Bacterial Adhesion of Streptococcus suis to Host Cells and Its Inhibition by Carbohydrate Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Streptococcus suis Adhesion
3. Virulence Genes with a Role in Adhesion
3.1. Regulators
| GENE ID | GENE DESIGNATION | MUTANT PHENOTYPES |
|---|---|---|
| Regulators with phenotype in adhesion | ||
| SSU0944, SSU0945 | ciaRH [24] | Two-component regulator, decreased adhesion to Hep-2 cells |
| SSU1873 not functional in P1/7, SSGZ1_1897 in S. suis GZ1 | revS [25] | Orphan regulator, decreased adhesion to Hep-2 cells |
| – | revSC21 [26] | Orphan regulator, decreased binding to Hep-2 cells |
| SSU0376 | luxS [36] | Quorum sensing regulator, decreased adhesion |
| SSU1789 | rgg-like regulator [34] | Negative transcriptional regulator, increased adhesion to Hep-2 cells |
| SSU1191 | covR [29] | Orphan regulator, increased adhesion to Hep-2 cells |
| SSU1202 | ccpA [37] | Carbon catabolite protein, decreased capsule thickness |
| Modulators of adhesion | ||
| SSU0516, SSU0519, SSU0520, SSU0517, SSU0535 | cps2B, cps2E, cps2F [15,38], cps2C [39], neuB [39] | Polysaccharide synthesis genes, increased adhesion of unencapsulated mutants |
| SSU0596, SSU1448 | dltA and pgdA [40,41] | Cell wall modification, upregulated upon contact with endothelial cells |
| Moonlighting or other cell wall proteins without signal sequence and known anchoring mechanism | ||
| SSU0187, SSGZ1_0184 | dpp4 [42] | Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, fibronectin binding |
| SSU1320 | eno [43,44] | Enolase, fibronectin and plasminogen binding, recombinant protein inhibits adhesion to Hep-2 cells |
| SSU0153 | GAPDH, [45] | Recombinant protein inhibits bacterial binding to porcine tracheal rings and Hep-2 cells |
| SSU1541 | gnd [46] | 6-Phosphogluconate-dehydrogenase, recombinant protein inhibits bacterial binding to Hep-2 and HeLa cells |
| SSU0157 | glnA [47] | Glutamine synthetase, decreased adherence to the Hep-2 cells |
| SSU1127 | atl, autolysin [48] | Biofilm and Hep-2 cell adhesion |
| SSU1311 | fbps [49] | Fibronectin binding |
| LPXTG-anchored proteins | ||
| SSU0925 | srtA [50] | Anchoring of cell wall proteins |
| SSU0879 | IgA1 protease [51,52] | Degradation of IgA protecting mucosal surfaces |
| SSU1474 (pseudo), SSUST1_ 1540 in S. suis ST1 | sof [53] | Lipoprotein degradation |
| SSU0757 | sspA, [54,55] | Subtilisin-like protease, induces secretion of cytokines and chemokines |
| SSU1143 | ssa [56] | Fibronectin/fibrinogen binding, reduced adhesion and invasion to Hep-2 cells |
3.2. S. suis Surface Glycoconjugates
3.3. Cell Wall Proteins
4. S. suis Carbohydrate-Specific Adhesion to Host Cells
4.1. Galabiose (Galα1-4Gal)-Specific Adhesion of S. suis
| Structure/Antigen a | Ligands | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adhesins | Toxins | ||
| GbO3 b | Galα1-4Galβ1-4Glcβ1-1'Cer/Pk | E. coli PapGI [79], S. suis SadP, P. aeruginosa Lectin I [80] | S. dysenteriae Shiga toxin [81], E. coli verotoxin 1, 2, 2c [82,83] |
| GbO4 | GalNAcβ1- 3Galα1-4Galβ1-4Glcβ1-1'Cer/P | E. coli PapGII [79] | E. coli verotoxin 2e [84] |
| GbO5 | GalNAcα1-3GalNAcβ1- 3Galα1-4Galβ1-4Glcβ1-1'Cer/Forssman | E. coli PapGIII [79] | |
4.2. The Galabiose-Binding Adhesin SadP
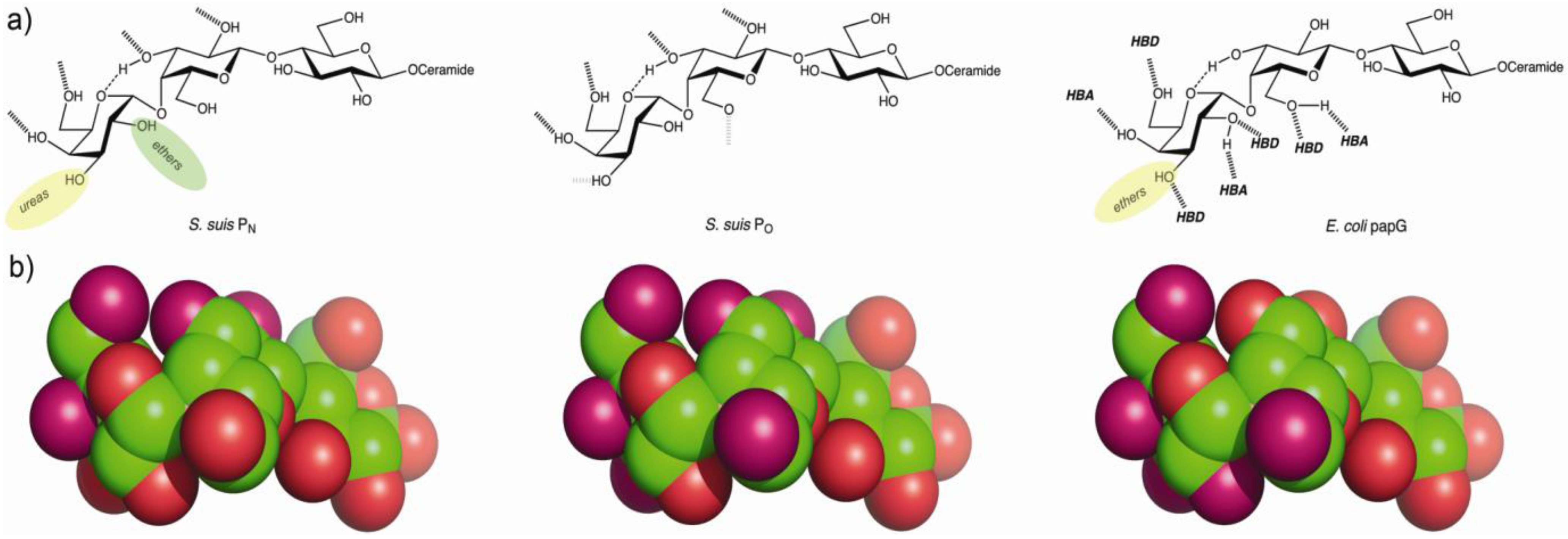
5. Towards the Development of Therapy Based on Prevention of Adhesion
5.1. Combinatorial Libraries of Receptor Carbohydrates
5.2. Dendrimers as Polyvalent Carbohydrate Inhibitors
| Bacterial strain and inhibitor | Valency of dendrimer | Relative potency | Potency per sugar |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. suis 628 a | |||
| Monovalent | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Divalent, short spacer | 2 | 13 | 7 |
| Divalent, long spacer | 2 | 12 | 8 |
| Tetravalent | 4 | 250 | 63 |
| Octavalent | 8 | 310 | 39 |
| Octavalent PAMAM | 8 | 260 | 32 |
| S. suis D282 b | |||
| Monovalent | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Divalent | 2 | 50 | 25 |
| Tetravalent | 4 | 170 | 42 |
| Tetravalent galatriose c | 4 | 8 | 2 |
| Octavalent | 8 | 100 | 13 |
| E. coli PapGJ96 a | |||
| Monovalent | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Divalent, short spacer arms | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Divalent, long spacer arms | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| Tetravalent | 4 | 8 | 2 |
