The Stone Moroko Pseudorasbora parva Altered the Composition and Stability of Sediment Microbial Communities Within the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Polyculture Pond
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Location and Design
2.2. Experimental Sample Collection and Methods
2.3. Characterization of Sediment Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Extraction and Sequencing of Microbial DNA from Pond Sediments
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
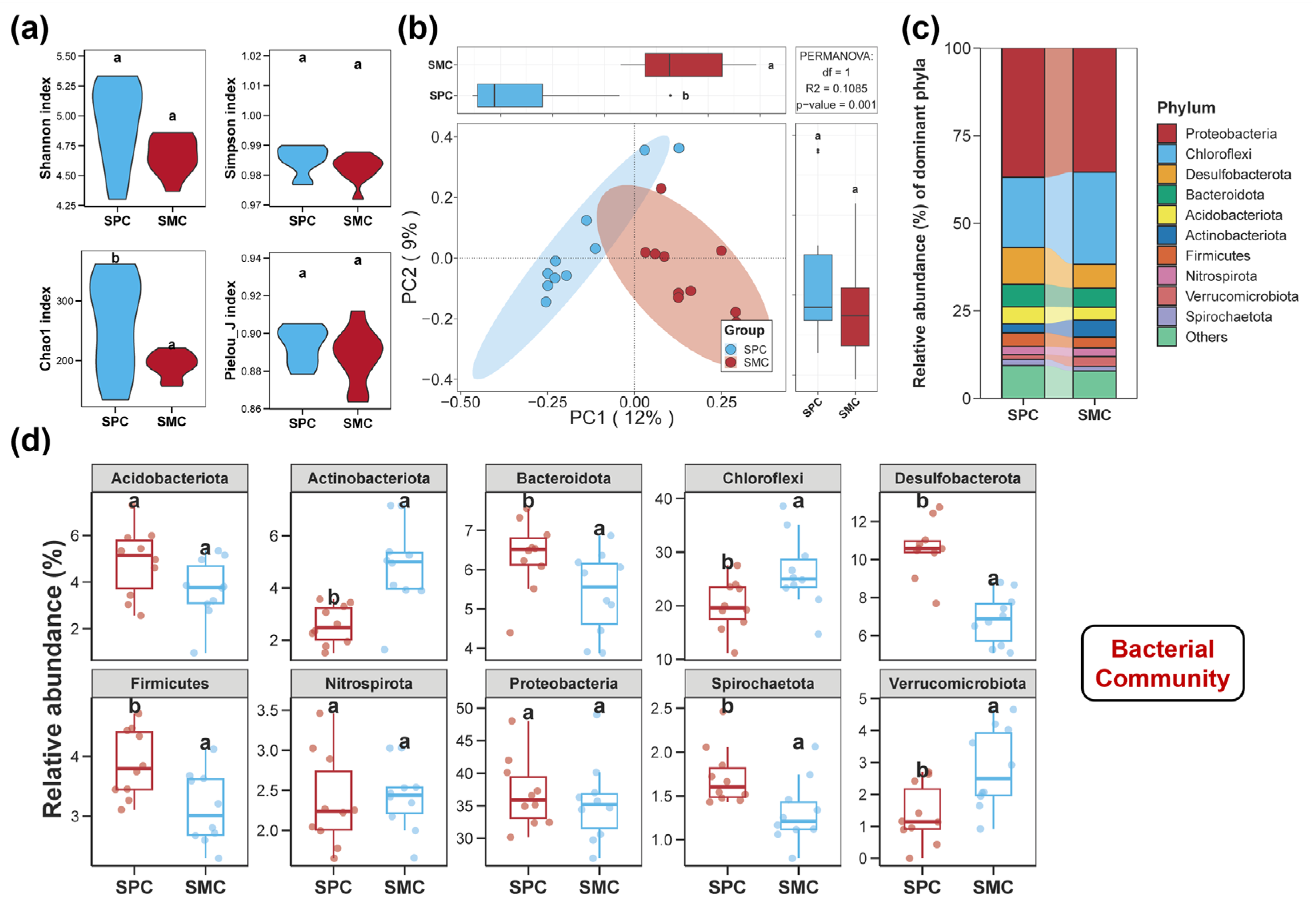
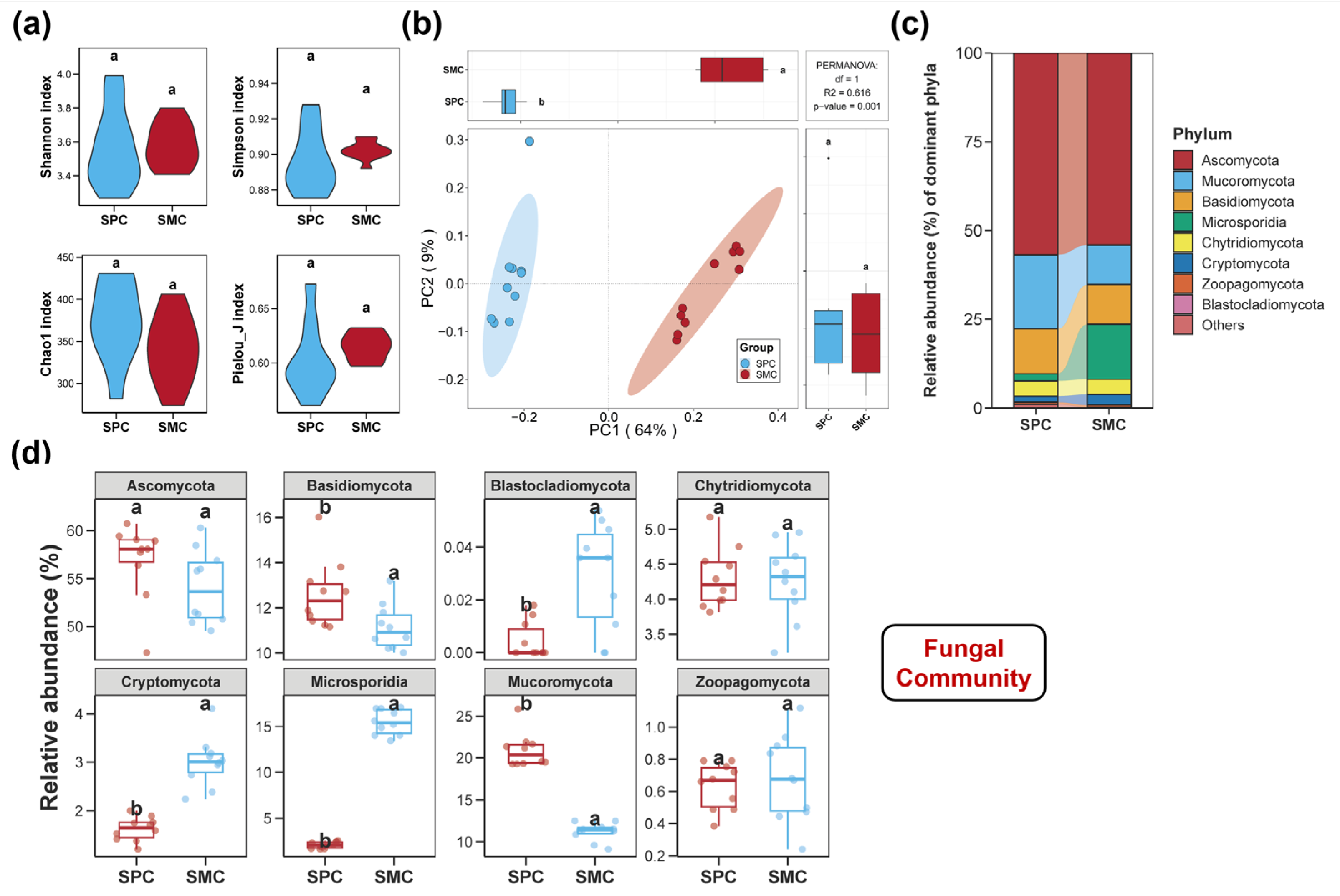
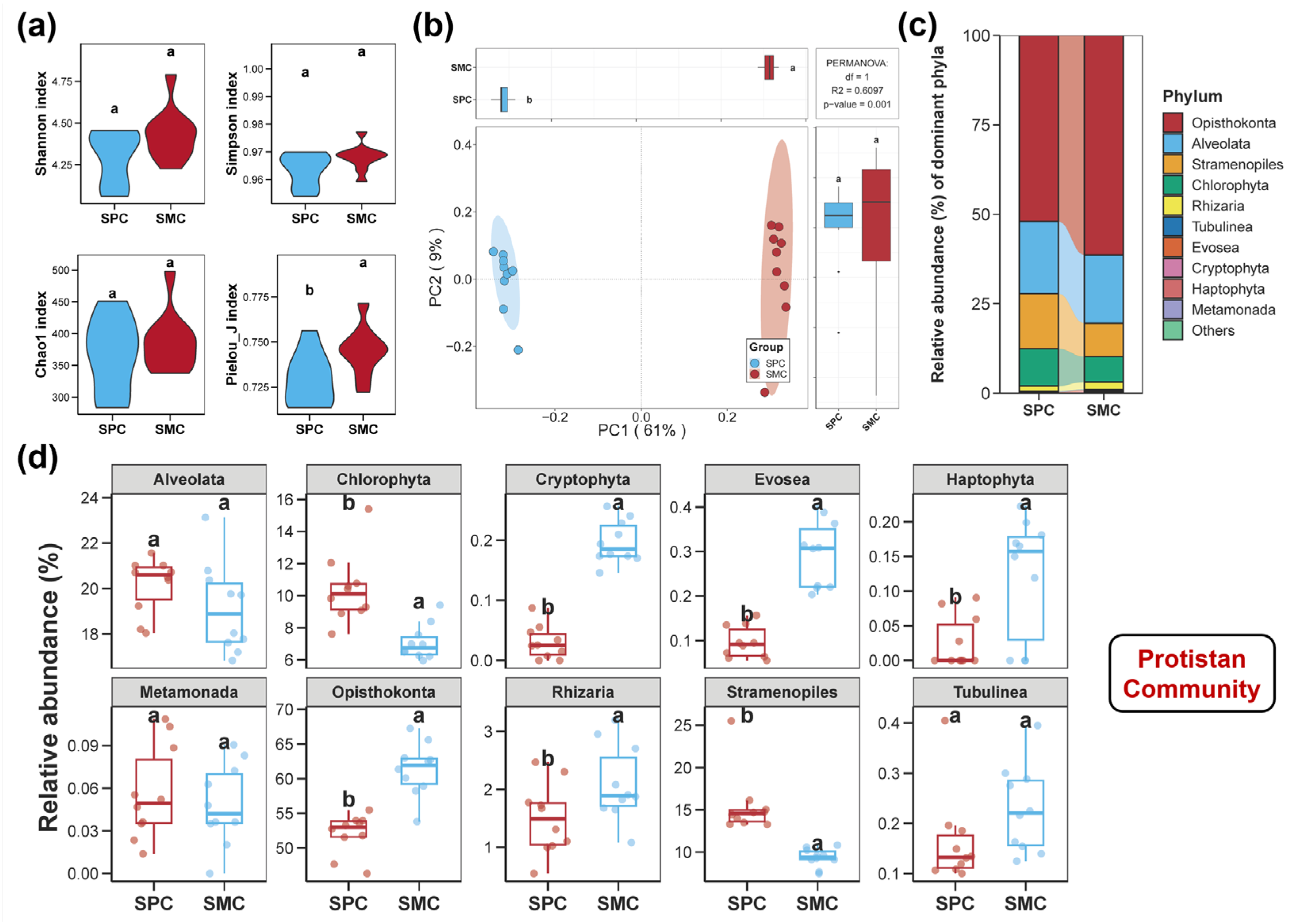
3.1. Diversities of the Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protistan Communities
3.2. Compositions of the Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protistan Communities
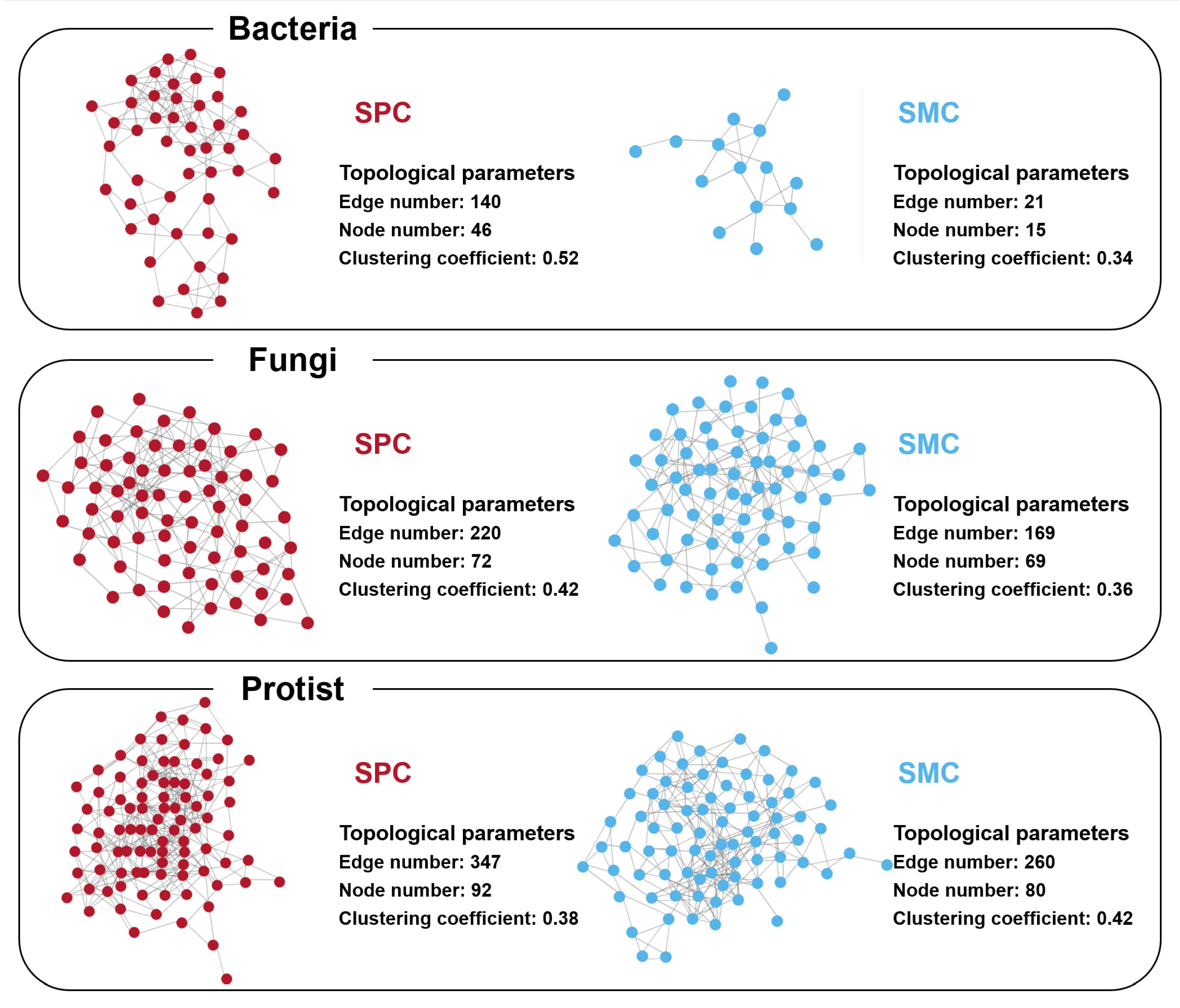
3.3. Co-Occurrence Networks and Stabilities of the Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protistan Communities
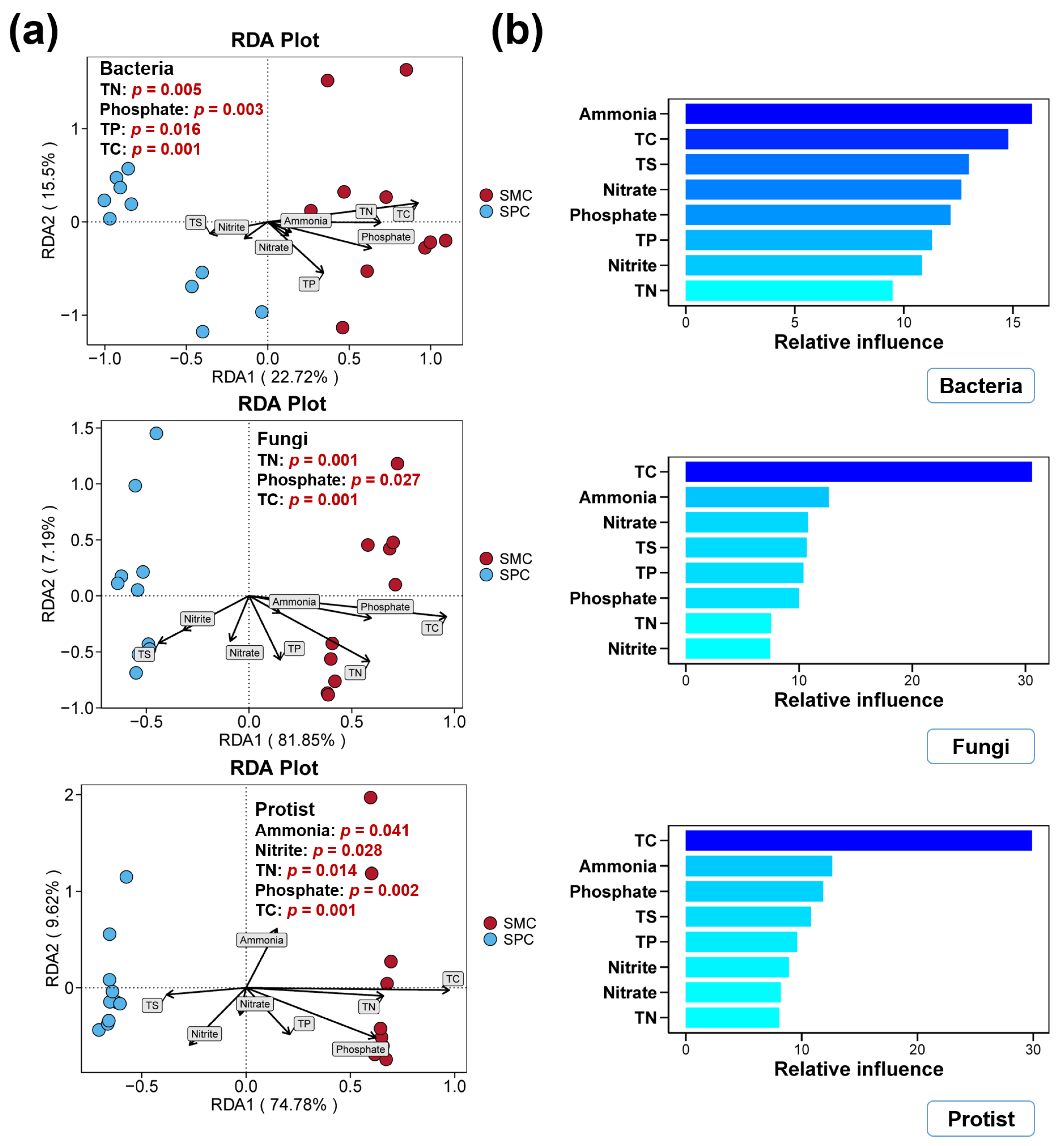
3.4. Environmental Factors in Pond Sediment and Their Correlations with Microbial Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Alterations in the Diversities and Compositions of the Sediment Bacterial, Fungal, and Protistan Communities
4.2. Changes in the Microbial Co-Occurrence Network and Stability
4.3. Alterations in Environmental Factors and Their Correlations with Bacterial, Fungal, and Protistan Communities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashaari, A.; Iehata, S.; Kim, H.J.; Rasdi, N.W. Recent advancement of zooplankton enriched with nutrients and probiotic isolates from aquaculture systems: A review. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2024, 52, 2417052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonidou, S.; Mente, E. Water Consumption and the Water Footprint in Aquaculture: A Review. Water 2024, 16, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lu, M. Tilapia polyculture: A global review. Aquac. Res. 2015, 47, 2363–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Pasquet, A.; Aubin, J.; Nahon, S.; Lecocq, T. When more is more: Taking advantage of species diversity to move towards sustainable aquaculture. Biol. Rev. 2020, 96, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.C.; Lin, T.H.; Qu, C. The role of pattern recognition receptors in the innate immune system of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Ning, B. Development and application of crab culture in the development of Chinese mitten crab industry of Shanghai. Aquac. Res. 2018, 50, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiaowen, L.; Deng, D.; Yongxu, C.; Xugan, W.; Loor, J.J. Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of carnitine palmitoyltransferases in Chinese mitten crabEriocheir sinensisand the effect of dietary fish oil replacement on their expression in the hepatopancreas. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201324. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs; National Fisheries Technology Extension Center; China Society of Fisheries. 2024 China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Gao, F. Polyculture Techniques for Farming Mandarin Fish in River Crab Ponds. Fish. Mod. 2003, 01, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. Key Techniques for Polyculture of Mandarin Fish in Ecological Farming of River Crabs in Gaochun. J. Aquac. 2020, 41, 65+67. [Google Scholar]
