Use of Tetravalent Galabiose for Inhibition of Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Infection in a Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
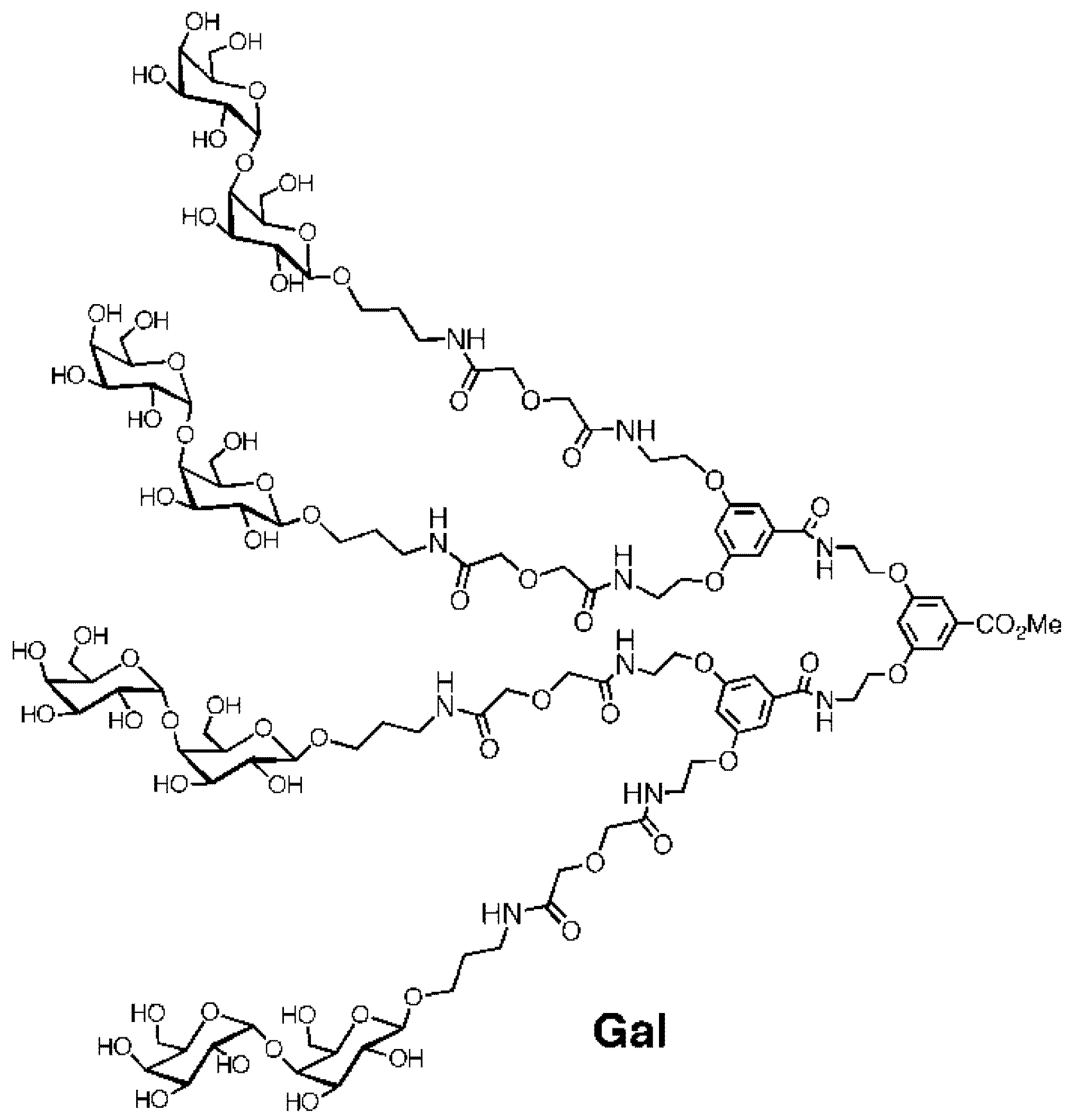
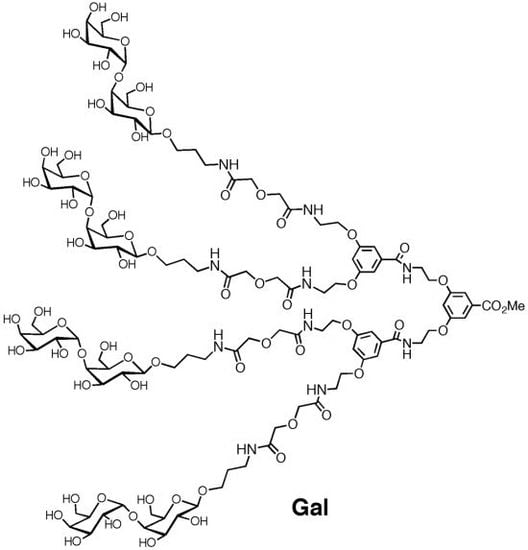
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Bacterial Strain, Growth Conditions and Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Infection Model
2.3. Characterization of Bacterial Isolates from Animal Organs
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Infection Model
3.2. Experimental Setup (IPO, IP1, IP2, IP3 and IP4)
3.2.1. IP0
| IP0 | IP1 | IP2 | IP3 | IP4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | A | B | C | D | 1 | 2 | 3 | A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C |
| Control to B | 24 h | Control to D | 48 h | Control | High | Low | Positive control | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Positive control | Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | Positive control | Post-treatment | Penicillin treatment | |
| Number of mice | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Dose volume, mL (inoculum) | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | - | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Inoculum conc., CFU/mL | ~107 a | - | 6.81 × 107 | 1.79 × 103 | 2.23 × 107 | 1.39 × 107 | 1.65 × 108 | |||||||||
| Dose volume, mL (Penicillin dose conc. = 10mg/mL) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 × 0.30 |
| Duration of infection | 0–24 h | 0–24 h | 0–48 h | 0–48 h | - | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h | 0–72 h |
| Gal treatment | 0 | 20 h | 0 | 24 h | - | - | - | - | ÷24 h | 24 h | - | ÷24 h | 24 h | - | 24 h | - |