| Octavalent | 8 | 43 | 5 |
| Octavalent PAMAM | 8 | 6 | 1 |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higgins, R.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcal diseases. In Diseases of Swine; Straw, B.E., Zimmerman, J.J., D’Allaire, S., Taylor, D.J., Eds.; University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2005; p. 769. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, H.F.; Nghia, H.D.; Taylor, W.; Schultsz, C. Streptococcus suis: An emerging human pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 617–625. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Gao, G.F. Uncovering newly emerging variants of Streptococcus suis, an important zoonotic agent. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, N.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Nga, T.V.; Linh le, D.; Chau, T.T.; Sinh, D.X.; Phu, N.H.; Chuong, L.V.; Diep, T.S.; Campbell, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis meningitis in adults in Vietnam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Jing, H.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Q.; Luo, X.; et al. Clinical, experimental, and genomic differences between intermediately pathogenic, highly pathogenic, and epidemic Streptococcus suis. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Cossart, P. Bacterial adhesion and entry into host cells. Cell 2006, 124, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, N.; Ofek, I. Safe as mother’s milk: Carbohydrates as future anti-adhesion drugs for bacterial diseases. Glycoconj. J. 2000, 17, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschioni, M.; Pansegrau, W.; Barocchi, M.A. Adhesion determinants of the Streptococcus species. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, M.T.; Hauser, H.; Sanders, M.; Ngo, T.H.; Cherevach, I.; Cronin, A.; Goodhead, I.; Mungall, K.; Quail, M.A.; Price, C.; et al. Rapid evolution of virulence and drug resistance in the emerging zoonotic pathogen Streptococcus suis. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6072. [Google Scholar]
- Ofek, I.; Hasty, D.L.; Sharon, N. Anti-adhesion therapy of bacterial diseases: Prospects and problems. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 38, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, N. Carbohydrates as future anti-adhesion drugs for infectious diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M.; Xu, J. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: The Chinese experience and the situation in North America. Anim. Health. Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Segura, M.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, M.; Segura, M.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Interactions between Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and different epithelial cell lines. Microbiology 2000, 146, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Benga, L.; Goethe, R.; Rohde, M.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Non-encapsulated strains reveal novel insights in invasion and survival of Streptococcus suis in epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, G.; Segura, M.; Friedl, P.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Invasion of porcine brain microvascular endothelial cells by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Tenenbaum, T.; Papandreou, T.; Gellrich, D.; Friedrichs, U.; Seibt, A.; Adam, R.; Wewer, C.; Galla, H.J.; Schwerk, C.; Schroten, H. Polar bacterial invasion and translocation of Streptococcus suis across the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in vitro. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerk, C.; Papandreou, T.; Schuhmann, D.; Nickol, L.; Borkowski, J.; Steinmann, U.; Quednau, N.; Stump, C.; Weiss, C.; Berger, J.; et al. Polar invasion and translocation of Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus suis in a novel human model of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30069. [Google Scholar]