- Che, B.; Wang, Q. SWOT Analysis and Countermeasures for the River Crab Farming Industry in Jiangsu Province. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 736–739. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhou, W.C.; Huang, S.; Wu, X.M.; Zhou, P.P.; Geng, Y.C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Wu, Y.D.; Chen, Q.Y.; et al. Promoting effect and mechanism of residual feed organic matter on the formation of cyanobacterial blooms in aquaculture waters. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 138068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.T.; Wang, P.D.; Li, J.L.; Luo, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.H.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.J.; Qin, Q.W. Comparative metagenomic analysis of microbial community compositions and functions in cage aquaculture and its nearby non-aquaculture environments. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1398005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.C.; Li, Y.F.; Zi, X.Y.; Gu, X.H.; Yuan, H.Z.; Jeppesen, E.; Zeng, Q.F. Nutrient enrichment drives the sediment microbial communities in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis culture. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F. A Brief Discussion on Healthy and Ecological Farming Techniques for Polyculture of Mandarin Fish in Crab Ponds. Fish. Guide Be Rich 2010, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Pond Polyculture Techniques for Crabs and Mandarin Fish. Curr. Fish. 2020, 45, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, C.; Guo, L.; Ni, L.; Luo, C. Silver carp exhibited an enhanced ability of biomanipulation to control cyanobacteria bloom compared to bighead carp in hypereutrophic Lake Taihu mesocosms. Ecol. Eng. J. Ecotechnology 2016, 89, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Gao, Q.F.; Dong, S.; Shin, P.K.S.; Wang, F. Uptake of farming wastes by silver carp Hypophthalmichthys molitrix in polyculture ponds of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella: Evidence from C and N stable isotopic analysis. Aquaculture 2013, 404, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Apex predators enhance environmental adaptation but reduce community stability of bacterioplankton in crustacean aquaculture ponds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jing, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D. Growth and mortality of topmouth gudgeon Pseudorasbora parva and evaluation on resource utilization in Taihu Lake. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2016, 31, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Li, B.; Jia, R.; Zhou, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, J. Effects of Different River Crab Eriocheir sinensis Polyculture Practices on Bacterial, Fungal and Protist Communities in Pond Water. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.X.; Xu, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.J.; Shao, X.H. Response of sediment bacterial communities to the drainage of wastewater from aquaculture ponds in different seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Jarvie, H.P. Delivery and cycling of phosphorus in rivers: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Dong, S.; Meng, Q.; Gao, Y. Review on Budgets and Environmental Loads of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Culture System. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2011, 30, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.P.; Liu, L.S.; Zheng, B.H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, X. Analysis of the bacterial community in the two typical intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China by pyrosequencing. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindienst, S.; Herbst, F.A.; Stagars, M.; von Netzer, F.; von Bergen, M.; Seifert, J.; Peplies, J.; Amann, R.; Musat, F.; Lueders, T.; et al. Diverse sulfate-reducing bacteria of the Desulfosarcina/Desulfococcus clade are the key alkane degraders at marine seeps. Isme J. 2014, 8, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nho, S.W.; Abdelhamed, H.; Paul, D.; Park, S.; Mauel, M.J.; Karsi, A.; Lawrence, M.L. Taxonomic and Functional Metagenomic Profile of Sediment from a Commercial Catfish Pond in Mississippi. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse-Buhl, U.; Schlief, J.; Mutz, M. Phagotrophic protists are a key component of microbial communities processing leaf litter under contrasting oxic conditions. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suberkropp, K.; Klug, M.J. The maceration of deciduous leaf litter by aquatic hyphomycetes. Can. J. Botany J. Can. De Bot. 1980, 58, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, G.R. Interactions between fungi, bacteria and beech leaves in a stream microcosm. Oecologia 1992, 89, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senga, Y.; Yabe, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kagami, M. Influence of parasitic chytrids on the quantity and quality of algal dissolved organic matter (AOM). Water Res. 2018, 145, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, A.; Pinn, D.; Peralta-Maraver, I.; Sweet, M.; Mauvisseau, Q.; Eyice, O.; Bulling, M.; Röthig, T.; Kratina, P. Predation increases multiple components of microbial diversity in activated sludge communities. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, B.; Boysen, A.; Carlson, L.; Groussman, R.; Heal, K.; Cain, K.; Morales, R.; Coesel, S.; Morris, R.; Ingalls, A. Sulfonate-based networks between eukaryotic phytoplankton and heterotrophic bacteria in the surface ocean. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Ye, S.; Liu, S.; Stirling, E.; Gilbert, J.A.; Faust, K.; Knight, R.; Jansson, J.K.; Cardona, C. Earth microbial co-occurrence network reveals interconnection pattern across microbiomes. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Preliminary analysis of the subseries taxonomy of the genus Eriocheir (Crustacea: Decapoda). Zool. Syst. 1988, 1, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Fauna Sinica: Osteichthyes, Order Cypriniformes (Middle Volume); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Dai, A. Atlas of Chinese Animals: Crustacea (Volume II); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B. Atlas of Chinese Animals: Fishes, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Gan, Y.; Wu, J.; Dai, J.; Chao, H.-J.; Yan, D. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane inhibits soil ammonia oxidation by altering ammonia-oxidizing archaeal and bacterial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Yu, X.L.; Gu, H.; Liu, F.; Fan, Y.J.; Wang, C.; He, Q.; Tian, Y.; Peng, Y.S.; Shu, L.F.; et al. Vertically stratified methane, nitrogen and sulphur cycling and coupling mechanisms in mangrove sediment microbiomes. Microbiome 2023, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, V.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Pardo, P.; Rauret, G.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P. Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J. Environ. Monit. JEM 2001, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Peng, G.; Wei, T.; He, J.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Distinctive patterns of bacterial community succession in the riverine micro-plastisphere in view of biofilm development and ecological niches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Zheng, C.; Suter, H.; Huang, Z. Different responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeck, T.; Bass, D.; Nebel, M.; Christen, R.; Jones, M.D.; Breiner, H.W.; Richards, T.A. Multiple marker parallel tag environmental DNA sequencing reveals a highly complex eukaryotic community in marine anoxic water. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillou, L.; Bachar, D.; Audic, S.; Bass, D.; Berney, C.; Bittner, L.; Boutte, C.; Burgaud, G.; de Vargas, C.; Decelle, J. The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): A catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D597–D604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Alexander, I.J.; Eberhardt, U.; Erland, S.; Høiland, K.; Kjøller, R.; Larsson, E.; Pennanen, T. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi–recent updates and future perspectives. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Gao, X.; Qiao, W.; Yang, Y. Assembly mechanisms of microbial communities in plastisphere related to species taxonomic types and habitat niches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lu, H.-P.; Sastri, A.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Chou, W.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H. Contrasting the relative importance of species sorting and dispersal limitation in shaping marine bacterial versus protist communities. ISME J. 2018, 12, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De’ath, G. Boosted trees for ecological modeling and prediction. Ecology 2007, 88, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Xiao, X.; Liang, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, K.; Che, K. Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes as the dominant microorganisms for ammonium nitrogen wastewater treatment with a low C/N ratio in BCOR. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 65, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Maria Saez, J.; Davila Costa, J.S.; Leticia Colin, V.; Soledad Fuentes, M.; Antonio Cuozzo, S.; Susana Benimeli, C.; Alejandra Polti, M.; Julia Amoroso, M. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, O.S.; Fernandes, A.S.; Tupy, S.M.; Ferreira, T.G.; Almeida, L.N.; Creevey, C.J.; Santana, M.F. Insights into plant interactions and the biogeochemical role of the globally widespread Acidobacteriota phylum. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mukhia, S.; Kumar, R. Microbial community dynamics from a fast-receding glacier of Western Himalayas highlight the importance of microbes in primary succession, nutrient recycling, and xenobiotics degradation. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Wang, L.; Du, J.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Hu, L.; Wei, H.; Fang, J.S.; Liu, R.L. Biogeographic distribution, ecotype partitioning and controlling factors of Chloroflexi in the sediments of six hadal trenches of the Paciflc Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Tran, P.Q.; Kieft, K.; Anantharaman, K. Genome diversification in globally distributed novel marine Proteobacteria is linked to environmental adaptation. Isme J. 2020, 14, 2060–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliyarsingh, B.; Dash, B.; Nayak, S.; Nayak, S.K. Soil Verrucomicrobia and Their Role in Sustainable Agriculture. In Advances in Agricultural and Industrial Microbiology: Volume 1: Microbial Diversity and Application in Agroindustry; Nayak, S.K., Baliyarsingh, B., Mannazzu, I., Singh, A., Mishra, B.B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, G.J.; Sole, M.; Krauss, G.; Schlosser, D.; Wesenberg, D.; Barlocher, F. Fungi in freshwaters: Ecology, physiology and biochemical potential. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2011, 35, 620–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, H.; Filip, Z. Degradation and transformation of aquatic humic substances by laccase-producing fungi Cladosporium cladosporioides and Polyporus versicolor. Acta Hydrochim. Et Hydrobiol. 1998, 26, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinhut, T.; Hertkorn, N.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Mechanisms of humic acids degradation by white rot fungi explored using 1H NMR spectroscopy and FTICR mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2748–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, A.Z.; Follows, M.J.