 | 7.29 | 0.007 |
| Error | 348 | 2,461,400 | 7073 | ||
| Total | 367 | 8,267,538 | |||
| Sediment density | |||||
| Depth | 15 | 18.6837 | 1.2456 | 11.22 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 3.6740 | 1.2247 | 11.03 | <0.001 |
| Burrow | 1 | 0.0568 | 0.0568 | 0.51 | 0.475 |
| Error | 348 | 38.6340 | 0.1110 | ||
| Total | 367 | 61.1392 | |||
| Fe (III) | |||||
| Depth | 11 | 91,702.6 | 8329.5 | 45.50 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 144.3 | 48.2 | 0.26 | 0.852 |
| Burrow | 1 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 0.03 | 0.874 |
| Error | 245 | 44,851.1 | 183.1 | ||
| Total | 260 | 136,702.6 | |||
| Fe (II) | |||||
| Depth | 11 | 6624.48 | 601.34 | 11.39 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 271.37 | 88.77 | 1.68 | 0.172 |
| Burrow | 1 | 502.46 | 502.46 | 9.52 | 0.002 |
| Error | 245 | 12,937.35 | 52.81 | ||
| Total | 260 | 20,335.67 | |||
| Porosity | |||||
| Depth | 15 | 3.46537 | 0.23102 | 5.61 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 2.53254 | 0.84139 | 20.42 | <0.001 |
| Burrow | 1 | 0.00073 | 0.00073 | 0.02 | 0.894 |
| Error | 348 | 14.33820 | 0.04120 | ||
| Total | 367 | 20.33684 | |||
| Water content | |||||
| Depth | 15 | 3030.04 | 202 | 10.69 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 1219.92 | 403.32 | 21.34 | <0.001 |
| Burrow | 1 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 0.887 |
| Error | 348 | 6578.14 | 18.90 | ||
| Total | 367 | 10,828.49 | |||
| Organic content | |||||
| Depth | 15 | 3082.75 | 205.52 | 9.52 | <0.001 |
| Habitat | 3 | 320.66 | 113.22 | 5.25 | 0.001 |
| Burrow | 1 | 58.21 | 58.21 | 2.70 | 0.101 |
| Error | 348 | 7510.79 | 21.58 | ||
| Total | 367 | 10,972.41 | |||
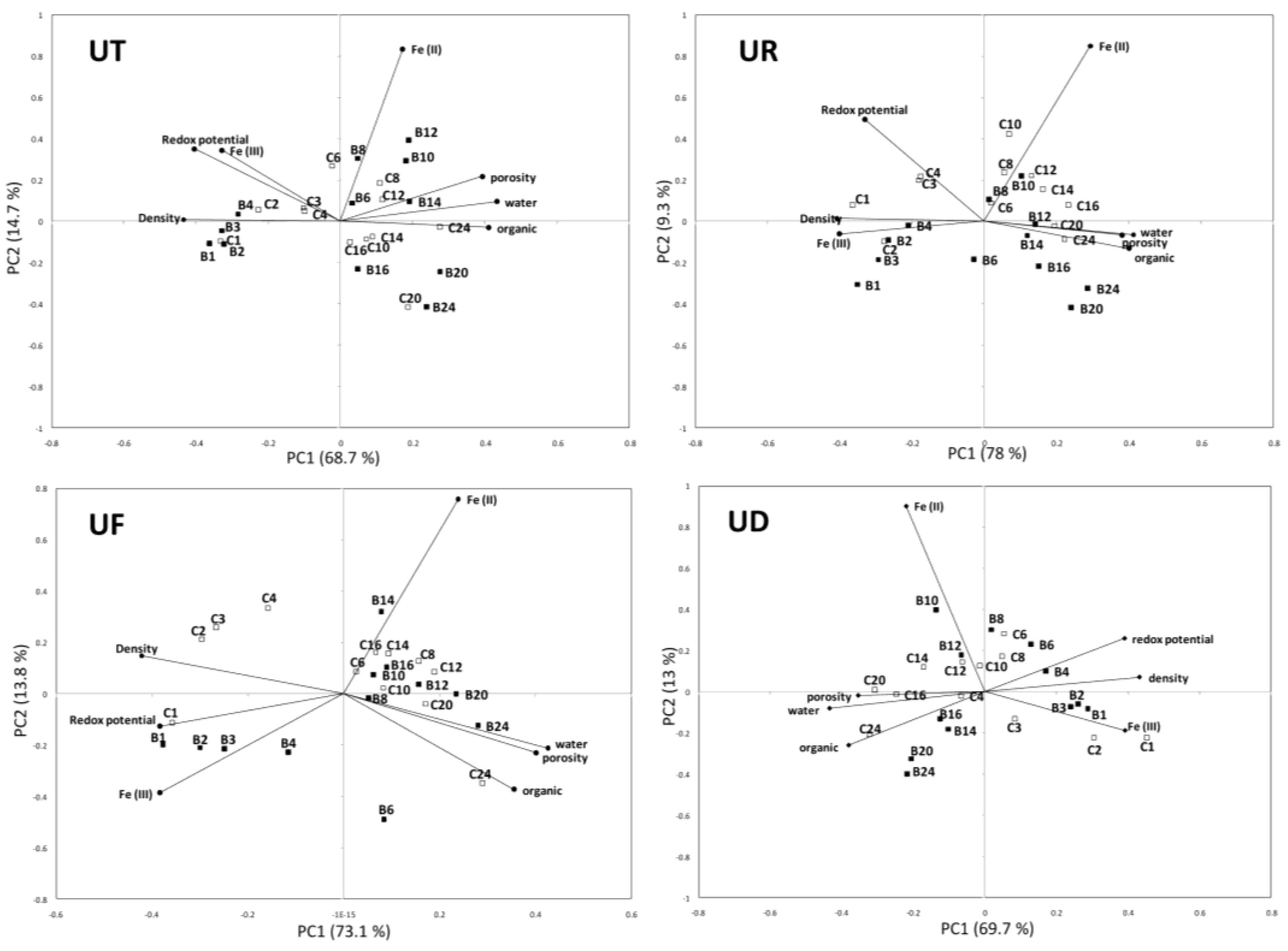
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Twilley, R.R.; Chen, R.H.; Hargis, T. Carbon sinks in mangrove forests and their implications to the carbon budget of tropical coastal ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1992, 64, 265–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, S.; Borges, A.V.; Castañeda-Moya, E.; Diele, K.; Dittmar, T.; Duke, N.C.; Kristensen, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Marchand, C.; Middleburg, J.J.; et al. Mangrove production and carbon sinks: A revision of global budget estimates. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Kauffman, J.B.; Murdiyarso, D.; Kurnianto, S.; Stidham, M.; Kanninen, M. Mangroves among the most carbon-rich forests in the tropics. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breithaupt, J.L.; Smoak, J.M.; Smith, T.J., III; Sanders, C.J.; Hoare, A. Organic carbon burial rates in mangrove sediments: Strengthening the global budget. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreetta, A.; Fusi, M.; Cameldi, I.; Cimò, F.; Carnicelli, S.; Cannicci, S. Mangrove carbon sink. Do burrowing crabs contribute to sediment carbon storage? Evidence from a Kenyan mangrove system. J. Sea Res. 2014, 85, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, S.; Koedam, N.; Raman, A.V.; Dehairs, F. Primary producers sustaining macro-invertebrate communities in intertidal mangrove forests. Oecologia 2002, 130, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Jennerjahn, T.C.; Ittekkot, V. Relevance of mangroves for the production and deposition of organic matter along tropical continental margins. Naturwissenschaften 2002, 89, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, C.; Disnar, J.R.; Lallier-Verges, E.; Lottier, N. Early diagenesis of carbohydrates and lignin in mangrove sediments subject to variable redox conditions (French Guiana). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; King, G.M.; Holmer, M.; Banta, G.T.; Jensen, M.H.; Hansen, K.; Bussarawit, N. Sulfate reduction, acetate turnover and carbon metabolism of the Ao Nam Bor mangrove, Phuket, Thailand. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 109, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Coastal Ecosystem Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; p. 419. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, D.M.; Tirendi, F.; Goldrick, A. Organic matter oxidation and sediment chemistry in mixed terrigenous-carbonate sands of ningaloo reef Western Australia. Mar. Chem. 1996, 54, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, O.I.; Kristensen, E.; Macintosh, D.J. Impact of fiddler crabs (Uca spp.) on rates and pathways of benthic mineralization in deposited mangrove shrimp pond waste. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 289, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Alongi, D.M. Control by fiddler crabs (Uca vocans) and plant roots (Avicennia marina) on carbon, iron, and sulfur biogeochemistry in mangrove sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.M.C., Jr.; Otero, X.L.; Marques, A.G.B.; Nóbrega, G.N.; Silva, J.R.F.; Ferreira, T.O. Selective geochemistry of iron in mangrove soils in a semiarid tropical climate: Effects of the burrowing activity of the crabs Ucides cordatus and Uca maracoani. Geo Mar. Lett. 2012, 32, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Botto, F.; Iribarne, O. Contrasting effect of two burrowing crabs (Chasmagnathus granulata and Uca uruguayensis) on sediment composition and transport in estuarine environments. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisey, D.J.; DeWitt, T.H.; Roper, D.S.; Williamson, R.B. Variation in the depth and morphology of burrows of the mud crab Helice crassa among different types of intertidal sediment in New Zealand. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 182, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCraith, B.J.; Gardner, L.R.; Wethey, D.S.; Moore, W.S. The effect of fiddler crab burrowing on sediment mixing and radionuclide profiles along a topographic gradient in a south eastern salt marsh. J. Mar. Res. 2003, 61, 359–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Mangrove crabs as ecosystem engineers; with emphasis on sediment processes. J. Sea Res. 2008, 59, 30–43. [Google Scholar]
- Reinsel, K.A. Impact of fiddler crab foraging and tidal inundation on an intertidal sandflat: Season-dependent effects in one tidal cycle. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 313, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.L.; Jones, C.G.; Groffman, P.M.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Iribarne, O.; Ribeiro, P.D.; Bruschetti, C.M. The contribution of crab burrow excavation to carbon availability in surficial saltmarsh sediments. Ecosystems 2006, 9, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.R.; Bancroft, K.; Vermeer, G.; Plaisier, K. Experimental studies on the foraging behavior of the sand fiddler crab Uca pugilator (Bosc, 1802). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1980, 44, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.R.; Newell, S.Y. Experimental studies of particle ingestion by the sand fiddler crab Uca pugilator (Bosc). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1982, 59, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’lafsson, E.; Ndaro, S.G.M. Impact of the mangrove crabs Uca annulipes and Dotilla fenestrata on meiobenthos. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 158, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, M.; Ghaffar, M.A.; Usup, G.; Cob, Z.C. Determination of key environmental factors responsible for distribution patterns of fiddler crabs in a tropical mangrove ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, E.J.P.; Lovely, D.R. Determination of Fe (III) and Fe (II) in oxalate extracts of sediment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, K.R. The biplot graphic display of matrices with application to principal component analysis. Biometrika 1971, 58, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkovich, I.; Smith, E.P. Biplot and singular value decomposition macros for excel. J. Stat. Softw. 