| Penicillin treatment | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 24 h and 48 h |
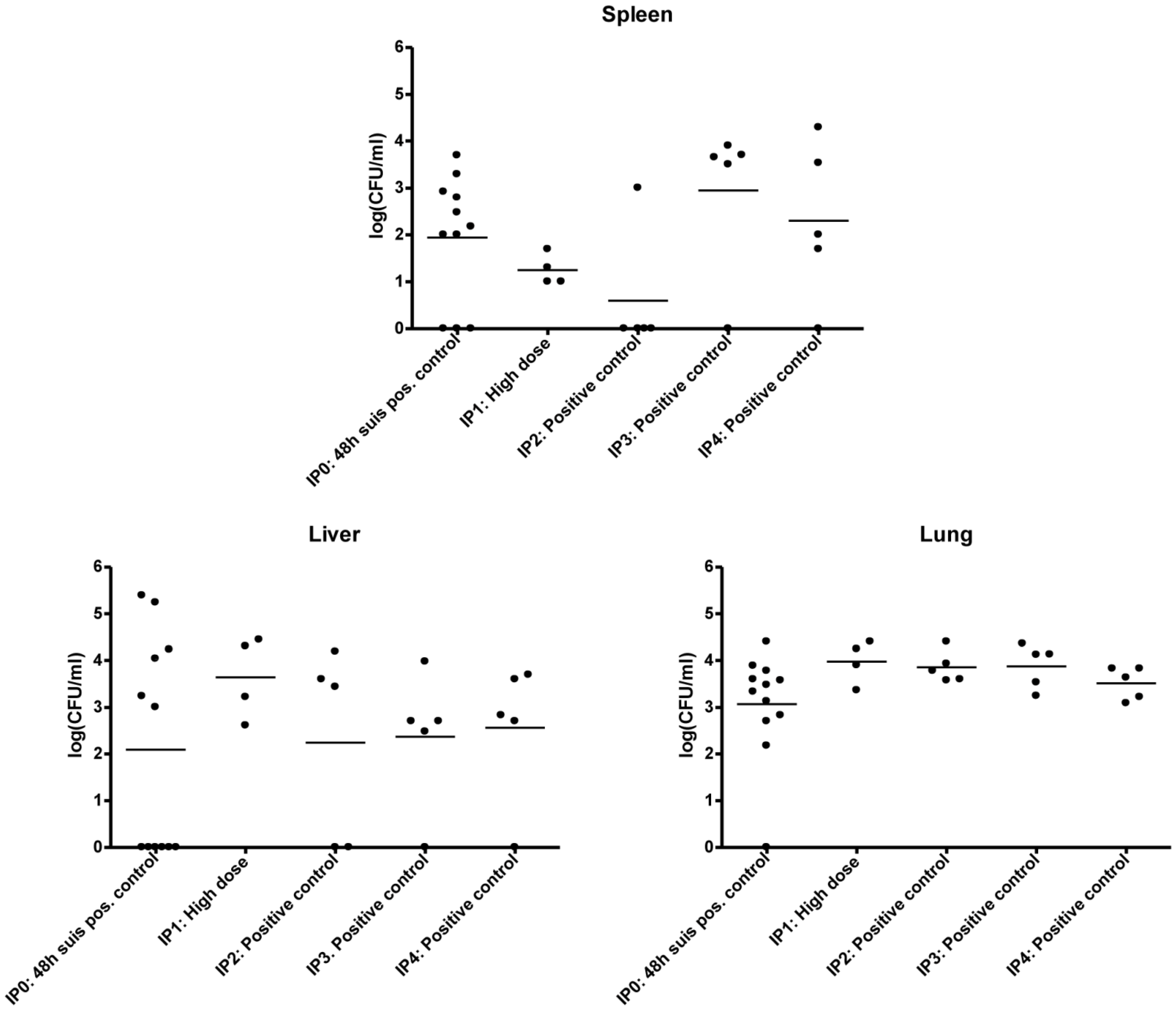
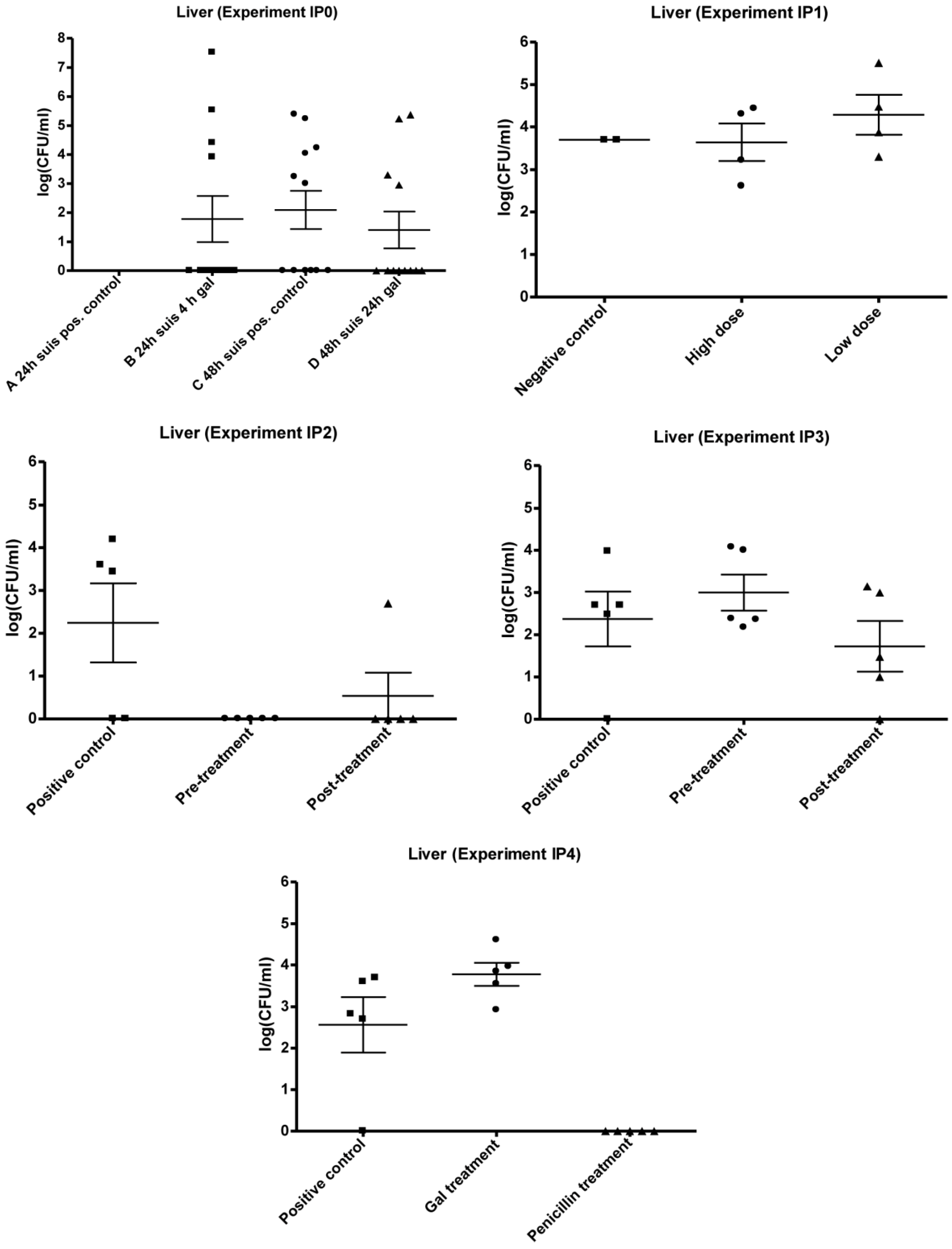
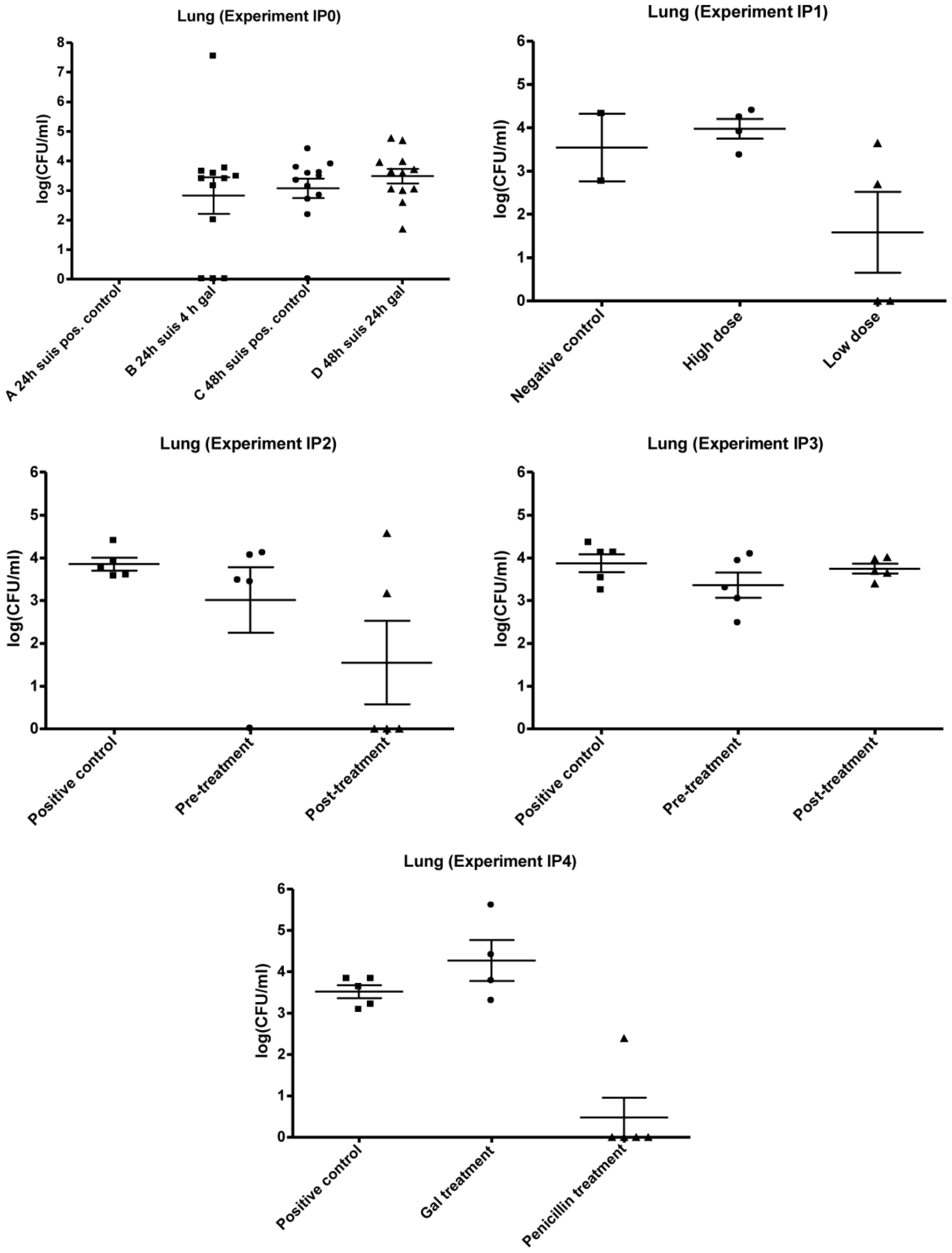
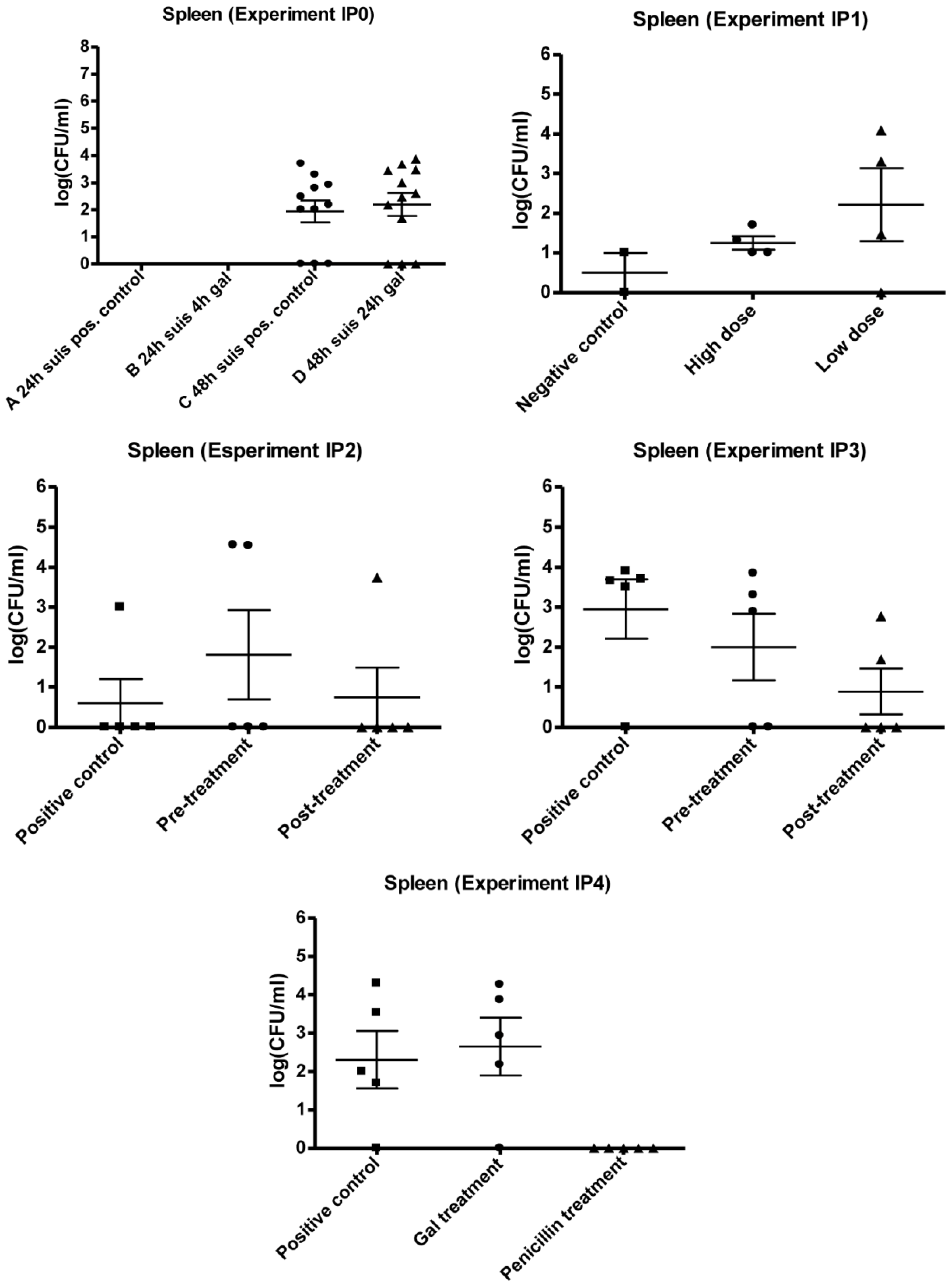
3.2.2. IP1
3.2.3. IP2 and IP3
3.2.4. IP4
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Reference and Notes
Reference and Notes
- Costa, A.T.R.; Lobato, F.C.F.; Abreu, V.L.V.; Assis, R.A.; Reis, R.; Uzal, F.A. Serotyping and evaluation of the virulence in mice of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from diseased pigs. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. S Paulo 2005, 47, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-T.; Teng, L.-J.; Ho, S.-W.; Hsueh, P.-R. Streptococcus suis Infection. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2005, 38, 306–313. [Google Scholar]
- Schultsz, C.; Jansen, E.; Keijzers, W.; Rothkamp, A.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; van der Ende, A. Differences in the Population Structure of Invasive Streptococcus suis Strains Isolated from Pigs and from Humans in the Netherlands. Plos. One 2012, 7, e33854. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Extracellular virulence factors of streptococci associated with animal disease. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1157–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.W.; Aalbæk, B.; Nielsen, O.L.; Jensen, H.E. Aerogenous infection of microbiologically defined minipigs with Streptococcus suis serotype 2. APMIS 2001, 109, 412–418. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, M.; Beineke, A.; Seele, J.; Fulde, M.