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Wilken, S.; Zimmerman, A.E.; Keeling, P.J. Rethinking the marine carbon cycle: Factoring in the multifarious lifestyles of microbes. Science 2015, 347, 1257594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, R.W. Mixotrophic protists in marine and freshwater ecosystems. J. Protozool. 1991, 38, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Karlsson, I.; Geisen, S.; Kowalchuk, G.; Jousset, A. Protists: Puppet masters of the rhizosphere microbiome. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkowski, M. Protozoa and plant growth: The microbial loop in soil revisited. New Phytol. 2004, 162, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirsová, D.; Wideman, J.G. Integrated overview of stramenopile ecology, taxonomy, and heterotrophic origin. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Yi, C.; Ni, L.; Guo, L. Fish-mediated changes in bacterioplankton community composition: An in situ mesocosm experiment. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Hu, G.; Qiu, L.; Meng, S.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Song, C.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Variations in bacterioplankton communities in aquaculture ponds and the influencing factors during the peak period of culture. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, R.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, J.; Huang, R.; Duan, M.; Yu, Z. Composition and co-occurrence patterns of Phragmites australis rhizosphere bacterial community. Aquat. Ecol. 2021, 55, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, G.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Jia, R.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J. Dynamic and assembly of benthic bacterial community in an industrial-scale in-pond raceway recirculating culture system. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 797817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Rui, J.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hedenec, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Pei, K.; Liu, C.; et al. Rate-specific responses of prokaryotic diversity and structure to nitrogen deposition in the Leymus chinensis steppe. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 79, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, P. A comparative study of network robustness measures. Front. Comput. Sci. 2017, 11, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Navarro, A.; Hiraldo, F.; Tella, J.L.; Blanco, G. Network structure embracing mutualism–antagonism continuums increases community robustness. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.N.; Kolasa, J.; Cottenie, K. Contrasts between habitat generalists and specialists: An empirical extension to the basic metacommunity framework. Ecology 2009, 90, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Xing, C.; Hou, D.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, R.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, Z.; Weng, S.; He, J.; et al. Distinct bacterial communities in the environmental water, sediment and intestine between two crayfish-plant coculture ecosystems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5087–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Q.; Wan, L.