2002, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Ahmed, S.I.; Devol, A.H. Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in marine sediment: Which is fastest? Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediments, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. Hydrobiologia 2000, 426, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D. Organism-sediment relations on the muddy seafloor. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1974, 12, 263–300. [Google Scholar]
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J.P. Manganese inhibition of microbial iron reduction in anaerobic sediments. Geomicrobiol. J. 1988, 6, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, D.; Appelo, C.A.J. Reduction of Mn-oxides by ferrous iron in a flow system: Column experiment and reactive transport modeling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, K.D.; Kristensen, E.; Jensen, M.H. The influence of water column hypoxia on the behaviour of manganese and iron in sandy coastal marine sediment. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E. Reactive iron in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kostka, J.E.; Gribsholt, B.; Petrie, E.; Dalton, D.; Skelton, H.; Kristensen, E. The rates and pathways of carbon oxidation in bioturbated saltmarsh sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Andersen, F.O.; Holmboe, N.; Holmer, M.; Thongtham, N. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in sediments of the Bangrong mangrove area, Phuket, Thailand. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 22, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamdrup, B. Bacterial manganese and iron reduction in aquatic sediments. In Advances in Microbial Ecology; Schink, B., Ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 41–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, T.O.; Otero, X.L.; Vidal-Torrado, P.; Macías, F. Effects of bioturbation by root and crab activity on iron and sulfur biogeochemistry in mangrove substrate. Geoderma 2007, 142, 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, D.M. The role of soft-bottom benthic communities in tropical mangrove and coral reef ecosystems. Rev. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 1, 243–280. [Google Scholar]
- Weis, J.S.; Weis, P. Behavior of four species of fiddler crabs, genus Uca, in southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. Hydrobiologia 2004, 523, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokhtari, M.; Abd Ghaffar, M.; Usup, G.; Che Cob, Z. Effects of Fiddler Crab Burrows on Sediment Properties in the Mangrove Mudflats of Sungai Sepang, Malaysia. Biology 2016, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5010007
Mokhtari M, Abd Ghaffar M, Usup G, Che Cob Z. Effects of Fiddler Crab Burrows on Sediment Properties in the Mangrove Mudflats of Sungai Sepang, Malaysia. Biology. 2016; 5(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokhtari, Mohammad, Mazlan Abd Ghaffar, Gires Usup, and Zaidi Che Cob. 2016. "Effects of Fiddler Crab Burrows on Sediment Properties in the Mangrove Mudflats of Sungai Sepang, Malaysia" Biology 5, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5010007
APA StyleMokhtari, M., Abd Ghaffar, M., Usup, G., & Che Cob, Z. (2016). Effects of Fiddler Crab Burrows on Sediment Properties in the Mangrove Mudflats of Sungai Sepang, Malaysia. Biology, 5(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology5010007