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. A novel intranasal mouse model for mucosal colonization by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisselink, H.J.; Smith, H.E.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Peperkamp, K.; Vecht, U. Distribution of capsular types and production of muramidase-relesed protein (MRP) and extracellular factor (EF) of Streptococcus suis strains isolated from diseased pigs in seven European countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.J. Intervention with bacterial adhesion by multivalent carbohydrates. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 796–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.J. Carbohydrate Mediated Bacterial Adhesion. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 715, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Kouki, A.; Haataja, S.; Loimaranta, V.; Pulliainen, A.T.; Nilsson, U.J.; Finne, J. Identification of a Novel Streptococcal Adhesin P (SadP) Protein Recognizing Galactosyl-alpha 1–4-galactose-containing Glycoconjugates convergent evolution of bacterial pathogens to binding of the same host receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38854–38864. [Google Scholar]
- Tikkanen, K.; Haataja, S.; Finne, J. The Galactosyl-(α1–4)-Galactose-binding adhesin of Streptococcus suis: Occurrence in strains of different hemagglutination activity and induction of opsonic antibodies. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3659–3665. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson, J.; Larsson, A.; Haataja, S.; Alajääski, J.; Stenlund, P.; Pinker, J.S.; Hultgren, S.J.; Finne, J.; Kihlberg, J.; Nilsson, U.J. Structure-activity relationships of galabioside derivatives as inhibitors of E. coli and S. suis adhesins: nanomolar inhibitors of S. suis adhesins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 886–900. [Google Scholar]