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Song, C. Bacterial Communities and Enzymatic Activities in Sediments of Long-Term Fish and Crab Aquaculture Ponds. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, D.; Huang, Z.; Fu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xue, T.; Zhang, T.; Lin, G. Effects of Shrimp-Vegetable Rotation on Microbial Diversity and Community Structure in Pond Sediment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 2651–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Different Fish Farming Patterns in Paddy Fields Substantially Impact the Bacterial Community Composition, Stability, and Assembly Processes in Paddy Water. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; Liao, Q.; Fu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Dai, Z.; et al. Monotonic trends of soil microbiomes, metagenomic and metabolomic functioning across ecosystems along water gradients in the Altai region, northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Li, L.; Adams, J.M.; Hedenec, P.; Tu, B.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Li, X. Nutrient resource availability mediates niche differentiation and temporal co-occurrence of soil bacterial communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolukirik, M.; Ince, O.; Cetecioglu, Z.; Celikkol, S.; Ince, B.K. Spatial and temporal changes in microbial diversity of the Marmara Sea Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorniak, A.; Więcko, A.; Cudowski, A. Fungi biomass in lowland rivers of North Eastern Poland: Effects of habitat conditions and nutrient concentrations. Pol J Ecol 2013, 61, 737–745. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Dou, H.; Wei, Q.; Ma, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, L.; Sha, W.; Zhang, H. Environmental factors and stochasticity affect the fungal community structures in the water and sediments of Hulun Lake, China. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBrun, E.S.; Taylor, D.L.; King, R.S.; Back, J.A.; Kang, S. Rivers may constitute an overlooked avenue of dispersal for terrestrial fungi. Fungal Ecol. 2018, 32, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Song, W.; Warren, A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; Al-Farraj, S.A.; Gong, J.; Hu, X. Planktonic protist communities in a semi-enclosed mariculture pond: Structural variation and correlation with environmental conditions. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2008, 88, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Yang, T.; He, Z.; Shu, L.; Xiao, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Yu, H.; Yan, Q. Sediment resuspension drives protist metacommunity structure and assembly in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) aquaculture ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-X.; Pang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-C.; Li, J.