- Jobin, M.C.; Fortin, J.; Willson, P.J.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. Acquisition of plasmin activity and induction of arachidonic acid release by Streptococcus suis in contact with human brain microvascular endothelial cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 252, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jobin, M.C.; Gottschalk, M.; Grenier, D. Upregulation of prostaglandin E2 and matrix metalloproteinase 9 production by human macrophage-like cells: Synergistic effect of capsular material and cell wall from Streptococcus suis. Microb. Pathog. 2006, 40, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pestova, E.V.; Havarstein, L.S.; Morrison, D.A. Regulation of competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae by an auto-induced peptide pheromone and a two-component regulatory system. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 21, 853–862. [Google Scholar]
- Alloing, G.; Granadel, C.; Morrison, D.A.; Claverys, J.P. Competence pheromone, oligopeptide permease, and induction of competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 21, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.H.; Stock, A.M. Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, S.; Hu, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Bei, W. The two-component regulatory system CiaRH contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Greeff, A.; Buys, H.; van Alphen, L.; Smith, H.E. Response regulator important in pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microb. Pathog. 2002, 33, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Chang, H.; Tan, C.; Bei, W.; Chen, H. The orphan response regulator RevSC21 controls the attachment of Streptococcus suis serotype-2 to human laryngeal epithelial cells and the expression of virulence genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 292, 170–181. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Pan, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Zheng, F.; Cao, M.; Dong, Y.; et al. SalK/SalR, a two-component signal transduction system, is essential for full virulence of highly invasive Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2080. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Zhong, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, S.; Chen, T.; Hu, F.; Li, M. Proteome Analysis of the Two-Component SalK/SalR System in Epidemic Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Ge, J.; Li, M.; Wu, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zheng, F.; Cheng, G.; et al. The orphan response regulator CovR: A globally negative modulator of virulence in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, S.; McShan, W.M.; Dunman, P.M.; Chaussee, M.S. Identification of Rgg binding sites in the Streptococcus pyogenes chromosome. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 4933–4942. [Google Scholar]
- Anbalagan, S.; Dmitriev, A.; McShan, W.M.; Dunman, P.M.; Chaussee, M.S. Growth phase-dependent modulation of Rgg binding specificity in Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3961–3971. [Google Scholar]
- Pulliainen, A.T.; Hytonen, J.; Haataja, S.; Finne, J. Deficiency of the Rgg regulator promotes H2O2 resistance, AhpCF-mediated H2O2 decomposition, and virulence in Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytonen, J.; Haataja, S.; Finne, J. Use of flow cytometry for the adhesion analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes mutant strains to epithelial cells: Investigation of the possible role of surface pullulanase and cysteine protease, and the transcriptional regulator Rgg. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Ji, H.; Cao, M.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Hu, F.; et al. Contribution of the Rgg transcription regulator to metabolism and virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/ (accessed on 30 April 2013).
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Lu, C. Functional analysis of luxS in Streptococcus suis reveals a key role in biofilm formation and virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 152, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenborg, J.; Fulde, M.; de Greeff, A.; Rohde, M.; Smith, H.E.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Goethe, R. Role of glucose and CcpA in capsule expression and virulence of Streptococcus suis. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.E.; Damman, M.; van der Velde, J.; Wagenaar, F.; Wisselink, H.J.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smits, M.A. Identification and characterization of the cps locus of Streptococcus suis serotype 2: The capsule protects against phagocytosis and is an important virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Cao, M.