- Haataja, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tikkanen, K.; Magnusson, G.; Finne, J. Determination of the cell adhesion specificity of Streptococcus suis with the complete set of monodeoxy analogues of globotriose. Glycoconjugate. J. 1999, 16, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurl, D.N.; Haataja, S.; Finne, J. Hemagglutionation activities of group B, C, D and G Streptococci: Demonstration of novel sugar-specific cell-binding activities in Streptococcus suis. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, O.; Fuchs, A.; Lindhorst, T.K. Evaluation of the carbohydrate recognition domain of the bacterial adhesin FimH: design, synthesis and binding properties of mannoside ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 3913–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Pinkner, J.S.; Ford, B.; Chorell, E.; Crowley, J.M.; Cusumano, C.K.; Campbell, S.; Henderson, J.P.; Hultgren, S.J.; Janetka, J.W. Lead Optimization Studies on FimH Antagonists: Discovery of Potent and Orally Bioavailable Ortho-Substituted Biphenyl Mannosides. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3945–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.J. Maximising multivalency effects in protein-carbohydrate interactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almant, M.; Moreau, V.; Kovensky, J.; Bouckaert, J.; Gouin, S.G. Clustering of Escherichia coli Type-1 Fimbrial Adhesins by Using Multimeric Heptyl alpha-D-Mannoside Probes with a Carbohydrate Core. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10029–10038. [Google Scholar]