-L.; Qin, S. Spatial variation of microbial communities in sediments along the environmental gradients from Xiaoqing River to Laizhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y. Machenism of mariculture self-pollution and its effects on environment. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2000, 19, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Cheng, J.; Xie, M. Impact of pond and fence aquaculture on reservoir environment. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Wang, W. Wastewater management in freshwater pond aquaculture in China. In Sustainability in Food and Water; Alliance for Global Sustainability Bookseries (Science and Technology: Tools for Sustainable Development); Sumi, A., Fukushi, K., Honda, R.K.H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.F.; Jiang, X.L. The application and research progress of bioremediation in pond aquaculture. Oceanol. et Limnol. Sin. 2013, 44, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.L.; Cao, X.Y.; Song, C.L.; Zhou, Y.Y. Environmental effects of organic matter enrichment and restoration strategy in sediment of aquaculture ponds. J. Hydroecology 2011, 32, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.G. Study on the Pond Aquaculture Pollution and Ecological Engineering Regulation Techniques; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, R.J. Overview of hypoxia around the world. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Lázaro, C.; Marín, A. Assessment of finfish aquaculture impact on the benthic communities in the Mediterranean Sea. Dyn. Biochem. Process Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. 2008, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, Y.; Bao, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhou, L.; Song, L.; Yang, B.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. The Stone Moroko Pseudorasbora parva Altered the Composition and Stability of Sediment Microbial Communities Within the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Polyculture Pond. Biology 2025, 14, 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091297
Hou Y, Bao Y, Jia R, Zhou L, Song L, Yang B, Li B, Zhu J. The Stone Moroko Pseudorasbora parva Altered the Composition and Stability of Sediment Microbial Communities Within the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Polyculture Pond. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091297
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Yiran, Yun Bao, Rui Jia, Linjun Zhou, Lili Song, Baojuan Yang, Bing Li, and Jian Zhu. 2025. "The Stone Moroko Pseudorasbora parva Altered the Composition and Stability of Sediment Microbial Communities Within the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Polyculture Pond" Biology 14, no. 9: 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091297
APA StyleHou, Y., Bao, Y., Jia, R., Zhou, L., Song, L., Yang, B., Li, B., & Zhu, J. (2025). The Stone Moroko Pseudorasbora parva Altered the Composition and Stability of Sediment Microbial Communities Within the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) Polyculture Pond. Biology, 14(9), 1297. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091297