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Geng, M.; Zheng, F.; Pan, X.; et al. Attenuation of Streptococcus suis virulence by the alteration of bacterial surface architecture. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 710. [Google Scholar]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D.; Harel, J.; Dominguez-Punaro Mde, L.; von Aulock, S.; Draing, C.; Marois, C.; Kobisch, M.; Gottschalk, M. D-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3587–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D.; de la Cruz Dominguez-Punaro, M.; Harel, J.; Bui, N.K.; Vollmer, W.; Gottschalk, M. Significant contribution of the pgdA gene to the virulence of Streptococcus suis. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Feng, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, F.; Wang, C.; Yin, Z.; Pan, X.; Tang, J. Inactivation of dipeptidyl peptidase IV attenuates the virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 that causes streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Esgleas, M.; Dominguez-Punaro Mde, L.; Li, Y.; Harel, J.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Gottschalk, M. Immunization with SsEno fails to protect mice against challenge with Streptococcus suis serotype 2. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Pan, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Shao, Z.; Ge, J.; Zheng, F.; et al. Streptococcus suis enolase functions as a protective antigen displayed on the bacterial cell surface. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, J.; Gottschalk, M.; Quessy, S. Cloning and purification of the Streptococcus suis serotype 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and its involvement as an adhesin. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Fu, S.; Liu, M.; Jin, M.; Liu, J.; Bei, W.; Chen, H. Cloning, expression and characterization of a cell wall surface protein, 6-phosphogluconate-dehydrogenase, of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yuan, F.; Chang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Cai, K.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Bei, W.; Chen, H. Contribution of glutamine synthetase to the virulence of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.X.; Gu, H.W.; Lu, C.P. Characterization and functional analysis of atl, a novel gene encoding autolysin in Streptococcus suis. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar]
- De Greeff, A.; Buys, H.; Verhaar, R.; Dijkstra, J.; van Alphen, L.; Smith, H.E. Contribution of fibronectin-binding protein to pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Vanier, G.; Sekizaki, T.; Dominguez-Punaro, M.C.; Esgleas, M.; Osaki, M.; Takamatsu, D.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Disruption of srtA gene in Streptococcus suis results in decreased interactions with endothelial cells and extracellular matrix proteins. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 127, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Mu, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Han, L.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Identification and characterization of IgA1 protease from Streptococcus suis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Mu, X.; Chen, B.; Han, L.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. IgA1 protease contributes to the virulence of Streptococcus suis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Baums, C.G.; Kaim, U.; Fulde, M.; Ramachandran, G.; Goethe, R.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Identification of a novel virulence determinant with serum opacification activity in Streptococcus suis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, P.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Teng, L.; Zhou, M.; Bei, W.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Identification of a cell wall-associated subtilisin-like serine protease involved in the pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 48, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bonifait, L.; Grenier, D. The SspA subtilisin-like protease of Streptococcus suis triggers a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages through a non-proteolytic mechanism. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wan, Y.; Tao, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R. A novel fibronectin-binding protein of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 contributes to epithelial cell invasion and in vivo dissemination. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Stroeher, U.H.; Paton, A.W.; Ogunniyi, A.D.; Paton, J.C. Mutation of luxS of Streptococcus pneumoniae affects virulence in a mouse model. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 3206–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.E.; Howery, K.E.; Ludewick, H.P.; Nava, P.; Klugman, K.P. Quorum sensing systems LuxS/AI-2 and Com regulate Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilms in a bioreactor with living cultures of human respiratory cells. Infect. Immun. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, M.; Lu, C. The novel virulence-related gene stp of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 strain contributes to a significant reduction in mouse mortality. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 51, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, K.; Haataja, S.; Francois-Gerard, C.; Finne, J. Purification of a galactosyl-alpha 1-4-galactose-binding adhesin from the Gram-positive meningitis-associated bacterium Streptococcus suis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28874–28878. [Google Scholar]
- Van Calsteren, M.R.; Gagnon, F.; Lacouture, S.; Fittipaldi, N.; Gottschalk, M. Structure determination of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 capsular polysaccharide. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis interactions with the murine macrophage cell line J774: Adhesion and cytotoxicity. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4312–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, M.; Gottschalk, M.; Gagnon, F.; van Calsteren, M.R.; Segura, M. Streptococcus suis capsular polysaccharide inhibits phagocytosis through destabilization of lipid microdomains and prevents lactosylceramide-dependent recognition. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 506–517. [Google Scholar]
- Wewer, C.; Seibt, A.; Wolburg, H.; Greune, L.; Schmidt, M.A.; Berger, J.; Galla, H.J.; Quitsch, U.; Schwerk, C.; Schroten, H.; et al. Transcellular migration of neutrophil granulocytes through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier after infection with Streptococcus suis. J. Neuroinflammation 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Gottschalk, M.; Vanier, G.; Daigle, F.; Harel, J. Use of selective capture of transcribed sequences to identify genes preferentially expressed by Streptococcus suis upon interaction with porcine brain microvascular endothelial cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4359–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobbs, A.H.; Lamont, R.J.; Jenkinson, H.F. Streptococcus adherence and colonization. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 407–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, B.; Martin, A. Bacterial virulence in the moonlight: Multitasking bacterial moonlighting proteins are virulence determinants in infectious disease. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3476–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Fleury, C.; Jalalvand, F.; Riesbeck, K. Human pathogens utilize host extracellular matrix proteins laminin and collagen for adhesion and invasion of the host. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 1122–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lu, C. Adhesion activity of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in a Chinese Streptococcus suis type 2 strain. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2007, 120, 207–209. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, F.; Dong, Y.; Pan, X.; Cheng, G.; Dong, R.; Hu, D.; Feng, X.; et al. The involvement of sortase A in high virulence of STSS-causing Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baums, C.G.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Surface-associated and secreted factors of Streptococcus suis in epidemiology, pathogenesis and vaccine development. Anim. Health. Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, M.; Takamatsu, D.; Shimoji, Y.; Sekizaki, T. Characterization of Streptococcus suis genes encoding proteins homologous to sortase of Gram-positive bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, D.; Nishino, H.; Ishiji, T.; Ishii, J.; Osaki, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Gottschalk, M.; Tharavichitkul, P.; Takai, S.; Sekizaki, T. Genetic organization and preferential distribution of putative pilus gene clusters in Streptococcus suis. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 138, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Takamatsu, D.; de la Cruz Dominguez-Punaro, M.; Lecours, M.P.; Montpetit, D.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T.; Gottschalk, M. Mutations in the gene encoding the ancillary pilin subunit of the Streptococcus suis srtF cluster result in pili formed by the major subunit only. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liukkonen, J.; Haataja, S.; Tikkanen, K.; Kelm, S.; Finne, J. Identification of N-acetylneuraminyl alpha 2-->3 poly-N-acetyllactosamine glycans as the receptors of sialic acid-binding Streptococcus suis strains. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 21105–21111. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.Z.; Yan, X.J.; Zhang, A.D.; Chen, B.; Shen, Y.Q.; Jin, M.L. Molecular mechanism by which surface antigen HP0197 mediates host cell attachment in the pathogenic bacteria Streptococcus suis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haataja, S.; Tikkanen, K.; Nilsson, U.; Magnusson, G.; Karlsson, K.A.; Finne, J. Oligosaccharide-receptor interaction of the Gal alpha 1-4Gal binding adhesin of Streptococcus suis. Combining site architecture and characterization of two variant adhesin specificities. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27466–27472. [Google Scholar]
- Kouki, A.; Haataja, S.; Loimaranta, V.; Pulliainen, A.T.; Nilsson, U.J.; Finne, J. Identification of a novel streptococcal adhesin P (SadP) recognizing galactosyl-{alpha}1-4-galactose-containing glycoconjugates: Convergent evolution of bacterial pathogens to binding of the same host receptor. J. Biol. Chem. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38854–38864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömberg, N.; Marklund, B.I.; Lund, B.; Ilver, D.; Hamers, A.; Gaastra, W.; Karlsson, K.A.; Normark, S. Host-specificity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli depends on differences in binding specificity to Gal alpha 1-4Gal-containing isoreceptors. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, B.; Nurisso, A.; Hollville, E.; Tetaud, C.; Wiels, J.; Pokorna, M.; Wimmerova, M.; Varrot, A.; Imberty, A. Structural basis of the preferential binding for globo-series glycosphingolipids displayed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectin I. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 383, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, A.A.; Brown, J.E.; Strömberg, N.; Westling-Ryd, M.; Schultz, J.E.; Karlsson, K.A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood, C.A.; Law, H.; Richardson, S.; Petric, M.; Brunton, J.L.; de Grandis, S.; Karmali, M. Glycolipid binding of purified and recombinant Escherichia coli produced verotoxin in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 8834–8839. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, J.E.; Perera, L.P.; Ward, S.; O’Brien, A.D.; Ginsburg, V.; Krivan, H.C. Comparison of the glycolipid receptor specificities of Shiga-like toxin type II and Shiga-like toxin type II variants. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 611–618. [Google Scholar]
- DeGrandis, S.; Law, H.; Brunton, J.; Gyles, C.; Lingwood, C.A. Globotetraosylceramide is recognized by the pig edema disease toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12520–12525. [Google Scholar]
- Francois-Gerard, C.; Gerday, C.; Beeley, J.G. Turtle-dove ovomucoid, a glycoprotein proteinase inhibitor with P1-blood-group antigen activity. Biochem. J. 1979, 177, 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Khoo, K.H.; Suzuki, N.; Johnson, J.R.; Lee, Y.C. N-glycan structures from the major glycoproteins of pigeon egg white: Predominance of terminal Galalpha(1)Gal. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23230–23239. [Google Scholar]