- Salminen, A.; Loimaranta, V.; Joosten, J.A. F.; Khan, A.S.; Hacker, J.; Pieters, R.J.; Finne, J. Inhibition of P-fimbriated Escherichia coli adhesion by multivalent galabiose derivatives studied by a live-bacteria application of surface plasmon resonance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- oosten, J.F.; Loimaranta, V.; Appeldoorn, C.C.; Haataja, S.; Ait El Maate, F.; Liskamp, R.M.J.; Finne, J.; Pieters R, J. Inhibition of Streptococcus suis adhesion by dendritic galabiose compounds at low nanomolar concentration. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 26, 6499–6508. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.C.; Haataja, S.; Finne, J.; Magnusson, G. Di-, tri-, and tetravalent dendritic galabiosides that inhibit hemagglutination by Streptococcus suis at nanomolar concentration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6974–6979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branderhorst, H.M.; Kooij, R.; Salminen, A.; Jongeneel, L.H.; Arnusch, C.J.; Liskamp, R.M. J.; Finne, J.; Pieters, R.J. Synthesis of multivalent Streptococcus suis adhesion inhibitors by enzymatic cleavage of polygalacturonic acid and 'click' conjugation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, N.P.; Kouki, A.; Haataja, S.; Branderhorst, H.M.; Liskamp, R.M. J.; Visser, G.M.; Finne, J.; Pieters, R.J. Detection of pathogenic Streptococcus suis bacteria using magnetic