- Pian, Y.; Gan, S.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Fhb, a novel factor H-binding surface protein, contributes to the antiphagocytic ability and virulence of Streptococcus suis. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2402–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, U.; Striker, R.T.; Hultgren, S.J.; Magnusson, G. PapG adhesin from E. coli J96 recognizes the same saccharide epitope when present on whole bacteria and as isolated protein. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striker, R.; Nilsson, U.; Stonecipher, A.; Magnusson, G.; Hultgren, S.J. Structural requirements for the glycolipid receptor of human uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 16, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihlberg, J.; Hultgren, S.; Normark, S.; Magnusson, G. Probing of the combining site of the PapG adhesin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli bacteria by synthetic analogs of galabiose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6364–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, K.W.; Pinkner, J.S.; Rose, T.; Magnusson, G.; Hultgren, S.J.; Waksman, G. Structural basis of the interaction of the pyelonephritic E. coli adhesin to its human kidney receptor. Cell 2001, 105, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, J.; Larsson, A.; Haataja, S.; Alajääski, J.; Stenlund, P.; Pinkner, J.S.; Hultgren, S.J.; Finne, J.; Kihlberg, J.; Nilsson, U.J. Structure-activity relationships of galabioside derivatives as inhibitors of E. coli and S. suis adhesins: Nanomolar inhibitors of S. suis adhesins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.J. Intervention with bacterial adhesion by multivalent carbohydrates. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 796–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, C.T.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J. Inhibition of galectins with small molecules. Chimia (Aarau) 2011, 65, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitov, P.I.; Sadowska, J.M.; Mulvey, G.; Armstrong, G.D.; Ling, H.; Pannu, N.S.; Read, R.J.; Bundle, D.R. Shiga-like toxins are neutralized by tailored multivalent carbohydrate ligands. Nature 2000, 403, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.C.; Haataja, S.; Finne, J.; Magnusson, G. Di-, tri-, and tetravalent dendritic galabiosides that inhibit hemagglutination by Streptococcus suis at nanomolar concentration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Loimaranta, V.; Joosten, J.A.; Khan, A.S.; Hacker, J.; Pieters, R.J.; Finne, J. Inhibition of P-fimbriated Escherichia coli adhesion by multivalent galabiose derivatives studied by a live-bacteria application of surface plasmon resonance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouki, A. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Adhesin of Streptococcus suis and its Use as a Target of Adhesion Inhibition and Bacterial Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Turku, Turku, Finland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Branderhorst, H.M.; Kooij, R.; Salminen, A.; Jongeneel, L.H.; Arnusch, C.J.; Liskamp, R.M.; Finne, J.; Pieters, R.J. Synthesis of multivalent Streptococcus suis adhesion inhibitors by enzymatic cleavage of polygalacturonic acid and ‘click’ conjugation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kouki, A.; Pieters, R.J.; Nilsson, U.J.; Loimaranta, V.; Finne, J.; Haataja, S. Bacterial Adhesion of Streptococcus suis to Host Cells and Its Inhibition by Carbohydrate Ligands. Biology 2013, 2, 918-935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2030918
Kouki A, Pieters RJ, Nilsson UJ, Loimaranta V, Finne J, Haataja S. Bacterial Adhesion of Streptococcus suis to Host Cells and Its Inhibition by Carbohydrate Ligands. Biology. 2013; 2(3):918-935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2030918
Chicago/Turabian StyleKouki, Annika, Roland J. Pieters, Ulf J. Nilsson, Vuokko Loimaranta, Jukka Finne, and Sauli Haataja. 2013. "Bacterial Adhesion of Streptococcus suis to Host Cells and Its Inhibition by Carbohydrate Ligands" Biology 2, no. 3: 918-935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2030918
APA StyleKouki, A., Pieters, R. J., Nilsson, U. J., Loimaranta, V., Finne, J., & Haataja, S. (2013). Bacterial Adhesion of Streptococcus suis to Host Cells and Its Inhibition by Carbohydrate Ligands. Biology, 2(3), 918-935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2030918