glycoparticles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2425–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.; Matsuoka, K.; Kita, E.; Okabe, N.; Mizuguchi, M.; Hino, K.; Miyazawa, S.; Yamasaki, C.; Aoki, J.; Takashima, S.; Yamakawa, Y.; Nishijima, M.; Terunuma, D.; Kuzuhara, H.; Natori, Y. A therapeutic agent with oriented carbohydrates for treatment of infections by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157: H7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7669–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Punaro, M.C.; Koedel, U.; Hoegen, T.; Demel, C.; Klein, M.; Gottschalk, M. Severe cochlear inflammation and vestibular syndrome in an experimental model of Streptococcus suis infection in mice. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.E.; Blakemore, W.F.; Alexander, T.J.L. A murine model of Streptococcus suis type 2 meningitis in the pig. Res. Vet. Sci. 1988, 45, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Beaudoin, M.; Higgins, R.; Harel, J.; Gottschalk, M. Studies on a murine model for evaluation of virulence of Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 isolates. Fems. Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 99, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, Y.; Haritani, M.; Mori, M.; Kishima, M.; Sugimoto, C.; Nakazawa, M.; Yamamoto, K. Experimental infections of mice and pigs with Streptococcus suis type 2. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1991, 53, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, I.D.; Blackmore, D.K. Experimental studies on the comparative infectivity and pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis type 2. II. Porcine and human isolates in laboratory animals. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotved, H-C.; Sauer, S.; Konradsen, H.B. False-negative results in typing of group B streptococci by the standard Lancefield antigen extraction method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1882–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecht, U.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Tetenburg, B.J.; Wisselink, H.J.; Smith, H.E. Virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2 for mice and pigs appeared host-specific. Vet. Microbiol. 1997, 58, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis interactions with the murine macrophage cell line J774: Adhesion and cytotoxicity. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4312–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benga, L.; Friedl, P.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Adherence of Streptococcus suis to Porcine Endothelial Cells. J. Vet. Med. 2005, B52, 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Vanier, G.; Segura, M.; Friedl, P.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Invasion of porcine brain microvascular endothelial cells by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, M.; Segura, M.; Lacouture, S.; Gottschalk, M. Interactions between Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and different epithelial cell lines. Microbiology 2000, 146, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. The pathogenesis of the meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis: the unresolved questions. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, J.J.; Feder, I.; Okwumabua, O.; Chengappa, M.M. Streptococcus: Past and present. Vet. Res. Commun. 1997, 21, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haataja, S.; Tikkanen, K.; Hytonen, J.; Finne, J. The Gal alpha 1–4 Gal-binding adhesin of Streptococcus suis, a gram-positive meningitis-associated bacterium. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 408, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pieters, R.J.; Slotved, H.-C.; Mortensen, H.M.; Arler, L.; Finne, J.; Haataja, S.; Joosten, J.A.F.; Branderhorst, H.M.; Krogfelt, K.A. Use of Tetravalent Galabiose for Inhibition of Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Infection in a Mouse Model. Biology 2013, 2, 702-718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020702
Pieters RJ, Slotved H-C, Mortensen HM, Arler L, Finne J, Haataja S, Joosten JAF, Branderhorst HM, Krogfelt KA. Use of Tetravalent Galabiose for Inhibition of Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Infection in a Mouse Model. Biology. 2013; 2(2):702-718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020702
Chicago/Turabian StylePieters, Roland J., Hans-Christian Slotved, Hanne Møller Mortensen, Lene Arler, Jukka Finne, Sauli Haataja, John A. F. Joosten, Hilbert M. Branderhorst, and Karen A. Krogfelt. 2013. "Use of Tetravalent Galabiose for Inhibition of Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Infection in a Mouse Model" Biology 2, no. 2: 702-718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020702
APA StylePieters, R. J., Slotved, H.-C., Mortensen, H. M., Arler, L., Finne, J., Haataja, S., Joosten, J. A. F., Branderhorst, H. M., & Krogfelt, K. A. (2013). Use of Tetravalent Galabiose for Inhibition of Streptococcus Suis Serotype 2 Infection in a Mouse Model. Biology, 2(2), 702-718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology2020702